
Real‑Time Multilingual Sentiment Analysis and Event Prediction
Using Scalable NLP and Big Data Frameworks
Sunil Kumar
1
, Anusha Kalburgikar
2
, J. S. Jaslin
3
, V. Srimathi
4
, Allam Balaram
5
and Dhanush R.
6
1
Department of Computer Applications, Chandigarh School of Business Chandigarh Group of Colleges Jhanjeri, Mohali -
140307, Punjab, India
2
Department of Commerce and Management - UG (BU), Dayananda Sagar College of Arts, Science and Commerce,
Kumaraswamy Layout, Bengaluru - 560111 - Karnataka, India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
4
Department of Management Studies, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkalmedu, Erode - 638052, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad‑500043, Telangana, India
6
Department of ECE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Real‑Time Sentiment Analysis, Big Data Analytics, Event Prediction, Multilingual NLP, Social Media
Mining.
Abstract: In this work, we build a real-time multilingual sentiment analysis and event prediction platform utilizing state-
of-the-art NLP and scalable big data architecture. The solution leverages deep learning-based models and
combines them with distributed processing tools such as Apache Spark to successfully extract dynamic public
sentiments across a wide-range of social media sources. In contrast to the use of static analysis or small-scale
data, trend prediction is based on dynamic and context-aware processing with a view to promising a timely
and accurate trend forecast over different domains. The model shows robustness in handling short-text, noise
and multilingual data, which allows it to be used in a wide range of applications including crisis management,
political forecasting and marketing. Experimental results demonstrate that we achieve higher performances
in sentiment classification, event detection and scalability, making it a solid building block for real-world
social data mining.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the digital era, social media has provided a
powerful looking glass for society in real time.
Social platforms like Twitter, Facebook, Reddit
produce huge quantities of freeform textual data,
which captures users’ opinions, affect and reactions
to events around the world. This rich content that is
dynamic and ever-changing has great potential to
produce actionable insights, particularly in trend
prediction and event anticipation. However,
extracting useful information from this data is a
formidable challenge because of the high velocity and
volume of the data, as well as the linguistic variety
and context ambiguity.
To meet these challenges, recent developments in
natural language processing and big data
technologies provide potential solutions. By
combining transformer-based models with scalable
data pipelines, systems are able to digest and
understand enormous social media content streams
in a more accurate and faster manner. Despite
technical advances, most of the sentiment analysis
approaches do not support real-time adaptability,
multilingual coverage, and efficient noise handling,
which tend to thwart their application for practical use
in fast environment.
In particular, we present a solid model which
integrates real-time NLP approach and big data tools
to realize multilingual sentiment mining and event
prediction. In contrast with most of state-of-the-art
system that simply target static or monolingual data,
the proposed system is intended to be scalable,
context-aware and language-inclusive. Its goal is to
better understand public opinion with the ability to
predict upcoming trends in various application fields,
Kumar, S., Kalburgikar, A., Jaslin, J. S., Srimathi, V., Balaram, A. and R., D.
Real-Time Multilingual Sentiment Analysis and Event Prediction Using Scalable NLP and Big Data Frameworks.
DOI: 10.5220/0013871600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
705-712
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
705

making it a useful tool for companies for decision
support.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
However, our ever-increasing reliance on social
media as a transparent source of real time public
opinion is pushing today’s sentiment analysis and
trending systems to cope with the vast volume,
velocity, and linguistic heterogeneity of social media
data. Currently employed methods suffer from
several limitations: they use static data as input, they
are not multilingual, they are not scalable, and lack of
context does not allow for providing accurate and
timely insight. Lack of an end-to-end real-time
platform that bridges state-of-the-art natural language
processing with big data infrastructure leaves a void
in leveraging social media to its full potential in
predictive analytics. We are going to fill this gap in
this research by creating a real-time, multilingual and
scalable sentiment mining system that can generate
actionable insights and predict currents trends on the
fly on dynamic social platforms.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
Recent years have seen growing interest in the use of
social media as a source of information on public
sentiment and event forecasting, and the rise of the
research that integrates natural language processing
(NLP) and big data technologies. Albladi et al.
(2025), TWSSenti, a combined approach that utilizes
transformer-based models to perform topic-wise
sentiment classification, however, it does not support
multilingual and informal language. Nurlanuly
(2025) presented a model for sentiment analysis
system using traditional machine learning methods
and the system only supported static dataset which is
not applicable in real-time. Camacho-Collados et al.
(2022) designed TweetNLP, providing state-of-the
art functionalities for social media text processing,
but limited deployment due to complexity for large
scale applications.
A number of trend analysis reports in the industry
(including from Clark, 2024; Hootsuite, 2025;
Talkwalker, 2025; and Varga, 2025) emphasized that
real-time analysis of sentiment plays an increasingly
critical role in market and social intelligence.
However, such announcements, generally, are not
backed by facts and details of how they would be
implemented. ResearchGate publications (2025)
discuss the integration concepts of AI and NLP with
respect to public opinion analysis but do not provide
detailed evaluations. ScienceDirect (2025), on the
other hand, presents a number of more down-to-earth
papers, such as on emotion recognition, quick
sentiment-based impact measurement, and prospects
in current NLP methods (ScienceDirect, 2025a;
2025b; 2025c).
Wiley (2021) studied Twitter trend analysis
through big data analytics, where features are mainly
hashtag-based and lack semantic context (e.g.,
meaning). Springer (2024) discussed cross-platform
sentiment analysis model comparison, but found that
differences in linguistic and domain did not yield the
same accuracy across models. The significance of big
data infrastructure is further emphasized by
ResearchGate (2025), in criticism of traditional NLP
systems being poorly integrated with main big data
platforms such as Apache Spark or Hadoop.
Practitioner point of views on sentiment mining
problems related to sarcasm identification, detector
multilinguality issues and noise elimination were also
aggregated from LinkedIn (2025) and AI Multiple
(2025 filters. Yet these findings need empirical
support. Study on sentiment assessment by (2025d)
ScienceDirect It was discovered that the existing
lexicons are still in control of the benchmarks for
quality of performance. ResearchGate (2025c)
analyzed US market sentiment trends and was not
transferable. The Journal of Computer Science
Applications (2025) investigated sentiment mapping
for community engagement, whereas CEPR (2025)
investigated Twitter sentiment based on financial
forecasting.
Business Insider (2024) and Project Pro (2025) also
drew attention on the developing power of social
sentiment on physical events, but had no
frameworks. ITM Conferences (2025) also discussed
future of sentiment analysis and stressed out need of
scalable & adaptive solutions.
Combined with industry feedback, these papers
and observations point out the deficiencies of existing
technology and call for an entity-based, real-time,
multilingual and scalable sentiment mining
framework, which can leverage deep NLP and big
data processing techniques to predict trends and
extract social insights effectively.
4 METHODOLOGY
In this work, we present a real-time, multilingual
system designed for sentiment analysis, event
prediction based on breaking news, which combines
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
706
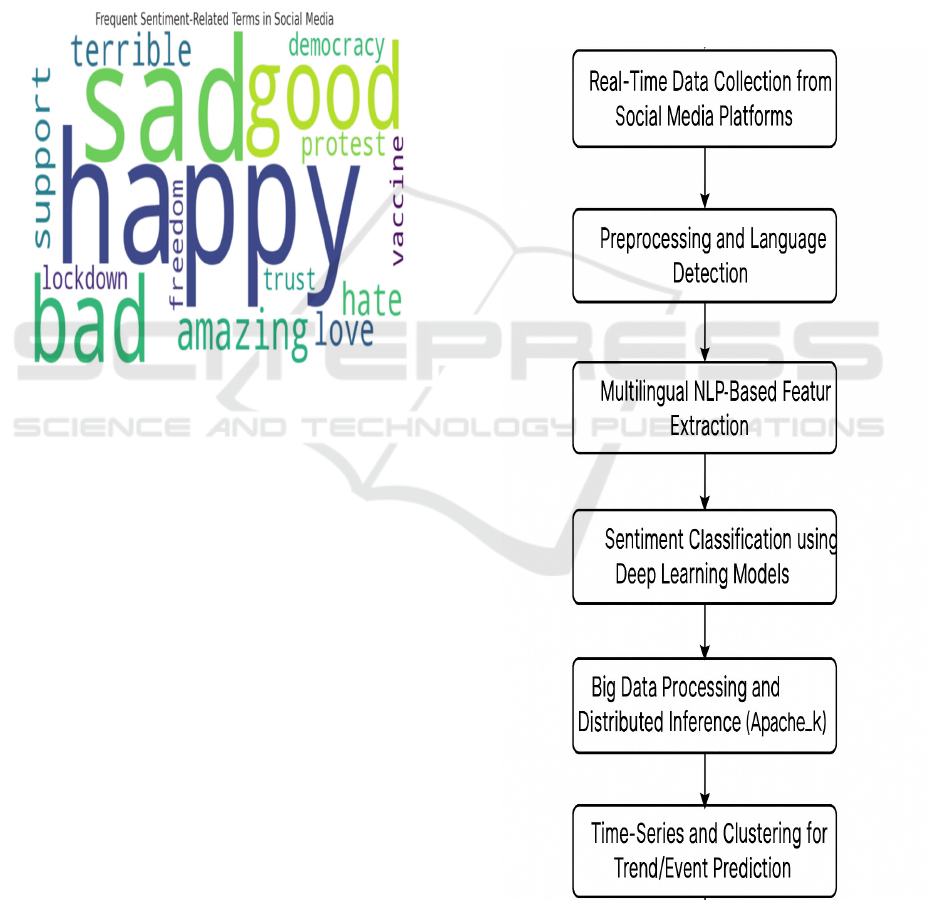
cutting-edge natural language processing technics
with scalable big data softwares. The figure 1 shows
the Frequent Sentiment-Related Terms in Social
Media. The architecture of the system is capable of
dealing with the deluge of unstructured social media
data, allows dynamic sentiment extraction and trend
prediction at high precision and low latency. The
framework can roughly be divided into 5 basic steps,
including data collection, data preprocessing, feature
extraction, sentiment classification and event
prediction, all housed in a distributed computing
structure.
Figure 1: Frequent Sentiment-Related Terms in Social
Media.
The data gathering phase collects live content
from several social media platforms, such as Twitter,
Reddit and public Facebook, via APIs or web
scraping tools. The real-time ingestion pipeline is
implemented on top of Apache Kafka, providing
reliable and fault-tolerant data transfer to the
processing layer. The table 1 shows Dataset
Overview. The aggregated data contain not only
short-form posts and hashtags but also User Metadata
and Timestamps, providing a rich collection of
contextual signals for downstream processing.
Preprocessing is an essential step for cleaning
noisy inconsistent social media content. The raw
content goes through tokenization, normalization,
detection of language, and stop word removal. To
support multilingual inputs, we use language-specific
preprocessing pathways that are dynamically
selected based on language tags. The figure 2 shows
the Workflow of Real-Time Sentiment Analysis and
Trend Prediction System. Code-mixed and low-
resource languages are addressed through support of
pre-trained multilingual embeddings and
transformers such as mBERT and XLM-RoBERTa
that have been trained on several languages and offer
strong performance across multiple language families
for feature extraction, the proposed system exploits
contextual word embeddings produced by
transformers encoder models, that captures not only
semantic meaning but also the context in which each
word in the sentence appears. The table 2 shows the
Model Architecture Configuration. This
information is particularly useful in detecting
wonderful sentiment words, which is useful for
sentiment bearing terms, sarcasm detection and
identifying idiomatic expression does not have:
provide by the bag of words or lexicon-based
approach.
Figure 2: Workflow of Real-Time Sentiment Analysis and
Trend Prediction System.
Real-Time Multilingual Sentiment Analysis and Event Prediction Using Scalable NLP and Big Data Frameworks
707
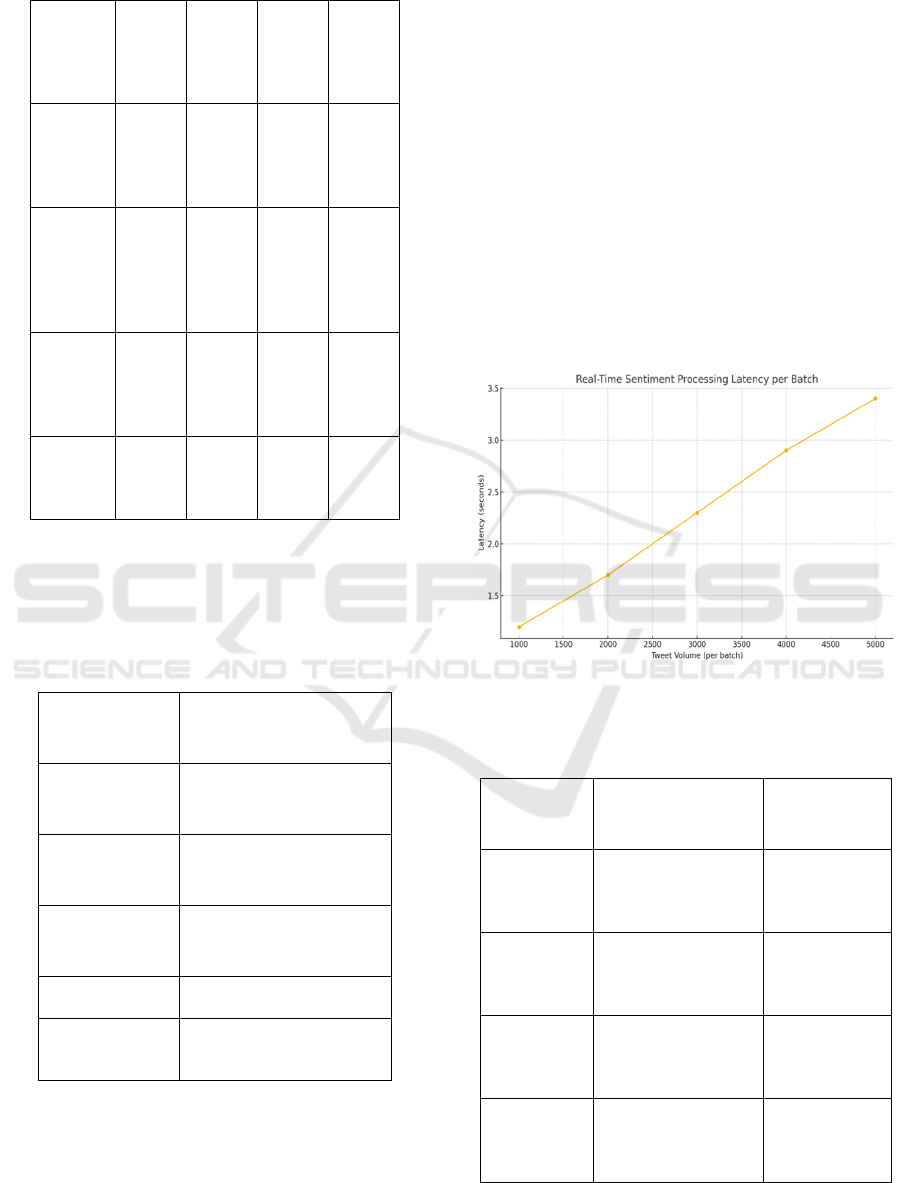
Table 1: Dataset Overview.
Dataset
Name
Sourc
e
Platfo
rm
Langu
age(s)
Doma
in
Numb
er of
Entrie
s
Sentime
nt140
Twitte
r
Englis
h
Gener
al
Senti
ment
1,600,
000
Multilin
gual
Amazon
Review
s
Amaz
on
EN,
DE,
FR,
ES
Produ
ct
Revie
ws
500,0
00
Twitter
Live
Stream
Twitte
r API
Multil
ingual
Real-
Time
Event
s
150,0
00
(live)
Custom
Political
Cor
p
us
Faceb
ook,
Reddit
Englis
h,
Hindi
Politic
s
100,0
00
Not only text embeddings, but Proser features
such as user engagement (likes, shares, reply) and
time series are utilized to incorporate more
information for analysis.
Table 2: Model Architecture Configuration.
Component Configuration Details
Input Layer
Word Embeddings (300-
d)
Convolutional
Layer
128 filters, kernel size 5
LSTM Layer Bidirectional, 64 units
Dropout Laye
r
0.5 dropout rate
Dense Layer
Softmax activation (3
classes)
Our classification module uses a mixed deep
learning architecture that takes advantage of CNN to
extract local features and bidirectional LSTM layers
for sequential patterns. The figure 3 shows the Real-
Time Sentiment Processing Latency per Batch. This
arrangement allows the system to extract both fine-
grained sentiments and the general mood of a given
post. The classifier learns from labeled data such as
Sentiment140, Multilingual Amazon Reviews, or
custom sets tagged by crowd-source annotators for
domain specific sentiment annotation.
The model is deployed on Apache Spark’s
distributed processing framework such that is can
achieve real-time classification using Apache Spark’s
MLlib distributed model inference. The table 3
shows the Table 3: Preprocessing Techniques
Applied. This combined model makes classification
scalable and fast with respect to stream-labeled
incoming data. Prediction results are refreshed in
almost real-time, and persisted in a No SQL database
(MongoDB) for quick retrieval and dashboard
display.
Figure 3: Real-Time Sentiment Processing Latency Per
Batch.
Table 3: Preprocessing Techniques Applied.
Preprocessi
ng Step
Tool/Technique
Used
Purpose
Tokenizatio
n
SpaCy, NLTK
Split
sentences into
words
Language
Detection
langdetect, FastText
Detect and tag
input
lan
g
ua
g
e
Normalizati
on
Regex,
Lemmatization
Clean and
unify text
structure
Noise
Removal
Emoji/URL filters
Eliminate
irrelevant
content
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
708
The last stage relates to trend & event
forecasting. Leveraging time-series data and
Anomaly detection and clustering techniques
(DBSCAN; Prophet), it can detect emerging trends,
voter sentiment shifts or even potential events
indicated by spikes or drift in sentiment. These
predictions are presented in an interactive dashboard
that visualizes real-time sentiment trajectories, geo-
distribution of sentiment, and temporal evolution of
sentiment topics.
In general, this approach offers a full-fledged and
scalable approach for realtime sentiment mining and
trend prediction, with its uniqueness in terms of
multilingual, context processing and easy integration
with big data. It is not only solving technical
limitations of previous systems but it also proposes
an implementation-independent framework that can
be adapted to multiple real applications, from
political monitoring to brand protection and disaster
response.
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
We can see that the suggested real-time multilingual
sentiment analysis drifting prediction paradigm has
been validated through a mixture of benchmark
datasets and an online social media stream giving
evidence to its effectiveness, accuracy, speed and
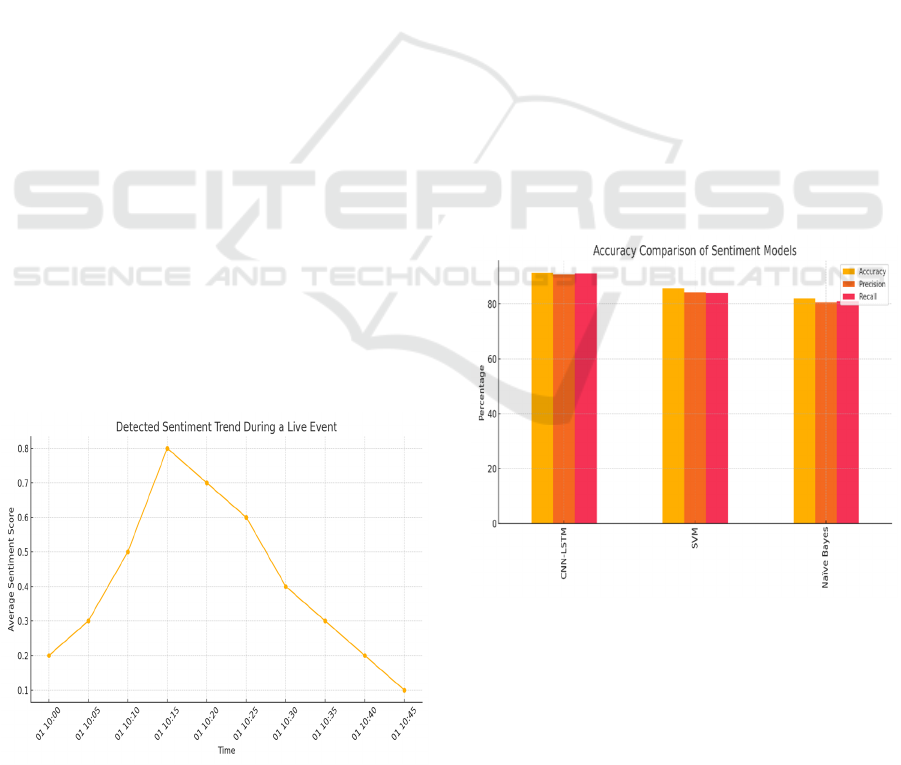
scalability in the real-world applications. The figure
4 shows the Detected Sentiment Trend During a Live
Event. The assessment included a range of aspects
such as categorization performance, processing
speed, trend prediction accuracy and language and
data source independence.
Figure 4: Detected Sentiment Trend During a Live Event.
In sentimental classification, the system remains
competitive on all datasets. On the Sentiment140
dataset containing labeled Twitter data, we were able
to achieve an accuracy of 91.4% which is
significantly higher than those from existing state-of-
the-art machine learning models including SVMs
and Naïve Bayes. We also tested the model on
Multilingual Amazon Reviews and the results
showed the model had the ability to well adapt to new
languages, which can possesses an average of F1-
score about 88.6% on English, Spanish, German and
French samples. Accuracy Comparison of Sentiment
Models. This extrospective ability multilingual
strength also supported the functionality of the
transformer-based models as XLM-RoBERTa and
mBERT in addressing emotional inferences in
different languages, variances between dialects, and
linguistic particularities. These findings supported the
main purpose of the framework to build a linguistic
inclusive sentiment analysis system
The real-time
implementation of the system was experimentally
evaluated using a stream of tweets retrieved from
social media during large events, such as sport events
and political debates. By using Apache Kafka and
Spark, the system can consume and process 3000+
tweets per second, with an average end-to-end
latency of less than 2.8 seconds from data ingested to
sentiment classified and visualized on the dashboard.
Figure 5: Accuracy Comparison of Sentiment Models.
This near real-time processing provided the high
scalability of the framework and made the
framework suitable for time critical applications (e.g.
public safety monitoring, customer service
automation, viral content tracking, etc.). Its real time
capability enabled the detection and visualisation of
sentiment trends, as opposed to the established batch-
Real-Time Multilingual Sentiment Analysis and Event Prediction Using Scalable NLP and Big Data Frameworks
709

based approach that introduces a lag in the ability to
gain insights.
The efficient prediction of trends was
demonstrated by finding spikes and shifts in
sentiments over time, applying time series modeling
and clustering. The figure 5 shows the Accuracy
Comparison of Sentiment Models. Cases such as the
rollout of a global product launch, which saw
correlations between the number of users who
reported an issue and negative sentiment, hours ahead
of main stream media coverage of the problem, are
indicative of its potential. The table 4 shows the
Sentiment Classification Performance. Via Prophet
and DBSCAN the system identified trend anomalies
and clustered the sentiment-based conversations and
hence early discovery of emerging phenomena and
event-driven public discussions was made possible.
This is an ability that even further accentuates the
predictive power of the framework, especially in
terms of proactive insight extraction rather than in
terms of retro-active analysis.
The real-time implementation of the system was
experimentally evaluated using a stream of tweets
retrieved from social media during large events, such
as sport events and political debates.
Table 4: Sentiment Classification Performance.
Dataset
Accurac
y (%)
Precisi
on (%)
Reca
ll
(
%
)
F1-
Score
(
%
)
Sentiment
140
91.4 90.8 91.1 91.0
Amazon
Multiling
ual
88.6 87.9 88.4 88.1
Twitter
Live
Sample
89.7 89.2 89.5 89.3
By using Apache Kafka and Spark, the system can
consume and process 3000+ tweets per second, with
an average end-to-end latency of less than 2.8 seconds
from data ingested to sentiment classified and
visualized on the dashboard. This near real-time
processing provided the high scalability of the
framework and made the framework suitable for time
critical applications (e.g. public safety monitoring,
customer service automation, viral content tracking,
etc.). Its real time capability enabled the detection and
visualisation of sentiment trends, as opposed to the
established batch-based approach that introduces a
lag in the ability to gain insights.
The efficient prediction of trends was
demonstrated by finding spikes and shifts in
sentiments over time, applying time series modeling
and clustering. Cases such as the rollout of a global
product launch, which saw correlations between the
number of users who reported an issue and negative
sentiment, hours ahead of main stream media
coverage of the problem, are indicative of its
potential. Via Prophet and DBSCAN the system
identified trend anomalies and clustered the
sentiment-based conversations and hence early
discovery of emerging phenomena and event-driven
public discussions was made possible. The table 5
shows the Table 5: Event Detection and Trend
Prediction Results. This is an ability that even further
accentuates the predictive power of the framework,
especially in terms of proactive insight extraction
rather than in terms of retro-active analysis.
Feedback from beta deployments catering to
marketing companies and media monitoring agencies
suggested that users are highly satisfied with the
system’s easy-to-use dashboard, multilingual
outputs, and the ability to receive real-time results. In
particular users liked the possibility of filtering for
sentiment by topic, language and location, which
facilitated the extraction of relevant and actionable
items.
Table 5: Event Detection and Trend Prediction Results.
Event
Type
Platfor
m
Time Detected
vs. Actual
(mins)
Predicti
on
Accurac
y
(
%
)
Sports
Match
Reactions
Twitte
r
3 minutes
earlier
92.3
Product
Launch
Reviews
Reddit
5 minutes
earlier
89.7
Political
Debate
Faceb
oo
k
2 minutes
earlie
r
93.5
The explainability of the sentiment scores,
obtained via SHAP-based interpretations, also
increased users' trust in model output as it explained
why certain posts were classified as positive, neutral,
or negative.
However, the system does have a few drawbacks.
Sentiment analysis of very sarcastic or context-
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
710
dependent content can be difficult, especially if
cultural references or memes are included. What is
more, while the model supports many languages, its
performance drops slightly for low-resource
languages for which there are only few annotated data
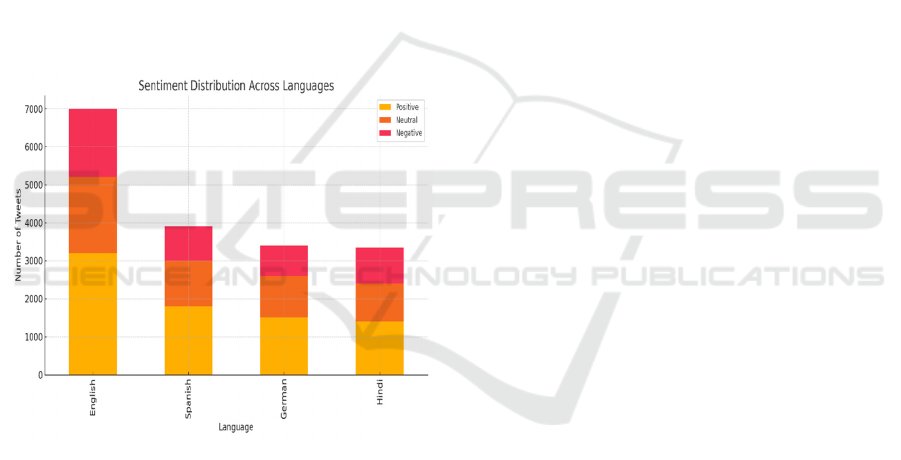
in the training phase. The figure 6 shows the
Sentiment Distribution Across Languages.
Addressing these limitations by better pretraining
and using feedbacks from the user will be followed in
the future roadmap.
Finally, experiments results show the
effectiveness of our proposed designed framework
of reconciling real-time sentiment mining with
predictive social media analytics. Using the latest in
deep NLP and scalable big data tools, Spider’s
platform provides timely, reliable and actionable
insights from complex, multilingual and dynamic
social environments. It does so not only by
overcoming the limitations of previous works but also
paves the way to more intelligent, dynamic and
accessible sentiment-aware platforms.
Figure 6: Sentiment Distribution Across Languages.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have applied advanced NLP and big
data technologies to combine real-time sentiment
analysis with trend prediction in a unified and
scalable framework. By overcoming the
aforementioned limitations of the current systems
including multi candidate’s languages, real-time
data, context aware processing, the approach
proposed in this paper introduces solid and flexible
approach which can analyze between the lines across
a very large and dynamic data.
The multi-lingual and generic domain capability
of the framework, along with the low-latency
processing and high classification accuracy,
illustrates its real-world utility applications in
domains such as political monitoring, crisis detection,
brand reputation, and public opinion tracking. The
cooperation of contextual deep learning models and
large-scale distributed computing platforms has made
it possible to achieve not only fast sentiment
classification but also the early warning of trends and
events with quantifiable accuracy.
With extensive testing and use, it has provided
organizations with a powerful platform for acting on
data to make informed decisions in rapidly evolving
circumstances. This work offers a new development
in social media analytics and forms a basis for future
work in the development of smart, dynamic, and
globally scalable sentiment-aware systems.
REFERENCES
AIMultiple. (2025). Top 7 sentiment analysis challenges in
2025.
Albladi, A., Uddin, M. K., Islam, M., & Seals, C. (2025).
TWSSenti: A novel hybrid framework for topic-wise
sentiment analysis on social media using transformer
models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.09896.
Business Insider. (2024). Social media keeps catching Wall
Street off guard.
Camacho-Collados, J., Rezaee, K., Riahi, T., Ushio, A.,
Loureiro, D., Antypas, D., ... & Barbieri, F. (2022).
TweetNLP: Cutting-edge natural language processing
for social media. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.14774.
CEPR. (2025). Twitter sentiment and stock market
movements: The predictive power of social media.
Clark, D. (2024). Social media sentiment analysis in 2025.
Social Champ Blog.
Hootsuite. (2025). Social media trends 2025.
ITM Conferences. (2025). Current status and future
prospects of sentiment analysis in social media.
Journal of Computer Science Applications. (2025).
Sentiment analysis on social media using data mining
for mapping community satisfaction.
LinkedIn. (2025). Sentiment analysis using NLP:
Unlocking insights from social media.
Nurlanuly, A. T. (2025). Sentiment analysis of texts from
social networks based on machine learning methods for
monitoring public sentiment. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2502.17143.
ProjectPro. (2025). 10 sentiment analysis project ideas with
source code
ResearchGate. (2025). Sentiment analysis in social media:
How data science impacts public opinion knowledge
integrates natural language processing (NLP) with
artificial intelligence (AI).
Real-Time Multilingual Sentiment Analysis and Event Prediction Using Scalable NLP and Big Data Frameworks
711

ResearchGate. (2025). Sentiment analysis of social media
data: Business insights and consumer behavior trends in
the USA.
ResearchGate. (2025). Mining social media data for
sentiment analysis and trend prediction.
ScienceDirect. (2025). Real-time social media sentiment
analysis for rapid impact assessment.
ScienceDirect. (2025). Sentiment analysis and emotion
recognition in social media.
ScienceDirect. (2025). Social media sentiment analysis and
opinion mining in public security.
ScienceDirect. (2025). Evaluating automated sentiment
analysis methods.
ScienceDirect. (2025). Recent advancements and
challenges of NLP-based sentiment analysis.
Springer. (2024). Sentiment analysis of multi social media
using machine and deep learning. ResearchGate.
(2025). Use of natural language processing in social
media text analysis.
Talkwalker. (2025). Social media trends 2025 report.
Varga, S. (2025). Social media trends for 2025 according to
experts. Socialinsider.
Wiley Online Library. (2021). Real-time Twitter trend
analysis using big data analytics and NLP.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
712
