
NDOL: An Enhanced Heart Disease Prediction System Using
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assisted Neural Decision Optimization
Logic
K. Venkatasalam, M. Desikan, S. Kalai Selvan, B. Saranraj and A. Sowkath Basha
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Mahendra Engineering College, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Deep Learning, Heart Disease, Artificial Intelligence, Disease Prediction, AI, Neural Decision Optimization,
NDOL, Support Vector Machine, SVM.
Abstract: Since cardiovascular diseases (CVD) remain one of the global leading causes of mortality, the urgent need
for new diagnostics and preventative therapies is evident. These are classified as a significant physical
condition leading to a high probability of death. Heart disease must then be diagnosed effectively and quickly
to avoid further harm to individuals. This study thus investigates whether a learning technique derived from
Artificial Intelligence (AI)- Neural Decision Optimization Logic (NDOL) - can be used to predict cardiac
illnesses to enable timely treatments and personalized healthcare plans. The suggested model is cross-
validated with a common learning model, Support Vector Machine (SVM) to investigate how well the
proposed model performs. ML tech, applied to vast volumes of data to identify complex patterns and
possibilities of danger from certain combinations that the naked eye cannot see, is what enables these ML
models. Some of the important technologies used to predict the probability of heart disease are neural
networks, decision trees, and ensemble learning. Also, this study further demonstrates the implementation of
artificial intelligence technologies in the clinical workflow to give timely risk assessment and improve patient
care and resource distribution. The goal of proactive and precision medicine may be within our reach through
AI-enabled heart disease prediction which will combine technical ingenuity with medical expertise to
revolutionize cardiovascular health care.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advent of artificial intelligence has
revolutionized healthcare sector especially in
diagnosis, treatment planning and prevention
1(
Archana Singh, et al., 2020). Predicting
cardiovascular disease is one of the most promising
applications for artificial intelligence. We cannot
stress enough the need for early identification and
appropriate management, as heart disease remains the
leading cause of death worldwide. Clinical exams,
imaging and blood testing are the hallmarks of
traditional heart disease diagnosis; however, those
tools don’t always catch threats early enough to
prevent a fatal event. This is where AI-powered
systems come into their own. AI-Powered Heart
Disease Forewarning: By applying machine learning
(ML) algorithms, this technology analyses extensive
and diverse datasets, such as clinical data, past
medical history, test results, genetic markers, and
lifestyle patterns, to identify trends that may indicate
a greater risk of cardiovascular conditions. AI data-
driven heart condition prediction enables early risk
detection of heart diseases so that care providers
initiate preventative therapeutic treatments or
recommend lifestyle modifications for these patients
4.
Artificial intelligence methods used to predict
cardiac complications are brain networks, ensemble
learning, decision trees, neural networks.] These
models can manage and analyse complex data which
often uncover latent associations, unlike more
traditional techniques. Correlations between
predictors such as age, prior smoking, blood pressure,
cholesterol, and diabetes create a fuller picture of the
individual’s risk profile. After training, these artificial
intelligence (AI) models demonstrate remarkable
precision in predicting the risk of the cardiovascular
disease. AI systems continuously learn and improve
over time as they are exposed to new data, ensuring
that. In addition, these models analyse huge amounts
672
Venkatasalam, K., Desikan, M., Selvan, S. K., Saranraj, B. and Basha, A. S.
NDOL: An Enhanced Heart Disease Prediction System Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assisted Neural Decision Optimization Logic.
DOI: 10.5220/0013871100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
672-679
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

of data at once, allowing doctors to act promptly for
critical patients (
Hosam El-Sofany, et al., 2024). AI-
powered heart disease prediction systems have the
potential to greatly enhance outcomes by enabling
early intervention, reducing healthcare costs, and
providing a more personalized approach to
cardiovascular health. The incorporation of the AI in
clinical practices would allow pre-emptive screening
and diagnosis of cardiac ailments, making it possible
for practitioners to make informed clinical decisions
in the future 7.
The identification of these issues early on
provides a means of preventing long-term health
problems, including heart disease, the leading cause
of death in the world. Traditional methods of spotting
heart disease are not always speedy or dependable
because they can overlook early symptoms or
understated signs. For improvements, AI-based
cardiac disease prediction tools are essential for
faster and accurate assessments. These algorithms
might breezily scour mountains of data a patient’s
medical records, their lifestyle choices, their test
results to reveal hidden threats. This enables cardiac
disease to be diagnosed in its earliest stages before
encountering the symptoms when the doctors can take
steps to intervene. AI also helps tailor therapy, as it
can factor in individual risk factors and provide
personalized advice. And by automating routine but
necessary processes like risk assessments, AI
systems might help free clinicians’ time for patients
with more acute conditions. Not just that, some of
these AI-powered devices might work in real-time,
monitoring a patient’s vitals and altering their risk
profile as appropriate. Saving lives, making
healthcare much more efficient and better managing
cardiac disease across the Globe is also what this
kind of technology, 9.
Artificial intelligence-based heart disease
prediction primarily aims to create a reliable
technique to predict a person' risk of developing
cardiovascular disease. One of the goals is to create
an AI model capable of predicting the onset of
cardiovascular disease on the basis of data acquired
from multiple sources such as medical history,
lifestyle habits, and test findings. The point of this
approach is to detect any cardiac issues before
symptoms appear, so that treatment can start sooner
rather than later. The system will generate risk
assessments that, based on individual patient medical
history, can be used to determine customized
treatment plans. Once incorporated into processes,
healthcare providers will have much ease in
employing it during routine health checks. The
system automates the risk evaluation process,
enabling medical personnel to spend more time and
effort on the highest risk profile patients. The end
goal is improved forecasts, lighter workloads for
healthcare workers and better, more efficient
treatment.
2 RELATED WORKS
At this time, cardiovascular disease ranks as the
leading death globally. It is difficult to predict cardiac
illness since it requires expertise and specific
information (
Padmakumari Pitchal, et al., 2024). Medical
facilities have just recently started collecting sensor
data using Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to
improve cardiac disease diagnosis and prognosis.
The results may not be trustworthy, despite the
extensive research on heart disease diagnosis. The
three primary steps of the automated model for
predicting cardiac problems—preprocessing, feature
extraction and prediction—are laid forth in this article.
The input data is preprocessed by using an upgraded
Z-score normalization. In order to train the prediction
model, feature extraction is used to get the important
features from the preprocessed data. Statistical
features, information gain characteristics, and
enhanced entropy are among the features that were
retrieved. The Improved Quantum Convolutional
Neural Network (IQCNN) uses the retrieved
characteristics to make predictions. We compare the
IQCNN's performance against that of previous
systems using a number of parameters. The proposed
IQCNN model achieves a learning rate of 70% and an
accuracy of 0.91 when compared to more
conventional methods for predicting cardiac
problems.
Each year, millions of people die from heart
disease, making it one of the most recognized and fatal
diseases in the world (
Ahmad Ayid Ahmad, et al., 2023).
The only avenue to save people's lives is through early
detection of this disease. Machine Learning (ML) is
an artificial intelligence technique that can diagnose
diseases quickly, easily, and inexpensively. Our
objective is to create a machine learning model that
can accurately forecast the onset of heart disease by
analyzing the Cleveland heart disease dataset. Model
performance is very sensitive to the properties of the
training dataset and the ML technique chosen. The
Jellyfish optimization approach was used to reduce the
Cleveland dataset to a lower dimensional subspace in
order to avoid overfitting. Overfitting is caused by the
curse of dimensionality and happens when a dataset
has too many characteristics. Finding the optimal
NDOL: An Enhanced Heart Disease Prediction System Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assisted Neural Decision Optimization Logic
673

features is made easy with the Jellyfish algorithm's
fast convergence speed and flexibility.
According to the World Health Organization,
cardiac-related diseases have increased. Therefore,
each year 17.9 million people die (
Vijeta Sharma, et al,
2020). Detecting and treating these patients earlier is
getting more difficult with the growing population. On
the other hand, many studies have shown that the
recent growth in technology has caused machine
learning techniques to accelerate the health-care field.
Hence, the purpose of this work is to build a machine
learning model for the prediction of heart disease
utilizing these significant characteristics. The heart
disease prediction dataset at UCI served as a standard
for this research; it contains fourteen separate
characteristics related to cardiovascular disease.
While building the model, many machine learning
approaches were employed, including Decision Tree,
Naive Bayes, Support Vector Machine (SVM), and
Random Forest. As part of our study, we utilized
traditional Machine Learning methods to identify
correlations between the dataset's many properties,
with the goal of applying these findings to the
prediction of heart disease risk. As compared to other
ML approaches, Random Forest provides more
accurate predictions in less time, according to the
results. As a decision-support system, this model can
be useful for doctors in the clinic.
In the last several decades, cardiovascular illness
(heart disease) has become the leading cause of
mortality worldwide (
Devansh Shah, et al., 2020). It
includes a broad variety of cardiac conditions. There
are a lot of things that may go wrong with a heart
attack, and it's critical that we find ways to diagnose
the condition quickly so that we can start treating it
effectively. Healthcare organizations often use data
mining as a method for coping with large data sets. In
order to aid medical professionals in the prediction of
heart illness, researchers examine large medical data
sets using various data mining and machine learning
methods. This research study's model exhibits several
characteristics linked to heart illness; it is constructed
using supervised learning techniques such Naïve
Bayes, decision trees, K-nearest neighbors, and
random forest. It draws on the Cleveland database at
UCI, which already has information on people with
cardiac disease. With 303 cases and 76 characteristics,
the data is rather extensive. We can actually evaluate
fourteen of those seventy-six attributes the ones that
matter most for comparing algorithm performance.
This study aims to assess the potential occurrence of
cardiovascular disease in individuals. The results
demonstrate that K-nearest neighbor offers the highest
level of accuracy.
Important medical duties include cardiovascular
disease diagnosis and prognosis to guarantee accurate
categorization, which aids cardiologists in treating
patients appropriately (
Chintan M. Bhatt, et al., 2023).
The ability of machine learning to identify patterns in
data has led to an upsurge in its use in the medical
field. To help diagnosticians decrease misdiagnosis,
machine learning may be used to categorize the
occurrence of cardiovascular illness. In an effort to
lower the death toll from cardiovascular disorders, this
study builds a model that can accurately forecast these
conditions. In order to enhance classification
accuracy, this research suggests a k-modes clustering
algorithm that starts with Huang. We employ models
like XGBoost, multilayer perceptron, decision tree
classifier and random forest. In order to get the best
possible outcome, the parameters of the applied model
were hyper-tuned using GridSearchCV. We test the
suggested model on a Kaggle dataset with 70,000 real-
world examples. Here is how the models were trained
using an 80:20 split of data and how they attained
accuracy: In the decision tree model, 86.37% of the
trials used cross-validation, while 86.53% did not. In
the XGBoost model, 87.12% of the trials used cross-
validation, while 87.05% used random forest. In the
multilayer perceptron model, 87.28% used cross-
validation, while 86.44% used non-validation. The
models that have been suggested have AUC (area
under the curve) values: XGBoost: 0.95, decision tree:
0.94, random forest: 0.95, multilayer perceptron: 0.95.
Based on these foundational studies, we know that
multilayer perceptron with cross-validation is the most
accurate method currently available. With an accuracy
of 87.28%, it was the most accurate.
3 METHODOLOGY
The significance of AI-based heart disease prediction
is Early prediction of heart disease even before people
develop any serious symptoms. When it is diagnosed
early, patients may have a better treatment experience
and better outcomes than if diagnosed late. AI can
assist doctors in more accurately assessing a person’s
risk for heart disease by analysing a patient’s history
and other lifestyle factors. This technology will also
improve the effect of health care, as it can accelerate
the initial assessment of risk, and enable providers to
focus on patients determined to have the greatest
need. This technology is integrated seamlessly within
healthcare systems, would provide efficiencies for
hospitals and doctors. With AI system powered
heart disease prediction services, more loved ones can
be reached at varying environmental conditions
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
674

including under-resourced settings. Artificial
intelligence and machine learning have been applied
to the health sector to improve diagnosis, treatment,
and patient care in various forms. These algorithms
can whittle down huge databases in search of patterns
and trends, offering the potential for better healthcare
decision making.
Deep learning and AI have many possible
applications in healthcare from disease prediction to
therapy personalization and automating tedious tasks.
Deep learning algorithms, for example, can often
identify abnormalities such as tumours in X-rays and
MRIs significantly faster than human doctors. AI can
analyse factors such as blood pressure, cholesterol
and lifestyle to predict diabetes, heart disease and
other chronic diseases. Deep learning and artificial
intelligence (AI), when used in the context of the
health-care industry, could significantly reduce
processing times for high-volume patient datasets.
This will be extremely useful in risk assessment and
suggesting preventive measures. These technologies
also aid in personalized medicine by enabling
therapies targeted to the needs of the patient through
the analysis of their hereditary make-up and medical
journey. Despite the promise of AI-assisted
diagnostics, there are significant barriers to adoption,
including the need for reliable datasets and the need
to address patient privacy, as well as the issue of
black-box AI models. However, AI and ML could
transform healthcare to a more organized, accurate,
and individualized experience, leading to better
outcomes at lower costs.
Over the years, heart disease risk prediction has
improved with the development of new risk
assessments tools. Traditional risk factors, such as
age, blood pressure, cholesterol, and smoking habits,
are handled by models like the Framingham Risk
Score. Statistical methods like logistic regression
work, but can miss complex patterns in the data.
Deep learning and deep learning methods combine
big data to detect relationships that no one has
observed before, yielding better predictions. Real-
time health data (now available through smartwatches
and other wearables) makes it much easier to monitor
your health and catch any potential problems early.
These advanced methods of modelling significantly
enhance cardiac disease prevention and treatment
when compared to previous models. Predicting
cardiovascular disease is important, but not without
hurdles. Data quality is a major concern simply due
to the prevalence of erroneous or missing records in
the medical record. These include heredity, lifestyle,
and environment, all significant contributors to heart
disease but are difficult to accurately represent in
models. One complex model that performs well, but
is rarely employed in the clinic, is deep learning,
because it is simply too difficult for doctors to
understand. The second part of the problem of data
bias is that models trained on specific, rather than
diverse, populations can have results that will be
incorrect. And smaller clinics may not be able to
afford the pricey, cutting-edge models, and there are
concerns over the privacy and security of patient
data. Finally, a majority of models are trained on
outdated data, even though a user’s health can
change as time goes on. There are many problems that
still need to be addressed for predictive models for
heart diseases to become available and reliable.
AI-based heart disease prediction systems still
have numerous unresolved matters. Firstly, the lack
of diversity in training datasets results in many
models’ performing poorly when they are deployed in
populations in the real world. The integration of these
tools into pre-existing hospital workflows is also not
easy. To make it worse, doctors may be reluctant to
trust AI predictions if they’re based on models that
are hard to understand.
It is common for existing systems to depend on
static data, which fails to consider how a patient's
health evolves over time. Concerns around patient
data privacy and ethics have not been addressed
either. Having said that, a lot of room for growth
exists and improving the accuracy of models for
various groups of individuals may be achieved
through the use of distinct datasets. Through the
utilization of AI, wearable gadgets may offer the
convenience of real-time health monitoring.
Increasing confidence among healthcare practitioners
can be achieved by making AI forecasts more
understandable. Personalized treatment regimens for
patients can also be assisted by AI. One last thing that
can be done to enhance healthcare outcomes is to
create systems that collaborate with doctors. The
following figure 1 shows the system flow design and
the following figure 2 shows the architectural
diagram.
Filling such gaps and pursuing such opportunities
can improve and make artificial intelligence systems
more widely accepted. There are several steps
involved in using AI to predict the incidence of
cardiovascular disease. Data cleaning means combing
through databases and medical records for errors and
missing information. First the research team needs to
decide which of the variables age, cholesterol, blood
pressure, etc. deserve most of the researchers’
attention. This data can be useful in training deep
learning models such as neural networks and decision
trees. Numerous performance metrics such as
NDOL: An Enhanced Heart Disease Prediction System Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assisted Neural Decision Optimization Logic
675
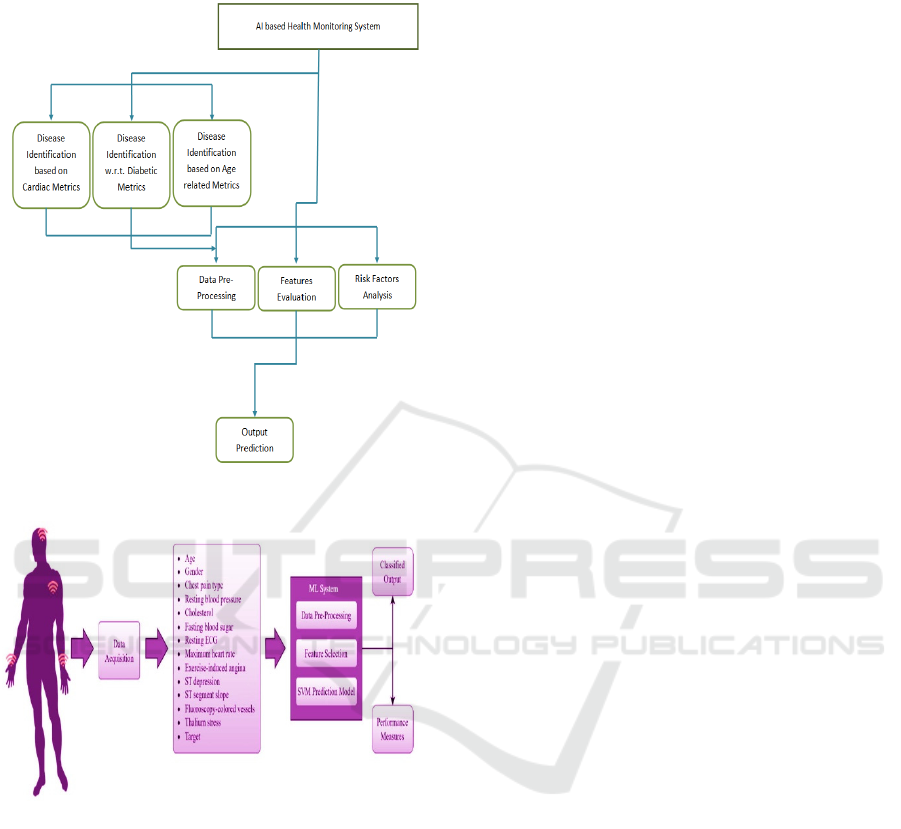
precision and accuracy are used to valid and tune the
model to ensure that it is as accurate as possible.
Figure 1: System Flow Design.
Figure 2: Architectural Diagram.
Finally, the model is built into a system that
doctors can use to evaluate possible risks to their
patients. This method provides assurance of the
system's reliability and usefulness in predicting heart
disease. The proposed methods NDOL achieves
better prognostication with respect to CVDs over
present SVM and enhance issues due to imbalanced
data. The proposed system, NDOL, is an AI-driven
early prediction system for cardiovascular disease
that would help doctors to more accurately assess the
risk for their patients. To assess vital signs such as
age, cholesterol and blood pressure, the system first
collects data from the patients’ medical records and
wearables, cleans it up to eliminate errors, before
deploying it. The system has a very user-friendly user
interface which helps Doctors as well as patients to
easily view results and insights. In addition, it can
streamline processes by integrating with other
healthcare systems. This method can help improve
patient outcomes in the form of early diagnosis,
tailored treatment plans, and the management of
cardiac disease.
• Data Collection and Preprocessing: To
construct a system for the prediction of heart
disease, data collection is the initial stage.
Information is collected from a wide range of
resources, including health records,
questionnaires, publicly accessible databases,
and wearable technology. Some examples of
the types of information included in this data
set are gender, age, BP, cholesterol, heart rate,
and lifestyle choices. For reliable forecasts,
you need data that is both varied and of high
quality.
• Data Preprocessing: Before data can be
analyzed, it must first be cleaned and
structured. Cleaning and structuring comprise
the following steps: Statistical methods are
applied to impute missing data or otherwise
remove incomplete records from the dataset,
when missing data has been identified;
Searching for and removing inconsistent data
records; Normalizing values, when possible,
to make numerical values more comparable
with deep learning algorithms; and Encoding
categorical (non-numerical) data, such as
gender or lifestyle choice, into numerical
representations that the model can understand.
Pre-processing improves the prediction
model’s accuracy and reliability because it
ensures the dataset is clean, consistent, and
ready to train on.
• Feature selection and Data
Transformation: An essential part of
developing a system to anticipate cardiac
problems is feature selection. The first step is
to sort the dataset by the variables that affect
the likelihood of heart disease. Type 2
diabetes, smoking, exercise, cholesterol, blood
pressure, heart rate, and gender are all
common characteristics. The accuracy of the
model and the reduction of complexity caused
by the elimination of extraneous data are both
enhanced by selecting useful characteristics.
Now that we are looking at the selected,
previously discovered features, it is very
important that the data is transformed into
shapes that are suitable for deep learning
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
676

algorithms. This also includes Building
scalable and Normalization, which is basically
the process of outscoring the numerical
variables (cholesterol values and blood
pressure etc) so as to enhance the efficacy of
the model. Encoding of categorical variables
refers to converting categorical non-
numerical variables, such as gender or lifestyle
features, to numerical values, by techniques
such as one-hot-encoding. Extract or combine
features to improve the representation of a set
of data. An example of this is using age and
body mass index (BMI) to predict potential
health problems and determining a more
effective and accurate risk prediction in heart
disease by selection and transformation of
relevant features.
• Developing the Model: The model building
process consists of several simple steps. The
first of which is aggregating data from
multiple touchpoints such as health devices
and hospital data. The data is than cleansed for
any errors present and it is also formatted in
order to make it prepared for analyzing. Older
age and cholesterol values are identified as
features to be included in the model. Deep
learning algorithms take this data as an input
to train the model. After training the model,
fine tuning is done to make predictions more
accurate. Finally, the model is validated on
new data to be sure it is accurate and how good
the performance and reliability are. Such a
method can be employed to build a model
which accurately predicts whether or not a
person is likely to develop heart disease.
• Performance Measures: Evaluation
measures are used to evaluate the usefulness
of the model for predicting cardiac events.
Accuracy shows the total number of correct
predictions. By observing the precision we
can know how accurate the positive
predictions (heart disease patients) are. Recall
measures how well the model is capturing
true positives.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The use of NDOL and support vector machines
(SVMs) to analyze complicated medical data for the
purpose of heart disease prediction has greatly
advanced the field of AI, which in turn has improved
patient outcomes and early detection. One example is
a research that suggested a new deep learning
architecture for determining if a person has heart
disease or not by utilizing optimization logics.
Compared to more conventional classification
algorithms, such as SVM, our model outperformed
them with a total prediction accuracy of more than
98.39%. Research has demonstrated that deep
learning models' prediction capabilities may be
significantly improved by utilizing feature
augmentation approaches. When combined with deep
learning methods, these approaches allowed
researchers to achieve a level of accuracy that was
noticeably higher than that of earlier approaches. This
paper's literature review sections emphasize the
significance of model selection and the integration of
diverse data sources to improve predictive accuracy,
and they also highlight the effectiveness of different
deep learning-based models in heart disease
prediction. Developing models with high accuracy
and reliability in heart disease prediction has been
made possible by integrating AI and deep learning. In
the long run, these innovations should lead to better
cardiovascular health outcomes for patients by
facilitating earlier diagnosis and treatment. Figures 3
and 4 show the proposed scheme's home page and
about us page designs, respectively.
Figure 3: Home Page.
The proposed scheme's health data gathering
portal and output prediction page architecture are
shown in Figures 5 and 6, respectively.
NDOL: An Enhanced Heart Disease Prediction System Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assisted Neural Decision Optimization Logic
677

Figure 4: About Us Page.
Figure 5: Health Data Collection Portal.
Figure 6: Output Prediction.
As shown in Figure 7, the proposed approach,
NDOL, is cross-validated with the traditional learning
model, Support Vector Machine (SVM), to see how
accurate it is in making predictions. Table 1 provides
a descriptive representation of the same.
Table 1: Comparison of Prediction Accuracy Between Svm and
Ndol.
No. of Days Tested SVM (%) NDOL (%)
5 77.12 98.09
7 78.54 97.71
10 77.64 96.63
14 79.52 97.42
15 79.89 98.39
18 76.17 97.48
27 74.45 96.57
29 75.25 96.26
33 76.44 97.19
36 76.12 98.14
Figure 7: Prediction Accuracy.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
SCOPE
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers enormous promise
to revolutionize healthcare with its application to the
prediction of cardiac disease. Artificial intelligence
models can aid in the early identification and
individualized therapy of cardiac disease by
providing predictions that are accurate, fast, and
consistent using sophisticated algorithms. Optimizing
resource allocation and overall care delivery are two
additional benefits of these systems that aid
healthcare practitioners in identifying high-risk
patients. AI's capacity to quickly and accurately
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
678

analyse huge amounts of data makes better clinical
decisions, with less room for human error and overall
better quality of care, possible. Additionally, its
scalability allows it to be employed in various
healthcare settings, from top hospitals to underserved
areas, thus broadening the reach of healthcare
globally. However, persistent oversight,
collaboration between medical professionals and
data scientists, and a focus on data security and
privacy are all essential for the successful integration
of AI into the healthcare system. AI heart disease
prediction: A promising need in heart disease
prediction leads to early diagnosis, improved patient
outcomes, and a revolutionized healthcare system.
Last but not least, AI-based prediction models of
cardiovascular disease have the potential to disrupt
the health-care system by providing more accessible,
faster, and accurate tools for prevention and
management of heart disease. Proper practice and
further development of AI have the ability to change
the approach to the treatment of cardiovascular
diseases. The model has paid off, in terms of correctly
and quickly predicting heart disease risk. It helps
healthcare practitioners to identify high risk
individuals at an early stage, through early detection.
The methodology enables better risk stratification to
categorize patients risk level clearly. It is faster and
yields more accurate predictions than more traditional
methods. Plus, it's scalable, so it can accommodate
large datasets, which is a benefit for all types of
healthcare organizations. The model is an important
tool in fighting and treating cardiovascular disease
because its findings are reliable and it can process
data quickly.
Moving forward, AI will enable continuous
monitoring of patients through wearables, helping to
assess heart disease risk in real time, and accelerating
the process to intervene if needed. These models will
also deliver more precise risk assessments, which will
assist doctors, aiming at high-risk patients and
allowing them to make educated decisions in regards
to their treatment options. Healthcare providers must
keep abreast of these latest advancements to harness
the full promise of AI to drive better diagnosis and
treatment of heart disease.
REFERENCES
Aashish Gnanavelu, et al., "Cardiovascular Disease
Prediction Using Machine Learning Metrics", Journal
of Young Pharmacists, 2025.
Ahmad Ayid Ahmad, et al., "Prediction of Heart Disease
Based on Machine Learning Using Jellyfish
Optimization Algorithm", Diagnostics, 2023.
Archana Singh, et al., "Heart Disease Prediction Using
Machine Learning Algorithms", International
Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
2020.
Chaimaa Boukhatem, et al., "Heart Disease Prediction
Using Machine Learning", Advances in Science and
Engineering Technology International Conferences,
2022.
Chintan M. Bhatt, et al., "Effective Heart Disease
Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques",
Algorithms, 2023.
Dengqing Zhang, et al., "Heart Disease Prediction Based on
the Embedded Feature Selection Method and Deep
Neural Network", Journal of Healthcare Engineering,
2021.
Devansh Shah, et al., "Heart Disease Prediction using
Machine Learning Techniques", SN Computer Science,
2020.
Hosam El-Sofany, et al., "A proposed technique for
predicting heart disease using machine learning
algorithms and an explainable AI method", Scientific
Reports, 2024.
Kaushalya Dissanayake, et al., "Comparative Study on
Heart Disease Prediction Using Feature Selection
Techniques on Classification Algorithms", Applied
Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing, 2021.
M. Kavitha, et al., "Heart Disease Prediction using Hybrid
machine Learning Model", 6th International
Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies,
2021.
Md Mamun Ali, et al., "Heart disease prediction using
supervised machine learning algorithms: Performance
analysis and comparison", Computers in Biology and
Medicine, 2021.
Mohammed Amine Bouqentar, et al., "Early heart disease
prediction using feature engineering and machine
learning algorithms", Heliyon, 2024.
Padmakumari Pitchal, et al., "Heart disease prediction:
Improved quantum convolutional neural network and
enhanced features", Expert Systems with Applications,
2024.
Rohit Bharti, et al., "Prediction of Heart Disease Using a
Combination of Machine Learning and Deep
Learning", Computational Intelligence and
Neuroscience, 2021.
Vijeta Sharma, et al., "Heart Disease Prediction using
Machine Learning Techniques", 2nd International
Conference on Advances in Computing,
Communication Control and Networking, 2020.
NDOL: An Enhanced Heart Disease Prediction System Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assisted Neural Decision Optimization Logic
679
