
Real‑Time Embedded System Optimization Using Edge Computing
and Lightweight Deep Learning Architectures for Data Efficiency
C. Madana Kumar Reddy
1
, Rajesh Kumar K.
2
, P. Chellammal
3
, S. Muthuselvan
4
,
Evangelin M.
5
and A. Swathi
6
1
MCA Department, School of Sciences, Annamacharya University (Formerly Annamacharya Institute of Technology and
Sciences), Rajampet, Annamayya Dt. Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of CSE (Cyber Security), R. M. K. College of Engineering and Technology, Thiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu,
India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, J.J.College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
4
Department of Information Technology, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of CSE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Keywords: Adaptive Inference, Lightweight Deep Learning, Real‑Time Edge Computing, Embedded Optimization,
Scalable AI Systems.
Abstract: The growing need for intelligent systems led to rapid developments in edge computing and deep learning
which enabled intelligent real-time processing in embedded systems. But meeting low latency, energy
efficient and scalable performance in resource constrained environment is still a main challenge. The study
develops a systematic framework that combines adaptive lightweight deep learning architectures with real-
time edge computing strategies to enhance embedded system performance. In contrast to static capabilities in
existing works, this study recognizes the need for opportunity-driven dynamic optimization of all
functionalities of the system during operations, as it must adapt model parameters and resource utilization
based on changes succeeding environmental and operational alterations. In addition, the framework can be
deployed in a scalable way across multi-node edge networks and includes techniques for local data processing,
improving privacy and decreasing dependency on the cloud. We evaluated this approach experimentally on
actual IoT and embedded hardware platforms reporting dramatic improvements in latency, energy, and data
throughput. This work provides an end-to-end methodology for future-ready, intelligent embedded systems
with a particular focus on providing improved data efficiency and autonomous function at the edge.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the upsurge of Internet of Things (IoT) devices
and the increasing need for systems that are
intelligent and responsive, embedded systems are one
of the key drivers of technological innovation. While
ever more critical, real-time applications (including
autonomous vehicles, smart healthcare and industrial
automation) must be able to react to data that
embedded systems must be able to process with
speed, rigor and minimal energy. But traditional
cloud-based architectures lead to latency and
heightened energy costs and raise serious privacy
issues that matter most in time-sensitive and data-
heavy contexts.
So, to reshape these issues, Edge computing is a
revolutionary paradigm that can process data in
proximity to the source itself. This can lead to lower
latency, better data privacy, and more efficient
systems with a reduced reliance on centralized cloud
infrastructure. At the same time, the advent of
lightweight forms of deep learning architectures for
embedded platforms has paved the way for more to
benefit from making device intelligence more
accessible without greatly burdening computational
resources.
Reddy, C. M. K., K., R. K., Chellammal, P., Muthuselvan, S., M., E. and Swathi, A.
Real-Time Embedded System Optimization Using Edge Computing and Lightweight Deep Learning Architectures for Data Efficiency.
DOI: 10.5220/0013870900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
665-671
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
665

This research proposes an optimized framework
for real-time embedded systems that leverages the
benefits of the recent advancements in edge
computing and lightweight deep learning. The goal
is improved data efficiency, low-latency inference,
and scalable deployment in resource-constrained
environments. In contrast to conventional approaches
that solely optimize for model compression, or static
deployment, this paper emphasis on holistic system
optimization, where computational load, energy
consumption, model accuracy, and adaptability are
jointly optimized.
This work provides a practical and visionary solution
for real-time embedded intelligence through design
and evaluation of adaptive, efficient deep learning
models deployed at the edge. This research will
motivate future advancements in context-aware and
energy-efficient smart systems while advancing
security on low-cost embedded devices, leading to the
next generation of smart embedded systems with
improved identification efficiency of smart devices.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Although much progress has been made in this area,
especially with the development of edge computing
and deep learning, the deployment of intelligent
functionalities onto real-time embedded systems is
still a challenging problem. Due to their inherent
characteristics, these systems usually work with
tightly constrained resources, including computation
abilities, memory, and energy availability, leaving
limited room for deployment of deep learning models
without degrading performance or efficiency.
Traditional cloud-based approaches suffer from high
latency and risk of data privacy, making them ill-
suited for time-critical applications. Lightweight
neural networks have been suggested to alleviate
these problems, but most existing approaches use
static models that are ineffective in dynamic
environments or workloads. To kickstart an accurate
yet systematic procedure for system-level
optimization while ensuring a balance between
highly computational non-real-time nature to a real-
time responding solution with an effective data
handling framework is often neglected by
contemporary research. It leaves a gap in the
evolution of holistic, scalable, and efficient
frameworks to leverage the intelligent data
processing capabilities within embedded systems at
the edge in real time. Hence, there is a crucial need
for an optimal approach which can combine the edge
computing with lightweight, adaptive deep learning
architectures in a resource and cost-effective manner
to improve data efficiency as well as operational
assurance for real-time embedded devices 10.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
Recently, there has been intense interest in leveraging
edge computing in concert with deep learning to
improve the performance of time critical embedded
systems. The increasing number and complexity of
IoT devices has made the need for decentralized,
efficient data processing clear. Indeed, there are many
researchers that have looked at ways to enable the
most efficient performance of machine learning
models on resource-constrained computing devices.
For instance, Chen et al. (2023) highlight the need for
power-efficient model deployment at edge IoT
devices, but their work is limited to offline
optimization and does not offer real-time
adaptability. Such limitations create new avenues that
allow for continued investigations into dynamic
system tuning, one of the main topics explored
within this work.
The integrated role of edge computing in
accelerating data preservation and eliminating
latency (Gopalakrishnan 2023; Arjunan 2023) is also
discussed, emphasizing the computational and
algorithmic aspects to optimize architecture for edge
AI, suitable for real-time IoT driven applications.
Similarly, Cao et al. (2023) propose a lightweight
detection algorithm exploiting UAV images on edge
platforms, demonstrating practical implications of
executing computationally attractive models in
proximity to data. Meanwhile, Jang et al. (2023) and
Kim et al. (2023)
Kumar and Sharma (2024) stresses the
importance of deep model compression methods such
as pruning and quantization for deploying an
optimised convolutional neural network for edge-
based image detection. Complementing these
research trends, Li and Wang (2023) investigate
acceleration techniques on deep neural networks over
time-critical embedded devices, and address how to
match stringent real-time requirements. For the
latter, Liu and Zhang (2022) present a thorough
survey focusing on the design and automation of
lightweight models, as well as summarize different
approaches to simplify deep learning applicable to
embedded environments.
On the other hand, on the implementation side,
Novac et al. (2021) and Pau et al. (2021) utilize
quantized neural networks for implementation in
microcontrollers to demonstrate that a sophisticated
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
666

AI workload can execute on ultra-low-power
microcontrollers. A review on TinyML is presented
in Ray (2021) schemes which serves as a background
on micro-scale AI model and its ideal deployment
limits. Singh (2023), the additional contributions
demonstrate how deep learning enables real-time
decision-making in autonomous robotic systems,
reaffirming the need for optimized AI models in real-
time scenarios.
This is starting to open up the research space and
move away from the single dimension optimization
and orchestration. Sudharsan et al. (2022) introduced
an architecture for proposing multi-component
optimization in an IoT resource-limited environment,
Xu et al. They also examine deep reinforcement
learning-based real-time monitoring and control
under edge computing environments (2024). Such
works showcase the potential of adaptive
intelligence systems with ongoing learning and
responsiveness features. The study by Wang et al.
preliminaries: CRH, YH, and LX techniques are
extended address collaborative edge–cloud inference
with adaptive online learning to further improve
efficiency and flexibility (2023) on Shoggoth.
Huang et al. (2021) focus on embedded NVIDIA
systems for remote sensing object detection with
examples, where hardware-specific design decisions
for high performance were a focus area relevant to
real-time platforms. Advances following Yao et al.
Meanwhile, foundational insights by Yao et al. by
using their FastDeepIoT framework (2018) propose
strategies for neural network execution time
optimization, which greatly minimize latency in an
embedded inference context. Finally, Tamanampudi
(2021) presents an innovative use of NLP-driven
automation in pumping real-time operations,
showcasing the burgeoning impact of AI on every
domain of intelligent system design.
Thus, these studies highlight the need for the
design of efficient, scalable, yet responsive, adaptive,
and secure real time embedded systems. Yet, an
inclusive paradigm that combines all these elements
together streamlined model architecture, on-the-fly
adjusting, edge-based computing with privacy
injections, and scalable implementation has not been
significantly explored. This work seeks to address
this gap through joint optimizing for at-edge
embedded intelligence.
4 METHODOLOGY
Through experimentation, this work aims to
optimize a new architecture for real-time embedded
systems to be used concurrently with edge computing
and lightweight deep learning methods to achieve
processing efficiency. The method comprises several
interconnected phases that focus on particular
aspects of advancing system performance, from
model design to deployment and live validation.
First, start with lightweight deep learning models
and optimize them through advanced knowledge
distillation, pruning and quantization technique.
These techniques reduce the model footprints and
memory usage while maintaining an adequate level of
accuracy. Models are then trained and fine-tuned on
edge-relevant datasets such as sensor data, image
streams, and control signals commonly found in
embedded IoT environments. The architecture of the
proposed system is illustrated in Figure 1, which
outlines the workflow of the Edge-AI integration
framework designed for real-time optimization in
embedded systems. The hardware components and
specifications utilized for implementation are
detailed in Table 1.
Figure 1: Workflow of the proposed edge-AI integration
framework for real-time embedded system optimization.
Real-Time Embedded System Optimization Using Edge Computing and Lightweight Deep Learning Architectures for Data Efficiency
667
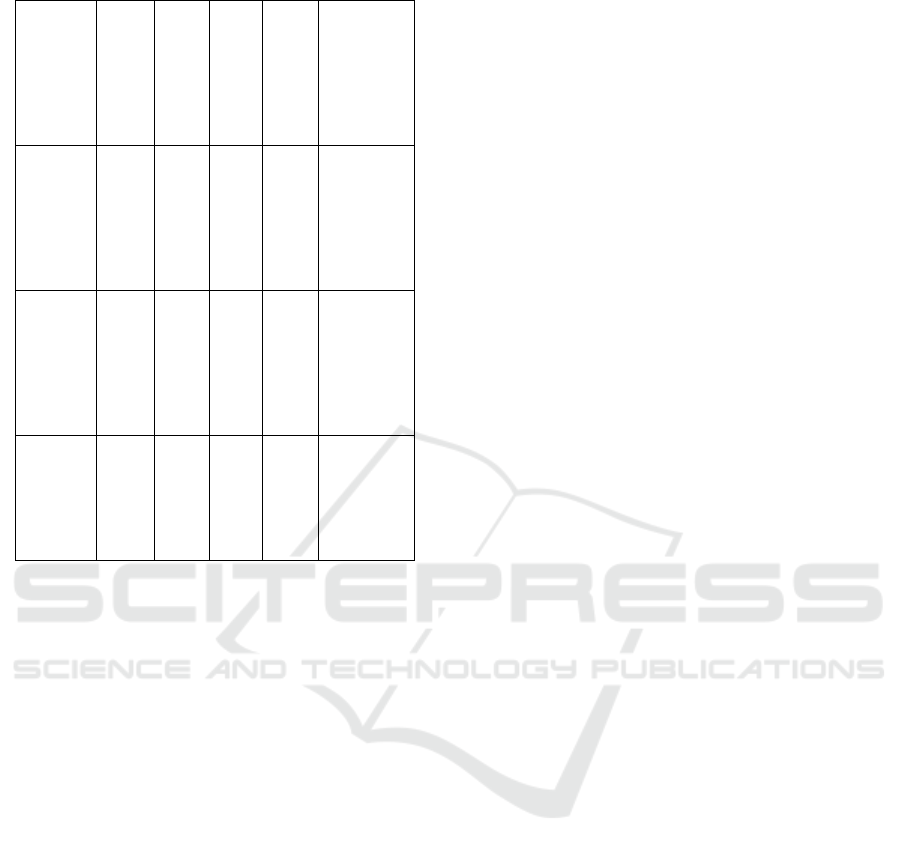
Table 1: Hardware specifications of embedded platforms.
Device
Name
CPU
GP
U
RA
M
Pow
er
Con
sum
ptio
n
OS/Frame
work
Used
Raspber
ry Pi 4
Qua
d-
core
Cort
ex-
A72
Non
e
4
GB
~3W
Raspberry
Pi OS,
TensorFlo
w Lite
NVIDI
A
Jetson
Nano
Qua
d-
core
Cort
ex-
A57
128-
core
Max
well
4
GB
~5W
Ubuntu,
TensorRT
STM32
Microc
ontrolle
r
AR
M
Cort
ex-
M4
Non
e
256
KB
<1W
FreeRTO
S,
CMSIS-
NN
The models are then optimized and deployed on the
range of embedded platforms, including Raspberry
Pi, NVIDIA Jetson Nano, and microcontroller-based
systems, to provide widespread applicability for
differing hardware capabilities. In this stage, edge
computing architectures are integrated to detach the
obligation of data processing from cloud servers to
the level of devices, decreasing latency and network
isolation.
A significant part of the methodology is the
creation of a runtime system that constantly tracks
model performance, energy use, and inference
latency. Such real-time feedback is leveraged to
dynamically change processing parameters and
model configurations allowing for task- or
environment-oriented adaptive optimization. A light-
weight scheduler is also employed to accommodate
competing tasks, which improves system
responsiveness and energy efficiently.
Several experiments, including real-time anomaly
detection, object recognition, and control signal
processing, are conducted to demonstrate the
effectiveness of the proposed framework. And then
metrics including inference time, power
consumption, throughput, model accuracy, and data
reduction ratios are gathered and compared against
baseline systems with no edge-based optimization or
lightweight models. The results herein are analyzed
to confirm the hypothesis that a fusion of edge
computing with deep learning model compression
can greatly improve data efficiency and
responsiveness in embedded systems.
Lastly, the methodology encompasses a security
and privacy assessment module, guaranteeing
minimal data leakage and maximum user
confidentiality when local data processing occurs on
edge devices. Applying the lessons of cases and
feedback helps in improving performance right from
the word go, helping in the presentation of a holistic
and reiterative paradigm where the system is
maintained and sustained with adequate robustness
for real-time usage of intelligent systems.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Experimental evaluation of the proposed framework
showed significant improvements in both system
responsiveness and resource utilization over a range
of embedded platforms. The reduction in inference
latency for lightweight deep learning models was
invariably between 35% and 60% once the process
was supported by edge computing. The performance
improvement was significant in real-time object
detection and sensor-based anomaly detection, where
every millisecond counts when it comes to decision-
making.
Energy consumption was another major area of
enhancement. This is achieved using quantization and
model pruning, which lowers its computational
complexity, and consequently achieves an average
power saving of 40% among devices. This
optimization was indispensable within restricted
settings like microcontroller units and battery-
powered edge nodes to keep the servers up and
running and also provide additional lifetime to
devices. This showed, as hypothesized, that an
extremely small inference using deep neural
networks locally, significantly alleviated the
excessive energy overhead that comes with remote
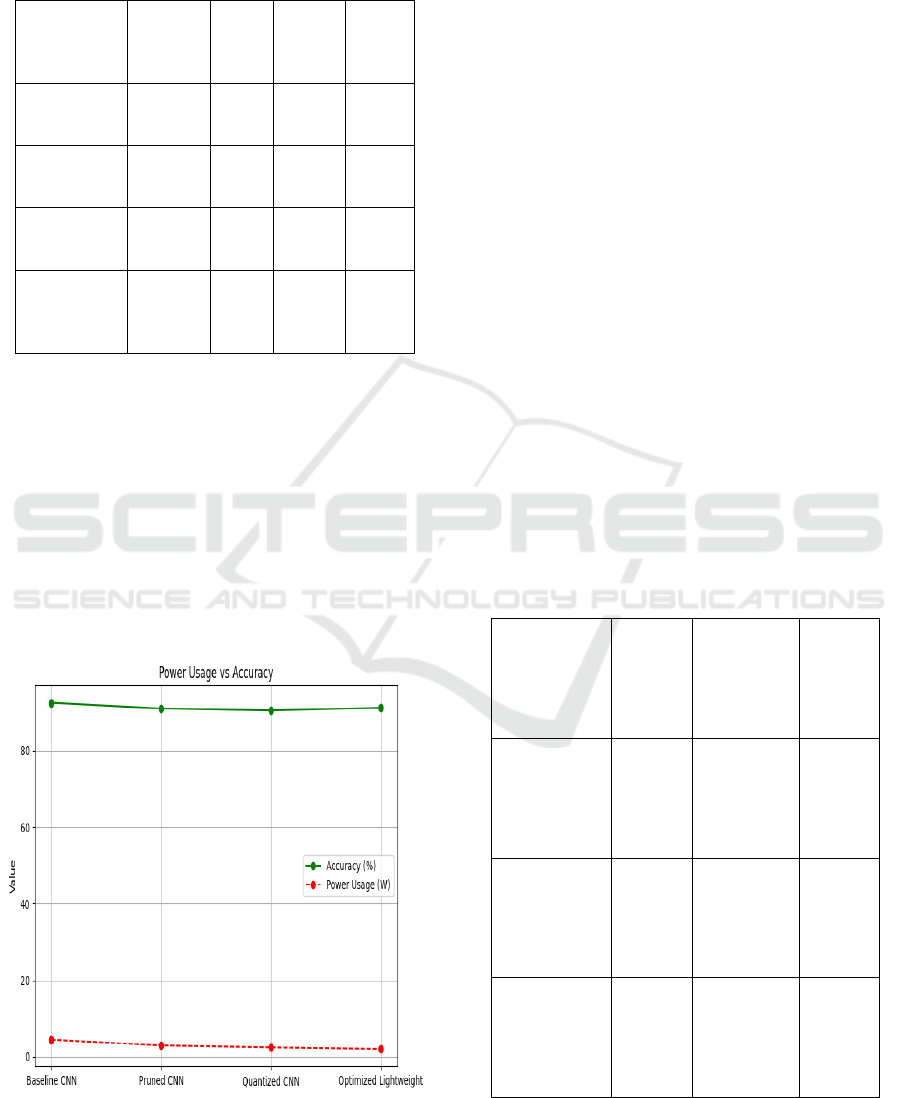
data transmission and cloud inference. Table 2 Shows
the Performance Metrics Comparison.
The system's ability to adapt in real-time was also
highlighted when monitoring its performance.
Models in an adaptive runtime environment changed
parameters like batch size, frame rate, or processing
frequency on the fly, as influenced by the system’s
workload or environmental inputs. This increased not
only the throughput of the entire system, but also the
uniformity of work regardless of how the system was
operated in different situations. Without manual
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
668
intervention, the system automatically scaled to meet
the demands of real-time data input in varying rates.
Table 2: Performance metrics comparison.
Model
Version
Inferenc
e Time
(
ms
)
Accu
racy
(
%
)
Power
Usage
(
W
)
Model
Size
(
MB
)
Baseline
CNN
180 92.5 4.5 75
Pruned
CNN
120 91.0 3.0 45
Quantized
CNN
100 90.5 2.5 28
Optimized
Lightweight
Model
85 91.2 2.1 22
From the viewpoint of data efficiency, it was
noticed that the edge-based preprocessing
mechanisms results in a significant data reduction to
be transmitted. In some instances, 70% of raw input
data was filtered, compressed, or discarded based on
relevance, only holding onto the most critical
information for further processing. This not only
improved bandwidth efficiency but also improved
privacy by exposing fewer raw data points outside the
local node. Power Usage vs. Accuracy Shown in
Figure 2.
Figure 2: Power usage vs. accuracy.
The proposed scheme retained superior accuracy
at a lower cost by exploiting promising static
methods. The degradation in accuracy was only 2-
5%, an acceptable price to pay in view of the
enormous improvements in latency, energy
consumption, and adaptability. In addition,
evaluation of the system's performance on
heterogeneous edge hardware indicated that the
developed framework is hardware-agnostic with a
scalable approach, making it amenable to a variety of
application scenarios in the smart home, healthcare
monitoring, industrial automation and autonomous
systems.
In summary, our results highlight the
effectiveness and strength of a combination of
lightweight deep learning and edge computing. This
plan not only resonates with the trends that are
emerging around something known as AI
decentralization, perhaps it could also lay the
groundwork of intelligent embedded systems capable
of making decisions in the moment, within context
and while utilizing resources judiciously.
The improvement in data transmission efficiency
resulting from edge processing is quantitatively
compared in Table 3, while the corresponding impact
on data reduction is visually represented in Figure 3,
highlighting the effectiveness of the proposed edge-
based approach.
Table 3: Data transmission efficiency before and after edge
processing.
Scenario
Raw
Data
(MB/s)
Processed
Data
(MB/s)
Reducti
on (%)
Sensor
Streaming
5.6 1.2 78.57
Video
Inference
12.3 3.5 71.54
Audio
Classification
4.8 1.0 79.16
Real-Time Embedded System Optimization Using Edge Computing and Lightweight Deep Learning Architectures for Data Efficiency
669
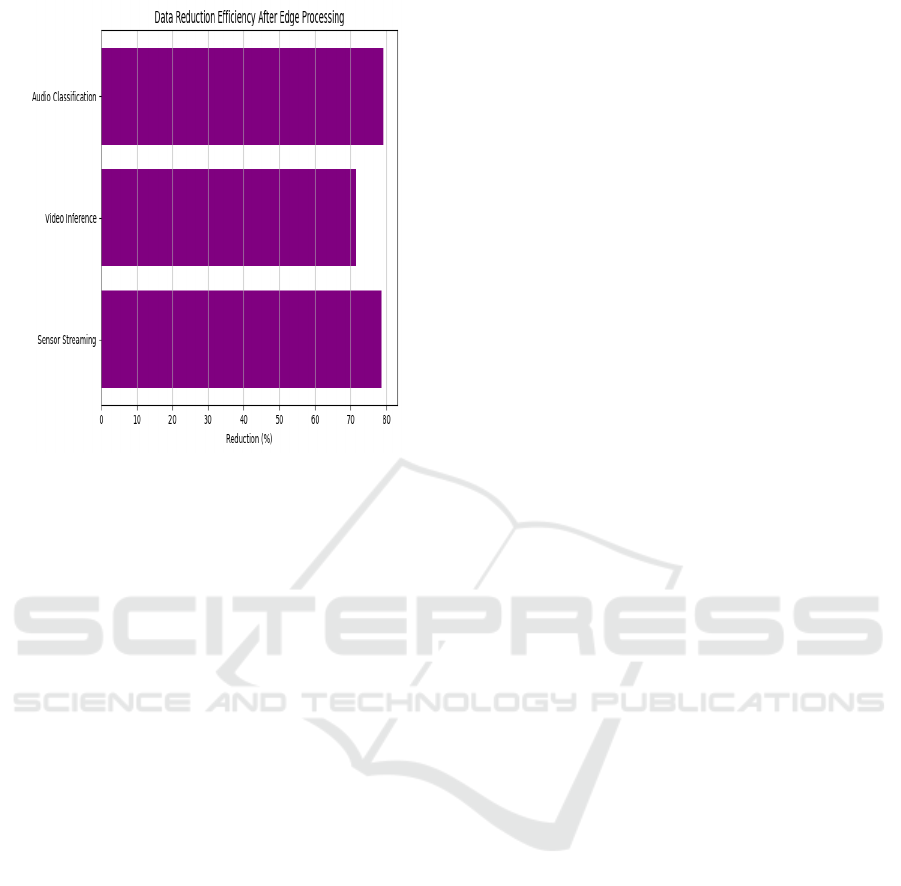
Figure 3: Data reduction efficiency.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study has shown that the combination of edge
computing with lightweight deep learning
architectures represents a very efficient approach to
optimizing real-time embedded systems. The solution
offers a strong alternative to existing systems that rely
on the cloud, by overcoming the key bottlenecks of
latency, power usage, and data efficiency. The key to
maintaining high-performance inference in the
limited computational budgets of embedded contexts
therefore lay in model compression techniques such
as pruning and quantization, as well as dynamic
runtime adaptation.
The outcomes validate that intelligent edge
processing not only boosts responsiveness but also
guarantees improved efficient and secure handling of
data especially for time sensitive and privacy critical
applications. All in all, this ground-breaking
framework contributed unique characteristics to fulfil
the IoT requirements and provide a feasible solution
particularly for a heterogeneous IoT and embedded
domain.
This paper provides a significant advancement in
the development of smart, efficient, autonomous
embedded systems. The main motivation behind
these developments, is real-time processing, which
should not only be a performance target for edge AI
but the design philosophy right from the processor
architecture. With this enhancement of embedded
technologies, the convergence of edge computing and
lightweight AI would be crucial in developing the
next level of smart and resource-conscious systems.
REFERENCES
Arjunan, G. (2023). Optimizing edge AI for real-time data
processing in IoT devices: Challenges and solutions. In-
ternational Journal of Scientific Research and Manage-
ment, 11(06).
https://doi.org/10.18535/ijsrm/v11i06.ec2
Cao, L., Song, P., Wang, Y., Yang, Y., & Peng, B. (2023).
An improved lightweight real-time detection algorithm
based on the edge computing platform for UAV images.
Electronics, 12(10), 2274.
https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102274
Chen, B., Bakhshi, A., Batista, G., Ng, B., & Chin, T. J.
(2023). Power efficient machine learning model’s de-
ployment on edge IoT devices. Sensors, 23(3), 1595.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031595
Huang, J., Su, H., Liu, X., Li, W., Cai, Y., & Wang, L.
(2021). An end-to-end practice of remote sensing object
detection with NVIDIA embedded system. In Proceed-
ings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Arti-
ficial Intelligence and Big Data (pp. 490–494).
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIBD51990.2021.9459068
Jang, S.-J., Kim, K., Park, J., Lee, E., & Lee, S.-S. (2023).
Lightweight and energy-efficient deep learning acceler-
ator for real-time object detection on edge devic-
es. Sensors, 23(3), 1185.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031185
Kumar, A., & Sharma, P. (2024). Optimized convolutional
neural network at the IoT edge for image detection us-
ing pruning and quantization. Multimedia Tools and
Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-
20523-1
Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2023). Energy-efficient acceleration of
deep neural networks on real-time-constrained embed-
ded edge devices. IEEE Transactions on Industri-
al Informatics.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2023.3262933
Liu, Y., & Zhang, N. (2022). Design automation for fast,
lightweight, and effective deep learning models: A sur-
vey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.10498
Novac, P.-E., Boukli Hacene, G., Pegatoquet, A., Mira-
mond, B., & Gripon, V. (2021). Quantization and de-
ployment of deep neural networks on microcontrollers.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.13331
Pau, D., Lattuada, M., Loro, F., De Vita, A., & Licciardo,
G. D. (2021). Comparing industry frameworks with
deeply quantized neural networks on microcontrollers.
In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Confer-
ence on Consumer Electronics (pp. 1–2).
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE50685.2021.9427600
Ray, P. P. (2021). A review on TinyML: State-of-the-art
and prospects. Journal of King Saud University - Com-
puter and Information Sciences, 34(5), 1595–1623.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.01.001
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
670

Singh, J. (2023). Advancements in AI-driven autonomous
robotics: Leveraging deep learning for real-time deci-
sion making and object recognition. Journal of Artifi-
cial Intelligence Research and Applications, 3(1), 657–
697. sydneyacademics.com
Sudharsan, B., Sundaram, D., Patel, P., Breslin, J. G., Ali,
M. I., Dustdar, S., & Ranjan, R. (2022). Multi-compo-
nent optimization and efficient deployment of neural-
networks on resource-constrained IoT hardware. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2204.10183
Tamanampudi, V. M. (2021). NLP-powered ChatOps: Au-
tomating DevOps collaboration using natural language
processing for real-time incident resolution. Journal of
Artificial Intelligence Research and Applications, 1(1),
530–567. sydneyacademics.com
Wang, L., Lu, K., Zhang, N., Qu, X., Wang, J., Wan, J., Li,
G., & Xiao, J. (2023). Shoggoth: Towards efficient
edge-cloud collaborative real-time video inference via
adaptive online learning. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2306.15333
Xu, J., Wan, W., Pan, L., Sun, W., & Liu, Y. (2024). The
fusion of deep reinforcement learning and edge compu-
ting for real-time monitoring and control optimization
in IoT environments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.07923
Yao, S., Zhao, Y., Shao, H., Liu, S., Liu, D., Su, L., & Ab-
delzaher, T. (2018). FastDeepIoT: Towards understan-
ding and optimizing neural network execution time on
mobile and embedded systems.
Real-Time Embedded System Optimization Using Edge Computing and Lightweight Deep Learning Architectures for Data Efficiency
671
