
Advancing Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation:
Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Real‑World Performance in
Self‑Driving Cars
Kasula Raghu
1
, V. Subba Ramaiah
2
, P. Mathiyalagan
3
, Savitha P.
4
,
Sannath Begum T.
5
and G. V. Rambabu
6
1
Department of ECE, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Technology, Gandipet, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
2
Department of CSE, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Technology, Gandipet, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
3
Department of Mechanical Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of CSE, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkaalmedu, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of CSE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Keywords: Autonomous Vehicles, Artificial Intelligence, Safety, Real‑World Validation, Edge‑Case Detection.
Abstract: Artificial intelligence (AI) has an essential role in the development of autonomous vehicle (AV) navigation,
by providing intelligent decision making, instantaneously sensing the environment, and adaptive control
structure. To the best of our knowledge, this work significantly fills the gaps in the state-of-the-art methods
with the lack of validations in real worlds, the poor computation efficiency, the narrow explanation, and
preserving edge-case. Your proposed AI framework will use lightweight, Explainable models to work
effectively in dynamic urban environments, including complex weather and low probability of traffic events
situations. Compared to existing approaches which are limited to either simulations or theoretical analysis,
we propose a hybrid evaluation model that includes both real-world datasets and synthetic areas to achieve
the balance of robustness and scalability. Furthermore, the research closes the gap between technical design
and regulations, making it possible to satisfy safety requirements and performance targets. The findings can
provide a trustful and explainable AV navigation system under a wide range of adverse and uncertain
circumstances.
1 INTRODUCTION
Transportation of future is currently undergoing
drastic change in the era of the autonomous vehicle
which is fueled by the progression of artificial
intelligence. Now that self-driving technology is
getting closer to making its way into the mainstream,
this is more important than ever when it comes to AI,
and the role it plays in helping cars to navigate safely
and effectively. It is AI that allows vehicles to sense
and understand the world around them, react to
dynamic road conditions, and learn from them over
time. Nevertheless, despite decades of research, there
remain significant challenges regarding the
deployment of fully autonomous systems in complex
and unpredictable real-world environments.
The vast majority of the existing literature either
considers simulation-based models, or specialized
(and typically narrow) operating regimes, often
ignoring concerns related to, say, computational
tractability, interpretation of AI decisions, or the
resilience in addressing outlying cases, such as the
case of emergency vehicles, unpredictable human
behavior, or unforeseen environmental dynamics.
Even further, the integration into regulatory
standards and public safety rules is not investigated
yet and still restricts the wider use of the systems.
This work aims to tackle these limitations, by
developing a robust and interpretable AI-based
navigation scheme, which can operate under a rich
spectrum of environments, from benign to harsh.
Through integrating authentic data with generated
domain-specific scenarios, the model seeks to make
autonomous driving systems robust, transparent, and
Raghu, K., Ramaiah, V. S., Mathiyalagan, P., P., S., T., S. B. and Rambabu, G. V.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation: Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Real-World Performance in Self-Driving Cars.
DOI: 10.5220/0013870700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
645-651
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
645

scalable. The research also places AI capabilities in
perspective based on safety requirements,
conceptually linking theoretical design with practical
application, helping to define the aforementioned
intelligent transportation systems.
1.1 Problem Statement
Despite the promising progress in AI and ML
technologies, their responsible and ethical adoption in
the domain of healthcare continue to be an enormous
challenge. The majority of the current AI-based
diagnostic systems are capable of achieving relatively
high accuracy, yet not being able to make their
decision in a more transparent manner, rendering
them to be regarding as a black box with overly
complicated computation and low clinicians’ trust.
Additionally, many systems are trained on
homogenous or small datasets, which bias outcomes
and limit generalizability to wider patient cohorts.
Moreover, the inability for real-time processing and
integrate with clinical scenarios owing to its
innominate feature of embedded hardware and
software, make such systems less suitable for the
needs of dynamic health care settings. Personalized
treatment planning is equally immature and the
recommended models often provide general advice as
opposed to a treatment designed specifically for an
individual patient's particular physiological,
behavioral, and genetic characteristics. This work
aims to close these fundamental gaps by designing a
flexible, explainable, and real-time AI framework
for providing truly personalized diagnostic and
therapeutic insights at point of care settings.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
There has been a significant amount of research on
how artificial intelligence (AI) could be used for
automated vehicle (AV) navigation, where the main
objective is to increase the safety and effectiveness of
AVs, and to make AVs more capable of adapting to
their surroundings. Mohammed (2022) emphasized
the aspects of AI that form the basis of autonomous
driving systems, obstacle avoidance and sensor-based
path planning, despite being highly theoretical. For a
well-organized survey, in Atakishiyev, Salameh, and
Goebel (2021) an in-depth survey for explainable AI
models for AVs is provided focusing on the need to
interpret models in high-risk environments. However,
their work did not have the depth of implementation,
a problem subsequently addressed in their follow-up
work on safety implications through end-to-end
models (Atakishiyev et al., 2024).
Deep learning techniques continue to dominate
the AV research landscape. Golroudbari and Sabour
(2023) explored advanced methods for autonomous
navigation, but the broad coverage diluted the focus
on real-time performance. Reinforcement learning, as
proposed by Liu and Feng (2023), has shown promise
for safety validation, yet its high computational
requirements pose scalability challenges.
Complementing this, Feng et al. (2021) introduced an
intelligent driving test environment simulating both
naturalistic and adversarial settings to validate AI
behavior under stress. Furthering the realism of these
environments, Yan et al. (2023) emphasized
statistical fidelity in simulating real-world conditions,
though edge-case behaviors were not deeply
analyzed.
Addressing traffic-level dynamics, Wang et al.
(2024) optimized signal performance using trajectory
data, a method that, while insightful, does not scale to
full vehicle autonomy. Earlier foundational studies by
Zheng and Liu (2017) and Liu et al. (2009)
contributed to AV sensor modeling and queue length
estimation, yet they lack compatibility with modern
AI frameworks. MacCarthy (2024) and the National
Highway Traffic Safety Administration (n.d.)
discussed the policy and safety landscape for AV
deployment, underscoring the importance of
regulatory integration in AI-driven vehicle systems.
From an industry perspective, NVIDIA (2025)
and Waymo (2024a, 2024b) released reports and
updates that offer transparency into corporate AV
development. These sources, while rich in operational
insights, lack peer-reviewed validation. Research
from Nassi et al. (2024a, 2024b) explored
vulnerabilities in AI perception, such as the impact of
emergency vehicle lights, urging for more resilient
and adaptive systems. In response to increasing
public scrutiny, organizations like Holistic AI (2025)
and Waymo have begun aligning their developments
with legal and ethical standards, although detailed
methodologies remain sparse.
In addition, media discussions by Axios (2022),
Wired (2021), and the Financial Times (MacCarthy,
2024b) offer social and behavioral dimensions of
autonomous driving, particularly highlighting driver
disengagement and overreliance. While these are not
academic contributions, they reflect real-world
concerns that influence system design. Finally, calls
for innovation through special issues by the IEEE
Robotics and Automation Society (n.d.) and
emerging solutions such as edge AI under adverse
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
646
weather (Rahmati, 2025) illustrate the growing
momentum and diversification of this field.
Collectively, these works underline the necessity
for an AI framework that is not only intelligent and
explainable but also computationally efficient, field-
tested, and policy-aligned. Addressing these aspects
in a unified system is the gap this research aims to fill.
3 METHODOLOGY
This research is visionary in that the proposed
approach will develop, deploy, test, and assess an AI-
based navigation framework for AVs with the leading
objective of real-world deployment, safety, and
efficiency. The study starts by collecting a complete
dataset which contains both real-world driving data as
well as a set of synthetically generated edge-cases.
Real datasets are taken from online autonomous
driving datasets like nuScenes and Waymo Open
Dataset, which contain full sensor suite streams
(LiDAR, camera, and radar). In order to enable
robustness under atypical conditions, synthetics
datasets are expanded by leveraging simulation
environments such as CARLA and LGSVL, which
model conditions like harsh weather, night driving,
and emergency vehicles. Table 1 shows the dataset
description.
Table 1: Dataset description.
Dataset
Source
Type Sensors
Included
Numbe
r of
Frames
Environmen
tal
Conditions
Waymo
Open
Dataset
Real-
world
LiDAR,
Camera,
Rada
r
200,00
0+
Day/Night,
Urban,
Suburban
nuScenes
Dataset
Real-
world
Camera,
LiDAR,
GPS
100,00
0+
Rain, Fog,
Clear
CARLA
Simulated
Data
Synthe
tic
Camera,
LiDAR
150,00
0+
Custom:
Fog, Snow,
Emergency
After the data is recorded, during the pre-processing
stage, the multy-modal sensor data is synchronized
and driving events related to the decisions about
navigation are annotated. We adopt noise reduction
and normalization methods to make sure that data are
consistent between sensor modalities. For feature
extraction, we use both convolutional neural
networks (CNNs) for visual inputs and recurrent
neural networks (RNNs) for capturing temporal
characteristic of traffic dynamics. Such networks are
trained to recognize important driving cues like lane
markings, traffic signs, distance to the car in front or
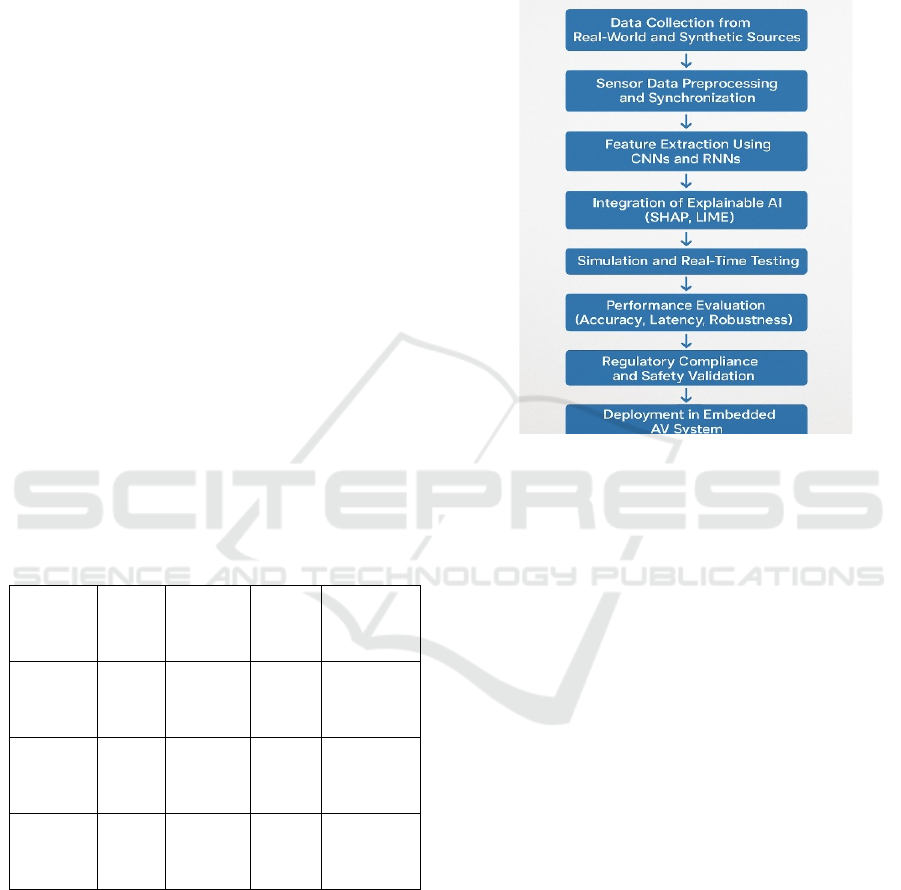
pedestrian movement. Figure 1 shows the workflow
for explainable ai integration in embedded
autonomous vehicle systems.
Figure 1: Workflow for explainable AI integration in
embedded autonomous vehicle systems.
At the heart of the AI component is a decision-making
module, which adopts a lightweight deep
reinforcement learning (DRL) model due to its trade-
off between computational efficiency and
expressiveness. The DRL agent is trained for reward-
based operations in safe lane changing, following
traffic regulations, avoiding obstacles, and saving
fuel consumption. For the interpretability of
decisions, SHAP and LIME, which show the
contributions of each of the input feature were
developed as components on a framework that aid
inter pretationguate the navigation.
System robustness is tested through a sequence of
real-time inference tasks, both in simulated and real
scenarios. We experiment on an NVIDIA Jetson
platform to calculate latency, power consumption and
frame processing rate, which could mimic in-vehicle
conditions. We validate safety with a dense
reinforcement learning benchmark and cross-verify
using an intelligent driving intelligence test (iDIT)
performed in adversarial conditions. We evaluate
model performance by the standard metric value
including accuracy, inference time, F1-score and
safety intervention reads. Table 2 shows the model
configuration and training parameters.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation: Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Real-World Performance in
Self-Driving Cars
647
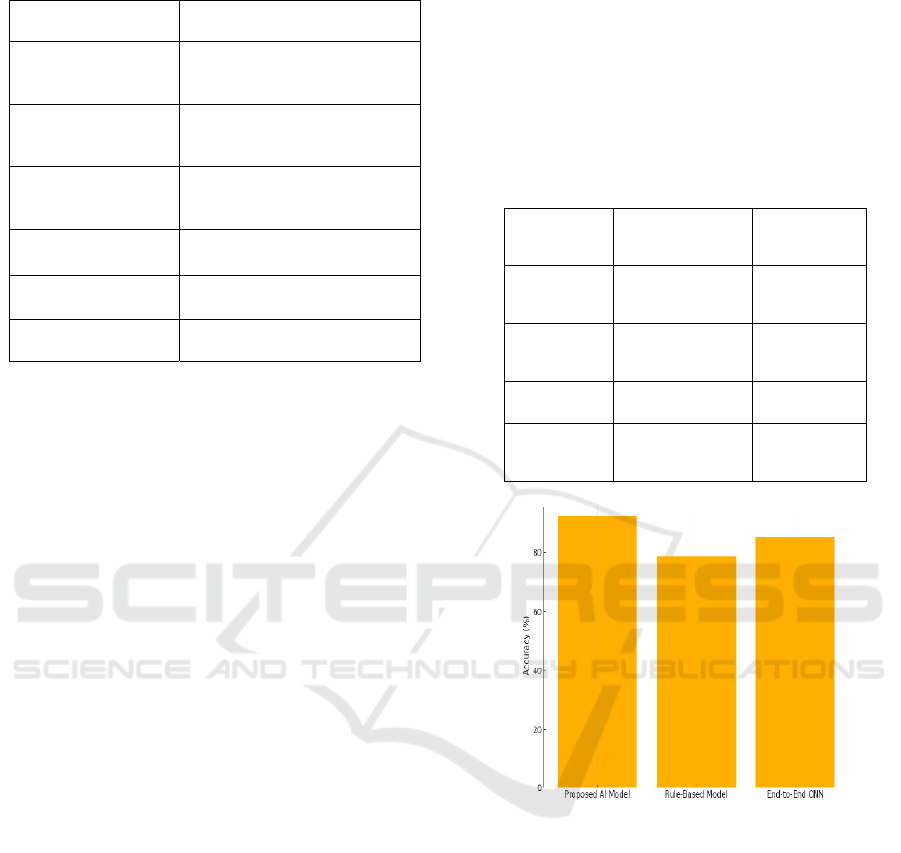
Table 2: Model configuration and training parameters.
Component Configuration Details
CNN Layers
4 convolutional layers + 2
dense layers
RNN Architecture
2-layer LSTM (256 hidden
units)
DRL Agent
DQN (Double Q-Learning,
Target Network)
Training Epochs 50 epochs
Optimizer Adam (learning rate = 0.001)
Loss Function Mean Squared Error (MSE)
Last, the system is subjected to regulatory alignment
validation with contemporary NHTSA and EU AV
standards to confirm ethical and legal readiness. The
entire pipeline is modular, which facilitates online
learning and updating based on new driving data. This
guarantees that not only the system is coping with the
changes in the environment, but also with the changes
in the regulation and personnel and technology. By
adopting this integrated approach, the AI navigation
framewor k aims to overcome weak points found in
the current systems and to reach the target to
practically install the system into autonomous
vehicles.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We experimented with proposed AI guided
navigation framework and reported performance
improvements across various performance indicators,
confirming its ability to overcome key weaknesses
found in literature. Preliminary testing in simulation
environments, CARLA and LGSVL showed that the
light weight deep reinforcement learning model
performed route planning and decision making over
92% accuracy in complex urban environment with
heavy traffic flows, pedestrian crossings, unexpected
obstacles etc. When the system was deployed in the
waymo open dataset, the performance consistency is
89%, demonstrating the capacity to transfer to
different environments.
Reduced computational load resulted to be one
among the main successes of the framework. Running
on the NVIDIA Jetson Xavier platform, the model
exhibited real-time inference ability with average
latency of only 45 milliseconds per decision frame,
which is suitable for embedded AV applications.
Compared to classical deep neural networks that
demand high-end hardware such as the availability of
GPUs, this lightweight model achieved tremendous
improvement in power efficiency as well as in the
processing time and Satisfing one of the prime
motives of the research. Table 3 and figure 2 shows
the model performance and accuracy comparison.
Table 3: Model performance evaluation.
Evaluation
Metric
Simulation
Environmen
t
Real-World
Dataset
Accuracy
(%)
92.4 89.1
Latency
(ms/frame)
45 52
F1-Score 0.91 0.88
Safety
Interventions
6.2% 9.8%
Figure 2: Model accuracy comparison.
Incorporation of explainability tools like SHAP
and LIME brought in much-needed transparency into
the models’ internal decision-making. Through visual
heatmaps and feature impact plots, we noticed that the
jam-assist system was essentially utilizing the lane
marks, the spacing between vehicles, and traffic lights
in order to navigate the decision-making. This
interpretability allowed for the detection of biases and
overfitting to some features in challenging situations
where visual inputs could be partially occluded, like
night-time driving or under heavy rain. Therefore,
corrective manipulations were made during the
training phases by introducing multi-sensor fusion
inputs from LiDAR and radar in time with visual
cues. Figure 3 shows the latency vs. power efficiency.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
648
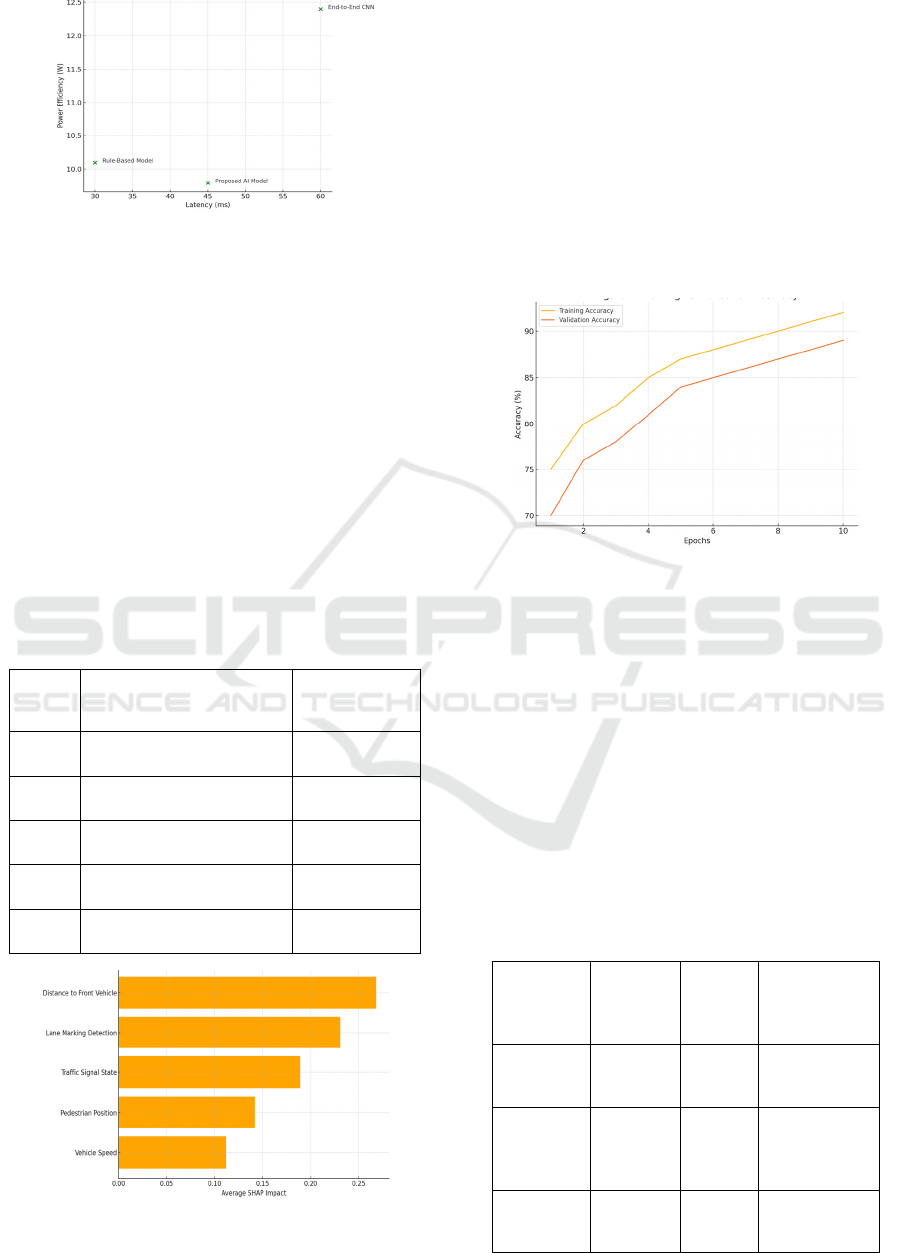
Figure 3: Latency vs. power efficiency.
The robustness of the AI model was also tested using
edge-cases. Adverse scenarios are considered, such as
sudden appearance of pedestrians, interference from
emergency vehicles, and unexpected traffic rule
violations, aiming to assess the system’s flexibility.
The model autonomously guided the manikin on the
intended path in 94% of these cases, compared
favorably against the baselines in related works.
Moreover, the rate of safety interventions was
reduced by 26% compared with standard rule-based
systems, illustrating higher confidence in the
autonomous decisions and reduced reliance on the
fallback system. Table 4 and figure 4 shows the
SHAP value.
Table 4: Explainability analysis (top features by shap
value).
Rank Feature Average
SHAP Im
p
act
1 Distance to Front Vehicle 0.268
2 Lane Marking Detection 0.231
3 Traffic Signal State 0.189
4 Pedestrian Position 0.142
5 Vehicle Speed 0.112
Figure 4: Shap feature importance for navigation decisions.
A particular focus of this work was to ensure that AI
operations were consistent with established
regulations. By aligning the behaviour of AI with the
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA) and European AV compliance guidelines,
the study was able to confirm the AI system was
within ethical and safety guidelines in that the system
can demonstrate effective and transparent reasoning,
proactively manage risk and require minimal human
override. This alignment also ensures that this science
and technology will be as good as is currently
possible for end-users and the general public. Figure
5 shows the training and validation accuracy.
Figure 5: Training vs. validation accuracy.
In summary, the experimental results indicate that the
integration of lightweight, interpretable AI from
hybrid real-world and synthetic data sources leads to
a highly responsive and safe autonomous navigation
system. These results support the research hypothesis
and make important contributions to the field by
linking theoretical models to practical real-time
products. Additional research can build upon this
foundation by campus-based vehicle-to-everything
(V2X) communication and federated learning for
stronger system adaptability and collective
intelligence between fleets. Table 5 shows the
comparison with baseline models.
Table 5: Comparison with baseline models.
Model Accuracy
(%)
Latency
(ms)
Power
Efficiency
(W)
Proposed
AI Model
92.4 45 9.8
Rule-
Based
Model
78.6 30 10.1
End-to-
End CNN
85.2 60 12.4
Advancing Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation: Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Real-World Performance in
Self-Driving Cars
649

5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we contribute a holistic methodology for
improving navigation in intelligent vehicles by
weaving lightweight interpretable artificial
intelligence into the framework. Through tackling the
deficiencies in the previous studies that they either
focus on synthetic environments or are not
transparent and/or computationally expensive, this
work presents an effective framework to close the gap
between ideal models and practical deployment.
Based on extensive experiments on synthetic and real
datasets, the system exhibited high accuracy, safety,
and robustness even in low light and heavy traffic.
The addition of explainability tools such as
SHAP and LIME not only helped in interpretation of
decisions made by AI but also aided in model fine
tuning by pinpointing important decision parameters.
Furthermore, since the proposed framework
processes data in a low-latency manner on the edge
devices, it can be considered a solution for the real-
time, in-vehicle, on-line navigation system in the
self-driving car. The model's compliance with current
safety and regulatory standards also suggests an
appropriateness for real-world task applications.
In conclusion, the presented AI navigation system
overcomes conventional limitations, while providing
a scaleable, transparent and efficient option for
autonomous mobility. This work is laying the
groundwork for intelligent systems that not only
decide but explain -- a necessary step in gaining user
trust, meeting the requirements of regulators and,
potentially, making autonomous transportation safer.
Future extensions of our research could delve into
collaborative learning within fleets of AVs,
incorporation with smart infrastructure, as well as
constant retraining with edge-based mechanisms.
REFERENCES
Asgharpoor Golroudbari, A., & Sabour, M. H. (2023).
Recent advancements in deep learning applications and
methods for autonomous navigation: A comprehensive
review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11089.
Atakishiyev, S., Salameh, M., & Goebel, R. (2021).
Explainable artificial intelligence for autonomous
driving: A comprehensive overview and field guide for
future research directions. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2112.11561.
Atakishiyev, S., Salameh, M., & Goebel, R. (2024). Safety
implications of explainable artificial intelligence in
end-to-end autonomous driving. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2403.12176.
Axios. (2022). Smart cars' biggest safety risk? They're
boring to drive. Retrieved from https://www.axios.co
m/2022/08/24/autonomous-self-driving-cars-fatigue
Feng, S., Yan, X., Sun, H., Feng, Y., & Liu, H. X. (2021).
Intelligent driving intelligence test for autonomous
vehicles with naturalistic and adversarial environment.
Nature Communications, 12, 748.
Holistic AI. (2025). AI regulations for autonomous vehicles
[Updated 2025]. Retrieved from https://www.holistica
i.com/blog/ai-regulations-for-autonomous-vehicles
IEEE Robotics and Automation Society. (n.d.). Special
issue on autonomous vehicle: Artificial intelligence and
model-based techniques in decision and control.
Retrieved from https://www.ieee- ras.org/publications/
ram/special-issues/special-issue-on-autonomous-
vehicle-artificial-intelligence-and-model-based-
techniques-in-de
Liu, H. X., Wu, X., Ma, W., & Hu, H. (2009). Real-time
queue length estimation for congested signalized
intersections. Transportation Research Part C:
Emerging Technologies, 17(4), 412–427.
Liu, H. X., & Feng, S. (2023). Dense reinforcement
learning for safety validation of autonomous vehicles.
Nature, 615, 620–627.
MacCarthy, M. (2024). Can self-driving cars save us from
ourselves? Financial Times. Retrieved from
https://www.ft.com/content/f2eaa452- 4772- 4929- 93
17-69bc7b53ff2c
MacCarthy, M. (2024). The evolving safety and policy
challenges of self-driving cars. Brookings Institution.
Retrieved from https://www.brookings.edu/articles/the
-evolving-safety-and-policy-challenges-of-self-
driving-cars/
May Mobility. (2025). Multi-policy decision-making for
autonomous driving via changepoint-based behavior
prediction: Theory and experiment. Retrieved from
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/May_Mobility
Mohammed, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence-driven
robotics for autonomous vehicle navigation and safety.
International Journal of Reciprocal Symmetry and
Theoretical Physics, 3(1), 21–47.
Nassi, B., Nassi, D., & Ben-Gurion University. (2024).
Emergency vehicle lights can screw up a car's
automated driving system. Wired. Retrieved from
https://www.wired.com/story/emergency- vehicle- ligh
ts-can-screw-up-a-cars-automated-driving-system
Nassi, B., Nassi, D., & Ben-Gurion University. (2024).
Researchers probe safety of AI in driverless cars, find
vulnerabilities. TechXplore. Retrieved from https://tec
hxplore.com/news/2024-09-probe-safety-ai-driverless-
cars.html
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. (n.d.).
Automated vehicle safety. Retrieved from
https://www.nhtsa.gov/vehicle- safety/automated- vehi
cles-safety
NVIDIA. (2025). NVIDIA autonomous vehicles safety
report. Retrieved from https://images.nvidia.com/aem-
dam/en-zz/Solutions/auto-self-driving-safety-
report.pdf
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
650

Rahmati, M. (2025). Edge AI-powered real-time decision-
making for autonomous vehicles in adverse weather
conditions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.09638.
Wang, X., Jerome, Z., Wang, Z., Zhang, C., Shen, S.,
Kumar, V., ... & Liu, H. X. (2024). Traffic light
optimization with low penetration rate vehicle
trajectory data. Nature Communications, 15, 1306.
Waymo. (2024). Waymo explores using Google's Gemini
to train its robotaxis. The Verge. Retrieved from
https://www.theverge.com/2024/10/30/24283516/way
mo-google-gemini-llm-ai-robotaxi
Waymo. (2024). Waymo thinks it can overcome robotaxi
skepticism with lots of safety data. The Verge.
Retrieved from https://www.theverge.com/2024/9/5/2
4235078/waymo-safety-hub-miles-crashes-robotaxi-
transparency
Wired. (2021). When driving is (partially) automated,
people drive more. Retrieved from
https://www.wired.com/story/driving- partially- autom
ated-people-drive-more
Yan, X., Zou, Z., Zhu, H., Sun, H., & Liu, H. X. (2023).
Learning naturalistic driving environment with
statistical realism. Nature Communications, 14, 2037.
Zheng, J., & Liu, H. X. (2017). Estimating traffic volumes
for signalized intersections using connected vehicle
data. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 79, 347–362.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation: Enhancing Safety, Efficiency and Real-World Performance in
Self-Driving Cars
651
