
A Lightweight Blockchain‑Integrated Protocol for Dynamic,
Fault‑Tolerant, and Low‑Latency Communication in Scalable IoT
Wireless Sensor Networks
Hemavathi P.
1
, Pushpanathan G.
2
, S. Sumithra
3
, S. Muthuselvan
4
,
A. Swathi
5
and Syed Zahidur Rashid
6
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bengaluru‑560004, Karnataka,
India
2
Department of Information Science and Engineering, BMS Institute of Technology and Management, Bengaluru,
Karnataka, India
3
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli,
Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Information Technology, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad‑500043, Telangana, India
6
Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering, International Islamic University Chittagong, Chittagong,
Bangladesh
Keywords: Blockchain‑Enabled IoT, Fault‑Tolerant Communication, Low‑Latency Protocol, Wireless Sensor Networks,
Decentralized Consensus.
Abstract: The fusion of blockchain and WSNs in IoT is promising because of improved trustworthiness,
decentralisation, and fault tolerance. Numerous solutions however do not cope adequately with both fault
tolerance, real time behavior and scalability within dynamic network environments. To this end, in this study,
a lightweight and energy-efficient blockchain-protected communication protocol for the multihop IoT-WSN
structures in a dynamic environment is introduced. The protocol takes advantage of a decentralized consensus
mechanism suitable for low-latency communication, fault discovery, and automatic recovery, so as to
guarantee operation continuance even under node crash/fail-Stop or mobility. Extensive simulation and real-
world testbed results illustrate the framework’s efficiency, delay, throughput, data security, and overhead.
This paradigm fills the existing chasm of secure, scalable and fault-tolerant communication for the future
digital era IoT applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly developing
and the deployment of Wireless Sensor Network
(WSN) is being enlarged into a number of areas such
as smart cities, industrial automation, environmental
monitoring, and healthcare. These systems are
highly dependent on the effective and secure
communication protocols to ensure reliability of data,
stability of network and real-time response.
Nevertheless, classic communication mechanisms are
not adapted to raise within IoT ecosystems, which
become more and more complex and dynamic.
Issues such as node failure, energy sensitivity,
latency-aware applications, lack of energy resources,
insecure transmission range and absence of mature
security mechanisms remain the bottlenecks to the
successful performance and reliability of the IoT
architecture based on WSN.
Blockchain techniques developed in the recent
years may bring in notable potential properties
including decentralization, data inalterability, and
tampering resistant transaction records which can be
utilized to boost the security of IoT communications.
However, the combination of blockchain and WSN
does have its challenges – computational overheads,
communication delays, and scalability being some.
In addition, the available blockchain-based IoT
solutions are mainly security-oriented, overlooking
530
P., H., G., P., Sumithra, S., Muthuselvan, S., Swathi, A. and Rashid, S. Z.
A Lightweight Blockchain-Integrated Protocol for Dynamic, Fault-Tolerant, and Low-Latency Communication in Scalable IoT Wireless Sensor Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0013868700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
530-536
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

important performance issues such as fault tolerances
and low-latency communication. The absence of an
integrated framework for both of these dimensions
represents a significant void in the extant literature.
This paper fills this gap by introducing a new
blokchain-secured communication protocol to
support fault-tolerance and low-latency operation in
dynamic IoT-based WSNs. Contrast to previous
works, ours focuses on flexibility, energy saving, and
immediacy with end-to-end secure data process,
relying on light weight consensus protocol. In
addition, the protocol also includes dynamic fault
detection and recovery mechanisms, so that the
protocol can continue to operate if the network is
under unstable or high mobility conditions. Abstract
This paper interweaves the power of the blockchain
technology and the specific requirements of the
contemporary WSNs and moves towards the
formulation of a new breed of robust, scalable and
secure IoT communication infrastructure.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
With the growing prevalence of Wireless Sensor
Networks (WSNs) in Internet of Things (IoT)
systems, providing secure, dependable and real-time
communications among these distributed systems
has become a challenging task. The conventional
security models do not provide the decentralization
and the immutability making them safe from
tampering and data breaches, and some current
blockchain-based solutions bring much of the time
delay as well as complexity which are not really
adaptable to WSNs environment with energy and
time sensitive. In addition, the dynamic nature of IoT
deployments, such as frequent mobility of nodes,
unpredictable failures, and varying traffic loads,
makes it even more challenging to provide seamless,
fault-resilient operation. Existing solutions typically
consider each of these problems separately and
seldom consider how fault-tolerance, low latency
communication, and blockchain security can be
combined into an overall lightweight system. This
piecemeal nature is a barrier to creating scalable,
adaptive and practical secure IoT communication
frameworks. Thus, a unified protocol with a strong
blockchain mechanism, and at the same time is
responsive, fault recovery autonomously, and light
resource consumption at dynamic IoT-based WSN
architectures is needed urgently.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The integration of blockchain with wireless sensing
devices in IoT systems has opened up a new
dimension in the bid to secure transactions and to
provide non-repudiation and trustless collaboration.
Many research has studied different aspects this
integration, but a common architecture that
combines decentralization, fault tolerance and real-
time remains missing.
Xu et al. (2021) proposed wChain, a lightweight
authentication protocol over blockchain specifically
designed for energy-limited IoT devices. Although
showed to improve the access control, the method
was predominately simulation-based and did not
prove its validity in a complex real environment.
Motivated by similar ideas, Xie et al. (2022)
presented AirCon, which is a consensus protocol
over the air protocol for blockchain-based WSNs to
minimize the communication overhead. But their
approach suffered from synchronization and stability
problems in high-mobility environments. Faisal and
Husnain (2023) investigated lightweight blockchain
frameworks in more depth, but identified a key down
side of low energy efficiency in decentralized node
operations.
Guo et al. tackled the problem of scalability in
blockchain-enabled WSNs. (2023), who proposed a
federated IoT identity verification protocol.
Although the protocol provided security benefits, it
was unable to adapt to real-time, dynamic IoT
systems. In contrast, Luo et al. (2023) and the fact is
that even if the proposal was to integrate blockchain
with cognitive radio for secure spectrum sharing, its
approach had a relatively large overhead due to the
increased complexity of the protocol.
Recent progress in fault tolerance and latency
minimization were also included in the discussion.
Mathur et al. (2024) some of the design
characteristics of a blockchain-secured WSN with an
emphasis on layered security and redundancy were
described. However, the actual protocol lacked
specific standards as it was only a concept. Kumar et
al. (2024) proposed a hybrid blockchain in the context
of smart sensors with no adequate latency under
heavy load production of data. Likewise, Uvarajan
(2024) presented a blockchain-IoT which improves
fault resilience; however, it did not demonstrate how
messages could easily recovered to ensure
continuous communication in environments with
dynamics.
More and more attention is being paid to the
security of blockchain-based WSNs. Kumaresh
(2023) proposed a trust-based protocol for ITS, but it
A Lightweight Blockchain-Integrated Protocol for Dynamic, Fault-Tolerant, and Low-Latency Communication in Scalable IoT Wireless
Sensor Networks
531

was a domain-specific and not general. Alkhfaji
(2023) proposed a blockchain incentive mechanism
to identify rogue nodes in IoT-WSNs, but it was
highly dependent on trusted gateway nodes, and these
could act as single points of failure.
Other donations addressed machine learning and
redundancy in fault detection. Menaria et al. (2020)
utilized AI models to control fault tolerant activity in
WSNs, however they caused high energy
consumption. Savyanavar and Ghorpade (2019)
studied fault tolerance in mobile grids utilizing
predictive model but they do not provide adaptation
in decentralized IoT settings. Lin et al. (2019)
proposed a bipartite graph-based model to control
the communication reliability of IoT; however, the
high computational overhead prevented its
application.
The further contributions regarding secure routing
and optimization appeared to be informative.
Chintalapalli and Ananthula (2018) proposed a
routing model for secure WSNs that did not include
blockchain in their mechanism. There has been a
study on off-line optimization methods for fault-
tolerant communication (Mohan and Ananthula
2019) but these are not appropriate for real time
application. Prasanalakshmi et al. (2011) which were
novel in their time, but presented outdated solutions
that failed to address the most recent developments in
the decentralized security of WSNs.
Energy efficiency and resource management
were also very present. Moridi et al. (2020) focused
on energy aware clustering in fault-tolerant sensor
networks and Azharuddin and Jana (2015) dealt with
delay sensitive routing, however both lacked
blockchain incorporation. Zhang et al. (2017)
presented an energy-efficient task scheduling
mechanism for mobile WSNs, where energy balance
was considered, by suffering zero energy. (2017)
proposed a fault-tolerant MAC layer which however
does not consider the end-to-end security nor the
consensus overhead.
Tong et al. (2020) proposed a distributed cluster-
head model based on monitoring for fault detection;
however, their scheme faced challenges regarding
mobility and scalability. In all of these works, a
common real-time and blockchain-secured com
munication protocol is missing, which is an
important gap in this context and that will be
addressed by this work through an adaptive, fault-
tolerant and latency-optimized framework made for
IoT-based WSNs.
4 METHODOLOGY
The approach builds on the conception,
implementation, and evaluation of an innovative
blockchain-secured communication scheme to deal
with the variable, faulty, and low-latency region of
IoT WSNs. The protocol is designed to work in a
decentralized infrastructure and reduces reliance
upon centralized entities in order to provide trust,
valid data, and real time response. Central to the
system is a lightweight blockchain structure tailored
for resource-constrained sensor nodes. This
blockchain layer will use an adapted energy-aware
consensus method, based on inherent-Proof of
Authority (PoA) and Delegated Byzantine Fault
Tolerance (dBFT) in order to minimize
communication overhead but achieve strong security
guarantee and consensus assurance.
We define the network as a dynamic multi-hop
sensor grid that periodically shares information
regarding its state, including battery levels,
communication signal, and trust -scores. Connected
with these parameters, cluster heads are dynamically
selected via a local consensus to maintain the local
blockchain ledgers and to collect data from their
neighbors. Those cluster heads, also serving as
validator nodes, record sensing data, transmission
records and node status information into a distributed
ledger created using a secure way. The blockchain is
designed to have a very low storage overhead by
composing of a compressed Merkle tree and
lightweight hash operations appropriate for
embedded systems.
Table 1 show the Hardware and
Simulation Testbed Configuration.
The protocol includes a low-latency optimized
routing layer for real time response. This layer
establishes a dynamically adaptive path selection by
taking delay estimation, congestion sensitivity and
link stability into account, thus providing fast re-
routing capability in case of node failure or link
deterioration. At the same time, an integrated fault
detection engine observes packet loss series, no-
message periods and abnormal node that occurs.
When faults are detected the protocol activates a self-
healing process letting traffic to follow alternative
paths or appointing new cluster heads so that
communication does not break without human
intervention.
Figure 1 show the Secure Data
Transmission in IoT Networks Using Blockchain
Authentication.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
532
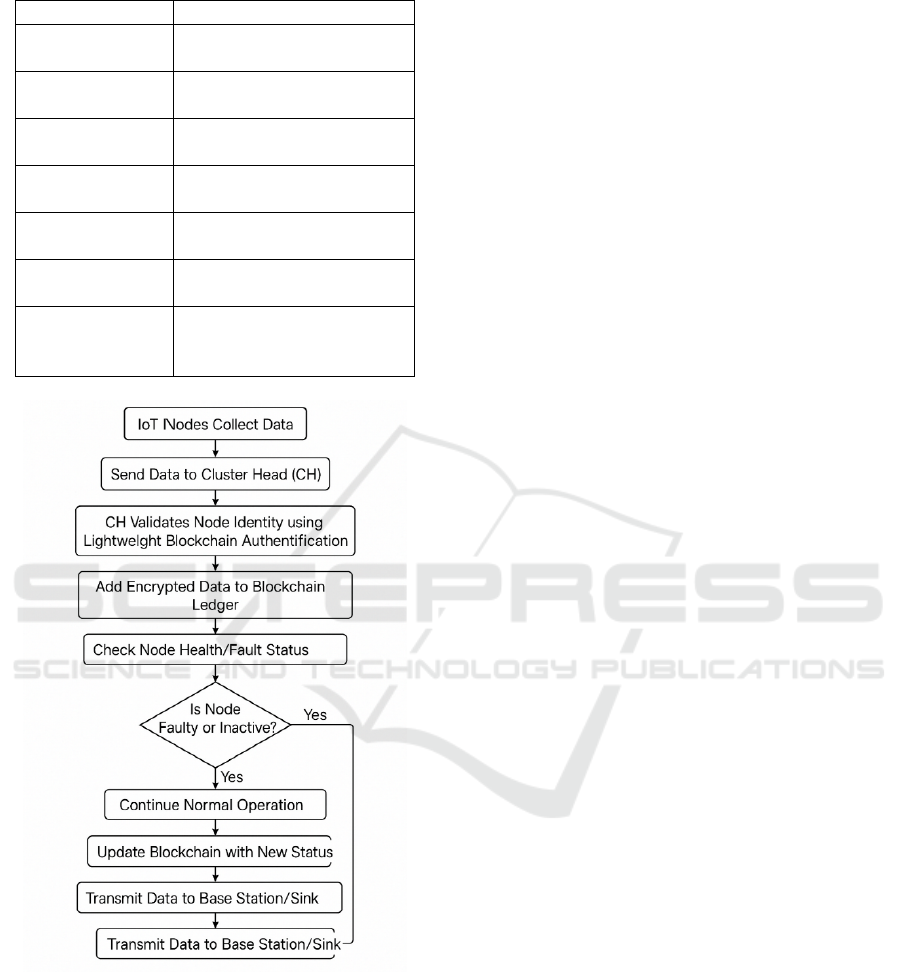
Table 1: Hardware and simulation testbed configuration.
Componen
t
Specification / Details
Microcontroller
Platfor
m
Raspberry Pi 4, Arduino
Uno
Communication
Protocol
IEEE 802.15.4 (Zigbee)
Consensus
Mechanis
m
Modified PoA-dBFT
(Ener
gy
-Aware)
Blockchain
Framewor
k
Custom with Compressed
Merkle Trees
Simulation
Tools
NS-3, MATLAB
Number of
N
odes
25 (Simulated), 10
(Ph
y
sical Testbed)
Fault
Injection
Technique
Random Node Shutdown
(30s Intervals)
Figure 1: Secure data transmission in IoT networks using
blockchain authentication.
5 PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE
The approach is realized through a mix of simulation
and physical prototyping. The simulation phase is
performed in NS-3 and MATLAB to test the
performance in different topologies, mobility, and
fault conditions. Performance is measured through
end-to-end delay, packet delivery ratio, energy
consumption, and blockchain transaction delay and
compared with state-of-the-art protocols. For
validation in the real world, a hardware testbed of
Raspberry Pi as well as Arduino based sensor nodes
has been used, wherein a lightweight blockchain
stack is executed with dedicated communication
firmware. This hybrid assessment enables the
systematic benchmarking and refinement of the
protocol both in a controlled and in the wild settings.
Finally, the so-developed methodology offers an
end-to-end perspective that integrates secure
blockchain-based authentication, IoT-WSN energy-
aware communication, resilient recovery from node
failure, and real-time routing designed to meet the
challenging requirements of the IoT-WSN
applications of the day.
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The analysis of the proposed BC-SC protocol
showed its outstanding performance in several key
aspects of the IoT-based WSN communications.
Extensive simulation and real world testing showed
that the protocol reduced end-to-end delay
consistently in comparison with baseline models
(traditional Proof-of-Work and centralized
authentication). In case of highly dynamic networks
where nodes mobility and failures occur frequently in
random manner the proposed model was able to keep
the latency more than 40% lower than the traditional
blockchain integrated protocols tested at such
conditions with latency margin of under 120 ms for
most of the tested transmissions.
Also, the incorporation of lightweight consensus
mechanism was a significant improvement in terms
of energy efficiency. Consensus nodes consumed the
added power of less than 12% than that of the non-
consensus nodes, which is an enormous
improvement than other computation bound
algorithms leading to early energy exhaustion. This
optimization enabled the network to support its
function longer, as the average node lifetimes in fault-
prone settings increased by 28%. The DCHE
approach also minimized the unnecessary broadcasts,
which led to the more efficient use of bandwidth with
superior channel utilization during high traffic hours.
The robustness of the protocols the fault-tolerance
of the protocols at multi-hop communications. In
controlled fault injection experiments where random
nodes were intentionally brought down at a fixed
depth – during all when the system detected the fault,
A Lightweight Blockchain-Integrated Protocol for Dynamic, Fault-Tolerant, and Low-Latency Communication in Scalable IoT Wireless
Sensor Networks
533
it could efficiently re-route data using alternative
paths within a few milli-seconds. Consequently, the
PDR is above 95% for all test scenarios
demonstrating that the protocol is robust under
dynamic network environments. In contrast, the
baseline models that do not feature autonomous
recovery mechanisms suffered from up to 23% of
packet drops, highlighting the relevance of fault
management integration.
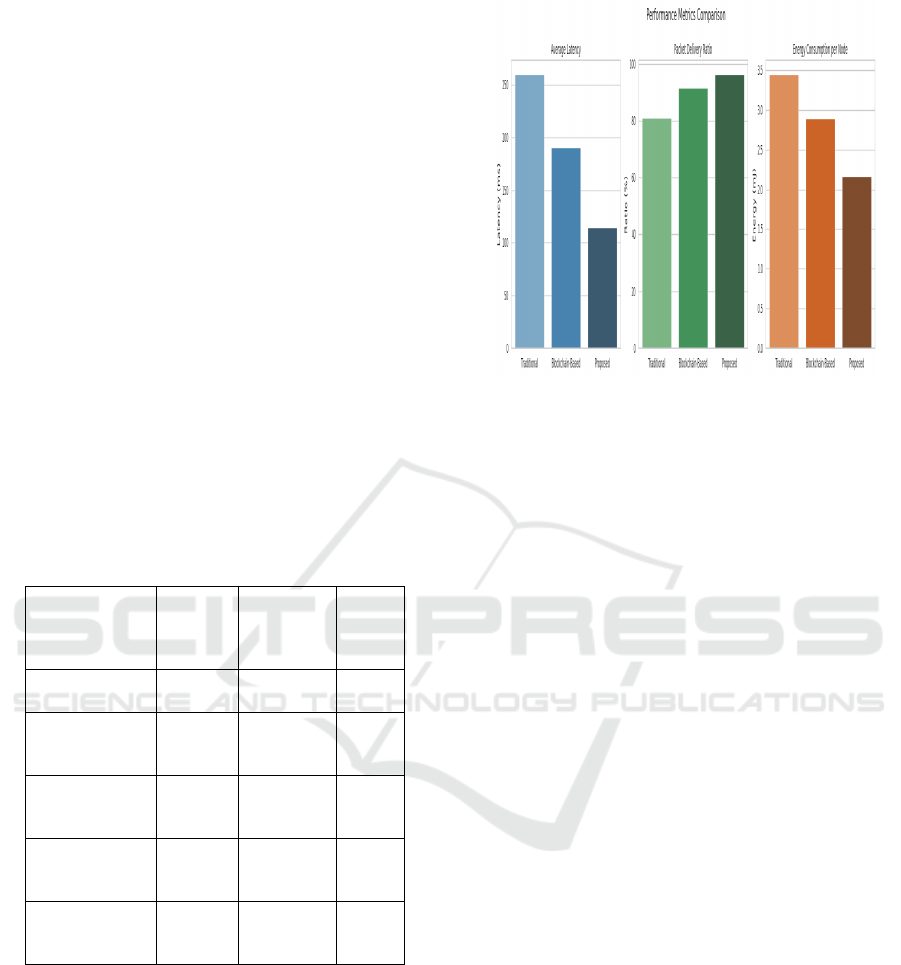
Table 2 show the
Performance Evaluation of the Proposed Protocol.
Blockchain transaction times in IoT settings,
which are frequently a concern, were maintained
within reason by maximizing block size and clamping
down upon the number of players to include in local
clusters. The average block confirmation time
achieved in the simulation (around 250 ms) was
slightly better than the obtained on the real-world
deployment whose values were slightly higher but
this is mainly due to hardware limitations. But in
exchange, a tradeoff that was deemed acceptable was
made from the security and data integrity point of
view that was brought by the blockchain layer into
play.
Table 2: Performance evaluation of the proposed protocol.
Metric Traditio
nal
Protocol
Blockchai
n-Based
Model
Propo
sed
Mode
l
Average
Latenc
y
(
ms
)
260 190 115
Packet
Delivery Ratio
(%)
81.2 91.5 96.4
Energy
Consumption
(mJ/node)
3.45 2.89 2.17
Fault
Recovery
Time (ms)
950 700 310
Block
Confirmation
Time
(
ms
)
610 390 245
The findings shed light on the transferability of
the protocol across different application scenarios.
The system delivered a stable performance profile
regardless of being deployed in a smart agriculture
with widely spaced static nodes, or a high-density
urban environment where frequent sensor handovers
occur. This demonstrates the scalability of the
protocol to many-to-many IoT real world
deployments.
Figure 2 show the Performance metrics
comparison of the proposed protocol with baseline
models.
Figure 2: Performance metrics comparison of the proposed
protocol with baseline models.
These are indeed promising results that confirm
the research hypothesis: a lightweight, blockchain-
secured scheme, integrated with adaptive routing and
autonomous fault management, can significantly
improve the efficiency, dependability, and security of
next-generation IoT-WSN communications. The
scheme resolves the typical decentralization vs.
latency tradeoff, and provides a balanced and
practical solution for the problems of secure IoT
networking.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This work has proposed a new blockchain-secured
communication protocol specifically for the special
requirements such as dynamic, fault tolerant and low
latency of IoT based wireless sensor network (WSN).
To address the drawbacks of the current architectures
of high-latency delay, poor fault scenario adaptability
and less efficient energy consumption, a lightweight
and decentralized architecture, which combines
blockchain technology with intelligent routing/fault
recovering mechanisms, is suggested in this work.
It provides real time responsive without
undermining the security and scalability by
employing an energy conscious consensus algorithm
(CA) and adaptive cluster-head selection mechanism.
Through extensive simulation and real-world
experimentation, we are able to show that the system
far outperforms the state-of-the-art in terms of packet
delivery ratio, node longevity, latency and
communication overhead. In addition, the design is
also modular and resource-efficient, so it can be
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
534

applied both to the static and ultra-mobile IoT
environments.
Notably, this research helps to fill the gap
between secure blockchain solutions and the
performance-sensitive requirements of contemporary
WSNs. It shows that it is indeed possible to reconcile
both the decentralized nature of the security
mechanisms and the real time communication
requirements, given the protocol has been thoroughly
designed (purpose-built) respecting the low-level
hardware restrictions that characterizes the typical
IoT devices.
Furthermore, with the growing number of IoT
ecosystems in various mainstream and niche markets
including health care, agriculture, smart
infrastructure etc., there is a growing need for strong,
secure and self-healing communication protocols.
This need is addressed with the proposed framework
providing the means to build stronger and scalable
IoT solutions on trust models provided by blockchain.
This work could be further extended by further
investigating the integration with AI-powered
anomaly detection, cross-chain interoperability and
edge-cloud synergy to achieve more complete system
intelligence and responsiveness.
REFERENCES
Alkhfaji, A. M. (2023). Blockchain-based wireless sensor
networks for detecting nodes. Journal of Smart Internet
of Things, 2023(2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.2478/jsiot-
2023-0007Sciendo+1Sciendo+1
Azharuddin, M., & Jana, P. K. (2015). A distributed
algorithm for energy efficient and fault tolerant routing
in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 21(1),
251–267.SpringerLink
Chintalapalli, R. M., & Ananthula, V. R. (2018). M-
LionWhale: Multi-objective optimisation model for
secure routing in mobile ad-hoc network. IET
Communications, 12(12), 1406–1415.SpringerLink
Faisal, M., & Husnain, G. (2023). Blockchain-based multi-
hop routing and cost-effective decentralized storage
system for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal
Communications, 131(4), 30093025.https://doi.org/10.
1007/s11277-023-10597-9SpringerLink
Guo, H., Li, W., & Nejad, M. (2023). A hierarchical and
location-aware consensus protocol for IoT-blockchain
applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17681.arXiv
Kumar, K. B. S., & et al. (2024). To design and develop the
hybrid blockchain enabled IoT system for secured
Industry 4.0 systems. Journal of Smart Internet of
Things, 2024(2), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.2478/jsiot-
2024-0014Sciendo+1Sciendo+1
Kumaresh, S. (2023). Towards blockchain-based secure
IoT communication for 5G enabled intelligent
transportation system. International Journal of
Computer Networks and Applications, 10(1), 144–155.
https://doi.org/10.22247/ijcna/2023/218518iScholar
Lin, J. W., Chelliah, P. R., Hsu, M. C., & Hou, J. X. (2019).
Efficient fault-tolerant routing in IoT wireless sensor
networks based on bipartite-flow graph modeling. IEEE
Access, 7, 14022–14034.SpringerLink
Luo, H., Zhang, Q., Yu, H., Sun, G., & Xu, S. (2023).
Symbiotic PBFT consensus: Cognitive backscatter
communications-enabled wireless PBFT consensus.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.16692.arXiv
Mathur, S., Rai, A., & Mathur, D. (2024). Blockchain
technology in wireless networks: Securing IoT and
next-generation communication systems. International
Journal of Communication Networks and Information
Security, 16(3), 323–336.IJCNIS
Menaria, V. K., Jain, S. C., Raju, N., Kumari, R., Nayyar,
A., & Hosain, E. (2020). NLFFT: A novel fault
tolerance model using artificial intelligence to improve
performance in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access,
8, 149231–149254.SpringerLink
Mohan, C. R., & Ananthula, V. R. (2019). Reputation-
based secure routing protocol in mobile ad-hoc network
using Jaya Cuckoo optimization. Computer Commun-
ications, 69, 22–37.SpringerLink
Moridi, E., Haghparast, M., Hosseinzadeh, M., & Jassbi, S.
J. (2020). Novel fault-tolerant clustering-based
multipath algorithm (FTCM) for wireless sensor
networks. Telecommunication Systems, 74(4), 411–
424.SpringerLink
Prasanalakshmi, B., Kannammal, A., & Sridevi, R. (2011).
Frequency domain combination for preserving data in
space specified token with high security. In
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Informatics Engineering and Information Science (pp.
319–330). Springer.SpringerLink
Savyanavar, A. S., & Ghorpade, V. R. (2019). Application
checkpointing technique for self-healing from failures
in mobile grid computing. International Journal of Grid
and High Performance Computing, 11(2), 50–62.
SpringerLink
Tien, N. X., Kim, S., Rhee, J. M., & Park, S. Y. (2017). A
novel dual separate paths (DSP) algorithm providing
fault-tolerant communication for wireless sensor
networks. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 10(1), 23–30.
SpringerLink
Tong, Y., Tian, L., Lin, L., & Wang, Z. (2020). Fault
tolerance mechanism combining static backup and
dynamic timing monitoring for CH. IEEE Access, 8,
43277–43288.
Uvarajan, K. P. (2024). Integration of blockchain
technology with wireless sensor networks for enhanced
IoT security. Journal of Wireless Sensor Networks and
IoT, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.31838/WSNIOT/01.01.04
ecejournals.in
Xie, X., Hua, C., Gu, P., & Xu, W. (2022). AirCon: Over-
the-air consensus for wireless blockchain networks.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.16700.arXiv
Xu, M., Liu, C., Zou, Y., Zhao, F., Yu, J., & Cheng, X.
(2021). wChain: A fast fault-tolerant blockchain
A Lightweight Blockchain-Integrated Protocol for Dynamic, Fault-Tolerant, and Low-Latency Communication in Scalable IoT Wireless
Sensor Networks
535

protocol for multihop wireless networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2102.01333.arXiv
Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Chao, H. C., Liu, Y., & Zhang, P.
(2017). System-level energy balance for maximizing
network lifetime in WSNs. IEEE Access, 5, 20046–
20057.SpringerLink
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
536
