
Experimental Evaluation of Deep Learning Based Plant Leaf Disease
Detection System Using Computer Assisted Image Processing
Techniques
P. Ramya, Mohanraj S., Mageshwaran N., Mohamed Shafeeq J. and Monishwar D. K.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Mahendra Engineering College, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Deep Learning, Leaf Disease, Plant Disease Detection, Image Processing, Neural Classification Network,
ENCN, Support Vector Machine, SVM.
Abstract: One of the most important contemporary agricultural techniques, plant disease detection aids in the early
diagnosis of crop illnesses, which allows for more effective management and the prevention of substantial
losses. Color changes, spots, lesions, or structural malformations are common visible indicators of plants
damaged by diseases. Handheld, drone-mounted, or integrated into smart agricultural automation systems,
high-resolution cameras or sensors record these symptoms. Computer Vision and Deep Learning (ML)
algorithms examine the gathered data for patterns in form, texture, and color to determine the presence of
illnesses. To achieve accurate disease identification in plant leaves, this paper proposes a novel deep learning
model which is Enhanced Neural Classification Network (ENCN). So, the performance of the model can be
tested by cross-validating it with a conventional learning scheme Support Vector Machine (SVM). An
accurate diagnosis enables farmers to implement timely countermeasures against diseases such as blast,
bacterial blight or powdery mildew. The system in many cases will recommend the use of pesticides, changes
to that amount of water or fertilizer that is applied to crops or quarantining sick plants to stop disease from
spreading, she said. The technology improves productivity, ensures accuracy, reduces costs, and promotes
sustainable farming practices by utilizing the resources that are already there more effectively. Recent
advancements in plant disease detection including integration of the internet of things and drone monitoring
result into crop management, high yield and sustainable agriculture environment. Beyond aiding early
diagnosis and management, predictive analysis from plant disease detection systems, based on patterns in
historical and environmental data, enables farmers to prepare for future crop disease outbreaks. For all, these
systems make it possible to monitor a vast area, which saves time and effort when evaluating the health of
enormous farmlands.
1 1 INTRODUCTION
Plant disease detection is an essentially significant
field of study using Deep Learning for the detection
and diagnosis of plant diseases (Wubetu Barud
Demilie,2024). Since they may seriously affect
agricultural production, it is very important to
diagnose these diseases in time and to take
precautions against them to guarantee food security
and healthy crops. (Payal Trivedi, et al.,2024) Firstly,
the process would have required a lot of time and
money from the specialists who had to work out, on a
laborious and error-prone way, the identification of
plant diseases. The following figure, Figure 1
represents the dataset image samples.
However, with the advent of AI and ML, one can
now automate the identification of plant diseases with
high accuracy and speed in modern agriculture, which
is very promising (3. Manjunatha Shetti gere Krishna,
et al.,2025).
One of the common techniques that many
researchers employ is using supervised learning to
build machine learning models for plant disease
diagnosis. The algorithms are trained over labeled
datasets, wherein the plant images are divided into
either healthy or diseased types of images (Priyanka
Pradhan, et al., 2024). The model learns to discriminate
between healthy and diseased plants by analysis of
millions of images and considered variables such as
color, texture, shape and some presence of unique
patterns characteristic to several diseases.
Ramya, P., S., M., N., M., J., M. and K., M.
Experimental Evaluation of Deep Learning Based Plant Leaf Disease Detection System Using Computer Assisted Image Processing Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0013867400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
443-452
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
443

Figure 1: Dataset Image Samples.
The advantage of proposed model ENCN lies in
their ability to process complex visual information
with the built-in automatic extraction of relevant
features from images. That is exactly why they are
used to mark subtler signs of plant diseases in
situations where conventional methods might not
work very well. The performance of the detection
system relies chiefly upon the quality of the dataset
on which the machine-learning models are trained.
The datasets contain both healthy and diseased plants,
including quality images of plants grown under
managed conditions. Datasets also have labels to
indicate the presence or absence of diseases. Several
of such datasets contain examples of three highly
frequent agricultural diseases: leaf rust, powdery
mildew, and blight; in training models to detect signs
of disease, these diseases are of outstanding
importance in biological and agricultural research.
(B.V. Nikith, et al., 2023). A robust model would
require a large, diverse and balanced dataset, which is
not very easy to establish (Cemal Ihsan SOFUOGLU, et
al., 2024). This dataset should include a range of plant
species and diseases.
As research progresses and various datasets
become more widely available, this will become a
useful tool for farmers to safeguard crops and,
therefore, increase global food security by providing
enhancements in the speed, accuracy, and scalability
of machine-learning algorithms to identify instances
of plant diseases (Alwan Fauzi, et al.,2023). First, one
has to collect a large number of datasets containing
images of good and poor conditions of plants as a
step-in kernel research of machine learning for plant
disease detection. Images of plants collected to be
labeled to show the absence or presence of certain
diseases have been captured by devices like mobile
phones, drones, or digital cameras. Next, these
images undergo preprocessing to enhanced form
features for appearance. This includes resizing,
normalization, and augmentation (such as rotating,
flipping, or scaling) in order to achieve data
heterogeneity, thus preventing overfitting. Image
preprocessing permits the machine learning model to
concentrate on the main features such as shape, color,
and texture, which are critical in the detection of
disease (Rashmi Ashtagi, et al.,2025). An important
aspect of autonomous feature extraction is deep
learning models such as CNNs, which enable the
system to internally learn complex patterns of input
images (Ashutosh Kumar Singh, et al.,2022). After
training on a labeled dataset, a model's performance
is evaluated using various metrics such as accuracy,
precision, and recall. In this case, a validation set is
used for this purpose. The model is capable of being
adjusted as necessary, in order to improve its
performance. Once the model is accurate enough, it
will be used in real-time applications, just like online
platforms or mobile applications, so that farmers can
identify disharmony in his/her crops by uploading
pictures. In order to help guide farmers toward the
rapid detection of possible illnesses, the software
analyses these images and provides predictions. In
addition, the system may improve itself over time in
terms of different plant species and climatic
conditions, since it learns from new data. There is
great potential for machine-learning-powered plant
disease detection to revolutionize the existing
agricultural sector by reducing losses on crops and
increasing food security.
The process of automating and improving the
accurate and timely diagnosis of plant disease can be
achieved through machine learning, especially via
convolution neural networks. Convolutional neural
networks, unlike any other machine learning
algorithm, learn salient features from raw image data,
such as pattern, texture, and shape specific to the plant
disease. Training on a large dataset of labeled images
allows convolutional neural networks to detect some
early signs of diseases that might not be perceivable
by the human eye. This allows prompt diagnosis,
enabling farmers to take corrective or preventive
measures before the disease spreads and causes large
crop losses (Kamaldeep Kaur, et al.,2024).
Wzw the ultimate goal is to implement an easy-
to-use living system to allow real-time diseases
identification in crops using different platforms such
as mobile application; this will allow farmers better
management of crop health and hence increased
agricultural yield.
(i) To enrich the model and avoid overfitting, image
synthesis is used to create additional images of
infested plants and hence augment the dataset.
(ii) In general, such approaches produce artificial
images of sick plants by training their convolutional
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
444

neural networks with the data definitions provided
through GANs. Where there is the absence of
adequate labeled datasets, this can prove useful.
(iii) Early prediction and curing of plant diseases and
minimizing losses to crops are made easier through
the use of synthetic images produced by image
synthesis, which increases the accuracy of disease
detection models.
(iv) Synthetic images of infected plants can be used
to fine-tune pre-trained CNN models. This allows
efficient transfer learning and more accurate disease
diagnosis.
2 RELATED WORKS
Plants form the basis of the world's food supply;
nonetheless, plant diseases cause considerable losses
in the output of crops, related to many environmental
conditions (Muhammad Shoaib, et al.,2025).
Nevertheless, Tropical plant disease identification
undertaken by people becomes a long and tedious
task. It is not always very reliable as a tool in Plant
Disease detection and control. One way to tackle
these difficulties is by implementing modern
technologies like Deep Learning (DL) and Machine
Learning (ML). These will allow for the early
detection of plant illnesses. This study delves into the
latest developments in plant disease diagnosis using
ML and DL approaches. The trials included in this
paper show that these methods can improve the
efficiency and accuracy of plant disease detection,
and the research focuses on publications from 2015 to
2022. Besides plant disease recognition, this paper
also covers the challenges and constraints of ML and
DL for plant diseases, such as lack of data, poor
images, healthy versus sick plant distinction, etc. The
survey provides a comprehensive review of the state-
of-the-art work on the detection of plant diseases,
along with their pros and cons, and recommendations
to overcome the challenges faced while employing
them. As a result, it is valuable for researchers,
practitioners, and industry professionals in this field.
Scientists are now adopting intelligent
agriculture-a means of greatly enhancing production
with the incorporation of the use of Artificial
Intelligence (AI)-to deal with various problems
within agricultural fields (Sherihan Aboelenin, et
al.,2025). There are a lot of illnesses that harm crop
yields, and there are a lot of plants in the globe, thus
finding and classifying plant diseases isn't an easy
task. Any AI-based system aims to accurately
classify plant illnesses and detect them early. In order
to greatly enhance the accuracy of plant leaf disease
categorization, this research suggests a hybrid
architecture. The power of Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViT) is
utilized in this suggested model. Robust global
features are extracted using an ensemble model that
includes the popular CNN designs VGG16,
Inception-V3, and DenseNet20. The next step in plant
disease detection with high accuracy is applying a
ViT model for local feature extraction. Under testing
in the apple and corn public datasets, there are four
classes per each dataset. The apple dataset has an
accuracy of 99.24% while the corn dataset has 98%.
This hybrid model will efficiently ascertain and
classify multi-class plant leaf diseases in reference to
other similar published models.
To protect agricultural crop output and guarantee
food security, early and precise identification of plant
leaf diseases is of the utmost importance (Sasikala
Vallabhajosyula, et al.,2024). Bacteria, fungus,
weather, and other environmental variables are
among the many causes of leaf diseases that plants
experience during their life cycles. By combining the
best features of the enhanced Vision Transformer
with ResNet9, the authors of this study provide a new
hierarchical residual vision transformer that can help
with the early diagnosis of leaf illnesses. By lowering
the number of trainable parameters and using fewer
calculations, the suggested model is able to extract
more relevant and discriminating features. Tests
using 13, 38, and 51 distinct leaf disease classes are
conducted on the Local Crop dataset, the Plant
Village dataset, and the Extended Plant Village
Dataset, respectively, to assess the efficacy of the
suggested approach. Using ResNet 9 for feature
classification and the optimal trail parameters from
Improved Vision Transformer, the suggested model
is trained. When tested on the aforementioned
datasets, the suggested model beat competitors like
InceptionV3, MobileNetV2, and ResNet50 across a
variety of metrics.
Agriculture is an essential need and their primary
source of domestic income for many countries (Anuja
Bhargava, et al.,2024). Plant diseases effected by
more than one pathogen (as in bacteria, fungus and
viruses) are so common that agricultural corporations
lose big bucks worldwide. It is critical to monitor
plant diseases in order to ensure the quantity and
quality of harvests. This highlights the critical nature
of plant disease detection. Symptoms of the plant
disease syndrome manifest in certain plant tissues.
Still, individual plant leaves are usually the first to
show signs of infection. Several researchers have
used computer vision, deep learning, few-shot
learning, and soft computing approaches to
Experimental Evaluation of Deep Learning Based Plant Leaf Disease Detection System Using Computer Assisted Image Processing
Techniques
445

automatically detect plant diseases from leaf images.
Quick and suitable efforts to prevent a decrease in
crop quality and quantity can also be achieved by
farmers using these strategies. By using these
methods to illness recognition, we may speed up
technology and research while avoiding the
drawbacks of origin by avoiding factious feature
selection and extraction. Additionally, specific
molecular methods have been developed to forestall
or lessen the impact of the infectious danger. Thus,
this research assists the researcher in designing
automated plant disease identification systems using
deep learning, machine learning, and few shots of
learning. It also gives specific diagnostic methods to
prevent disease. We also discuss some of the next
steps in illness categorization.
Reducing economic repercussions and optimizing
agricultural output require precise and timely
detection of plant leaf diseases (Eman Abdullah
Aldakheel, et al.,2024). The problem with precisely
identifying certain illnesses is that farmers rely on
traditional manual approaches, which makes it
difficult. Applying the YOLOv4 algorithm to the
problem of plant leaf disease detection and
identification is the focus of this study. The big Plant
Village Dataset is composed of more than 50,000
pictures of healthy and diseased plant leaves from
fourteen different species; the study prepares the very
general advanced systems for prediction of
agricultural diseases. To enhance the dataset and
fortify the model's durability, data augmentation
techniques such horizontal flip and histogram
equalization were employed. We compared the
YOLOv4 algorithm's performance against that of
other well-known target recognition methods, such as
Densenet, Alexanet, and neural networks, as part of
our thorough evaluation. An astounding 99.99%
accuracy was attained by YOLOv4 when applied to
the Plant Village dataset. The proposed method was
verified based on consistently very high values, with
0.99 scores for all the following metrics: accuracy,
precision, recall, and F1-score. The findings of this
study highlight the remarkable progress made in plant
disease detection and highlight the potential of
YOLOv4 as an advanced tool for precise disease
prediction. Because they increase our ability to
manage diseases and safeguard crops, these
innovations are incredibly important for researchers,
farmers, and everyone else working in the agricultural
sector. After the model is developed, it has to be
trained using a large number of pictures that have the
necessary objects tagged. Keep in mind that the
EfficientNetV2B1model can only learn to
differentiate between the classes if the input is
balanced. After that, you need to feed the data into
the EfficientNetV2B1 model. Dataset size
determines whether this is best done in batches or in
one continuous run. Next, a suitable optimizer, such
as Adam or SGD, has to be used to train the model.
In order for the model to learn to identify different
objects in the images, its weights are modified
continually during the training phase. After then, the
testing set may be used to assess the model's
correctness. The model's performance may be
evaluated using a variety of measures, including
recall, precision, and F1 score. We may measure the
model's performance by keeping track of how many
images are appropriately classified.
3 METHODOLOGY
Deep learning for the recognition of diseases in plants
employs deep learning and some old techniques. In
general, visual-based plant disease classification has
leveraged conventional deep learning techniques,
such as Random Forest, Naive Bayes, Support Vector
Machines, and K-Nearest Neighbors. On the other
hand, deep learning such as convolutional neural
networks has exhibited exceedingly effective
performance in identifying plant diseases present in
photos. Transfer learning employing pre-trained
ENCN models is yet another application for the
identification of plant diseases. Hybrid techniques,
combining methods such as SVM with ENCN, have
also been developed to capture the best of both
worlds. Other methods that help prepare the dataset
and enhance it are data augmentation, image
processing, and feature extraction techniques. Upon
using popular datasets such as Plant Village and IPM
Images for training and testing these models, deep
learning shows a promising technique for reliable and
quick plant disease identification. Here are some
drawbacks of the procedure.
• Inadequate or biased training data might
cause plant disease detection algorithms to
incorrectly diagnose illnesses.
• Models for plant disease detection based on
deep learning are difficult to implement on
low-power devices due to the high memory
and processing requirements of these
models.
• High-quality images are crucial to
conventional plant disease detection models,
but these images are susceptible to errors
caused by things like lighting, camera
quality, and image processing.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
446
The first phase of collecting data for the system
would involve collecting a large dataset of healthy
and diseased plants images from different sources.
After this, images should be normalized to a certain
size, their pixel values normalized, and data should be
enhanced and diversified through data augmentation
techniques for use in analysis. To be able to
accomplish this, a ENCN that consists of
convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully
connected layers is trained. By using k-fold cross-
validation, taking precision, recall, and F1 score
along with accuracy matrixes for the evaluation
comes the next part on the addition of images from
the users for diagnosis of the specific plant species or
diseases via transfer learning which can allow fine-
tuning. Certainly, asked for diagnosis, this web or
mobile application is also usable for resolvable fine-
tuning through transfer learning for a specific plant
species or diseases. Indeed, easy usage interface in
the system provides sufficient support for specialists
in agriculture and farmers to utilize it for disease
diagnosis and treatment suggestions. The system,
therefore, can combine and work together with
various technologies, like satellite imaging or drones,
allowing small and large-scale infection detection and
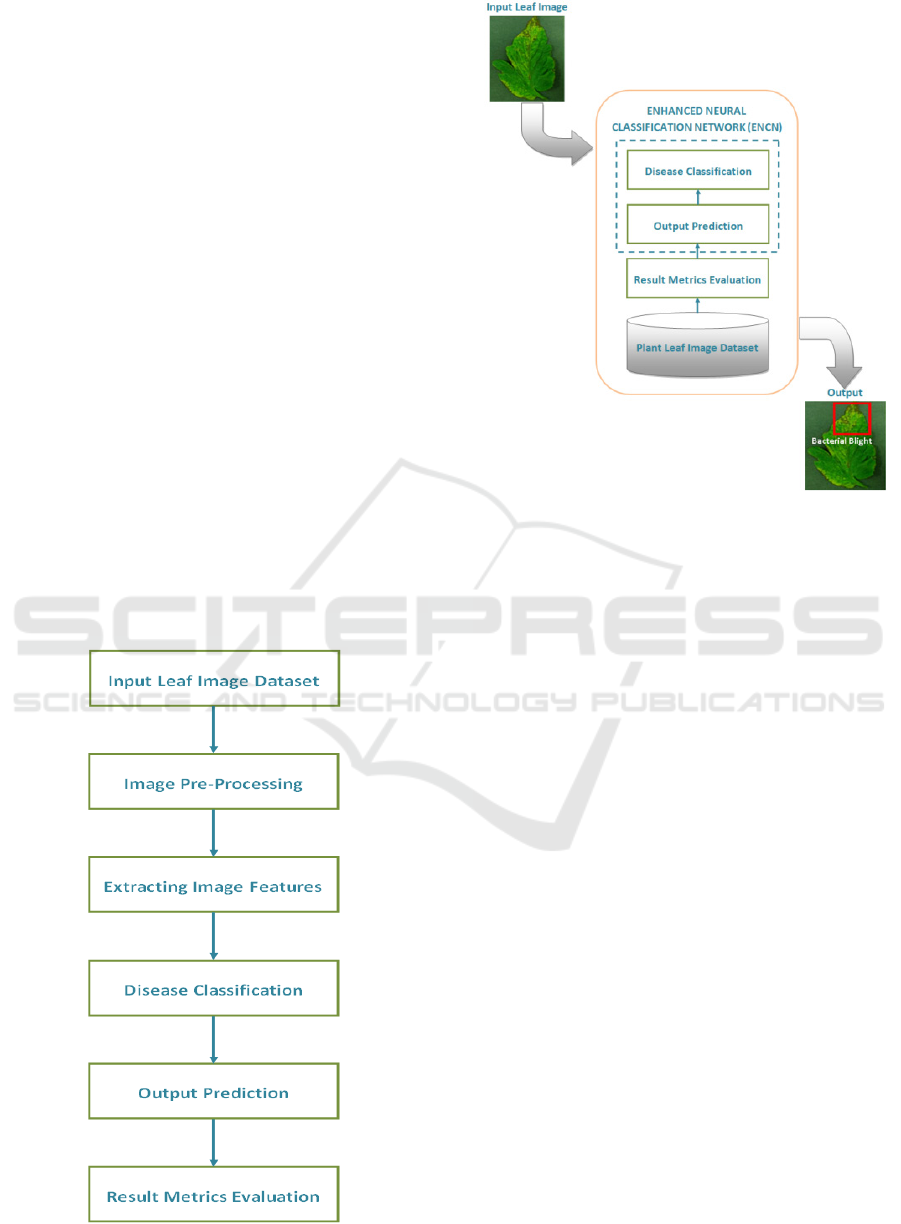
monitoring. The following figures, Figure 2 and
Figure 3 show the flow diagram and system
architecture of the proposed approach.
Figure 2: System Flow Diagram.
Figure 3: System Architecture.
The process of plant disease detection starts with
acquiring a large dataset of images from healthy and
diseased plants and working on them to standardize
diversity. This is followed by designing a ENCN
architecture and training using the preprocessed
dataset, resorting to methods like data augmentation
and transfer learning to facilitate better learning.
Subsequent to this step, accuracy and F1-score
metrics should be used to assess the model and deploy
it through a web or mobile application so that farmers
and agricultural specialists can upload images for
disease detection. Eventually the model continues to
get new updates from data again to learn and improve
its performance in providing proper diagnosis with
the required treatment suggestions. Below are the
advantages:
• The use of deep learning in the ENCN
algorithms for plant disease recognition can
have several benefits; it, first and foremost,
removes the long, tedious, and error-prone
human examination and diagnosis of plant
diseases. Such detection, therefore, becomes
more efficient and more accurate.
• ENCN models train actually to recognize
diseases early by noticing features and
patterns within the images that are difficult
for a human to perceive. In addition, deep
learning systems can learn through huge
datasets and continuously improve their
performances in detecting some diseases.
Experimental Evaluation of Deep Learning Based Plant Leaf Disease Detection System Using Computer Assisted Image Processing
Techniques
447

• With precise insights and treatment
recommendations from the ENCN algorithm
that can be performed by the agricultural
experts and farmers, preemptive measures
will, thus, be taken to control the outbreak of
the diseases.
3.1 Data Collection
It is challenging to guarantee the efficacy of transfer
learning because the initial MobileNet pre-trained
model was trained on the ImageNet dataset, which
does not only include the pictures that are required.
So, in order to train the model, we require a dataset
that includes trash photos. There is currently no fixed
dataset that is universally used for trash
categorization jobs. The TrashNet dataset is used for
rubbish classification; however it doesn't adequately
reflect the real situation of residential waste
categorization in India since it contains too few
categories. Consequently, this article builds a dataset
specifically for visual trash sorting using network
retrieval and real-world scene imaging in the lab,
covering both single-object and multiple-scene
scenarios.
3.2 Image Processing
To augment and normalize images of plants so that
accuracy in identification of plant disease is
improved, an Image Preprocessing obtains images.
Depending on the kind of input image it is processing,
it resizes images into fixed resolution, normalizes
pixel values, incorporates some augmentation
techniques, removes noise or other irrelevant
qualities, and enhances image quality with
brightening, contrast, and saturation enhancing. The
whole model is thus reinforced, has less influence
from external variables, and improves the accuracy in
diagnosis. The current discussion revolves around
whether a new medium can replace or precedes
existing media, particularly when the new channel
offers similar functionality as the old one. To perceive
the impact of a novel media on a preexisting one, it is
crucial to analyze customer perspectives about the
Modern channel and its potential to substitute the
current one.
3.3 User Interface
Dataset was divided into three subsets: validation,
training, and testing. User Explanation provides a
user-friendly interface for farmers and agricultural
experts to receive disease diagnosis and
recommendations for treatment. It explains the
detected disease, its symptoms, causes, and
prevention methods, enabling users to take informed
decisions about crop management and disease
control. Also, the process will provide users with
personal advice on pesticide application, fertilizer
application, and irrigation management, allowing
users to optimize their farm management systems. It
also provides information on how the disease may
potentially affect crop yield and quality, enabling
users to plan accordingly. Likewise, a feature on the
process will track the disease's history and give alerts
for possible outbreaks of the disease, allowing users
to implement some of their proactive measures to
avoid the spread of any disease.
3.4 ENCN Architecture
Following preprocessing, we select an ENCN
architecture that works best for trash picture
classification. Our classification model of choice is
EfficientNetV2B1. We loaded the model weights
from a source similar to EfficientNetV2B1. The
models can be found within deep learning tools,
namely, TensorFlow or PyTorch. The pretrained
EfficientNetV2B1 model has been modified by
removing the previous classification head (fully-
connected layers) and inserting a new classification
head corresponding to the number of garbage
categories in our dataset. We used ENCN layers as
feature extractors to educate the model in such a way
as to extract hierarchical and discriminative qualities
from the garbage images. It is thereby necessary to
use an optimizer, such as AdamorSGD, to work to
adjust model weights through back propagation, as
well as a suitable categorical cross-entropy loss
function for multi-class classification.
3.5 Model Training
Following model creation, it is necessary to train the
model using a large number of photographs annotated
with the necessary items. If you want the
EfficientNetV2B1model to learn to differentiate
between the different classes accurately, you must
ensure that the data is balanced. Once the data is
available, it has to be loaded into the
EfficientNetV2B1 model. Depending on the dataset
size, this can be done in batches or all at once. Then
we proceed to model training, using an appropriate
optimizer (Adam or SGD). During training, the model
adjusts its weights to recognize objects within the
images. In the next step, the model could be tested
with the testing set to check its performance. Recall,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
448
accuracy, and F1 score are all some ways we can
evaluate the model. A common way to evaluate
model performance is by quantifying how many
photos it can correctly label. It can be used on unseen
data to further test the generalizability of the model.
This will demonstrate how well the model can
predict using unobserved data.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
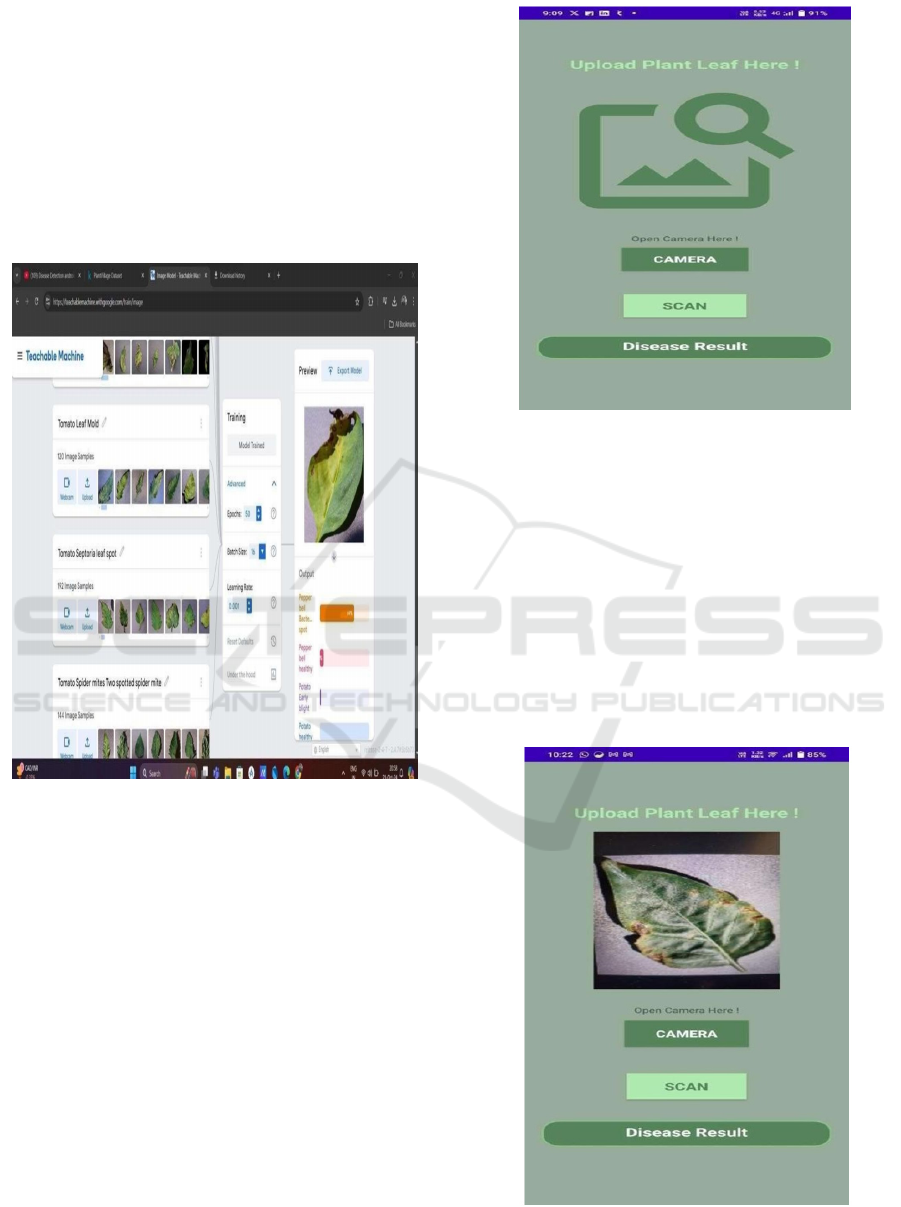
Figure 4: Dataset Uploading Port.
Using deep learning techniques to plant leaf
disease detection systems has improved agricultural
diagnostics extensively. The proposed
representations are fed into different deep learning
architecture such as Enhanced Neural Classification
Network (ENCN) to identify and categorize the
diseases based on leaf images. Consequently, they
facilitate early intervention and improved crop
management. Applications of deep learning models
like the ENCN in Android apps make real-time
detection and classification of maize and other cereal
problems fast and efficient. Precision farming
undergoes a paradigm shift with the implementation
of deep learning for the identification of plant leaf
maladies. The high accuracy and efficacy of these
models suggest that they may be widely accepted in a
variety of agricultural settings.
Figure 5: Validation Image Uploading Port.
Future research should focus on the inclusion of
these systems in readily accessible platforms for
farmers and other experts, the enhancement of model
resilience under diverse environmental conditions,
and the expansion of the diversity of plant species and
illnesses that are addressed. Figure 5 clearly shows
the testing image uploading portal that was created
using an Android application; Figure 4 shows the
dataset uploading site of the suggested method. Image
pre-processing and leaf disease prediction results of
the suggested approach are shown in Figures 6 and 7,
respectively.
Figure 6: Image Pre-Processing.
Experimental Evaluation of Deep Learning Based Plant Leaf Disease Detection System Using Computer Assisted Image Processing
Techniques
449
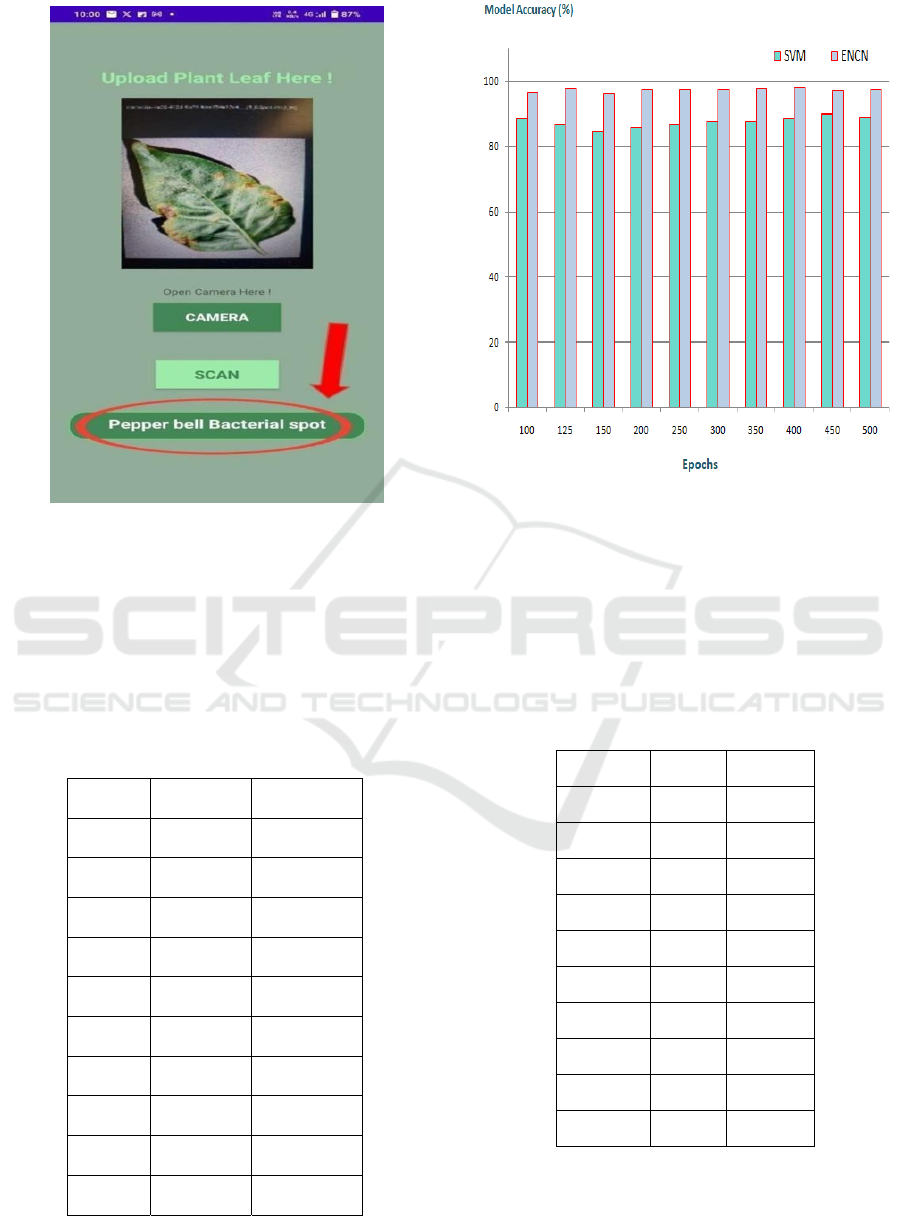
Figure 7: Disease Prediction.
Figure 8 shows the results of a cross-validation
test between the suggested model ENCN and a
traditional learning model known as SVM, which was
used to determine the model's prediction accuracy.
Table-1 provides a descriptive representation of the
same.
Table 1: Prediction Accuracy Comparison between SVM
and ENCN.
Epochs SVM (%) ENCN (%)
100 88.62 96.27
125 86.61 97.63
150 84.43 95.87
200 85.71 97.31
250 86.62 97.11
300 87.62 97.35
350 87.63 97.58
400 88.62 97.82
450 89.73 96.79
500 88.92 97.29
Figure 8: Model Prediction Accuracy.
The proposed ENCN loss ratio assessment is
presented in the following figure, Figure 9. In this
assessment, we will cross-validate the previous
scheme's proposed scheme with a classical learning
model referred to as SVM to find the proposed
scheme's loss ratio. The same is described in the next
table called Table 2.
Table 1: Comparison of Loss Ratio Between Svm and Encn.
Epochs SVM ENCN
100 6.34 1.19
125 6.62 1.26
150 4.79 1.34
200 6.27 1.82
250 6.36 1.94
300 5.29 2.65
350 4.73 2.72
400 4.50 2.66
450 6.69 2.67
500 6.47 2.88
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
450
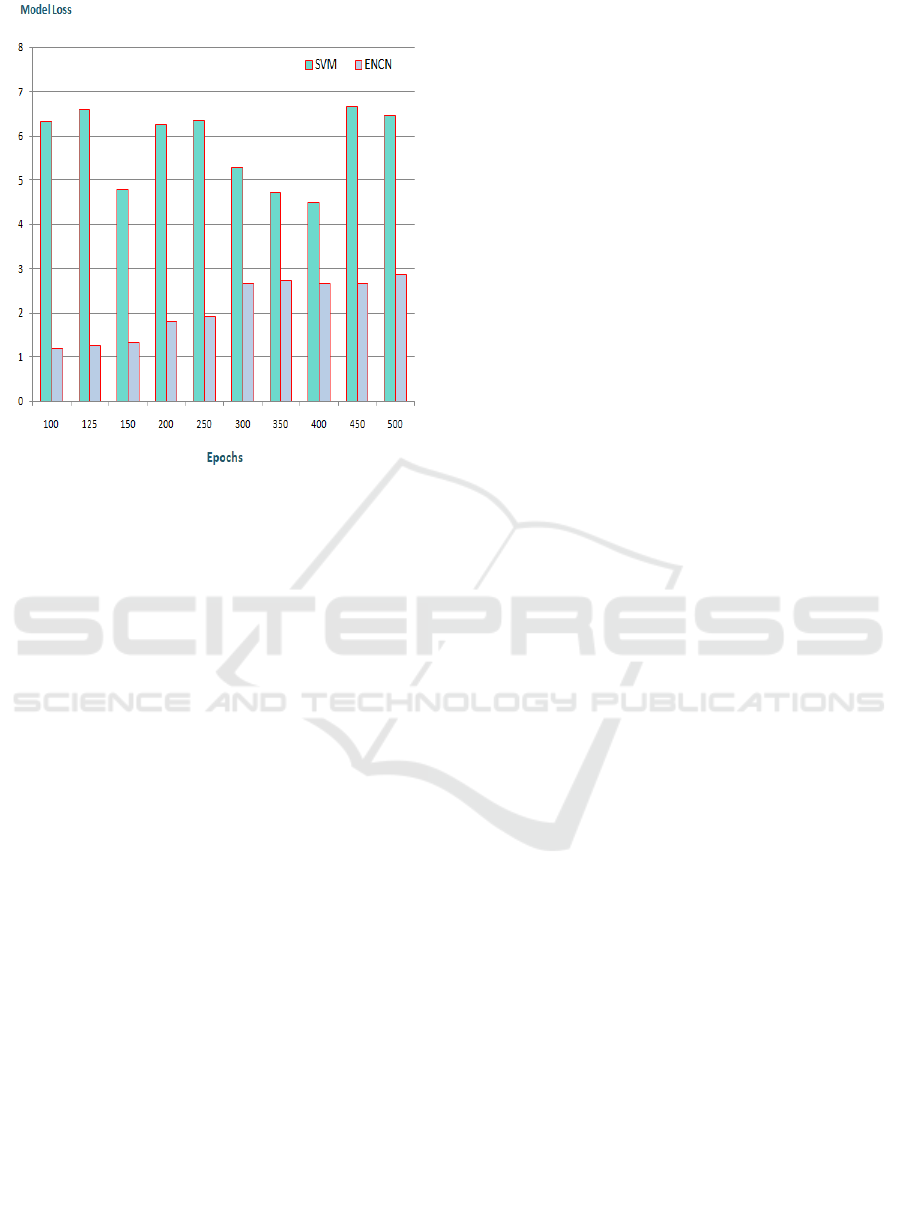
Figure 9: Loss Ratio.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Plant disease detection detected plant sickness using
ENCN deep learning and computer vision approach
have proven highly effective in accurately identifying
and tackling plant disease. By automating the process
of disease detection, this approach reduces manual
labor, enhances productivity, and allows for early
diagnosis of diseases, minimizing damage to crops
and losses. Moreover, the disease diagnosis accuracy
of the system is high, thereby minimizing the chances
of treating wrong disease. It has the potential to
develop further in the future through transfer
learning, more disease detection and IoT sensors
integration. In summary, the Plant Disease Detection
system is a powerful tool that aids farmers and
researchers alike in maintaining optimal crop health
and productivity, playing a crucial role in ensuring
global food security and sustainability. The Plant
Disease Detection system has far-reaching
implications for global food security and
sustainability. With unparalleled disease diagnosis
accuracy, it ensures that researchers and producers
have a reliable tool to prevent misdiagnosed and
mismanaged. Potential for integration with IoT
sensors, multi-disease detection, and transfer learning
provides a wide avenue for further enhancement of
this system which in turn will help for having more
sustainable and resilient agricultural systems.
In addition, the system can be adapted to detect
several illnesses at once, which decreases the need
for separate models and increases overall efficiency.
The application of transfer learning will also enable
the system to adjust to new, previously unseen
ailments while alleviating the need for significant
retraining. An app will make the system easy to use
which will promote the wide use of the system
between farmers and researchers. By incorporating
explain ability and interpretability methods, users will
be able to understand how and why the system came
to a particular decision, leading to increased trust and
understanding amongst users. Transfer learning: The
system must be able to adapt with the new unknown
diseases, without retaining from scratch. The
development of explainable/ interpretable techniques
will provide insights into how the system makes
decisions, while a future mobile application will act
as a bridge between farmers and researchers.
REFERENCES
Alwan Fauzi, et al., "Development of a Mobile Application
for Plant Disease Detection using Parameter
Optimization Method in Convolutional Neural
Networks Algorithm", International Journal of
Engineering Technology, 2023.
Anuja Bhargava, et al., "Plant Leaf Disease Detection,
Classification, and Diagnosis Using Computer Vision
and Artificial Intelligence: A Review", IEEE Access,
2024.
Ashutosh Kumar Singh, et al., "Hybrid Feature-Based
Disease Detection in Plant Leaf Using Convolutional
Neural Network, Bayesian Optimized SVM, and
Random Forest Classifier", Journal of Food Quality,
2022.
B.V. Nikith, et al., "Leaf Disease Detection and
Classification", Procedia Computer Science, 2023.
Cemal Ihsan SOFUOGLU, et al., "Potato Plant Leaf
Disease Detection Using Deep Learning Method",
Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024.
Eman Abdullah Aldakheel, et al., "Detection and
identification of plant leaf diseases using YOLOv4”
Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024.
Kamaldeep Kaur, et al., "Enhancing Plant Disease
Detection using Advanced Deep Learning Models",
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 2024.
Manjunatha Shettigere Krishna, et al., "Plant Leaf Disease
Detection Using Deep Learning: A Multi-Dataset
Approach", J, 2025.
Muhammad Shoaib, et al., "An advanced deep learning
models-based plant disease detection: A review of
recent research Updated", Frontiers in Plant Science,
2023.
Experimental Evaluation of Deep Learning Based Plant Leaf Disease Detection System Using Computer Assisted Image Processing
Techniques
451

Payal Trivedi, et al., "Plant Leaf Disease Detection and
Classification Using Segmentation Encoder
Techniques", Open Agriculture, 2024.
Priyanka Pradhan, et al., "Plant disease detection using leaf
images and an involutional neural network",
Environment Conservation Journal, 2024.
Rashmi Ashtagi, et al., "Fusion of AI Techniques: A Hybrid
Approach for Precise Plant Leaf Disease
Classification", Journal of Electrical Systems, 2025.
Sasikala Vallabhajosyula, et al., "A novel hierarchical
framework for plant leaf disease detection using
residual vision transformer", Heliyon, 2024.
Sherihan Aboelenin, et al., "A hybrid Framework for plant
leaf disease detection and classification using
convolutional neural networks and vision transformer",
Complex Intell. Syst., 2025.
Wubetu Barud Demilie, "Plant disease detection and
classification techniques: a comparative study of the
performances", Journal of Big Data, 2024.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
452
