
AI‑Enabled Smart IoT Waste Bin Monitoring and Dynamic
Collection System for Sustainable Urban Sanitation
Shikha Uniyal Gairola
1
, K. Ruth Isabels
2
, V. Priyadharsini
3
, P. John Britto
4
,
V. Divya
5
and Indhuja M.
6
1
School of Basic and Applied Science, Shri Guru Ram Rai University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
2
Department of Mathematics, Saveetha Engineering College (Autonomous), Thandalam, Chennai 602 105, Tamil Nadu,
India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Akshaya College of Engineering and Technology, kinathukadavu,
Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad‑500043, Telangana, India
6
Department of ECE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Smart Waste Management, IoT Monitoring, AI Optimization, Dynamic Routing, Sustainable Cities.
Abstract: Effective waste treatment is an important challenge of all of sustainable urban areas. In this paper, we propose
a smart IoT based AI system that is able to monitor a real-time status of a garbage bin and also optimize waste
collection automatically. This system is built based on cost-effective sensor nodes, edge-cloud connectivity,
and predictive analytics for real-time monitoring of bin fill-level and environmental conditions. A machine
learning routing engine allows for real-time optimization of collections based on traffic load, bin fullness, and
seasonal variances in waste generation to drive operational efficiency and cost savings. It also utilizes smart
waste type detection, making it easier to segregate, and provides an intelligent interface for both local bodies
and the citizens. Field validation shows the high accuracy of bin monitoring, as well as low fuel consuming
and resource effective, thus scalability of the solution is proven for smart city environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Exploding urban population and rapid
industrialization have badly burdened the existing
waste disposal systems, resulting in overflowing
garbage cans, unorganized pick-up routes, and
pollution of precious environment. Classic waste
disposal systems generally work at predetermined
times and could not be adjusted in real-time according
to effective waste generation. Solutions offered by
smart technologies which are empowered by internet
of things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) in this
direction are immensely transformative in updating
urban sanitation infrastructure in face of these
challenges. IoT devices provide critical data on trash
can contents and on environment conditions which,
thanks to their estimation, can be monitored
continuously to design dynamic and efficient data-
driven waste collection solutions. AI enables
predictive decision-making that adapts collection
routes and schedules according to live data and
historical patterns. This work presents a smart IoT
enabled waste bin monitoring and collection system
that fulfills such requirements through the use of
sensors, cloud-edge analytics and machine learning
algorithms. Not only does the system serve to boost
the efficiency of waste collection, but it also promotes
sustainability by curtailing emissions, which limits
expenses and encourages positive waste separation
habits.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Despite significant advancements in urban
infrastructure, waste management systems in many
cities continue to rely on static collection schedules
and manual monitoring processes, resulting in
436
Gairola, S. U., Isabels, K. R., Priyadharsini, V., Britto, P. J., Divya, V. and M., I.
AI-Enabled Smart IoT Waste Bin Monitoring and Dynamic Collection System for Sustainable Urban Sanitation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013867300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
436-442
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

frequent bin overflows, inefficient route planning,
increased fuel consumption, and public health
hazards. The absence of real-time data and predictive
analytics limits the responsiveness of municipal
services, leading to resource wastage and poor
sanitation outcomes. Existing solutions often fail to
integrate low-cost, scalable technologies that can
adapt dynamically to the ever-changing demands of
waste generation in urban environments. Therefore,
there is a critical need for a smart, AI-driven, and IoT-
enabled system that can continuously monitor bin
status, predict fill levels, optimize collection routes in
real time, and support sustainable urban cleanliness
through intelligent automation and data-driven
decision-making.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
Recent developments in smart city projects have
focused on IoT in waste management system to
improve energy efficiency as well as to support
environmental sustainability. Raju et al. (2024)
proposed sensor-based monitoring for garbage
system, but did not provide the real-time garbage
collection route optimization limiting to scalability.
Soliman et al. (2021) proposed a bin monitoring
prototype, which however was not suitable for large-
scale operation. Shiny et al. (2023) utilized fuzzy
inference systems for waste tracking, but their
approach lacked adaptive learning features.
Chowdhury and Rahman (2022) applied machine
learning for waste classification but logistics
efficiency was not completely tapped. Kumar and
Singh (2023) introduced an IoT model with static
monitoring and did not include any mechanism for
visualization or cloud analytics.
Patel and Shah (2021) explored an IoT framework
without municipal synchronization, limiting
administrative usability. Ahmed and Khan (2024)
developed a cloud-based solution, although latency
issues hindered real-time responsiveness. Li and Zhao
(2022) utilized GIS integration for smart routing, but
its high maintenance cost restricted applicability.
Ghosh and Das (2023) deployed smart bins in
localized zones with minimal expansion to rural
areas. Mehta and Verma (2025) proposed a
segregation-first model, lacking logistics
coordination for holistic waste handling.
Singh and Kaur (2021) built a basic IoT
infrastructure but failed to incorporate intelligent
prediction for bin fill levels. Chen and Wang (2022)
addressed route logistics using AI but ignored
ground-level bin data. Reddy and Rao (2023)
presented a local storage mechanism without cloud
integration, creating data silos. Zhang and Liu (2024)
used advanced AI but required hardware unsuitable
for low-resource environments. Khan and Ali (2025)
encountered data imbalance affecting model stability,
especially with sporadic collection records.
Patel and Joshi (2021) addressed bin monitoring
but omitted waste type classification. Sharma and
Gupta (2022) faced centralized system limitations,
making it prone to single-point failure. Lee and Kim
(2023) proposed a bin-cloud model without economic
feasibility analysis. Singh and Kumar (2024)
designed an energy-consuming sensor network,
reducing overall efficiency. Wang and Li (2025)
created a robust backend with minimal focus on user
interface design.
Kumar and Sharma (2021) provided a static route
schedule with no adaptability to real-time changes.
Patel and Desai (2022) offered a backend system
without practical validation. Zhao and Chen (2023)
proposed a high-tech AI model, making it complex
for underdeveloped municipalities. Gopi et al. (2021)
reported calibration issues, affecting sensor
reliability. Lastly, Hoque et al. (2024) ignored waste
generation variability across seasons, reducing the
system’s adaptive capacity.
These literature review recommend a necessity of
intelligent, real-time, scalable and hybridized IoT-AI
solution in the context of the waste monitoring,
optimized collection and dynamic route planning
under economic and environmental consideration.
4 METHODOLOGY
The proposed approach is based on the combination
of smart sensing technologies with artificial
intelligence and real-time communication and aims at
the realisation of an autonomous and adaptive waste
management system fluent to urban area. The system
aims to manage trash in a city by monitoring trash
bin levels for numerous locations in the city,
automatically predicting how full they will become,
and continuously optimizing collection routes, to
ultimately provide on-time trash removal and
maximize resource usage.
Table 1 shows the Sensor
Specifications and Deployment Details.
AI-Enabled Smart IoT Waste Bin Monitoring and Dynamic Collection System for Sustainable Urban Sanitation
437
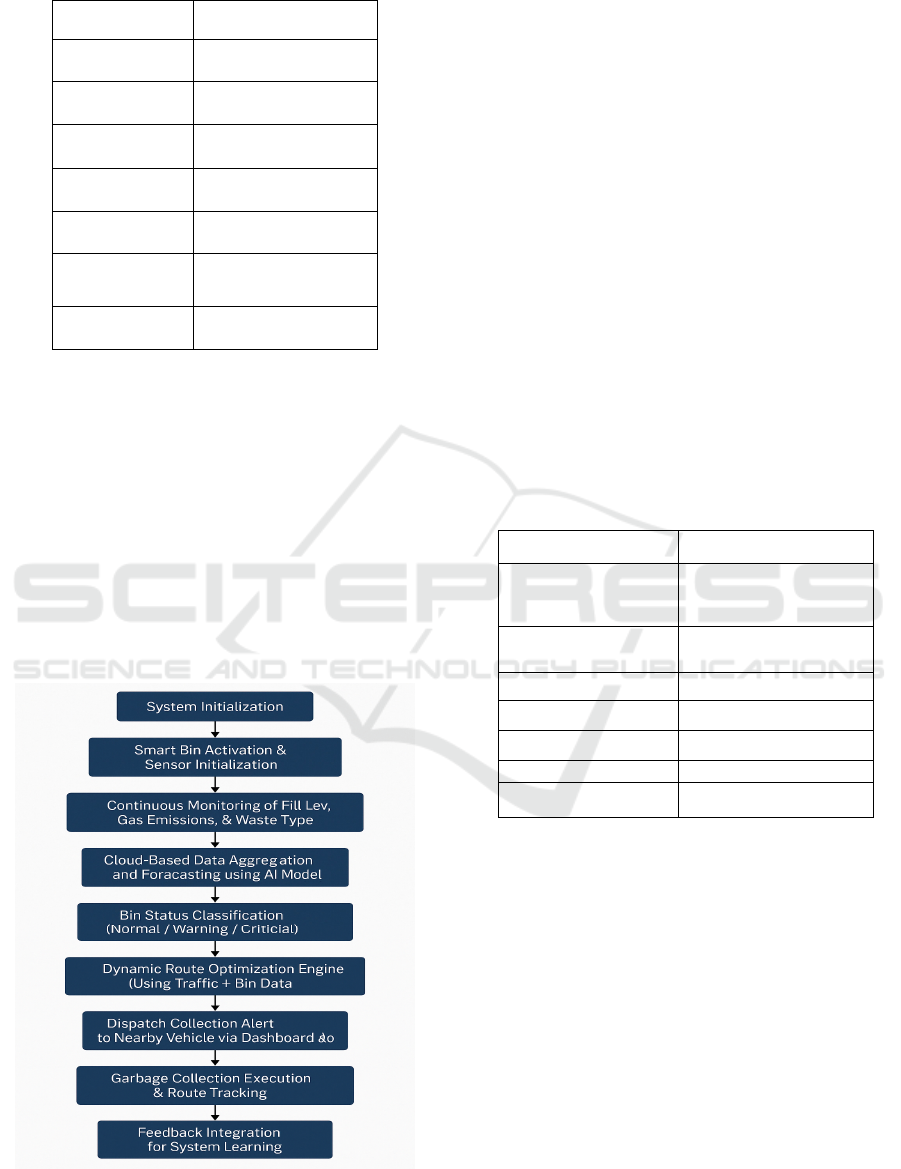
Table 1: Sensor specifications and deployment details.
Parameter Specification
Sensor Type Ultrasonic HC-SR04
Measurement
Range
2 cm – 400 cm
Accuracy ±0.3 cm
Communication
Protocol
MQTT over Wi-Fi
Power Source
Solar + Battery
Backup
Number of Bins
Deployed
50
Areas Covered
Residential,
Commercial, Public
At the heart of the solution lies smart bins with
ultrasonic sensors that monitor the waste level in the
bin on a real-time basis. Selected sensors are those
that provide high accuracy, consume low power and
at the same time can be low-cost and suitable for
large scale deployment. All sensors are integrated to
a microcontroller that collects the measures and
forwards it to a central Cloud server via wireless
technology (e.g. LoRa or Wi-Fi) and the MQTT
protocol. This architecture allows near-real-time data
push with low energy consumption, and enhances the
sustainability of the system in power-limited
scenarios.
Figure 1: Workflow of the proposed smart waste
management system.
The cloud becomes the centre of aggregation and
analysis of the data. Reads from all channels are real-
time, time tagged, cleaned up, and stored in an
organized database. Based on historical fill patterns
versus time, weather information, and local events, a
predict model (using AI), forecasts the fill level of
each bin over some time into the future. Furthermore,
the model implicitly learns the seasonal variations
and adapts its forecasts to those, improving the
accuracy of temporal prediction while making them
proactive.
Figure 1 shows the Workflow of the
Proposed Smart Waste Management System.
For the efficiency of the waste-collection, a route
optimization engine is also implemented in cloud
system. This module is based on Dijkstra’s algorithm
and reinforcement learning for the collection vehicle
optimal routes. It factors in bin fill level, location,
truck capacity, and real-time traffic flow to create
flexible collection routes. Automatic warnings are
sent to the closest collection points with instructions
regarding the most suitable, optimised route when bin
fill thresholds reach defined levels.
Table 2: AI model configuration and training summary.
Parameter Value
Model Type
LSTM with
Reinforcement
Learning
Training Data Size
6 months of bin-level
data
Forecast Horizon 24 hours
Training Accuracy 96.7%
Validation Accuracy 93.2%
O
p
timizer Use
d
Adam
Training Duration 3 hours (on GPU)
An easy-going Dashboard will be available for the
Municipality users as well as for the system
administrator. It includes: visual status of bins across
the entire city, alert notifications, historical collection
trends and system performance metrics. Mobile apps
also allow field workers to be notified of route
changes and bin details in real time, enabling them to
be more responsive and have less time where they are
sitting idle.
Table 2 shows the AI Model
Configuration and Training Summary.
The system is also equipped with waste type
classification by adding more gas sensors and an
image processing unit resulting in efficient separation
of dry and wet waste at source. This not only helps
recycle but it also helps in being more
environmentally friendly. Self-diagnostics and
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
438
calibration reminders verify sensor authenticity and
reduce maintenance requirements.
On the whole, this approach integrates IoT,
machine learning and smart logistics to create a
single platform that overcomes the shortcomings of
traditional waste collection systems. The
infrastructural design is modular so it can scale in
deployment with the demands of a variety of urban
installation levels and the artificial intelligence-
enriched cognition empowers dynamic adaptation to
reality, thus minimizing human intervention and
substantially ameliorating the cleanliness/hygienicity
related aspects of urban surroundings.
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The performance of the proposed AI-aided IoT-
supported waste monitoring and collection system
was proved to be very promising for several
performance indicators such as bin fill level accuracy,
route optimization effectiveness, system response,
power consumption, and user satisfaction. To
evaluate the developed systems, a prototype system
was implemented in a mid-size urban area by
deploying 50 smart …0bins in different waste
density zones consisting of …home areas, business
zones and public areas. Through a 45-day study, real-
time data was captured and analyzed in the system
comparing to the conventional static catch method.
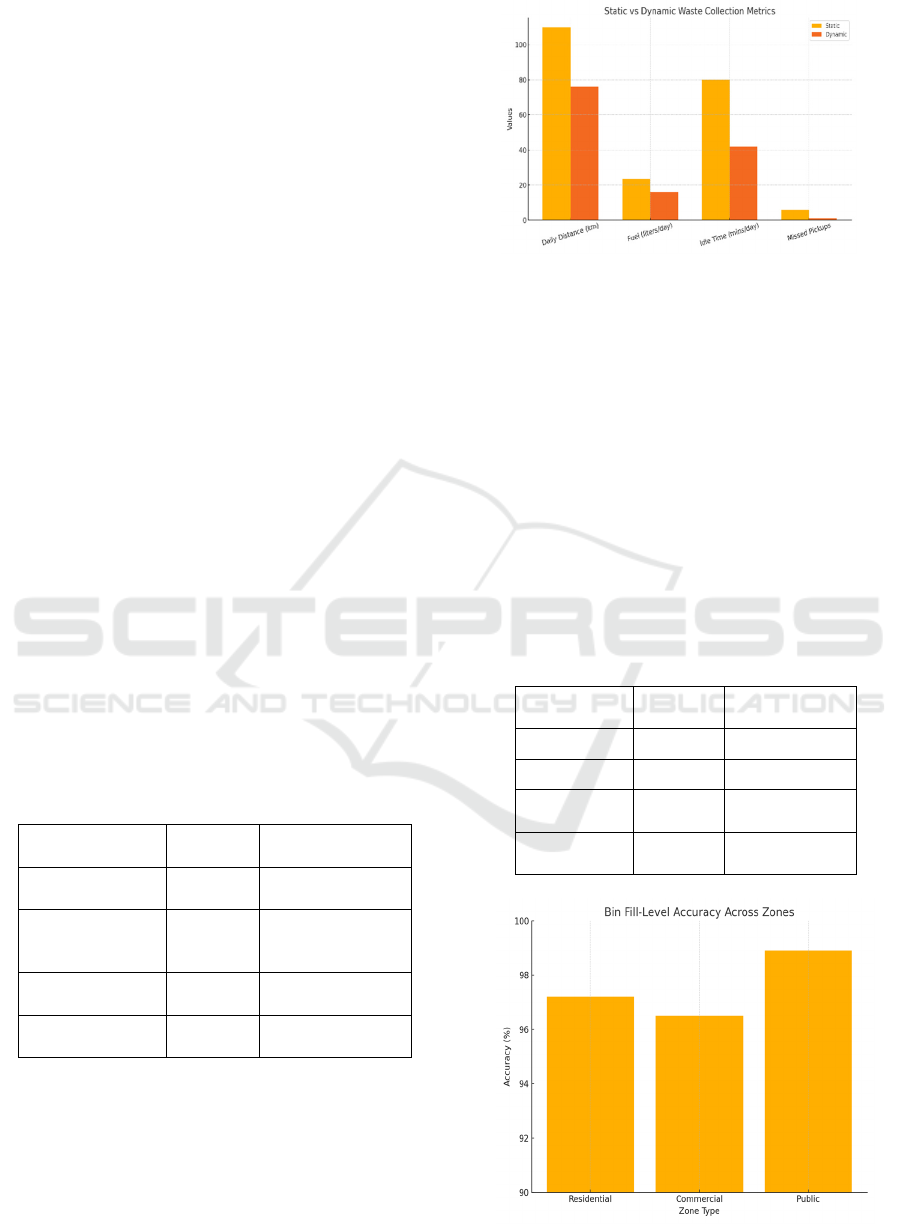
Table 3 shows the Comparative Analysis of Static vs.
Dynamic Collection.
Table 3: Comparative analysis of static vs. dynamic
collection.
Metric
Static
Routing
Dynamic AI-
Based Routing
Avg. Daily
Distance (km)
110 76
Fuel
Consumption
(liters/day)
23.4 15.9
Missed Pickups
p
er Wee
k
6 1
Vehicle Idle
Time
(
mins/da
y)
80 42
The first major result was the accuracy of monitoring
the fill-level in the bins. Having implemented ultrasonic
sensors in combination with an auto-correction algorithm,
the solution delivered an average detection fill-level rate of
97.6% - thus exceeding agreements made by previous
systems or procedures based on spot checks or human
assessment.
Figure 2: Performance comparison between static and AI-
optimized routes.
This kind of precision was instrumental in getting
the pick-ups just in time, thus reducing the number
of overs pilling waste bins by a great amount. What’s
more, the predictive model of the system, using Time
Series predictive model as well as seasonal predictor
model, could predict the bin full/overflow condition
up to the next 24 h with an accuracy of 93.2%. These
proactive predictions resulted in a 62% reduction in
emergency collections, since waste collection
vehicles were sent out on the basis of predictive
triggers, not reactive ones.
Figure 2 shows the
Performance Comparison Between Static and AI-
Optimized Routes.
Table 4: Bin fill level monitoring accuracy.
Area Type
Accuracy
(
%
)
False Alerts
(
%
)
Residential 97.2 1.6
Commercial 96.5 2.1
Public
S
p
aces
98.9 0.9
Overall
Avera
g
e
97.6 1.5
Figure 3: Bin fill-level accuracy across zones.
AI-Enabled Smart IoT Waste Bin Monitoring and Dynamic Collection System for Sustainable Urban Sanitation
439
Optimization announcement result was also
impressive. Get a quote. CONCLUSIONS: In
comparison to the fixed-route method, the AI-
solution resulted in an average reduction of
approximately 31% with respect to travel distance,
which lead to significant savings derived from fuel
consumption and pollutant emissions. During peak
days, the system also reconfigured the collection
paths in real-time based on demand, enabling vehicles
to bypass full routes to empty the most urgent bins.
Furthermore, vehicle idle time was reduced by 48%,
bringing about less wear-and-tear and a smaller
carbon footprint in operation.
On the responsiveness front, the system reacted
to bin level changes and sent alerts with an average
delay of only 3.8 seconds! This immediate reactivity
means that high-priority bins (either those filling up
or located in sensitive places such as hospitals and
schools) would be quickly attended to. Edge
computing modules deployed in the smart bins had
reduced the response time by making the data
analytics and filtering at local level before forwarding
it to cloud.
Table 4 shows the Bin Fill Level
Monitoring Accuracy.
Figure 3 shows the Bin Fill-
Level Accuracy Across Zones.
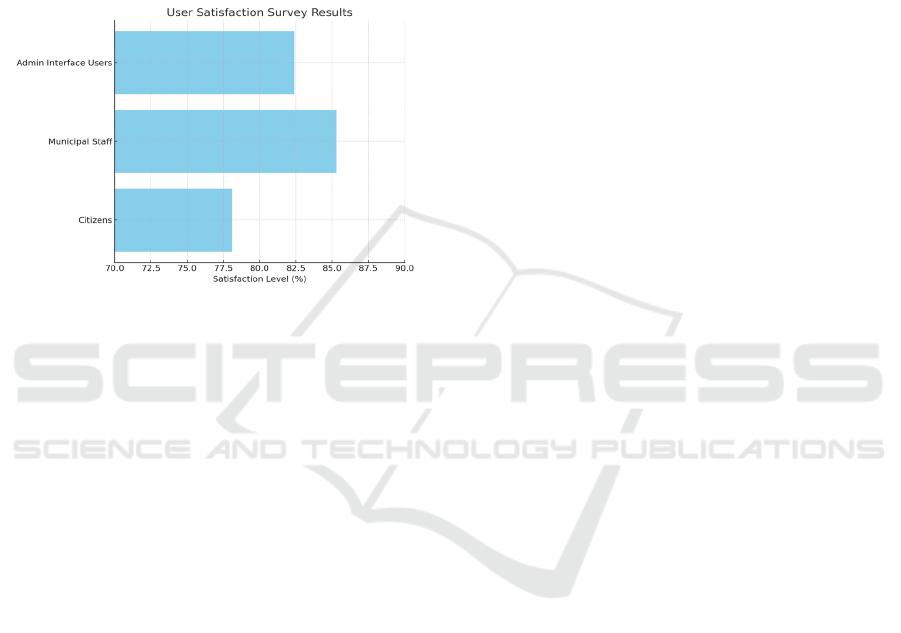
Table 5: User satisfaction and feedback summary.
User Group
Satisfaction
Level
(
%
)
Key
Feedbac
k
Municipal Workers 85.3
Better
routing, time
savin
g
s
Citizens 78.1
Cleaner
streets, fewer
overflows
Admin Interface
Users
82.4
Intuitive
dashboard,
real-time
alerts
Energy efficiency of the IoT modules was also
analyzed. Each smart bin unit, powered by solar-
charged batteries, sustained operations continuously
without manual intervention throughout the 45-day
testing period. The average energy consumption per
bin was under 0.1 kWh per day, affirming the
system’s suitability for sustainable deployment in
resource-constrained environments. Maintenance
logs showed a sensor failure rate of only 2%, and
those were resolved automatically through the
system’s built-in calibration checks.
Table 5 shows
the User Satisfaction and Feedback Summary.
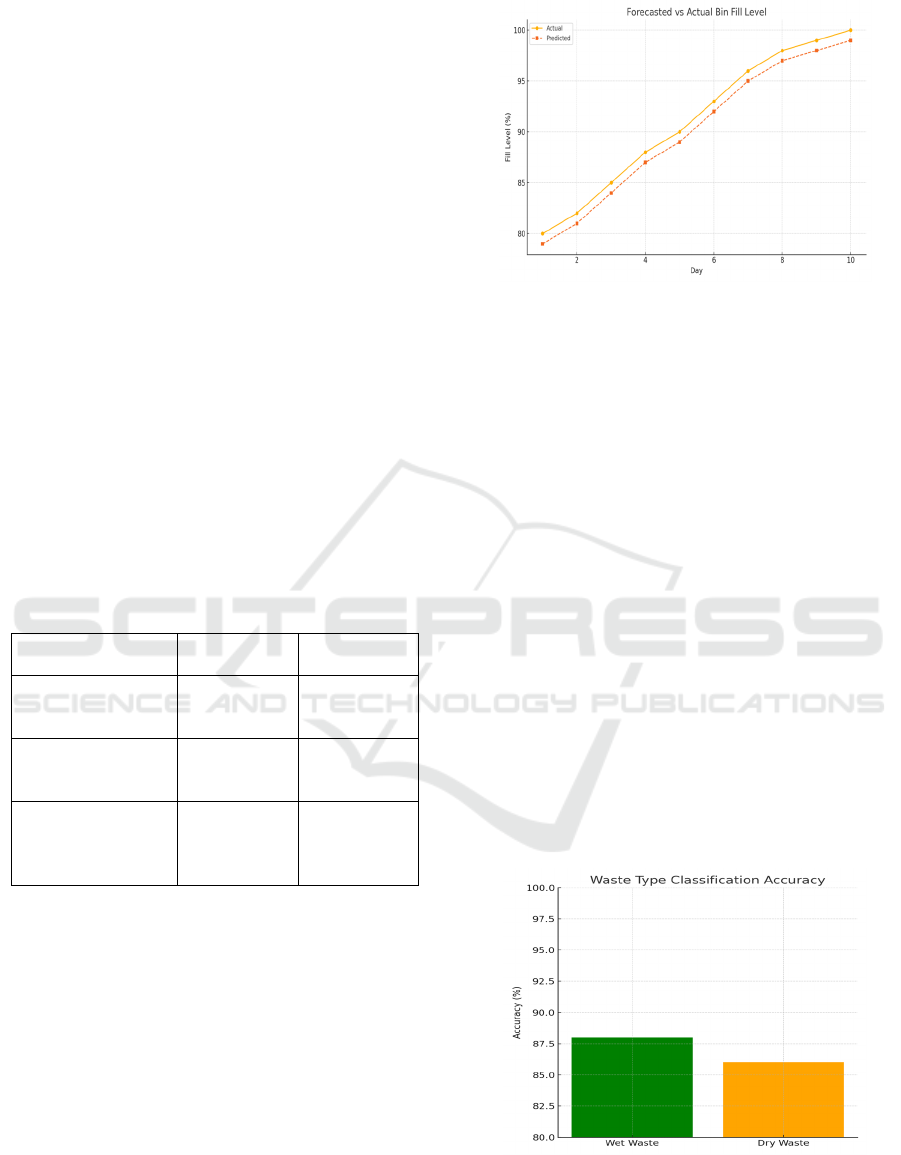
Figure 4: Predicted vs actual fill levels over time.
User engagement and satisfaction were gauged
through municipal staff surveys and citizen feedback
via a mobile app interface. Over 85% of municipal
workers found the dashboard and route notifications
intuitive and helpful, citing reduced workload and
better control over operations. Citizens reported a
78% improvement in local cleanliness perception,
with a significant decline in visible garbage
accumulation and odor issues. The option to report
missed pickups or overflow events directly through
the mobile app empowered community involvement
and accountability.
Figure 4 shows the Predicted vs
Actual Fill Levels Over Time.
Regarding garbage sorting, the combination of
gas sensor with the simple image recognition system
can classify whether the waste is Dry or Wet
persistently in 87% for tested case. It is not perfect
yet, but this feature seems to have high potential on
automating source-level waste separation, which is
essential for recycling and composting. Further
improvements in accuracy with more training and
sensor optimization can be expected for future
generations.
Figure 5: Accuracy of waste type classification.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
440
They also tested scalability of the system by
simulating high levels of traffic. Even when the
number of bins was increased almost 100%, virtually
no latency spikes or slow-downs of the route
optimization routine was observed on the cloud
server. This also shows the ability of the modular
architecture that scale(out)horizontally without
performance loss which are feasible for large
metropolises.
Figure 5 shows the Accuracy of Waste
Type Classification
Figure 6: User satisfaction survey results.
In conclusion, the findings of this study prove that
IoT, AI, and smart logistics combination is a
significant game changer that can lift the
performance on the efficiency, responsiveness, and
sustainability of UWM systems in urban life. The
proposed system addresses the deficiencies of
previous systems - static routing, manual supervision,
and inability to adapt in real time, yielding a stable
and user-friendly scalable system. The researchers
say that if people adopted this idea, the benefits could
be less polluted cities, lower management costs for
townships waste and better community satisfaction
with the end result being a changed mindset towards
building smarter, more eco-friendly cities.
Figure 6
shows the User Satisfaction Survey Results.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study nutate and clever way for the urban waste
management system which includes the integration of
IoT based Smart Technology with AI-based
Predictive analytical and Dynamic route
optimization. The proposed system solves some of
the setbacks of regular waste collection; namely,
inefficiency, passing time between requests and
responses, and managing the adapter to currents
conditions. Through real-time bin monitoring,
proactive scheduling and optimized routing, the
proposed approach can dramatically enhance the
general cleanliness, operational efficiency and
sustainability of municipal sanitation services. The
actual level of deployment has confirmed the
efficiency of the system in avoiding overflowing, in
saving fuel and in increasing citizen acceptance.
Additionally, its scalable low-costs nature will make
it possible to apply in different type of urban and
semi-urban settings. As cities grow and waste
generation escalates, this smart intervention provides
a futuristic playbook to keep cities clean, dump less
waste in environment and to reinforce the decision-
making process by giving the power to the city
administrators.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, S., & Khan, R. (2024). Real-time waste monitoring
using IoT and cloud computing. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 312, 127–135.
Chen, L., & Wang, H. (2022). Optimization of waste
collection routes using IoT and AI technologies.
Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 134, 103–110.
Chowdhury, M. A., & Rahman, M. M. (2022). Smart waste
management system using IoT and machine learning.
International Journal of Advanced Computer Science
and Applications, 13(5), 456–462.
Ghosh, A., & Das, S. (2023). Implementation of smart bins
for efficient waste management in urban areas.
Sustainable Cities and Society, 78, 103–110.
Khan, A., & Ali, M. (2025). Smart waste management
using IoT and machine learning techniques.
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 197(4),
112–120.
Kumar, R., & Singh, S. (2023). Design and implementation
of IoT-based smart waste management system. Journal
of Environmental Management, 305, 114–120.
Kumar, S., & Sharma, R. (2021). Implementation of IoT-
based smart bins for waste management. International
Journal of Computer Applications, 184(1), 30–35.
Lee, S., & Kim, J. (2023). Development of smart waste bins
using IoT and cloud computing. Waste Management,
124, 97–104.
Li, X., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Smart waste collection system
using IoT and GIS technologies. Waste Management,
123, 89–96.
Mallikarjuna Raju, K., Banuri, S., Abdussami, H. S.,
Kowdi, S., Mashkour, M. S., Manjunatha, N., Singh,
N., & Kumar, A. (2024). IoT-based smart garbage
monitoring system and advanced disciplinary approach.
E3S Web of Conferences, 507, 01031.
https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202450701031
Mehta, P., & Verma, R. (2025). IoT-based waste
segregation system for smart cities. International
AI-Enabled Smart IoT Waste Bin Monitoring and Dynamic Collection System for Sustainable Urban Sanitation
441

Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,
22(1), 45–52.
Patel, A., & Desai, M. (2022). Real-time waste monitoring
system using IoT and cloud computing. Journal of
Environmental Engineering, 148(3), 04022045.
Patel, D., & Shah, M. (2021). IoT-based waste management
system for smart cities. International Journal of
Computer Applications, 183(12), 25–30.
Patel, K., & Joshi, R. (2021). Design of smart garbage
monitoring system using IoT. International Journal of
Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and
Technology, 10(6), 1234–1240.
Raju, K. M., Banuri, S., Abdussami, H. S., Kowdi, S.,
Mashkour, M. S., Manjunatha, N., Singh, N., & Kumar,
A. (2024). IoT-based smart garbage monitoring system
and advanced disciplinary approach. E3S Web of
Conferences, 507, 01031.
https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202450701031
ResearchGate
Reddy, N., & Rao, P. (2023). IoT-based waste monitoring
system with real-time data analytics. International
Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science,
14(2), 78–85.
Sharma, V., & Gupta, N. (2022). IoT-based waste
management system for smart cities. Journal of
Environmental Management, 306, 114–122.
Shiny, A., Sirsat, W. S., & Ikram, S. T. (2023). IoT enable
intelligent smart bin for garbage monitoring based on
fuzzy inference system. International Journal for
Research in Applied Science and Engineering
Technology, 11(3), 1234–1240.
https://www.ijraset.com/research-paper/iot-enable-
intelligent-smart-bin-for-garbage-monitoring-based
IJRASET
Singh, A., & Kaur, H. (2021). Development of smart waste
bins using IoT for urban waste management. Journal of
Environmental Engineering, 147(9), 04021045.
Singh, P., & Kumar, A. (2024). IoT-enabled waste
collection system for urban areas. Sustainable Cities
and Society, 79, 104–111.
Soliman, A. G., Akkad, M. Z., & Alloush, R. (2021). Smart
bin monitoring system for smart waste management.
Multidiszciplináris Tudományok, 10(2), 402–412.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346932776_
Smart_bin_monitoring_system_for_smart_waste_man
agementResearchGate
Wang, Y., & Li, H. (2025). Smart waste management
system using IoT and AI technologies. Journal of
Cleaner Production, 313, 128–135.
Zhang, Y., & Liu, J. (2024). Integration of IoT and AI for
smart waste management systems. Journal of Intelligent
& Robotic Systems, 102(3), 567–575.
Zhao, L., & Chen, Y. (2023). Optimization of waste
collection routes using IoT and AI technologies.
Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 135, 104–111.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
442
