
Evolution of Machine Learning Applications in IoT Security: A
Critical Analysis and Future Perspectives
Vaishali N. Rane and Arunkumar
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr.Sagunthala R& D Institute of Science and
Technology, Avadi, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Internet of Things, Machine Learning, IoT Security, DDoS, Adversarial Attacks, Artificial Intelligence.
Abstract: The continuously advancing field of Internet of Things (IoT) has given rise to technologies that are crucial to
protect IoT systems from various attacks. Conventional security methods have their own bottlenecks and fail
to effectively deal with the security of IoT systems. This review explores the existing Artificial Intelligence
and Machine Learning (ML) based approaches for IoT security. Covering researches mainly done in 2023-
24, we have discovered that AI-enabled security solutions have better accuracy in detecting threats, more than
90%. On the other hand, they keep a check on the computational cost to prevent any cost overruns. Our key
takeaways include the integration of multiple ML algorithms as a hybrid system, adversarial attack handling
mechanisms and other techniques to handle targeted attacks. However, challenges persist, including resource
constraints, ease of deployment, adaptability, robustness etc. Our review addresses these challenges and
provide direction for future research along with the aim to offer valuable insights from relevant researches
aimed at enhancing IoT security through Machine Learning Techniques.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapidly growing use of IoT devices in our daily
lives has completely changed how we interact with
such systems across homes, offices, and other
spheres. While offering numerous advantages to users
worldwide, the concern for security and data privacy
needs be addressed properly. Our review highlights
the bottlenecks of traditional IoT security systems and
in accordance with the research by (Ali & Rani,
2024), where they have stated that current systems are
not sufficient to protect against sophisticated and
more advanced attacks targeting IoT network.
The shift towards Machine Learning based
solutions is rapidly being preferred over traditional
methods as a solution for security challenges in this
domain. Unlike traditional approaches which are
based on static-rules and pre-defined conditions, ML
introduces dynamic and adaptable systems which can
protect against threats which learning from the data
continuously to keep itself updated with latest threats.
This milestone is described in the paper by (Saumya
et al.,2024) as a significant point in the building of
IoT security architectures. Table 1 shows the
Projected IoT connections worldwide.
The prime advantage of using machine learning
and AI in IoT security is its ability to deal with big
data and understand hidden patterns that normal
systems fail to uncover. This allows for better
protection in IoT environments where standard
protocols aren’t that much efficient in detecting
advanced cyberattacks. However, integrating AI/ML
in legacy IoT systems has its own set of challenges.
Some of them are resource constraints, low-power
operations, communication protocols, and
interoperability with various IoT devices. (Omarov et
al.,2024) have described these challenges in depth in
their research where they indicated that traditional
systems fail to maintain a balance between security
and simplicity of algorithm and how Machine
Learning based algorithms are better.
Rapid progress has been seen in past few years in
the field of Machine Learning in IoT. Some use cases
like real-time threat detection and prevention systems
have achieved accuracy as high as 97%. Research by
(Alomiri & AlShehri, 2024) describes how delay in
identification of threat can cause serious data
breaches and compromises in security.
Although research in this domain is going on, the
practical implementation of theoretical models and
systems has several challenges. One of the primary
Rane, V. N. and Arunkumar,
Evolution of Machine Learning Applications in IoT Security: A Critical Analysis and Future Perspectives.
DOI: 10.5220/0013866600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
409-414
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
409
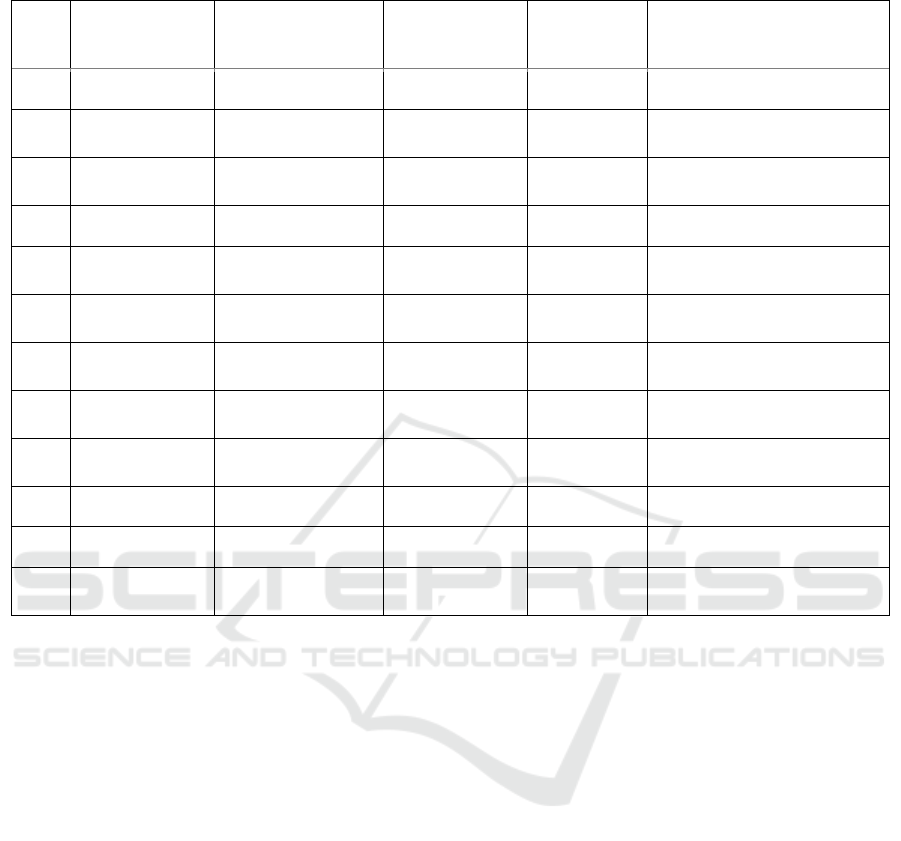
Table 1: Projected IoT Connections Worldwide.
Year
IoT Connections
(Min, in
b
illions)
IoT Connections
(Max, in billions)
YoY Growth
(%) (Min)
YoY Growth
(%) (Max)
Key Observations
2022 13.8 13.8 - - Baseline Year
2023 15.9 16.6 15.2% 20.3%
Expansion of 5G and smart
devices
2024 18.0 18.8 13.2% 13.3%
Increased industrial IoT
ado
p
tion
2025 20.1 20.1 11.7% 6.9% Growth in smart city projects
2026 22.4 22.4 11.4% 11.4%
IoT penetration in healthcare
and AI
2027 24.7 24.7 10.3% 10.3%
Rise of edge computing and
6G research
2028 27.1 27.1 9.7% 9.7%
Autonomous vehicles and
AIoT sur
g
e
2029 29.6 29.6 9.2% 9.2%
Mass adoption of industrial
IoT
2030 32.1 40.0 8.5% 21.6%
IoT becoming mainstream in
dail
y
life
2031 34.6 34.6 7.8% -13.5% AI-driven IoT innovation
2032 37.1 37.1 7.2% 7.2% Global IoT regulations evolve
2033 39.6 39.6 6.7% 6.7%
IoT surpasses 39 billion
devices
challenges is adversarial attacks which manipulate
the training process and introduce errors in the
algorithm which makes it helpless against some
targeted attacks. (Harbi et al., 2024) have described
the risk of such attacks and how they disrupt the
machine learning model. Moreover, they have
highlighted the need for careful optimization of ML
models so they can perform efficiently under limited
resource conditions as well.
Another area of application, the Industrial Internet
of Things or IIoT has benefitted from the provision of
AI/ML based security systems. Adaptive models
allow autonomous handling of attacks, minimizing
human intervention. These systems can detect various
cyber threats including both known and new,
improving real-time monitoring and mitigation of
threats. (Wankhade et al., 2024) have described the
advancements in the field of IIoT and security
measures focusing mainly on precision, reliability
and real-time functioning.
Current trends mainly focus on the development
of hybrid machine learning models, combining more
than one algorithm to enhance it while overcoming
the limitations of one single algorithm. For instance,
combination of supervised and unsupervised
Machine Learning Algorithms has resulted in
increased threat detection accuracy and reduced false
positives as evaluated by (Iqbal et al., 2024).
Additionally, Pareto-optimal models have also been
discussed.
Significance of the Study. Understanding the role of
ML in IoT security and its impact, are crucial for
designing and developing advanced security
solutions. As cyber threats are getting advanced day
by day, so as the need to have adaptive and intelligent
security systems. This review summarizes the current
state of ML in IoT security highlighting various
techniques, major trends and key inferences which
can be derived from the study alone. The limitations,
challenges and future directions are clearly discussed
to help the researchers infer and conclude. Moreover,
it acts as a fundamental base, by providing the
directions of future research which can focus on
safety and reliability of IoT Environments and
optimization of complex ML algorithms to work
better with IoT units.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
410
2 CURRENT STATE OF ML IN
IoT SECURITY
2.1 Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) have emerged as
powerful tools for identifying and classifying threats
in IoT ecosystems. Their job is to detect any anomaly
in the system or network and alert the user before the
threat actually affects the system. Recent studies
show that Random Forest has displayed the accuracy
of 92.72% in binary classification of threats and
92.40% in multiclass classification tasks. Therefore,
it can be considered as a reliable choice for threat
detection systems. This review and comparison have
been done by (Saumya et al., 2024).
Figure 1: Advantages and disadvantages of Hybrid
approaches in IDS.
Similarly, other algorithms like Support Vector
Machines (SVM) have shown notable accuracy in
recall metrics, which makes them highly preferable
for detecting variety of tasks that too with greater
precision.
The performance of IDS can be further improved
using hybrid approaches. (Iqbal et al., 2024) have
experimented that integration of Supervised and
Unsupervised machine learning algorithms have
improved the detection accuracy and adaptability of
system to detect new and unknown threats, which the
traditional systems fail to identify. Advantages and
Disadvantages of Hybrid approaches in IDS is given
in figure 1.
2.2 Feature Selection and Performance
Optimization
Feature Engineering is crucial when we have mixed
and heterogeneous data to work upon. Since ML
model’s performance is determined by the quality of
training data, having features in bulk require Feature
selection and optimizing the process of feature
selection is a key requirement to identify which
weight vector is most important. According to (Htwe
et al., 2024), combining one-hot encoding with
Pearson correlation can achieve high accuracy while
maintaining computational load. This helps in
applications where we have limited resources like
computation, storage and network.
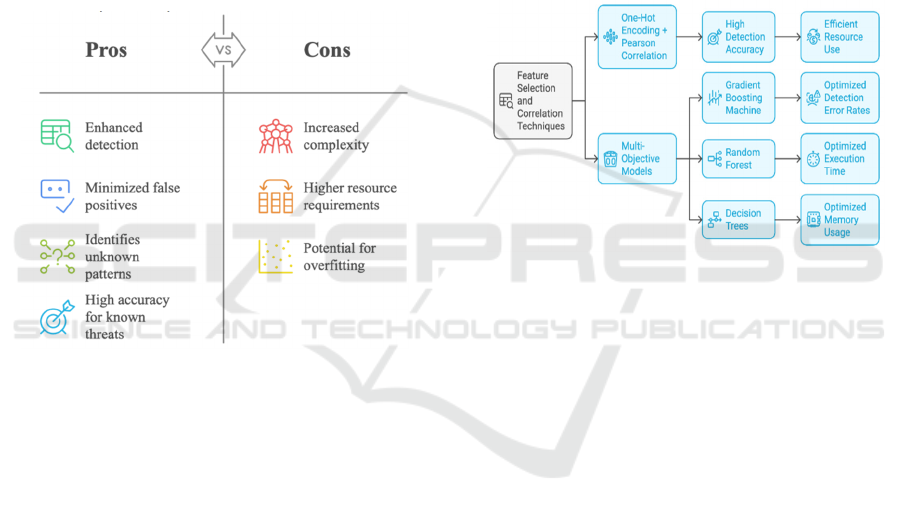
Figure 2: Enhancing ML Models in IoT security.
Pareto-optimal machine learning work best when
you have multiple performance objectives. (Wu et al.,
2024) highlights Gradient Boosting, Random Forest
and Decision Trees as some of the highly effective
machine learning approaches for building an anomaly
detection model. They primarily deal with the
detection accuracy, execution time and memory
usage and are mainly used in resource-constrained
environments. Enhancing ML Models in IoT Security
is shown in figure 2.
2.3 Real-Time Threat Detection
Another key feature of ML-based models is Threat
detection in real-time. Some systems have resulted
accuracy of over 97% in identification of network
threats (Alomiri & AlShehri, 2024). Also, in IIoT
systems, adaptive models have demonstrated high
accuracy and better threat response, by monitoring
data streams and based on that pattern, detect
anomaly in data and behavior. (Wankhade et al.,
2024) have explained how these models continuously
upgrade their threat detection capabilities, thus
providing robust security in dynamic environments.
Evolution of Machine Learning Applications in IoT Security: A Critical Analysis and Future Perspectives
411
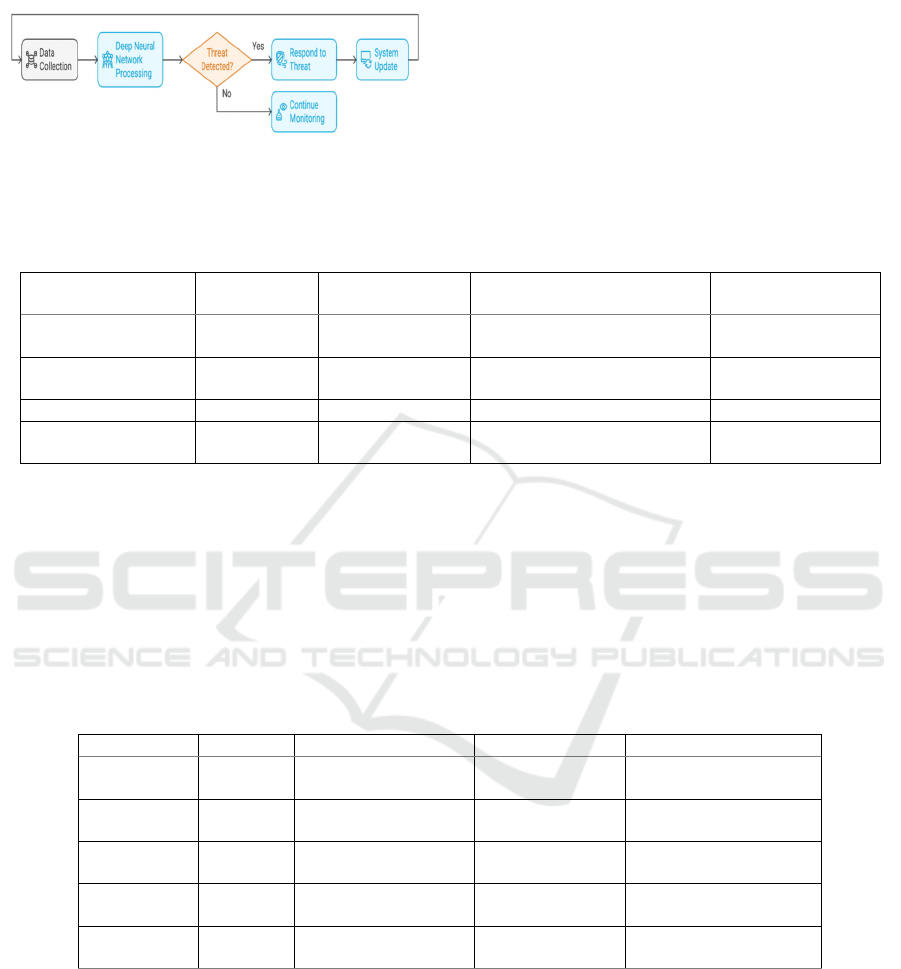
Figure 4 depicts the Real-time threat detection in
IIoT.
Figure 3: Real-time threat detection in IoT.
2.4 DDoS Attack Detection and
Mitigation
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks pose a
significant threat to network-based IoT systems. It
works by disrupting the availability of services and
data to various nodes. This is done by tampering data
nodes at network level. Recent studies have down that
Machine Learning based techniques have better
performance in detection and mitigation of DDoS
attacks (table 2).
Table 2: ML approaches for DDoS attack detection in IoT.
ML Technique
Detection
Rate
False Positive
Rate
Key Features Reference
Deep Neural
Networks
97.3% 2.1%
Real-time detection
ca
p
abilities
Kumar et al., 2024
Ensemble Learning 95.8% 1.8% Multi-vector attack detection
Wankhade et al.,
2024
SVM 94.2% 2.8% Low com
p
utational overhea
d
Saum
y
a et al., 2024
Random Forest 96.5% 1.5%
Effective for volumetric
attacks
Omarov et al., 2024
3 KEY TAKEAWAYS
The table 3 shows a comparative analysis of various
machine learning models where we can infer that
Tree-based algorithms, particularly Random Forest
and Decision Trees, deliver best performance with
different datasets. Even with default parameters,
these models prove to be highly effective for IoT
Security in Cyber-attack detection with an accuracy
close to 99% in CIC-IoT2023 dataset. (Islam Jony &
Arnib, 2024).
Table 3: Performance comparison of ML algorithms in IoT security.
Algorithm Accurac
y
Use Case Dataset Reference
Random
Forest
92.72% Binary Classification UNSW-NB15 Saumya et al., 2024
Random
Forest
92.40% Multiclass
Classification
UNSW-NB15 Saumya et al., 2024
Ridge
Classifie
r
97.00% Real-time Threat
Detection
IoT Network
Traffic
Alomiri&AlShehri,
2024
Decision
Tree
99.19% Cyber-attack
Detection
CIC-IoT2023 Islam Jony&Arnob,
2024
Random
Forest
99.16% Cyber-attack
Detection
CIC-IoT2023 Islam Jony&Arnob,
2024
4 CHALLENGES AND
LIMITATIONS
4.1 Adversarial Attacks
One of the key challenges in using Machine Learning
models is their vulnerability to adversarial attacks.
(Harbi et al., 2024) highlights one of such attacks
named Fast Gradient Signed Method (FGSM) which
is a common attack technique that disrupts and
manipulate the training process by introducing certain
samples, that obfuscate the security systems and
cause the model to make incorrect predictions
bypassing security. (Ibitoye, 2024).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
412

In order to overcome these attacks, proper
adversarial training is needed. This can be done by
training the model with some adversarial samples
beforehand to ensure robustness against such attacks.
However, this will further increase the training cost
as additional samples need to be used for training
process. This can become a bottleneck as IoT systems
are generally designed with limited resource
availability in mind.
4.2 Dataset Considerations
The UNSW-NB15 dataset has been widely used for
evaluation and validation of proposed systems in real-
world scenarios. Selecting the right dataset with
balanced samples is crucial for validation of your
model. (Omarov et al., 2024). Similarly, CIC-
IoT2023 dataset has proved to be the most reliable
dataset on which accuracy rates of 99.19% and 99.17
percent are achieved by (Islam Jony & Arnob, 2024)
as mentioned in Table 3.
5 FUTURE RESEARCH
DIRECTIONS
With the review of current state of ML in IoT
Security, further researches can be based on resource
optimization in Machine Learning models, aiming to
create light-weight models which can operate
efficiently in constrained environments. Research by
(Wu et al, 2024) have focused on the Pareto-optimal
solutions, which can be the key focus area for future
researchers. Moreover, Hybridization of approaches
can be done to improve performance of existing
systems or to deal with challenges in existing
systems. (Iqbal et al., 2024).
Network-based threats like DDoS needs
innovative detection and mitigation strategies as a
preventive measure in network systems. Future
research can focus on adaptive and intelligent defense
systems which can adapt to varying attack patterns
and can function without manual intervention and
rule base. (Wankhade et al., 2024) have laid the
foundation by introducing these models in IIoT
application, introducing real-time threat response
systems.
According to Harbi et al. (2024), Adversarial
attacks need to be addressed as they disrupt the
fundamental functioning of ML-based security
systems. New systems should balance out the
efficiency and resource usage, for making it easier to
deploy and integrating ML in existing IoT
environments.
Advanced approaches like Federated learning and
collaborative defense mechanisms can be used along
with basic machine learning models, to further
strengthen the system security and focusing on
privacy of data while sharing it in IoT ecosystem.
This will further reduce the risk of data breach and
cyber-attack. Also, Explainable AI in security
solutions can be researched upon as the present focus
is on the model interpretability and the need to make
the model more understandable by the user. (Islam
Jony&Arnob, 2024).
6 CONCLUSIONS
With the comprehensive review of the various
technologies being used to enhance security in IoT
systems, we can conclude by saying that ML has
made a profound impact this domain, particularly in
IDS and threat response systems. Using AI/ML
approaches, we can increase the efficiency of existing
systems and make them autonomous, which will
reduce human dependency and need to manually
program rules for security systems to stay up to date
with latest threats. Table 4 gives the Performance
Comparison of ML Algorithms in IoT Security.
Table 4: Performance comparison of ML algorithms in IoT security.
Trend Key Features Benefits References
Hybrid Learning
Approaches
Combination of Supervised &
Unsupervised Methods
Improved Detection Rates,
Reduced False Positives
Iqbal et al.,
2024
Adaptive ML
Models
Real-time Learning
Capabilities
Dynamic Threat Response Wankhade et
al., 2024
Feature Correlation Optimized Feature Selection Reduced Computational
Overhea
d
Htwe et al.,
2024
Adversarial Defense Robust Model Training Enhanced Security Against
ML Attacks
Ibitoye, 2024
Evolution of Machine Learning Applications in IoT Security: A Critical Analysis and Future Perspectives
413

The Models will evolve along with the threats.
Recent advancements highlight the exceptional
performance of Random Forest with (92.72%)
accuracy and other improvements like self-learning
algorithms and hybrid systems which have
transformed the scenario of security In IoT. Other
improvements highlight the role of ML in proactive
threat detection, real-time response systems and
threat mitigation.
However, despite of all these benefits, some
challenges like balancing the computational overload,
integration into existing systems, vulnerability
against adversarial attacks etc. is still there. Model
manipulation prevention and feature selection
optimization are crucial for training quality models.
Particularly in case of DDoS attacks, and other
network-based attacks, it is crucial for a ML model to
be adaptive, updated with the latest threats and
resource-efficient. Moreover, hybrid systems are
beneficial to overcome shortcoming and boosting
efficiency of IoT security systems. Resource efficient
defense mechanisms will play a major role in creating
resilient frameworks that are well-suited for various
IoT applications.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, Alomiri., Mohammed, AlShehri. (2024).
Machine Learning-Based Security Mechanism to
Detect and Prevent Cyber-Attack in IoT Networks.
International Journal of Computing and Digital
Systems, doi: 10.12785/ijcds/160148
Akinul, Islam, Jony., Arjun, Kumar, Bose, Arnob. (2024).
Securing the Internet of Things: Evaluating Machine
Learning Algorithms for Detecting IoT Cyberattacks
Using CIC-IoT2023 Dataset. International Journal of
Information Technology and Computer Science, doi:
10.5815/ijitcs.2024.04.04
Atul, Kumar., Kalpna, Guleria., Rahul, Chauhan., Deepak,
Upadhyay. (2024). Enhancing Security in CIC IoT
Networks through Machine Learning Algorithms. doi:
10.1109/iciteics61368.2024.10625536
Bauyrzһan, Omarov., Omirlan, Auelbekov., Bakhytzhan,
Kulambayev., Батырхан, Омаров. (2024). Iot network
intrusion detection using machine learning on unsw-
nb15 dataset. ĶazaķstanBritantehnikalyķ universitetìnì
ņ habaršysy, doi: 10.55452/1998-6688-2024-21-3-48-
57
Chaw, Su, Htwe., Zin, Myint., Yee, Mon, Thant. (2024).
IoT Security Using Machine Learning Methods with
Features Correlation. Journal of Computing Theories
and Applications, doi: 10.62411/jcta.11179
Haifa, Ali., Vakula, Rani, J. (2024). Machine Learning for
Internet of Things (IoT) Security: A Comprehensive
Survey. International journal of computer networks and
applications, doi: 10.22247/ijcna/2024/40
Kapil, Wankhade., Ravi, Chandra., Kishore, V, Krishnan.,
Srikanth, Arasavilli., Manoj, Chandra, Undi., Amit,
Choudhary. (2024). Mathematical Approach towards
Adaptive Machine Learning Models for Dynamic
Security Threats in Industrial IoT. Advances in
Nonlinear Variational Inequalities, doi:
10.52783/anvi.v27.1359
Olakunle, Ibitoye. (2024). Robust Defenses Against
Adversarial Machine Learning in IoT Security. doi:
10.22215/etd/2024-16076
Xin-Wen, Wu.,Yongtao, Cao., Richard, Dankwa. (2024).
Pareto-Optimal Machine Learning Models for Security
of IoT Applications. doi: 10.1109/smartnets61466.202
4.10577739
Y, M, Saumya., P.V., Vinay., C., Ariel, Pinto., Natasha,
Elizabeth, Correia., Melanie, Crystal, Miranda.,
Joyline, Rencita, Dsouza. (2024). SmartDefend - IoT
Security Using Machine Learning. doi: 10.1109/disco
ver62353.2024.10750744
Yasmine, Harbi., Khedidja, Medani., Chirihane, Gherbi.,
Zibouda, Aliouat., Saad, Harous. (2024). Roadmap of
Adversarial Machine Learning in Internet of Things-
Enabled Security Systems. doi: 10.3390/s24165150
Zafar, Iqbal., Ahthasham, Sajid., Muhammad, Nauman,
Zakki., Adeel, Zafar., Arshad, Mehmood. (2024). Role
of Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms in Secure
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) for IoT &
Smart Cities. International Journal of Information
Technology, Research and Applications, doi:
10.59461/ijitra.v3i4.111
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
414
