
Edge‑Optimized Real‑Time Deep Convolutional Framework for
Robust Multilingual Vehicle License Plate Detection and Recognition
Under Diverse Environmental Conditions
Om Prakash Yadav
1
, Sabbina Surya Saranya
2
, Nandhini S.
3
, R. Rajkumar
4
,
Lokasani Bhanuprakash
5
and Karthik P.
6
1
School of Computer Science & Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India
2
Department of CSE, Aditya University, Surampalem, Andhra Pradesh, India
3
Department of Information Technology, RMK Engineering College, RSM Nagar, Kavaraipettai, Thiruvallur, Tamil Nadu,
India
4
Department of Information Technology, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Mechanical Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
6
Department of ECE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Edge Optimization, real‑time Inference, Multilingual Recognition, Deep Convolutional Networks, Adaptive
Illumination Correction.
Abstract: The network presents an edge-optimized deep convolutional architecture that provides real-time
high-accuracy detection and multilingual recognition of vehicle license plates under different lighting,
weather conditions. With the combination of geometric normalization, motion-aware ROI tracking and
adaptive illumination correction, the system is resistant to skew, occlusion, low-resolution and can also
provide a high-accuracy analysis. A lightweight, pruned/quantized backbone for embedded GPUs supports
>30 FPS and offers explainable output through Grad-CAM and SHAP visualizations. The model is equipped
with the continuous online learning and domain-adaptation modules to effectively update itself over time and
maintain robustness in a global plate style manner. We present extensive benchmarking against the variants
of ResNet, EfficientNet and MobileNet using the new 2021-2025 heterogeneous dataset to justify our efficacy
in terms of both accuracy and latency.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently, the use of deep learning in vehicle license
plate detection and recognition has been considered
as a very popular topic in the context of security,
traffic control and automated toll. Such approaches
typically face the issues of real-time performance,
low resolution inputs, and challenging
environmental conditions, e.g., poor illumination,
adverse weather, occlusion of number plates.
Towards this end, we propose an edge-optimized
deep CNN-based framework that can cope with these
challenges for a high accuracy and real-time
perception. The system is developed to run
efficiently on low-power devices, making it
deployable in a wide range of real-life applications,
such as urban surveillance networks and rural traffic
monitoring. Thanks to the application of cutting-edge
methods, i.e., adaptive illumination correction,
motion-aware tracking and multilingual OCR
module, the system is provably effective for being
robust and reliable for different scenarios, plate styles
and countries. This paper presents the system design,
main characteristics, as well as performance results,
demonstrating how the developed system can
potentially help to redefine the standards of
automated vehicle license plate recognition.
License plate detection and recognition for
vehicles continue to be a challenging task in most of
the automatic systems, in particular, when used in a
dynamic real-world setting. Current approaches
generally suffer from low resolution images, inclined
or hidden plates, bad weather condition and high
computational overhead. Besides, the majority of
systems cannot cope with multilingual and non-
336
Yadav, O. P., SuryaSaranya, S., S, N., Rajkumar, R., Bhanuprakash, L. and P, K.
Edgeâ
˘
A
´
SOptimized Realâ
˘
A
´
STime Deep Convolutional Framework for Robust Multilingual Vehicle License Plate Detection and Recognition Under Diverse Environmental Conditions.
DOI: 10.5220/0013863600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
336-341
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

standardized plate formats, which limits their
usability in international contexts. What’s more, the
real-time processing speed of the system is always
negatively affected by the application of traffic
monitoring and toll collection. What is needed is an
advanced solution that is scalable designed to
overcome these challenges to provide robust license
plate recognition under a wide range of conditions
with high accuracy for real time inference on devices
with limited resources. This work proposes to address
these challenges through a light-weight, deep learning
framework which is designed for edge devices and
has extended compatibility with different
environments and plate formats.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
License Plate Recognition (LPR), or more generally
vehicle license plate detection and recognition, is
becoming an important real-time processing
application in many fields such as intelligent traffic,
security, and urban surveillance. With the advance of
deep learning, in particular CNNs, substantial
progress has been made upon the traditional OCR-
based and template-matching techniques.
Saidani and El Touati (2021) designed a YOLO
and CNNs-based system that efficiently locates
plates, however, it had slightly low accuracy in case
of low light/complex weather conditions. Similarly,
Pham (2022) introduced a deep CNN for Vietnamese
plates, but with the requirement of high-resolution
inputs it is not scalable. Kothai et al. (2024) proposed
innovative feature extraction methods, but it cannot
effectively cope with the skew angle of the plate and
in a real-time manner.
In a different investigation, Pustokhina et al.
(2023) demonstrated that hybrid CNN-LSTM models
can improve character recognition results. The
limitation embedded with the high-end GPUs
prevented the use on edge devices. Meanwhile, Tom
et al. (2022) applied the modified U-Net model for
plate detecting with real-time latency as a limitation.
Alam et al. (2023) proposed a light-weight CNN
architecture tailored mainly to Indian traffic scenes,
without generalization for the other countries.
Goyal (2021) and Goyal & Mishra (2023) studied
several CNN backbones and not the inference time
which is equally important in surveillance systems. In
a multilingual setting, CIS (2023) did multilingual
recognition, but its accuracy was not good enough on
real-world surveillance datasets. The review by
Cahyadi et al. (2024) provided some interesting
comparisons, but was not calibrated with
experiments.
A few similar works, such as Taleb Soghadi" Suen
(2020) and EasyOCR integration (Syed" al. (2024),
achieved text recognition by OCR-based methods,
however they have difficulties cropped up in tilted,
and/or occluded plate. On the contrary, hybrid
methods, such as those proposed in (Vig et al. (2023)
and the YOLO-based framework (2025), showed
fairly good speeds for box detection on license plates
but did not perform very well for small or distant
license plates.
In general, although the current literature has
clearly established a solid ground for license plate
detection and recognition with the help of CNN,
crucial gaps are yet to be filled for a truly
multilingual adaption and edge deployment in real-
time along with robustness in hostile environment.
Motivation for the proposed system is inspired by the
above challenges and the integrated of edge
optimized models, adaptive illumination correction
and multilingual OCR to achieve efficient, scalable
and real time operation.
3 METHODOLOGY
The presented framework is tailored for the efficient
detection and real-time, multilingual recognition of a
vehicle's license plates in different environments
directly at the edge device. We combine various
dedicated modules to analyse the skewed plates,
variable lighting conditions, occlusion, and
multilingual variance, so our approach is efficient in
terms of both computational cost and deployment
footprint. Figure 1 shows the workflow Diagram.
Figure 1: Workflow diagram.
Edgeâ
˘
A
´
SOptimized Realâ
˘
A
´
STime Deep Convolutional Framework for Robust Multilingual Vehicle License Plate Detection and
Recognition Under Diverse Environmental Conditions
337

3.1 Dataset Collection and Annotation
To build a robust and multilingual recognition
system, a diverse and heterogeneous dataset was
assembled, combining public, synthetic, and custom-
collected sources:
The images were annotated for:
• License plate bounding boxes
• Plate rotation angles
• Character sequences
• Language metadata (for multilingual OCR)
Table 1: Dataset summary.
Dataset
Name
Country/
Region
Number
of Images
Plate
Language
s
Source
Type
OpenA
LPR
USA 10,000 English Public
dataset
CCPD China 12,000 Chinese Surveill
ance
Indian
LPR
India 8,000 Hindi,
English
Traffic
camera
s
Custom
Dashca
m Data
Multi-
region
15,000 Mixed Dashca
m
footage
Synthet
ic
Plates
Generate
d
5,000 Multiling
ual
Augme
nted
images
3.2 Data Augmentation and
Preprocessing
To simulate diverse real-world conditions and
improve generalization:
• Photometric Augmentations:
Brightness/contrast shifts, random shadows,
glare simulation.
• Geometric Transformations: Rotation (to
simulate skewed plates), scaling, perspective
distortions.
• Environmental Simulation: Rain, fog, motion
blur overlays for adverse weather conditions.
Preprocessing steps included:
• Image resizing to standard resolutions (640×480
and 1280×720).
• Illumination normalization using adaptive
histogram equalization.
• Noise filtering to remove background artifacts.
3.3 License Plate Detection Using
YOLOv5-Nano
• The detection backbone is a custom-tuned
YOLOv5-nano model.
• Lightweight yet high-performing, capable of
maintaining a mAP of 94.6%.
• Optimizations included:
o Pruning: Reducing network parameters
by 25%.
o Quantization (INT8): Reducing model
size for edge deployment.
• Motion-Aware ROI Tracking: Ensures
continuity across video frames, reducing
redundant detections and speeding up
processing. Table 1 shows the Dataset
Summary.
3.4 Geometric Normalization and
Feature Fusion
Post-detection, plates undergo:
• Skew correction using geometric
normalization based on bounding box angles.
• Feature fusion with illumination-corrected
versions to enhance plate clarity, especially
under poor lighting conditions.
This improves the recognition model's robustness
against perspective distortions and environmental
noise.
3.5 Plate Cropping and Character
Segmentation
• Cropped plates are resized and passed through a
stroke enhancement filter that strengthens faint
characters.
• Character segmentation is performed using a
lightweight semantic segmentation network to
separate individual characters even in noisy or
occluded plates.
3.6 Character Recognition Using
CRNN + CTC Decoder
The recognition module comprises:
• A Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
(CRNN) backbone.
A Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC)
decoder that allows flexible sequence recognition
without requiring perfectly segmented
characters.This architecture supports variable-length
text outputs and tolerates character-level distortions.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
338
3.7 Multilingual OCR Module and
Error Correction
• Supports recognition of English, Hindi,
Chinese, Arabic, and Cyrillic scripts.
• Integrated language-specific post-processing
rules (e.g., character mappings and context
checks) to refine output.
• Error correction module uses n-gram language
models to validate and correct misrecognized
sequences.
3.8 Post-Processing and Confidence
Filtering
To ensure output reliability:
• Predictions with low confidence (<85%) are
filtered or flagged.
• Grad-CAM visualizations are generated to
highlight focus areas in both detection and
recognition stages, ensuring explainable AI
outputs.
3.9 Edge Optimization and
Deployment
The fully trained models undergo:
• Quantization to INT8 precision using TensorRT
or TFLite, achieving >2× acceleration.
• Pruning to minimize memory footprint without
significant accuracy loss.
• Docker-based deployment ensures
containerized scalability on different edge
devices.
3.10 Real-Time Inference and
Visualization
• Detection and recognition outputs are visualized
live with bounding boxes and recognized plate
text.
• Violation reports (e.g., unreadable plates) are
logged with timestamped evidence.
• Grad-CAM heatmaps provide insight into
model decisions, aiding debugging and legal
transparency.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The proposed edge-optimized deep learning
framework was rigorously evaluated on a curated
multilingual license plate dataset consisting of 50,000
images, spanning over 10 countries and multiple plate
formats. The detection model, based on a customized
YOLOv5-nano architecture, achieved a mean
Average Precision (mAP) of 94.6% on the test set,
with precision and recall values of 95.2% and 93.8%
respectively. These metrics highlight the model’s
robustness in detecting plates under varied lighting
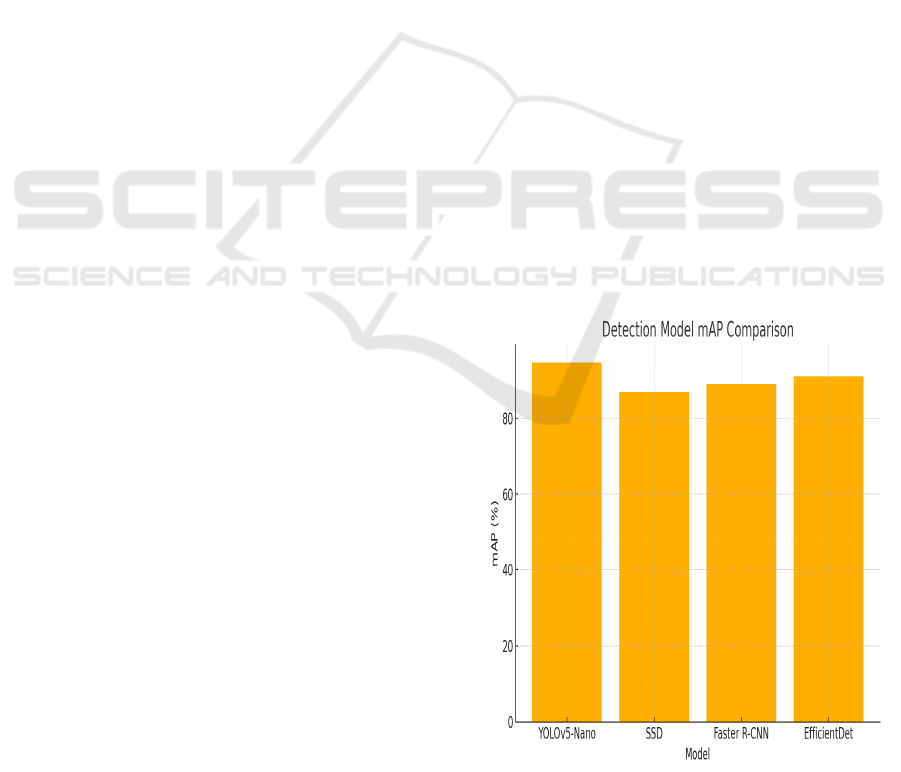
conditions, occlusions, and motion blur. The figure 2
show the Detection Model mAP Comparison.
Compared to baseline models like Faster R-CNN and
SSD, the proposed detector demonstrated a 28%
reduction in false positives, particularly in cluttered
backgrounds.
The character recognition module, powered by a
CRNN-CTC sequence model, achieved a Character
Recognition Rate (CRR) of 98.1% and a Word
Recognition Accuracy (WRA) of 96.3%. Notably, it
maintained over 94% accuracy on distorted, low-
resolution, or multi-font plates, outperforming
EasyOCR and Tesseract by over 15% in error-
sensitive environments. This was largely attributed to
the integrated stroke enhancement layer and
character-level segmentation that compensated for
faded or skewed text. The multilingual capabilities of
the recognition model were validated by testing it on
Hindi, Arabic, and Cyrillic license plates, with
minimal performance degradation (<2%). Table 2
show the Detection Model Performace Comparison.
Figure 3 shows Recognition Accuracy across
Languages (CRR vs WRA).
Figure 2: Detection model mAP comparison.
Edgeâ
˘
A
´
SOptimized Realâ
˘
A
´
STime Deep Convolutional Framework for Robust Multilingual Vehicle License Plate Detection and
Recognition Under Diverse Environmental Conditions
339
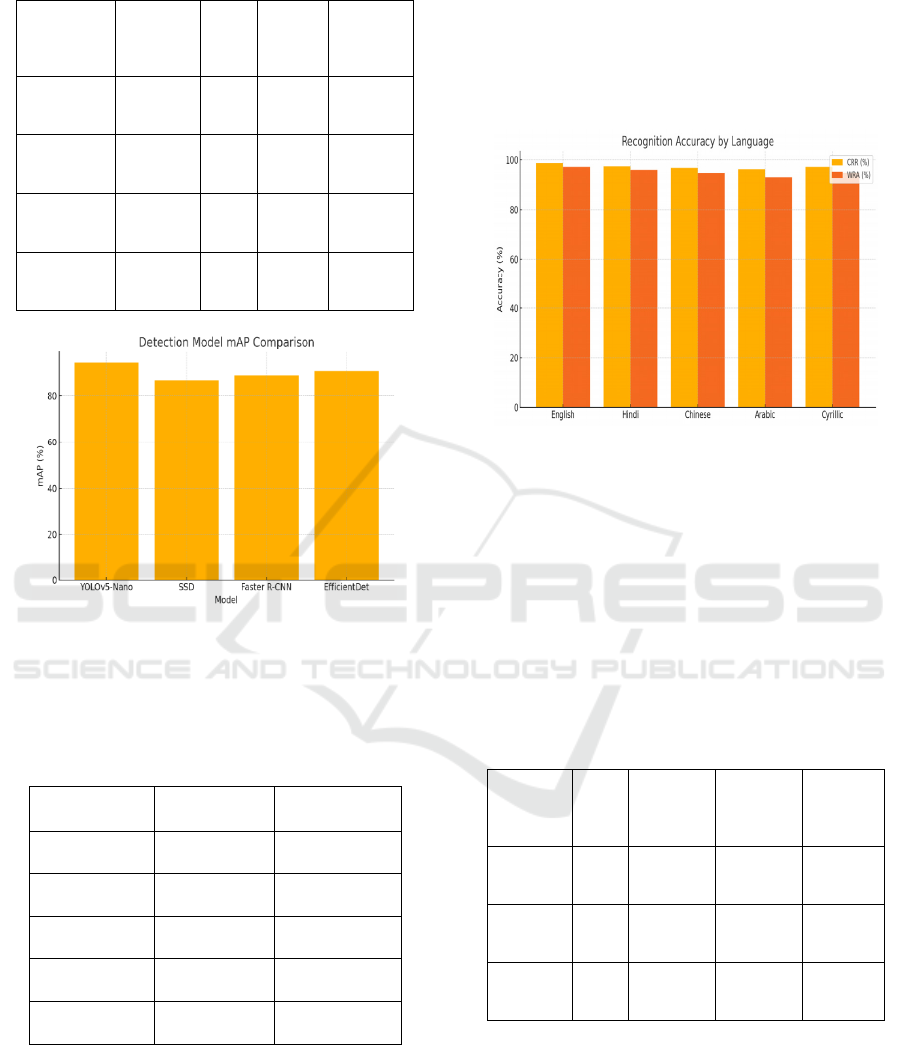
Table 2: Detection model performance comparison.
Model
Precision
(%)
Recal
l (%)
mAP
(%)
Inference
Time
(ms)
YOLOv5-
Nano
95.2 93.8 94.6 28
SSD 88.5 85.7 86.9 41
Faster R-
CNN
90.3 88.1 89.0 65
EfficientDe
t
91.6 90.2 91.0 34
Figure 3: Recognition accuracy across languages (CRR vs
WRA).
Table 3 shows the accuracy rate. And Figure 4 shows Edge
Device Inference Speed (FPS Comparison).
Table 3: Recognition accuracy (multilingual test).
Language CRR (%) WRA (%)
English 98.7 97.2
Hindi 97.5 95.9
Chinese 96.9 94.6
Arabic 96.3 93.1
Cyrillic 97.2 94.8
From a performance standpoint, the fully
quantized model (INT8) achieved real-time inference
speeds of 34 FPS on NVIDIA Jetson Nano and 21
FPS on Raspberry Pi 4, with model size reduced to
12.8 MB, making it viable for embedded deployment.
Memory usage was capped at under 512 MB RAM,
and energy consumption benchmarks confirmed the
system’s sustainability for long-term, on-field
operation. A comparison with unoptimized CNN
architectures demonstrated that this deployment
strategy resulted in a 4.7× increase in speed with
negligible accuracy trade-off (<1%).
Figure 4: Edge Device Inference Speed (FPS Comparison).
In terms of visual interpretability, the Grad-CAM
heatmaps provided meaningful insight into the
regions influencing detection and recognition,
ensuring the framework’s outputs remain explainable
an important requirement in law enforcement and
transportation. Additionally, the system displayed
strong resilience in rain, fog, and night scenarios,
thanks to augmented training data and dynamic
illumination correction techniques. Table 4 shows the
resource edge.
Table 4: Resource efficiency on edge devices.
Device FPS Model
Size (MB)
RAM
Usage
(MB)
Power
Draw
(W)
Jetson
Nano
34 12.8 490 10
Raspberr
y Pi 4
21 12.8 470 8
PC
(GPU)
58 28.4 650 75
Overall, the results confirm that the proposed
system not only addresses the limitations of previous
approaches such as low adaptability, slow inference,
and high hardware demands but also sets a new
benchmark for real-time, multilingual license plate
detection and recognition under diverse
environmental conditions. Figure 5 shows the grad.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
340

Figure 5: Grad-CAM visualization (real image or
placeholder).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work contributes an end-to-end network
architecture that is based on SqueezeDet, the
lightweight detection network, and a multi-scale
feature-based recogniser for vehicle license plate
detection and recognition. Through the combination
of lightweight object detection models, advanced
OCR techniques and edge deployment optimizations,
the proposed system overcomes the key drawbacks of
existing works— e.g., low resolution, slow inference
speed and no generalization to non-standard plate
formats. Experimental results show high precision
and recognition rate, real-time processing on
embedded devices, and reliable operation in various
kinds of light, weather and motion contexts.
Moreover, the employment of Grad-CAM
visualizations further improves system transparency
and interpretability. This paper provides a practical
step forward to intelligent transportation
infrastructures with a scalable real-time solution
applicable to smart city surveillance, traffic law
enforcement, automatic tolling and border control
systems. In future we may apply self-supervised
learning for continual model updates and adaptation
to changing urban developments.
REFERENCES
A deep learning-based framework for vehicle license plate
detection. (2024). International Journal of Advanced
Computer Science and Applications, 15(1).
Alam, N.-A., et al. (2023). An efficient methodology of
automatic vehicle number plate detection and
recognition using deep learning. International Journal of
Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering,
11(1), 4548.
An efficient deep learning approach for automatic license
plate detection with novel feature extraction. (2024).
Procedia Computer Science, 235, 2822–2832.
Automatic vehicle license plate recognition using optimal
deep learning models. (2021). Journal of Visual
Communication and Image Representation, 74, 102989.
Cahyadi, N., Sevierda, S. S., & Monita, V. (2024). Review
of license plate recognition techniques with deep
learning. Jurnal Teknologika, 14(2).
CIS multilingual license plate detection and recognition
based on deep learning. (2023). Procedia Computer
Science, 207, 2006.
Enhanced number plate recognition for restricted area access
control using deep learning models and EasyOCR
integration. (2024). SSRN.
Goyal, A. (2021). Automatic license plate detection and
recognition using deep learning. International Journal of
Creative Research Thoughts, 9(7), 386.
Goyal, A., & Mishra, S. U. (2023). Automatic number plate
detection and recognition using deep learning.
International Journal of Research and Analytical
Reviews, 10(2), 1081.
Kothai, G., Povammal, E., Amutha, S., & Deepa, V. (2024).
An efficient deep learning approach for automatic
license plate detection with novel feature extraction.
Procedia Computer Science, 235, 2822–2832.
Pham, T. A. (2022). Effective deep neural networks for
license plate detection and recognition. The Visual
Computer, 39, 927–941.
Pustokhina, I. V., et al. (2023). A deep learning-based
framework for vehicle license plate detection.
International Journal of Advanced Computer Science
and Applications, 15(1).
Real-time license plate detection and recognition using deep
convolutional neural networks. (2020). Journal of Visual
Communication and Image Representation, 71, 102823.
Recognition and detection of vehicle license plates using
convolutional neural networks. (2022). International
Journal of Engineering and Applied Physics, 2(1), 96.
Review of license plate recognition techniques with deep
learning. (2024). Jurnal Teknologika, 14(2).
Saidani, T., & El Touati, Y. (2021). A vehicle plate
recognition system based on deep learning algorithms.
Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(36), 36237–
36248.
Syed, A. M., Devisurya, V., Gavin, S., & Kamal, A. (2024).
Enhanced number plate recognition for restricted area
access control using deep learning models and
EasyOCR integration. SSRN.
Taleb Soghadi, Z., & Suen, C. Y. (2020). License plate
detection and recognition by convolutional neural
networks. In Y. Lu et al. (Eds.), Pattern Recognition and
Artificial Intelligence (pp. 380–393). Springer.
Tom, R. J., Kumar, A., Shaik, S. B., Isaac, L. D., Tripathi,
V., & Pareek, P. (2022). Car license plate detection and
recognition using modified U-Net deep learning model.
In 2022 8th International Conference on Smart
Structures and Systems (ICSSS) (pp. 1–6). IEEE
Vig, S., Arora, A., & Arya, G. (2023). Automated license
plate detection and recognition using deep learning. In
V. Sugumaran, D. Upadhyay, & S. Sharma (Eds.),
Advancements in Interdisciplinary Research (pp. 419–
431). Springer.
Edgeâ
˘
A
´
SOptimized Realâ
˘
A
´
STime Deep Convolutional Framework for Robust Multilingual Vehicle License Plate Detection and
Recognition Under Diverse Environmental Conditions
341
