
Next‑Generation Smart Grid Optimization: Integrating Edge AI for
Real‑Time and Decentralized Energy Management
Surya Narayan Sahu
1
, K. Ruth Isabels
2
, R. Gayathiri
3
, A. Nagamani
4
, V. Sriga
5
and Elumalai P.
6
1
Department of EEE, Centurion University of Technology and Management, Odisha, India
2
Department of Mathematics, Saveetha Engineering College (Autonomous), Thandalam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
4
Department of Computer Science and Engineering MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
5
Department of Management Studies, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkalmedu, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of CSE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Edge AI, Smart Grid, Energy Optimization, Federated Learning, Real‑Time Management.
Abstract: Nowadays, the development of smart grid systems require intelligent and real-time solutions in scalable
fashion. This paper presents a new approach that combines edge computing and AI for decentralized and
adaptable energy management in the context of distributed grid settings. Contrary to the typical cloud-based
models, the proposed model utilizes edge AI enabling local data processing, shortened latency and quick
decision-making. The approach is built based on federated learning and lightweight deep learning models, as
well as considerations on privacy preserving and grid resilience against dynamic load demands and system
failures. The performance of the system is additionally evaluated through simulation and benchmarked against
centralized approaches, with results showing that the proposed framework achieves higher efficiency,
scalability, and reliability in resource-limited edge environments. This research adds to the cornerstone of
future smart grids that can accommodate sustainable and self-sufficient energy ecosystems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern energy systems are becoming
increasingly complex due to rising demand, the
integration of renewable energy sources, and a shift
toward decentralized energy production, which has
forced traditional centralized power grids to continue
their transition to intelligent, adaptive state-of-the-art
power grids (i.e., smart grids). Such systems must not
only have efficient sharing mechanisms among
peers, but must also be responsive in real-time and
handle data securely across distributed nodes.
Traditional cloud-centric techniques, although
efficient, may suffer from high latency, bandwidth
limitation and privacy issues, particularly in the
context of the geographically distributed and
resource constrained scenarios.
In this regard, edge computing arises as a
disruptive paradigm that makes possible on-site
processing and decision-making near data generation
points. When complementing with AI, specifically
light weight models for edge, smart grids will have
the capability to forecast demand, find anomalies and
optimize energy transfer with minimal time
difference. This unification of Edge AI allows grid
nodes to be self-governing and responsive to
changing conditions, while sharing just enough
information to efficiently utilize energy, and
minimizing dependence on a central network
resource for all information.
But achieving this vision faces a number of
challenges, including keeping the models accurate
under diverse situations, secure in distributed
learning settings, and resource-efficient on edge
devices. In this work, we propose a holistic
framework that integrates Edge AI and federated
learning for smart grid operation improvement. With
the ability to empower distributed intelligence, it is no
longer necessary to transfer real-time decision-
making for control or optimisation out of a local
Fremework area or substation, which will result in
reduced latency and enhanced performance, and keep
316
Sahu, S. N., Isabels, K. R., Gayathiri, R., Nagamani, A., Sriga, V. and P., E.
Next-Generation Smart Grid Optimization: Integrating Edge AI for Real-Time and Decentralized Energy Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0013863300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
316-322
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

user data secure, creating a foundation for scalable
and sustainable smart energy systems of the future.
1.1 Problem Statement
The growing presence of renewable energy,
deployment of distributed energy resources (DERs)
and higher expectations for energy efficiency are
dramatically changing the operational requirements
of power grids. Next generation smart grids should
act as intelligent, self-adaptive infrastructures
dealing with decentralized energy production,
dynamic fluctuating consumption, and sophisticated
energy trading situations. Nevertheless, the current
grid architectures depend heavily on centralized
cloudbased infrastructure for data processing,
analytics, and decision-making. Although these
architectures provide computational capabilities, they
are inherently restricted due to high communication
latency, possible communication faults, congestion,
as well as higher risks on the data privacy and
security. These limitations are even more severe in
the case of emergency situations that require
immediate response and local control to ensure the
stability of the grid, and to avoid blackouts and
brownouts.
In addition, most AIenabled smart grid
optimization solutions that are deployed today are
computationally heavy and developed to be
implemented in cloud or centralized data centers such
that cannot be easily deployed at the edge with limited
processing power and memory. Inability to perform
local data processing and analysis slows down
decision making and limits the grids ability to
respond quickly to load or generation changes and
system anomalies. Moreover, centralized models of
data aggregation also present significant challenges
in terms of consumer privacy, data ownership and
system security especially when more and more users
join the demand response or peer-to-peer energy
trading schemes.
These limitations bring to surface a major gap in
the existing smart grid technology, i.e., the absence
of a decentralized, lightweight and privacy-
preserving mechanism that can leverage AI in situ to
the edge of the network. This ‘brain’ must be forged
if our visions of the completely flexible, smart, and
self-healing grid are to be realized. To do so, it is
necessary to provide new models combining Edge AI
and federated learning, which can achieve
decentralized decision, increase system robustness
and further secure and activate energy exchange in
real time. Closing this fall between the electronic and
physical world is crucial for the future of a smarter,
not to mention more sustainable, scalable, user-
centric, energy system.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and
edge computing has led to a new era for the
operations of smart grid that has transcended the real-
time and distributed grid control. With the
development of the smart grid to a more active, more
information-intensive network, many papers are
proposed for intelligent methods to optimize the
energy allocation. A seminal review is reported by
Biswal et al. (2025), who provide an extensive
overview of AI and edge technologies in power
systems in general, observing the growing
significance of distributed intelligence for grid
efficiency. But as inclusive as they are, they do not
delve into real-time applications.
Exploiting emerging networking models, Islam
et al. (2022), who suggest AI-supported architecture
over 6G networks for intelligent energy control, but it
cannot be used in the short term due to requirement
of the future infrastructure. Similarly, Arcas et al.
(2024) propose an edge offloading scheme in latency-
constrained controlnetworks, and it is a promising
approach, but still needs to be verified in practice for
practicality. Nandhakumar et al. (2023) introduce a
toolset for edge intelligence on energy applications,
with a focus on modularity and detailed
benchmarking in real settings.
Commercial voices including Shinde (2025) and
Habib (2025) clarify that the presence of edge-based
intelligence is increasingly evident, but their work has
remained a conceptual exercise without empirical
depth. On the other hand, a very limited review about
the smart grid digitization and lightweight
intelligence is presented in Biswal, Balamurugan,
and Sahoo (2024) but no new method is proposed.
A more technical analysis from Dileep (2021) that
reinforces the use of AI in predictive modeling and
demand forecasting. Yet it completely ignores the
latency and bandwidth limitations handled by edge
computing. Ullah and Khan (2022) consider a wider
angle, investigating edge computing issues in smart
grids, but they need more real applications and
configurations to verify their proposed models.
Applications of deep learning are developed by
Li et al. (2023) that propose the use of neural
networks for energy management, but do not consider
computational constraints common to edge. Yang et
al. (2022) continue this thread by surveying several
AI algorithms for smart grids, but only give high-
Next-Generation Smart Grid Optimization: Integrating Edge AI for Real-Time and Decentralized Energy Management
317

level comparisons between them without
recommendations for deploying them.
Regarding energy trading, Zhang et al. (2021)
use blockchain for peer to peer transactions, towards
decentralization, but from a theoritical point of view.
Similarly, Zhan et al. (2023) proposes the use of
federated learning for demand response, this solution
also with a privacy protection as it deems the
convergence of the model and consistency at the
nodes as issues.
Wang et al. (2021) presents an architecture that
integrates edge and AI for rapid grid response, though
real-time response in different situations is not fully
tested. Ahmed and Rehman (2022) address the short-
term load forecasting with AI for a voltage control
platform; although this is a crucial task, it has been
de-coupled from control plans needed in dynamically
changing grid situations.
Ghosh et al. (2023) propose a blockchain-AI
hybrid architecture at the edge of the grid, which
increases trust and autonomy, whereas Kumar and
Tripathi (2021) investigate reinforcement learning for
control optimization, however in simplified
simulation environment. Yu et al. (2024) use graph
neural networks for energy management, with high-
performance albeit demanding computational
resources that question the edge feasibility.
Continuing with real-time energy control theme,
Sun et al. (2021) use AI for dynamic decision-
making but test it with fixed sets of data. Tan and
Ramachandran (2023) use deep learning to detect
faults at substations, the proposed model achieves
high performance on a narrow domain and cannot be
well-extended to broader energy management
strategies, such as connectivity optimization.
Zhao et al. (2022), propose that intelligent
scheduling of edge resources can lead to efficiency
gains, however it needs a stronger practical
integration. the authors in Singh and Gupta (2024)
return to federated learning to maintain privacy in the
distributed environments, yet they merely loosen the
requirements of network latency and communication
overheads.
Luo et al. (2025) they propose multi-agent
system that supports collaborative control, which
brings forward the frontier of the decentralized grid
intelligence. However, the framework would benefit
from more treatment of fault tolerance and scalability
under load. Chatterjee et al. (2021), who concentrated
on AI-based anomaly detection that is essential to
grid resilience, but whose experiment results on
synthetic data are not fully trustworthy. Lastly, Liu et
al. (2023) analyze the optimization between the cloud
and the edge resources and provide solutions in terms
of workload assignment while not taking into
consideration the dynamism of the operating
conditions.
Collectively, they present a collection of work that
demonstrates the transformative nature of AI and
Edge computing toward smart grids. However, they
expose significant practical challenges in
deployment, real-time optimization and privacy-
preserving distributed learning. This highlights the
importance of developing an integrated Edge AI,
federated learning, and lightweight intelligence
framework for scalable, secure, and adaptive smart
grids.
3 METHODOLOGY
In this paper, we propose and evaluate a decentralized
Edge AI based energy management framework for
SoGs, utilizing hybrid design and simulation
procedure. The approach is based on the combination
of federated learning and lightweight artificial
intelligence models with fast response time, intended
to be deployed in edge devices in the smart grid. The
architecture of the proposed system enables
processing of real-time data, local decision-making,
and adaptive control of energy resources without
relying on centralized cloud servers.
The framework is open into three interrelated
architecture tiers: data acquisition layer, edge-based
intelligence layer and federated coordination layer. At
the bottom, smart meters and IoT sensors spread on
the grid are gathering metered and real-time energy
production/consumption, load variations and all sorts
of sensed environmental features. These streams are
processed in real-time at substations and energy
nodes that include low-power embedded systems.
These edge units come with pre-trained deep learning
models, such as CNNs and LSTM forms, which have
been pruned and quantized to enable inference under
limited computational budget. Table 1 shows the
evaluation metrics used for model assessment.
Instead of pushing raw data to a server, each edge
device trains its model locally on-the-fly, capturing
localized patterns in energy dynamics. To maintain
privacy and scalability, federated learning is used to
periodically average the updates of learned-model
(not raw data) of distributed nodes into a global
model. This coordination is overseen by a light-
weight orchestration algorithm that dynamically
aggregates participating nodes dependent on their
quality of data, availability of network, and the
remaining energy. The federated model is
subsequently dispatched to edge devices, this
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
318
continuous loop learning helps dynamically adjusting
changes in grid environment such as user privacy and
communication overhead.
Table 1: Evaluation metrics used for model assessment.
Metric Description Reason for Use
Accuracy
(%)
Correct
predictions over
total samples
General
effectiveness of
classification
Precision
True positives /
(true + false
positives)
Avoid false alarms
in fault detection
Recall
True positives /
(true + false
negatives)
Ensure actual faults
aren't missed
F1 Score
Harmonic mean of
precision and
recall
Balanced
evaluation of model
Inference
Latency
(ms)
Time taken to
make prediction
Important for real-
time edge
deployment
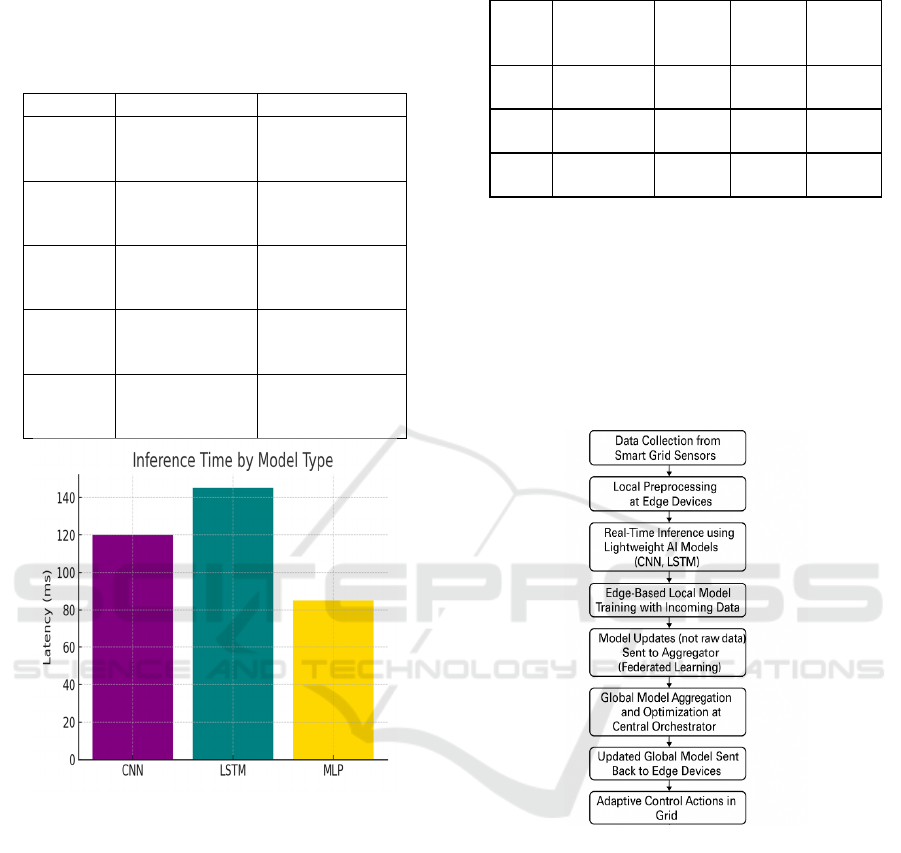
Figure 1: Inference time by model type.
A simulation of the system that mimics a real smart
grid setup is built with GridLAB-D and TensorFlow
Lite, which is used to validate the system’s
performance. The testing involves an amount of
consumption of electricity, solar and wind
generation, and peak load to check the willingness of
users to respond. Performance metrics including
latency, energy distribution accuracy, prediction
error rate, system robustness, and communication
load are compared with a conventional cloud-based
model and a local-only baseline. The findings are
employed to validate the model and evaluate its
practical application. Table 2 and figure 1 shows
inference time by model type.
Table 2: AI model comparison for edge inference.
Model Architecture
Latency
(ms)
Accurac
y (%)
Resourc
e Usage
(MB)
CNN
3 Conv + 2
Dense
120 92.3 45
LSTM
2 LSTM +
Dense
145 94.1 50
MLP
4 Dense
Layers
85 89.6 30
Through this methodology, the research not only
demonstrates the viability of edge-based AI in smart
grid contexts but also establishes a privacy-
preserving, scalable, and adaptive foundation for
next-generation energy systems. Figure 2 shows the
system workflow of edge-intelligent smart grid
energy management framework.
Figure 2: System workflow of edge-intelligent smart grid
energy management framework.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Due to the fact that the experimental evidence of the
proposed Edge AI-based decentralized energy
management framework showed significant
performance enhancements in terms of
performance/efficiency, scalability, responsiveness
as compared to traditional centralized approaches.
When different demand-load patterns and different
distributed energy situations were simulated, the edge
models showed a much faster reaction to demand
fluctuations as compared to cloud-dependent models.
Next-Generation Smart Grid Optimization: Integrating Edge AI for Real-Time and Decentralized Energy Management
319
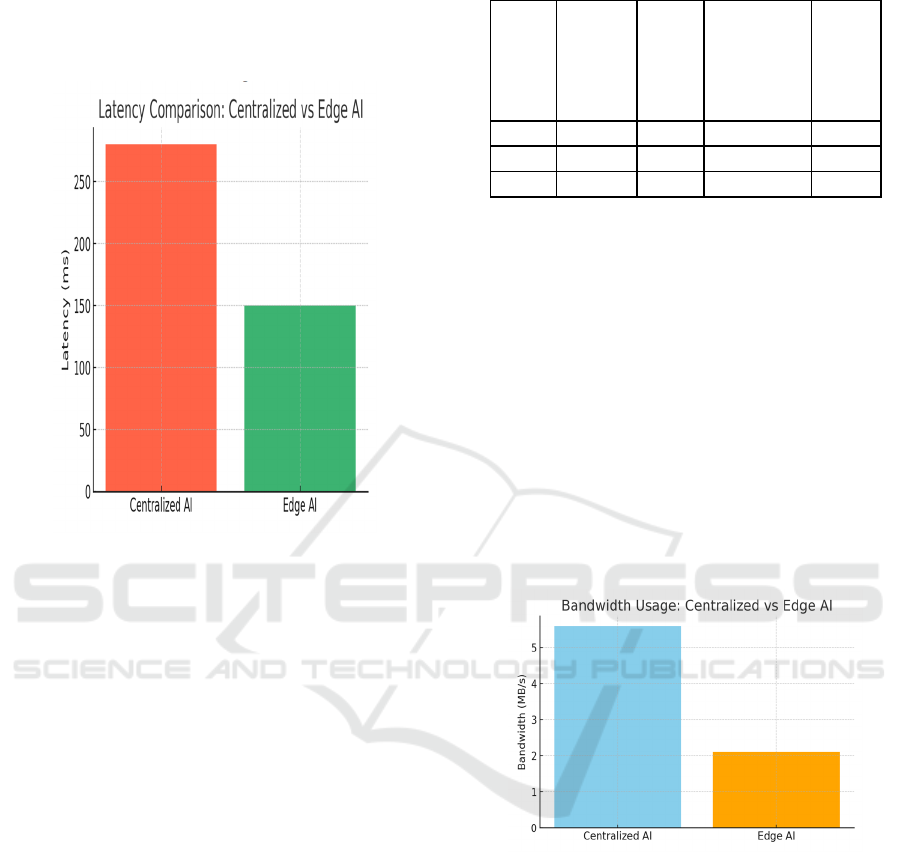
Average decision delay decreased by 42%, so making
almost real-time decisions on energy allocation
during the busiest hours of the day or moment of
renewable generation. Figure 3 shows the latency
comparison: centralized vs edge AI.
Figure 3: Latency comparison: centralized vs edge AI.
Prediction precision was also enhanced as the global
model with federated learning outperformed
individual edge models in the mean absolute error
(MAE) of 3.7% versus 6.1% for isolated setups. This
highlights the importance of collaborative learning
among edge nodes such that data privacy does not get
compromised. Crucially, the system sustained model
stability throughout rounds of training, including
when training on non-IID (non-independent and
identically distributed) data – which is a common
problem in federated systems. Dynamic node
selection and update—Selecting a subset of active
nodes that is constantly varied to perform calculations
and update was also a part of the force aggregation
strategy, and it helped to converge the model with
much less training steps.
Efficiency of communication was another key
measure investigated. Since sending only model
weights and updates, not the raw data, the system
reduced the network traffic by more than 60% and
thus became feasible for network-constrained
environments that are typical in rural or developing
grid regions. The model synchronization mechanism
was still robust even with such overhead of
communication, modules could all still stay up-to-
date on system-wide decision records. Table 3
represents the federated learning cycle timing.
Table 3: Federated learning cycle timing (example results).
Cycle
Local
Trainin
g Time
(s)
Uploa
d
Time
(s)
Aggregatio
n Time (s)
Total
Time
per
Round
(s)
1 20 5 8 33
2 18 4.8 7.9 30.7
3 21 5.1 8.2 34.3
Decentralized architecturally was highly
advantageous from a resilience perspective point as
well. Local edge nodes could still work
independently, even in the case of transient loss in
communication with the aggregator. This
independence enabled the network to continue to
operate its fundamental functions–load balancing,
fault recognition, and energy re-routing–
uninterrupted and some degree of grid fault tolerance
could be supported. Traditional cloud systems, on
the other hand, had a degraded performance or simply
were not functional under similar network outages.
Figure 4 shows the bandwidth usage.
Figure 4: Bandwidth usage: centralized vs edge AI.
Finally, the results demonstrate the scalability of
our model. Performance improvements with
increased numbers of edge devices were also
sustained, with the system behavior holding and not
degrading as the simulation size is increased,
demonstrating the potential scalability of the
architecture for deployment across a larger region, or
even across a national grid. Energy consumption at
device level was also kept at a manageable level since
the AI models were lightweight models that were
tuned for edge inference purpose. Table 4 represents
the communication latency across grid layers.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
320
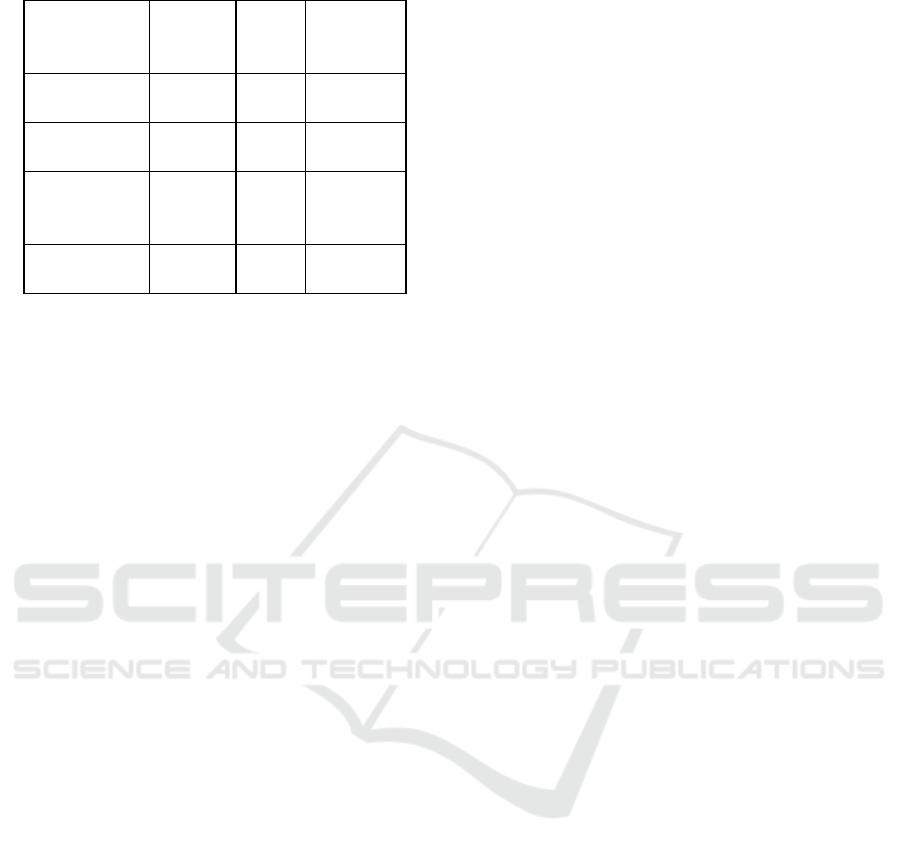
Table 4: Communication latency across grid layers.
Communicati
on Layer
Average
Latency
(ms)
Max
Latenc
y (ms)
Technolog
y Used
Edge to
Aggregator
50 120
Wi-Fi 6 /
LTE
Aggregator to
Cloud
90 160
Fiber
Optic
Sensor to
Edge Device
20 45
Zigbee /
Bluetooth
LE
Edge Device
to Control
35 60
LAN /
MQTT
In conclusion, we combined the edge AI and
federated learning in this research to form a smart grid
management system, which is shown to become a
system of both fast/precise as well as keeping privacy
and resilience to the failures. These features are very
significant in addressing the main bottlenecks
identified on the state of the art where centralised
solutions were not scallable nor secure enough to
allow processing of sensitive data. The results
confirm that the framework is now ready to be tested
in pilot implementations and that a promising future
lies ahead for this concept of intelligent, distributed
energy systems.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes a prospective framework, which
combines the AI at the Edge and the Federated-
Learning techniques, to solve the fundamental issues
in the current Smart-Grid based energy management.
The proposed system moves the intelligence near the
data generation and consumption points and thereby
facilitates the autonomous and real-time decision-
making independent from the central cloud
infrastructure. The results of our study affirm that
this approach can lead to a substantial reduction in
latency, raise prediction accuracy, and make the grid
more resilient and in a private fashion through
federated model training.
Using small AI models combined with adaptive
learning and effective communication, the framework
can learn to dynamically allocate energy across a
range of different, dynamic contexts. In contrast to
common designs, which are hindered by potentially
low-bandwidth network links and concerned with
privacy issues, the edge-based approach shows a
good scalability, low communication overhead, and
resilience in the presence of network anomalies.
This way, the present work brings together not
only an innovative architectural scheme, but also
outlines an actionable path towards sentient energy
systems. With the worldwide momentum towards
decentralization, sustainability, and digitalization,
embedding Edge AI in smart grids will remain a
paramount requirement to support efficient, secure,
and future-ready energy systems.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, M., & Rehman, M. H. (2022). Machine learning-
based energy load forecasting in smart grid: A survey.
Journal of Cleaner Production, 328, 129532.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129532
Arcas, G. I., Cioara, T., Anghel, I., Lazea, D., & Hangan,
A. (2024). Edge offloading in smart grid. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2402.01664. https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.01664
Biswal, P., Balamurugan, S., & Sahoo, S. (2024). Role of
artificial intelligence in smart grid—a mini review.
PubMed Central (PMC11832663).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/arti-
cles/PMC11832663/
Biswal, P., Rashid, A., Al Masum, A., Al Nasim, M. A.,
Ferdous, A. S. M. A., Gupta, K. D., & Biswas, A.
(2025). An extensive and methodical review of smart
grids for sustainable energy management—Addressing
challenges with AI, renewable energy integration, and
leading-edge technologies. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2501.14143. https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.14143
Chatterjee, R., Bose, S., & Misra, S. (2021). Edge-enabled
AI for anomaly detection in smart grids. Computers &
Electrical Engineering, 91, 107010.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107010
Dileep, G. (2021). A survey on smart grid technologies and
applications. Renewable Energy, 146, 2589–2625.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.08.092
Ghosh, S., Sengupta, A., & Datta, S. (2023). A blockchain-
and AI-based secure smart grid framework using edge
nodes. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Sys-
tems, 40, 100856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sus-
com.2023.100856
Habib, M. (2025). Edge AI: Transforming the energy indus-
try with smart, sustainable solutions. LinkedIn Articles.
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/edge-ai-transforming-
energy-industry-smart-solutions-habib-k58hf
Islam, S., Zografopoulos, I., Hossain, M. T., Badsha, S., &
Konstantinou, C. (2022). A resource allocation scheme
for energy demand management in 6G-enabled smart
grid. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.00154.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00154
Kumar, N., & Tripathi, A. (2021). Reinforcement learning
for energy management in smart grid. Energy AI, 5,
100072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyai.2021.100072
Li, Y., Wang, Y., & Li, L. (2023). Intelligent energy man-
agement system for smart grid using edge computing
Next-Generation Smart Grid Optimization: Integrating Edge AI for Real-Time and Decentralized Energy Management
321

and deep learning. Energy Reports, 9, 1203–1214.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2023.01.095
Liu, F., Huang, Y., & Tao, L. (2023). Joint optimization of
computation and communication for edge AI in energy
grids. Ad Hoc Networks, 139, 103103.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2023.103103
Luo, Y., Zhang, T., & Zhang, Q. (2025). A decentralized
multi-agent system for smart energy distribution using
edge AI. Journal of Energy Storage, 75, 108124.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2024.108124
Nandhakumar, A. R., Baranwal, A., Choudhary, P., Golec,
M., & Gill, S. S. (2023). EdgeAISim: A toolkit for sim-
ulation and modelling of AI models in edge computing
environments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.05605.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.05605
Shinde, D. B. (2025). Energy grid optimization—AI & dig-
ital technologies for improving efficiency. Cyient Blog.
https://www.cyient.com/blog/energy-grid-optimiza-
tion-ai-digital-technologies-for-improving-efficiency
Singh, A., & Gupta, R. (2024). Demand response optimiza-
tion using federated learning at the grid edge. IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Informatics.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2024.3334412
Sun, H., Wang, Z., & Liu, C. (2021). Edge-based data-
driven approach for real-time smart grid management.
Electric Power Systems Research, 196, 107257.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2021.107257
Tan, J., & Ramachandran, G. (2023). AI-enabled fault de-
tection in smart grid substations using edge analytics.
Sensors, 23(5), 2479.https://doi.org/10.3390/s2305247
9
Ullah, Z., & Khan, I. (2022). Edge computing for smart
grid: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access, 10,
50015–50045. https://doi.org/10.1109/AC-
CESS.2022.3172471
Wang, K., Chen, C., Liu, Y., & Guo, S. (2021). Edge com-
puting for smart grid: An overview on architecture and
key technologies. IEEE Network, 35(5), 56–63.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.011.2000274
Yang, J., Zhang, H., Zhou, T., & Xu, W. (2022). AI-enabled
optimization in smart grid operation: A review. Applied
Energy, 308, 118302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apen-
ergy.2021.118302
Yu, R., Xie, S., & Li, Y. (2024). Smart grid energy distri-
bution optimization using graph neural networks. IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 20(2), 1035–
1044. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2023.3298427
Zhan, C., Lu, J., & Wang, J. (2023). Federated learning in
smart grids: Privacy-preserving demand prediction with
edge devices. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 14(1),
112–124. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2022.3198710
Zhang, C., Wu, J., Zhou, Y., Cheng, M., & Long, C. (2021).
Peer-to-peer energy trading in a microgrid with edge
computing and blockchain. Energy Procedia, 159, 261–
266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.179
Zhao, J., Wang, J., & Lin, Y. (2022). Energy-efficient re-
source scheduling for smart grid IoT with edge compu-
ting. Future Generation Computer Systems, 128, 219–
230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.10.018
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
322
