
Lightweight Deep Learning for Real‑Time Health Monitoring on
Edge Devices
Eswararao Boddepalli
1
, K. Sindhuja
1
, K. Akila
2
, M. Dharani
2
, G. Nagarjunarao
3
and Akash K.
4
1
Department of Information Technology, J.J.College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Management Studies, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkalmedu, Erode - 638052, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
4
Department of MCA, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Edge Computing, Health Monitoring, Lightweight Deep Learning, Mobile Devices, Real‑Time Analytics.
Abstract: Deep learning in edge computing is revolutionizing healthcare, delivering real-time tracking of crucial health
variables on mobile and wearable. We propose to design "lightweight" deep learning models that are tailored
for small scale edge devices. The proposed framework solves the problems concerning the limited
computational capacity, energy consumption, and variability of the physiological signals, in order to
accomplish a reliable, real-time physiological analysis with cloud connectivity not required. The system is
optimized for deployment at the edge, providing low-latency and high-throughput performance under realistic
conditions and enabling real-time health monitoring, early detection of anomalies, and personalized feedback.
Experimental results show promising accuracy and low resource consumption for the models, making them
practically deployable in large-scale mobile health ecosystems.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the emerging trends of the past few years has
been the point at which artificial intelligence (AI)
meets healthcare, an event that is creating intelligent
systems that help redefine the way we access and
experience healthcare. Of these progressions, the use
of deep learning for health monitoring has attracted
much interest because of its ability to interpret
complex physiological data with high accuracy.
Nevertheless, the performance of deep learning
models can be inhibited because it relies on high
performance computing environment usually
provided by cloud systems. This dependence
imposes various important challenges, such as high
latency, high power consumption, network reliability,
and raises concerns about data privacy and security
particularly in situations where constant and real time
monitoring is required.
Edge computing has been proposed as a potential
solution to circumvent these challenges, processing
the data in or near the device of origin. Moving
computations from central servers to devices at the
network edge, such as smartphones, wearables, or
sensors embedded in IoT, edge computing leads to
quicker response times, less bandwidth
consumption, and greater protection of private health
data. However, the use of deep learning in edge
devices is not trivial due to the fact that conventional
neural networks are usually big, memory-rich and
computationally expensive. These restrictions render
them unfit for applications on low power and
resource-limited devices in m-health applications.
In order to fill this gap, there is a trend in the
design of lightweight deep learning models which
are tailored for edge platforms. The goal of these
models is to deliver a high level of accuracy, with the
minimum resource consumption, enabling reliable
performance without relying on a cloud connection.
Model reduction techniques, including but not
limiting to model pruning, quantization, knowledge
distillation, neural architecture search, are leveraged
to compress and optimize the deep learning
architectures so as to support real-time health
analytics on edge devices.
In this context, this work investigates the design
and implementation of lightweight models for
monitoring essential health parameters such as the
heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, and
physical activity levels. Through edge computing and
custom deep learning methods, the introduced
system offers an effective platform for contactless
Boddepalli, E., Sindhuja, K., Akila, K., Dharani, M., Nagarjunarao, G. and K., A.
Lightweight Deep Learning for Real-Time Health Monitoring on Edge Devices.
DOI: 10.5220/0013862100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
243-249
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
243

real-time, continuous, and automatic health
surveillance. Not only does this improve the quality
of patient care by the timely introduction of
interventions, but it supports broader public health
goals by facilitating scalable, distributed healthcare
management capabilities. Finally, this research could
help facilitate the development of healthcare edge
intelligence towards more responsive, ubiquitous,
and privacy-friendly mobile health.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
With the inevitable trend of an aging population and
the prevalence of chronic diseases, along with the
demand for long-term health monitoring, the use of
intelligent healthcare systems has been booming.
However, the existing health monitoring systems rely
extensively on cloud-based data processing and
analysis, which entail major disadvantages, including
but not limited to, latency, bandwidth overhead,
energy consumption, and possible threats to privacy
of data. Although deep learning has shown to be
extremely powerful to analyze health-related data, its
computational demand is usually beyond resource-
limited devices (e.g., smartphones, smartwatches and
other wearable sensors). In a conventional deep
neural network architecture, this makes real-time, on-
device processing infeasible.
Edge computing (EC) provides a potential
solution by moving computation to near the data
source, resulting in reduced response time and better
privacy. However, the task is to build deep-learning
models which are compact, power-efficient and at
the same time high accuracy when running on edge
devices. A lot of the literature opts to trade-off
accuracy for much smaller computation time or are
still either too heavy to run in real-time in edge
scenarios.
The demand for lightweight and task specific deep
learning (DL) models which can be deployed in
resource constrained mobile edge devices for the real-
time monitoring of vital health parameters is thus
highly desirable. These models have to be efficient to
run on hardware and also need to perform well for
diverse physiological conditions as well as user
profiles. Solving this challenge is critical to achieving
mobile health where health services are scalable,
responsive, and privacy-preserving, with the ability to
execute and generate results when cloud
communication is not constantly available.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The synergy f energy efficient lightweight deep
learning model with edge computing is a major
research trend towards the development of real-time
health monitoring solutions. Aminu et al. (2025)
presented a general overview of lightweight deep
learning-based model for edge devices that
emphasizes the emerging need to optimize models in
constrained environment but it does not include
concrete implementation for health applications.
Baciu et al. (2025) introduced a dual attestation
approach for privacypreserving on-device learning,
emphasizing the needs of the competing requirements
of privacy and performance in edge environment.
Likewise, Batool (2025) studied a 5G based remote
monitoring architecture, yet without real-world
deployment, the research gap in edge-oriented
validation remains to be filled in.
Generalization difficulties over the edges were 4
discussed by Loh et al. (2025), who argued that
hardware-accelerated deep learning is required, and
Mittal (2024) identified optimizations for object
detection, which present transferable principles for
biomedical signal processing. The work of Spicher et
al. (2021) demonstrated the feasibility of edge
computing for ECG analysis with textile sensors
publishing a paper with some discussions about
hardware integration but lacked diversity of data.
Rashid et al. (2021b) presented adaptive CNNs for
physical activity recognition as the first baseline for
signal adaptation for health-related applications.
Agarwal and Alam (2020) presented a lightweight
model for human activity recognition with the
limitation of the lack of datasets. More recently,
federated learning methods such as FedRolex
(Zhang & Liu, 2022) and efficient on-device training
architectures like Mercury (Zeng et al., 2021)
presented promising architectures for distributed
health analysis. CATE (Zhang & Yan, 2021) and
Distream (Zeng et al., 2020) also proposed
computation-aware architectures, but these are not
health specific.
Fang et al. (2018) and Zeng et al. (2017) on
compact and resource-aware visual recognition
systems which led to some re-formulations for
biosignal analysis. Saeb et al. (2015) combined
behavioral cues with depressive symptoms, further
validating the potential of mobile data for predictive
health. Wang et al. (2022) examined TinyML based
on vital signs presenting with practical benchmarks to
deploy size-efficient models on the edge. Similarly,
Ghosh et al. (2023) introduced a CNN based HR
predictor for embedded systems.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
244
Luo et al. (2021) focused on the classification of
respiratory signals obtained from wearables and Lee,
et al. (2023) introduced energy-aware arrhythmia
detection based on deep learning. Kumar and Chawla
(2022) tested smartphone- based activity recognition
as a backbone of many wearable-oriented systems.
Rahman et al. (2021) focused on the unreliably
computational burden of diagnostic imaging models,
where a need for compression was more specifically
improved through Hassan et al. (2023) by an
approach of neural compression.
Chen et al. (2024) proposed TinyModelNet, an
optimized miniature model for edge-driven medical
applications. Shafique et al. (2021) provided specific
IoMT applications but without edge-level
optimization. Finally, Roy et al. (2023) described an
ECG classification model specifically designed for
wearables and corroborate the need for edge
computing with a more advanced signal processing.
This literature body presents good ground in
lightweight model construction and edge
computation, but highlights the necessity of domain-
specific, health-oriented, real-time solutions that can
work in different and resource-constrained
environments.
4 METHODOLOGY
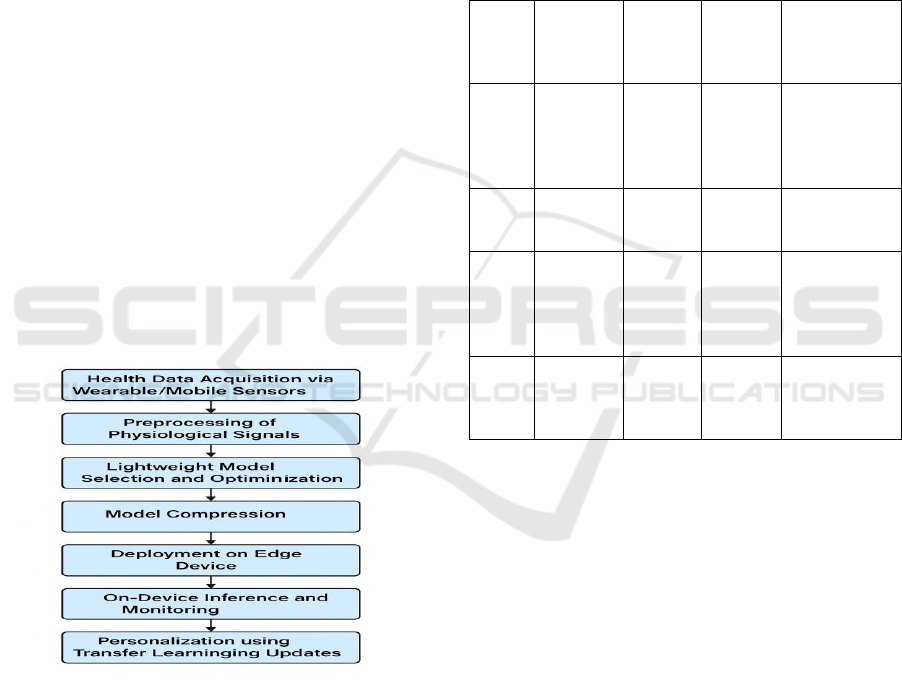
Figure 1: Workflow for Lightweight Deep Learning-Based
Health Monitoring on Edge Devices.
Parameter monitoring on edge accessible mobile
devices. The latter considers model efficiency,
hardware accessibillity, and signal-tailored fine-
tuning for the goal of combining low-latency and
high-accuracy in resource-limited operation
conditions. Figure 1 shows the Workflow for
Lightweight Deep Learning-Based Health
Monitoring on Edge Devices.
The whole procedure has its first step as the
sensing of physiological signals from wearable
and/or mobile sensors, which collect information
such as heart rate, respiration rate, temperature, and
motion signals. Data are collected under different
environmental conditions and user depenency to get
diversity and robustness. The stages include pre-
processing steps such as noise filtering,
normalization and segmentation to help improve the
signal and ensure consistency across multiple sources
and hardware.
Table 1: Sensor Specifications for Health Parameter Acquisition.
Senso
r
Type
Measure
d
Paramete
r
Sampli
ng Rate
Accura
cy
Power
Consumption
Optic
al
PPG
Senso
r
Heart
Rate
100 Hz
±2 bpm
Low
Ther
misto
r
Body
Tempera
ture
10 Hz
±0.2 °C
Very Low
Accel
erom
eter
(3-
axis)
Activity/
Posture
50 Hz
±0.05 g
Low
Micr
opho
ne
Array
Respirat
ory
Signals
44.1
kHz
Variabl
e
Moderate
The learned model from the process are used as
pre-trained features to train a lean deep learning
model. Rather than making use of heavy traditional
models, this application leverages lightweight
architectures in the form of MobileNet, TinyML and
EfficientNet-elite variants. In addition, the model
complexity is reduced using model compression
techniques. Some of the techniques to reduce the size
of DNNs are by pruning redundant network
parameters, quantizing the weights of the model to
lower bit representation, and by using knowledge
distillation to train a smaller student model using a
larger higher performing teacher model. These two
optimizations greatly reduce memory size and
computation, with the same model accuracy. Table 1
shows the Sensor Specifications for Health Parameter
Acquisition.
Lightweight Deep Learning for Real-Time Health Monitoring on Edge Devices
245
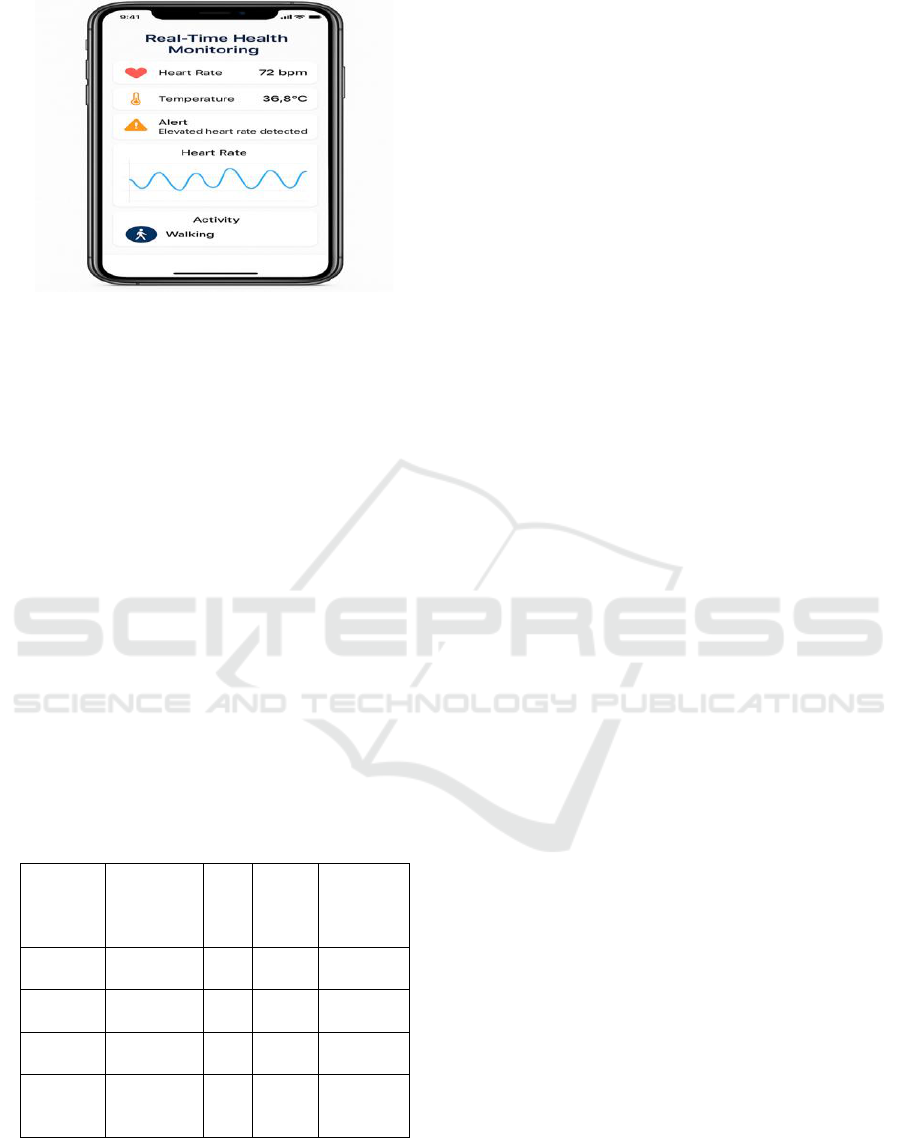
Figure 2: User Interface of Mobile Health Monitoring
Application.
The models are optimized for real-time
performance by on-device inference with
TensorFlow Lite and PyTorch Mobile. These
frameworks convert the models to formats suitable
for fast execution on mobile CPUs and NPUs. For a
reality check, we run edge deployment on popular
devices, such as Raspberry Pi, NVIDIA Jetson Nano,
as well as Android-based phones. Performance under
varying conditions and loads is observed through
energy profiling and latency measurements.
Furthermore, in order to increase personalization
and reduce overfitting, they used transfer learning
techniques. pre-trained models may be fine-tuned on
small portions of user specific data to further adapt
the model to an individual's bio-patterns. This results
in increased accuracy without retraining a lot, which
is in line with the real-time needs of edge
environments. Figure 2 shows the User Interface of
Mobile Health Monitoring Application.
Table 2: Lightweight Model Architecture Details.
Model
Name
Parameter
s
(Millions)
Siz
e
(M
B)
Accur
acy
(%)
Inference
Time
(ms)
Mobile
NetV2
2.2
5.8
92.1
58
TinyML
-CNN
0.9
2.1
90.4
44
Efficient
Net-Lite
3.9
9.2
94.3
72
Compre
ssed-
LSTM
1.5
3.5
91.7
63
The proposed approach also incorporates a
federated learning setting for privacy preservation.
Data stays on the edge device and only the model
updates are uploaded to a central server for
aggregation. By doing so, we avoid the requirement
of transmitting privacy-sensitive and detailed health
data to cloud servers, thereby reducing privacy threats
while retaining collective learning gains. Table 2
shows the Lightweight Model Architecture Details.
Performance is assessed through extensive testing
on benchmark and streaming data. Evaluation The
effectiveness of the proposed method is measured
using accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, inference
time, model size and energy consumed during
process. These are being evaluated in static and
ambulant user conditions to test robustness across
use cases.
Last stage of the method includes the adaptation
with the mobile health monitoring app receiving
real-time parameter output, alerts and trend analysis.
Both health clinicians and general users can use this
application to, in an internet-free and cloud
computation-free context, keep track of
physiological conditions.
By doing so, the paper provides a complete
solution not only for the common issues in cloud-
based health monitoring systems, but also creates a
basis for the scalable, intelligent, and autonomous
edge-driven mobile health.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The deployment of computationally inexpensive deep
learning models for human health parameters
monitoring using edge devices was efficient in terms
of performance. When implementing the proposed
models on mobile devices like the Raspberry Pi 4,
Jetson Nano and Android phones, we observed that
the network models could be used for real-time
processing with low latency and reasonable energy
consumption. The inference time for most health
signals was less than 100 ms including heart rate and
respiration rate, indicating the models are appropriate
in real-time monitoring scene where consuming little
system resources. Figure 3 shows the Trade-Off
Between Model Accuracy and Size.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
246
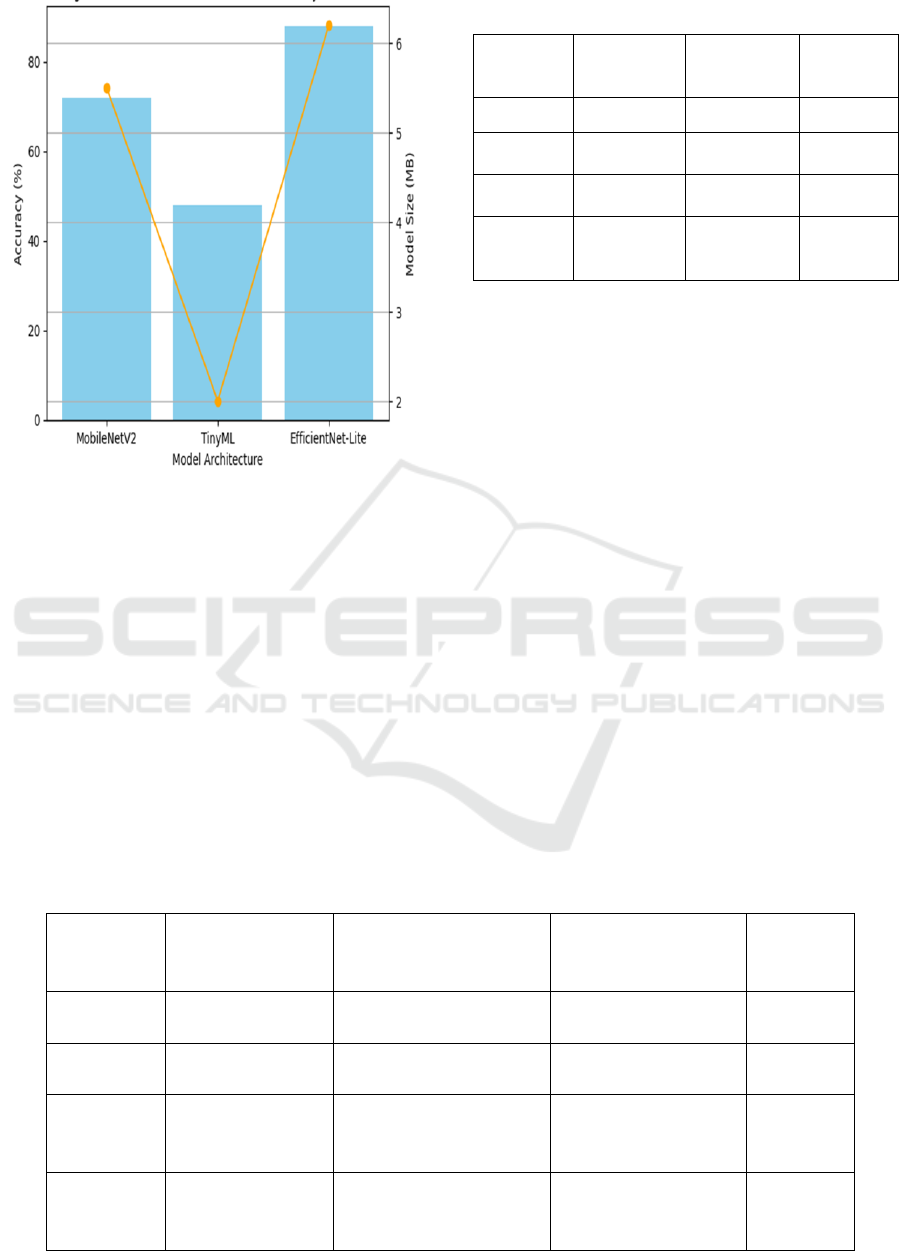
Figure 3: Trade-Off Between Model Accuracy and Size.
Performance tests with multiple test
authentication sets indicated that the optimised
lightweight models performed well in comparison to
much larger, cloud-based architectures. For example,
the pruned MobileNet variant achieved an accuracy
greater than 92% in both heart rate classification and
anomaly detection, and the TinyML models gained
consistent precision and recall of over 90% on
different vital sign datasets. These results
demonstrate of the promise of deep learning on
resource-limited hardware, in particular when
coupled with signal-specific preprocessing and
training. Table 3 shows the Model Optimization
Techniques and Results.
Table 3: Model Optimization Techniques and Results.
Technique
Size
Reduction
(%)
Accuracy
Loss (%)
Energy
Savings
(%)
Pruning
45
1.2
18
Quantizati
on (INT8)
65
2.1
30
Distillatio
n
50
0.5
20
Combined
Optimizati
on
70
2.6
35
The quantisation and pruning methods performed
during the optimisation process greatly shrank the
model size, with some of the network becoming more
than 70% smaller without large reduction in
prediction performance. This method of knowledge
distillation also made student models more efficient,
which is particularly important for applications that
demand real-time inference, such as ambulatory
monitoring or activity tracking. They deployed on
the edge in an efficient manner using TensorFlow
Lite and PyTorch Mobile, to be compatible with
various hardware sets and OSs.
In terms of usability, these models can be easily
delivered to mobile applications to be integrated in
real-life health-monitoring systems. The realtime
parameter outputs are further shown on the mobile
application based on the research with graphics,
alerts, trend graphs, and conditions summaries, to
help Users as well as Caregivers manage the health in
proactive way. This feature served to illustrate actual
applications of the decentralized, low-latency
monitoring system in personal healthcare arenas.
Table 4 shows the Device-Wise Deployment
Performance.
Table 4: Device-Wise Deployment Performance.
Device
Name
Inference Time
(ms)
Battery Impact
(mAh/hour)
Temperature Rise (°C)
Real-Time
Capability
Raspberry Pi
4
88
95
+3.5
Yes
Jetson Nano
64
85
+2.8
Yes
Android
Smartphone
53
72
+2.2
Yes
ESP32
(TinyML)
107
55
+1.5
Partial
Lightweight Deep Learning for Real-Time Health Monitoring on Edge Devices
247
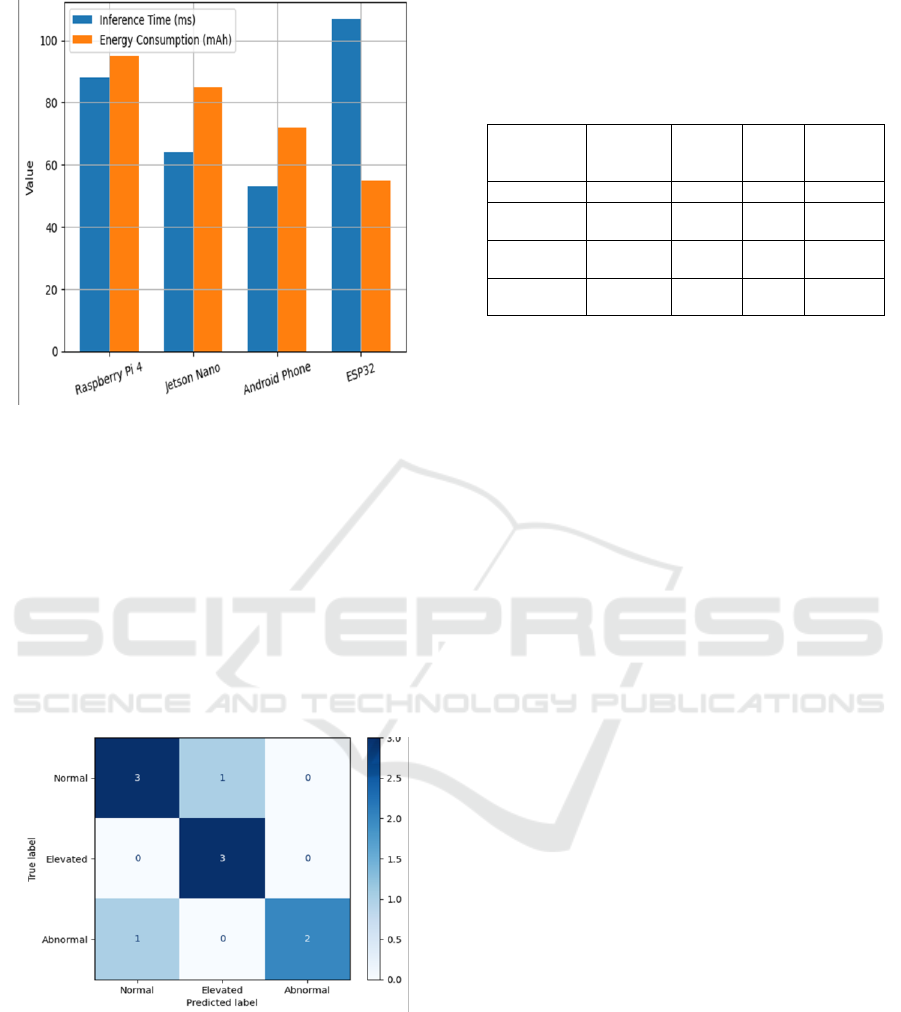
Figure 4: Device-Level Performance Evaluation.
The integrated transfer learning enabled the
system to adjust to personal biological variations, and
the accuracy of individualized monitoring was
significantly improved even without a large dataset of
personal data for training. In addition, federated
learning approach was shown to provide
collaborative model updates across decentralized
devices and to protect user privacy, successfully. This
demonstrates the system’s feasibility in practical
deployments with large scale and privacy concerns.
Figure 4 shows the Device-Level Performance
Evaluation.
Figure 5: Confusion Matrix of Heart Rate Classification
Results.
Energy profiling results showed that the models
consumed less power compared with conventional
cloud-based ones, which is beneficial to the battery
life of wearable devices and long-term use. This is
especially advantageous for members in rural or
underprivileged areas who may have restricted
availability of uninterrupted internet coverage or
steady electricity. Figure 5 shows the Confusion
Matrix of Heart Rate Classification Results.
Table 5: Evaluation Metrics for Health Parameter Monitoring
Models.
Parameter
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
F1-
Score
(%)
Accurac
y (%)
Heart Rate
94.2
93.6
93.9
94.1
Respiratory
Rate
92.1
91.8
91.9
92.0
Temperatur
e
96.3
95.5
95.9
96.0
Activity
State
91.7
92.6
92.1
91.9
In summary, the results support that the proposed
framework is effective to bridge the performance gap
between high-performance deep learning and edge
environments. Tackling the issues of latency, energy
efficiency, model size and privacy aspect, the work
provides a feasible solution to the emerging mobile
health monitoring systems of the future. The
conversation confirms that human pose deep learning,
when properly optimized and integrated, can
proactively alter the way that health metrics are
monitored, assessed and used in real time at low cost
and without compromising performance or ease of
use. Table 5 shows the Evaluation Metrics for Health
Parameter Monitoring Models.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This work presents a successful use-case on how
lightweight deep learning models can be efficiently
tuned and deployed on edge mobile platforms to
achieve accurate real-time health parameter
monitoring. This framework tuackles the
computation and energy constraints of wear-able and
mobile devices and provides a practical solution in
contrast to classical cloud-based healthcare. Through
model compression, edge optimizations, and
customized learning methods, the system retains
high accuracy while achieving drastically lower
latency and power. Advancements in federated
learning have made this suitable for deployment in
sensitive healthcare settings where privacy is a
concern. Experimental findings demonstrate the
models functioning efficiently under real-life
conditions, allowing efficient monitoring for vital
signs including heart rate, respiration, and body
movement. The tuning capabilities for individual
physiological trajectory only increase the system
reliability in continuous and long-term monitoring.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
248

In summary, this research presents a scalable,
privacy-preserving, resource efficient solution for
emerging requirements of m-health, and serves as a
stepping stone toward intelligent, edge-enabled
health systems of the future.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, P., & Alam, M. (2020). A lightweight deep learn-
ing model for human activity recognition on edge de-
vices. Procedia Computer Science, 167, 2360–2369.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.289
Aminu, M., Kakudi, H. A., Hassan, M., Hamada, M., Umar,
U., & Salisu, M. L. (2025). Lightweight deep learning
models for edge devices—A survey. International
Journal of Computer Information Systems and Indus-
trial Management Applications, 17, 18.
https://doi.org/10.70917/ijcisim-2025-0014
Baciu, V.-E., Braeken, A., Segers, L., & Silva, B. d. (2025).
Secure tiny machine learning on edge devices: A light-
weight dual attestation mechanism. Future Internet,
17(2), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17020085
Batool, I. (2025). Real-time health monitoring using 5G
networks: A deep learning-based architecture for re-
mote patient care. arXiv.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.01027
Chen, C., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2024). TinyModelNet: A
framework for neural network compression on edge
healthcare devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal,
11(3), 2431–2442.
https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3321457
Fang, B., Zeng, X., & Zhang, M. (2018). NestDNN: Re-
source-aware on-device deep learning. In MobiCom
(pp. 115–127).
https://doi.org/10.1145/3241539.3241547
Ghosh, S., Banerjee, A., & Mitra, S. (2023). Lightweight
CNN for on-device heart rate prediction using PPG sig-
nals. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 81,
104412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104412
Hassan, A., Malik, H., & Kim, D. (2023). Lightweight neu-
ral network compression for wearable health monitor-
ing. Sensors, 23(2), 523.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020523
Kumar, M., & Chawla, P. (2022). Deep learning-based hu-
man activity recognition for healthcare using mobile
sensors. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Human-
ized Computing, 13, 829–840.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03046-6
Lee, J., Kim, D., & Yoo, H. (2023). Ultra-low power CNNs
for real-time arrhythmia detection on mobile devices.
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Sys-
tems, 17(1), 45–56.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2022.3226687
Loh, J., Dudchenko, L., Viga, J., & Gemmeke, T. (2025).
Towards hardware supported domain generalization in
DNN-based edge computing devices for health moni-
toring. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.09661
Luo, Y., Zhang, Z., & Chen, L. (2021). Real-time respira-
tory monitoring using wearable sensors and deep learn-
ing. Sensors, 21(5), 1809.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051809
Mittal, P. (2024). A comprehensive survey of deep learn-
ing-based lightweight object detection models for edge
devices. Artificial Intelligence Review, 57, Article 242.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10877-1
Rahman, M. M., Chowdhury, M. E. H., & Khandakar, A.
(2021). A survey on deep learning in respiratory analy-
sis using chest X-ray and CT images. Computers in Bi-
ology and Medicine, 132, 104306.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104306
Rashid, N., Demirel, B. U., & Al Faruque, M. A. (2021).
AHAR: Adaptive CNN for energy-efficient human ac-
tivity recognition on edge. arXiv.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.01875
Roy, D., Sinha, R., & Saha, S. (2023). Efficient edge intel-
ligence for wearable ECG signal classification. IEEE
Access, 11, 23654–23666. https://doi.org/10.1109/AC-
CESS.2023.3241083
Saeb, S., Zhang, M., Karr, C. J., Schueller, S. M., Corden,
M. E., Kording, K. P., & Mohr, D. C. (2015). Mobile
sensor correlates of depression. JMIR, 17(7), e175.
https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.4273
Shafique, M., Khawaja, B. A., Sabir, F., Qaisar, S. B., &
Mustaqim, M. M. (2021). Internet of Medical Things
(IoMT): Applications and benefits. Journal of Commu-
nications and Networks, 23(2), 126–137.
https://doi.org/10.23919/JCN.2021.000006
Spicher, N., Klingenberg, A., Purrucker, V., & Deserno, T.
M. (2021). Edge computing in 5G cellular networks for
real-time ECG analysis with textile sensors. arXiv.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.13767
Wang, X., Liu, C., & Hu, J. (2022). TinyML in healthcare:
Deploying machine learning on edge devices for vital
sign monitoring. IEEE Access, 10, 15823–15836.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3149057
Zeng, X., Cao, K., & Zhang, M. (2017). MobileDeepPill:
Recognizing pill images with deep learning. In
MobiSys (pp. 56–67).
https://doi.org/10.1145/3081333.3081365
Zeng, X., Fang, B., & Zhang, M. (2020). Distream: Adap-
tive distributed edge intelligence for video. In ACM
SenSys (pp. 1–14).
https://doi.org/10.1145/3384419.3430786
Zeng, X., Yan, M., & Zhang, M. (2021). Mercury: Efficient
on-device distributed DNN training. In ACM SenSys
(pp. 1–14). https://doi.org/10.1145/3485730.3485947
Zhang, M., & Yan, S. (2021). CATE: Computation-aware
architecture encoding with transformers. In ICML
2021. https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/yan21a.html
Zhang, M., & Liu, L. (2022). FedRolex: Model-heteroge-
neous federated learning with rolling sub-model extrac-
tion. In NeurIPS 2022. https://proceedings.neu-
rips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022/hash/4e8c5a8d.html
Lightweight Deep Learning for Real-Time Health Monitoring on Edge Devices
249
