
Research on the Synergistic Effect of Global Supply Chain
Visualization and Data Technology
Zixing Wang
a
School of Economics, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
Keywords: Global Supply Chain, Data Technology, Synergy Effect, Internet of Things, Blockchain.
Abstract: With the deepening development of globalization, global supply chains play a crucial role in connecting
production and consumption. However, the issue of transparency in the supply chain is becoming increasingly
prominent, and phenomena such as information asymmetry, data silos, and difficult traceability seriously
constrain the efficiency and security of the supply chain. This article focuses on the synergistic effects of
global supply chain visualization and data technology, aiming to explore how to use advanced technologies
such as the Internet of Things, blockchain, and augmented analytics to improve supply chain transparency,
reduce risks, and enhance overall performance. Based on the differences in digital practices in different
regions and their influence on supply chain performance, this study proposes a series of practical suggestions,
including developing targeted digital transformation strategies based on regional characteristics and market
demand, strengthening the application and promotion of advanced technologies in the supply chain, etc. These
suggestions aim to help enterprises better cope with challenges and seize opportunities in the process of digital
transformation, thereby enhancing the transparency and overall performance of the global supply chain.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of a globalized economy, the
importance of the supply chain as a key link between
production and consumption is becoming
increasingly prominent. The transparency of the
current global supply chain is facing many challenges.
These challenges mainly stem from the complexity of
the supply chain, the wide geographical distribution,
and the diversity of participating entities. These
factors work together to make information acquisition
and transmission exceptionally difficult (Sun,2025).
The complexity of the supply chain is one of the
important reasons for the decrease in transparency.
Global supply chains often involve multiple links and
numerous participants, from raw material
procurement to production, transportation, and
distribution, each link may generate a large amount of
data and information. The fragmentation and
dispersion of this information make it very difficult to
comprehensively and accurately grasp the overall
situation of the supply chain. At the same time,
different links in the supply chain may involve
different industries, countries, and regions, and their
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-1957-4618
operating models and regulatory environments are
also different, which further increases the difficulty of
information integration.
Regional distribution is also an important factor
affecting supply chain transparency. The various
links in the global supply chain are often distributed
in different countries and regions, even spanning
multiple time zones. This geographical dispersion not
only increases the cost of information communication
and coordination but may also lead to delays and
distortions in information. In addition, differences in
regulations, culture, language, and other factors
among different countries and regions may also pose
obstacles to the transmission and understanding of
information. By comparing and analyzing the
differences in supply chain digitalization practices in
different regions, enterprises can identify the gaps
between themselves and advanced regions and thus
learn from successful experiences in a targeted
manner, formulate supply chain visualization and
data technology application strategies that are more in
line with their actual situation, and enhance their
competitiveness in the global supply chain.
766
Wang, Z.
Research on the Synergistic Effect of Global Supply Chain Visualization and Data Technology.
DOI: 10.5220/0013860500004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 766-771
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

The diversity of participants is also an undeniable
reason for the issue of supply chain transparency.
Participants in the global supply chain include
multiple roles such as suppliers, manufacturers,
distributors, and retailers, each with their own
interests and information needs. The existence of
such diversity makes the flow of information in the
supply chain more complex and difficult to control.
Meanwhile, due to the potential for information
asymmetry and conflicts of interest among
participants in the supply chain, this also increases the
likelihood of information fraud and risk.
This study aims to explore in depth the synergistic
effects of global supply chain visualization and data
technology to address the challenges of supply chain
transparency. By leveraging advanced technologies
such as the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and
augmented analytics, this study highlights the
significant potential of these innovations in
enhancing supply chain transparency, mitigating risks,
and optimizing operational efficiency. This study will
also compare and analyze the differences in supply
chain digitalization practices in different regions, to
provide more targeted practical suggestions for
enterprises. By drawing on successful experiences
from advanced regions and combining them with the
actual situation of the enterprise, it can more
effectively promote the application of supply chain
visualization and data technology, thereby enhancing
its competitiveness in the global supply chain.
2 GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN
TRANSPARENCY
CHALLENGES AND CORE
PAIN POINTS
The challenges faced by global supply chain
transparency are multifaceted, with information
asymmetry and traceability difficulties being the core
pain points. These pain points not only compromise
the efficiency and flexibility of the supply chain but
also escalate the operational risks and costs for
enterprises.
Asymmetric information is due to the
involvement of multiple links and numerous
participants in the supply chain, which often hinders
the acquisition and transmission of information. For
example, in the procurement process, suppliers may
provide incomplete or false information, which may
prevent the purchaser from accurately assessing the
supplier's capabilities and reputation, thereby
affecting procurement quality and cost control; In the
sales process, distributors may exaggerate market
demand to seek high profits, which in turn leads to
overproduction and inventory accumulation by the
production side, increasing the operating costs and
risks of the enterprise; During the consumption
process, consumers may choose low-quality and low-
priced products based on limited information, which
may affect the promotion of high-quality products.
Traceability difficulty is another important issue
in the global supply chain. In the supply chain, the
production and circulation of products involve
multiple links and participants. Once a problem arises,
it is often difficult to quickly identify the cause and
the responsible person. This difficulty in tracing not
only increases the quality risk and cost of the
enterprise but also reduces consumers' trust in the
product. Especially in the fields of food safety, drug
quality, etc., traceability difficulties may lead to
serious social problems and legal consequences.
3 PATH OF DATA-DRIVEN
SUPPLY CHAIN
VISUALIZATION
TECHNOLOGY
3.1 Internet of Things and Edge
Computing
The combination of the Internet of Things and edge
computing has brought significant advantages to
supply chain management. Firstly, this combination
enables enterprises to monitor the status of their
supply chain in real-time. Whether it is the inventory
situation in the warehouse, the transportation progress
of goods, or even the quality status of products, they
can be tracked in real time through IoT devices.
Secondly, through real-time analysis of the collected
data through edge computing, enterprises can quickly
find problems in the supply chain, such as inventory
backlog, transportation delay, or abnormal product
quality, to take timely measures to correct them. This
real-time monitoring and instant response capability
is crucial for improving the transparency and
efficiency of the supply chain. The improvement of
transparency means that enterprises can more
accurately understand the actual situation of the
supply chain and make wiser decisions. The
improvement of efficiency is directly reflected in
reducing unnecessary waste, speeding up the flow of
goods, and ultimately improving the competitiveness
of enterprises. The combination of the Internet of
Things and edge computing has laid a solid
Research on the Synergistic Effect of Global Supply Chain Visualization and Data Technology
767

foundation for supply chain visualization, while
blockchain and data sharing further promote the
development of supply chain visualization from
another angle (Lin,2025).
3.2 Blockchain and Data Sharing
In supply chain management, blockchain technology,
with its decentralized nature, means that data no
longer relies on a single central institution or server
for storage and verification, thereby reducing the risk
of data tampering or forgery. Every transaction and
flow of information is permanently recorded on the
blockchain, forming an immutable data chain that
greatly enhances the authenticity and credibility of
the data (Wang,2025).
The data sharing mechanism of blockchain
technology enables various links in the supply chain
to obtain and update information in real time. This not
only includes basic information such as product
production, transportation, and sales, but may also
cover more dimensions of data such as quality
inspection, certification, tariffs, etc. In this way,
blockchain helps eliminate information silos,
allowing all stakeholders to work collaboratively in a
shared and transparent environment, with real-time
updates and verification of information at each stage,
thereby reducing unnecessary intermediate links and
improving the operational efficiency and adaptability
of the supply chain (Yin,2022).
For example, in the automotive supply chain, data
sharing is achieved between different component
suppliers, vehicle manufacturers, and dealers through
blockchain technology, eliminating information silos,
improving the collaborative efficiency of the supply
chain, and reducing production delays and cost
increases caused by information opacity.
Furthermore, the data traceability function of
blockchain is also of great significance for addressing
issues in the supply chain. Once problems arise, such
as product quality issues or transportation delays,
companies can quickly trace the source of the
problem through blockchain and take timely
measures to correct them. This ability not only helps
companies improve the speed and accuracy of
problem response but also prevents similar problems
from happening again to a certain extent (Feng,2020).
3.3 Augmented Analytics
Augmented analytics play a crucial role in visualizing
global supply chains. By utilizing advanced
algorithms such as machine learning and natural
language processing, this technology can deeply
explore the potential value in supply chain data,
providing enterprises with more accurate and
comprehensive operational insights (Alghamdi,2022;
Prat,2019).
In supply chain management, data is the
foundation of decision-making. Augmented analytics
technology can automatically screen, integrate, and
analyze large amounts of data, simplify the data, and
present clear results. Users can get rid of subjective
opinions and biases, gain true insights, and quickly
and accurately act based on the data, providing
powerful support for enterprise decision-making
(Andriole, 2019).
More importantly, augmented analytics not only
focus on historical data, but also reveals possible
future market changes and supply chain risks through
predictive analysis. By predicting key factors such as
future demand changes and price fluctuations,
companies can prepare in advance, adjust production
and operational strategies to address potential market
challenges.
In practical applications, augmented analytics has
demonstrated its powerful potential. For example, in
terms of inventory management, by analyzing
historical sales data and combining it with market
trends and consumer behavior predictions, companies
can more accurately develop inventory plans to avoid
inventory backlog or stockouts. In terms of risk
management, enhancing analytical techniques can
help companies detect abnormal situations in the
supply chain promptly, such as supplier instability,
transportation delays, etc., and take timely measures
to respond.
3.4 Synergistic Effects of Technological
Paths
When exploring the synergistic effects of
technological paths such as the Internet of Things,
blockchain, and augmented analytics in supply chain
visualization, cannot help but mention how these
technologies complement and promote each other to
jointly promote the improvement of global supply
chain transparency.
As a pioneer in supply chain data collection, IoT
technology captures raw data from each link in real
time, providing basic support for subsequent links.
Blockchain technology ensures the openness,
transparency, and immutability of data, greatly
enhancing its credibility and establishing a
foundation of trust for analysis and application.
Augmented analytics technology utilizes AI to deeply
mine data, predict demand, optimize operations, and
warn of risks. Its insight value highly depends on the
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
768

quality and credibility of the data provided by the first
two.
When the three are closely combined, the
synergistic effect becomes apparent: the Internet of
Things provides real-time data sources; Blockchain
ensures its authenticity and security; Enhanced
analysis involves deep processing and prediction
based on trustworthy data, producing high-value
insights. This closed-loop, trustworthy intelligent
analysis system significantly improves the efficiency,
visualization level, and risk response capability of
supply chain management.
4 COMPARISONS OF THE
IMPACT OF REGIONAL
DIGITALIZATION LEVEL ON
SUPPLY CHAIN
PERFORMANCE
4.1 EU Compliance-Oriented Digital
Practices
In the EU region, the digitalization of supply chains
is heavily influenced by compliance orientation.
While pursuing supply chain efficiency and cost
optimization, enterprises must strictly comply with
various regulatory standards, including
environmental protection, safety, and data protection.
To satisfy various compliance requirements,
enterprises are increasingly adopting IoT technology
to enable real-time monitoring across the supply
chain. Through the installation of sensors and RFID
tags, organizations can continuously track the
location, status, and transportation environment of
goods. This capability ensures adherence to relevant
regulatory standards throughout the supply chain
process. Beyond ensuring compliance, real-time
monitoring also enhances supply chain transparency
and responsiveness, thus improving overall supply
chain performance.
Chinese battery company Sunwoda is responding
to the EU's battery regulations by collecting real-time
data on the entire lifecycle of batteries (such as raw
material traceability and carbon emissions) through
IoT sensors and using blockchain technology to
ensure that the data is tamper proof, meeting the EU's
mandatory requirements for supply chain
transparency. At the same time, integrate production,
recycling, and other full chain data to generate
automated compliance reports, avoiding market
access risks; Analyze supply chain bottlenecks and
optimize production scheduling to increase partner
inventory turnover by 15%. This transformation
transforms the initial compliance investment into a
competitive barrier, shortens the order response cycle
by 20%, and supports the expansion of overseas
markets. EU policies force companies to tilt their
digital resources towards building auditable data trust
chains (such as blockchain traceability), converting
compliance costs into long-term market access
advantages (Zhou,2025).
4.2 Efficiency-Oriented Digital
Practices in China
In China, efficiency-oriented digital practices have
become an important trend in supply chain
management. By deeply mining and analyzing the
massive data generated in the supply chain,
enterprises can more accurately understand market
demand, optimize inventory management, improve
logistics paths, and predict future market changes.
This not only helps companies make wiser decisions
but also significantly improves the responsiveness
and flexibility of the supply chain.
Intelligent management is another key to
improving supply chain efficiency. With the help of
IoT, big data, and AI, enterprises can achieve real-
time monitoring and intelligent scheduling of various
links in the supply chain. For example, by using IoT
technology to track goods in real-time, companies can
ensure the safe transportation of goods and respond
promptly to emergencies; By optimizing warehouse
management through artificial intelligence
technology, enterprises can increase inventory
turnover and reduce warehousing costs. At the same
time, in digital practice, these enterprises also focus
on introducing quality management systems and risk
assessment tools to ensure the stability and
sustainability of the supply chain.
Taking Guizhou Fengmao Chemical Logistics
Enterprise as an example, its independently
developed intelligent logistics system (RMS)
embodies the logic of efficiency priority: by
monitoring the transportation status of hazardous
chemicals through on-board sensors, AI dynamically
schedules thousands of vehicles, achieving a 40%
increase in order matching efficiency and a 25%
reduction in empty driving rate. Integrate warehouse
and transportation data into the dashboard operation,
automate financial processes with robots, and save
1.5 million yuan in labor costs annually; A 50%
decrease in accident rate indirectly reduces insurance
expenses. This system increases daily transportation
volume by 30%, achieves a 98% order fulfillment rate,
Research on the Synergistic Effect of Global Supply Chain Visualization and Data Technology
769
and achieves a dual reduction in operating costs and
risks (Wang,2025).
4.3 Comparative Analysis
To clearly present the essential differences in the
impact of digital practices on supply chain
performance under the EU compliance orientation
and China efficiency orientation, this study extracts
key comparative dimensions based on the practices of
Sunwoda (EU compliance case) and Guizhou
Fengmao (China efficiency case), as shown in Table
1.
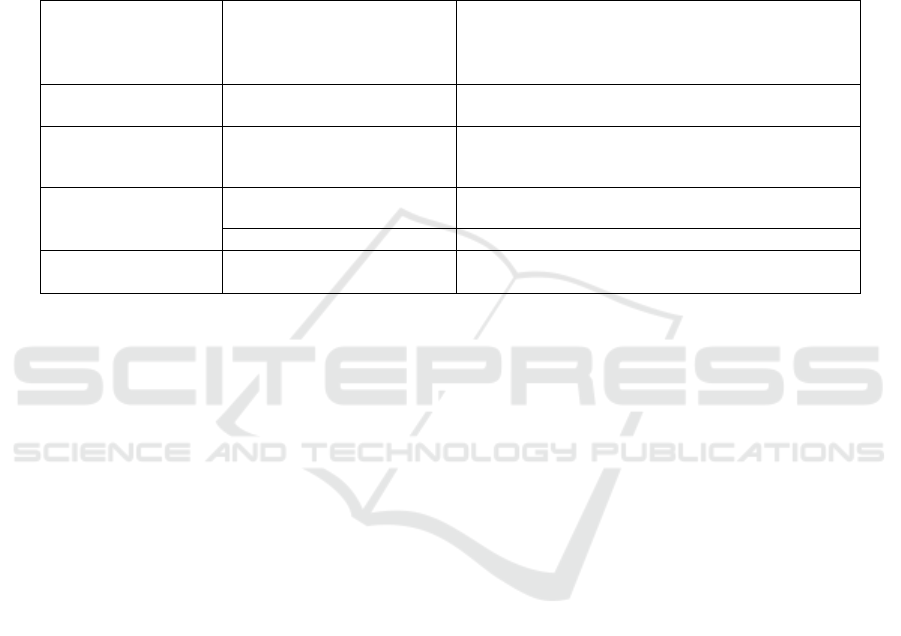
Table 1. A comparison of the impact of digital Practices on Supply Chain Performance under the EU Compliance Orientation
and China Efficiency Orientation (Zhou,2025; Wang,2025).
Dimension
EU Compliance Orientation
(Xinwangda Case)
China Efficiency Orientation (Case Study of
Fengmao, Guizhou)
Core objective
Meet regulatory audits (such
as batter
y
p
ass
p
orts
)
Reduce transportation/warehousing costs
Technical weight
Blockchain>Internet of
Things>Augmented analytics
Internet of Things=AI>Blockchain
Performance Focus
Avoid the risk of fines/bans Vehicle/warehouse utilization rate
Full chain traceability Order response speed
Benefit cycle
Breaking through long-term
market barriers
Significant decrease in short-term costs
5 CONCLUSIONS
This article systematically studies the collaborative
mechanism between data technology and supply
chain visualization through literature analysis, case
studies, and comparative analysis. Research has
found that global supply chains are facing core
challenges of insufficient transparency: complexity
and globalization lead to frequent information gaps,
data silos, and traceability difficulties. The
technology triangle, consisting of the Internet of
Things, blockchain, and augmented analytics, is
restructuring the supply chain management model -
the Internet of Things enables real-time data
collection throughout the entire chain, blockchain
establishes a decentralized trust network, and
augmented analytics optimizes inventory turnover
through machine learning. The collaborative
application of the three promotes the supply chain to
enter an intelligent closed loop of "perception
analysis decision-making". Based on research
findings, enterprises implementing digital
transformation need to follow three core paths:
Construction of technology integration
architecture: Establish an integrated database of IoT
and blockchain technology, realize real-time data
collection and dynamic monitoring of the entire
supply chain through IoT, and synchronously use
blockchain to build a decentralized and tamper-proof
data sharing network. The architecture needs to be
compatible with 5G, edge computing, and other new
infrastructures, ensure the security and timeliness of
the whole link of data from acquisition, storage
transmission, and provide high-quality data input for
intelligent decision-making.
Deployment of intelligent decision-making
center: Build a data processing platform with
enhanced analysis as the core, integrating technology
modules such as machine learning and natural
language processing. The system needs to have multi-
dimensional data analysis, real-time risk warning, and
adaptive optimization functions, and achieve
intelligent demand forecasting, inventory
optimization, and logistics scheduling through deep
mining of data correlations, forming a closed-loop
decision-making mechanism from data insight to
execution feedback.
Regional adaptation strategy design: Develop
differentiated technology application plans, deploy
data traceability and transparency systems in
compliance-oriented markets, build a digital
governance framework that complies with ESG
standards, strengthen the integration of IoT and
intelligent algorithms in efficiency priority areas, and
develop agile, responsive supply chain models. At the
same time, establish a dynamic learning mechanism
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
770

and continuously absorb international advanced
practices for localization transformation.
In future implementation, attention should be paid
to the three core dimensions of technology
aggregation, data liquidity, and organizational agility.
Through systematic engineering such as building a
technology platform, optimizing data governance,
and reshaping business processes, the supply chain
can be continuously upgraded from visualization to
predictability and adjustability. Enterprises should
establish a collaborative mechanism between
technological iteration and organizational change to
enhance supply chain resilience in dynamic balance.
REFERENCES
Alghamdi, N. A., & Al-Baity, H. H., 2022. Augmented
analytics driven by AI: A digital transformation beyond
business intelligence. Sensors, 22(20), 8071.
Andriole, S. J., 2019. Artificial intelligence, machine
learning, and augmented analytics. IT Professional,
21(6), 56-59.
Feng, H., Wang, X., Duan, Y., Zhang, J., & Zhang, X., 2020.
Applying blockchain technology to improve agri-food
traceability: A review of development methods,
benefits and challenges. Journal of Cleaner Production,
260, 121031.
Lin, J., Yin, X., Huang, X., Li, M., Duo, B., & Sun, H., 2025.
TD3 based resource scheduling and energy efficiency
optimization for air mobile edge computing. Internet of
Things Technology, 15(10), 56-62+66.
Prat, N., 2019. Augmented analytics. Business &
Information Systems Engineering, 61, 375-380.
Sun, Z., 2025. Research on risk management strategies in
supply chain management modernization of shopping
malls, (11), 63-65.
Wang, J., & Liang, J., 2025. The application and challenges
of blockchain in various fields of supply chain
management. Logistics Technology, 48(09), 120-123.
Wang, Y., 2025. Guizhou Fengmao: Digitalization
empowers efficient management of transportation
capacity. https://rb.gywb.cn/epaper/gyrb/html/2024-
10/18/content_14378.htm#.
Yin, W., & Ran, W., 2022. Utilizing blockchain technology
to manage the dark and bright sides of supply network
complexity to enhance supply chain sustainability.
Complexity, (1), 7734580.
Zhou, Z., 2025. Sunwoda leads the new revolution of
battery passports and jointly explores the path to
upgrading the core competitiveness of the industry.
https://news.solarbe.com/202505/23/389532.html.
Research on the Synergistic Effect of Global Supply Chain Visualization and Data Technology
771
