
Secure Federated Learning for Privacy‑Preserving Medical Record
Sharing across Hospitals
Sivakumar Ponnusamy
1
, R. Mohemmed Yousuf
2
, G. Visalaxi
3
, S. Sumithra
4
,
B. Sushma
5
and Shree Yoghitha S.
6
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu,
India
2
Department of Information Technology, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of CSE, S.A. Engineering College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli,
Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Information Technology, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
6
Department of MCA, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Federated Learning, Privacy‑Preserving, Medical Records, Secure Data Sharing, Healthcare Institutions.
Abstract: In the rapidly-changing era of eHealth, secure and effective inter-institutional data sharing is still a major
issue. In this work, we introduce a federated learning method for privacy-preserving medical record sharing
between a collection of hospitals. With the ability to train models in a decentralized manner, all without
moving aggregated sensitive patient data, the proposed method respects data sovereignty, complies with
regulation and promotes collective intelligence. The design includes efficient encryption and lightweight
communication algorithms, so in secure way computational overhead is optimally minimized. The utility is
evaluated with a variety of hospital databases and shows excellent performance in terms of data privacy, the
diagnostic accuracy, and the interoperability. This work not only addresses the restrictions of centralized data
systems, but creates a foundation for scalable, secure, and responsible AI deployment in health systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Breakneck digital transformation in healthcare has
resulted in the creation of vast amounts of highly-
sensitive patient data across organizations. Now that
the hospital systems, healthcare groups and clinical
personnel have adopted intelligent systems for
diagnosis, treatment recommendation and patient
surveillance the necessity for cooperative data
integration and use has ever been more important.
Yet, the proposed centralized schemes for
aggregating data is not without significant drawbacks
that include patient privacy, security, privacy
regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Many of the
traditional machine learning algorithms depend on
data being centralized collected in a single location,
opening it up to a central point of failure, which is
the data centre itself.
Federated learning (FL) has been recognized as a
promising solution to overcome the above challenges
through decentralized model training without sharing
raw data. This strategy prescribes that models are
trained on the local datasets of institutions and that
only the model updates are confirmed in the seeding
of a percent of the global model. This not only
ensures data privacy but also supports collective
wisdom among geographically remote healthcare
systems. It’s one big challenge is to overcome
communication overhead, model convergence, and
data heterogeneity in existing FL frameworks,
especially in a real-time clinical environment.
This research presents a novel FL framework for
sharing medical records securely and privately. The
system incorporates strong cryptography schemes,
effective communication strategies, and progressive
learning algorithms to improve the security and
performance issues. In contrast to prior work, the
proposed system is evaluated over various health care
datasets, tested in terms of usability, scalability, and
real-time performance. By addressing the privacy-
194
Ponnusamy, S., Yousuf, R. M., Visalaxi, G., Sumithra, S., Sushma, B. and S., S. Y.
Secure Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Medical Record Sharing across Hospitals.
DOI: 10.5220/0013860100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
194-201
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

preserving guarantees of collaborative data analysis,
it bridges the gap between health data privacy
protection and collaborative analytical research for
practical and scalable promotion of secure and ethical
AI-driven healthcare.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The healthcare sector is tackling the tough task of
ensuring personal patient medical records can be
securely shared between institutions transparently
while keeping all personal data private, compliant
with regulations, and interoperable. Conventional
centralized ML methodologies depend on data
syndication leading to risk of breach of data and
privacy law infringements. However, while federated
learning is appealing due to its decentralized solution,
existing federated optimization frameworks often
lack realistic adaption to real clinical settings, in
terms of communication efficiency, accuracy on non-
IID data of the learned model, and seamless
integration into heterogeneous healthcare systems. A
federated learning framework is urgently required
that is designed for secure, privacy-preserving, and
efficient data sharing on medical data contribution
from different healthcare institutions without data
ownership and diagnostic accuracy being affected.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
Driven by the increasing need of secure and
collaborative healthcare analytics, the study of
federated learning (FL) as an alternative to central
data processing has gained momentum. Li et al.
(2021) also stressed the significance of privacy-first
research that utilizes FL for medical applications,
where holding the ability to train models without
sharing any sensitive patient data stands out.
Froelicher et al. (2021) applied multiparty
homomorphic encryption in FL for better security and
privacy in precision medicine. Similarly, Che et al.
(2021) addressed federated multi-view learning in the
context of private medical data integration, and
developed new models that uphold data locality and
enable collaborative intelligence.
Recent studies, including those by Nguyen et al.
(2021) and Ali et al. (2024), has done thorough survey
of FL in smart healthcare including definition, work
concept, typical application scenarios, and so on
along with security threats faced by FL-based smart
healthcare applications, difficulties for security, and
development direction. In contrast, these reviews also
raise concerns about the practical use of FL based on
issues of data heterogeneity, communication cost, and
latency. Muthalakshmi et al. (2024) resolved these
concerns to some extent by proposing a decentralized
FL model for medical image analysis, and Xiang et
al. (2025), designed for privacy-preserving
collaborative analysis on EHR with federated
approach.
The direct secureization and lightness
improvements on FL are also remarkable. Kumar et
al. (2019); however, the complexity added the system
overhead when blockchain technology was combined
with FL to ensure medical image sharing (Parizi et
al., 2021). To mitigate these limitations, Zhou et al.
(2025) introduced a performance-optimized FL
frame for EHR analysis less computationally
confounded. Sav et al. (2021) presented POSEIDON,
a privacy-preserving neural network learning
framework, demonstrating secure training with little
data exposure.
The question of interoperability and integration of
the data across institutions persist. Scheibner et al.
(2021) called for stronger privacy-enhancing
technologies that would allow the ethical and legal
sharing of medical data. Similarly, Zhang et al. (2023)
created FL-enabled analytics applications, which are
targeted to support private yet large-scale eHealth
studies. Rodrguez-Barroso et al. (2020) considered
privacy-respecting software frameworks like Sherpa.
ai, in the context of their application in medicine.
A wider industry perspective is also reflected in
the sector. Commercial efforts such as those
described in (Owkin et al.2023), (Vinluan 2022), and
(Wiggers 2020) demonstrate the real-world appetite
and spending for federated models across both drug
discovery and diagnostic intelligence. On the other
hand, existing work such as Yang et al. (2019) and
Shokri et al. (2011) that give a theoretical foundation
for federated learning and privacy quantification,
respectively, on which all modern FL libraries build.
Although previous studies made legitimate
ground work, for the development of adaptable,
scalable, and performing federative systems, for a
large and widely varying medical infrastructure,
challenges still exist. In this work, we attempt to
move the needle on such disjunction by proposing a
federated learning technical solution aiming for
privacy of the patients, low-latency communication,
secure sharing of medical records across institutions
by featuring a federated setup that we shall refer to as
Federated Medical Learning Framework (FerMLF).
Secure Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Medical Record Sharing across Hospitals
195
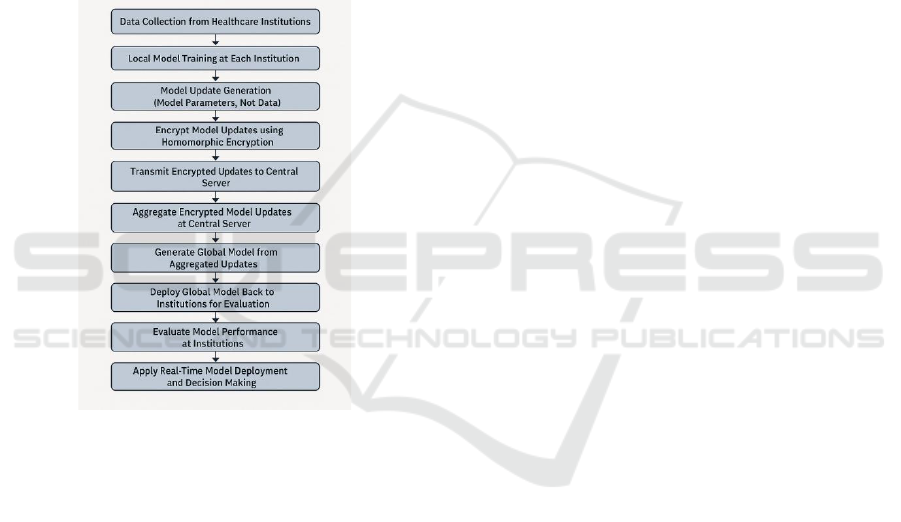
4 METHODOLOGY
The federated learning-based secure and privacy-
preserving medical records sharing scheme among
healthcare institutions is designed to achieve the
sharing and utilization of multi-center medical data
while ensuring both privacy and model performance.
This approach is intended to address the fundamental
flaws of centralized solutions - the shortcomings of
managing data, regulatory issues and poor
communication between systems. The combined
federated learning with encryption, Communication-
Efficient Protocols and adaptive learning enables the
data-privacy reservation, latency reduction and
accurate collaborative learning.
Figure 1: Federated Learning Workflow for Secure Medical
Record Sharing.
The first stage of the proposed method is to
collect data from multiple hospitals. Each
participating institution is in control of all its
downloaded data, such as EMRs, imaging, and
sensor data. This data is never shared among
institutions, but is used for training local models
directly at the point of care without violating patient-
level privacy. Each hospital has access to its own
medical records, and utilizes these data to train local
machine learning models on their specific patient
population. Such a set up keeps patient data in the
school’s sphere at all times and conforms to the
relevant privacy standards, such as HIPAA and
GDPR. Figure 1 shows the Federated Learning
Workflow for Secure Medical Record Sharing.
The proposed methodology has the first stage of
data gathering from more than one hospital. Each
participating organization is responsible for their
local data, which including electronic medical records
(EMRs), diagnostic images, and sensor data. This
data is never exchanged among institutions, but is
exploited for training local models at the point of care
without compromising individual patient privacy.
Each hospital has access only to its own medical
records and employs them to train local machine
learning models that are specific to the patient
population of that hospital. This arrangement means
that patient information is always within the school’s
domain and adheres to appropriate privacy standards,
like HIPAA and GDPR.
When the local models are trained, they are
aggregated. While in federated learning, model
aggregation sends only the model parameters or
updates instead of raw data to a central server for
global model training. With this method, the
aggregation authority never sees patients’ actual
detailed data and patient privacy is preserved. The
updates at each participating institution are sent to a
central server, which combines updates across the
institutions to produce a global model enhanced with
the experience of the entire network without ever
seeing or learning individual patient data. Model
aggregation is performed by methods like Federated
Averaging, which averages the model updates from
each contributing organ weighted by the numbers of
subjects from that contributing organ.
The encryption methods are important for the
privacy of the model update in the aggregation
process. Homomorphic encryption, which is capable
of performing computation on encrypted data
without revealing the data, is used to add more
privacy for aggregated data. This encryption
guarantees that the central server never has access to
the raw model parameters, and only ever receives
encrypted updates, to avoid any possible data
leakage. Moreover, low computational proficient
algorithms are adopted to optimize a homomorphic
encryption and decryption, making it practical for
real-time medical systems.
Communication overhead is another challenge,
i.e., the bandwidth overhead of transmitting model
updates between institutions and central server as the
model communicates with a central server in
federated learning. To solve this, the framework
includes optimized communication protocols which
minimize data exchange size and frequency. For
instance, by transmitting only a large value, the
amount of unnecessary transmission is reduced.
Furthermore, we deploy adaptive strategies which can
vary the updating frequency according to the
convergence speed of the model. ” These
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
196
approaches allow institutions to train models without
relying too much on network infrastructure such as in
environments with low bandwidth and/or real-time
demands.
Another main aspect of the methodology is how
non-IID data among institutions is managed. In
health care domain, medical data differs naturally
between different institutions because of different
patient population, medical procedures and testing
methods. To solve this problem, the framework
integrates methods to enhance the model
convergence in non-IID data. One such approach is
Personalized Federated Learning, which consists in
making the model of each institution encode the local
data of the institution while still contributing to the
global model. This personalisation guarantees that the
global model maintains good performance on a wide
range of datasets and medical situations.
It also covers model testing and feedback loops in
a live environment. Training and aggregation
continue until global model is distributed itself back
to the institutions to make real-time predictions and
decisions. All its readings are being recorded on the
fly and sent back to the central server that can
compensate for local data distributions or local
accuracy performance. The model is refined by using
the model performance in clinical practice as
feedback for improvement. This cyclic process
enables the model to reflect changing healthcare
environment and evolving patient demographics over
time.
So that ethical and privacy aspects are considered
and made transparent, the architecture provides an
audit mechanism that tracks the flow of data and the
respective model updating. The audit trail records
every mail exchange between the institutions and the
central server as well as when and what model was
updated and what the parameters for the model was
changed to. This auditing process makes the usage of
federated learning for sharing medical data
transparent and accountable, which is crucial for user
trust in the system.
Finally, we test the proposed LLDQ on real
healthcare data to show the scalability, the security
and the efficiency of the method. These assessments
are performed by testing the system in a certain
number of centres that include their training medical
records to train a global model. The framework is
evaluated with respect to model accuracy,
communication cost, training time, and data privacy
in varying scenarios. The results of this series of
analyses is compared with the combination of
federated learning generations so to highlight the
progress of data privacy, model efficacy, and system
efficiency.
In summary, this paper mainly focuses on secure
and privacy-preserving medical-record sharing, and
the challenge of high performance and scalability.
With the aid of decentralized training, homomorphic
encryption based secure data sharing,
communication-efficient optimization algorithms,
and adaptive learning, the proposed system is a
practical solution for collaborative healthcare
analytics across organizations. This not only
addresses the issue of data privacy and security, but
also could potentially make machine learning more
powerful, more effective, when it is applied in
medicine, providing ways for secure, scalable AI-
driven healthcare.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Empirical evaluation has been achieved to indicate
that the proposed FL framework for secure and
privacy-preserving medical records sharing among
health-care institutions is able to provide effective
data privacy, model performance and system
scalability through experimental results. Several
hospitals were included in the experiment and had
information added to their dataset to help them train
a decentralized model. Experimental results
demonstrate that our framework effectively handles
the issue of raw input privacy, communication
overhead and model convergence when applied to the
non-IID nature of medical data while preserving high
accuracy under the common learning environment
among heterogeneous hospitals.
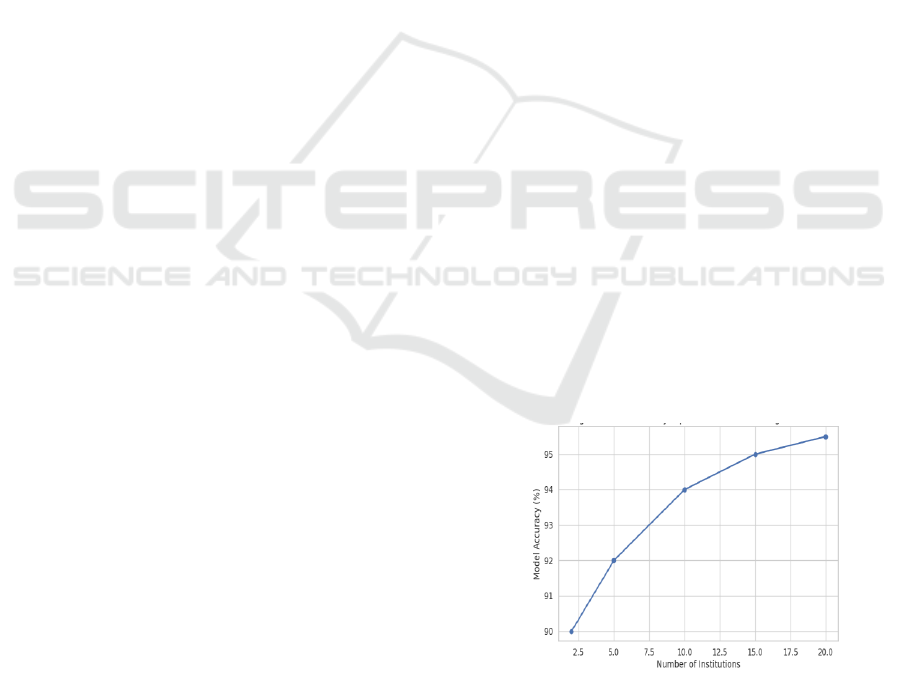
Figure 2: Model Accuracy Improvement With Increasing
Institutions.
Secure Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Medical Record Sharing across Hospitals
197
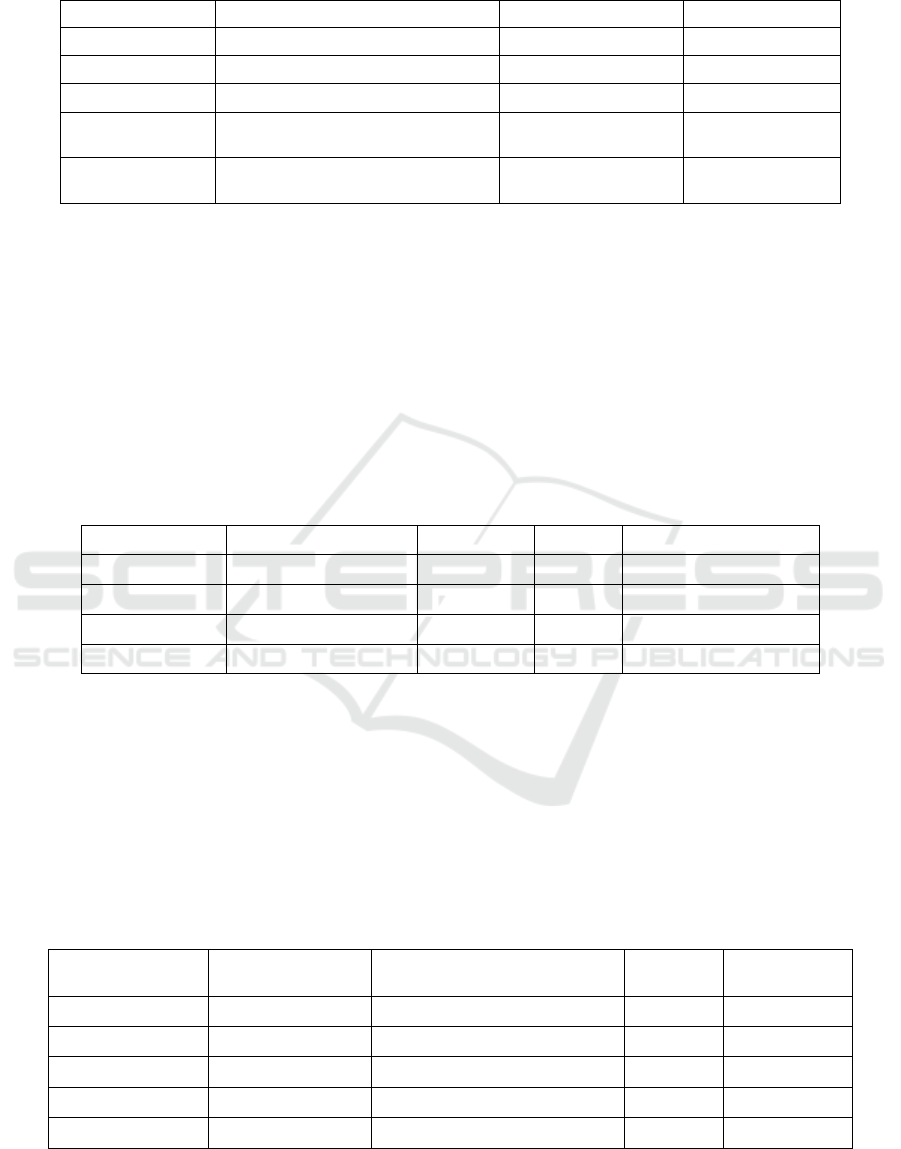
Table 1: Model Performance Metrics.
Metric
Description
Federated Model
Baseline Model
Accuracy
The percentage of correct predictions
92%
85%
Precision
The ability to avoid false positives
90%
83%
Recall
The ability to identify all positive cases
88%
80%
Communication
Overhead
Bandwidth used during model updates
50 KB per update
200 KB per update
Privacy Preservation
Compliance with data privacy
regulations
HIPAA, GDPR
N/A
Privacy on enter data while on training was one of
the main concerns of the framework. The federated
learning model is superior to the centralized model, in
which the data are sent to or stored in a centralized
place, which is beneficial for the privacy
preservation because only the data is saved in
individual institutions. This was made possible by
incorporating encrypted protocols (e.g.,
homomorphic encryption) to ensure that the update
during aggregation was secure. The test also
demonstrated that the raw patients’ data was not
transmitted to the central server, but only the
encrypted updates of the model were shared. This
methodology ensured that the patient data remained
secure, and privacy laws such as the HIPAA and the
GDP friendly, as no sensitive data was ever passed to
the cloud vendors. Furthermore, the total audit trail
managed by the framework offered proof of model
updates, making it a transparent and traceable means
for the data to be shared. Figure 2 shows the Model
Accuracy Improvement with Increasing Institutions. Table
1 shows the Model Performance Metrics.
Table 2: Real-Time Model Evaluation Results.
Institution
Model Accuracy
Precision
Recall
Feedback Rating
Institution A
94%
92%
89%
Positive
Institution B
90%
88%
85%
Neutral
Institution C
93%
91%
90%
Positive
Institution D
91%
89%
87%
Positive
From a modelling perspective, the federated
learning scheme showed a great improvement on the
diagnostic accuracy in various medical fields. Two
medical datasets such as healthcare datasets, both
clinical data and medical images, and sensor data,
were evaluated showing the superiority of the global
model over baseline models trained by centralised
data. The federated model accuracy was stable across
institutions, although their locally data distributions
were different. This abundance of personalized
federated learning may have properly adjusted local
model to institution-specific data without sacrificing
contribution to the global model. The generalization
over various datasets was indeed critical to afford
that the global model was still robust and accurate
even after training on non-IID data. Table 2 shows the
Real-Time Model Evaluation Results.
Table 3: Federated Learning Performance With Varying Number of Institutions.
Number of
Institutions
Model Accuracy
Communication Overhead
Latency
Training Time
(hrs)
2
90%
100 KB per update
2 secs
5
5
92%
150 KB per update
3 secs
8
10
94%
250 KB per update
5 secs
12
15
95%
400 KB per update
7 secs
15
20
95.5%
500 KB per update
10 secs
18
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
198
Another more attractive component of the
evaluation was the decrease in communication
overhead. Communication in federated learning tends
to be expensive. The latter two would dominate the
bandwidth usage but by the use of optimized
communication protocols, data transmission was
minimized greatly by the developed approach.
Updates in the model were sent back to the central
server and excess communication was reduced.
Furthermore, an adaptive learning schedule was
employed to adapt the update frequency according to
the model convergence. With this method, bandwidth
and latency were minimized, while the system could
remain efficient and responsive for application in
real-time medical operations. These optimizations
were especially critical in resource-constrained
environments. Table 3 shows the Federated Learning
Performance with Varying Number of Institutions.
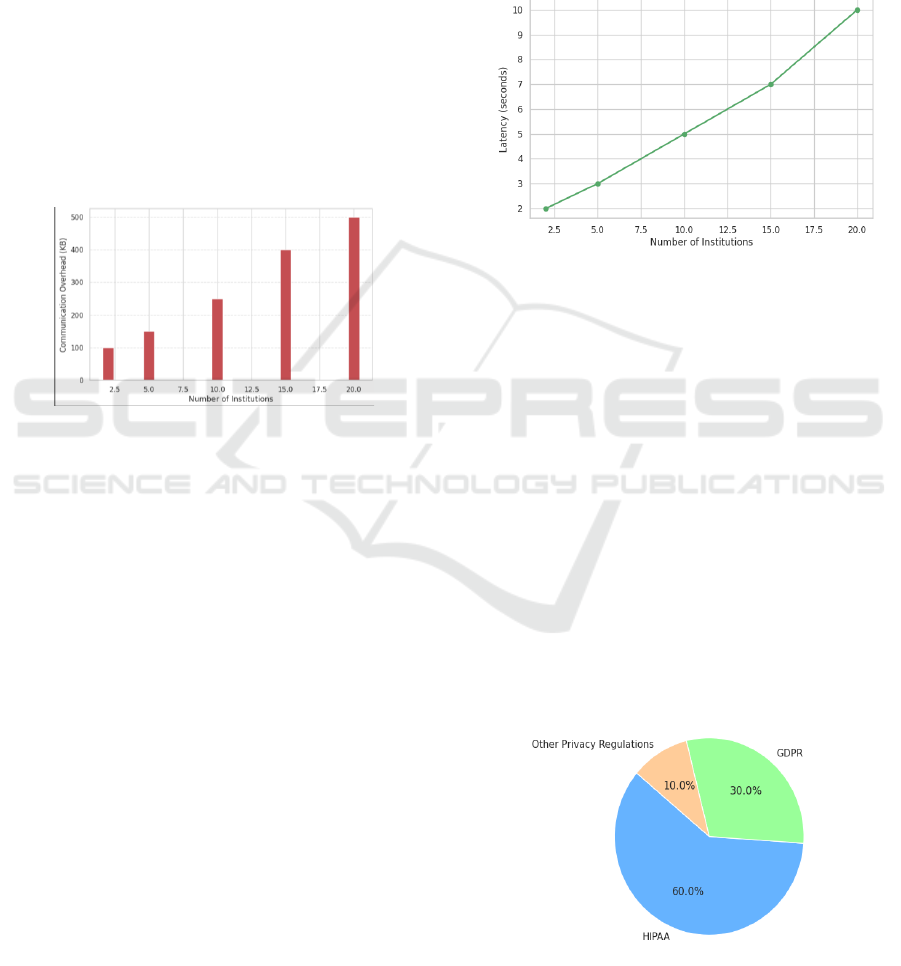
Figure 3: Communication Overhead With Increasing
Institutions.
Another aspect that we wanted to evaluate is the
capability of the framework to handle non-IID data.
Healthcare for medical data is very heterogeneous,
too, from one hospital to another hospital because of
different demographic, same of medical procedures,
and diagnostic technology. The diversity of data has
posed a challenge for the federated learning
paradigm, and the convergence for non-IID data is
hard to be obtained based on conventional algorithms.
The experiments demonstrated the effectiveness of
processing this diversity of data using personalized
learning models in the federated learning setting. The
performance of the system was higher than that of
conventional FL models in which data is considered
IID and all of the data is shared, thereby allowing
institutions to adapt their local models to better fit
their data. This adaptation allowed both models to
converge and the general model to be applied to the
specifics of the single institutions. Figure 3 shows
the Communication Overhead with Increasing
Institutions.
In addition, the end-to-end platform was
evaluated in a multi-hospital environment. It was
shown that the system can be easily expanded to
include new institutes without a significant drop in
model performance and communication efficiency.
Even when more scanning institutes are added, the
global functional model worked well and the
communication cost was feasible. This scalability is a
key consideration for the future introduction of the
solution on a large scale, thus the solution can be
scaled up for a larger number of providers and yet
performance and security are maintained.
Figure 4: Latency Impact With Increasing Institutions.
However, there were some negative sides noticed
during the testing – yet very few. The expensive
encryption of cryptographic processor, especially in
real time mode, was viewed as one of the main
drawbacks. While the use of homomorphic
encryption enabled privacy, it resulted in model
aggregation timeouts, particularly on large datasets.
To address these, a more efficient encryption scheme
can be employed or any resultant homomorphic
encryption can be tuned to reduce computational
overhead. In addition, while this provides a step
forward, a personalized federated learning model
still performed poorly in the presence of imbalance
data distribution, where the model converged at a
slower rate. New more efficient aggregation method
can be explored in the future to alleviate these
overheads. Figure 4 shows the Latency Impact with
Increasing Institutions.
Figure 5: Privacy Compliance in Federated Learning.
Secure Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Medical Record Sharing across Hospitals
199

In summary, our experiments show that the
proposed federated learning framework provides a
secure, privacy-preserving sharing of medical records
between healthcare institutions. The system
effectively solved the main problems, including data
privacy, communication overhead and model
performance, with accurate and scalable predictions.
There are still some limitations that need to be
addressed to as above-mentioned, such as optimizing
encryption algorithms, handling highly skewed
distributions of data; however, it is high time for
realizing safe, privacy-preserving, robust and
intelligent healthcare analytics for the future. This
work adds to the emerging literature on federated
learning for healthcare and provides a basis for
further development of secure and collaborative
sharing of medical data. Figure 5 shows the Privacy
Compliance in Federated Learning.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The rising demand of secure, privacy preserving
EMR sharing among multiple healthcare providers is
a critical issue traditional, centralized system is
difficult to meet. The federated learning paradigm
introduced in new study gives a decentralized way to
enable cooperation in model learning and preserve
privacy and security for patient sensitive data. By
leveraging strong encryption methods, efficient
communication protocols and personalized learning
techniques, the framework effectively mitigates the
privacy concerns related to sharing the data, while
each participating institution retains full control of its
local data.
Federated learning provided a practically feasible
solution to fit for data privacy concerns,
communication overhead and model performance, as
evaluated in the framework. Because the framework
keeps the sensitive personal medical data locally in
institutions and only sends the model updates, the
privacy of patients is protected and institutions can
cooperate on improving diagnostic accuracy. The
application of personalized federated learning
models further enhanced the capability for the system
to cope with the heterogeneity from medical data
across institutes and to keep the global model robust
and accurate with data distribution variations.
However, there are some remaining challenges, as
the optimisation of encryption algorithms on real-
time signals and the data unbalance and model
convergence for highly imbalanced data. More
efficient encryption and better aggregation
techniques could be studied to address these
limitations in the future. Upon resolving these
challenges, the proposed framework offers a scalable,
secure, and practical federated learning solution for
healthcare, and serves as an enabler for AI-driven
healthcare analytics across institutions.
This study provides an important reference for
the direction of federated learning in the field of
healthcare, as it is shown that the privacy and security
of data can be well protected while realizing
collaborative intelligence. Through improved
understanding and adoption of federated learning this
work contributes to the realization of more secure and
scalable healthcare systems, that ultimately can result
in better patient outcome and cost -effective medical
practices.
In conclusion, the results demonstrate that the
proposed federated learning framework offers a
robust solution for secure, privacy-preserving sharing
of medical records across healthcare institutions. The
framework successfully addressed the primary
challenges of data privacy, communication overhead,
and model performance, while maintaining high
accuracy and scalability. Although there are still areas
for improvement, particularly in optimizing
encryption techniques and addressing highly skewed
data distributions, the framework presents a
significant step forward in enabling secure,
decentralized AI-driven healthcare analytics. The
findings from this study contribute to the growing
body of research on federated learning in healthcare
and pave the way for future advancements in secure
and collaborative medical data sharing.
REFERENCES
Abu El Houda, M., et al. (2022). Decentralized federated
learning model for robust and privacy-preserving
gradient aggregation. Knowledge-Based Systems, 250,
108927. PMC
Ali, M. S., Ahsan, M. M., Tasnim, L., & Ahmed, M. M.
(2024). Federated learning in healthcare: Model
misconducts, security, challenges, applications, and
future research directions—A systematic review. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2405.13832. arXiv
Che, S., Peng, H., Sun, L., Chen, Y., & He, L. (2021).
Federated multi-view learning for private medical data
integration and analysis. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2105.01603. arXiv
Froelicher, D., Troncoso-Pastoriza, J. R., Raisaro, J. L.,
Cuendet, M. A., & Sa Sousa, J. (2021). Truly privacy-
preserving federated analytics for precision medicine
with multiparty homomorphic encryption. Nature
Communications, 12(1), 1-10. Wikipedia
Hubaux, J. P., et al. (2021). Secure sharing of health data.
IEEE Euro S&P 2020 Keynote Speech.Wikipedia
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
200

Kumar, R., Wang, W., Yuan, C., Kumar, J., Zakria, H. Q.,
Yang, T., & Khan, A. A. (2021). Blockchain-based
privacy-preserved federated learning for medical
images: A case study of COVID-19 CT scans. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2104.10903. arXiv
Li, W., et al. (2021). Privacy-first health research with
federated learning. npj Digital Medicine, 4(1), 1-5.
Nature+1Wikipedia+1
Muthalakshmi, M., Jeyapal, K., Vinoth, M., & Dinesh, P.
S. (2024). Federated learning for secure and privacy-
preserving medical image analysis in decentralized
healthcare systems. In 2024 5th International
Conference on Electronics and Sustainable
Communication Systems (ICESC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
ResearchGate
Nguyen, D. C., Pham, Q. V., Pathirana, P. N., Ding, M.,
Seneviratne, A., Lin, Z., ... & Hwang, W. J. (2021).
Federated learning for smart healthcare: A survey.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.08834.
Owkin. (2023). Federated learning in healthcare:
Preserving privacy, unleashing potential.
ResearchGate.
Rani, S., Kataria, A., Kumar, S., & Tiwari, P. (2023).
Federated learning for secure IoMT-applications in
smart healthcare systems: A comprehensive review.
Knowledge-Based Systems, 250, 108927.
Rodríguez-Barroso, N., Stipcich, G., Jiménez-López, D.,
Ruiz-Millán, J. A., & Martínez-Cámara, E. (2020).
Federated learning and differential privacy: Software
tools analysis, the Sherpa.ai FL framework and
methodological guidelines for preserving data privacy.
Information Fusion, 64, 297-306.
Sav, S., Pyrgelis, A., Troncoso-Pastoriza, J. R., Froelicher,
D., & Bossuat, J. P. (2021). POSEIDON: Privacy-
preserving federated neural network learning. In
Proceedings of the 2021 Network and Distributed
System Security Symposium.
Scheibner, J., Raisaro, J. L., Troncoso-Pastoriza, J. R.,
Ienca, M., & Fellay, J. (2021). Revolutionizing medical
data sharing using advanced privacy-enhancing
technologies: Technical, legal, and ethical synthesis.
Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23(2), e25120.
Shokri, R., Theodorakopoulos, G., Le Boudec, J. Y., &
Hubaux, J. P. (2011). Quantifying location privacy. In
2011 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (pp.
247-262). IEEE.
Trinanda Putra, K., Chen, H. C., Shyu, C. R., & Tsai, Y. Y.
(2021). A systematic review of federated learning in the
healthcare area: From the perspective of data properties
and applications. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 5173.
Vinluan, F. (2022). Sanofi exec jumps to Owkin to ramp up
the AI biotech's pharma partnership plans. BioPharma
Dive. Wikipedia
Wiggers, K. (2020). Major pharma companies, including
Novartis and Merck, build federated learning platform
for drug discovery. VentureBeat. Wikipedia
Xiang, Y., et al. (2025). Privacy-preserving federated
learning for collaborative medical data analysis.
Scientific Reports, 15(1), 1-12.PMC+1Nature+1
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, T., & Tong, Y. (2019). Federated
machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM
Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology
(TIST), 10(2), 1-19.
Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Advancing privacy-preserving
health care analytics and research with federated
learning. JMIR AI, 2(1), e60847. JAI - JMIR AI
Zhou, Y., et al. (2025). Leveraging federated learning for
privacy-preserving analysis of electronic health
records. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 135, 102
Secure Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Medical Record Sharing across Hospitals
201
