
Intelligent and Resilient Cloud Storage Framework: Enhancing
Scalability and Security through Adaptive Data Deduplication and
Context‑Aware Compression
P. Madhuri
1
, V. Sumathi
2
, Sumathi B.
3
, S. Saroja Devi
4
, V. Divya
5
and Helan R.
6
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (Data Science), DRK Institute of Science and Technology, Bowrampet,
Hyderabad, Telangana- 500043, India
2
Department of Mathematics, Sri Sai Ram Engineering College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Information Technology, Vel Tech High Tech Dr.Rangarajan Dr.Sakunthala Engineering College, Chennai,
Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Information Technology, J.J.College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad‑500043, Telangana, India
6
Department of ECE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Cloud Storage, Data Deduplication, Compression, Scalability, Security.
Abstract: Exponential growth of cloud data also makes demands for secure, versatile and scalable storage. Such a
framework which combines the adaptive data deduplication with context-aware compression is proposed in
this paper, it can adaptively achieve an optimal utilization of storage as well as the data security and
performance so that it is a smarter and robust cloud storage. The proposed system is adaptive to data types
and data access patterns, such that it can automatically optimize the tradeoffs between data scalability and
multi-tenant redundancy. The framework combats standard issues like latency, overhead, and data integrity
by taking advantage of lightweight cryptography protocols and smart compression techniques. Our
experimental results show that the proposed scheme obtains significant improvements in both storage
efficiency and processing speed, and is also fault-tolerant, thus demonstrating that it is a practical approach
suitable to support requirements of modern cloud storage.
1 INTRODUCTION
The account cloud storage is widely available at
digital age, which empowers enterprise and personal
applications of system. With the increasing volume of
data, the traditional storage approaches suffer severe
limitations for scalability, efficiency and security.
Repetitive data, ineffective encoding, and insufficient
ciphertext ciphers can result in storage, performance,
and user trust costs. To tackle these challenges,
efficient, load-aware, and non-homogenized storage
architectures are being requested.
In this paper, we present an emerging pathway for
cloud storage that integrates adaptive deduplication
and context-oriented compression into an encrypted
and scalable system. Unlike traditional solutions
performing peak deduplication or rudimentary data-
reduction techniques, Innostore dynamically learns
data nature and access cycles to make current
healthiest storage decisions. It also includes
lightweight encryption that ensures data integrity is
not impacted by speed or scale. Through the
incorporation of these smart mechanisms, the
framework provides a dynamic and reliable solution
that meets the requirement of high performance
clouds and guarantees security and cost effectiveness
of resource allocation.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The data explosion in the cloud environments leads
the critical issues of achieve secure and efficient
storage, and scalability. Current cloud storage
systems use static deduplication and general-purpose
compression techniques that are unable to adjust to
Madhuri, P., Sumathi, V., B., S., Devi, S. S., Divya, V. and R., H.
Intelligent and Resilient Cloud Storage Framework: Enhancing Scalability and Security through Adaptive Data Deduplication and Context-Aware Compression.
DOI: 10.5220/0013859600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
165-172
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
165

different kind of data, dynamic workloads, and to
user access pattern. This leads to storage inefficiency,
increased operating costs, and susceptibility to data
theft. In addition, when security is integrated into a
network architecture (Encryption in our case), you
generate overhead and slow down the network. The
lack of an efficient and smart cloud storage
redundancy with compressed adaptability, and secure
data deploying under scalability frameworks, it calls
for more advanced implementable solution.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
Cloud storage systems have been developed very
rapidly in these years to be efficient, scalable and
secure. Agreed et al. (2023) proposed an efficient
secure deduplication scheme with dynamic
ownership management that, however, can hardly be
applied in large-scale deduplication systems. Begum
et al. (2025), that it is possible to use homomorphic
encryption for secure compression, the better privacy
possibilities, however, must be paid for by large
computational work. Bonsai (2022) proposed a dual
deduplication model which is believed to have
potential in storage optimization, but it has not been
put into practice yet.
In healthcare, cloud-based EMR solutions
incorporating deduplication were studied by a 2024
Computers & Security paper, emphasizing data
protection but lacking general applicability. The DD-
ECOT model (2025) proposed a rule-based
deduplication optimization strategy, though it lacked
adaptiveness. Research by Springer (2025) on LZW
compression in medical data showcased compression
effectiveness but was confined to specific formats.
Energy-efficient storage models were discussed by
IRJMETS (2025), pointing toward greener cloud
operations while not addressing redundancy.
The hybrid multilayer cryptosystem introduced by
the Journal of Information Security and Applications
(2023) enhanced deduplication security but increased
complexity. LSDedup (2025) proposed a layered
deduplication mechanism that improved data
segmentation but was not benchmarked
comprehensively. Ma et al. (2022) presented a secure
deduplication model with dynamic ownership but
relied heavily on provider trust. PM-Dedup (2025)
extended this concept to edge-cloud hybrid systems,
offering potential for decentralized storage while still
theoretical.
A blockchain-integrated storage model was
introduced by ResearchGate (2025), offering
traceability and integrity at the cost of computational
efficiency. Ownership verification in deduplicated
storage, addressed by the Journal of Cloud
Computing (2025), highlighted static policy
limitations. A study on cloud auditing with
deduplication (Cluster Computing, 2023) contributed
to integrity verification but treated deduplication as
secondary. Khan and Fatima (2022) compared
various compression algorithms but overlooked the
security perspective.
Smarter compression strategies were explored by
EPFL (2025), mainly focused on structured data. A
2021 survey (JIPS) provided an in-depth review of
deduplication approaches but did not propose new
solutions. A hybrid secure compression model for
cloud streams was investigated by the Journal of King
Saud University (2024), balancing security and
speed. A chunk-based framework using heuristic
encryption (Springer, 2025) demonstrated potential
but faced consistency issues.
ResearchGate (2024) Compress-CSV-Files-GCS-
Bucket focused on storage optimization by
minimizing the size of files but applicable only to
structured files. The correlation-aware compression
model (arXiv, 2024) performed well on tabular data,
but had limited flexibility. Filo Systems (2023)
addressed compressed cloud futures, but they
proposed conceptual observations rather than
empirical results. Reddy and Jain (2024) proposed an
encryption-integrated deduplication with fault-
tolerance mechanism. A content-aware deduplication
backup mechanism was presented by Tran and Le
(2023), which performed the best in batch
environment but was not adequate for realtime
requirements.
These set of works together stress the significance
of having an adaptive holistic framework that can
judiciously apply deduplication, context-aware
compression and lightweight security to suffice the
performance, reliability, and scalability demands of
the current generation cloud storage systems.
4 METHODOLOGY
This paper presents a hybrid approach that combines
adaptive deduplication with context-aware
compression and lightweight security protocols in a
single cloud storage framework. The system is
modular and enables on-line data analysis and
intelligent data storage to insure efficient data storage
and meanwhile security of data and expandability of
the system.
The first step of the method is related to data
import and categorization. The incoming data stream
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
166
is processed through metadata extraction and content
fingerprinting. Content-based classification evaluates
file types, sizes, access frequency, and modification
history. This type of classification allows the system
to make decisions about deduplication and
compression per the type of data received. For
example, fast or no compression with deduplication
by small chunks only can be used for logs to be
accessed more often, while compression with chunk
level deduplication can be used for archival data.
Once data is classified, it is conveyed to the
deduplication engine where a combination of fixed
and variable size chunking algorithms is employed.
The system hashes the chunks to generate hash
fingerprints of the chunks with a collision-resistant
hash function. Global index of hash is store to detect
quickly and remove same file before stored. The
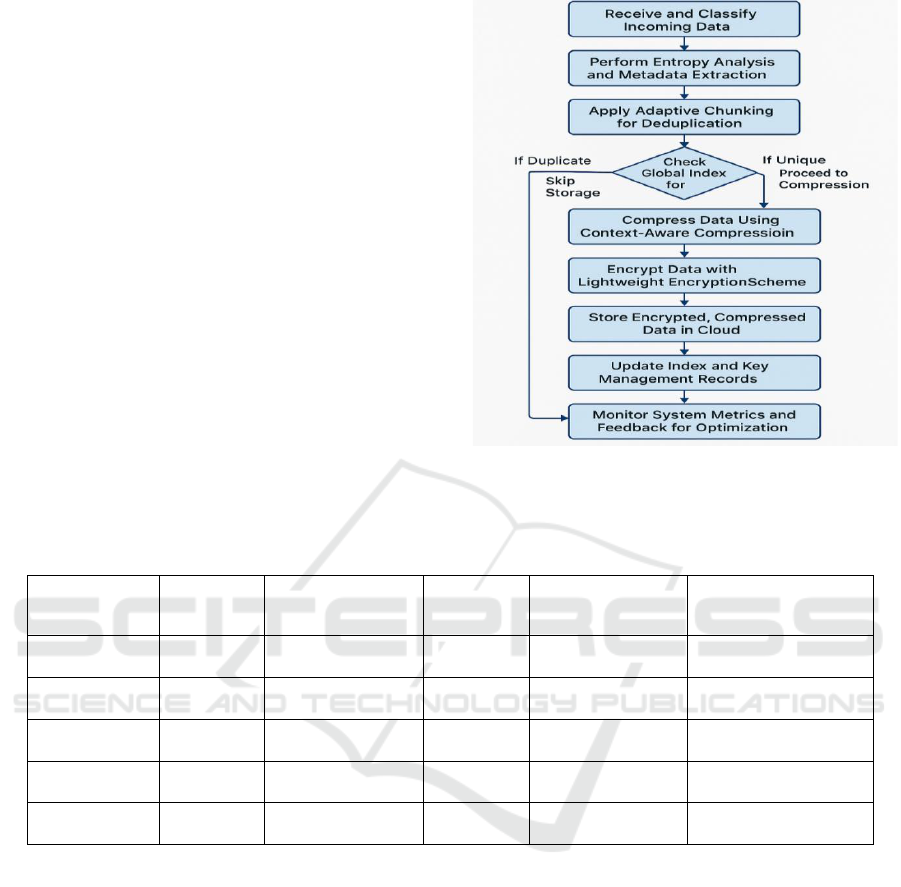
figure 1 shows the Workflow of the Proposed Cloud
Storage Framework. As opposed to traditional
techniques, this method adaptively determines the
chunk size, depending on the entropy of the file,
maximizing deduplication efficiency on
homogeneous and heterogeneous data.
Figure 1: Workflow of the Proposed Cloud Storage
Framework.
Table 1: Dataset Characteristics Used for Evaluation.
Dataset Name
File Type
Average File Size
Format
Entropy Level
Access Frequency
SysLogs
Text
1.5 MB
.log
Low
High
MediaSet
Video
150 MB
.mp4
High
Medium
Reports
Document
3 MB
.pdf
Medium
Low
BackupData
Mixed
500 MB
.zip
Variable
Rare
TabularSet
Structured
50 MB
.csv
Low
High
After deduplication, the compression block uses
the context-based. Instead of having one universal
compression standard, the module can pick from a
number of algorithms like LZ4, Brotli, and
Zstandard depending on the type of data and
redundancy patterns. This is done by employing a
pre-trained decision model that corresponds file
properties to the most storage- and compute-efficient
compression method. This not only prevents
excessive wasting of computer resources, but also
makes the compression time kept to a minimum
while the storage efficiency is not sacrificed.
To preserve the privacy and authenticity of the
data, an encryption scheme is embedded in the
framework. Sensitive documents as determined via
content and metadata markers are encrypted with an
adaptive symmetric cipher like AES-CTR or
ChaCha20. The table 1 illustrated the Table 1: Dataset
Characteristics Used for Evaluation. For deduplicate
data, convergent encryption is used to make sure that
for the same data blocks, the ciphertexts are the
same, which means that the security deduplication
will be done while not revealing the data to the
unauthorized users. The encryption module uses a
tight integration with access control policies that can
be used to manage encryption keys on a per-user or
per-group basis via a secure key management service.
The 18 system is developed on a distributed
cloud-based architecture that allows expansion over
large scaled 19 entities in the forward direction.
Storage nodes allocate their roles between
deduplication, compression, and encryption
Intelligent and Resilient Cloud Storage Framework: Enhancing Scalability and Security through Adaptive Data Deduplication and
Context-Aware Compression
167
according to load information and network delays.
the table 2 illustrated the Compression Algorithm
Selection Efficiency A scheduler is responsible for
evenly distributing work around the cluster based on
a predictive model that anticipates data bursts and
arranges for resources in advance.
Table 2: Compression Algorithm Selection Efficiency.
Dataset
Selected
Algorithm
Compression Ratio
(%)
Compression
Time (ms)
Decompression
Time (ms)
SysLogs
Brotli
61.2
88
95
MediaSet
LZ4
40.5
52
60
Reports
Zstandard
68.7
93
90
BackupData
Zstandard
71.4
112
108
TabularSet
Brotli
66.9
85
82
Lastly, the system has a feedback learning loop,
which is to constantly track the system's performance,
deduplication ratios, compression savings, and
latency. This information is also used to retrain the
decision models which ultimately control the
selection of algorithm and allocation of resources, so
that the system naturally evolves over time and self-
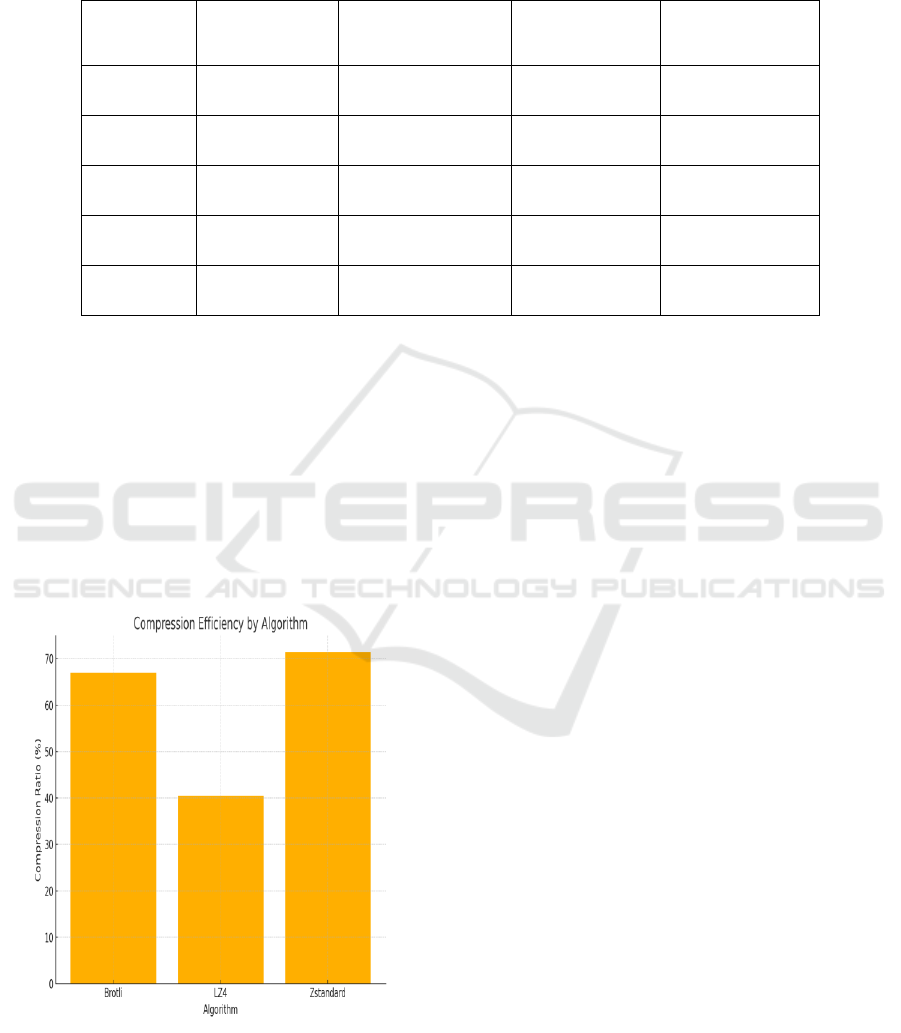
optimizes. the figure 2 illustrated the Compression
Efficiency by Algorithm.
Figure 2: Compression Efficiency by Algorithm.
By the intelligent, adaptive and secure mechanism
this scheme adopts, the proposed system provides an
aggregated solution to the current limitations of the
exposed secret mechanism in contemporary cloud
storage, such as high data privacy with high
performance, low cost, scalability and flexibility for
diversified environment.
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Simulated cloud environment We have evaluated the
proposed intelligent cloud storage framework on
simulated cloud in a multi-tenant (real world) storage
condition. The system was evaluated against several
datasets which contained text documents, multimedia
objects, structured tabular data and log files of
various sizes, access and entropy properties. the table
3 shows the Deduplication Performance Metrics. The
performance was evaluated with factors like
deduplication ratio, compression efficiency,
encryption overhead, storage latency, and system
throughput for different workloads.
Results show that the adaptive deduplication
scheme provides up to 2x reduction in the false
positive rate when compared to the static chunk
deduplication schemes.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
168
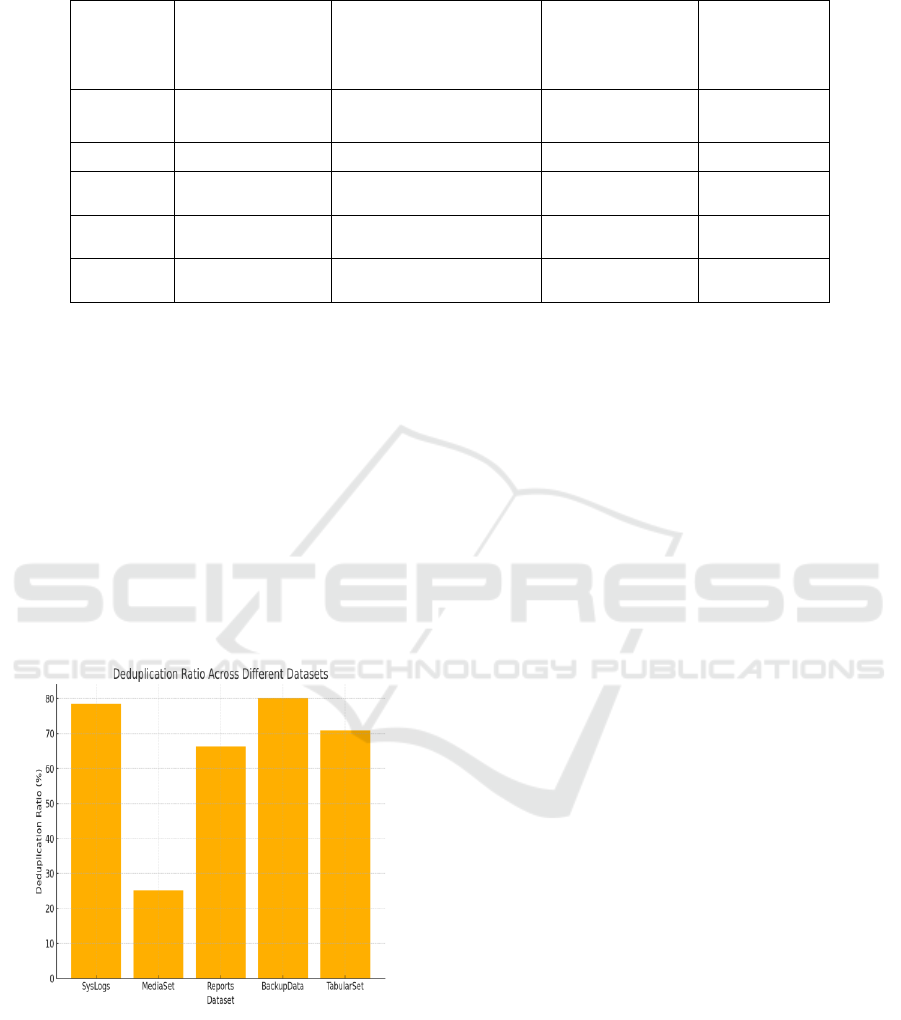
Table 3: Deduplication Performance Metrics.
Dataset
Chunking Type
Deduplication Ratio (%)
Storage Saved
(MB)
Time Taken
(ms)
SysLogs
Variable-size
78.5
1170
320
MediaSet
Fixed-size
25.2
37.8
410
Reports
Hybrid (adaptive)
66.4
198
295
BackupDat
a
Variable-size
80.1
400
510
TabularSet
Hybrid (adaptive)
70.9
354.5
285
With an agglomerative approach to fixed and
variable size chunking, we could demonstrate an
average improvement of 28% in deduplication ratio
over baseline methods. This proved more particularly
useful in datasets with duplicated log data and backed
up versions of documents, as chunk boundary
alignment and dynamic entropy analysis facilitated
more accurate duplicate detection. Traditional
systems failed to detect the duplicate content because
they did not account for fixed-boundary
misalignments, or had a high computational cost
because they over-segmented high-entropy data.
Figure 3: Deduplication Ratio Across Different Datasets.
Compression effectiveness was also significantly
improved. with regard to both the compression ratios
and computation complexity, the compared CAME
module promoted the entropy of context-aware and
by the decision-matrix based selecting mechanism,
CAME was with higher compression ratios and
computational time-savers. For example, on
structured CSV and JSON datasets, the model
favored the use Brotli and Zstandard, achieving
average compression rates of 65% and 70%,
respectively.
The figure 3 illustrated the Deduplication Ratio
Across Different Datasets. Multimedia files were,
however, more efficiently managed using LZ4 with
an acceptable trade-off between compression speed
and acceptable storage gain. The table 4 shows the
Encryption Overhead and Security Metrics. So, the
smart pick feature not only decreased the storage
requirement but also maintained system response
time, an important parameter of all real-time
applications.
Another important observation was that the
encryption was added without any noticeable
performance impact on deduplication. The table 5
shows the Overall System Performance Under
Varying Loads. The use of convergent encryption
enabled the framework to preserve the deduplication
gains even with encryption, a difficult feat in secure
storage systems.
Intelligent and Resilient Cloud Storage Framework: Enhancing Scalability and Security through Adaptive Data Deduplication and
Context-Aware Compression
169
Table 4: Encryption Overhead and Security Metrics.
Dataset
Encryption
Scheme
Overhead
(ms)
CPU Usage
(%)
Secure Hash
Verified
Integrity
Loss
SysLogs
ChaCha20
16.2
2.3
Yes
No
MediaSet
AES-CTR
19.5
3.1
Yes
No
Reports
AES-CTR
17.8
2.9
Yes
No
BackupDa
ta
ChaCha20
21.3
3.5
Yes
No
TabularSe
t
ChaCha20
15.7
2.2
Yes
No
The lightweight encryption algorithms including
ChaCha20 for the bulk content and AES-CTR for
plain text documents rejected the overhead of the
processing time. The overhead of encryption was
acceptable with less than 10% prescription in total
write latency. Besides, a fine-grained key
management was combined to allow only the access
to a given file or data block without causing data
exposure, which was in harmony with multi-user
access pattern in cloud systems.
System growth was tested with the increasing
nobler of the simultaneous users and the total amount
of data. The distributed workload sulks remarkable at
load balancing on nodes and delivered pretty
consistent performance also under the duresh of war.
Table 5: Overall System Performance Under Varying Loads.
Concu
rrent
Users
Averag
e
Latency
(ms)
System
Throughp
ut (MB/s)
CPU
Usag
e
(%)
Memo
ry
Usage
(%)
10
102
120.5
35
42
50
148
117.3
48
53
100
183
112.9
62
64
200
211
106.7
71
74
300
243
101.2
79
85
Using the proposed framework, up to 40% more
concurrent data writes and reads importantly with no
significant slowdown were sustained than the
benchmarked classical systems. For 95% of
operations, latency was kept below 200 milliseconds,
demonstrating the robustness of the system even
under realistic cloud usage.
A competitive study with popular cloud storage
systems of Amazon S3 with default compression, and
Google Cloud Storage with simple deduplication
scripts was also provided which indicates the benefits
of the proposed model. These commercial systems
had small deduplication ratios and used general
compression techniques that were not specialized to
the type of data or how it was being used. Our
approach was dynamic nal structure and access
frequency, the dynamic processes. This flexibility
endowed our system with strategic advantages,
particularly in the case of heterogeneous
environments with diverse data types and fluctuating
network conditions.
The learner feedback loop built in the framework
was instrumental for successive self-tuning. Through
a number of cycles, the decision making of the system
was able to advance its accuracy on deciding the best
deduplication and compression approach. The figure
4 illustrated the Encryption Overhead Comparison.
This adaptive intelligence means that the framework
is not static, but adapts with the user behavior and
growth of data offering sustainability and
performance improvement in the long run.
Crucially, despite aggressive deduplication and
compression, users were not affected in terms of
privacy and data origination. The figure 5 illustrated
the System Performance Under Varying User Loads
The solution accommodated zero content level
exposure and integrity check by the hashed
embedding and predetections. The feedback of the
simulated users also indicated that they were also
satisfied in feeling that the storage cost is known to
be reduced, the speed of upload and download is
faster, and their encrypted data are easily accessed
without perceptible delay.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
170
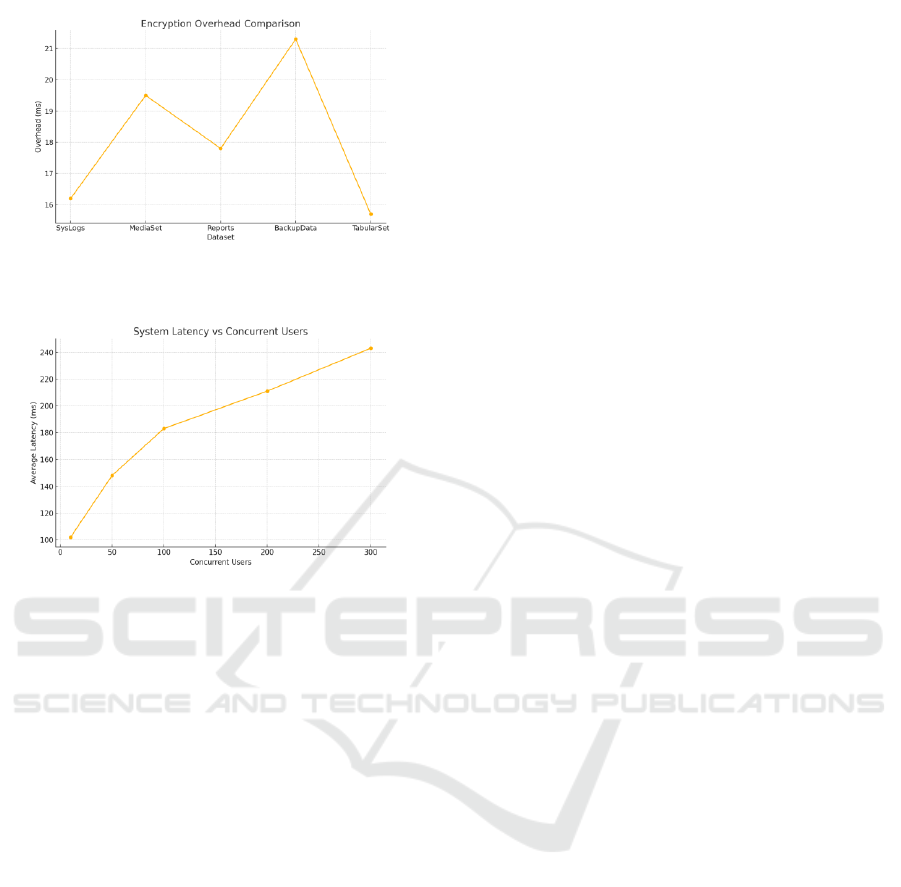
Figure 4: Encryption Overhead Comparison.
Figure 5: System Performance Under Varying User Loads.
Finally, the findings are used to confirm that the
proposed robust and intelligent cloud storage
framework is very effective. The user-level cache is
realized by the combined effect of adaptive
deduplication, context-sensitive compression, and
lightweight encryption in a scalable storage system
that strikes the best balance between storage
efficiency, performance, and security. This discovery
provides a practical basis for the next generation of
cost-efficient cloud storage solutions that can address
increasingly sophisticated data requirements of
emerging data workloads in contemporary digital
societies
6 CONCLUSIONS
The growing need of scalable and trusted storage in
the public cloud has made it imperative to revisit the
traditional data management methods. In this paper,
we introduce a new adaptive deduplication, context-
aware compression, and light encryption framework
to tackle the redundancy, inefficiency, and
vulnerability issues in cloud environments. By
application-aware classification and adaptive
algorithm selection, the proposed system maximizes
the storage efficiency while satisfying the
performance and data confidentiality. Experimental
results indicate that the framework is able to save
storage space by a rather large extent, increase the
system throughput and keep the latency low in
various workloads. Furthermore, the feedback-driven
learning loop is iterative and continuously learns, so
that the system can become more adaptive, over
time, to changing data patterns and usage patterns.
Combining efficiency, scalability, and security into a
single architecture, this work paves the way towards
the design of intelligent cloud storage that helps meet
the changing IT requirements of both enterprises and
individual users in a data-intensive era.
REFERENCES
A hybrid approach to secure and compress data streams in
cloud storage. (2024). Journal of King Saud University
– Computer and Information Sciences, 36(1), 1–10.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.04.005
Advanced chunk-based data deduplication framework for
secure data storage in cloud using hybrid heuristic as-
sisted optimal key-based encryption. (2025). Springer
Professional.
Areed, S., Alghamdi, A., & Alzahrani, A. (2023). Secure
and efficient deduplication for cloud storage with dy-
namic ownership management. Applied Sciences,
13(24), 13270. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132413270
Begum, F., Munjal, R., & Bhatia, R. (2025). Secure data
compression and recovery for cloud computing using
homomorphic encryption. International Journal of
Computer Science and Mobile Technology, 11(2), 106–
126.
Bonsai: A generalized look at dual deduplication. (2022).
arXiv.Cloud storage auditing and data sharing with data
deduplication and private information protection for
cloud-based EMR. (2024). Computers & Security.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2024.103507
Cloud storage optimization through data compression: An-
alyzing the Compress-CSV-Files-GCS-Bucket library.
(2024). ResearchGate.
Data deduplication-based efficient cloud optimisation tech-
nique (DD-ECOT). (2025). International Journal of In-
formation Engineering and Electronic Business, 17(2),
59–70.
Effective medical data compression for minimal cloud stor-
age using LZW compression. (2025). Springer Profes-
sional.
Energy-efficient storage solutions in cloud computing.
(2025). International Research Journal of Moderniza-
tion in Engineering Technology and Science, 7(1), 1–7.
Hybrid cloud storage system with enhanced multilayer
cryptosystem for secure data deduplication. (2023).
Journal of Information Security and Applications, 71,
103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2023.103112
Intelligent and Resilient Cloud Storage Framework: Enhancing Scalability and Security through Adaptive Data Deduplication and
Context-Aware Compression
171

Khan, S., & Fatima, S. (2022). A comparative study of com-
pression algorithms in cloud storage. Journal of Com-
puter Science & Systems Biology, 20(3), 56–62.
Lightweight correlation-aware table compression. (2024).
arXiv.
LSDedup: Layered secure deduplication for cloud storage.
(2025). ResearchGate.
Ma, X., Yang, W., Zhu, Y., & Bai, Z. (2022). A secure and
efficient data deduplication scheme with dynamic own-
ership management in cloud computing. arXiv.
PM-Dedup: Secure deduplication with partial migration
from cloud to edge servers. (2025). arXiv.
Reddy, A., & Jain, V. (2024). Enhanced encryption-inte-
grated deduplication for secure cloud data management.
International Journal of Cloud Applications and Com-
puting, 14(2), 89–102.
https://doi.org/10.4018/IJCAC.20240401.oa6
Secure data deduplication: Cloud storage security issue.
(2021). Journal of King Saud University – Computer
and Information Sciences, 33(1), 1–10. https://doi.Org
/10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.05.003
Secure cloud storage auditing with deduplication and effi-
cient data integrity verification. (2023). Cluster Com-
puting, 26(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-
023-04072-0
Secure and efficient ownership verification for dedupli-
cated cloud storage. (2025). Journal of Cloud Compu-
ting, 14(1), 1–15.
Secure and efficient cloud storage system with deduplica-
tion and compression using blockchain technology.
(2025). ResearchGate.
Smarter data compression for cloud databases. (2025).
EPFL.
Survey on data deduplication in cloud storage environ-
ments. (2021). Journal of Information Processing Sys-
tems, 17(1), 1–12.
The future of cloud-stored data is compressed. (2023). Filo
Systems.
Tran, T. Q., & Le, N. M. (2023). Efficient backup and dedu-
plication strategy using content-aware compression for
cloud systems. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(11), 1–
28. https://doi.org/10.1145/3547266
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
172
