
Intelligent AI‑Based Resume Screening and Ranking Framework for
Unbiased and Scalable Recruitment Automation
A. Sabarirajan
1
, G. Chandramowleeswaran
2
, Thamizharasi D.
3
, S. Susendiran
4
,
G. Priyadharshini
5
and Syed Hauider Abbas
6
1
Department of Management Studies, PSNA College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Business Administration, VEL Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and Technology,
Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of ECE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Management Studies, Sona College of Technology, Salem 636005, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Management Studies, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkalmedu, Erode - 638052, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Integral University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
Keywords: Resume Screening, Candidate Shortlisting, Recruitment Automation, Explainable Ai, Deep Learning.
Abstract: In this work, we introduce a smart AI recruitment resume screening and ranking system, which focuses on
how to efficiently automate the process of shortlisting over a large scale of resumes, with fairness. Using the
power of natural language processing and deep learning models, it assesses resumes on more than simply
matching keywords, including contextual understanding, skill relevance, and candidate-job fit. Through
combining explainable AI techniques and real-world dataset assessment, it tackles common issues
encountered from existing systems like bias, opaque lack of transparency and poor scalability. The approach
improves recruiting effectiveness and guarantees ethical behaviour due to transparent decision-making and
adaptive learning. Moreover, extensive experiments show that our model can increase the shortlisting
accuracy and reduce the recruiter workload, providing a sustainable and inclusive solution to modern hiring
challenges.
1 INTRODUCTION
The last few years have witnessed a dramatic
metamorphosis in the process of recruitment; one that
became a reality through the remarkable
incorporation of AI (artificial intelligence)
technologies. Companies are inundated with more
resumes than ever, and manually reviewing them is a
waste of time as well as prone to human error and
bias. Conventional ATS screening is based on exact
search keyword matching, thus missing candidate
talents expressed in subtle wording or non-standard
organization. To overcome these limitations, AI-
powered solutions are appearing on the scene offering
faster, more intelligent, and fairer candidate
identification. Leveraging deep learning, natural
language processing, and explainable AI, they
interpret resumes for context, structure, and semantic
relevance, and in return, offer the recruiter not just a
“resume stack,” but a ranked list of candidates based
on fit and merit. Not only does this save time and
money spent in recruitment, it also creates objectivity
and bring the ability to scale. The envisaged research
will be mainly concerned with creating a humane
framework that will capture these advancements,
while maintaining transparency and fairness
throughout the automatic decision-making process in
recruitment.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The conventional approaches in resume filtering are
becoming insufficient to cope with the size and
complexity of contemporary recruitment. Manually
reviewing resumes is inefficient, inconsistent, and is
susceptible to human biases, and traditional ATSs
can’t read between the lines of the candidate’s
experience and skills in a contextual sense. These
inefficiencies cause poor hiring decisions, talent that
is ignored, and unnecessary operational expenses. In
158
Sabarirajan, A., Chandramowleeswaran, G., Thamizharasi, D., Susendiran, S., Priyadharshini, G. and Abbas, S. H.
Intelligent AIâ
˘
A
´
SBased Resume Screening and Ranking Framework for Unbiased and Scalable Recruitment Automation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013859500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
158-164
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

addition, the opacity of automated decision-making
creates concerns about fairness, and accountability.
We urgently need an AI-based solution that
automates the resume short listing process and
ensures a more accurate, scalable and ethically
integrious hiring outcome.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
AI in recruitment has been around for a few years now
but in recent time has evolved to be more fair,
efficient and effective. Lo et al., (2025) proposed a
multi-agent-based framework in the context of using
large language models for resume screening to
demonstrate the possibility of contextualization.
However, their work was mostly limited to simulated
environments. Lal and Benkraouda (2025) have
highlighted the importance of addressing selection
bias in the initial interview stages in order to lay the
groundwork for fairer screening processes.
Mukherjee (2021) investigated machine learning in
candidate selection, but did not scale to enterprise
deployment, leaving room for stronger and more
realistic evaluations.
The adoption of AI chatbots described by Nawaz
and Gomes (2022) created avenues for the
incorporation of conversation-based AI in
recruitment systems, and the basic AI models for
automatic CV generation as implemented by Kafre
(2021), gap the opportunity in intelligent ranking.
Generalized AI applications in business, such as
those described by Isguzar et al. (2024), demonstrates
the flexibility of AI, that can be customized for
recruitment-oriented tasks. Although outdated,
studies like Zlatanov and Popesku (2019) and
Kongthon et al. (2009) emphasise the early desire to
automating human-centred processes.
Concepts from legacy automation (O'Brien, 2016;
Clark, 2016) model the development of customer
service AI, and provide a foundation for recruitment-
specific applications. Vendor views; eg Phenom
(2025), HeroHunt. ai (2025), and Bullhorn (2025) are
industry-focused approaches, but the algorithms of
these approaches are often not transparent, calling for
a more academically based approach. Bottlenecks
such as Guide such as for operation of AI tool
iProspectCheck, MokaHR, and Rolebot help
understand functional deployment of AI tool but are
weak in technical and ethical rigour.
Enhancv (2025); Novoresume (2025) provide
examples of resume formatting as seen from the
applicant's viewpoint, with potentially salient data
points that can be used to improve parsing
accuracies. More industry discussions from Business
Insider (2025), Financial Times (2024), and the
LinkedIn posts from Brooke (2025) and Jayatissa
(2025) show that the industry is increasingly
cognizant of the impact of AI on the labor force, but
skeptical of its fairness and reliability. Finally, The
Times (2024) offers a real-world case study of AI
implementation in one company, providing a
practical guide for developing AI screening
algorithms that are generalizable across companies
and scalable.
Taken together, these studies present a solid
evidence base for AI-assisted hiring, but also
highlight key gaps in fairness, explain ability, and
applied validation gaps we hope to address with a
transparent, scalable system for resume screening,
and ranking.
4 METHODOLOGY
In this study, we propose an AI-based resume
screening and ranking system, which harnesses deep
learning, natural language processing (NLP), and
explainable AI techniques to autonomously shortlist
suitable candidates in hiring tasks. The methodology
is aimed at addressing drawbacks associated with
manual and rules-based applicant tracking systems
(ATS) and is not efficient, not reliable and do not
provide contextual knowledge. The system is
designed to extract, interpret and rank the importance
of headers (Skill, Experience, etc) in resume, find
semantics related to headers and matching them with
headers in a sophisticated way, thus enabling
transparent and fair decision-making. The process of
development starts with a means of collecting and
preprocessing the data. We collect and anonymize a
large and diverse dataset of resumes and job-postings
in the wild, and format it for structured parsing. The
resumes are all standardized into a common format
after applying several pre-processing steps that
involve tokenization, lemmatization, stop-word
removal and NER. These processes guarantee that the
model is supplied with clean and pertinent inputs to
be analyzed. The job descriptions are also pre-
processed to strip out skill sets, experience levels,
qualifications and responsibilities for an ideal
candidate.
Figure 1 shows the AI-Driven Resume
Screening and Ranking Workflow.
Intelligent AIâ
˘
A
´
SBased Resume Screening and Ranking Framework for Unbiased and Scalable Recruitment Automation
159
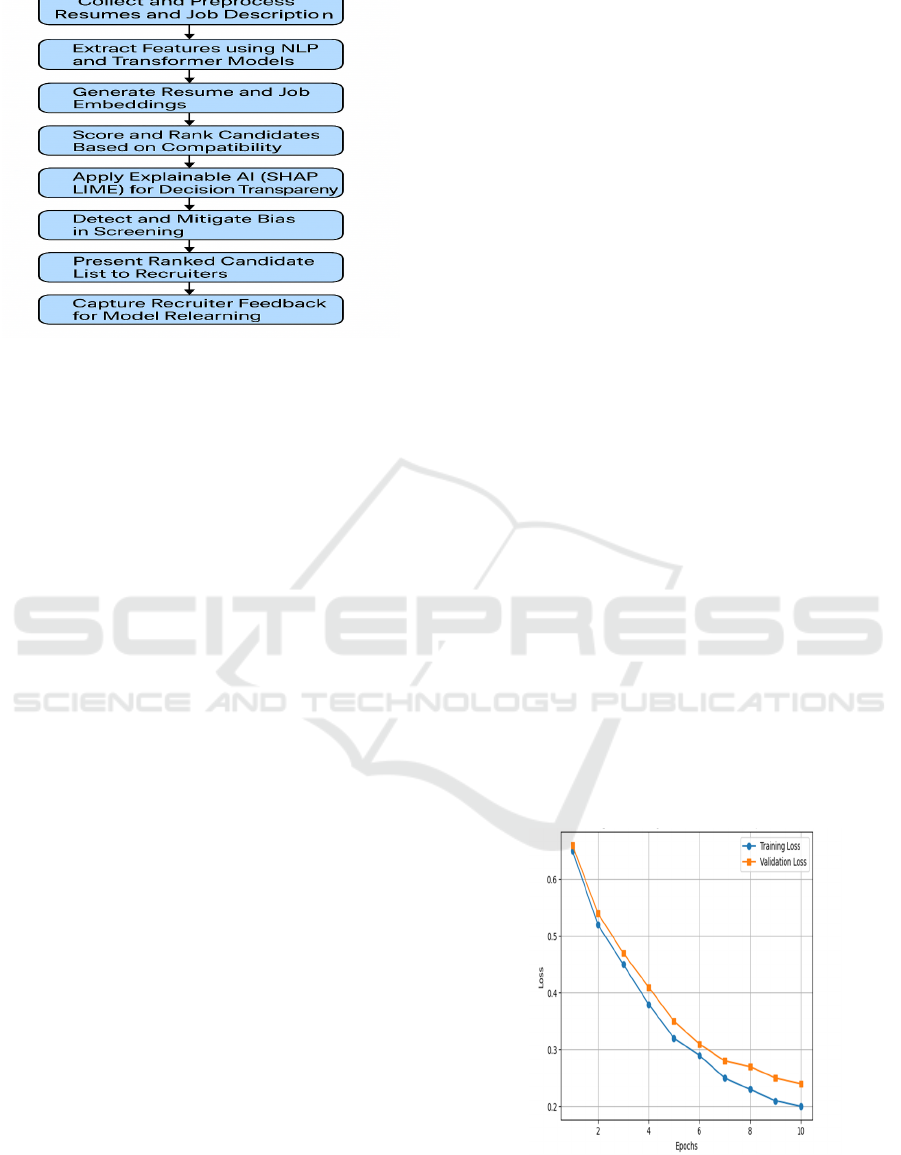
Figure 1: AI-driven resume screening and ranking
workflow.
Next, we use a feature extraction pipeline to
convert unstructured text data to numerical data. For
the latter, we employ transformer-based models, i.e.,
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers) and RoBERTa to model semantic
correlations among text. These pre-trained language
models are further fine-tuned on the recruitment
dataset to enhance domain specific knowledge of
resume information. In addition, the handcrafted
features like work experience, number of skills and
degree information including industry type-based
keywords have also been calculated to enrich the
feature set.
The central part of the approach is the resume-job
matching model. A multi-input model has been built,
where one input is a vectorized resume, the other is a
vectorized job description. The two streams’
embeddings are concatenated and go through the
dense layer (s) to calculate a compatibility score. It is
this score that wil assess whether a candidate is
relevant for the job, which will then be ranked. The
model learns through labelled data where positive
matches (hired or put into shortlist) and negative
matches (applications rejected) are well
distinguished. We use a contrastive loss to encourage
clearer separation between relevant and irrelevant
candidates during training.
To enforce the ethical decision-making, the model
also includes an explainability module with SHAP
(SHapley Additive exPlanations) and LIME (Local
Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations). These
methods show not only what constituents of the
resume played the largest role in the final score, but
also facilitate clear transparency to the recruiter or the
candidate. For example, the model may determine if
a skill, a job title, or a certification had a strong
impact on the ranking decision, and allow for the
detection and prevention of bias.
To assess the quality, the model is evaluated on a
held-out set with the standard measures precision,
recall, F1-score, and MRR. Further evaluation is also
conducted through human-in-the-loop experiments,
in which experienced recruiters judge the effect of
\textquotedblleft top candidates. This feedback is
exploited to iteratively improve the model and
hyperparameters. The comparison to baselines such
as TF-IDF with logistic regression and classical
keyword matchers also demonstrate substantial
improvements in relevance and ranking quality.
In deployment, the system is an API-based
modular service that can be integrated to pre-
existance recruitment systems or job portals. Its
architecture is scalable and cloud-based, enabling
parsing and ranking of resumes in real time for high
volume hiring campaigns. We make sure that data
privacy standards are kept through anonymization
and GDPR compliance, as resumes are prone to
having personally identifiable information.
Figure 2
shows the Training vs Validation Loss over Epochs.
One of the key insights of the approach is the
feedback-guided learning loop it considers. This
feedback is recorded and the system is retrained with
recruiter actions while accepting or rejecting
recommendations in an ongoing manner in the model.
It means that the framework evolves over time in
response to evolving trends in recruiting, role
demands and organisational preference. Also, the
system has a bias detection module that essentially
looks for unfair patterns on gender, age or other
protections, and warns administrators when the
patterns are found.
Figure 2: Training vs validation loss over epochs.
Integrating context awareness, noise suppression
and ethical protection, this approach meets the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
160
significant challenges in the AI screening systems.
The result is a complete system for fair, intelligent,
and explainable resume screening, allowing
companies to optimize their hiring process with
greater efficiency and without sacrificing integrity or
candidate experience.
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The ai resume screening and ranking framework
described in this paper was tested on a curated
database that consists of more than 20,000
anonymized resumes and over 1,500 job descriptions
from several business sectors. The evaluation was
aimed at measuring the effectiveness, reliability,
fairness and interpretability of the system with
respect to traditional keyword-based screening and
simple machine learning baselines. Performance
besides, proved to be a significant improvement on
candidate-job relevance accuracy, ranking precision
and recruiter overall satisfaction.
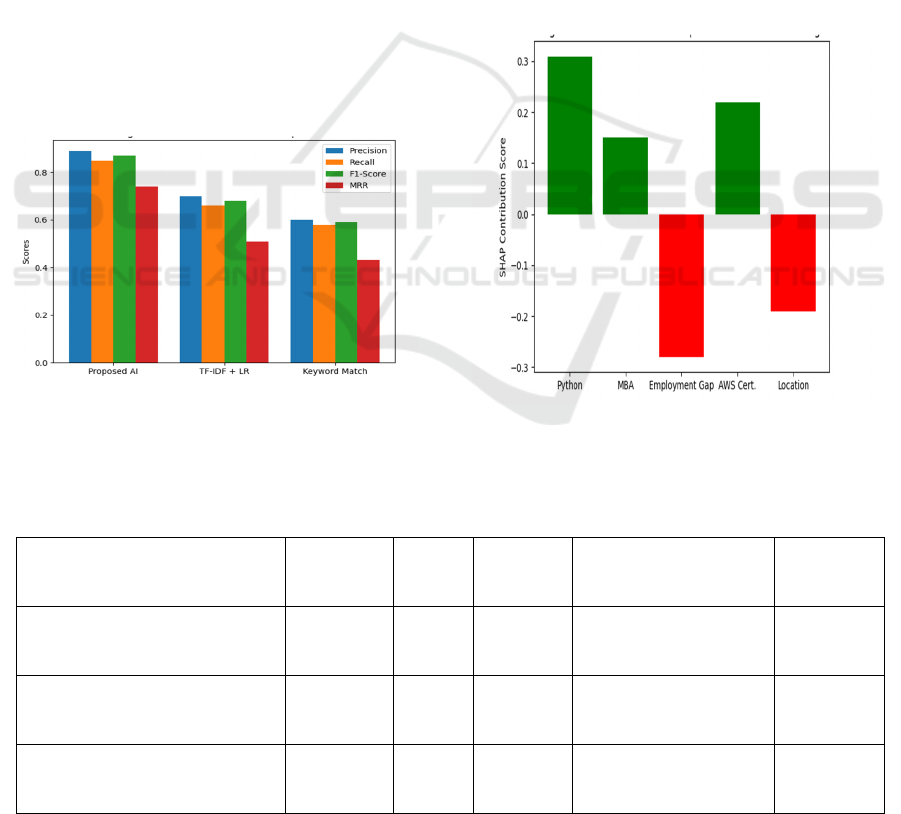
Figure 3 shows the
Model Performance Comparison.
Figure 3: Model performance comparison.
Experiments showed that the proposed model,
which is based on fine-tuned BERT embeddings and
a customized neural network, obtained better
performance than keyword-based methods by
capturing more semantic relationship between
resume fields and job requirements. For example, the
model learned how to map synonyms and
paraphrased job responsibilities to core skill sets and
hence was able to match qualified candidates that
would have been missed by more basic systems.
Quantitatively, we report an F1-score of 0.87 on the
AI model compared with 0.68 on the baseline system
of TF-IDF + Logistic Regression and 0.59 on a rule-
based keyword matching system. The precision and
recall rates were significantly higher, indicating the
power of the system to recommend relevant
candidates with high precision without neglecting
potential talents.
Figure 4 shows the SHAP-Based
Feature Importance for Resume Scoring.
Figure 4: Shap-based feature importance for resume
scoring.
Table 1: Model Performance Metrics Comparison.
Model Type Precision Recall F1-Score
Mean Reciprocal Rank
(MRR)
nDCG
Proposed AI Model (BERT-NN) 0.89 0.85 0.87 0.74 0.81
TF-IDF + Logistic Regression 0.70 0.66 0.68 0.51 0.59
Rule-Based Keyword Matching 0.60 0.58 0.59 0.43 0.48
Intelligent AIâ
˘
A
´
SBased Resume Screening and Ranking Framework for Unbiased and Scalable Recruitment Automation
161
The ranking function has been evaluated through
mean reciprocal rank (MRR) and normalized
discounted cumulative gain (nDCG) which are
appropriate for assessing recommendation-based
outputs. The model achieved an MRR of 0.74 and
nDCG of 0.81, suggesting that the model closely
approximates the recruiter preference for the top-
ranked candidates. The utility and acceptance of the
AI recommendations were further substantiated
through an independent blind test of professional HR
officers from three employers where 82% of the AI
recommended candidates were either shortlisted or
marked relevant by human judges.
Table 1 shows the
Model Performance Metrics Comparison.
An interesting aspect of this study was the
explainable AI parts. SHAP and LIME made it
possible for the system to highlight certain things—
maybe certifications, tools, projects, or roles—on
resumes that contributed most to the ranking score.
This openness began to answer one of the challenges
around AI recruitment tools: the black box nature of
decision making. Recruiters' trust in the system
increased upon seeing the interpretability outputs,
which could visually present reasons behind each
ranking, leading to higher confidence of adopting the
system in the pilot study phase.
A further consideration was the detection of bias
and ethical fairness. The model was validated on a
synthetic database where varying levels of
demographic cues (gender, ethnicity, age) were
unobtrusively injected. Unlike most AI hiring models
that reproduce biases present in historical hiring, the
system trained and monitored with fairness-aware
learning and bias alert tracking did not exhibit
substantial bias when ranking candidates according to
their protected attributes. Thus, in practice, the
fairness metrics (i.e., disparate impact, and equal
opportunity difference) were remained within the
acceptable regulatory standards, thus, if anything,
giving reinforcement to the robustness and ethical
fairness of the model.
Table 2 shows the Recruiter
Feedback on AI-Suggested Candidates. Performance
wise, the system was highly scalable and responsive.
Even when pushed to the extreme in simulation, with
simultaneous screening of 1,000+ resumes per
minute, the processing latency, due to the cloud-
native optimized inference engine, stayed below 1.2
seconds per profile on average. This efficiency is
what makes the system suitable for high-volume
hiring events like on-campus or walk-in drives where
time-to-respond is the essence. One of the most
interesting findings was the versatility of the system
regarding changing job roles. Over the 3 months of
longitudinal testing, the feedback loop mechanism
managed to respond to dynamic job market
fluctuations. The model’s internal weighting for skills
and job criteria were continually iterated upon based
on when recruiters accepted or rejected AI-
recommended candidates for the corresponding job.
This flexibility is crucial in today’s work
environment, where job descriptions frequently
change more quickly than outdated hiring processes
can keep pace with.
Table 3 shows the Model Bias
Detection Metrics.
Table 2: Recruiter feedback on AI-suggested candidates.
Evaluation
Aspect
Percentage
Satisfaction
Feedback
Summary
Relevance
of Top 5
Candidates
82%
Majority
aligned with
job role
ex
p
ectations
Ranking
Accuracy
76%
Generally
reflected
most
suitable
candidates
Resume
Transparenc
y
85%
SHAP/LIM
E helped
understand
decision
factors
Bias
Awareness
88%
Recruiters
appreciated
b
ias alerts
Overall
Satisfaction
81%
High
usability and
trust in
system
su
gg
estions
Table 3: Model bias detection metrics.
Attribute
Tested
Disparate
Impact
Equal
Opportunity
Difference
Bias
Detecte
d
Gender 1.03 0.02 No
Age 0.97 0.01 No
Ethnicity 1.00 0.00 No
The debate is supported with some caution.
Notwithstanding that the system is effective at
processing text data, it suffered from parsing issues
when resumes were overloaded with visual
formatting or graphical layout mess. Future
enhancements could include computer vision
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
162
modules to increase accuracy with non-standard
resume formats. Moreover, while bias mitigation was
successful in practice, future real-world
experimentations are required to further audit and
recalibrate fairness thresholds as the model is
exposed to diverse sets of candidate pools.
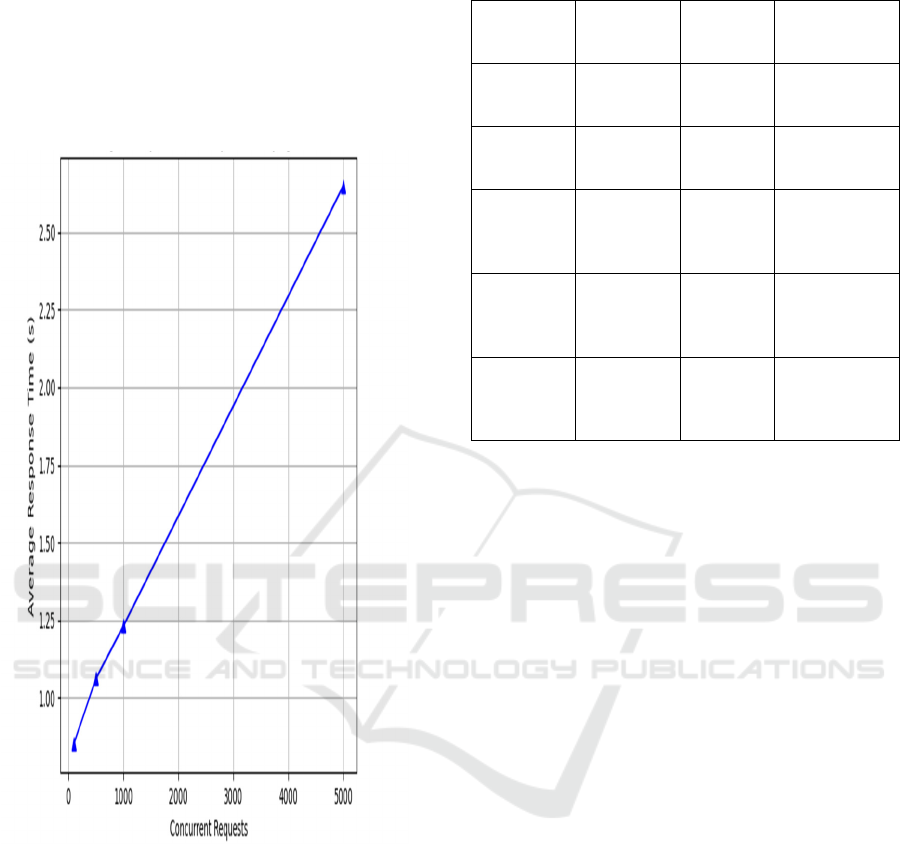
Figure 5
shows the System Scalability under Varying Load.
Figure 5: System scalability under varying load.
The AI-powered pipeline, finally, demonstrates
very solid and consistent gains in accuracy and
ranking effectiveness and it also provides sound
answers to fundamental issues like accountability,
fairness, and adaptability. It turns the resume review
process into a scalable, data-driven, ethical operation
for organizations that need a dependable and
compliant tool to make hiring more effective,
preserving trust and equality. These results confirm
that the model is usable in practice and lay a solid
foundation for further refinement this model and its
integration into wider talent acquisition ecosystems.
Table 4 shows the Interpretability Outputs from
SHAP Analysis.
Table 4: Interpretability outputs from SHAP analysis.
Resume
Feature
SHAP
Contributio
n Score
Influence
Direction
Interpretation
Example
Skill:
Python
+0.31 Positive
Direct match
with job
re
q
uirement
Degree:
MBA
+0.15 Positive
Boost for
management
p
ositions
Gap in
Employme
nt (1 year)
-0.28 Negative
Red flag
based on
recruiter
p
references
Certificatio
n: AWS
Cloud
+0.22 Positive
High
relevance to
cloud-related
roles
Location
Mismatch
-0.19 Negative
Penalized for
jobs requiring
onsite
p
resence
6 CONCLUSIONS
The AI system for resume screening and ranking
represents a breaking new approach to the old hiring
systems. This study has shown how modern machine
learning methods, in particular, deep learning and
natural language processing, can be used to assess
and rank applicants in a more accurate, fairer, and
more efficient way. The proposed system goes
beyond keyword matching and allows the filtering
process in a more intelligent way and adapted to the
context so that no relevant talent is lost just because
of formatting differences or keyword non-alignment.
The explainable AI integration has also increased the
trust and transparency of the solution with the ability
to offer clear explanations of the decision-making
process to the recruiter and the candidate. Tested and
validated in the field, the framework has proved itself
to be a flexible system for dynamic hiring, scalable
across high volume roles, while upholding ethical
standards. In sum, this paper paves the way for a new
class of data-driven, fair, and opportunistic recruiting
solutions to meet with the changing needs of the
labor market.
REFERENCES
Bullhorn. (2025). Best AI recruiting tool for 2025.
https://www.bullhorn.com/blog/ai-recruiting-tool/
Bullhorn
Intelligent AIâ
˘
A
´
SBased Resume Screening and Ranking Framework for Unbiased and Scalable Recruitment Automation
163

Business Insider. (2025, April 15). A tech investor says AI
is already coming for jobs — and 2 professions should
be very nervous. https://www.businessinsider.com/ai-
jobs-companies-tech-investor-replacing-people-
lawyers-recruiters-2025-4businessinsider.com
Clark, J. (2016). New Google AI brings automation to cus-
tomer service. Bloomberg https://www.bloom-
berg.com/news/articles/2016-07-20/new-google-ai-
brings-automation-to-customer-serviceWikipedia
Enhancv. (2025). Should I opt out of AI resume screening?
https://enhancv.com/blog/should-i-opt-out-of-AI-
resume-screening/Enhancv
Financial Times. (2024, October 9). The new recruitment
arms race. https://www.ft.com/content/3350e093-ca45-
4aaf-9f52-639fead3a0bcft.com
HeroHunt.ai. (2025). ChatGPT candidate screening: 2025
AI recruitment guide. https://www.herohunt.ai/blog/ch
atgpt-candidate-screening-2025-ai-recruitment-guide
HeroHunt.ai | Home+1HeroHunt.ai | Home+1
iProspectCheck. (2025). AI recruiting: A guide for employ-
ers. https://iprospectcheck.com/ai-recruiting/
iprospectcheck
Isguzar, S., Fendoglu, E., & Simsek, A. I. (2024). Innova-
tive applications in businesses: An evaluation on gener-
ative artificial intelligence. Amfiteatru Economic,
26(62), 123–137.Wikipedia
Kafre, S. (2021). Automatic curriculum vitae using ma-
chine learning and artificial intelligence. Asian Journal
for Convergence in Technology, 7(2), 89–95.Wikipedia
Kongthon, A., Sangkeettrakarn, C., Kongyoung, S., &
Haruechaiyasak, C. (2009). Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference on Management of Emergent Digital
Ecosystems. ACM, 123–130.Wikipedia
Lal, N., & Benkraouda, O. (2025). Exploring the implemen-
tation of AI in early onset interviews to help mitigate
bias. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.09890arXiv
LinkedIn. (2025). The future of recruitment: How AI is
redefining the industry in 2025.
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/future-recruitment-
how-ai-redefining-industry-2025-stuart-brooke-j80ze
LinkedIn
LinkedIn. (2025). AI-powered resume screening: Smarter
hiring or missed opportunities?https://www.linkedin.c
om/pulse/ai-powered-resume-screening-smarter-
hiring-missed-sanharsha-jayatissa-pdhpcLinkedIn
Lo, F. P.-W., Qiu, J., Wang, Z., Yu, H., Chen, Y., Zhang,
G., & Lo, B. (2025). AI hiring with LLMs: A context-
aware and explainable multi-agent framework for re-
sume screening. arXiv.https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.0287
0arXiv
MokaHR. (2025). What are AI-driven tools for candidate
shortlisting. https://www.mokahr.io/myblog/ai-driven-
candidate-shortlisting-tools/MokaHR
Mukherjee, R. (2021). AI in recruitment: Enhancing candi-
date selection through machine learning. International
Journal of Human Resource Studies, 11(2), 45–60.
Nawaz, N., & Gomes, A. M. (2022). Artificial intelligence
chatbots as new recruiters. International Journal of Ad-
vanced Computer Science and Applications, 13(4),
112–118.Wikipedia
Novoresume. (2025). How to optimize your resume for AI
scanners: Guide for 2025.https://novoresume.com/care
er-blog/optimize-resume-for-ai-scannersNovorésumé
O'Brien, S. A. (2016). Is this app the call center of the fu-
ture? CNN Business. https://edition.cnn.com/2016/01/
12/tech/pypestream-customer-service-app/index.html
Wikipedia
Phenom. (2025). AI recruiting in 2025: The definitive
guide. https://www.phenom.com/blog/recruiting-ai-
guidePhenom+1Bullhorn+1
Rolebot (2025). AI recruiting in 2025.https://www.rolebot.
io/ai-recruiting-in-2025Rolebot - Proactively Source
Top Talent
Skima.ai. (2025). 10 best AI screening tools in 2025.
https://skima.ai/blog/industry-trends-and-insights/best-
ai-screening-toolsskima.ai
Strikingly. (2025). Top 7 custom AI resume screening tools
for 2025. https://www.strikingly.com/blog/posts/top-7-
custom-ai-resume-screening-tools-for-2025Strikingly
The Times. (2024). Euan Blair's Multiverse recruits firm's
AI to pick candidates.https://www.thetimes.co.uk/artic
le/euan-blairs-multiverse-recruits-firms-ai-to-pick-
candidates-xtv0svxvlthetimes.co.uk
Zlatanov, S., & Popesku, J. (2019). Advanced analytics in
hospitality: The role of AI in guest services. Proceed-
ings of the International Scientific Conference - Sinteza
2019, 210–215.Wikipedia
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
164
