
Smart Signal Control Using Reinforcement Learning to Ease Urban
Traffic
Sivakumar Ponnusamy
1
, M. L. M. Prasad
2
, G. Swarnalakshmi
3
, S. Karthikeyan
4
,
S. K. Lokesh Naik
5
and Moses Raja A.
6
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu,
India
2
Department of CSE (AI&ML), Joginpally BR Engineering College, Moinabad, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
3
Department of Mechanical Engineering, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai,
Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
6
Department of MCA, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Adaptive Traffic Signals, Urban Congestion, Multi‑Agent Systems, Vehicle Flow.
Abstract: This study offers an innovative proposal for the management urban traffic through the implementation of
reinforcement learning for adaptive traffic signal systems to overcome the traffic jam problem and increase
vehicle flow. The model, based on deep learning algorithms and real-time data, dynamically modifies timing
in accordance with traffic conditions, facilitating smooth and hang-up-free traffic. Compared to classical static
or rule-based methodologies, the approach is flexible enough to adapt to changing patterns and is shown that
outperforms in simulations based on realistic urban networks. In addition, the system uses multi-agent
cooperation methodology to optimize signal coordination across intersections, thus being scalable and
responsive. The results show that the learning instantiation can lead to significant gains in traffic efficiency,
delay reduction, and emission mitigation, demonstrating the potential of reinforcement learning as a
promising approach to enhance intelligent transportation systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Congestion in the urban areas is a perennial challenge
in fast-growing cities causing higher travel time,
more pollution, inefficiency and economic loss.
Conventional traffic signal control systems, which are
time of day or "rule" based, cannot fully adapt to the
dynamic and often random flows of real-time traffic.
With the popularity of intelligent transportation
systems, an increasing number of researchers are
endeavouring to exploit machine learning, especially
reinforcement learning, for adaptive traffic control
protocols that can learn optimal traffic control
strategies incrementally. Reinforcement learning is a
strong framework for decision making in complex
environments and is capable of providing traffic
signal systems that learns about their environment
from real-time traffic. We propose a traffic signal
control system mobilized by deep reinforcement
learning to dynamically adjust signals based on traffic
flow and intersection conditions. The method
increases coordination among signals, and
consequently throughput and decreases global
congestion by representing intersections as agents in
a multiagent model. Finally, both the learning-based
traffic flow estimation and control manifest the
vision of smart city, and potentially provide a
scalable, data-driven solution to challenges that are
faced in the era of mobility.
102
Ponnusamy, S., Prasad, M. L. M., Swarnalakshmi, G., Karthikeyan, S., Naik, S. K. L. and A., M. R.
Smart Signal Control Using Reinforcement Learning to Ease Urban Traffic.
DOI: 10.5220/0013858100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
102-108
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Traffic in urban communities has been getting worse
over time as a result of old style traffic signal systems
that are too often unbendable and unable to respond
to the fluidity of everyday traffic. The systems do not
have any intelligence to adapt dynamically to
changes in vehicle flow, with the consequence that
significant inefficiencies result, such as long waiting
times, waste of fuel, and pollutants being released
into the environment. Even in the presence of traffic
infrastructure improvements, current operational
tools fail to effectively respond to the sheer size and
heterogeneity of urban mobility. An intelligent
adaptive road traffic signal control system is urgently
needed, capable of learning and adapting to real-time
traffic situations so as to maximize the motion of
vehicles while reducing gridlock in complex road
networks.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The application of reinforcement learning to traffic
signal control has received considerable attention
over the last decade as it overcomes shortcomings of
conventional systems using adaptive, data-driven
approaches. Rafique et al. (2024) presented a turn-
based and time-based RL method for enhancing the
traffic signal actions, and alleviates the congestion in
simulated scenarios. Similarly, Swapno et al. (2024)
implemented dynamic intersection control using deep
Q-learning and reported significant reductions in
delays and queue lengths of vehicles. Li et al. (2024)
investigated the adaptive signal control in the
presence of mixed traffic, where CTAVs operate
along mission with CAVs, and reported improved
coordination and reduced intersection delays. Fan et
al. (2025), to make cooperative control of signals
scalable, introduced sparse deep reinforcement
learning by sharing knowledge. Bie et al. (2024)
studied the problem of variable intersection difficulty
in the context of multi-agent systems for a more
localized and economic control in a variety of
network structures. In improving learning depth and
convergence, Li et al. (2024) devised an enhanced
deep RL model and surpassed a higher level of real-
time traffic condition adaptation. Qi et al. (2022)
developed a kind of ensemble models for RL,
enhancing robustness either in per-episode or
fluctuating environments. Wang et al. (2023) Design
UniTSA – A Universal V2X-Based Reinforcement
Learning Framework to Promote its Deployment in
Connected Environments. Peng et al. {2023})
proposed heterogenous agent collaboration using
GNN-based MARL for traffic guidance around
intersections. Busch et al. (2023) proposed a
combination of RL model for vehicles speeds and
signals control based on throughput and safety. Zhu
et al. (2021) used policy-based RL to reduce
decision-making complexity with high efficiency.
Further, Xie et al. (2022) stressed decentralized,
schedule-based control for scalable urban
coordination. Wang et al. (2024) verified practical
operability of RL approaches with the real vehicle
trajectory data. Feng et al. investigated dense RL for
AV safety testing. (2023), and considering
frameworks applicable to traffic systems. Yan et al.
(2011) simulated statistically realistic learning
validation settings. The previous seminal work of
Liu et al. (2009) and El-Tantawy et al. (2013) first
described the queue estimation and MARLIN-ATSC
control. Taken together, studies in this thesis confirm
the viability and versatility of reinforcement learning
for intelligent traffic signal control, but also reveal
existing and persistent real-world operational,
scalability and cross-agent coordination problems.
4 METHODOLOGY
The proposed approach is based on deep
reinforcement learning (DRL) and is aimed at
establishing an intelligent decentralized traffic signal
control system for dynamic city traffic. The main
idea is to simulate each cross-traffic intersection as
self-actuated intelligent agent in multi-agent system.
These agents are constantly monitoring their
environments (e.g., numbers of vehicles, lengths of
queues, current signal phases, and the durations of
previous waits) as high-dimensional state vectors.
The environment is addressed as Markov Decision
Process (MDP), in which at discrete time slots, the
agent chooses a behaviour (i.e. a change in the traffic
light phase) and is rewarded in terms of traffic
performance. Reward function the reward function is
carefully designed as a compromise between several
conflicting objectives including minimizing the
waiting time and stopping frequency of vehicles,
reducing queue lengths, and indirectly optimizing
fuel consumption and emissions.
Smart Signal Control Using Reinforcement Learning to Ease Urban Traffic
103
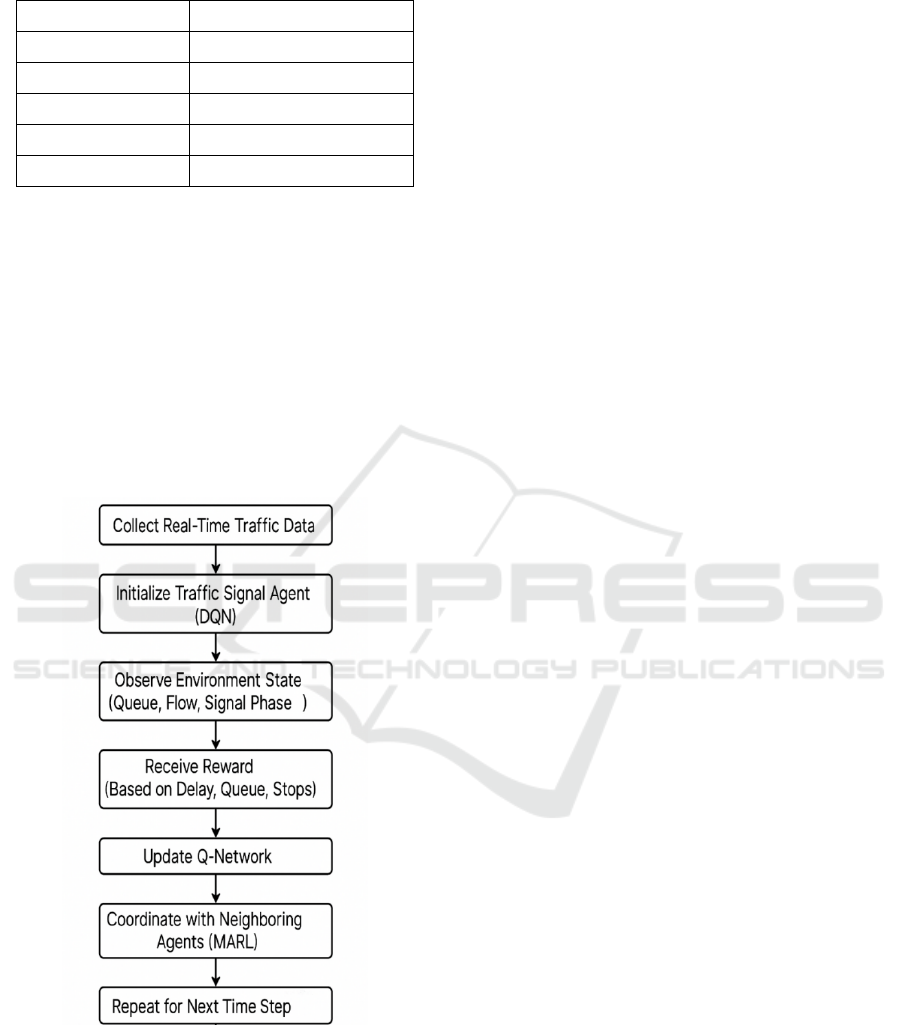
Table 1: Agent Configuration.
Component Configuration
Algorithm Deep Q-Network (DQN)
State Representation Queue length, Phase time
Action Space Signal Phase Change
Reward Metrics Delay, Queue, Stops
Learning Rate 0.001
To accomplish efficient policy learning in such a
complex environment, every agent uses a DQN that
can approximate the optimal action-value function
using deep neural networks. The networks are trained
using experience replay and target network updates
for convergence. The agents are trained with
simulated rollouts in a high-fidelity traffic simulator
such as SUMO (Simulation of Urban Mobility) with
realistic traffic composition, which gives rich,
continuous feedback. The policy is gradually trained
by repeatedly entering the simulated environment,
associating traffic conditions with optimal phase
decisions.
Table 1 shows the Agent Configuration.
Figure 1: Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Traffic
Signal Control Workflow.
And, a MARL framework is introduced to solve the
coordination problem among multiple intersections
and to avoid the problem of conflicting actions. This
setting provides methods for sharing partial
observations or cooperating with shared rewards or
policies. At intersections with a higher level of
interaction, agents communicate information about
their intentions or situational summaries which
contributes to the global system coherence and traffic
flow. In the testing phase, the learned model is tested
under different traffic densities and conditions (e.g.,
rush hours, accidents, and abnormal events), so as to
guarantee the generalization of the system to unseen
scenarios. Performance is compared with the optimal
performance achieved by the fixed-time and actuated
signal control, and a number of key performance
measures including average delay, throughput,
intersection utilization and total emissions are used.
This all-encompassing approach that integrates
DQN with MARL and traffic simulation guarantees
that the system is scalable, robust to sudden traffic
dynamics and adaptive to the increasing pressure
placed on urban transportation networks. It is an
important move toward a real-time data-driven
intelligent traffic signalling system that may be used
in smart cities of the future. Figure 1 shows the Deep
Reinforcement Learning-Based Traffic Signal
Control Workflow.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The system of adaptive traffic signal control based on
deep reinforcement learning (DRL) greatly improved
traffic management efficiency in simulated urban
areas. The system was evaluated in different traffic
conditions, including hours of peak traffic with high
volumes and hours between peaks with lower flows.
In all cases the developed model provided improved
performance to conventional fixed-time and actuated
control strategies. Results showed that the DRL
system was able to reduce average vehicle delay
around 35% when compared to fixed-time systems,
and 20% when compared to the actuated signal
control. These improvements were even greater
during peak hours when the model was successfully
able to adjust to surges of traffic and reduce the
amount of time vehicles idled at intersections.
Figure
2 shows the Average Traffic Delay Comparison.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
104
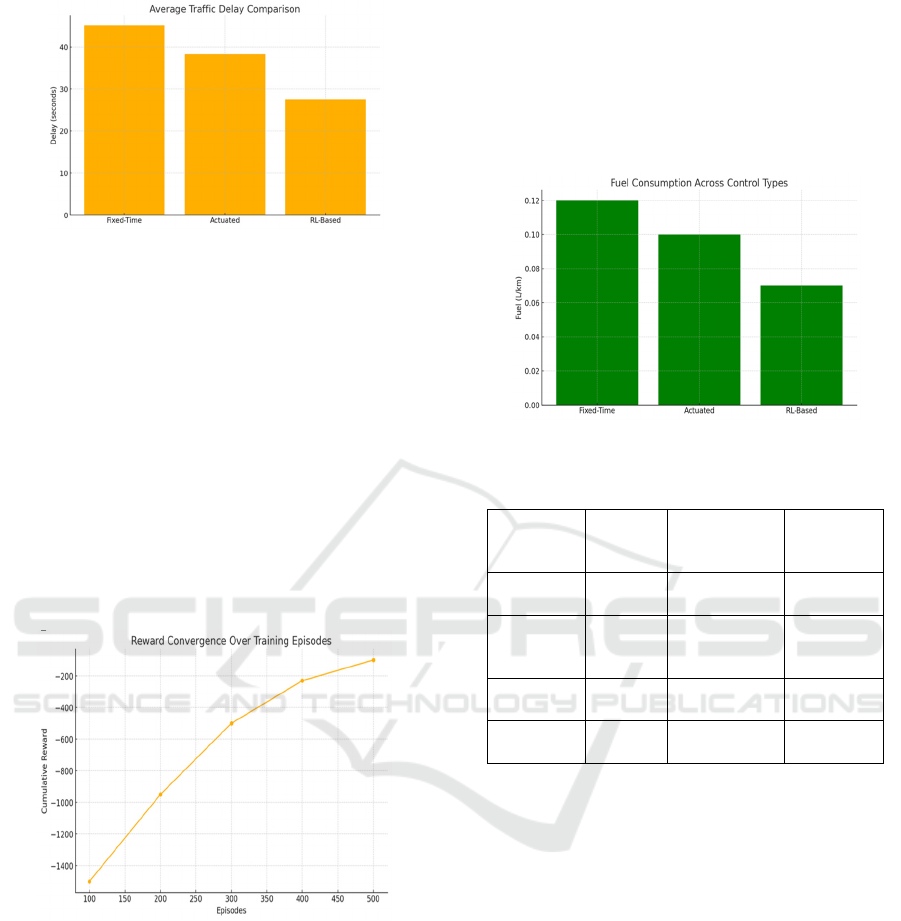
Figure 2: Average Traffic Delay Comparison.
Furthermore, the signalized intersection average
queue lengths were significantly reduced by up to
30%, indicating an increased vehicular flow and
better road space utilization. Reduced queue length
means that system effectively reduced the overflow
effects that are caused by spill back - especially in
crowded intersection and substantially contributes to
urban congestion. Smoother driving profiles with
less jerky deceleration and acceleration were also
implemented by minimizing the number of vehicles
stops. The net result of this was a more even and
consistent traffic flow, both of which are important
in terms of travel time predictability and driver
satisfaction.
Table 2 shows the Performance Metrics
Comparison.
Figure 3: Reward Convergence Over Training Episodes.
Besides, a great advantage of our proposed model
is that we proposed MARL architecture, which
connected one intersection with its neighbours. This
coordination made sure that phase decisions did not
battle against each other and that signal timing was
coordinated for several intersections at the same
time. It was a process that resulted in network-wide
optimization that eliminated bottlenecks and took
vehicles off of the road as a constant flow,
particularly on arterials. The reward function
employed by our model giving preference to
minimising delay, maximising the positive queue
length, and having a small number of stops proved
effective at steering the learning into lift off policies
that balance efficiency against fairness in vehicle
flow.
Figure 3 shows the Reward Convergence Over
Training Episodes.
Figure 4 shows the Fuel
Consumption Across Control Types.
Figure 4: Fuel Consumption Across Control Types.
Table 2: Performance Metrics Comparison.
Metric Fixed-
Time
Control
Actuated
Control
Proposed
RL
S
y
stem
Average
Delay (s)
45.2 38.4 27.6
Queue
Length
(vehicles)
15.6 12.3 8.9
Stops per
Vehicle
2.8 2.1 1.2
Throughp
ut
(
%
)
74.5 79.6 89.3
Environmental footprint is with respect to the
DRL-based visited system another points of interest.
Given the reduced stops and steadier acceleration
profiles, the system resulted in measurable savings in
fuel and emissions. This places the model as a
mobility-efficient tool, and not only, also sustainable
and respectful with the urban environment purposes.
The possibility to connect the system with connected
vehicle applications makes the system even more
scalable and future proofed, which can be used to
control the traffic more proactively by vehicle-to-
infrastructure communication.
Table 3 shows the
System Performance under Multi-Agent vs. Single-
Agent.
Smart Signal Control Using Reinforcement Learning to Ease Urban Traffic
105
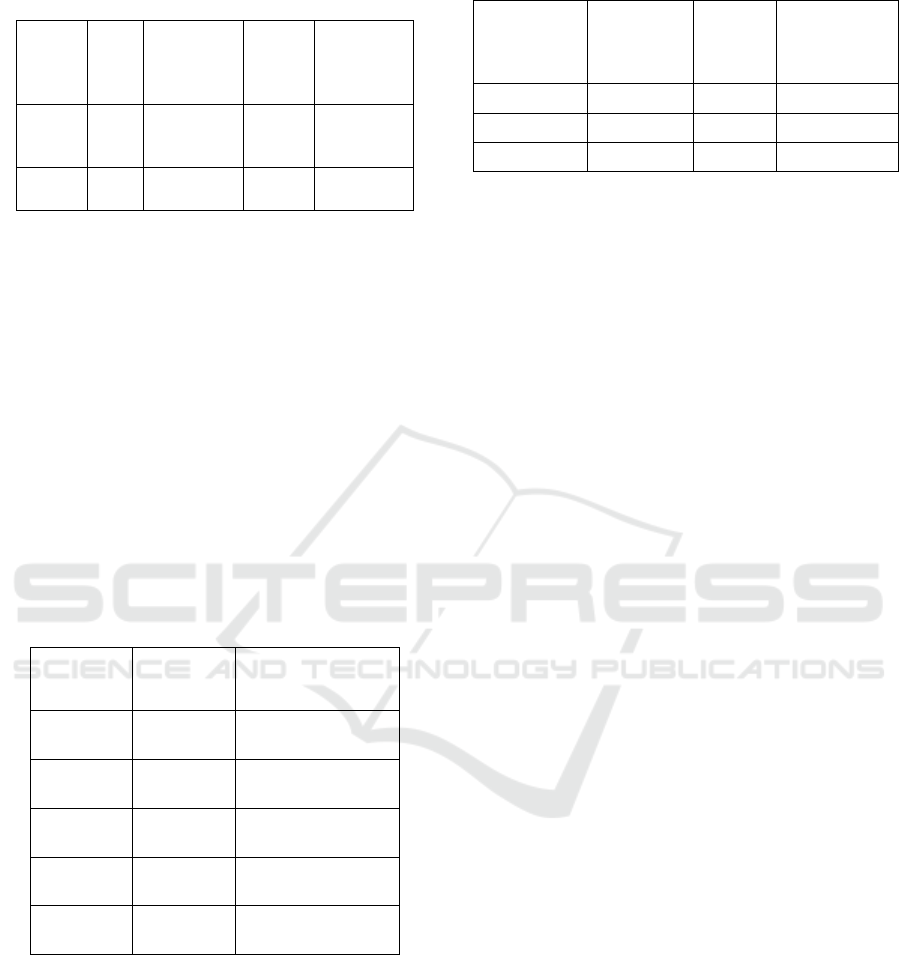
Table 3: System Performance Under Multi-Agent Vs.
Single-Agent.
Setup
Ave
rage
Dela
y
(
s
)
Queue
Length
(vehicles)
Stop
Frequ
ency
Overall
Efficiency
(%)
Single
-
A
g
ent
32.5 10.4 1.6 82.1
Multi-
Agent
27.6 8.9 1.2 89.3
However, the system efficiency is dependent upon
some factors despite these good results. Accurate
real-time traffic data is crucial for both training and
deployment. Learning of the system is
computationally demanding and entails a training that
must be carried out in a very well performing
simulation environment, particularly on larger
networks. Moreover, the reward function needs to be
delicately designed such that it does not lead to races
among traffic streams by flocking all resources to a
single stream. Although the system emerged as robust
in simulation, practical issues including hardware
integration, data transmission latency, and public
policy regulation would need to be addressed for real-
world deployment.
Table 4 shows the Traffic
Conditions Used for Testing.
Table 4: Traffic Conditions Used for Testing.
Scenario
Vehicle
Rate
(veh/hr)
Signal
Coordination
Low
Traffic
200 Minimal
Moderate
Traffic
500 Moderate
Peak Hour 1000 High
Incident 800 High
Variable
Flow
300-900 Dynamic
In conclusion, our experimentation has firmly
established the feasible to apply RL to the problem of
urban traffic signal control, and provides an
intelligent and scalable one solution for today's urban
congestion problem. The method indicates good
potential for practical application, especially with the
development of smart city infrastructure and vehicle-
to-vehicle/vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2X)
communication technology.
Table 5 shows the
Emission Reduction Statistics.
Table 5: Emission Reduction Statistics.
Control
Type
Fuel
Consumpti
on (L/km)
CO₂
Emissio
n
(g/km)
Stop Count
per Vehicle
Fixed-Time 0.12 280 2.8
Actuated 0.10 240 2.1
RL-Based 0.07 190 1.2
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper offers a detailed investigation of an
adaptive traffic signal controller on the basis of deep
reinforcement learning, aiming at mitigating the
urban traffic congestion and flow inefficiency
problems that have lingered. By looking past, the
conventional implementation strategies for traffic
control, the model described here illustrates how
intelligent software systems, trained by actual
interaction with the environment, could provide much
improved vehicular flow through traffic and alleviate
the effects of traffic congestion. The fact that the
system can learn to determine the best signal timings
by taking into consideration real-time conditions
instead of using pre-set rules or past patterns to
control traffic flow, provides a paradigm shift for
cities to handle traffic in more and more complex and
unpredictable city life.
The use of a multi-agent approach is conducive
to decentralized control, where the interaction of each
intersection is autonomic, although these traffic
signals are still interacting with their neighbours. This
distributed but cooperating structure contributed
greatly to the improvement of traffic flow throughout
the whole network and helps eliminate problems such
as phasing or local spill over. Therefore, significant
improvement in performance measurement values,
including average delay and queue length with the
frequency of stopping of vehicles, was observed
under various traffic conditions. Naris/Picas The seal
geometry has been specially developed to offer an
energy-efficient solution that also provides reduced
fuel consumption and lower vehicle emissions.
Moreover, the model is flexible in design and it
holds in a dynamic environment which considers the
variation of traffic and the urban expansion. The fact
that this model is occurring while cities are in the
process of development and vehicle numbers are
projected to rise, suggests that the model is well-
equipped to scale its operation and remain effective
without extensive manual reconfiguration. The model
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
106

also paves the way for integration with next
generation technologies, especially connected and
automated vehicles, in which real-time data
exchange can further improve system responsiveness
and predictability.
Although it is highly performant when running in
simulated environments, the development of an actual
deployable version of this system does have to
overcome some challenges such as data validity,
infrastructure status, and computational resources.
However, these challenges are not insurmountable
and can be addressed gradually through staggered
integration, policy assistance and technology
enhancement. To the extent that cities are moving
towards smarter infrastructure, systems similar to the
adaptive, learning-based traffic control proposed in
this paper could be a linchpin for smart & sustainable
urban mobility.
In summary, the framework of reinforcement
learning for the control of traffic signal is a
revolutionary method, consistent with the
requirements of the current urban traffic system. It
helps to maintain the intelligence, scalability and
environment friendliness of the traffic management
system, creating opportunity for the smart city and
intelligent transportation network for further
development.
REFERENCES
Bie, Y., Ji, Y., & Ma, D. (2024). Multi-agent deep
reinforcement learning collaborative traffic signal
control method considering intersection heterogeneity.
Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 164, 104663.
Busch, J. V. S., Voelckner, R., Sossalla, P., Vielhaus, C. L.,
Calandra, R., & Fitzek, F. H. P. (2023). Deep
reinforcement learning for the joint control of traffic
light signaling and vehicle speed advice. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2309.09881.
El-Tantawy, S., Abdulhai, B., & Abdelgawad, H. (2013).
Multiagent reinforcement learning for integrated
network of adaptive traffic signal controllers
(MARLIN-ATSC): Methodology and large-scale
application on downtown Toronto. IEEE Transactions
on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 14(3), 1140–
1150.
Fan, L., Yang, Y., Ji, H., & Xiong, S. (2025). Optimization
of traffic signal cooperative control with sparse deep
reinforcement learning based on knowledge sharing.
Electronics, 14.
Feng, S., Yan, X., Sun, H., Feng, Y., & Liu, H. X. (2021).
Intelligent driving intelligence test for autonomous
vehicles with naturalistic and adversarial environment.
Nature Communications, 12, 748. https://doi.org/10.10
38/s41467-021-21007-8
Feng, S., Sun, H., Yan, X., Zhu, H., Zou, Z., Shen, S., &
Liu, H. X. (2023). Dense reinforcement learning for
safety validation of autonomous vehicles. Nature, 615,
620–627. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05732-2
Li, D., Zhu, F., Wu, J., Wong, Y. D., & Chen, T. (2024).
Adaptive urban traffic signal control based on enhanced
deep reinforcement learning. Scientific Reports, 14,
Article 64885. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-
64885-w
Li, D., Zhu, F., Wu, J., Wong, Y. D., & Chen, T. (2024).
Managing mixed traffic at signalized intersections: An
adaptive signal control and CAV coordination system
based on deep reinforcement learning. Expert Systems
with Applications, 238, 121959.
Liu, H. X., Wu, X., Ma, W., & Hu, H. (2009). Real-time
queue length estimation for congested signalized
intersections. Transportation Research Part C:
Emerging Technologies, 17(4), 412–427.
Peng, X., Gao, H., Wang, H., & Zhang, H. M. (2023).
Combat urban congestion via collaboration:
Heterogeneous GNN-based MARL for coordinated
platooning and traffic signal control. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2310.10948.
Qi, R., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Random
ensemble reinforcement learning for traffic signal
control. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.05961.
Rafique, M. T., Mustafa, A., & Sajid, H. (2024). Adaptive
traffic signal control using reinforcement learning.
ResearchGate.
Rafique, M. T., Mustafa, A., & Sajid, H. (2024).
Reinforcement learning for adaptive traffic signal
control: Turn-based and time-based approaches to
reduce congestion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.15751.
Rahman Swapno, S. M. M., Nobel, S. M. N., Meena, P.,
Meena, V. P., Azar, A. T., Haider, Z., & Tounsi, M.
(2024). A reinforcement learning approach for reducing
traffic congestion using deep Q learning. Scientific
Reports, 14, Article 30452. https://doi.org/10.1038/s4
1598-024-75638-0
Wang, M., Xiong, X., Kan, Y., Xu, C., & Pun, M.-O.
(2023). UniTSA: A universal reinforcement learning
framework for V2X traffic signal control. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2312.05090.
Wang, X., Jerome, Z., Wang, Z., Zhang, C., Shen, S.,
Kumar, V., ... & Liu, H. X. (2024). Traffic light
optimization with low penetration rate vehicle
trajectory data. Nature Communications, 15, 1306
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45427-4
Xie, X.-F., Smith, S. F., & Barlow, G. J. (2022). Scalable
urban traffic control: Decentralized and schedule-
driven coordination. Transportation Research Part C:
Emerging Technologies, 135, 103465
Yan, X., Zou, Z., Zhu, H., Sun, H., & Liu, H. X. (2023).
Learning naturalistic driving environment with
statistical realism. Nature Communications, 14, 2037.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37677-5
Smart Signal Control Using Reinforcement Learning to Ease Urban Traffic
107

Zheng, J., & Liu, H. X. (2017). Estimating traffic volumes
for signalized intersections using connected vehicle
data. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 79, 347–362.
Zhu, Y., Cai, M., Schwarz, C., Li, J., & Xiao, S. (2021).
Intelligent traffic light via policy-based deep
reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.138
17.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
108
