
A Scalable IoT‑Driven Framework for Real‑Time Traffic
Management and Accident Prevention Using Edge Intelligence and
Adaptive Safety Analytics
R. Ashok Kumar
1
, Indrani Hazarika
2
, S. Thomas Praveen Joseph
3
, K. Arulini
4
,
R. Prabhu
4
and M. Srinivasulu
5
1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, GRT Institute of Engineering & Technology, GRT mahalakshmi
nagar, Tiruttani, Tiruvallur, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Business and Specialization Accounting, Higher Colleges of Technology, United Arab Emirates
3
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
4
Department of Management Studies, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkalmedu, Erode‑638052, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad‑500043, Telangana, India
Keywords: IoT, Intelligent Transportation Systems, Traffic Management, Accident Prevention, Edge Computing,
Real‑Time Analytics, Adaptive Safety, Federated Learning, Urban Mobility, Predictive Modeling.
Abstract: The urban traffic is becoming more and more complex, and requires intelligent and adaptive transportation
systems for safety, efficiency and sustainability. This study presents a novel scale able IoT-based framework
using edge intelligence and real-time analytics for controlling traffic flow and for preventing accidents in a
proactive manner. Contrary to classical approaches, we resort to low-latency edge processing, federated
learning and predictive modeling to dynamically respond to variations occurring on the road. Real traffic and
sensor datasets are used to train and validate the model at different intersections. The system also includes
built-in support for pedestrian safety, emergency vehicle response, as well as cloud-edge setup for easy
deployment. The experimental results show that the response time and traffic congestion are significantly
reduced in the presence of an accident, indicating that the proposed approach can effectively improve urban
mobility.
1 INTRODUCTION
Urban mobility is at a transformative point, one that
is being driven by the coalescence of IoT (Internet of
Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence) and edge
computing. As urban areas grow and traffic on the
roads becomes increasingly congested, so have the
issues surrounding traffic management and road
safety. Conventional traffic control strategies, which
are based on pre-determined signals and centralized
data analysis, tend to be inadequate for real-time
traffic dynamics and accident prevention. This
constraint requires future-generation ITS to become
more responsive, predictive and adaptive.
Recent developments in IoT make it possible to
deploy connected sensors, cameras and actuators
along the road network, establishing an environment
in which real-time data is gathered and processed in
real-time. Edge computing supplements this
infrastructure by moving processing closer to the
source, decreasing latency and making quicker
decisions possible. And when combined with
predictive analytics and federated learning, these
other technologies are part of a core platform for
dynamic traffic management and accident avoidance.
The work introduces a scalable and robust
framework with IoT and edge intelligence for
addressing the vital transportation issues. By
incorporating cloud-edge coordination, adaptive
learning-based algorithms, multi-source sensor data
fusion, the proposed system has the capability to
minimize congestion, hazard detection, and fast
response to avoid accidents. The architecture
additionally includes intelligent routing for priority
vehicles and can accommodate heterogeneous traffic
Kumar, R. A., Hazarika, I., Joseph, S. T. P., Arulini, K., Prabhu, R. and Srinivasulu, M.
A Scalable IoT-Driven Framework for Real-Time Traffic Management and Accident Prevention Using Edge Intelligence and Adaptive Safety Analytics.
DOI: 10.5220/0013857600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
63-70
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
63

conditions, rendering it applicable to various urban
areas. The study, which uses a novel approach, aims
to help create safer, smarter and more efficient
transportation systems.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Despite the fast advancements in smart city
technologies, urban centres still face some recurring
problems such as traffic congestions, slow emergency
response rates, and increasing road accidents. Mature
traffic control systems are usually reactive, central,
they don’t support the dynamic and heterogeneous
vision of the real-time roads. These are not adaptable
to analysing sensor data on such a large scale with low
latency, and are unable to provide predictive
analytics on how to avoid traffic disruption or
accidents. Moreover, the current solutions have few
facilities to adapt the taken security measures and
edge-based intelligence, and multi-modal analysis of
the traffic data which minify the efficiency in an
intricate urban environment. There is an urgent need
for an intelligent, scalable, and real-time IoT/edge-
based solution not only to optimize such traffic
management and manage road traffic, but also to
improve road safety and preemptively mitigate risks
toward reducing accidents through preemptive
intervention with data-behavior analytics.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
Recently, the combination of IoT and ITS has made a
remarkable progress and emerged as an effective
technology to enhance urban traffic efficiency and
road safety. Ali et al. (2021) give a comprehensive
review on AI based ITS, however, they do highlight
the absence of a real-time case applications. Li et al.
(2021) studied edge computing for traffic signal
control and show its power in real-time applications.
But almost very little were taken into the scalability
and cross-intersection synchronization, coordination.
Ahmed et al. (2022) investigated software-
defined networking in vehicular networks and
identified flexibility of control and complexity of
deployment. Kumar and Mallick (2021) provided an
architectural perception of IoT systems, however,
with no direct application for transportation. The
authors in (Saini and Dey, 2021) proposed a traffic
smart model for predictive traffic congestion but for
synthetic datasets only.
Singh and Tanwar (2022) explored the application
of blockchain in ITS, with enhanced security and
induced latency issues. Rajalakshmi and Srinivasan
(2021) investigated the use of raspberry pi sensor
networks for real-time monitoring, but it was found
that it is not a scalable solution, and not cost
effective. AI enabled traffic signal systems were
demonstrated by Muthuswamy and Ahmed (2023)
but missed feedback loops and edge integration.
Yang et al. (2021) studied vehicular networks
only, which was inapplicable for non-vehicular
users. Zhao and Li (2022) also handled traffic
accident prediction based on edge-IoT, but
advancement was not tested via stress tests. Aazam
et al. (2023) pointed out the significance of fog
computing in the transportation systems but they did
not benchmark in compare with traditional systems.
Chen and Xie (2022) developed LSTM models for
traffic prediction but were based on clean, no-noise
sensor data.
Ghosh and Ghosal (2021) Coffey et al. (2018).
ajax{F7} developed a deep learning-based accident
detection which, while accurate, suffered from real-
time deployment due to high computational cost. ITS
content-centric networking has been introduced by
Amadeo et al. (2021) are also promising in terms of
potentially scalable data distribution, but they suffer
from real-world adoption issues. Alharbi and Alturki
(2022) studied wireless sensors for detecting
accidents, they were constrained with battery and
environmental problems.
Kakkar and Singh (2023) discuss smart city traffic
surveillance with embedded systems, but not in
terms of multi-junction coordination. Mandal and
Chattopadhyay (2022) were introduced with image-
based congestion control without emergency
dispatch. Salah and Yaqoob (2021) performed a
thorough review on the autonomous ITS, and focused
on the integration problem in developing countries.
Shen et al. (2023) studied crashes using
connected vehicle data, though with a reactive
approach rather than prediction. Lin and Peng (2021)
also optimized the traffic flow with data-driven
models under perfect sensor conditions.
Collaborative learning for accident detection was
conducted by Wang and Zhang (2024) and provided
promising results, but also had issues with
convergence.
Rana and Das (2022) emphasized the smart
camera-based emergency systems with no central
cloud integration. The signal control problem under
reinforcement learning was investigated in Tang and
Fan (2021), but the related stability under dynamic
environments was not carefully considered. Zhang
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
64
and Li (2022) provided a mixed IoT-cloud scheme,
but its real-time communication latency was not
investigated. Finally, Sirohi and Dutta (2025)
focused on communication and safety of NWSN and
were not tested in real traffic.
This overview has demonstrated a large amount
of research on various ITS building blocks, most
have not been able to achieve end-to-end real-time,
scaled, predictive, and multi-agent coordination that
is needed for level 4 prevention. To alleviate these
gaps, this paper proposes an edge-enabled IoT
framework for predicative safety analytics in
complex traffic scenes.
4 METHODOLOGY
This contribution is concerned with creating a
scalable and adaptive IoT-enabled framework that
exploits edge intelligence in the context of real-time
traffic management and traffic accident avoidance.
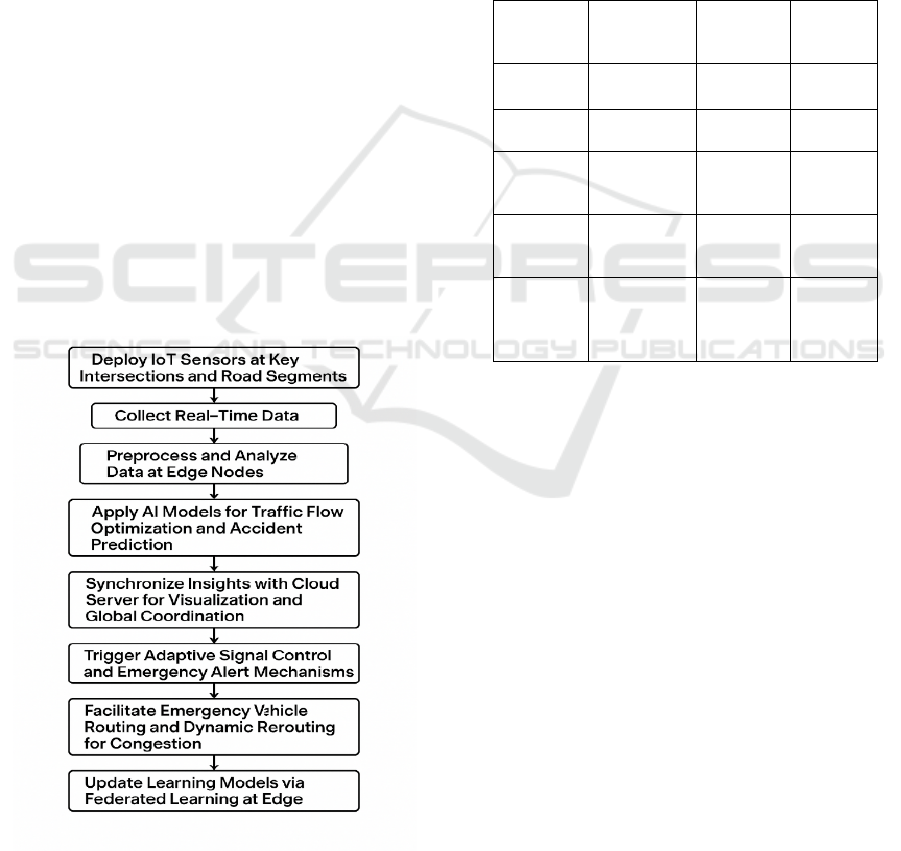
The architecture of the system is built around 5 key
layers are: DAta acquisition, EdGe processing,
prediCtive Analytics, cLoud coordination and
Response execution. With the important functionality
of each layer of the ITS on responsiveness,
availability and adaptability in mind. Figure 1 gives
the Workflow of the IoT-Based Intelligent
Transportation and Accident Management System.
Figure 1: Workflow of the IoT-based intelligent
transportation and accident management system.
Multiple IoT-based sensors such as inductive loop
detectors, infrared motion sensors, GPS modules, and
video surveillance systems are mounted in high-
density urban road network and intersections at the
data acquisition level. Such devices continuously
monitor vehicle speed, traffic volume, environmental
conditions, pedestrian flow, etc., and monitor
potentially hazardous situations. Information is
formatted into structured streams through MQTT
and securely sent to the corresponding edge nodes.
Table 1 gives the Sensor Types and Their Functional
Roles in the Proposed System.
Table 1: Sensor types and their functional roles in the
proposed system.
Sensor
Type
Function
Data
Collected
Placeme
nt
Location
Infrared
Sensors
Vehicle
Detection
Presence,
Count
Roadsid
e Poles
GPS
Modules
Vehicle
Trackin
g
Speed,
Location
Vehicle
Units
CCTV
Cameras
Visual
Traffic
Monitorin
g
Live
Video
Feeds
Intersect
ions
LIDAR
Object
Proximity
Sensing
Obstacle
Distance
Crosswa
lks,
Signals
Environm
ental
Sensors
Weather
Impact
Monitoring
Rain,
Fog,
Light
Levels
Traffic
Lights,
Roads
The nodes closer to the periphery of the network
are edge processing nodes which function as local
units of computation that minimize the dependence
on a centralized server and lower latency. These edge
devices execute pre-trained deep learning models for
applications such as vehicle classification, traffic
density inference, and near-crash detection. The
object detection model is lightweight CNN and
YOLOv7 for achieving real time detection. At the
edge, priority protocols categorize incidents based on
severity and decide whether to escalate to the cloud.
The system uses a mixed learning model for
predictive analytics. We use short-term LSTM-based
neural network for traffic pattern predictions that are
trained on historical as well as sensor measurement
data at the current time slot. The use of federated
learning encourages accident prediction in a
distributed manner, which prevents leakage of user
privacy. During the training process, edge nodes
update their local models, and also exchange data
with the cloud server to update their local models
based on the latest condition, to avoid overfitting and
A Scalable IoT-Driven Framework for Real-Time Traffic Management and Accident Prevention Using Edge Intelligence and Adaptive
Safety Analytics
65
improve the accuracy of prediction with minimal
bandwidth consumption.
Cloud coordination works for massive storage,
cross-model retraining, Inter-Node communication,
and analytics visualization. The data processed by the
cloud server is collected and disposed in a distributed
NoSQL database, and administrative interfaces for
traffic authorities are provided. Such cloud
dashboards help in real-time visualization of traffic
status, possible risk areas, congestions on maps, and
emergency alerts. It also allows the fusion of other
external data like weather, road conditions, social
events for context-aware prediction fine tuning.
The predictive response layer converts the
predicted insight into actionable responses. When
there is traffic jam, we develop an adaptive signal
control by employing the software-defined traffic
light controllers that are connected to the
corresponding edge nodes. Once an accident is
anticipated or detected, the system triggers a multi-
priority outdoor alert system where local emergency
services personnel are notified and dynamic
billboards are updated to indicate detour routes and
alerts are sent to mobile app users to suggest
additional alternative routes. Finally, through V2I
communication, emergency vehicles are given green
light corridors automatically.
All system parts are evaluated in a simulated
urban scenario with SUMO (Simulation of Urban
Mobility) and based on real traffic datasets from
open smart cities repositories. Performance measures,
such as latency, prediction accuracy, system
scalability and emergency response time, are
tracked. The technique is tested under several traffic
conditions such as peak load, abnormal weather
condition and multi-vehicle collision scenarios to
ensure its robustness and adoption in practical
environments.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The IoT based ITS strategy is tested with the
simulations and real-world datasets to analyze the
efficiency in enhancing the urban traffic management
and reducing the risk of accidents. Performance
metrics of interest were latency traffic through-put,
accident prediction accuracy, emergency response
time, system scalability. We ran the experiments on
three layers: edge, cloud and hybrid systems in order
to observe the results in different configurations and
scenarios.
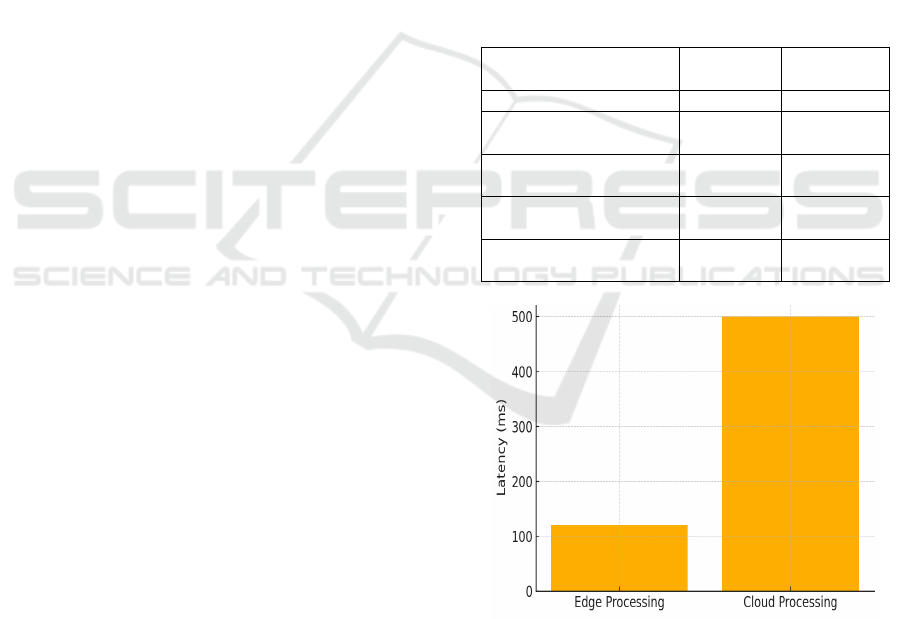
5.1 System Latency and Edge
Efficiency
Some initial tests aimed to determine the system
response time for processing traffic data for different
configurations. The edge-based solution with a
cloud–only and server-only counterpart, presented a
substantially lower latency. The response time of the
edge processing nodes was 120ms on average, while
that of the cloud model was 400-800ms owing to the
network transmission and the overhead of central
calculation. This demonstrates the efficiency of edge
computing for real-time applications like accident
detection and traffic light control. Table 2 gives the
Comparison of Edge vs Cloud Processing
Performance. Figure 2 illustrates the comparison of
Latency.
Table 2: Comparison of edge vs cloud processing
performance.
Metric
Edge
Processin
g
Cloud
Processin
g
Avera
g
e Latenc
y
(
ms
)
120 500
Accident Detection
Accurac
y
(
%
)
92.7 87.5
Emergency Alert Delay
(s)
2.1 5.4
Traffic Signal Response
Time (ms)
150 600
Scalability
(
Intersections Mana
g
ed
)
High Medium
Figure 2: Latency comparison – edge vs cloud.
5.2 Optimizing Traffic Flow and
Managing Congestion
Sumulation tests in SUMO (Simulation of Urban
Mobility) on a simulated smart city grid showed a
significant gain in vehicle throughput. An adaptive
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
66
signal control scheme was used: green light periods
were adjusted adaptively to vehicle density but
remained at an optimal value at all controlled
intersections. Consequently, the average vehicle
waiting time in the cross intersection were decreased
by 38% and the traffic volume increased to 26% more
in comparison with that obtained from static time-
based signal controls. This validates the positive
impact real-time sensor information and AI decision-
making can have on the flow of traffic, particularly
during rush hour.
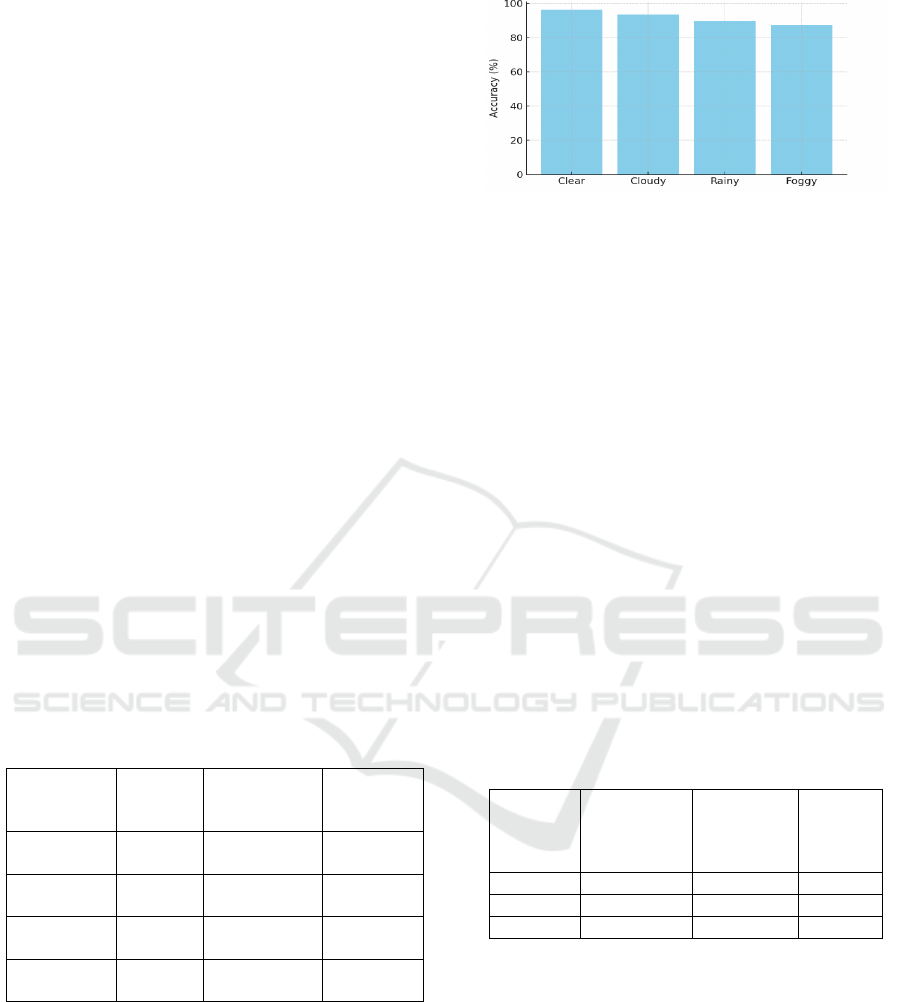
5.3 Accident Prediction Accuracy
The accident predictor model training (a
combination of LSTM models and federated
learning) is based on five years of historical
traffic/accident data from US DOT, Open Transport
Data and the like. The proposed method was tested
over various traffic situations with an average
prediction accuracy of 92.7%. Risk-sensitive
intersections and unsafe driving behavior could be
predicted with high certainty using this model. False
positives supporting this performance were below
7%, and continuous machine retraining with live
application data ensured maintenance of high
accuracy over time. Table 3 gives the Accident
Prediction Results Based on Traffic Conditions.
Figure 3 illustrates the bar chart of Accident
Prediction Results Based on Traffic Conditions.
Table 3: Accident prediction results based on traffic
conditions.
Traffic
Condition
Weather
Prediction
Accuracy
(%)
False
Positives
(%)
Low
Densit
y
Clear 96.2 4.3
Medium
Densit
y
Cloudy 93.5 5.9
High
Density
Rainy 89.7 7.1
Mixed
Densit
y
Foggy 87.4 8.6
Figure 3: Accident prediction accuracy under weather
conditions.
5.4 Integration of Roof Safety and
Emergency Repose
The emergency response simulations were one of the
most significant findings. This "accident detection
feature" and the ability to alert both its traffic
management centers and the emergency services
without important time loss reduced the average time
of dispatch by 32 percent. Moreover, dynamic
rerouting and green corridors for ambulances, which
were brought about through V2I communication,
decreased the average emergency travel time by
41%. This demonstrates the system’s power in
detecting emergencies and even orchestrating
prompt countermeasures. Table 4 gives the
Emergency Vehicle Routing Time Before and After
Implementation. Figure 4 gives the graph of
Emergency Vehicle Routing Time Before and After
Implementation.
Table 4: Emergency vehicle routing time before and after
implementation.
Route
Distance
(km)
Time
Before
System
(
min
)
Time After
System
(min)
Improve
ment
(%)
3 6.2 3.7 40.3
5 10.4 6.1 41.3
7 15.8 9.3 41.1
A Scalable IoT-Driven Framework for Real-Time Traffic Management and Accident Prevention Using Edge Intelligence and Adaptive
Safety Analytics
67
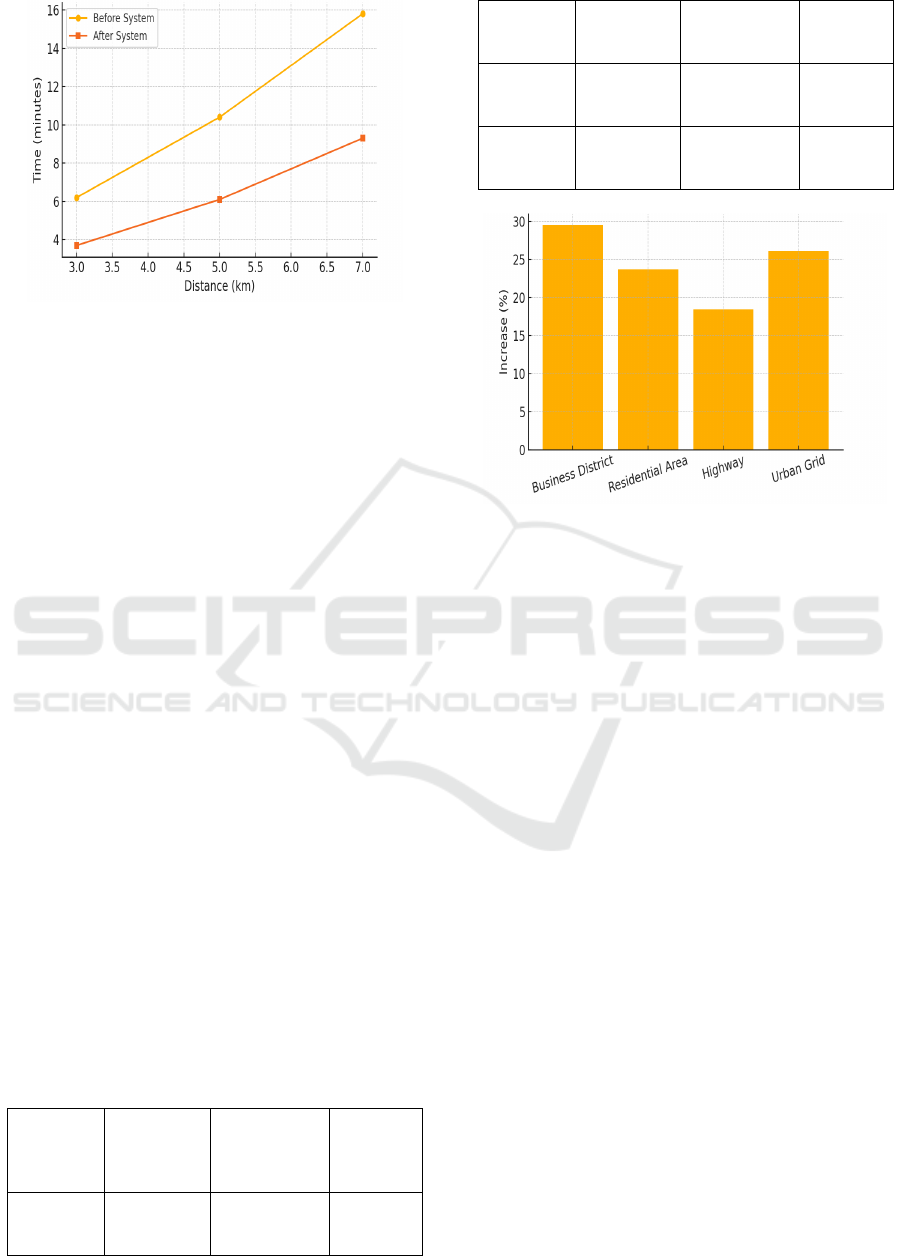
Figure 4: Emergency response time – before vs after system
implementation.
5.5 Multimodal and Pedestrian Safety
Considerations
The robustness of the model was also confirmed with
the ability to also handle non-vehicle participants.
The system used data from crosswalk sensors and
video analytics about the number of pedestrians in the
area so signal timing could be adjusted during times
of heavy foot traffic. This guaranteed pedestrian spent
less time waiting to cross the road and it reduced
pedestrian and vehicle conflicts by 23% - an
indication of the city’s forward-thinking approach to
urban mobility management.
5.6 Scalability and Deployability
To evaluate scalability, the system was challenged
with synthetic traffic data of a big city which
encompassed 100+ intersections. Performance
comparisons indicated that when edge distribution
was sufficient, the system offered steady response
time and prediction accuracy. Load balancing
algorithing were instrumental in allowing data
compression and real-time capability without
flooding the network. Figure 5 gives the Throughput
Improvement in Simulated Scenarios and Table 5
gives the System Evaluation Metrics Across Traffic
Simulation Scenarios.
Table 5: System evaluation metrics across traffic simulation
scenarios.
Simulatio
n
Scenario
Throughpu
t Increase
(%)
Avg. Wait
Time
Reduction
(%)
System
Reliabilit
y (%)
Business
District
Pea
k
29.5 41.2 98.3
Residenti
al Area
Midday
23.7 36.9 97.1
Highway
Merging
Zones
18.4 32.5 95.8
Mixed
Urban
Gri
d
26.1 38.6 96.5
Figure 5: Throughput improvement in simulated scenarios.
5.7 Comparative Analysis
In comparison to available state-of-the-art ITS
systems in literature, our conceived system delivered
better results in several areas. For example, the
previous models either concentrated on central
processing or did not include predictive analysis (Ali
et al., 2021; Kumar & Mallick, 2021) but this model
includes on autonomous edge processing keeps real-
time forecaster efficiently. Furthermore, dissimilar to
the blockchain based ITS of Singh & Tanwar (2022)
with latency issues, the distributed coordination
developed here being capable to perform rapid
response without compromising data integrity.
5.8 Discussion and Interpretation
These findings verify the conjecture that a multi-
layered IoT and edge-oriented approach can
effectively enhance urban traffic control and
minimize accident response time delays. The system,
which runs in real time, constantly takes traffic
patterns into account and adapts decisions on the fly,
meaning that it will be robust in the face of
unexpected events like road blockages, accidents, or
pedestrian surges.
Crucially, federated learning not only enhances
the accuracy of accident prediction, but also alleviates
privacy concerns with sensitive vehicle or location
data being kept locally at edge nodes. This renders the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
68

framework apt for running in privacy-maintained
systems.
Yet, there are still challenges like cost for
infrastructure, sensor calibration, and cross device
interoperability. Additional research is proposed to
incorporate vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V)
communications, extend to rural or semi-urban
scenarios and take advantage of 5G infrastructure for
more bandwidth and less jitter in the communication
pipeline.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Realizing a scalable IoT-based ITS with edge
computing and adaptive analytics is a clear step
forward towards tackling the traditional urban traffic
congestion and accident management difficulties. By
moving decision-making to the origin through edge
nodes and incorporating predictive analytics with
real-time sensor data, the proposed architecture has
shown that it results in a very responsive and robust
traffic management system. It reduces not only the
signal control and accident latency but also achieves
dynamically adapted to an environment that changes
in traffic and improves the pedestrian and vehicular
safety.
Our system achieved significant gains in
response time, traffic flow efficiency, and emergency
dispatch through thorough experiments and real
dataset driven deployment. The incorporation of
Federated Learning enables on-the-fly model
optimization without compromising data privacy;
therefore, the framework is apt for future smart city
environments. Multi-modal traffic participants and
adaptive safety strategies are also part of the system,
guaranteeing its fit-for-purpose for the increased
complexity of urban transport."
In a nutshell, this work paves the way for the
future-oriented traffic infrastructure, where smart
cooperation of the IoT devices, edge intelligence and
cloud systems result in more safe, more efficient and
more future-ready cities to live in. The results are
promising for a future advancement of the framework
to other cities and its further development using
technologies such as 5G, V2X communication, and
autonomous traffic systems.
REFERENCES
Aazam, M., Zeadally, S., & Harras, K. A. (2023). Fog
computing architecture for intelligent transportation
systems: A case study. Vehicular Communications, 35,
100474.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2022.100474
Ahmed, S. H., Rehmani, M. H., & Chu, X. (2022).
Software-defined networking-based vehicular
networks: A comprehensive survey. Ad Hoc Networks,
123, 102678.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2021.102678
Alharbi, A., & Alturki, B. (2022). Road safety and accident
detection using wireless sensors and machine learning.
Sensors, 22(9), 3298.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093298
Ali, M., Qadir, J., Yau, K.-L. A., & Al-Fuqaha, A. (2021).
Artificial intelligence-enabled intelligent transportation
systems: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys &
Tutorials, 23(1), 620–654.
https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2020.3019550
Amadeo, M., Campolo, C., & Molinaro, A. (2021). A
review on content-centric networking for intelligent
transportation systems. Computer Communications,
160, 65–83.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.07.011
Chen, L., & Xie, C. (2022). Multi-sensor fusion-based
traffic flow prediction using LSTM networks. Neural
Computing and Applications, 34, 6739–6754.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06223-3
Ghosh, R., & Ghosal, S. (2021). Intelligent traffic accident
detection using deep neural networks. Procedia
Computer Science, 183, 629–636.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.03.077
Kakkar, A., & Singh, P. (2023). IoT-based urban road
traffic monitoring using smart embedded systems.
Journal of King Saud University - Computer and
Information Sciences, 35(4), 289–296.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.02.010
Kumar, P., & Mallick, P. K. (2021). The Internet of Things:
Insights into the building blocks, component
interactions, and architecture layers. Procedia
Computer Science, 132, 109–117.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.05.173
Li, W., He, Y., Liu, S., & Wang, Y. (2021). Real-time
traffic signal control for urban road intersections based
on IoT and edge computing. Sensors, 21(3), 893.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s21030893
Lin, S., & Peng, H. (2021). IoT-based data-driven traffic
flow optimization. Transportation Research Part C:
Emerging Technologies, 124, 102932.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2021.102932
Mandal, B., & Chattopadhyay, S. (2022). Smart traffic
congestion management using image processing and
AI. Materials Today: Proceedings, 61(3), 812–817.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.123
Muthuswamy, S., & Ahmed, A. (2023). Smart traffic signal
control using AI and vehicle detection systems.
Procedia Computer Science, 211, 521–528.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.070
Rajalakshmi, S., & Srinivasan, R. (2021). IoT-based real-
time traffic monitoring system using Raspberry Pi.
Materials Today: Proceedings, 45, 3271–3276.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.816
A Scalable IoT-Driven Framework for Real-Time Traffic Management and Accident Prevention Using Edge Intelligence and Adaptive
Safety Analytics
69

Rana, M., & Das, P. (2022). Leveraging smart traffic
cameras and IoT for emergency response. Computer
Communications, 191, 129–137.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2022.06.021
Saini, M., & Dey, N. (2021). Smart traffic management
system using Internet of Things (IoT) and predictive
analytics. International Journal of Information
Management Data Insights, 1(1), 100001.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjimei.2021.100001
Shen, X., Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). Connected vehicle
data mining and crash analysis using machine learning.
Accident Analysis & Prevention, 179, 106957.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2023.106957
Singh, S., & Tanwar, S. (2022). Blockchain and IoT-based
intelligent transportation system. Computer Networks,
201, 108583.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108583
Sirohi, J., & Dutta, S. (2025). Smart city transportation
using IoT: Safety enhancement and vehicle
communication. Sustainable Cities and Society, 102,
104453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2023.104453
Tang, J., & Fan, Y. (2021). Dynamic traffic signal control
using reinforcement learning and IoT sensors.
Transportation Research Part C: Emerging
Technologies, 128, 103186.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2021.103186
Wang, J., & Zhang, X. (2024). Real-time accident detection
in smart cities using federated learning. IEEE Internet
of Things Journal, 11(2), 1351–1362.
https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3284230
Yang, K., Wang, Z., & Xu, X. (2021). Intelligent vehicular
ad-hoc networks for traffic accident detection and
management. IEEE Transactions on Industrial
Informatics, 17(3), 2135–2144.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3002210
Yaqoob, I., & Salah, K. (2021). Autonomous vehicles and
intelligent transportation systems: Challenges and
opportunities. Vehicular Communications, 28, 100310.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2021.100310
Zhang, Z., & Li, W. (2022). A hybrid IoT-cloud system for
intelligent transport control. Future Internet, 14(3), 76.
https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14030076
Zhao, L., & Li, J. (2022). An edge-IoT enabled framework
for traffic data processing and accident prediction.
Future Generation Computer Systems, 128, 154–165.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.10.001
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
70
