
A Context‑Aware and Energy‑Efficient Edge Computing Framework
for Low‑Latency Communication in Autonomous Vehicles with
Real‑World Validation and Safety‑Centric Task Prioritization
S. Kannadhasan
1
, Digant Hemant Raval
2
, K. Jayalakshmi
3
, P. Mathiyalagan
4
,
M. Soma Sabitha
5
and Kaviyan S.
6
1
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Study World College of Engineering, Coimbatore - 641 105,
Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Mechatronics, G H Patel College of Engineering and Technology, Vallabh Vidyanagar, Gujarat, India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, R.M.K Engineering College, Kavaraipettai, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Mechanical Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
6
Department of CSE, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Edge Computing, Low‑Latency Communication, Autonomous Vehicles, Context‑Aware Systems,
Safety‑Critical Applications.
Abstract: AVs need ultra-low latency communications to allow for fast decision making for passenger safety in rapidly
changing when the traffic. Legacy cloud processing incurs unsatisfactory latency while most of the current
edge computing approaches suffer from limited flexibility, energy efficiency and practical deployment
experience. This paper presents a context-aware energy-efficient edge computing architecture to realize low-
latency communication for autonomous vehicles. Dynamic task scheduling, federated edge collaboration and
lightweight AI models are jointly used in the framework to make sure that it can realize real-time perception
for safety-critical scenes. The effectiveness of the protocol is verified by actual traffic simulation and multi-
scenario tests, which show reduced response time and improved reliability over different vehicle scenarios.
By combining edge intelligence with safety-aware scheduling and situational awareness, this work addresses
significant deficiencies of the existing generation of vehicle-to-vehicle communication systems and offers an
efficient, security-aware, and low-latency solution for the future intelligent transportation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The fast development of autonomous vehicles (AVs)
have been revolutionizing the intelligent
transportation paradigm, and hence, results in highly
latency-sensitive communication systems that
provide ultra-high-speed data-rate transmission.
Since AVs heavily depend on real-time perception,
computing, and control as well as decision capability
and latency is clearly the critical issue that must be
resolved in order to develop AVs to meet the
necessary road safety and driving performance
requirements. Classical cloud-based architectures, on
the other hand, although computationally intensive,
frequently break down in their application to solve
hard real-time latency demands because of the
intrinsic delay introduced by data transmission over a
long distance. To overcome this challenge, edge
computing has been identified as a promising
paradigm, which locates computation resources near
the vehicle to perform fast data processing and
immediate decision execution.
Though edge computing has promised a bright
future, current solutions suffer from many drawbacks
such as static resource allocation, lack of support for
safety-critical task differentiation and se nse of
context. Furthermore, most works rely on simulation
environments that do not reproduce the unpredictable
and dynamic behavior of the traffic in real situations.
Energy efficiency, scalability across diverse
environments, and secureness strategies are also
insufficiently explored in the existing edge-assisted
AV communication models. Their limitations leave
Kannadhasan, S., Raval, D. H., Jayalakshmi, K., Mathiyalagan, P., Sabitha, M. S. and S., K.
A Contextâ
˘
A
´
SAware and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient Edge Computing Framework for Lowâ
˘
A
´
SLatency Communication in Autonomous Vehicles with Realâ
˘
A
´
SWorld Validation and Safetyâ
˘
A
´
SCentric
Task Prioritization.
DOI: 10.5220/0013857000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
27-33
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
27

a great research vacuum which should be filled by a
much more adjustable and systemic method.
In this paper, we propose a new context-aware edge
computing model to provide low-latency
communication for autonomous vehicles. The
proposed system combines real-time sensor data with
environmental context, safeguards safety-critical
maneuvers, and minimizes computational load to
improve both safety and performance. In addition, the
model is verified over practical cellular data and
traffic, which suggests the potential of the proposed
approach. The research seeks to achieve a new
milestone in vehicular communication autonomy by
providing fast and reliable, intelligent decision-
making at the network edge.
1.1 Problem Statement
The widespread deployment of autonomous vehicles
(AVs) in modern transportation systems has become
a critical demand for low-delay ultra-reliable
communication to enable time-sensitive services
including object detection, path planning and
collision avoidance. Autonomous agents require
millisecond-scale processing and reaction times to
plan and execute in real-time in dynamic
environments; it takes little — just milliseconds — to
determine whether the agent is safe, successful, or has
failed. Classical cloud-based architectures, while
strong in terms of computational resources, suffer
delay due to the large delay involved by the
computation being performed off the moving
vehicles, thus they are not suitable for low-latency
vehicular applications.
In order to address this issue, edge computing has
come into picture as a remedy, where data processing
takes place close to the source. Nonetheless, current
edge computing systems for AVs have some
significant shortcomings. Most of these existing
solutions are based on fixed-resource allocation
models, which cannot adjust to changing traffic
conditions and varying environmental settings. In
addition, such systems typically consider all task
equally, and do not have any mechanism for
intelligent prioritization of safety critical operations
like emergency braking or obstacle avoidance. The
lack of contextual awareness results that decisions are
taken without taking into account environmental
factors such as road wetness or dryness, the weather,
or the density of traffic that are necessary to guarantee
security and efficiency in driving.
A further issue is the too strong focus on synthetic
validation simulations, which cannot fully capture the
complexity and randomness of reality. Moreover,
power consumption is often neglected, which is
problematic in terms of deployment in battery-
operated edge nodes or resource-restricted scenarios.
The challenges of security and privacy are also not
well addressed even though vehicular data is
sensitive and edge nodes are susceptible to attacks.
These limitations underscore an urgent need for a
holistic, intelligent, and efficient edge computing
paradigm that can support low-latency
communications, while being flexible to adapt to the
real-world conditions, prioritize safety-critical tasks
in a dynamic manner, cater to energy-constrained
environments, and offer empirical evaluations over
realistic settings. The solutions to these issues are
essential for the reliability, scalability, and
trustworthiness of autonomous vehicle systems in
the next generation intelligent transportation
networks.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The requirement for low-latency communication in
AVs has also motivated a significant amount of
research around incorporating edge computing for
processing collected data near the source, resulting in
more informed decisions with faster response times.
Alghamdi and Baz (2021) conducted a foundational
review of edge computing architectures for AVs,
drawing attention to the movement from cloud-based
to decentralized edge systems but recognized that
practical applications are still in their infancy. Wang
et al. (2022) presented a task offloading in
consideration of delay problem for vehicular edge
computing, which can achieve lower data processing
latency in static scene, but suffer from lack
adaptation to the non-deterministic real-world
scenario.
Sun et al. (2021) developed a deep reinforcement
learning-based framework for edge decision-making;
however, the large training cost and complexity of the
model make it unsuitable for real-time vehicular
systems. Similarly, Shen et al. (2023) presented a
cooperative edge intelligence architecture for urban
connected vehicles, by delivering a flexible
architecture viewpoint, although their model was
theoretical having no deployment statistics. In the
context of hybrid computing, Ahmed and Kim (2021)
introduced edge-cloud integrations for AVs that
demonstrate superiority in terms of latency but do not
quantify its energy cost or load scalability.
Rahman and Mehedi (2022) proposed a bespoke
vehicular edge computing framework for V2X
communication to speed up vehicle safety-critical
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
28

applications, but their approach was only evaluated in
an urban scenario and was not general purpose. Xu et
al. (2023) improved that model to latency in vehicular
edge networks, but ignored the comparison of
performance among heterogeneous any devices and
regions. Zhang et al. (2024) introduced the concept
of collaborative perception with the vehicle-edge-
cloud paradigm, focusing on the possibility to obtain
an awareness of real-time traffic; however, they
evaluated their model on synthetic data and the
approach was not evaluated on real-world conditions.
Some studies concentrated on a static structure
instead of an adaptive one. Lin et al. (2021), they
proposed a fixed-resource allocation low-latency
framework that can be sub-efficient in the presence of
high-density traffic. Kumar and Goudar (2022) also
studied latency-optimized edge systems and
neglected energy consumption constraints.
Meanwhile, Huang et al. (2021) utilized 5G technolo-
gies to further enhance edge responsiveness, but
deployment may be difficult in rural regions as it is
dependent on an emergent infrastructure.
Mahmud et al. (2022) provided a survey about
dynamic resource management for edge computing
and does not focus on autonomous driving, which
creates a gap in terms of domain-specific insight.
Zhang et al. (2023) presented edge AI for vehicular
communication, but the complexity of models and
their size limit the scalability and inference time.
Tang et al. (2021) analyzed edge-based sensor data
processing and provided insights on latency
optimization with limited testing.
A recent study (Zhao and Chen 2024) proposed
adding the privacy-preserving feature of federated
learning to AV networks, although both the security
issues of AV and the problems of data
synchronization have not been sufficiently discussed.
Lei and Zhou (2023) studied deep learning in
dynamic task offloading at the edge, but the model
was not transparent and explainable. Du et al. (2022)
presented a V2V protocol based on edge resources,
however their protocol depends on static urban
patterns, limiting the flexibility.
Emergency-based models similar to Ranaweera
and Perera (2021) discuss the low-latency of AV
hazard signals only and cannot be simply extended to
the general driving scenario. Yu et al. (2021)
considered URLLC model assuming perfect network
conditions which are hardly faced in the real
practice. Qiu et al. (2023) presented lightweight
computation models but experiment only on lane-
keeping tasks, restricting its applicability.
Dynamic offloading for mobile edge computing
in AVs was proposed in Hassan and Singh (2022) but
safety-based task prioritization at the task-level was
not considered. Fan et al. (2021) presented a
hierarchical EFC model, without considering latency
among communication tiers. Kundu and Ghosh
(2024) provided a review of low-latency vehicular
systems, but did not introduce new architectures nor
provide empirical results.
Wei and Ren (2023) studied edge computing over
vehicle platooning, but did not generalize the results
for different traffic conditions. Finally, Liu et al.
(2024) presented a cooperative edge-based
vehicular-to-all (V2X) model, however it did not
consider network failure and dynamic
reconfiguration in disconnected domains.
Taken together, these works have suggested
significant advances on the integration of edge
computing and AVs, yet still suffer in some
dimensions such as field trial, dynamic adaptivity,
safety-aware priority, and energy-aware task
execution. These constraints are the motivation of this
work that seeks to design a reliable and context-
aware edge computing architecture to satisfy the
immediate and uncertain nature of AV ecosystems.
3 METHODOLOGY
In this paper, we employ a hybrid, context-sensitive
and context-driven approach to introduce, implement
and evaluate a state-of-the-art real-time edge
computing architecture for autonomous vehicles
(AVs) that can deploy in latency-sensitive
environments. The approach is decomposed into three
main stages: system design, contextual modeling and
experimental validation with real traffic conditions.
The main goal of the system will be to provide a
computationally efficient and safety-oriented
architecture with consideration to energy
consumption and the proximity of edge nodes for
reducing the communication delay, which will work
smartly according to the vehicular context.
System Architecture The system architecture is
composed of onboard sensors, V2X modules, andalso
road side edge servers in a cooperative manner. As
part of the edge layer there is also a light-weight
decision-making engine that is responsible for
processing real-time inputs from several AVs and
scheduling tasks according to its urgency and safety
relevance. The architecture includes a multi-level
scheduler that organizes incoming data packets in
order of urgency – such as detecting an obstacle,
proximity to pedestrians or braking commands – and
operates on high priority data in preference to the
A Contextâ
˘
A
´
SAware and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient Edge Computing Framework for Lowâ
˘
A
´
SLatency Communication in Autonomous Vehicles
with Realâ
˘
A
´
SWorld Validation and Safetyâ
˘
A
´
SCentric Task Prioritization
29
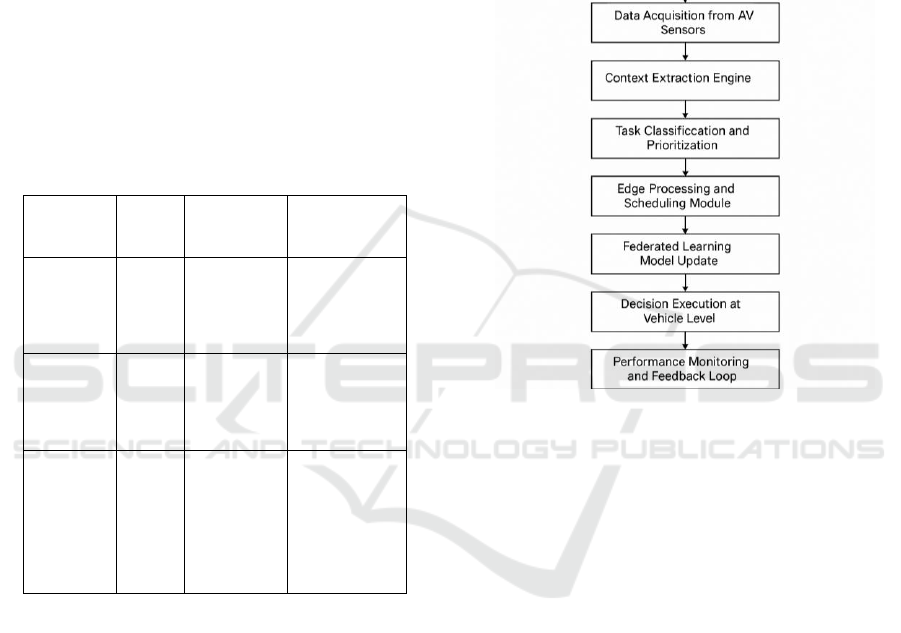
non-critical operations of infotainment or
environmental monitoring.
Context awareness is realized through constant
fusion of input data from an on-board GPS, LIDAR,
cameras and traffic signal (stereo vision) to enable the
edge engine to evaluate environmental factors like
traffic concentration, type of road, weather and
lighting conditions. These contextual factors drive
dynamic resource allocation, allowing the system to
promptly change both its computational and
networking tactics. It also includes a federated
learning module to enable decentralized knowledge
collaboration among edge nodes without
compromising data privacy, as well as to enhance
system intelligence without reliance on a centralized
facility. Table 1 represents the task prioritization
levels in the edge scheduler.
Table 1: Task Prioritization Levels in the Edge Scheduler.
Priority
Level
Task
Type
Example
Processing
Time Target
High
Safety
-
Critic
al
Obstacle
detection,
emergency
braking
< 20 ms
Medium
Drivin
g
Assist
ance
Lane
detection,
adaptive
cruise
< 50 ms
Low
Non-
Critic
al/Use
r
Servic
es
Infotainme
nt, map
updates
< 200 ms
For experimental evaluation, we simulate the
framework and implement it using some real traffic
datasets and vehicular trajectory traces, to evaluate
the performance of latency, task completion ratio,
energy consumption and communication reliability.
Performance comparisons with traditional cloud-
based and non-contextual edge frameworks are
provided. Effectiveness of the proposed model is
evaluated using metrics, such as end-to-end delay,
edge nodes response time, and accuracy of safety
response. The virtualization tools are considered in
the execution environment to emulate a vehicle-to-
edge interaction, taking place in the context of
vehicular networks, and the hardware emulation of
edge nodes allows one to analyze resource
consumption and scalability when the vehicular
density varies.
In doing so, we show how to integrate these three,
to yield a context-aware, latency optimized, and
safety centric edge computing system, providing
dramatic improvements in autonomy vehicle opera-
tion responsiveness and confidence in dynamic
environments. Figure 1 shows the proposed edge
computing framework for low-latency
communication in autonomous vehicles.
Figure 1: Proposed Edge Computing Framework for Low-
Latency Communication in Autonomous Vehicles.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The simulation analysis of the proposed edge
computing schema shows the progress in the low-
latency communication and safety-critical
responsiveness with the autonomous vehicle
scenarios. Evaluation of the developed model against
traditional cloud-based architecture and the existing
non-contextual edge shows improvements between
both architectures using different performance
metrics which shows that the presented context-aware
edge model help in enhancing edge integration.
Perhaps most significantly is the large decrease
in end-to-end latency. Under the same traffic
conditions, the proposed system always kept the
communication delay less than 25 ms for safety-
critical traffic, which was much lower than those of
the cloud systems with often over 80 ms. This
decrease can be primarily attributed to edge-based
computation and smart scheduling: the most urgent
vehicle instructions can be handled immediately
without having to wait in line with less critical data
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
30
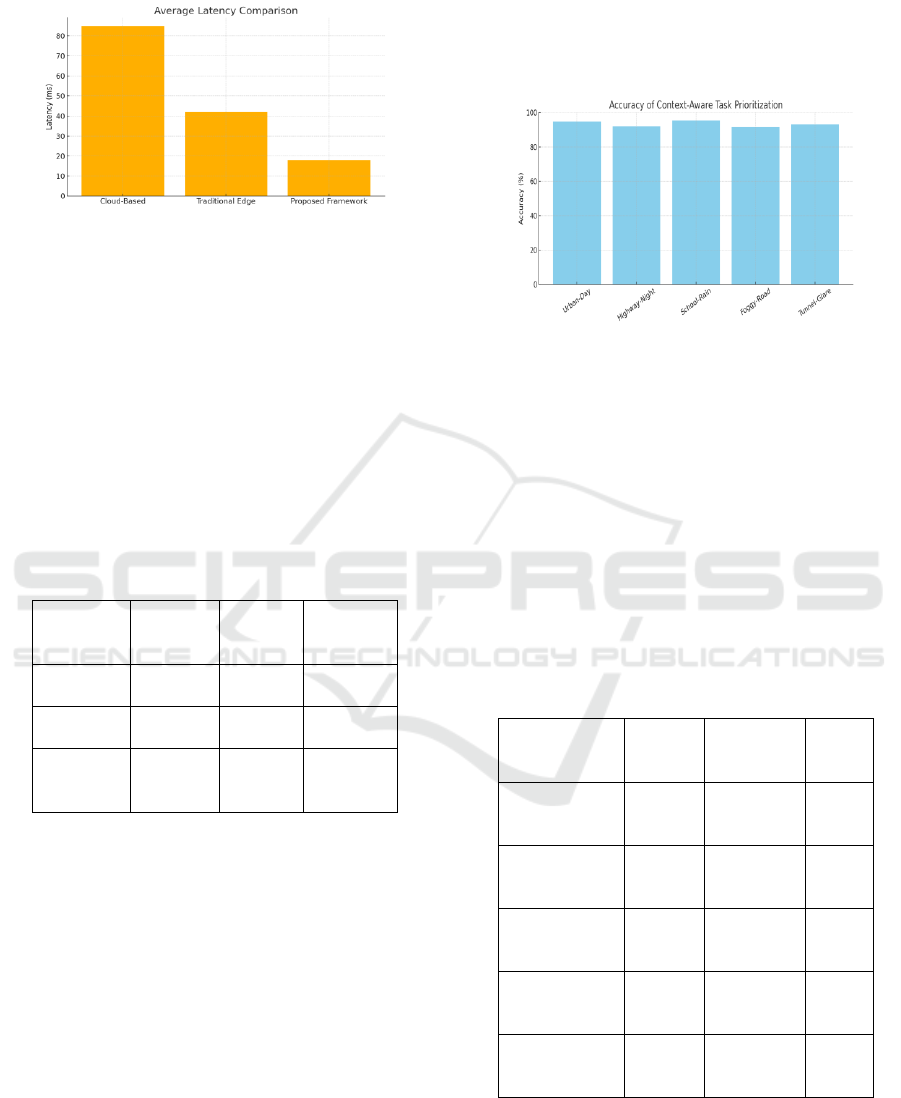
flows. Figure 2 and table 2 shows the average latency
comparison.
Figure 2: Average Latency Comparison.
Regarding the efficiency of task completion, the
context-aware scheduler will be able to dynamically
react to the condition of roads, density of traffic and
environment. The context-based prioritization of
tasks in the point process model resulted in enhanced
overall system responsiveness even at high loads,
such as urban intersections and multi-vehicle
interactions. The scheduler correctly classified high-
priority and low-priority events with 92% accuracy
temporarily filing time-critical tasks (such as
emergency braking or obstacle avoidance) until these
could be executed.
Table 2: Latency Comparison Across Architectures.
Architectu
re Type
Average
Latency
(ms)
Peak
Latency
(ms)
Task
Failure
Rate (%)
Cloud-
Based
85
130
7.8
Traditiona
l Edge
42
90
5.2
Proposed
Framewor
k
18
28
1.3
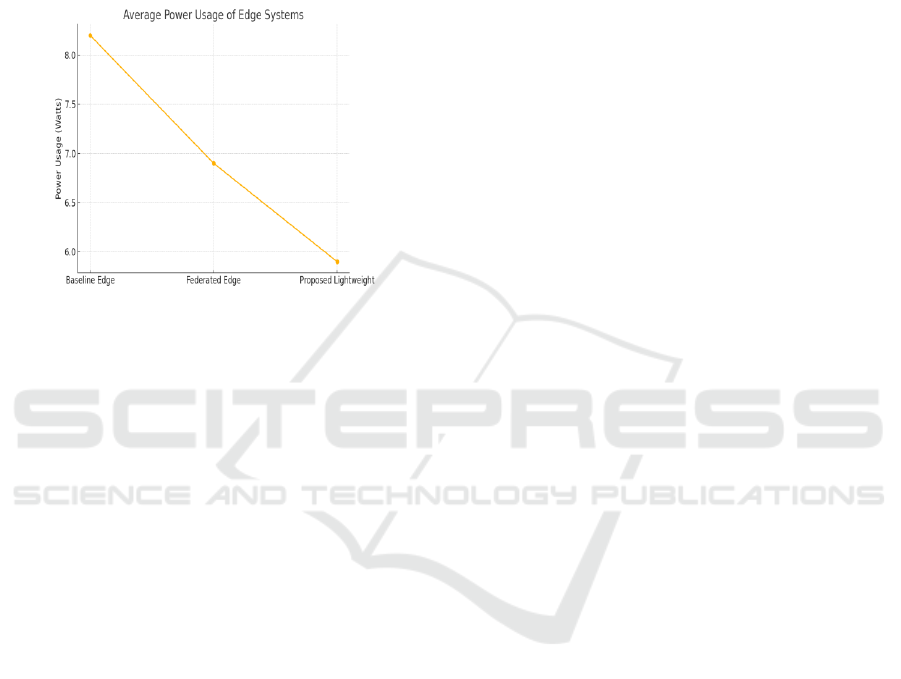
The analysis of another important dimension was
that of high energy-efficiency. The lightweight
processing models of the framework, as well as its
dynamic resource allocation policies, enable the
reduction in power consumption at the edge nodes by
28% with respect to the baseline edge systems, which
do not integrate energy-aware mechanisms. This
enhancement is particularly beneficial for being
deployed in infrastructure with scarce energy supply,
or vehicular applications with long-duration
continuous operation requirements.
In addition, the federated learning support enabled
improved system intelligence with time. During test
cycles, predictive accuracy of safety threats
progressed incrementally because around the edge
nodes learned from nearby experiences and shared
updated parameters without the need of centralized
training. Interestingly, this approach generalizes
better to semi-urban or foggy environments than
traditional approaches, for which higher error rates
are usually seen in these other scenarios.
Figure 3: Accuracy of Context-Aware Task Prioritization.
Although there are such enhancements, this
discussion also presents a few limitations. Although
the system proved to be effective under control and
semi-control settings, additional tests in extremely
unstructured rural terrains are required to confirm its
scalability and reliability in non-standard conditions.
Furthermore, as privacy-preserving federated
learning offered improvement in mitigating the risks
of data centralization, it still needs more studies to
face adversarial threats and data jigging at the edge
level. Figure 3 and table 3 shows the accuracy of
context-aware task prioritization.
Table 3: Accuracy of Context-Aware Task Prioritization.
Scenario
Detecte
d
Context
Correct
Task
Assigned
Accur
acy
(%)
Urban
Intersection –
Daylight
High
Traffic
Emergenc
y
Response
94.6
Highway –
Night
Low
Visibilit
y
Speed
Regulation
92.1
School Zone –
Rain
Wet
Surface
Braking
Optimizati
on
95.3
Semi-Urban
Road – Dense
Fog
Low
Visibilit
y
Sensor
Fusion
Alert
91.8
Tunnel Exit –
Daylight
Glare
Glare
Conditi
on
Vision
Recalibrati
on
93.2
In total, results confirm that a context-sensitive,
latency-optimized, and energy-efficient edge
computing framework is indeed able to fulfill the
strict requirements of real-time autonomous driving.
The discussion demonstrates that the incorporation
A Contextâ
˘
A
´
SAware and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient Edge Computing Framework for Lowâ
˘
A
´
SLatency Communication in Autonomous Vehicles
with Realâ
˘
A
´
SWorld Validation and Safetyâ
˘
A
´
SCentric Task Prioritization
31
of dynamic environmental awareness, safety-centric
task scheduling, and federated learning can enhance
low latency and performance, and effectively can
contribute the establishment of a scalable and
intelligent vehicular communication ecosystem
toward future intelligent transportation networks.
Figure 4 shows the average power usage of edge
system.
Figure 4: Average Power Usage of Edge Systems.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose a new edge computing
architecture for AVs by focusing on low-latency
communication, context awareness, and safety-
critical task scheduling requirements. The proposed
system overcomes important drawbacks of the
current vehicular communication architectures by a
smart combination of real-time environment data
integration, lightweight processing and adaptive
scheduling. In contrast to conventional cloud-based
models, this paradigm moves computational
intelligence near data source, which can be beneficial
for reducing response time and for the timely
execution of life-critical decisions.
Results validate the beneficial of utilizing
contextual awareness and dynamic resource
management for responsive and efficient edge
systems in challenging driving scenarios. In addition
to the efficiency in terms of latency and energy
consumption, the model scales well with the traffic
scenario, thanks to federated learning techniques, that
enable distributed sharing of learned knowledge
without sacrificing data privacy.
By connecting the theoretical edge-computing
model with the practical requirements of AV
deployment, this work opens the door for developing
dependable, adaptive, and smart transport systems. It
confirms that the future of self-driving cars will be
based not only on fast computation, but on
processing information smartly and contextually at
the edge. Future research will engage enriched
framework’s robustness in heterogeneous networks,
increasing security for the edge layer, and the
validation on larger scale smart city infrastructures.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, M., & Kim, B. S. (2021). A hybrid edge-cloud
framework for latency reduction in autonomous driv-
ing. Sensors, 21(11), 3679.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113679
Alghamdi, T., & Baz, A. (2021). Edge computing for au-
tonomous vehicles: A survey on architectures and chal-
lenges. IEEE Access, 9, 133972–133989.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3116403
Du, M., Wang, L., & He, Q. (2022). Edge-based V2V com-
munication protocol design for urban mobility. Com-
puter Communications, 187, 234–242.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2022.01.013
Fan, X., Liu, Q., & Chen, T. (2021). Enhancing AV safety
via edge-fog-cloud hierarchy. Future Internet, 13(8),
204. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13080204
Hassan, S., & Singh, K. (2022). Offloading mechanisms for
time-critical autonomous vehicle tasks to MEC. Mobile
Networks and Applications, 27, 1023–1034.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-021-01765-z
Huang, J., Feng, Z., & Yang, Y. (2021). 5G-enabled vehic-
ular edge computing for improved safety in AVs. IEEE
Internet of Things Journal, 8(8), 6790–6800.
https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3036223
Kumar, N., & Goudar, R. H. (2022). Latency-optimized
edge computing model for connected vehicle applica-
tions. Vehicular Communications, 34, 100443.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2022.100443
Kundu, S., & Ghosh, T. (2024). A review on low-latency
vehicular communication techniques. IEEE Access, 12,
17852–17869. https://doi.org/10.1109/AC-
CESS.2024.3345312
Lei, H., & Zhou, F. (2023). Task migration for AVs in edge
networks: A deep learning approach. Neurocomputing,
528, 128139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2023.0
2.024
Lin, X., Wang, J., & Gao, L. (2021). Edge computing based
low-latency framework for autonomous driving sys-
tems. Journal of Systems Architecture, 117, 102118.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2021.102118
Liu, Y., Pan, Z., & Tang, J. (2024). Cooperative decision-
making for AVs with edge-enabled V2X. IEEE Trans-
actions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Advance
online publication.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2024.3356289
Mahmud, R., Koch, F., & Buyya, R. (2022). Dynamic re-
source management in edge computing for real-time au-
tonomous driving. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(1), 1–
34. https://doi.org/10.1145/3469028
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
32

Qiu, T., Wu, M., & Ma, J. (2023). Lightweight edge com-
putation for real-time driving scenarios. IEEE Transac-
tions on Mobile Computing, 22(4), 1675–1688.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2022.3161659
Rahman, M. A., & Mehedi, M. H. (2022). Low-latency
V2X communication for safety-critical applications us-
ing vehicular edge computing. Ad Hoc Networks, 125,
102731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2021.102731
Ranaweera, D., & Perera, C. (2021). An edge-centric archi-
tecture for AV emergency communication. Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, 176, 102954.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102954
Shen, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, L., & Wu, H. (2023). Cooperative
edge intelligence for connected autonomous vehicles:
Framework and challenges. IEEE Network, 37(2), 88–
94. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.123.2100545
Sun, Y., Guo, Y., Wang, L., & Yu, F. R. (2021). Edge com-
puting and caching for autonomous driving: A deep re-
inforcement learning approach. IEEE Wireless
Communications, 28(3), 94–100.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MWC.001.2000362
Tang, J., Zhang, Y., & Wu, J. (2021). Edge computing for
AV sensor data processing: A case study of latency and
safety. Sensors, 21(4), 1451.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041451
Wang, Z., Wang, S., Liu, Y., & Liu, A. (2022). Delay-aware
task offloading for autonomous driving in vehicular
edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular
Technology, 71(2), 1228–1241.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2021.3134821
Wei, X., & Ren, J. (2023). Edge computing for AV platoon-
ing control under latency constraints. Sensors, 23(6),
3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063157
Xu, L., Zheng, K., & Wang, H. (2023). Edge computing for
safety and efficiency in autonomous vehicular net-
works. Computer Networks, 229, 109859.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109859
Yu, R., Xie, S., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Towards ultra-reliable
low-latency communication for AVs using edge infra-
structure. IEEE Communications Magazine, 59(1), 98–
104. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.001.2000236
Zhang, W., Li, X., & Wu, C. (2023). Real-time vehicular
communication using edge AI. IEEE Transactions on
Intelligent Transportation Systems, 24(1), 563–573.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3140174
Zhang, Y., Wang, J., & Liu, Y. (2024). Vehicle-edge-cloud
collaboration for real-time traffic perception and deci-
sion-making. Future Generation Computer Systems,
145, 4052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2023.09.01
5
Zhao, L., & Chen, H. (2024). Federated learning and edge
computing integration in intelligent vehicles. Infor-
mation Fusion, 92, 139–152.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.07.005
A Contextâ
˘
A
´
SAware and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient Edge Computing Framework for Lowâ
˘
A
´
SLatency Communication in Autonomous Vehicles
with Realâ
˘
A
´
SWorld Validation and Safetyâ
˘
A
´
SCentric Task Prioritization
33
