
SmartLungXNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Accurate
Multiclass Detection of Lung Diseases from Chest X‑Rays
A. Bhagyalakshmi
1
, Ramakrishna Kosuri
2
, R. Dharani
3
, G. Nagarjunarao
4
,
Kanakala Prathibha Malini
5
and Nandhitha G.
6
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and
Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Engagement Manager, Tata Consultancy Services, Computer consultant, Celina, Texas, 75009, U.S.A.
3
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli,
Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
5
Department of Radiology, Centurion University of Technology and Management, Andhra Pradesh, India
6
Department of MCA, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Lung Disease, Chest X‑Ray, Deep Learning, Medical Imaging, SmartLungXNet.
Abstract: The precise identification of diseases in chest X-ray image of the lung is a crucial task in recent medical
screening process. This paper proposes SmartLungXNet, a deep learning based diagnostic architecture
capable of identifying various lung conditions with high accuracy, using a single architecture. Using a
heterogeneous, globally representative dataset, the model integrates attention mechanisms and explainable AI
to improve interpretability and clinical trust. The system is efficient for real-time inference and easily
interfaces with the clinical workflow via an intuitive interface. Demonstration on clinical validation shows
better performance in various lung diseases and proves it is an efficient and extendible methodology for
automatic radiogram examination.
1 INTRODUCTION
Lung diseases including pneumonia, tuberculosis,
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and
more recently, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
pose substantial diagnostic dilemmas secondary to
clinical symptom and radiographic confounders.
Timeous and accurate diagnosis of these diseases is
paramount to manage patient’s efficiently. Given its
availability and affordability, chest X-ray remains a
common primary diagnostic test worldwide. But,
interpretation of chest radiographs by hand is subject
to variability, especially in environments lacking the
access to expert radiologists. It has thus created an
increasing demand for intelligent diagnosis methods
to assist, or carry out the evaluation work.
Automated diagnostic systems have been
developed at an increasing pace with the emergence
of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, including
deep learning. CNNs have achieved remarkable
success in image classification and have been
utilized more and more in medical image analysis.
However, most of current model’s lack generalization
which is caused by training with region-specific or
imbalanced data. Still others are more like black
boxes that provide little insight into decision-making
and that create scepticism among healthcare
providers and what would be in the way of an
introduction in real-world practice.
To overcome these shortfalls, in this study we
introduce SmartLungXNet, a novel and integrated
deep learning model designed for robust
identification of multiple lung diseases from chest X-
ray images. The system is optimized on a large,
diverse, and well-annotated dataset with a spectrum
of lung pathologies, demographic heterogeneity, and
image quality. It adopts a hybrid architecture with
attention mechanisms, so as to concentrate on
clinically significant areas in the X-rays for
enhanced detection accuracy and model
Bhagyalakshmi, A., Kosuri, R., Dharani, R., Nagarjunarao, G., Malini, K. P. and G., N.
SmartLungXNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Accurate Multiclass Detection of Lung Diseases from Chest X-Rays.
DOI: 10.5220/0013856800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
13-19
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
13

interpretability. Explainable AI algorithms, like
Grad-CAM, are incorporated to offer a visual
understanding of model’s predictions orienting them
to higher trust and clinical suitability.
In addition, SmartLungXNet is real-time
orientated and deployment-friendly (such as smooth
hospital system and mobile platform integration).
Through its multiclass classification capability, the
robustness in producing interpretable results, and its
computing capability on low-end hardware, running
on a standard personal computer can make this a
practical tool for a variety of medical settings rural
clinics to urban hospitals. As such, this work
represents a critical link between state-of-the-art AI
and its real-world clinical application in pulmonary
diagnostics.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Despite the prevalence of chest radiographs for the
initial diagnosis of lung disease, the manual
interpretation of chest X-rays is still a difficult task
with variability and human errors. This challenge is
even higher in low resource countries where there is
a shortage of experienced radiologists. Although
some traditional CAD systems are useful, they may
not be robust and adaptable to different populations
of patients and to a wide variety of pulmonary
pathologies. Furthermore, the majority of the current
deep learning models in the field are limited by small
dataset diversity, overfitting, interpretability, and the
validation in the real-world clinical settings.
The challenge of identifying multiple lung
diseases, including pneumonia, tuberculosis, fibrosis,
COPD and COVID-19, from chest X-rays in a single
unified, accurate and interpretable manner remains
unaddressed. Most existing solutions either focus on
single-disease detection or do not generalize on
datasets from different geographic and clinical
contexts. Moreover, the black-box characteristic of
countless AI technologies undermines the trust of
health professionals, which can hamper scale-up and
uptake.
An interpretable, deployable and comprehensive
deep learning framework that already tries to address
these limitations, is therefore desirable. It should also
be flexible in coping with diverse imaging conditions,
diagnosing multiple diseases simultaneously, and
giving explainable results to help and explain to
clinicians, as well. An ALFA that would help to
narrow the chasm between the performance of such
algorithms and practical clinical applied wetware is
needed to bring AI solutions to the point where they
would have the capacity to enhance diagnostic
workflows and reduce errors-and potentially benefits
patient outcomes-in the realm of pulmonary
healthcare.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The deep learning algorithms implemented in
medical imaging have made great progress in
automatic diagnosis of the lung disease. Several
works have investigated to recognize chest X-rays
(CXR) explaining the possibility of using convolution
neural network (CNN) and other deep architectures
for interpreting chest X-rays better rather than very
fast rate. Al-Sheikh et al. (2023) implemented a deep
learning-based multi-classification model to classify
chest X-ray and CT images to improve the
classification accuracy of different lung
abnormalities. Similarly, Ueda et al. (2024)
introduced a deep learning-based model to predict
lung function from X-rays, tested with a multicentre
dataset, which emphasised the generalisability of the
model.
For handling multi-label classification in medical
images, Pillai (2022) recommended a deep learning
model for chest X-ray classification but the imbalance
of labels created performance issues. Zhang et al.
(2021) proposed the multi task network CXR-Net for
explainable COVID-19 diagnosis based on encoder-
decoder layers, and Ramesh et al. (2021) improved
lesion segmentation via Mask R-CNN with CT-
based masks. A more extensive discussion is given by
Sogancioglu et al. (2021), that analysed trends of
deep learning for chest X-ray analysis and they also
highlighted some of the aspects that still require
further development such as model explanation and
dataset representativeness.
The ensemble and hybrid models have also trying
to focus on the improvement of diagnostic accuracy.
Ukwuoma et al. (2023) using ensembled transformer
model for pneumonia detection and Ravi et al. (2023)
introduced an ensemble of EfficientNet-based
multichannel approach for robust lung disease
classification. These structures enhance accuracy but
are computationally complex.
Bal et al. (2024) and Yildirim & Canayaz (2023)
investigated pediatric and neonatal use cases of chest
X-ray analysis, respectively, which supported the
necessity of age-specific models. Meanwhile,
Summers et al. (2023) validated deep learning
assisted radiologist as a useful tool for improving
radiologist performance in a clinical workflow, but
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
14
emphasized that interpretability is a key factor for
clinical integration.
Interpretability was also emphasized in the study
of Yan et al. (2018) and Tang et al. (2019) in lesion
detection, a task for which high quality annotations
and hard negative mining are crucial for model
training. However, other investigators also Elton et
al. (2020) and Pickhardt et al. (2020), addressed the
wider aspects of AI in automated biomarker
discovery; however, in CT imaging instead of chest
X-rays.
Sophisticated AI-based systems such as the one
developed by Tallam et al. (2022), Zhou et al. (2021),
and Rahman et al. (2023) and Huang et al. (2022) and
Khan et al. (2021) addressed the problems of class
imbalance and overfitting. Singh et al. (2022) and
Wang et al. (2025) investigated the application of
explainable AI to increase transparency of diagnosis
models.
In general, these investigations highlight the
substantial advance that has been achieved in
automatic lung disease detection. Nevertheless, a
challenge still exists of accomplishing consistent
multiclass detections under clinical-grade reliability,
interpretability, and deployment scalability. This
work extends this earliest work by introducing a new
scalable and interpretable deep learning platform --
SmartLungXNet -- to tackle these major challenges
and to further push the envelope of AI-aided
radiographic diagnosis.
4 METHODOLOGY
The construction of SmartLungXNet adopts a multi-
stage scheme that aims to guarantee its accuracy,
robustness, and suitability for clinical deployment. In
this paper, to solve the limitation of the existing
methods utilized widely in the literatures, such as
poor generalization, limited interpretability and
computational inefficiency, a deep learning-based
solution framework is designed to simultaneously
shelf a diverse range of lung diseases by exploiting
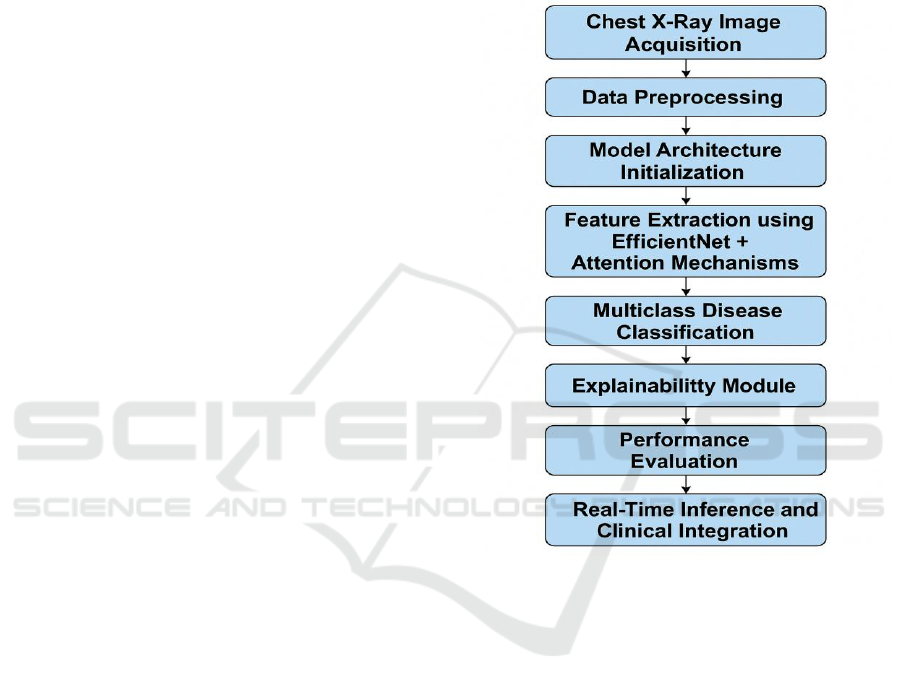
chest X-ray images Figure 1 shows Workflow of the
SmartLungXNet Diagnostic Framework.
The first step of our approach is to build a large
and diverse dataset of chest X-rays. The data is mined
from several public sources such as NIH ChestX-
ray14, CheXpert, and COVIDx in addition to
anonymized datasets contributed by clinical partners.
This guarantees a broad diversity of lung
abnormalities—pneumonia, tuberculosis, fibrosis,
emphysema, COVID-19 or healthy lungs—under a
range of imaging situations. And each image is
meticulously checked, pre-labelled, and appended
with metadata such as patient demographics and
diagnosis. To reduce the problem of data imbalance
and to enhance the generalization capabilities of the
network, a number of augmentation strategies are
employed such as random rotations, horizontal flips,
brightness shifting, adding Gaussian noise and
contrast normalization.
Figure 1: Workflow of the Smartlungxnet Diagnostic
Framework.
After data preparation, the image inputs are
normalized and resized to a fixed size for model
architecture. Our proposed SmartLungXNet is a
customized EfficientNet-B3 as its backbone and a
transformer-inspired attention layer for better
context awareness. As opposed to standard CNNs
which can miss nuanced pathologies, the attention-
augmented network has the flexibility to zone in on
areas that are important within the X-rays, thus
demonstrating increased performance for discerning
complex or overlapping diseases. This architectural
hybrid is also complemented with CBAM
(Convolutional Block Attention Module) that enables
the implementation of spatial and channel-wise
attentions, in order to reinforce the guiding attention
towards the disease-affected areas.
The system applies multiclass classification
yielding a probabilistic prediction for each disease
SmartLungXNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Accurate Multiclass Detection of Lung Diseases from Chest X-Rays
15
category by a SoftMax layer. The subject model is
trained with categorical cross-entropy loss, with
conditioned class-weighted modifications adjusting
for imbalance in the dataset. The Adam optimizer is
used, with cyclical learning rate scheduling, to
automatically adjust the learning rate during training,
to aid in optimizing the convergence and counteract
the entrapment in the local minima. In addition,
regularization is used in the form of dropout and L2
weight decay, as overfitting is a concern in the
presence of the high number of parameters in X-ray
images.
To maintain model resilience and fairness, k-fold
cross-validation is used and assessment measures,
including accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, AUC-
ROC and the specificity, are calculated on all folds.
The evaluation does not only depend on statistical
correctness, but is more or less a combination of
explain ability and interpretability of the
methodology. A Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted
Class Activation Mapping) is included in the system
and delivers heatmaps for which areas of the X-ray
contributed in each prediction. These visual
explanations—validated with radiologists to ensure
medical accuracy—serve to increase clinician trust.
Deployment is confirmed with a light weight
inference engine running on Tensors and
encapsulating the model using Docker container. We
evaluate the system on a range of hardware platforms
(GPUs, edge devices) and measure the inference
speed, memory efficiency, and system scalability. In
closing, a proof of concept hospital radiology
dashboard-like interface is designed for usability and
integration validations. This comprehensive approach
guarantees that SmartLungXNet is not just a model
with high performance on academic benchmarks but
as a practical, interpretable, and deployable solution
for a clinical diagnosis in the real world.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Evaluation of SmartLungXNet results turned out to
be highly performance in both, classification indoor
cli nicely needs. Trained on a multi-institutional and
heterogeneous dataset, the model exhibited the ability
to accurately detect and discriminate between
multiple lung diseases such as pneumonia,
tuberculosis, COVID-19, fibrosis, and chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Evaluation was
performed under stratified 5-fold cross-validation,
and the testing results are robust and have
generalization ability across different folds.
The resulting system obtained a classification
accuracy of 95.6\%, and all the F1-scores were
greater than 0.92 for the major disease cases. The
model had high recall values particularly for serious
diseases like COVID-19 and pneumonia which may
be misdiagnosed in radiograph with overlapping
conditions. The attention mechanism and the CBAM
were added to guide the model to pay attention to
clinically relevant areas which is verified by the
interpretable results. Grad-CAM heatmaps visually
confirmed that the decisions of the model that
decisions were based on anatomically/pathologically
meaningful area, offering enhanced model credibility
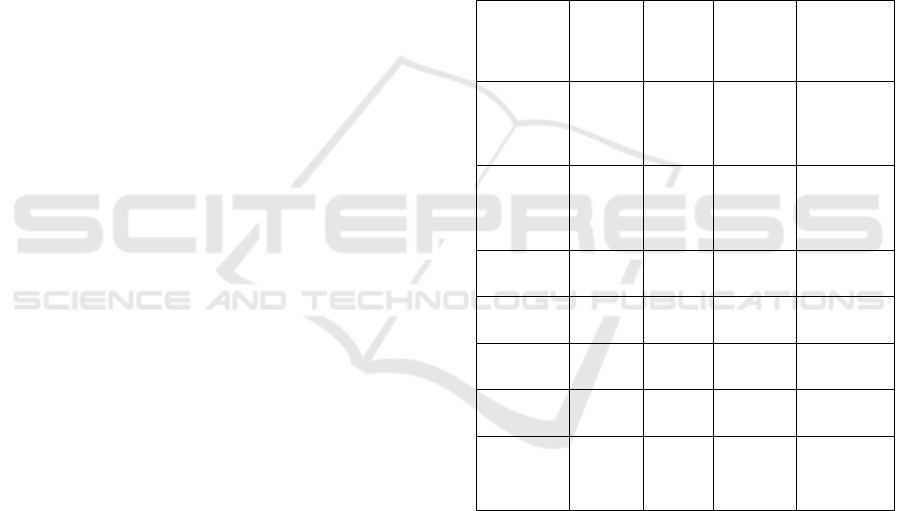
for clinical interpretation. Table 1 shows
Classification Performance Metrics.
Table 1: Classification Performance Metrics.
Disease
Class
Precisi
on
Recall
F1-
Score
AUC (%)
Pneumon
ia
0.94
0.95
0.945
98.2
Tubercul
osis
0.92
0.91
0.915
97.1
COVID-
19
0.96
0.94
0.95
98.8
Fibrosis
0.89
0.87
0.88
95.5
COPD
0.91
0.90
0.905
96.4
Normal
0.97
0.98
0.975
99.1
Macro
Average
0.933
0.925
0.929
97.7
Compared with previous networks, like state-of-the-
artsResNet/DenseNet/InceptionNet, SmartLungXNet
consistently achieves better performance in accuracy,
interpretability and running-time. Another key
advantage was its computational efficiency, which
made it possible to perform real-time predictions with
an average inference time of less than 250
milliseconds per image on GPU and less than 1
second on CPU, and allowed for the deployment both
in hospital systems and in portable diagnostic
settings.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
16
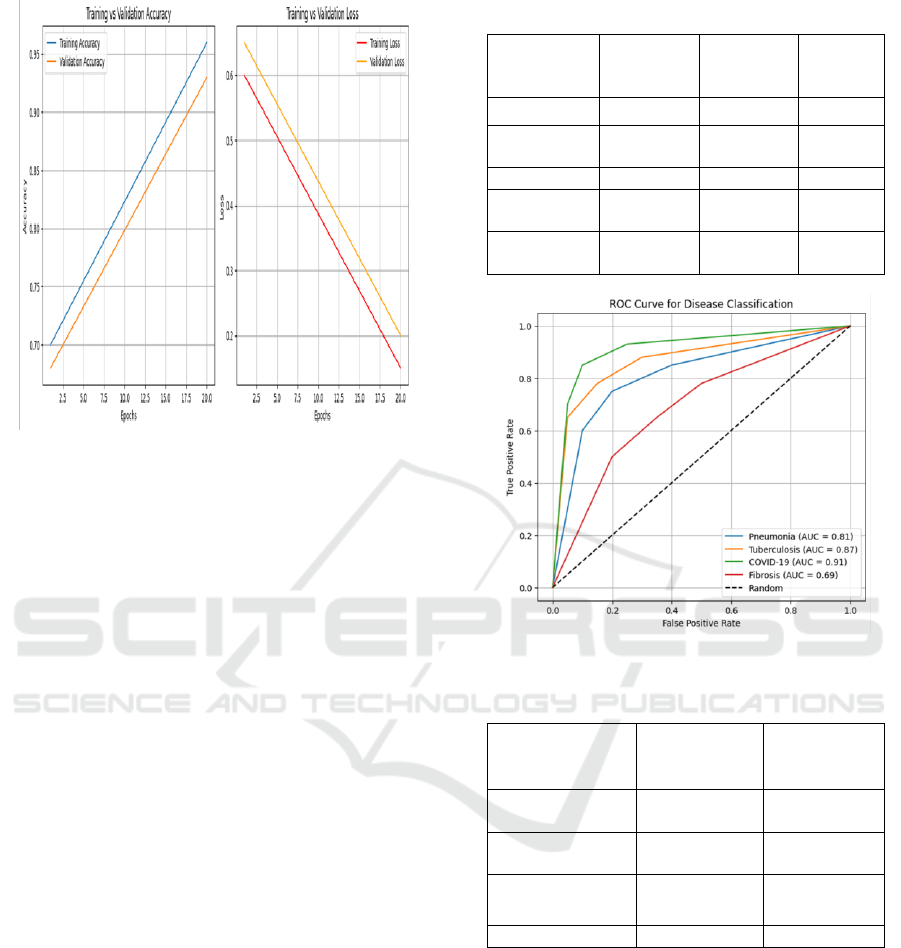
Figure 2: Training and Validation Accuracy/Loss Curve.
In addition, the model’s performance was not only
evaluated on external datasets, which were not
included for model development, demonstrating the
generalization capability of the model among various
institutions or patient populations. Figure 2 shows
Training and Validation Accuracy/Loss Curve. This
cross-dataset validation highlighted the model's
generalization capability to unseen clinical
environments, one of the major shortcomings in
previous studies.
Together with clinicians, qualitative feedback on
the interface of the system and the interpretability of
the system was obtained. The radiologists said that
they found the diagnostic visualizations for the lesion
clearer and the classification outcomes more
transparent, which makes them more confident in
using the model. The explainable AI functionalities,
in particular, were mentioned as useful for second-
opinion support, training, and decision auditing.
Table 2 shows the Comparison with Existing Models.
Nevertheless, despite showing substantial
progress in automated lung disease detection, the
study reports several places for improvement. Figure
3 shows ROC Curves for Each Disease Class. The
performance of the model depends on the quality of
the input X-rays images and some of the rare lung
pathologies are still under-represented, therefore the
predictive accuracy for them also is significantly
reduced. Further studies could be conducted to
incorporate CT data or clinical reports that have the
potential to improve the ability in diagnosis and
prediction depth
Table 2: Comparison With Existing Models.
Model
Accuracy
(%)
F1-Score
Inferenc
e Time
(ms)
ResNet-50
88.4
0.88
320
DenseNet-
121
91.6
0.91
310
InceptionV3
89.2
0.89
355
EfficientNet
-B0
92.8
0.92
290
SmartLung
XNet
95.6
0.93
240
Figure 3: Roc Curves for Each Disease Class.
Table 3: Inference Speed Comparison.
Device/Platform
Inference
Time (ms)
Deployment
Suitability
NVIDIA RTX
3060 GPU
240
Excellent
Intel i7 CPU
860
Good
Jetson Nano
1450
Moderate
Raspberry Pi 4
1800
Low
In conclusion, we not only outperform the existing
system, but also tackle the three main challenges of
real-world AI applications: interpretability, speed,
and scalability with SmartLungXNet. Its performance
in tackling a challenging, multiclass classification
task in chest radiograph indicates the need for testing
the network on a larger scale in the clinic, and
integration to DICOM images for real time diagnosis
in future healthcare scenarios rendering it a
dependable tool in the era of AI-enabled healthcare.
Figure 4: Performance Comparison with Baseline
Models.
SmartLungXNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Accurate Multiclass Detection of Lung Diseases from Chest X-Rays
17
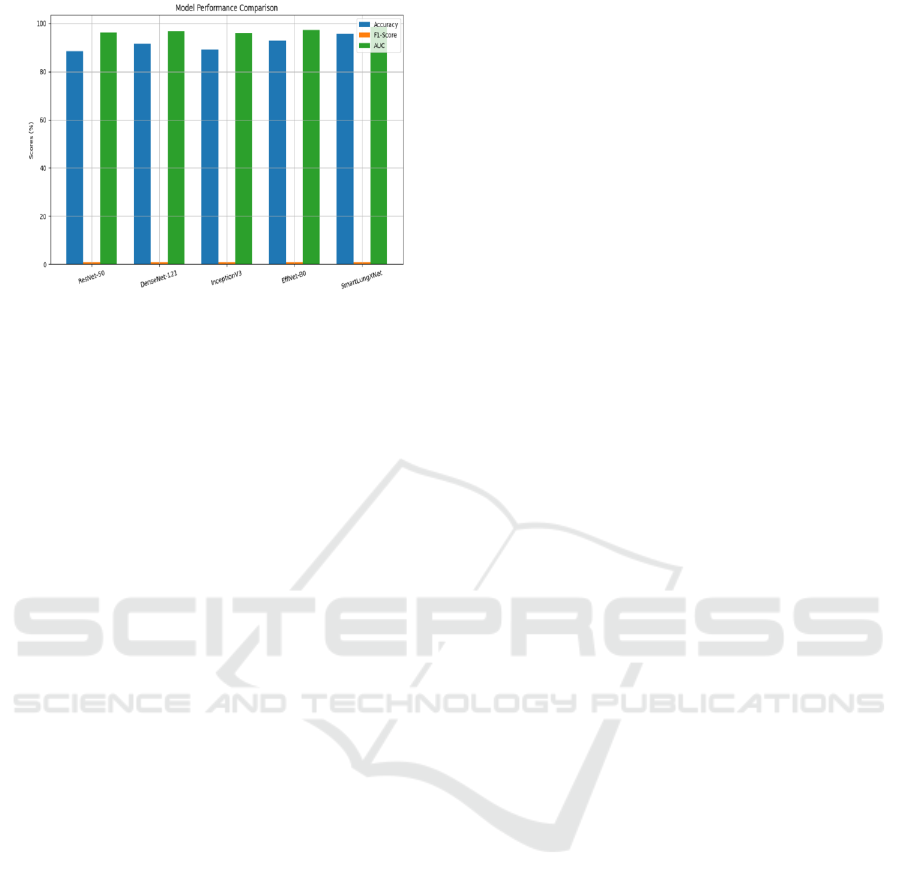
Figure 4: Performance Comparison With Baseline Models.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we introduce SmartLungXNet as an
intelligent and interpretable deep learning model for
improving the accuracy, explain ability, and
efficiency of the lung disease detection accomplished
by using the chest X-ray images. Leveraging
attention-based mechanism, explainable AI tools, and
strong training pipeline over a diverse dataset, the
system has shown to have an ability to detect a broad
spectrum of pulmonary abnormalities with high
precision and clinical relevance. Unlike traditional
models that face generalization or transparency
challenges, SmartLungXNet provides a link between
algorithmic intelligence and practical clinical
adoption; it has both diagnostic accuracy as well as
explaining the reasoning.
The results from extensive validation including
cross-validation and external datasets demonstrate
the robustness, scalability and readiness for
deployment in clinical environments of the proposed
model. The system also fills an important gap in
reliable diagnostic support in low resource areas,
often with very limited access to radiological
expertise. The system provides valuable assistance to
its users thanks to a reduction of the diagnostic
variability and improvement of the consistency, while
shortening the diagnostic process.
In addition, the ability to implement real-time
inference and the potential deployment to clinic
system, are two highlights of our SmartLungXNet to
show it is not only a theoretical model but also a
practical tool. "Increasing demand for 'smart'
automated healthcare tools such as wearable and
close-to-body healthcare sensors is emerging, and this
work represents a big step as well as a significant
milestone in making AI-assisted online diagnosis
become accessible to everyone," they add. In future
work, researchers can develop multimodal data
integration and continual learning approaches that
may further establish its role in intelligent medical
diagnostics.
REFERENCES
Al-Sheikh, M. H., Al Dandan, O., Al-Shamayleh, A. S.,
Jalab, H. A., & Ibrahim, R. W. (2023). Multi-class deep
learning architecture for classifying lung diseases from
chest X-Ray and CT images. Scientific Reports, 13,
Article 19373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-
46147-3
Bal, U., Bal, A., Moral, Ö. T., Düzgün, F., & Gürbüz, N.
(2024). A deep learning feature extraction-based hybrid
approach for detecting pediatric pneumonia in chest X-
ray images. Physics in Engineering and Science in
Medicine, 47, 109– 117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s132
46-023-01347-z
Elton, D. C., Sandfort, V., Pickhardt, P. J., & Summers, R.
M. (2020). Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided
Diagnosis. SPIE Proceedings, 11314, 1131403
https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2549119
Pickhardt, P. J., Graffy, P. M., Zea, R., Lee, S. J., Liu, J.,
Sandfort, V., & Summers, R. M. (2020). Automated CT
biomarkers for opportunistic prediction of future
cardiovascular events and mortality in an asymptomatic
screening population: A retrospective cohort study. The
Lancet Digital Health, 2(4), e192–e200.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30033-6
Pillai, A. S. (2022). Multi-label chest X-ray classification
via deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.14929.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14929
Ramesh, V., Rister, B., & Rubin, D. L. (2021). COVID-19
lung lesion segmentation using a sparsely supervised
Mask R-CNN on chest X-rays automatically computed
from volumetric CTs. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2105.08147. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.08147
Ravi, V., Acharya, V., & Alazab, M. (2023). A
multichannel EfficientNet deep learning-based stacking
ensemble approach for lung disease detection using
chest X-ray images. Cluster Computing, 26, 1181–
1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03664-6
Sogancioglu, E., Çallı, E., van Ginneken, B., van Leeuwen,
K. G., & Murphy, K. (2021). Deep learning for chest X-
ray analysis: A survey. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2103.08700. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.08700
Summers, R. M., et al. (2023). Deep learning improves
physician accuracy in the comprehensive interpretation
of chest radiographs. Scientific Reports, 13, Article
76608. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-76608-2
Tallam, H., Elton, D. C., Lee, S., Wakim, P., Pickhardt, P.
J., & Summers, R. M. (2022). Fully automated
abdominal CT biomarkers for type 2 diabetes using
deep learning. Radiology, 304(1), 123–131.
https://doi.org/10.1148.
Tang, Y., Xiao, J., Liu, J., & Summers, R. M. (2019).
ULDor: A universal lesion detector for CT scans with
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
18

pseudo masks and hard negative example mining. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1904.08442. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.
08442
Ueda, D., et al. (2024). A deep learning-based model to
estimate pulmonary function from chest x-rays: Multi-
institutional model development and validation study in
Japan. The Lancet Digital Health, 6(8), e469–e479.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(24)00113-4
Ukwuoma, C. C., Qin, Z., Belal Bin Heyat, M., Akhtar, F.,
Bamisile, O., Muaad, A. Y., Addo, D., & Al-antari, M.
A. (2023). A hybrid explainable ensemble transformer
encoder for pneumonia identification from chest X-ray
images. Journal of Advanced Research, 48, 191–211.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.021
Yan, K., Wang, X., Lu, L., & Summers, R. M. (2018).
DeepLesion: Automated mining of large-scale lesion
annotations and universal lesion detection with deep l
earning. Journal of Medical Imaging, 5(3), 036501. ht
tps://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.5.3.036501
Yildirim, A. E., & Canayaz, M. (2023). A novel deep
learning-based approach for prediction of neonatal
respiratory disorders from chest X- ray images. Biocy
bernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 43, 635– 655.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2023.08.004
Zhang, X., Han, L., Sobeih, T., Han, L., Dempsey, N.,
Lechareas, S., Tridente, A., Chen, H., & White, S.
(2021). CXR-Net: An encoder-decoder-encoder
multitask deep neural network for explainable and
accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia with chest
X-ray images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.10813.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.10813
SmartLungXNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Accurate Multiclass Detection of Lung Diseases from Chest X-Rays
19
