
Estimation of Rate-Dependent Hammerstein Model
of Piezo Bender Actuator
Lenka Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a Pavelkov
´
a
a
The Czech Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Theory and Automation
Pod Vod
´
arenskou v
ˇ
e
ˇ
z
´
ı 4, 182 00, Prague 8, Czech Republic
Keywords:
Rate-Dependent Hysteresis, Hammerstein Model, ARX Model, Particle Swarm Optimization, Splines,
Piezoceramic Actuator.
Abstract:
The paper presents a Hammerstein model of a commercial piezoelectric bender PL140 from Physik Instru-
mente Co. The model consists of a nonlinear static part that describes the inherent hysteresis and a linear
dynamic part that is represented by the auto-regressive model with exogenous input. The linear model pa-
rameters are estimated one-time using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The rate-dependent nonlinear
part is identified using input voltage data, along with a hidden variable that is obtained with the help of the
inverted linear part. The experimental data are generated by a PL140 Simscape model with parameters set in
accordance with catalog data.
1 INTRODUCTION
Piezoelectric actuators (PEAs) are essential in the
field of modern science and engineering. Their high
resolution and fast response distinguish them from
other actuator types, such as shape-memory alloys.
This makes them invaluable in a wide range of appli-
cations, including precision positioning in manufac-
turing, microfluidics control, medical ultrasonic ther-
apy, and robotics (Zhou et al., 2024).
A significant challenge in PEAs is the hysteresis
effect, a nonlinear relationship between input voltage
and output displacement. This nonlinearity depends
on input voltage amplitude and rate, causing position-
ing errors of 10-15% or higher at increased frequen-
cies. It can degrade system performance and poten-
tially lead to instability (Yuan et al., 2024).
To address the hysteresis problem, various math-
ematical models have been developed. These can
be categorized into physics-based models and phe-
nomenological models. Physics-based models are de-
rived from the fundamental physical principles of the
material but are often complex and not universally ap-
plicable (Yuan et al., 2024).
Phenomenological models employ mathematical
representations to characterize observed hysteresis ef-
fects, often without offering a physical explanation.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5290-2389
They can be categorized into the following method-
ological groups: operator-based models, differential-
equation-based models, and other models. Operator-
based models define hysteresis through a composition
of elementary memory operators. This approach al-
lows for high accuracy but can lead to increased com-
putational complexity. The most popular models in-
clude Preisach model, Krasnosel’skii-Pokrovkii (KP)
model, Prandtl-Ishlinskii (PI) model, and Maxwell
Model (Yuan et al., 2024). Differential-equation
based models describe hysteresis through differen-
tial equations that capture the memory-dependent be-
haviour of PEAs. The main representatives are Bouc-
Wen model, Duhem model, and Dahl model (Dai
et al., 2023; Yuan et al., 2024). Other methods in-
clude models such as neural networks (Son et al.,
2021), Gaussian processes (Meng et al., 2022) or
polynomial-based models (Yang et al., 2020).
Models can also be categorized according to
whether their behavior is influenced by the rate of
change of the input voltage. Rate-independent models
are suitable for low-frequency inputs. They are val-
ued for simplicity and low computational cost, though
inadequate for dynamic conditions. Rate-dependent
models better capture high-speed behavior. They are
suitable for integration into advanced control schemes
(Gan and Zhang, 2019).
The above mentioned phenomenological models
are predominantly static. To capture a dynamic be-
532
Kuklišová Pavelková, L.
Estimation of Rate-Dependent Hammerstein Model of Piezo Bender Actuator.
DOI: 10.5220/0013855300003982
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 22nd Inter national Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2025) - Volume 1, pages 532-538
ISBN: 978-989-758-770-2; ISSN: 2184-2809
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

havior, it is convenient to use the Hammerstein model
that offers a structured, phenomenological approach
to modeling hysteresis by decoupling the static non-
linear hysteresis characteristics from the dynamic be-
havior of the system (Dai et al., 2023). This model
consists of two parts connected in series: a static non-
linear component that captures the hysteresis effects
and a linear dynamic block that reflects the system’s
dynamic response.
This method provides a significant degree of flex-
ibility. The nonlinear block can be represented by
any of the above mentioned phenomenological mod-
els making the Hammerstein model adaptable to di-
verse hysteresis behaviours (Dai et al., 2023).
From now on, we will focus on the Hammerstein
model of a piezo actuator with a rate-dependent non-
linear static part. In this context, the static nonlin-
earity is usually described by the Bouc-Wen model.
In (Zhang et al., 2021) and (Barbosa et al., 2020),
it is coupled with auto-regressive exogenous (ARX)
model, in (Liu et al., 2023), with a mass-spring-
damper system and in (Yang et al., 2022), with a frac-
tional dynamic model. Modified PI model together
with online infinite impulse response is used in (Yi
et al., 2022). In (Zhang et al., 2023), a static Preisach
model and a dynamic transfer function are combined.
In (Jin et al., 2024), Hammerstein model consists of
an optimized composite neural network and an auto-
regressive exogenous model in series.
Here, we will focus on a rate-dependent Hammer-
stein model of a specific piezo actuator, the PL140
model from Physik-Instrumente. We will build on
a recently published study (Pavelkov
´
a Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a and
Belda, 2024) that describes the mentioned piezo actu-
ator using an Hammerstein model but does not con-
sider rate dependency. We will extend the model ap-
plicability to rate-dependent scenarios. Our aim is to
build a simple and reliable algorithm that can be eas-
ily integrated into a control system with piezoelectric
actuator.
2 HAMMERSTEIN MODEL
This section presents a rate-dependent Hammerstein
model of a piezo bender actuator a its estimation.
A discrete time Hammerstein model is a well-
established framework for data-driven PEA descrip-
tion. It consists of a nonlinear static part serially
connected with a linear dynamic part, see Figure 1.
The block NLS describes the static hysteresis non-
linearity and the block LD describes the linear dy-
namic characteristic of the piezoelectric actuator.
In general, the linear and nonlinear parts of the
Figure 1: Block diagram of Hammerstein model – NLS
corresponds to a static non-linearity, LD represents a lin-
ear dynamic behavior, u
t
, z
t
, ε
t
, and y
t
are an input, hidden
non-measurable variable, noise, and output, respectively;
t ∈ {1,2,··· ,t} denotes a discrete time.
Hammerstein model are coupled during the identifi-
cation process. However, under particular conditions,
they can be identified separately (Bai, 2004). If the
system is excited by an input in the form of pseudo-
random binary sequences (PRBS) with sufficiently
small amplitude, then non-linearity is not activated.
As a result, it holds z
t
∼ u
t
. The linear part LD can
therefore be identified independently.
Subsequently, after the excitation with a “rich”
signal, the inverse LD model can be used to estimate
the hidden variable z
t
. Then, based on this and using
knowledge of the input, it is possible to identify the
NLS part.
2.1 Estimation of LD Part
The LD part of Hammerstein model, Figure 1, can be
represented by an auto-regressive model with external
input (ARX model) (Dai et al., 2023).
Here, we consider a 2
nd
order ARX model, as it is
an accepted method to represent electro-mechanical
systems (Wilkie et al., 2002). It is defined as follows
y
t
= ψ
T
t
θ + ε
t
(1)
where
t ∈ {1,2, ·· · ,t} denotes discrete time,
y
t
is an observable output,
u
t
is an optional known input,
ψ
t
= [y
t−1
, y
t−2
, u
t
, u
t−1
, u
t−2
]
T
is the regression
vector,
θ = [a
1
, a
2
, b
0
, b
1
, b
2
]
T
, is the vector of unknown
regression coefficients,
T denotes the transposition,
ε
t
is a white noise, independent and identically dis-
tributed.
The least square (LS) method is typically used
to estimate the ARX model (1) parameters, espe-
cially when the parameters need to be estimated re-
cursively (Ljung, 1998). Here, we only need a one-
time estimate of this model. We will use the parti-
cle swarm optimisation (PSO) method (Shi and Eber-
hart, 1998), which is simple to implement, flexible
Estimation of Rate-Dependent Hammerstein Model of Piezo Bender Actuator
533

and more robust comparing to recursive LS (Jahan-
dideh and Namvar, 2012).
Note that recently, the PSO method was used
in the context of a Hammerstein rate-dependent dy-
namic hysteresis modeling to calculate the parameters
of the Bouc-Wen model (Fu et al., 2024).
PSO is an algorithm that simulates social behav-
ior, such as a flock of birds, to find optimal solutions
to problems. It uses a swarm of S particles, where
each particle goes around a D-dimensional problem
space and represents a potential solution. In PSO, par-
ticles adjust their positions based both on their own
experience and the experience of the entire group.
Each particle maintains a velocity vector v
m
and a po-
sition vector x
m
, where index m = 1,2, ···, S.
PSO estimation starts with a random initialization
of vectors v
m
and x
m
. In each iteration, the value of
a given fitness function f is used to update the best
solution for each particle as well as the best solu-
tion for the whole swarm. The PSO estimation ter-
minates when either the global optimum or the maxi-
mum number of iterations is reached.
The evolution of a velocity and a position of m-th
particle at the i-th iteration is as follows:
v
m,i+1
= w
i
v
m,i
+ c
1,i
r
1
(p
bm,i
− x
m,i
)
+ c
2,i
r
2
(g
bi
− x
m,i
) (2)
x
m,i+1
= x
m,i
+ v
m,i+1
(3)
where i means iteration, w represents inertia weight,
c
1
is a cognitive acceleration parameter, c
2
is a so-
cial acceleration parameter, r
1
, r
2
∈ ⟨0, 1⟩ are random
numbers, p
bm,i
is the best location found by the m-th
particle and g
bi
is the global best location of all the
particles at the i-th iteration. The best locations are as
follows:
p
bm,i
=
p
bm,i−1
, if f (x
m,i
) ≥ f (p
bm,i−1
)
x
m,i
, if f (x
m,i
) < f (p
bm,i−1
)
g
bi
= arg min
x
m,i
f (x
m,i
), 1 ≤ m ≤ S (4)
The tuning parameters of PSO algorithm, i.e. c
1
, c
2
and w maintain the balance between global discov-
ery and local detection. We have used the follow-
ing approved setting (Fang et al., 2023; Belda and
Pavelkov
´
a Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a, 2023) that prevent a trapping
PSO in a local minima:
• time-varying acceleration coefficients
c
1,i
= 2.5 − 2 i/α (5)
c
2,i
= 0.5 + 2 i/α (6)
where α denotes the total number of iterations.
• linearly decreasing inertia weights
w
i
= w
max
− (w
max
− w
min
)i/α (7)
where w
max
and w
min
denote the maximal
and minimal inertia weight, respectively.
The algorithmic summary of the ARX model (1) esti-
mation using PSO is as follows:
1) Initialise the PSO algorithm parameters,
i.e., the swarm size S, inertia weight w,
acceleration coefficients c
1
, c
2
, maximum
number of iterations α, and maximum
velocity V
max
.
2) Set a swarm of S particles of dimension D = 5
that corresponds to the size of θ in (1).
3) Initialise the position x
m,1
and velocity v
m,1
,
and p
bm,1
of each particle (m = 1, 2, · ·· , S);
and initialise g
b1
of the swarm.
4) Calculate each particle’s fitness f value that corre-
sponds to the absolute prediction error
f =
N
∑
i=1
|y(i) − ψ
T
ˆ
θ
i
|
5) Update best local position p
bm,i
and global posi-
tion g
bi
according to (4).
6) Update velocity v
m,i
(2) and position x
m,i
(3)
of each particle.
7) If either iterations number α or fitness f value
reaches the threshold then END, else GO to the
step 4).
2.2 Estimation of NLS Part
The NLS part of the Hammerstein model, Figure 1,
can be identified with the help of a data set u
t
and
z
t
. Inputs u
t
are available. Hidden variables z
t
can be
estimated from corresponding outputs y
t
by the help
of the inverted LD part, i.e., ARX model (1), obtained
in the previous step (Bai, 2004; Pavelkov
´
a Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a
and Belda, 2024).
The inverted ARX model (1) with input y
t
and out-
put z
t
, neglecting the noise term, has the following
form:
z
t
=
1
b
0
(y
t
− a
1
y
t−1
− a
2
y
t−2
− b
1
z
t−1
− b
2
z
t−2
)
(8)
where a
1
, a
2
, b
0
, b
1
and b
2
correspond to the regres-
sion parameters of the ARX model (1).
Using an inverse model (8) and outputs y
t
, that are
obtained as responses to “rich” inputs u
t
, i.e., inputs
that sufficiently excite the hysteresis of the identified
PEA, a hidden variable z
t
can be estimated.
Then, the NLS block of Hammerstein model, Fig-
ure 1, can be identified based on generated inputs u
t
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
534
together with estimated hidden variables z
t
. The pro-
cess of identifying hysteresis is as follows. We have
a pair of data points [u,z] that form a hysteresis loop
when graphically displayed. First, we split this loop
into two parts to obtain two sets of values correspond-
ing to two nonlinear functions, an “upper” one and
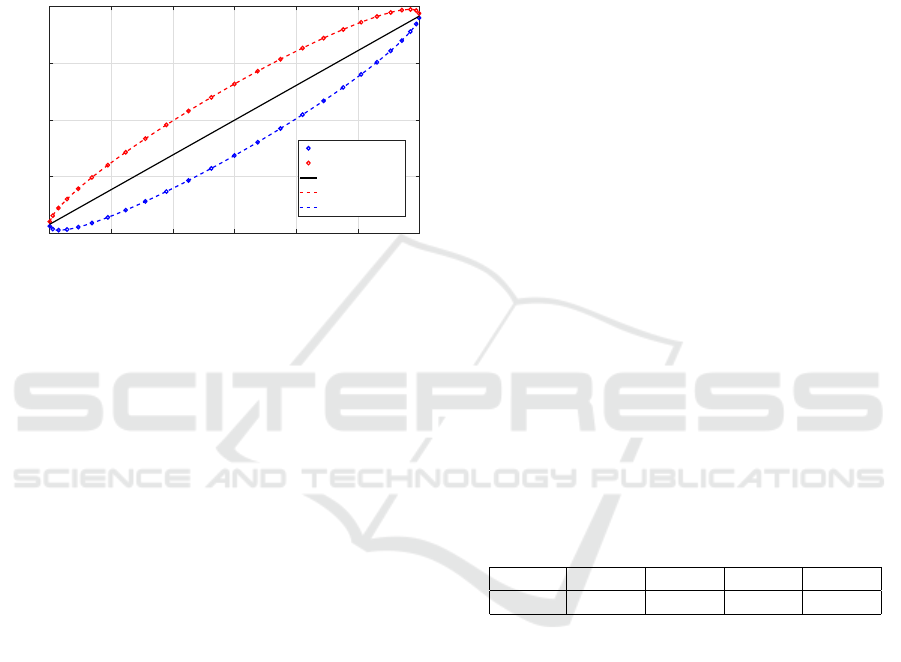
a “lower” one, see an illustrative example in Fig. 2.
Then, we can interpolate the points in both sets using
splines (De Boor and De Boor, 1978).
u
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30
z
-200
-100
0
100
200
lower data
upper data
separating line
lower spline
upper spline
Figure 2: Data pairs [u,z] for estimation of NLS block of
Hammerstein model divided to the lower (blue) and upper
(red) parts with separating line depicted.
Having two nonlinear functions, the identified
NLS block performs as follows:
- if u
t
> u
t−1
, then the value z
t
is read from the “up-
per” function,
- otherwise, it is read from the “lower” function.
2.3 Estimation Summary
Consider the Hammerstein model of PEA in Figure 1.
Then, the estimation is as follows:
1) Generate outputs y
t
by stimulating identified PEA
with PRBS.
2) Estimate the parameters of the LD block in
Hammerstein model, Fig. 1, represented by the
ARX model (1) using PSO algorithm in Sec-
tion 2.1 using the PRBS data.
3) Generate outputs y
t
by stimulating identified PEA
with “rich” data, e.g. sin waveform.
4) Estimate z
t
in Hammerstein model, Fig. 1, accord-
ing to (8) using y
t
from 3) as inputs.
5) Identify the NLS block in Hammerstein model as
described in Subsection 2.2 using input data u
t
from 3) and output data ˆz
t
from 4)
6) Generate new “rich” data set as described in 3) to
test the identified Hammerstein model accuracy.
3 EXPERIMENTS
In this section, the Hammerstein model, Fig-
ure 1, of the piezo bender actuator PL140 (Physik-
Instrumente, 2025) is identified. The data for esti-
mation are obtained using a “digital twin” of the real
bender that is realized as a Simulink/Simscape model
(Pavelkov
´
a Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a and Belda, 2024). Material
constants are set according to the catalog data.
Experiments were performed for various frequen-
cies of input signal. The sampling period was set
T
s
= 5 × 10
−4
s. Note that the estimation of the
LD part of Hammerstein model is rate-independent.
The parameter estimation of the corresponding ARX
model is therefore performed only once. The fixed
inverse model is then used continuously for the calcu-
lation of a rate-dependent non-linearity.
Estimated parameters of the ARX model (1) that
represents the LD part are presented in Table 2. The
estimation process for 500 iterations of PSO algo-
rithm (see Section 2.1) is shown in Figure 3.
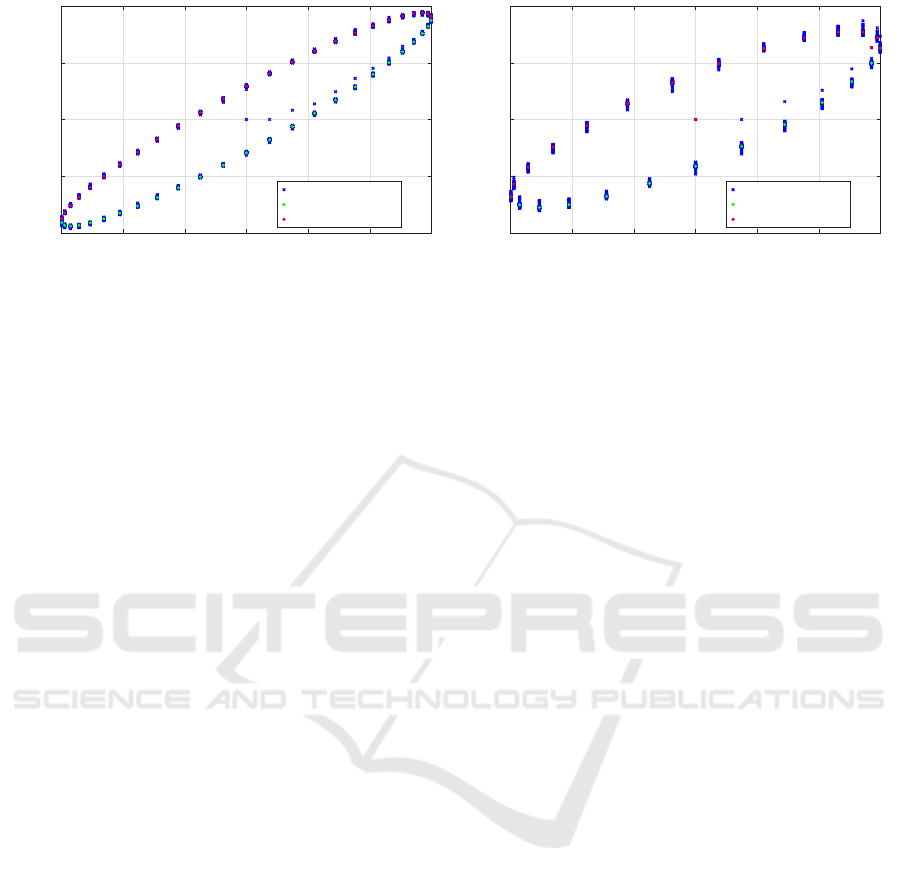
Estimated hysteresis loops for various frequencies
of input signal are depicted in Figures 4 and 5. The
Figures show how the loops are split in two parts
corresponding to the values of two nonlinear func-
tions. The interpolation by splines as described in
Section 2.2 is done using Matlab function spline.
The performance of the identified Hammerstein
model was tested by a periodic step-wise signal of
various frequency. The mean square error between
simulated and predicted outputs for various frequen-
cies are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: MSE.
f (Hz) 5 20 40 80
MSE 0.0129 0.0155 0.0180 0.0322
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents an approach for modeling the
rate-dependent hysteresis behavior of the piezoelec-
tric bender actuator using a Hammerstein model
structure. The main contribution is in incorporating
a rate-dependent nonlinear static (NLS) block repre-
sented by two spline functions. Since the proposed
model can be easily estimated, it has the potential to
be used for model predictive control.
The experiments demonstrate that the Hammer-
stein model is suitable for capturing the hysteresis
characteristics of the actuator across different input
frequencies. The proposed method separates the esti-
mation of the LD and NLS parts. The proposed model
Estimation of Rate-Dependent Hammerstein Model of Piezo Bender Actuator
535
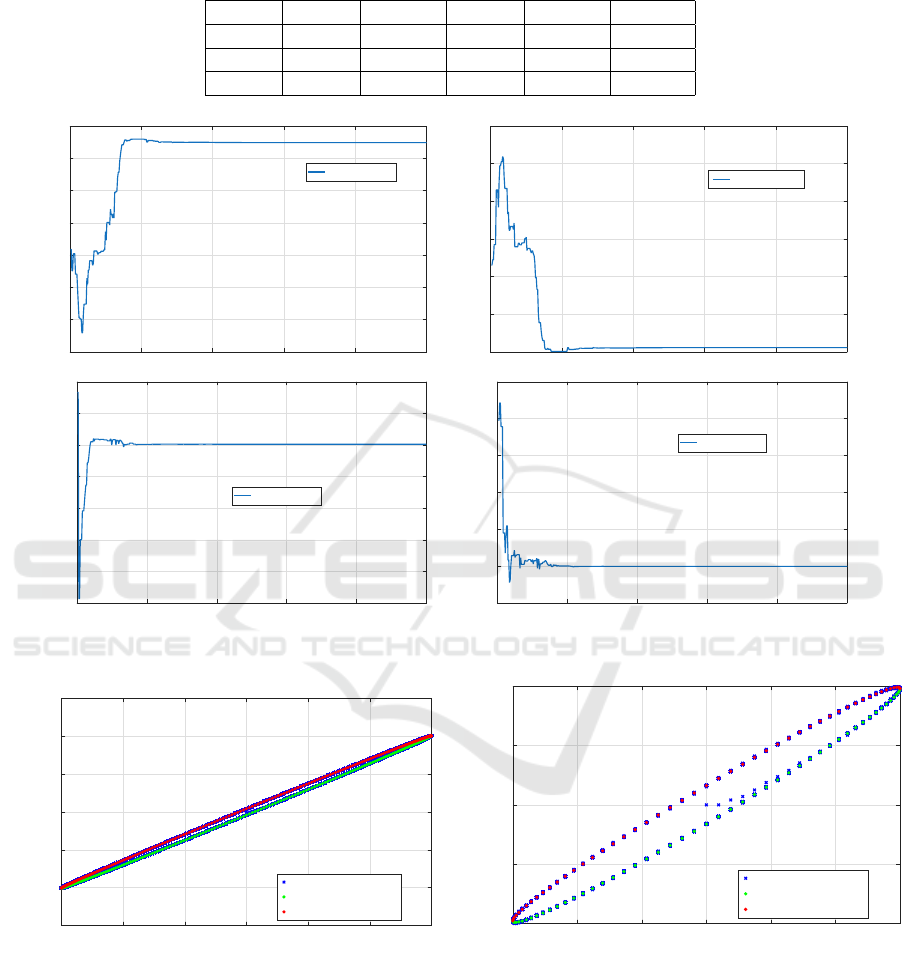
Table 2: Estimated regression coefficients of the ARX model representing the LD part of Hammerstein model depending on
the frequency f of input sine signal.
f (Hz) a
1
a
2
b
0
b
1
b
2
5 1.7424 -0.9453 0.0012 -0.0004 -0.0003
50 1.7424 -0.9453 0.0011 -0.0004 -0.0003
80 1.7424 -0.9453 0.0011 -0.0004 -0.0003
0 100 200 300 400 500
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
a
1
estimate
0 100 200 300 400 500
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
a
2
estimate
0 100 200 300 400 500
-0.25
-0.2
-0.15
-0.1
-0.05
0
0.05
0.1
b
0
estimate
0 100 200 300 400 500
-0.05
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
b
1
estimate
Figure 3: The courses of parameter estimation of the ARX model (1) for 500 iterations of the PSO algorithm.
u (V)
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30
z
-300
-200
-100
0
100
200
300
hysteresis curve
lower reduced part
upper reduced part
u (V)
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30
z
-200
-100
0
100
200
hysteresis curve
lower reduced part
upper reduced part
Figure 4: Hysteresis curve representing a NLS part of Hammerstein model of PL140 (blue) with indicated averaged upper
(red) and lower (green) parts for f = 5 Hz (left) and f = 20 Hz (right).
yields a consistent performance across frequencies up
to ca 80 Hz. For higher frequencies, the error grew
rapidly. The resonance frequency of PL140 is 160 Hz.
Above this frequency, the estimated hysteresis curve
even became inverted. The cause may be both the
simplicity of the presented model and problems re-
lated to the sampling period. This could be a topic for
the further research, together with the testing on a real
piezo actuator.
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
536
u (V)
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30
z
-200
-100
0
100
200
hysteresis curve
lower reduced part
upper reduced part
u (V)
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30
z
-200
-100
0
100
200
hysteresis curve
lower reduced part
upper reduced part
Figure 5: Hysteresis curve representing a NLS part of Hammerstein model of PL140 (blue) with indicated averaged upper
(red) and lower (green) parts for f = 40 Hz (left) and f = 80 Hz (right).
REFERENCES
Bai, E.-W. (2004). Decoupling the linear and nonlinear
parts in Hammerstein model identification. Automat-
ica, 40(4):671–676.
Barbosa, M. P. S., Rakotondrabe, M., and Ayala, H. V. H.
(2020). Deep learning applied to data-driven dynamic
characterization of hysteretic piezoelectric microma-
nipulators. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53(2):8559–8564.
Belda, K. and Pavelkov
´
a Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a, L. (2023). Particle
swarm optimisation for model predictive control adap-
tation. page 144 – 149.
Dai, Y., Li, D., and Wang, D. (2023). Review on the non-
linear modeling of hysteresis in piezoelectric ceramic
actuators. Actuators, 12(12).
De Boor, C. and De Boor, C. (1978). A practical guide to
splines, volume 27. springer New York.
Fang, J., Liu, W., Chen, L., Lauria, S., Miron, A., and
Liu, X. (2023). A survey of algorithms, applications
and trends for particle swarm optimization. Interna-
tional Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence,
2(1):24–50.
Fu, Y., Gao, S., Li, L., Chen, C., and Melnikau, S. (2024).
Rate-dependent hysteresis modeling of piezoceramic
actuators and parameter identification with an im-
proved genetic algorithm. In 2024 9TH INTERNA-
TIONAL CONFERENCE ON ELECTRONIC TECH-
NOLOGY AND INFORMATION SCIENCE, ICETIS
2024, pages 82–86.
Gan, J. and Zhang, X. (2019). A review of nonlinear hys-
teresis modeling and control of piezoelectric actua-
tors. AIP Advances, 9(4).
Jahandideh, H. and Namvar, M. (2012). Use of pso in pa-
rameter estimation of robot dynamics; part two: Ro-
bustness. In 2012 16th International Conference on
System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC),
pages 1–6.
Jin, J., Sun, X., and Chen, Z. (2024). Inverse feedfor-
ward control of piezoelectric actuators using opti-
mized composite neural network-based hammerstein
model. JOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT MATERIAL
SYSTEMS AND STRUCTURES, 35(20):1558–1575.
Liu, D., Dong, J., Guo, S., Tan, L., and Yu, S. (2023). Pa-
rameter identification of model for piezoelectric actu-
ators. Micromachines, 14(5):1050.
Ljung, L. (1998). System Identification: Theory for the
User. Pearson Education.
Meng, Y., Wang, X., Li, L., Huang, W., and Zhu, L.
(2022). Hysteresis modeling and compensation of
piezoelectric actuators using gaussian process with
high-dimensional input. In Actuators, volume 11,
page 115. MDPI.
Pavelkov
´
a Kukli
ˇ
sov
´
a, L. and Belda, K. (2024). Identifica-
tion of piezoelectric actuator using bayesian approach
and neural networks. In Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference on Informatics in Control, Automa-
tion and Robotics, volume 1, page 591 – 599.
Physik-Instrumente, S. E. (2025). PICMA Bender PL112
- PL140 Datasheet. https://www.physikinstrumente.
com/en/products/piezoelectric-transducers-actuators/
pl112-pl140-picma-bender-103000. [Accessed
22-07-2025].
Shi, Y. and Eberhart, R. (1998). A modified particle swarm
optimizer. In IEEE Int. Conf. on Evolutionary Com-
putation Proceedings. IEEE World Congress on Com-
putational Intelligence, pages 69–73.
Son, N. N., Van Kien, C., and Anh, H. P. (2021). Hysteresis
compensation and adaptive control based evolution-
ary neural networks for piezoelectric actuator. Inter-
national Journal of Intelligent Systems, 36(10):5472–
5492.
Wilkie, J., Johnson, M., and Katebi, R. (2002). Simple sys-
tems: second-order systems, pages 173–195. Macmil-
lan Education UK, London.
Yang, C., Verbeek, N., Xia, F., Wang, Y., and Youcef-
Toumi, K. (2020). Modeling and control of piezoelec-
tric hysteresis: A polynomial-based fractional order
disturbance compensation approach. IEEE Transac-
tions on Industrial Electronics, 68(4):3348–3358.
Yang, L., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Y., and Li, D. (2022). Rate-
dependent modeling of piezoelectric actuators for
nano manipulation based on fractional hammerstein
model. MICROMACHINES, 13(1).
Yi, S., Zhang, Q., Xu, L., Wang, T., and Li, L. (2022).
Estimation of Rate-Dependent Hammerstein Model of Piezo Bender Actuator
537

Hysteresis online identification approach for smart
material actuators with different input signals and
external disturbances. NONLINEAR DYNAMICS,
110(3):2557–2572.
Yuan, Z., Zhou, S., Zhang, Z., Xiao, Z., Hong, C., Chen,
X., Zeng, L., and Li, X. (2024). Piezo-actuated smart
mechatronic systems: Nonlinear modeling, identifi-
cation, and control. MECHANICAL SYSTEMS AND
SIGNAL PROCESSING, 221.
Zhang, M., Cui, X., Xiu, Q., Zhuang, J., and Yang, X.
(2023). Dynamic modeling and controlling of piezo-
electric actuator using a modified preisach operator
based hammerstein model. INTERNATIONAL JOUR-
NAL OF PRECISION ENGINEERING AND MANU-
FACTURING, 24(4):537–546.
Zhang, Q., Gao, Y., Li, Q., and Yin, D. (2021). Adaptive
compound control based on generalized bouc–wen in-
verse hysteresis modeling in piezoelectric actuators.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 92(11).
Zhou, X., Wu, S., Wang, X., Wang, Z., Zhu, Q., Sun, J.,
Huang, P., Wang, X., Huang, W., and Lu, Q. (2024).
Review on piezoelectric actuators: materials, classifi-
cations, applications, and recent trends. Frontiers of
Mechanical Engineering, 19(1):6.
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
538
