
A Difference-in-Differences Analysis on the Impact of the Covid-19
Pandemic on Drinking and Binge Drinking in the United States
Yuxiang Liu
a
School of Energy Science and Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, China
Keywords: Binge Alcohol Use, Alcohol Use, COVID-19, United States.
Abstract: The COVID-19 pandemic has brought profound and complex impacts on the global society and economy,
and it has also revealed many problems in sanitation field. At the beginning of the pandemic, countries around
the world experienced sudden lockdown policy that disrupted supply chains and led to a continuous downward
trend of economic. Meanwhile, lifestyle has tremendous changes, with working at home, online teaching and
isolation becoming part of daily life. The pandemic not only brings about challenges to economic development,
but also has a long-term impact on people's mental health and social interaction. This study analysis estimated
numbers of alcohol use and alcoholism in each state of United States before and after the pandemic, providing
a scientific basis for countries to formulate policies to solve public health problems. Deploying a Difference-
in-Differences analysis to analyse the impact of the pandemic on drinking and alcoholism in the United States
before and after the epidemic. The result indicates that before and after the pandemic, the number of people
who drinking and alcoholism has not changed in the United States.
1 INTRODUCTION
The pandemic had an impact on worldwide economic,
society and sanitation. The pandemic not only has
affected trade between countries, but also posed
unprecedented challenges to society and public
security. Among the social problems triggered by the
epidemic, the changes in drinking and alcoholism
deserve thorough exploration. Drinking may bring a
sense of relief in short term, but this behaviour may
gradually get out of control and develop into
alcoholism once the dependence is formed. Alcohol
abuse leads to a broad spectrum of liver diseases,
collectively termed alcoholic liver diseases
(Jisoo2025) and these lockdown policies tend to
increase the occurrence of domestic violence because
of isolation, coupled with economic and psychological
stress (Sibiziwe2025). It has an influence on public
health, closely affected social stability and economic
development. Under the above background, this paper
would analyse the reasons of drinking behaviour
changes and the impacts on society.
The impact of the pandemic on traditional
economic is manifested in the reduction of trade
between countries and transnational investment due to
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-7564-3393
lockdown policies and travel restrictions. During the
pandemic, many countries implemented lockdown
policies, causing cross-border logistics and supply
chains disruptions, which affected the trade of raw
materials, components and products. The tourism
sector was classified among the fast-growing and
uncompetitive sectors before the pandemic. However,
during the pandemic, it became a slow-growing and
competitive sector (Liyushiana2022). Traditional
service industries such as tourism and aviation have
been severely affected. Enterprises are facing
problems such as reduced transnational investment,
program delays or cancellations, which further affect
the global economy.
The pandemic has given rise to new economic
opportunities, accelerated digital transformation and
nurtured new economic forms. During the pandemic,
in order to maintain the stability of enterprises’
business, they adopted digital methods such as remote
working and online retail, accelerating the
transformation of information technology and
business models. New business models like digital
platforms, online education and telemedicine have
risen rapidly, these models not only bring new
development opportunities to enterprises, but also
730
Liu, Y.
A Difference-in-Differences Analysis on the Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Drinking and Binge Drinking in the United States.
DOI: 10.5220/0013853200004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 730-737
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

provide more convenient service to consumers.
Companies should enhance supply chain relationship
management and optimize the supply chain structure
to reduce risk transmission and maintain sustainability
(Shengmei2025).
The epidemic also had a negative impact on the
economy. During the pandemic, due to differences in
lockdown policies, economic foundations and policies
among different countries and regions, there were
significant variations in economic growth rates, which
led to more uneven global economic growth. Many
business organizations have implemented various
remote-work arrangements. These arrangements have
spurred the use of digitalization strategies and have
landed many employees in the vulnerable virtual
workplace (Low2021). The pandemic has generally
affected low-income people and medium-sized
enterprises. These groups have difficulty in obtaining
support, which has led to reduced income and
exacerbated unemployment, further widening the gap
between the rich and the poor.
This paper analysis estimated numbers of alcohol
use and alcoholism in various states of United States
before and after the pandemic, providing a basis for
governments to formulate policies to solve sanitation
problems. Employing a Difference-in-Differences
analysis to demonstrate the impact of the pandemic on
drinking and alcoholism in the United States before
and after the epidemic. Research results can provide
intervention strategies for various countries’
governments when facing similar public health
emergencies in the future. For instance, if alcohol
abuse shows a significant increase during the
pandemic, it may be necessary to enhance mental
health consulting, promote preventing alcohol abuse
public education and adjust relevant regulations.
2 INFLUENCE FACTORS OF
DRINKING UNDER THE
PANDEMIC BACKGROUND
2.1 The Psychological Pressure
Brought About by the Pandemic
The pandemic has given rise to new working and
learning approaches such as working at home and
online learning. For many people, this pattern has
changed the original daily routine. On the one hand,
the overlap of work and family roles compresses
people's time schedule. On the other hand, unable to
directly obtain social feedback also makes people
have self-doubt and a sense of helplessness. Data
from several international studies indicate that
healthcare workers are prone to developing mental
health problems such as anxiety and depression
(Temsah2020). When people receive negative news
and pandemic transmission data every day, negative
emotions and stress also increased. Long-term home
quarantine, concern about the pandemic transmission,
difficulty in distinguishing the authenticity of
information and uncertainty of future have intensified
public anxiety. Making people worry about
themselves’ and families’ health condition and
causing difficulties in making rational judgments,
which lead to psychological problems such as
anxiety, panic and depression. In a social
environment where pressure is constantly increasing,
some residents tend to relieve panic and anxiety by
drinking alcohol, leading to drinking or even
alcoholism behaviours.
2.2 The Economic Conditions Changes
Caused by the Pandemic
At the beginning of the epidemic, many countries
adopted measures such as lockdown policy and cross-
border trade restriction to prevent and control the
epidemic, which leaded to temporary global supply
chain disruptions. Many manufacturing enterprises
have experienced a period of resuming work after
suspension. It not only exposed a global supply chain
problem that excessive dependent on few countries or
regions, but also drove enterprises and governments to
rethink how to build more flexible and resist risk
supply chain. The pandemic has leaded to a large
number of enterprises laying off staff and halting
recruitment, which has severely impacted the labour
market. The pandemic has leaded to the deterioration
of the employment environment and instability of
economic. Many people’s economy and life condition
are facing huge adjustments. Changes in the
employment environment led to job stress in
employees, which in turn increased employee job
burnout and turnover intention (Shin2021). Income
reducing with unstable jobs or unemployment,
coupled with the continual life burden during the
pandemic have added a lot of physical and mental
pressure on people. Many people may drink alcohol as
a temporary approach to escape reality, binge drinking
has become a tool to deal with anxiety and depression.
2.3 The Social Interaction Changes
Caused by the Pandemic
The long-term lockdown policies and social
restrictions have significantly reduced traditional
A Difference-in-Differences Analysis on the Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Drinking and Binge Drinking in the United States
731

face-to-face social activities. Many people lost their
normal social activities during home quarantine,
making people lost the emotional support of face-to-
face communication. The decrease in social
interaction and increase in loneliness during the
pandemic due to government directive, along with
concerns of contracting the virus highlight the
importance of digital services for adults to keep them
connected and supported remotely (Wong2021). In
the past, drinking alcohol as a social protocol was
often restricted and supervised in friends’ gatherings,
family dinners, bars and restaurants. However, the
restraint was broken during the pandemic and many
drinking behaviours shifted to individuals make it
difficult to restrict. Although online socializing and
video gatherings have become new social interaction
forms, they are difficult to completely replace the
emotional interaction and atmosphere brought by
traditional socializing. In face of loneliness and loss,
people are more likely to rely on alcohol as an
emotional companion, making alcohol a tool to
relieve loneliness and loss when interpersonal
communication decreases. Among those drinking
more than once a week, increased alcohol
consumption is associated with loneliness
(Konno2022).
3 RESEARCH HYPOTHESES
When studying the impact of the pandemic on
drinking and alcoholism behaviour in each state of the
United States, this paper should analysis data before
and after the epidemic as well as before and during
the epidemic. These two comparisons can better
reflect the impact of the epidemic on drinking and
alcoholism behaviour, revealing the differences
between short-term and long-term effects. In fact,
comparing people's drinking behaviour during and
before the epidemic can analyse the short-term
impact. It helps us understand people's short-term
alcohol consumption changes due to psychological
pressure rise caused by lockdown policies and home
quarantines.
Hypothesis 1. Before and after the pandemic,
drinking and binge drinking in the United States has
changed. After the pandemic, more people would be
drinking and binge drinking than before the pandemic.
After the pandemic, people's drinking behaviour
may return to normal and reveal long-term changes.
By comparing the data before and after the epidemic,
it is possible to realize whether short-term changes
have an impact on long-term drinking behaviour and
whether there is an upward trend after the epidemic,
thereby providing a scientific basis for formulating
more effective intervention policies.
Hypothesis 2. Before and during the pandemic,
drinking and binge drinking in the United States has
changed. During the pandemic, more people would be
drinking and binge drinking than before the pandemic.
In conclusion, analysing drinking and alcoholism
data before and after the epidemic as well as before
and during the epidemic can not only help researchers
to understand the short-term and long-term impacts of
the epidemic on sanitation more comprehensively,
but also provides basis for government to deal with
similar crises in the future.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Data
The National Survey on Drug Use and Health
(NSDUH) releases state estimates for a limited
number of substance use and mental health measures.
They are generally based on two years of combined
data and cover each state and the District of
Columbia. This study obtains the estimated figures
(in thousands) of alcohol use and alcoholism. The
figures are among people aged 12 to 20 in various
states of the United States, which could be found on
NSDUH State Releases platform.
4.2 Identification Strategy
This paper employs a natural experiment, which
could clearly demonstrate the casual inferences
(Christine2005). Apart from that, employ DID
analysis to evaluate the P-value of the interaction
term.
This study employs two DID analyses. First, the
propose is to find out how drinking and alcoholism
change in U.S. before and after the pandemic. Second,
the propose is to find out how drinking and
alcoholism change in U.S. before and during the
pandemic. The control group is alcohol use estimate
and the treatment group is binge alcohol use estimate.
4.3 Model Building
To evaluate the influence of pandemic on the drinking
behavior, this paper measures the number of people
who using alcohol in one outcome variables:
Estimated Numbersit. The Estimated Numbersit is in
group i at time t, where i represents the treatment or
control group. The paper compares the estimated
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
732
numbers of the treatment groups and the control
group when before and after(during) the pandemic:
itit
it
it
eTreatedPeriodTreated
TreatedPeriodTreated
cNumbersEstimated
+×+
+
+=
)(
δ
γβ
(1)
where eit is the error term. The dummy variable
Treatedi equals 1 means binge alcohol using and 0
otherwise. The dummy variable Treated Periodt
equals 1 means before the pandemic and 0 means
after(during) the pandemic. The coefficient δ
evaluates the estimated number difference across
before and after(during) the pandemic.
5 DRINKING AND BINGE
DRINKING CHANGE IN U.S.
5.1 Drinking and Binge Drinking
Change in U.S. Before and after the
Pandemic
Alcohol abuse is defined as consuming five or more
glasses of alcohol (for men) and four or more glasses
of alcohol (for women) on at least one day within last
month. It is clear to see that 2018 and 2019 means
before the pandemic and 2022 and 2023 means after
the pandemic. This study downloads the raw data,
after that, filter and categorize the data. Table 1 and
Table 2 show the alcohol use and alcoholism
estimated figures in last month among people aged 12
to 20 (in Thousands).
Table 1: Before the pandemic (2018 and 2019)
Order State
Alcohol Use in Past Month
Estimate
Binge Alcohol Use in Past
Month Estimate
1 Alabama 91 57
2 Alaska 14 9
3 Arizona 141 82
4 Arkansas 61 37
5 California 800 471
6 Colorado 143 86
7 Connecticut 121 82
8 Delaware 21 11
9
District of
Columbia
11 6
10 Florida 428 235
Table 2: After the pandemic (2022 and 2023)
Order State
Alcohol Use in Past
Month (Estimate)
Binge Alcohol Use in Past Month
(Estimate)
1 Alabama 94 62
2 Alaska 11 6
3 Arizona 125 75
4 Arkansas 49 29
5 California 618 345
6 Colorado 117 64
7 Connecticut 74 44
8 Delaware 16 9
9 District of Columbia 9 5
10 Florida 335 167
Table 3 shows drinking and binge drinking
change in United States before and after the pandemic.
Figure 1 shows the DID analysis time series. The
objective is to compare whether alcoholism is
significantly more than drinking before and after the
pandemic or not.
A Difference-in-Differences Analysis on the Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Drinking and Binge Drinking in the United States
733
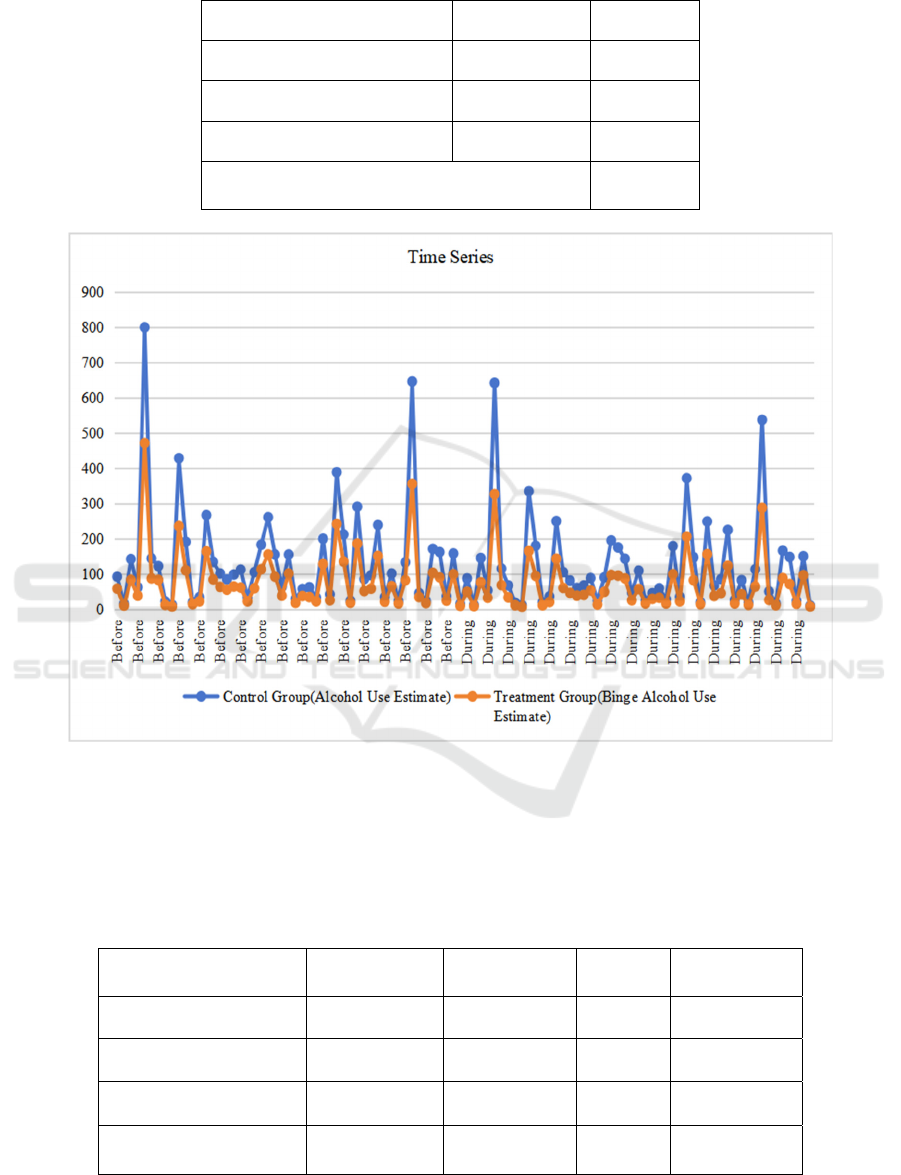
Table 3: DID calculation before and after the pandemic
Before After
Control Group 139.1 111.9
Treatment Group 83.8 63.1
Difference -55.3 -48.8
Difference in Differences 7
Figure 1. Time series before and after the pandemic (Picture credit : Original)
Table 3 and Table 4 show the DID analysis. There
are the results of the DID analysis and the regression
results. The result of DID analysis before and after the
pandemic is 7, which means that the estimated
number increase by 7 after the pandemic. It is clear to
see that the P-value is 0.83, which is much higher than
0.05, means the impact is not statistically significant.
Table 4: Regression results before and after the pandemic
Coefficients Standard Error t Stat P-value
Intercept 139.12 15.72 8.85 0.00
After -27.24 22.24 -1.22 0.22
Treated -55.33 22.24 -2.49 0.01
Interaction Term
(After*Treated)
6.57 31.45 0.21 0.83
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
734
5.2 Drinking and Binge Drinking
Change in U.S. Before and During
the Pandemic
It is clear to see that 2018 and 2019 means before the
pandemic and 2021 and 2022 means during the
pandemic. Table 1 and Table 5 show the alcohol use
and alcoholism estimated figures in last month among
people aged 12 to 20 (in Thousands).
Table 5: During the pandemic (2021 and 2022)
Order State
Alcohol Use in Past
Month (Estimate)
Binge Alcohol Use in Past
Month (Estimate)
1 Alabama 86 48
2 Alaska 11 7
3 Arizona 144 75
4 Arkansas 52 31
5 California 642 326
6 Colorado 114 67
7 Connecticut 66 32
8 Delaware 17 10
9 District of Columbia 10 5
10 Florida 334 164
Table 6 shows drinking and binge drinking
change in United States before and during the
pandemic. Figure 2 shows the DID analysis time
series. The objective is to compare whether
alcoholism is significantly more than drinking before
and during the pandemic or not.
Table 6: DID calculation before and during the pandemic
Before After
Control Group 139.1 117.3
Treatment Group 83.8 64.0
Difference -55.3 -53.3
Difference in Differences 2
A Difference-in-Differences Analysis on the Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Drinking and Binge Drinking in the United States
735
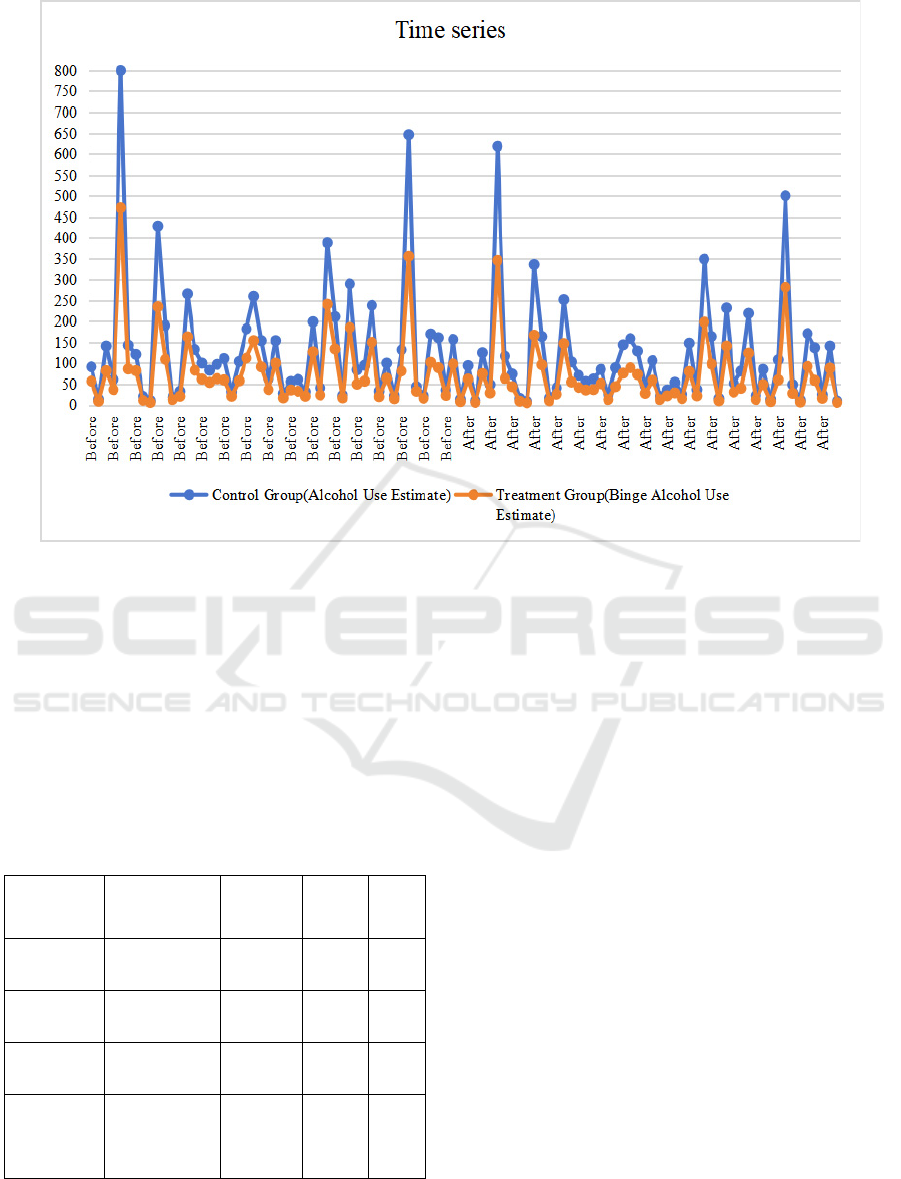
Figure 2. Time series before and during the pandemic (Picture credit: Original)
Table 6 and Table 7 show the DID analysis. There
are the results of the DID analysis and the regression
results. The result of DID analysis before and during
the pandemic is 2, which means that the estimated
number increase by 2 during the pandemic. It is clear
to see that the P-value is 0.95, which is much higher
than 0.05, means the impact is not statistically
significant.
Table 7: Regression results before and during the pandemic
Coefficients
Standar
d Error
t Stat
P-
valu
e
Intercept 139.12 15.95 8.72 0.00
After -21.84 22.55 -0.97 0.33
Treated -55.33 22.55 -2.45 0.01
Interaction
Term
(After*Tre
ated
)
2.08 31.89 0.07 0.95
6 DISCUSSION
The results indicate that the alcoholics were not
specifically affected. The interaction term did not
significantly indicate that the additional impact on
binge alcohol user is different from which to alcohol
user before and after the pandemic.
Although people's stress and anxiety increased
during the epidemic, the number of people who
drinking and binge drinking did not increase
significantly. Binge drinking users’ behaviour is often
closely related to social occasions, such as bars,
family dinners or gatherings with friends. During the
epidemic, due to the prevention policies restrictions,
social activities and home quarantine, traditional
drinking places and social activities have decreased
significantly. The lack of drinking occasions may
cause some binge alcohol users to increase their
drinking frequency at home. However, the absence of
large-scale social activities keeps the number of
drinkers remain stable.
The pandemic has changed people's daily life and
consumption custom. People began to live at home
during the pandemic and their attention to health were
also increased. Meanwhile, economic pressure and
concerns about future have also prompted some
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
736

people to reduce non-essential consumption. It has
led to a downward trend in the amount and frequency
of alcohol consumption due to the lack of drinking
occasions.
Drinking behaviour is a kind of habit. Long-term
heavy drinkers often have formed a fixed drinking
frequency and will not increase their drinking
frequency due to external environment changes, for
those who do not drink or drink moderately, the
pandemic has not prompted them to develop new
alcohol abuse behaviours. Although some people may
increase drinking frequency due to psychological
stress, the overall number of people who drinking and
alcoholism has not increased. These two parts balance
each other, thus keeping the overall number of people
remain stable.
7 CONCLUSION
Through research, this paper finds that the impact of
the COVID-19 pandemic on drinking and binge
drinking before and after(during) the pandemic is not
statistically significant. Therefore, the result indicates
that the number of people who drinking and
alcoholism remain stable, their attention to health is
increased, heavy drinkers have formed a fixed
drinking frequency and would not increase that
during the pandemic, for those who never drink or
drink moderately, the pandemic has not prompted
them to develop new alcohol abuse behaviours.
Overall, the COVID-19 pandemic has not only
posed challenges to global society and economy, but
also made us more clearly about the importance of
drinking problem in public health field. In the future,
each country needs to take a long-term perspective to
improve sanitation policies, and comprehensively
address the health, social and economic issues
exposed by the epidemic, which in order to promote
the overall social health level and economic steady
improvement.
This paper has a few limitations. First, this study
analysis estimated numbers of alcohol use and binge
alcohol use in each state of United States. However,
this paper is unable to take the inherent difference of
each state into account, such as population,
geographical location and lockdown policy. Future
research could take the inherent difference into
account to carry out further study. Second, this paper
analysis estimated numbers in each state of United
States. However, this paper is unable to analysis the
substate data, such as estimated numbers in different
county of each state. Future research can take the
county data into account to carry out further study on
this issue.
REFERENCES
Anderson-Cook, C. M., 2005. Experimental and quasi-
experimental designs for generalized causal inference.
Journal of the American Statistical Association,
100(470), 708-708.
Chen, S., & Ren, G., 2025. The impact of exogenous shocks
on the sustainability of supply chain relationships:
Evidence from the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability,
17(7), 2828-2828.
Kang, J., Park, S. H., Khanam, M., Park, S. B., Shin, S., &
Seo, W., 2025. Impact of binge drinking on alcoholic
liver disease. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 48(3),
1-12.
Konno, Y., Okawara, M., Hino, A., Nagata, T., Muramatsu,
K., Tateishi, S., ... & Fujino, Y., 2022. Association of
alcohol consumption and frequency with loneliness: A
cross-sectional study among Japanese workers during
the COVID-19 pandemic. Heliyon, 8(12), e11933-
e11933.
Liyushiana, Sibarani, R., Purwoko, A., & Emrizal, 2022.
The contribution of the tourism sector to the regional
spatial economy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
International Journal of Sustainable Development and
Planning, 17(8).
Low, M. P., & Bu, M., 2021. Examining the impetus for
internal CSR practices with digitalization strategy in the
service industry during COVID-19 pandemic. Business
Ethics, the Environment & Responsibility, 31(1), 209-
223.
Shin, D., Kim, Y., & Kim, B., 2021. Understanding job
stress and organizational effectiveness of airline
employees due to changes in the employment
environment under COVID-19 — Focusing on the
difference in the GAD-7 of employees. Sustainability,
13(24), 13722-13722.
Shumba, S., Muyangata, J., & Nyangari, E., 2025. The
COVID-19 pandemic and domestic violence: A case of
African Christian women in Gwanda district,
Zimbabwe. Inkanyiso, 17(1), e1-e10.
Temsah, M. H., & Alenezi, S., 2020. Understanding the
psychological stress and optimizing the psychological
support for the acute-care health-care workers during
the COVID-19 pandemic. Saudi Critical Care Journal,
4(5), 25-27.
Wong, Z. X., Phua, A., Chew, K. A., Mohamed, J. S., Pé
rez, K. M., Mangialasche, F., ... & Chen, C., 2021.
Impact of Covid-19 pandemic on lifestyle in a middle-
aged and elderly population. Alzheimer's & Dementia,
17(S10).
A Difference-in-Differences Analysis on the Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Drinking and Binge Drinking in the United States
737
