
Research on Green Supply Chain Management in New Energy
Vehicle Industry: A Case Study of BYD
Yuxuan Lou
a
Business College, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, China
Keywords: New Energy Vehicles, Green Supply Chain, BYD, Green Development.
Abstract: Nowadays, the environmental awareness of society as a whole is constantly improving, and the new energy
industry is also developing rapidly. The development and demand for green supply chains in various industries
are increasing daily. To achieve sustainable development, the automotive industry, as a high-energy-
consuming and polluting industry, has gradually changed its products and production methods. Based on the
purpose of green development, it not only embodies the concept of green environmental protection in terms
of energy use, but also undergoes green transformation in the industrial chain and supply chain, aiming to
achieve low-carbon emission reduction and minimize environmental harm as well as full-chain costs. As a
trailblazer in China's new energy vehicle industry, BYD has paved the way for the exploration of green and
sustainable development by making significant contributions. The purpose of this study is to investigate the
construction and management of a green supply chain system in the new energy vehicle industry, using BYD
as an example.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to the advancement of industry and human
society, the global economic pattern has been deeply
reconstructed. The global climate is undergoing
drastic changes, and resource and environmental
problems are becoming prominent. The climate crisis
cannot be delayed (Liu & Yan, 2025). The
international community is adopting various
sustainable development plans and means to
implement emission reduction and ecological
civilization construction. How to improve the ability
to manage the climate crisis from all dimensions and
achieve green development has also become a key
issue in the meantime. The green supply chain
represents the cross-integration of environmental
consciousness, efficient resource utilization and all
supply chain links. It constitutes a significant
mechanism for realizing green manufacturing and
promoting sustainable development. The goal is to
achieve maximum resource efficiency across the
supply chain ecosystem through systematic
management, all while reducing environmental
impact to the lowest feasible level. The traditional
supply chain system cannot be compared to the green
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-3679-6653
supply chain system, which integrates the concept of
the whole life cycle of products and the extension of
producer responsibility with the traditional supply
chain. It uses the huge power of the government,
enterprises and public consumption to drive the green
transformation. The development of green supply
chains has become unstoppable and has become a key
driving force for global supply chains and industrial
chains (Liu & Yan, 2025). As the low-carbon
economy continues to improve, China has set the
Dual Carbon Goals of reaching carbon peaking by
2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060.The CO2
emissions of the automotive industry are significantly
higher than those of other industries, so new energy
vehicles have emerged. Meanwhile, the global energy
system is undergoing a profound revolution and the
electric vehicle industry is gradually occupying an
important strategic position in green development.
The global new energy vehicle industry has
experienced rapid growth in recent years, driven by
factors such as increasing environmental awareness,
technological advancements, and supportive
government policies and is expected to dominate the
automotive market in the coming years. The
technological innovation of eco-friendly vehicles is
Lou, Y.
Research on Green Supply Chain Management in New Energy Vehicle Industry: A Case Study of BYD.
DOI: 10.5220/0013852600004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 705-710
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
705

constantly advancing. Battery technology is gradually
maturing, and autonomous driving is constantly
developing. Governments around the world are
increasingly investing in the construction of charging
facilities for new energy vehicles. The upstream and
downstream enterprises of the industrial chain
cooperate more closely. Various parts enterprises and
vehicle enterprises develop together. However,
within the supply chain, carbon emissions and
resource waste from logistics operations have become
major environmental concerns. From production to
sales, manufacturing and processing time constitutes
merely 10%, with nearly 90% of the total time
attributed to logistics processes, including
warehousing, transportation, loading/unloading, sub-
packaging, distribution processing, and information
handling. Upstream energy consumption is high, and
carbon emissions are huge, so supply chain emission
reduction actions deserve more research. For the
purpose of achieving sustainable development and
reducing operational costs, the new energy vehicle
(NEV) industry places emphasis on building a green
supply chain system. Consumers are more likely to
select companies that have environmental
responsibility for their product selection due to the
growing awareness of environmental protection
throughout society.
This study seeks to evaluate the current state of
green supply chain management and investigate the
creation of a green supply chain system in the new
energy vehicle market. BYD is the market leader
when it comes to new energy vehicles. Its green
supply chain is integral to the automotive industry
process and its business encompasses the entire
industrial chain of new energy vehicles, with a
complete system and typical characteristics. Taking
BYD as an example, this study examines the current
state of BYD's supply chain and proposes
development suggestions for the advancement of
green supply chain management in NEV.
2 THE STATUS QUO OF GREEN
SUPPLY CHAIN
MANAGEMENT IN NEV
2.1 Industrial Policy Environment
Driven by technological breakthroughs, the NEV
industry has become a trailblazer for innovation in the
global automotive sector, providing new
development opportunities for China to transform
from a Big Country of Imitation to a Strong Country
of Automobile Manufacturing. To promote the early
achievement of the national carbon peak goal, the
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology
(MIIT) issued the Measures for the Parallel
Management of Corporate Average Fuel
Consumption and New Energy Vehicle Credits for
Passenger Vehicles in September 2017. Among these,
the Double Credit carbon emission management
model and national subsidy policies have driven the
transformation of the traditional automotive industry
toward new energy vehicles. China's NEV production
climbed from 84,000 units in 2014 to 9.587 million
units in 2023, indicating significant progress in
China's transition to a green and electrified
automotive industry (Sun, 2025). In the context of
phased NEV development , the upstream raw
material manufacturers of green energy vehicles
account for a huge proportion of carbon emissions
(Yang & Xuan, 2025). According to McKinsey,
emissions from the production of materials for
electric vehicles are expected to account for 45% of
total vehicle life cycle emissions by 2025 and about
85% by 2040 (Yang & Xuan, 2025). Although the
carbon emissions of new energy vehicles relying on
electric vehicles in the process of driving are zero all
carbon emissions are transferred to the production
end (Chen , 2018). Qiao ( Qiao, Zhao, Liu, Jiang &
Han, 2017) et al. compared the carbon emissions of
pure electric vehicles and traditional fuel vehicles in
China from three aspects: different materials,
components and energy consumption, and the results
showed that the carbon emissions of pure electric
vehicles were 15.0~15.2t, about 50% higher than that
of traditional fuel vehicles (Yang & Xuan, 2025).
The Guiding Opinions of the General Office of the
State Council on Actively Promoting Supply Chain
Innovation and Application issued by the General
Office of the State Council in October 2017 shows
that new development is a defining characteristic of
the supply chain concepts , such as innovation,
coordination, green, openness and win-win, thereby
fostering supply chain innovation and growth. This
approach facilitates mutually beneficial collaboration
and synchronized development among upstream and
downstream enterprises in the supply chain, while
promoting the establishment of a green industrial
system covering all links. Green supply chain
management is promoted throughout the product life
cycle and the demonstration is carried out in the
automobile and other industries, which will
strengthen supervision, establish a harmonized green
standard, certification and labeling regime , support
green industries and facilitate the construction and
sustainable development of green supply chain
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
706
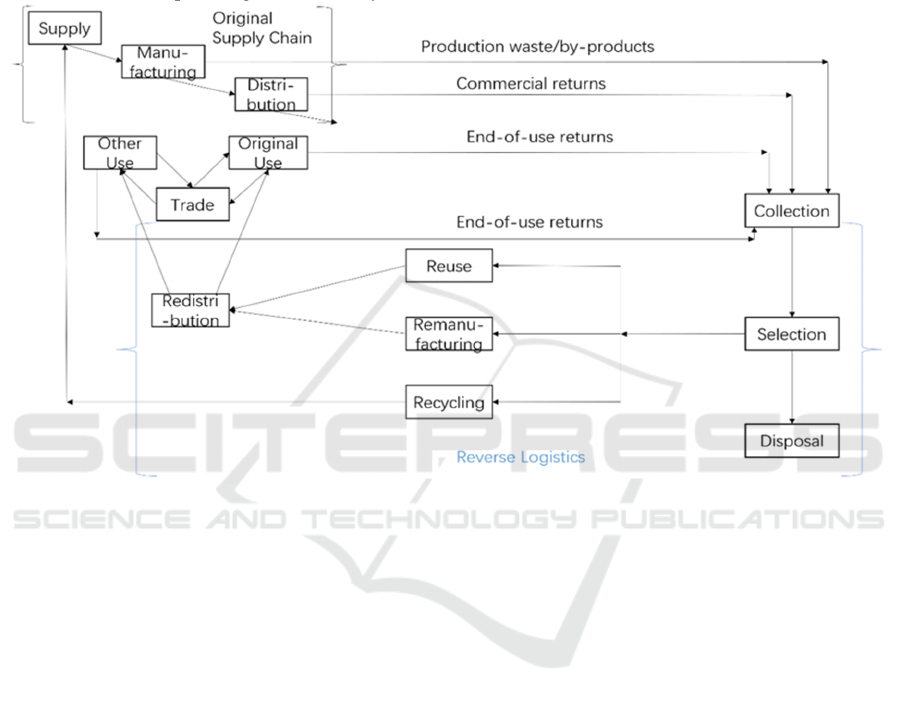
systems. Reverse logistics is encouraged to be
constructed based on the supply chain,as shown
Figure 1. Reverse logistics distinguishes itself from
the traditional supply chain. Its extension part realizes
the improvement of resource utilization in the chain,
focusing on the recycling and reuse of products from
multiple parties in the automobile, electronics and
other industries and optimizing the network layout of
reverse logistics. The supply chain of new energy
vehicles encompasses vehicle manufacturers, parts
producers, suppliers, retailers, and other enterprises.
Across the entire industry, low-carbon innovation in
the NEV supply chain has emerged as an unavoidable
trend and a critical pathway to drive the transition
toward low-carbon emission reduction.
Figure 1: Reverse logistics. (Picture credit: Original)
2.2 Industrial Chain Structure and Key
Links
With regard to the new energy vehicle industry, the
supply chain spans multiple stages, including the
procurement, production, and distribution of critical
components such as power batteries, motor drives,
electronic control units, and body structural parts. In
recent years, the price fluctuations of key raw
materials have been obvious, which has increased the
difficulty of cost control. The inventory turnover of
various production bases needs to be improved and the
planning of logistics and distribution links is not good.
The arising of various issues has led to an increase in
supply chain costs. Therefore, the improvement and
resolution of existing problems is made possible
through the improvement of the supply chain
management system. Unlike the linear flow of
traditional supply chains, reverse logistics introduces
a return-and-recycle mechanism, thus transforming
the supply chain into a closed loop. Based on
traditional supply, production and marketing, the
recyclable materials in the process are re-put into the
industrial chain for use, improving resource
utilization, while reducing carbon emissions and costs.
The Ministry of Industry and Information
Technology's Green Supply Chain Management
Evaluation Requirements pointed out that the green
supply chain will run through the concept of
environmental protection and resource conservation
throughout the whole process of enterprises from
product design to raw material procurement,
production, transportation, storage, sales, use,
scrapping and recycling, so that enterprises can
achieve environmental protection while carrying out
economic activities. Integrated green supply chain
activities include green procurement, logistics, design,
products, packaging, sales, and waste recycling. Its
specific performance in the new energy vehicle
industry chain can be manifested in the supply of
sustainable raw materials and environmentally
friendly parts (green procurement), the substitution of
clean energy for the use of non-renewable energy and
production quality control (green production), low-
carbon transportation modes such as railway
transportation and water transportation as well as
Research on Green Supply Chain Management in New Energy Vehicle Industry: A Case Study of BYD
707
intelligent physical management (green logistics),
power battery recycling and recycling of waste parts
(waste recycling), etc.
3 CASE STUDY OF BYD's GREEN
SUPPLY CHAIN
MANAGEMENT
3.1 Company Profile of BYD
BYD stands as a globally leading integrated
enterprise in the new energy and technology domains.
Originating from the production of rechargeable
batteries, it first ventured into the lithium-ion battery
industry in 1997, and became Nokia's first Chinese
lithium-ion battery supplier in 2002. The business
scope of the BYD brand covers four major fields:
electronics, automobiles, new energy, and rail transit.
With over 30 industrial parks worldwide, it has
completed a strategic deployment across six
continents. BYD takes battery technology as the core
to promote the iteration of new energy vehicles,
energy storage systems and other technologies. It has
rich experience in research and development in the
field of new energy vehicles and strong technical
strength. Its products also have high visibility and
competitiveness in the global market. BYD has made
a series of important achievements in the field of
NEV. The industrial chain layout is strengthened and
R&D technology is continuously developed, BYD
will continue to strive to advance new energy vehicle
technology innovation and foster the sustainable
development of the global NEV industry. It will
continue to be committed to helping achieve the Dual
Carbon goal through zero-emission solutions (Yang,
2024).
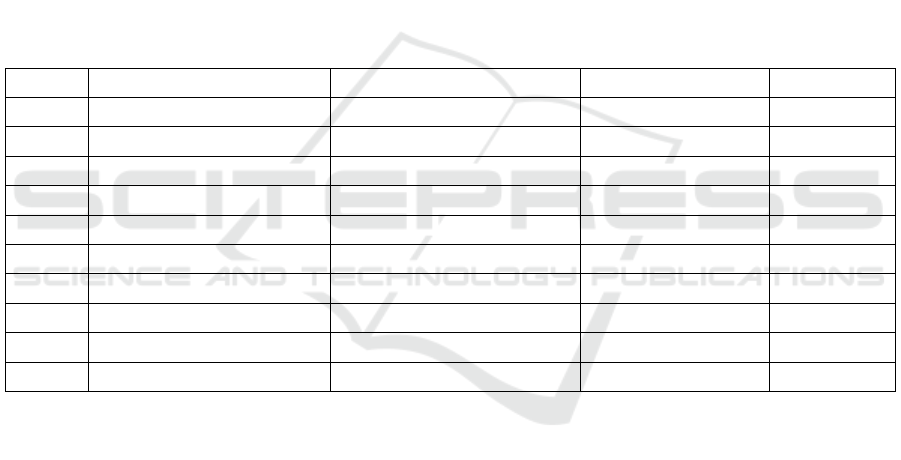
Table 1: From January to November 2024,China's New Energy Vehicle Manufacturers will be Ranked TOP10 in Retail Sales
Rank The name of the business Sales volume(10,000) units Year-on-year growth Market share
1 BYD Auto 331.52 37.80% 34.50%
2 Geely Automobile 75.41 94.30% 7.90%
3 Tesla China 57.42 8.80% 6.00%
4 SAIC GM-Wuling 55.71 42.60% 5.80%
5 Changan Automobile 55.03 60.60% 5.70%
6 Ideal car 44.20 35.70% 4.60%
7 Cialis Motors 35.58 379.20% 3.70%
8 Chery Automobile 35.39 252.30% 3.70%
9 GAC Aion 33.08 -24.80% 3.40%
10 Great Wall Motors 25.33 21.30% 2.60%
As can be seen from Table 1, BYD is the new
energy vehicle manufacturer with the highest sales
volume and market share, which has great reference
value for other automobile companies in the same
industry when studying enterprise value. In addition,
BYD has repeatedly received an A ESG rating,
indicating that BYD is doing well in promoting its
sustainable development strategy. Therefore, BYD
was selected as the research object to explore its green
supply chain management (Sun, 2025).
3.2 BYD's Green Supply Chain
Management Strategy
By embedding green supply chain management into
its corporate strategy, BYD has set a benchmark for
the automotive industry to demonstrate how
environmental responsibility can be integrated with
business growth, aiming to achieve sustainable
growth through low-carbon procurement, eco-
friendly production, and responsible distribution. It
has built a low-carbon supply chain system covering
the whole life cycle of R&D, production, logistics and
recycling around the three major contents of
technological innovation, full-chain collaboration
and a standardization system. BYD has established a
carbon data management platform covering suppliers,
following ISO14067 unified data collection standards
and training suppliers to improve data quality to
ensure transparency and traceability of scope
emissions. For the procurement of materials, BYD
gives priority to low-carbon material suppliers,
incorporates environmental protection indicators into
the supplier assessment system and forces upstream
enterprises to upgrade their technology.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
708

3.3 Green Supply Chain Management
Practices
BYD has invested more than 150 billion RMB in
technology R&D and innovation, covering battery
technology, photovoltaic energy storage, intelligent
logistics and other fields, providing underlying
support for carbon reduction in the supply chain.
BYD's independently developed blade battery has
initiated a new form of energy storage. Employing a
lithium -iron-phosphate (LFP) structure, the blade
battery has a milder environmental impact compared
to the common nickel-cobalt-manganese (NMC) and
nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) compositions
utilized by the majority of other EV producers.
Additionally, it achieves a 30% boost in energy
density and a cumulative decrease of 65 million tons
in carbon emissions. LFP batteries also feature higher
recyclability at the end of their lifecycle, enhancing
environmental sustainability while cutting production
costs. (de Sousa, C., Daniel Morais, 2024). However,
the blade battery faces some problems, for example,
the discharge capacity of the blade battery is only
80% of the normal temperature in a low temperature
environment (-20°C), while the ternary lithium
battery can be maintained at 86%. This attenuation of
low-temperature endurance may weaken consumers'
confidence in lithium iron phosphate batteries and
affect the purchase decisions of users in the north.
BYD has deep technology accumulation and a
complete industrial chain layout in the field of
photovoltaic energy storage. Its technology covers
core links such as photovoltaic power generation,
energy storage batteries, energy management systems
(EMS), and intelligent inverters, forming an
integration of photovoltaic and storage. BYD's
photovoltaic module technology uses high-efficiency
monocrystalline silicon PERC cell technology, with a
conversion efficiency of more than 22%, supporting
bifacial power generation design and increasing
power generation per unit area. At the same time,
lightweight flexible components have been
developed, which are suitable for special scenarios
such as industrial and commercial roofs and carports,
reducing installation costs.
BYD set up China's first zero-carbon park
headquarters for an automaker in 2022, which has
become a model for other zero-carbon parks in the
country. At the Pingshan headquarters park, BYD has
achieved 100% utilization of new energy vehicles. In
the park, all production processes utilize its self-
developed pure electric forklifts, pallet trucks,
cleaning vehicles, etc., aiming to realize 100% green
logistics and achieve a cumulative reduction of
245,681.89 tons of carbon dioxide equivalent.
(Zhang, 2023).
3.4 Digital Empowerment
BYD has built a full-chain digital system covering
R&D, production, supply chain, marketing and
service through the model of technology self-research
+ ecological integration to promote the digital
transformation of enterprises to intelligence. To
facilitate digital transformation, the company has
formed a steering committee for digital
transformation and a dedicated office, tasked with
ensuring its efficient advancement and practical
implementation (Zhou & Zhang, 2025). In terms of
technology manufacturing, BYD has realized the
digital upgrade of the whole process, introduced AI
visual inspection in the production process of
batteries and monitored the surface quality of battery
cells in real time with a detection accuracy of 99.99%,
reducing labor costs by 70%. BYD's Pingshan plant
uses an EMS system to visualize water, electricity and
gas consumption data, reducing unit energy
consumption by 18%. In the realm of integrating
photovoltaic (PV) power generation with energy
storage, BYD has linked its PV power generation and
energy storage system to an intelligent microgrid,
boosting the self-sufficiency rate of green electricity
to 45%.
4 CONCLUSIONS
There is a definite positive correlation between
BYD's green supply chain management and its
corporate value, which is not only the practice of
environmental responsibility, but also an important
source of its technical barriers and cost advantages,
establishing a reproducible model of mutual
commercial and social value for the global NEV
sector. Building on the above findings, NEV
companies can benchmark against BYD to
systematically enhance their supply chain
management capabilities. Enterprises are advised to
further strengthen the green supply chain
management standard system, ensuring that green
transformation can be implemented across the entire
supply chain. Enterprises should also take a leading
role in enhancing collaboration with suppliers,
distributors, and other upstream and downstream
enterprises. This involves optimizing procurement
strategies, strengthening the alignment of
environmental protection standards, achieving
efficient resource utilization and waste reduction, and
Research on Green Supply Chain Management in New Energy Vehicle Industry: A Case Study of BYD
709

jointly advancing the sustainable development of
green supply chains. Enterprises should continue to
strengthen the construction and management of the
green information platform, improve the level of
information transparency in the whole chain, create a
green image of enterprises, and enhance corporate
visibility and social recognition. In the long run,
although the company's R&D expenditure and
production costs may be increased in the early stage,
enterprises must reinforce their ability to innovate
independently, continuously improve the technology
level of new energy vehicles, and invest in green
production and logistics. Enterprises should improve
resource utilization, strive to reduce carbon emissions
in the production and transportation process and
maximize the market competitiveness of products by
reducing the environmental impact and optimizing
the production process. Enterprises need to
dynamically track green manufacturing policies and
actively participate in certification to enhance brand
premium. Enterprises should also proactively engage
in international environmental protection cooperation
and exchanges, draw insights from global practices,
and actively compete with international counterparts
to continuously enhance their green development
capabilities.
REFERENCES
Chen, X., 2018. Research on the Environmental Benefits of
Electric Vehicles Based on the Life Cycle of Coal
Power. Wuhan University of Technology.
de Sousa, C., & Morais, D., 2024. Electric vehicle
manufacturer BYD expansion into europe: A case
study. (Order No. 31902934). (3196617178).
Liu, X., & Yan, F., 2025. Accelerate the construction of a
green supply chain system. Party and Government
Cadres Forum, (03), 27-29.
Peng, W., 2025. Research on BYD's supply chain cost
control from the perspective of green development.
Automotive Knowledge, 25(05), 244-246.
Qiao, Q., Zhao, F., Liu, Z., Jiang, S., & Hao, H., 2017.
Cradle-to-gate greenhouse gas emissions of battery
electric and internal combustion engine vehicles in
China. Applied Energy, 204, 1399-1411.
Sun, W., 2025. The impact of green supply chain
management on the value of new energy vehicle
enterprises: A case study of BYD. World Journal of
Management Science, 3(1).
Yang, Q., & Xuan, F., 2025. Research on the development
of closed-loop supply chain of new energy vehicles
under the background of "dual carbon". Modern
Commerce & Trade Industry, (02), 73-76.
Yang, S., 2024. Research on Green Development and
Sustainable Development Strategy of Automobile
Industry: A case study of BYD Co., Ltd. Modern
Industrial Economics and Informatization, 14(08), 187-
188+191.
Zhang, J., 2023-03-23. BYD's ESG secret. Securities
Times, A05.
Zhou, Z., & Zhang, Q., 2025. Digital transformation path
and case study of automobile manufacturing industry:
A case study of BYD group. Times Automobile, (08),
25-27.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
710
