
Influence of Supply Chain Geographic Proximity and Concentration
on Financial Performance of Chinese Automakers
Chengbo Li
a
School of Business, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Keywords: Supply Chain Geographic Proximity, Supply Chain Concentration, Inventory Turnover Ratio.
Abstract: China’s automobile manufacturing industry has dominated the world’s automaking market for over a decade.
However, given the trend of globalization and the intensified competition in the industry, supply chain
network structure plays a vital role in Chinese automakers' financial performance. This paper utilized the
inventory turnover ratio to evaluate the impact of supply chain concentration and geographic proximity on
firms’ financial performance in China’s automotive manufacturing industry. To assess the impact, this
research uses data of 83 firms listed on Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges in China’s automotive
manufacturing industry from year of 2010 to 2023. The main findings are: first, supply chain geographic
proximity is negatively related to the inventory turnover ratio; second, supply chain concentration are
negatively related to the inventory turnover ratio. Therefore, both supply chain geographic proximity and
concentration can negatively impact Chinese automakers’ financial performance. This research provides
insightful implications to firms and managers on how supply chain structure can impact financial performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
China’s automobile manufacturing industry stands
out due to its scale, quality, efficiency, and diversity.
In 2024, China produced over 31.4 million vehicles,
including 12.9 million new energy vehicles, which
accounted for approximately one-third of the world
total vehicle production and over two-thirds of the
world's electric vehicle production (Zhang, 2025).
China has maintained to be the world's largest
automobile manufacturing powerhouse for 15 years
since 2009, and for the first time in 2024 it surpassed
Japan and Germany, becoming the world's largest
automobile exporter (Chang & Bradsher, 2024).
However, given the dominant position of China’s
automobile manufacturing industry in the world, it
also faces tremendous internal and external
challenges and uncertainties, such as geopolitical
risks, environmental impacts, digital transformation,
industrial upgrading, and natural disasters. To tackle
these challenges and remain a sustainable and
competitive advantage in the global market, it is vital
to evaluate the impact of Chinese automakers’ supply
chain network structure on their financial
performance. Many studies have been conducted to
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-5566-5518
demonstrate supply chain factors that can influence
the financial performance of China’s automobile
manufacturing industry, including visibility,
digitalization, network complexity, inventory
management, and communication. However, as
critical structural components of supply chain
network, the influence of geographic proximity and
concentration on the financial performance of
Chinese automakers remain under-investigated.
Inventory turnover ratio is a perfect metric to measure
both the supply chain and financial performance of
firms. It not only evaluates how quickly a firm can
sell its inventory in a given period, which is closely
related to a firm’s supply chain management capacity,
but also is commonly referred to as a common metric
to measure sales efficiency, which reflects a firm’s
financial performance (Kwak, 2019). Thus, the
objective of this research is to explore and evaluate
the correlation among supply chain proximity,
concentration, and business performance based on a
firm’s inventory turnover ratio within China’s
automobile manufacturing industry. Particularly, this
paper seeks to answer two questions: First, does
supply chain proximity significantly impact China’s
automobile manufacturing firms’ financial
698
Li, C.
Influence of Supply Chain Geographic Proximity and Concentration on Financial Performance of Chinese Automakers.
DOI: 10.5220/0013852500004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 698-704
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

performance? Second, does supply chain
concentration significantly impact businesses’
financial performance within China’s automobile
manufacturing industry?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Impact of Supply Chain
Concentration on Financial
Performance
Supply chain concentration measures a company's
dependence on a small group of up and downstream
critical business partners. Thus, high supply chain
concentration indicates that an organization is highly
dependent on its suppliers and customers on raw
materials and sales channels. Scholars have
conducted various academic research on supply chain
concentration and its impact on business financial
performance. It is evident that supply chain
concentration is capable of influencing supply chain
resilience as it reflects a firm’s dependence on its
major trading partners (Jiang et al., 2023). Supplier
concentration generally represents the degree of a
firm’s raw material or service dependence on its
major suppliers. Therefore, high supplier
concentration, meaning a firm’s physical and
informational resources are predominantly obtained
from a few upstream suppliers, would hinder a firm’s
inventory, production, and operation when risks
occur to its suppliers. However, low supplier
concentration usually means a low level of
collaboration between the firm and suppliers, which
would increase the firm’s supply chain network the
complexity and potentially magnify the bullwhip
effect within its supply chain. Similarly, customer
concentration usually indicates the portion of a firm’s
sales revenue generated from a small group of large
customers (Chen & Xu, 2024; Jiang et al., 2023).
Hence, high customer concentration indicates that a
firm’s product sales are primarily reliant on a few
selected customers, which would become an
operational obstacle when disruption happens to
downstream major customers. Whereas, low
customer concentration usually indicates poor
customer collaboration and relationship management.
Additionally, according to Porter’s (2008) theory,
firms lose tremendous bargaining power and
competitive advantages when their operations rely
too much on a small group of suppliers or customers.
Therefore, supplier and customer concentration can
significantly influence a firm’s supply chain
resilience, which in turn affects its overall financial
performance.
2.2 Impact of Supply Chain
Geographic Proximity on Financial
Performance
Supply chain geographic proximity is also referred to
as the spatial distance between a firm and its suppliers
or customers (Cortes, 2023). It was largely considered
a major role that affects communication efficiency
between organizations. For instance, previous studies
show that companies within a proximity tend to have
a better communication channel to share information,
thereby promoting collaborations and improving
visibility (Yang & Ren, 2021). However, given the
modern technology development, especially the
development of the internet, communication between
organizations is no longer considered a major factor
that affects firms’ selection of supply chain partners
on the basis of geographic location. Despite the
communication efficiency between firms no longer
relies entirely on the distance, other factors that
associated with geographic proximity remain playing
critical roles influencing firms’ decision on suppliers
and customers selection as supply chain complexity
increases. For example, supplier selection is generally
based on consideration of cost, efficiency, time,
product quality, and variety. Therefore, companies
within a proximity would benefit from lower
transportation costs, shorter lead time, and more agile
inventory policies, which in turn enhance the overall
supply chain resilience (Lorentz et al., 2012).
Furthermore, a resilient supply chain could reduce
overall operating costs, hence, improve firm’s overall
financial performance.
2.3 China’s Auto Manufacturing
Industry Supply Chain
Characteristics
Despite the current dominant position of China’s
automobile manufacturing industry in the global
market, the industry is currently facing many
complex supply chain problems due to its rapid
development history and the current fast-paced
transition to new energy vehicles. Over recent
decades, China’s automaking sector has evolved from
a highly decentralized structure to industrial clusters
where manufactures and suppliers operate within the
same geographic regions (Cao et al., 2022; Y. Huang
et al., 2020; Sun & Abdullah, 2025). This clustering
structure offers automakers with significant
advantages, including low transportation costs and
Influence of Supply Chain Geographic Proximity and Concentration on Financial Performance of Chinese Automakers
699

low production delay risks. Thus, firms naturally
prefer to trade with businesses with who they have
already established a good relationship and within
close geographic proximity (Cao et al., 2022).
However, supply chain tension occurred with the
growing expansion of the industry. Especially when
there are hundreds of automakers and thousands of
component manufactures, not to mention the fact that
these numbers are still growing rapidly (Y. Huang et
al., 2020). The increasingly crowded supply chain
would intensify not only the competition across the
entire industry, but also the corporate decision-
making process regarding trading partner selection
and management, which in turn exacerbate the supply
chain complexity of the industry (Z. Huang et al.,
2024; Sun & Abdullah, 2025). Moreover, the trend of
new energy vehicle transition introduces additional
layers of supply chain complexity. Conventional
automakers and their suppliers have to both
collaborate with and compete against newly formed
new energy vehicle manufacturers and their
specialized suppliers due to differences in
manufacturing technology, supplier specification,
and customer segmentation (Cao et al., 2022). On one
hand, conventional automakers must cooperate with
and learn from new energy vehicle firms to achieve
their industrial upgrading and transition objectives;
on the other hand, conventional automakers face
intensifying competition from the same new energy
vehicle manufacturers for critical suppliers and
customers. Additionally, some industry clusters
centered by new energy vehicle manufacturers
established in regions that are geographically distant
from conventional automakers, creating spatial
fragmentation in China’s automotive supply chain
network which resulting in new challenges in
logistics coordination and supply chain integration
(Cao et al., 2022). Consequently, this makes the
supply chain of the whole industry even more
complex. Therefore, it is significant to investigate the
impact of supply chain distance and concentration on
automakers' financial performance.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection and Processing
All data was extracted from the CSMAR (China
Stock Market and Accounting Research) database,
which is an intensive, definitive, and reliable
research-oriented platform in line with global
professional standards highlighting China’s finance
and economy while incorporating China’s exclusive
national characteristics. Therefore, data from 83 firms
listed on Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges in
China’s automotive manufacturing industry as
samples provides a solid foundation supporting this
research to answer the above research questions. The
earliest available data of both supply chain
geographic distance index and supply chain
concentration index of China’s automobile
manufacturing industry can be tracked from 2001,
whereas firms’ financial information only started to
be disclosed from 2010. Therefore, key metrics in
each dataset, including end date, stock symbol, and
industry classification code, were used to consolidate
all necessary and meaningful data into one unified
dataset. Consequently, all the data of Chinese
automakers used in this research were based on the
combination of the above datasets, from year of 2010
to 2023.
3.2 Variable Measurements
Types, abbreviations, and descriptive statistics of
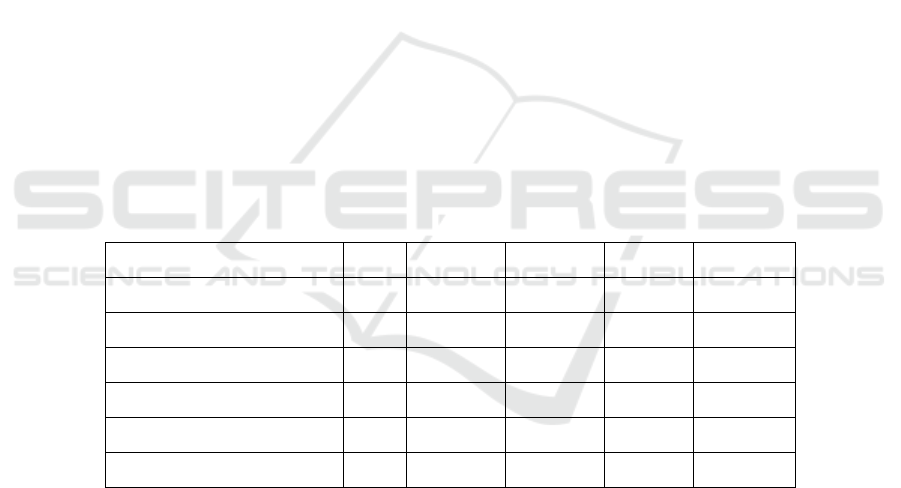
variables are presented in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1: List of variables, abbreviations, and data sources
Type Variable Abbreviation Data Source
Dependent Variable Inventory turnover ratio ITR CSMAR
Independent
Variables
Spatial distance SD CSMAR
Major customer ratio MCR CSMAR
Major supplier ratio MSR CSMAR
Customer concentration CC CSMAR
Supplier concentration SC CSMAR
Control Variables
Close proximity CP CSMAR
Same province SP CSMAR
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
700
3.2.1 Dependent Variable
To evaluate the impact of supply chain metrics on
financial performance, the inventory turnover ratio
was selected as the dependent variable. It measures a
firm’s efficiency in selling out its inventory in a given
period, which in turn reflects not only a firm’s overall
supply chain management capacity but also shows its
financial performance. A high inventory turnover
ratio is always favorable to firms since it
demonstrates their high financial liquidity level and
supply chain efficiency level.
3.2.2 Independent Variable
As shown in the Table 1, independent variables used
in this research were spatial distance, major customer
ratio, major supplier ratio, customer concentration,
and supplier concentration.
Spatial distance was selected to assess the
geographic distance between a firm and its supplier or
customer, which helps to evaluate the impact of
supply chain proximity on financial performance.
Major customer ratio was calculated by dividing a
firm’s revenue from its single largest customer by its
yearly total sales. This metric quantifies the
dependence level of the firm to the largest customers.
Major supplier ratio was derived by dividing a
firm’s annual procurement from the single largest
supplier by the firm’s yearly total purchasing volume.
This variable assesses the dependence level of a firm
on the largest supplier.
Customer concentration was calculated by
dividing the revenue generated from the top five major
customers by a firm’s yearly total sales. This variable
reflects a firm’s sales channel dependence on key
customers.
Supplier concentration was derived by dividing a
firm’s annual purchases from its top five suppliers by
its total annual purchases. This variable measures a
firm’s source of goods dependence on major suppliers.
3.2.3 Control Variable
Close proximity dummy variable was constructed as
a control variable. It is assigned 1 if the distance
between a firm and its supply chain partner (supplier
or customer) is less than 300 km, and 0 otherwise.
Same province dummy variable was included as a
control variable to show whether a supply chain
partner (supplier or customer) is located in the same
province as the firm. It is 1 if they are in the same
province, and 0 otherwise.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics
Variables Obs. Mean S.D. Min. Max.
Inventory Turnover Ratio 452 5.490 3.838 1.480 39.955
Spatial Distance 452 559.432 583.062 0.706 2418.294
Major Customer Ratio 452 22.930% 15.196% 0.890% 78.210%
Major Supplier Ratio 452 14.621% 13.407% 1.780% 63.300%
Customer Concentration 452 47.376% 23.013% 4.110% 99.300%
Supplier Concentration 452 31.867% 17.777% 6.740% 89.380%
3.3 Analysis
The regression model can be specified as follow:
βββ
β
β
β
+++
++=
CCMSR
MCRSDITR
43
210
(1)
Where ITR is the dependent variable inventory
turnover ratio; SD is the spatial distance between
firms and suppliers or customers; MCR represents the
major customer ratio; MSR represents the major
supplier ratio; CC is the customer concentration; SC
is the supplier concentration; SP and CP denote
control variables same province indicator and
proximity indicator, respectively.
4 RESULTS
This section shows the results of this analysis with
interpretations. The variance inflation factor (VIF)
was employed in all regression analyses to detect
potential multicollinearity problems. As a result,
multicollinearity is not an issue in this analysis since
all regressions displayed a VIF coefficient lower than
5.
Influence of Supply Chain Geographic Proximity and Concentration on Financial Performance of Chinese Automakers
701
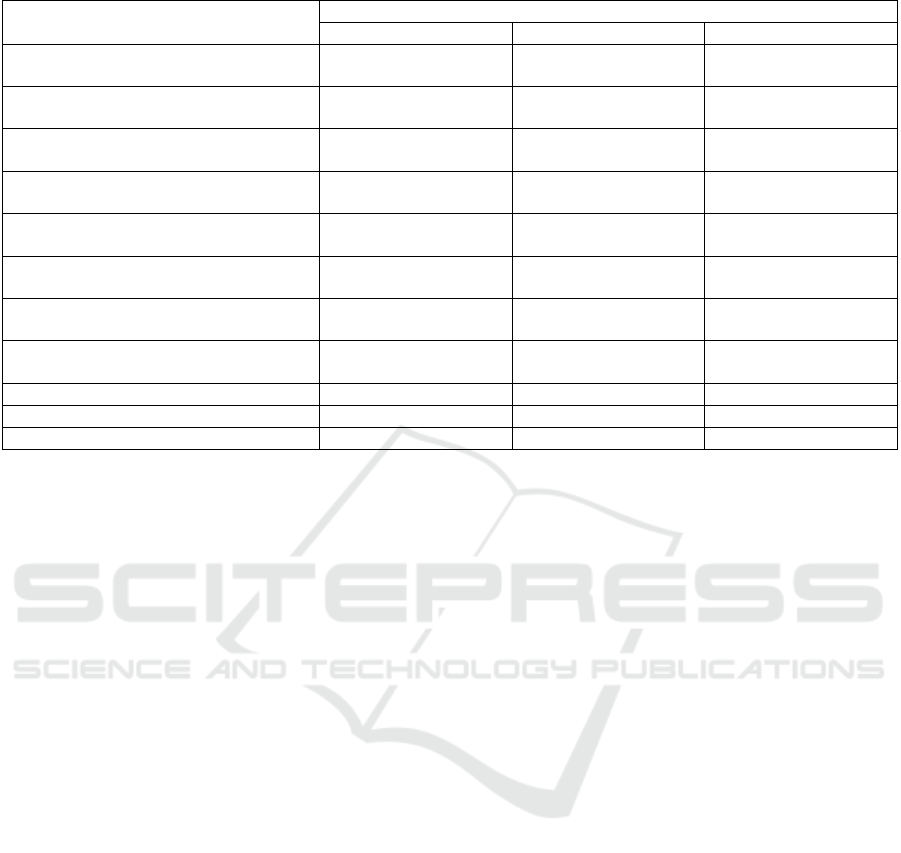
Table 3: Regression results.
Variables
Dependent Variable: Inventory Turnover Ratio
(1) (2) (3)
Intercept
8.796***
(15.487)
7.697***
(17.980)
7.275***
(17.275)
Spatial Distance
-0.001**
(-0.096)
-0.001***
(-4.532)
-0.001***
(-4.051)
Major Customer Ratio
0.062***
(
3.922
)
--- ---
Major Supplier Ratio
0.032
(1.524)
--- ---
Customer Concentration
-0.063***
(-6.086)
---
-0.023***
(-2.987)
Supplier Concentration
-0.062***
(
-3.937
)
-0.045***
(
-4.288
)
---
Same Province
1.107***
(
2.589
)
--- ---
Close Proximity
-0.818
(-1.553)
--- ---
N 452 452 452
R2 0.229 0.081 0.061
F 16.237 18.014 14.496
Note: *, **, and *** represents the significance at 10%, 5%, and 1% level, respectively. Values in parentheses are t-
statistics.
4.1 Impact of Supply Chain
Geographic Proximity on Inventory
Turnover Ratio
Table 3 shows the regression analysis results of the
impact of supply chain geographic proximity on the
inventory turnover ratio of China’s automakers.
Column 1 shows the overall impact of supply chain
geographic distance on a firm’s inventory turnover
ratio. The results indicate that the distance between
firms and their up and downstream trading partners is
negatively and significantly related to firms’
inventory turnover ratio (B = -0.001, p < 0.05). The -
0.001 coefficient denotes that each kilometer increase
in distance between a firm and its supply chain
partners, the firm’s inventory turnover ratio drops
0.001 times per year. For instance, if the distance
between a firm and its supplier increased 1000
kilometers, then based on the results, the firm’s
inventory turnover ratio would decrease for 1 time per
year. Moreover, firms and their trading partners
located within the same province can positively and
significantly impact firms’ inventory turnover ratio
(B = 1.107, p < 0.01). The coefficient of the Same
Province dummy suggests that a firm’s inventory
turnover ratio would increase 1.107 times per year
when intra-province collaboration occurred.
Furthermore, the individual impact of supplier
distance and customer distance on inventory turnover
ratio are shown in column 2 and 3, respectively. The
results confirm that supplier distance is negatively
and significantly related to a firm’s inventory
turnover ratio (B = -0.001, p < 0.01), and customer
distance is negatively and significantly related to a
firm’s inventory turnover ratio (B = -0.001, p < 0.01).
Additionally, the R
2
value of the regression model is
0.229, signifying that 22.9% of the variance in the
dependent variable can be explained by the
independent variables. This R
2
value is statistically
acceptable as the purpose of this research was to
explore the causal relationship instead of the
predictive modeling.
4.2 Impact of Supply Chain
Concentration on Inventory
Turnover Ratio
The regression results of the impact of supply chain
concentration on Chinese automakers’ inventory
turnover ratio are shown in Table 3. The overall
impact of supply chain concentration on businesses’
inventory turnover ratio can be found in column 1.
The results indicate that both up and downstream
trading partner concentration are negatively and
significantly related to firms’ inventory turnover ratio,
with a B value of -0.063 (p < 0.01) and -0.062 (p <
0.01), respectively. The coefficient of customer
concentration denotes that for every 1% increase in
the customer concentration the inventory turnover
ratio would decline 0.063 times per year. For example,
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
702

if a firm’s customer concentration increased 20%, its
inventory turnover ratio will decrease 1.26 times per
year. Similarly, the coefficient of supplier
concentration indicates that for every 1% higher in
the supplier concentration, the inventory turnover
ratio drops 0.062 times per year. Thus, a 20% growth
in supplier concentration would result in a 1.24 times
per year reduction in inventory turnover ratio.
Moreover, the individual impact of supplier or
customer concentration on inventory turnover ratio is
shown in column 2 or 3, respectively. The results
indicate that supplier concentration is negatively and
significantly related to inventory turnover ratio (B = -
0.045, p < 0.01), and customer concentration is also
negatively and significantly related to inventory
turnover ratio (B = -0.023, p < 0.01). Overall, the
above statistic results offer a basic answer to the
second research question.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research evaluates the impact of supply chain
geographic proximity and concentration on the
financial performance of China’s automobile
manufacturing firms. This study utilized data from 83
firms listed on Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock
Exchanges in China’s automotive manufacturing
industry from 2010 to 2023.
First, the empirical results confirmed that the
geographic distance between automakers and their
supply trading partners can negatively impact their
inventory turnover ratio. Specifically, each kilometer
increased in supplier or customer distance reduced
inventory turnover ratio by 0.001 times per year.
Moreover, the inventory turnover ratio increased
significantly when intra-province collaboration
occurred. This indicates that the impact of geographic
proximity on inventory turnover is not a simple linear
relationship, but rather demonstrates a threshold
effect: negative impacts intensify when distance
exceeds a certain range, whereas closer proximity
within same province displays significant positive
effects. The primary drivers behind this phenomenon
includes transportation cost, transit duration, and
manufacturing lead times. These factors not only
hinder firms’ financial performance due to cost
escalations, but also result in unexpected production
schedule disruptions due to extra logistics cycles.
Therefore, to address geographic proximity
challenges, managers should prioritize intra-province
collaboration to reduce transit time and costs. For
instance, firms could invest in industrial parks to
utilize the proximity benefits.
Second, the empirical findings revealed a negative
correlation between supply chain concentration and
the inventory turnover ratio. Specifically, an increase
in supply chain concentration reduces the inventory
turnover ratio. Moreover, it is noteworthy that a
firm’s dependence on the largest customer is
negatively related to its inventory turnover ratio,
whereas its financial dependence on its largest
supplier did not show a significant relation to its
inventory turnover ratio. For firms with high supply
chain concentration, their upstream sources of
materials and downstream sales channels are highly
dependent on their major trading partners.
Consequently, firms would have minimal bargaining
power regarding price, quantity, and variety of goods
they purchase and products they sell. This
substantially impacts firms’ financial independence,
profitability, supply chain effectiveness, and product
diversity, which in turn reduces firms’ inventory
turnover ratio, supply chain resilience, and supply
chain agility. Therefore, firms should reduce reliance
on major trading partners, especially the single large
customer, and build alternative supply chain networks
for sources of materials and streams of revenue to
avoid a financial bottleneck.
This research is subject to limitations. First, the
data used in this research were extracted and
combined from multiple datasets based on the date,
stock symbol, and industry classification code. Thus,
given the availability of the primary metrics differs in
these datasets, not only was the data size significantly
reduced, but also much additional useful information
from these datasets was excluded during the data
integration phase. Hence, future research could utilize
multiple sources of information to enhance data
availability when acquiring research data. Second,
this research only focused on the impact of two
supply chain parameters on one business financial
indicator. Future research could combine other
statistical measures, including firm size, location, and
other financial ratios, to comprehensively understand
the impact of supply chain proximity and
concentration on financial performance.
REFERENCES
Cao, L., Deng, F., Zhuo, C., Jiang, Y., Li, Z., & Xu, H.,
2022. Spatial distribution patterns and influencing
factors of China's new energy vehicle industry. Journal
of Cleaner Production, 379, 134641.
Chang, A., & Bradsher, K., 2024. How China became the
world's largest car exporter. The New York Times.
Chen, R., & Xu, H., 2024. Supply chain relationships,
resilience, and export product quality: Analysis based
Influence of Supply Chain Geographic Proximity and Concentration on Financial Performance of Chinese Automakers
703

on supply chain concentration. Sustainability, 16(20),
8743.
Cortes, J. D., 2023. A review of the proximity literature:
Supply chain's missing link. Transportation Journal,
62(2), 209-248.
Huang, Y., Han, W., & Macbeth, D. K., 2020. The
complexity of collaboration in supply chain networks.
Supply Chain Management: An International Journal,
25(3), 393-410.
Huang, Z., Zhou, Y., Lin, Y., & Zhao, Y., 2024. Resilience
evaluation and enhancing for China's electric vehicle
supply chain in the presence of attacks: A complex
network analysis approach. Computers & Industrial
Engineering, 195, 110416.
Jiang, S., Yeung, A. C. L., Han, Z., & Huo, B., 2023. The
effect of customer and supplier concentrations on firm
resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic: Resource
dependence and power balancing. Journal of
Operations Management, 69(3), 497-518.
Kwak, J. K., 2019. Analysis of inventory turnover as a
performance measure in manufacturing industry.
Processes, 7(10), 760.
Lorentz, H., Töyli, J., Solakivi, T., Hälinen, H., & Ojala, L.,
2012. Effects of geographic dispersion on intra-firm
supply chain performance. Supply Chain Management:
An International Journal, 17(6), 611-626.
Porter, M. E., 2008. The five competitive forces that shape
strategy. Harvard Business Review, 86(1), 78-137.
Sun, T., & Abdullah, M. A. B., 2025. Impact of industrial
agglomeration on the upgrading of China's automobile
industry: The threshold effect of human capital and
moderating effect of government. Sustainability, 17(7),
3090.
Yang, H., & Ren, W., 2021. Research on the influence
mechanism and configuration path of network
relationship characteristics on SMEs' innovation—The
mediating effect of supply chain dynamic capability
and the moderating effect of geographical proximity.
Sustainability, 13(17), 9919.
Zhang, W., 2025. Automotive manufacturing industry in
China. Statista.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
704
