
The Impact of Brand Personality on Brand Loyalty and Its Indirect
and Moderating Effects: An Empirical Study Based on Nike
Xiangjie Xu
a
Economics and Management, National University of Malaysia, Bangi, 43600, Malaysia
Keywords: Brand Personality, Brand Loyalty, Brand Identification, Brand Trust, Social Media Engagement.
Abstract: Brand personality is a critical factor influencing brand loyalty. This study integrates two mediating variables
(brand identification and brand trust) and two moderating variables (social media engagement and brand-
cultural congruence) to systematically examine their multilevel mechanisms. Empirical analysis focusing on
the Nike brand demonstrates that competence and ruggedness dimensions exert significant positive effects on
brand loyalty (β = 0.158/0.390; R² = 60.4%). Brand identification (accounting for 50.68% of the total effect)
and brand trust (37.39%) form critical chain indirect effects, with the total indirect effects constituting 62.36%
of the overall influence. While social media engagement (β = 0.37) and brand-cultural congruence (β = 0.383)
significantly enhance brand loyalty, their moderating effects were not statistically significant. The research
validates the integrated indirect pathway in which personality influences identification/trust, which in turn
influences loyalty, confirms the effects of other moderating variables, and provides theoretical support for
differentiated marketing strategies in sportswear brands.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the past several years, academics have turned
their attention to brand personality, elevating it to a
key subject within marketing and brand management
scholarship. In his classic study, Aaker (1997)
proposed the Five-Dimension Brand Personality
Model, which includes sincerity, excitement,
competence, sophistication, and ruggedness, and
pointed out that different brand personalities have
varying degrees of influence on consumers’ brand
loyalty. In today’s highly competitive market
environment, brand loyalty has been proven to be one
of the key factors for long-term success of enterprises.
Loyal consumers tend to repeatedly purchase the
same brand’s products and actively recommend them
to others, thereby bringing long-term value to the
brand (Mabkhot & Salleh, 2017). In the field of brand
marketing, brand personality is considered an
important factor influencing brand loyalty (Alowaidi,
Alhaelegy & Kadhim, 2024). Some scholars also
believe that brand personality can enhance brand
loyalty by jointly strengthening consumers’ brand
trust and brand identification (Kim, Han & Park,
2001). At the same time, research has shown that
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-4375-3762
social media engagement and brand-cultural
congruence are important moderating variables, and
the significant way in which they affect consumers’
brand loyalty is by altering consumers’ perception
and interpretation of brand personality (Hudson et al.,
2020). However, the relative influence of a series of
variables and the impact of brand personality on
brand loyalty still lack systematic quantitative
research. Studying this issue is not only of great
practical significance, as it helps enterprises to
formulate more precise brand marketing strategies,
but also provides data reference for other researchers.
This research examines how brand personality drives
brand loyalty by first evaluating the relative influence
of its distinct dimensions, then uncovering the dual
mediation pathways, namely through brand
identification and brand trust, along with their
respective indirect effect proportions, and finally
assessing whether social media engagement and the
alignment between brand values and cultural norms
moderate the link between personality and loyalty. By
constructing an integrated theoretical model of the
four variables and using empirical methods to
quantify the influence magnitudes of the indirect and
moderating effects, the study verifies the applicability
Xu, X.
The Impact of Brand Personality on Brand Loyalty and Its Indirect and Moderating Effects: An Empirical Study Based on Nike.
DOI: 10.5220/0013845600004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 389-394
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
389

of the theoretical model and evaluates the interaction
relationships among the variables, thereby providing
empirical support. The research not only fills the
academic gap in the multi-layered impact mechanism
of brand personality but also provides a strategic basis
for enterprises to optimize and shape brand
personality and enhance brand loyalty. This study
selects Nike as a typical case, and its appropriateness
lies in the fact that the brand is typical of the global
sports market, with a universal user base across age
and gender, and a systematic construction of brand
personality. As a paradigm of brand symbolization
practice, Nike continuously shapes the core value of
the sports spirit by establishing core personality
dimensions (Manivel, 2024). Using Nike as a case
provides an ideal observation field for exploring the
impact mechanisms of multiple variables of brand
personality on brand loyalty.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Brand personality refers to the anthropomorphic
characteristics exhibited by a brand in the minds of
consumers. It differentiates the brand from its
competitors and helps consumers establish an
emotional connection (Aaker, 1997). In his classic
study, Aaker (1997) proposed the Five-Dimension
Brand Personality Model, which has become an
important theoretical framework in the field of brand
marketing. At the same time, Muniz & Marchetti
(2022) studied the applicability of brand personality
in different markets and suggested that some brands
may combine multiple dimensions rather than fitting
into a single category. Brand loyalty is a
comprehensive manifestation of consumers' sustained
preference for and repeat purchase behavior of a
particular brand, reflecting consumers' long-term
commitment to the brand on both psychological and
behavioral levels (Oliver, 1999). Existing research
indicates that brand loyalty primarily includes two
dimensions: Behavioral Loyalty and Attitudinal
Loyalty, which interact and jointly shape consumers’
brand loyalty (Punniyamoorthy & Prasanna Mohan
Raj, 2007). Behavioral Loyalty refers to the brand
loyalty demonstrated through actual purchase
behavior and can be measured by repeat purchase
rate, purchase share, and purchase inertia indicators.
Attitudinal Loyalty reflects consumers' emotional
attachment and psychological identification with the
brand, manifested through brand preference,
recommendation willingness, and emotional
commitment (Dick & Basu, 1994). Research has
shown that cultivating a unique brand persona can
indirectly boost consumer loyalty by first fostering
brand identification and subsequently building brand
trust (Kimpakorn & Tocquer, 2010). Brand
identification is mainly based on Self-Congruity
Theory, where consumers tend to choose brand
personalities that align with their Actual Self or Ideal
Self (Usakli & Baloglu, 2011). According to
Signaling Theory, a company's consistent
performance in brand personality can be seen as a
credible signal of quality commitment, reducing
consumers' decision-making risks (Islam & Rahman,
2016). In recent years, studies have shown that social
media engagement and brand-cultural congruence are
two key moderating variables, and both significantly
affect consumers’ brand loyalty by altering their
perception and interpretation of brand personality
(Hudson et al., 2020). The moderating effect of social
media engagement is reflected in the interactivity and
content co-creation features of social media, which
significantly amplify the psychological penetration
efficiency of brand personality for consumers. The
moderating effect of brand-cultural congruence is
reflected in the alignment between brand personality
and local cultural values, which directly affects the
conversion efficiency of brand loyalty. Existing
research has revealed the dynamic evolution of the
relationship between brand personality and brand
loyalty. From the early direct effect theory of brand
personality proposed by Aaker (1997)—where for
every one standard deviation increase in personality
distinctiveness, repeat purchase intention grows by
14%—it has gradually developed into indirect path
analysis based on Self-Congruity Theory. For
example, Huang et al. (2020) verified that the dual
joint indirect effect of brand identification and brand
trust is significantly stronger than the single
mechanism. However, existing research still suffers
from a lack of integration and has yet to construct a
framework integrating multiple mediating and
moderating variables, leading to insufficient
explanatory completeness and practical consistency
regarding the multi-layered impact mechanism of
brand personality.
Based on relevant theories and literature analysis,
this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H1: Brand personality positively affects brand
loyalty.
H2: Brand identification and brand trust have a
chain-mediated effect between brand personality and
brand loyalty.
H3: Social media engagement and brand-cultural
congruence have a moderating effect on the
relationship between brand personality and brand
loyalty.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
390
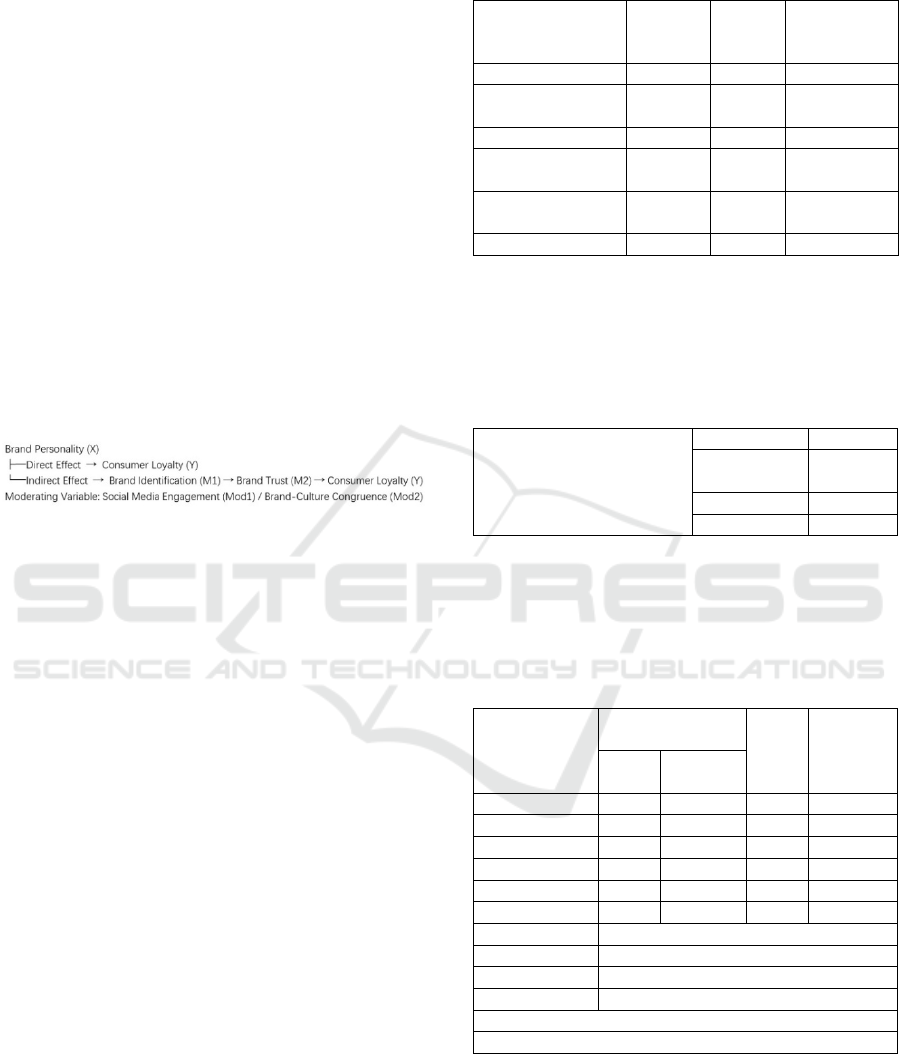
3 RESEARCH DESIGN
This study will use Nike as a case and collect
numerical data through a structured questionnaire
survey with a Likert scale. The research will utilize
multiple linear regression alongside the Bootstrap
technique for examining mediation models, as well as
other appropriate statistical procedures to evaluate the
stated hypotheses. It will assess the direct influence
of brand personality on loyalty, trace indirect
pathways via brand identification and trust, and
explore how social media engagement and brand–
culture alignment moderate these effects, thereby
enabling rigorous statistical inference about how
these variables interrelate. The research framework
follows the path of "independent variable (brand
personality) mediating variables (identification/trust)
→ dependent variable (loyalty)" and integrates
moderating variables (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The Influence Path Model of Brand Personality
on Brand Loyalty.
4 DATA COLLECTION
The items related to core variables in the survey
questionnaire developed for this study are adapted
from widely used and validated scales in the
marketing field, such as those by Aaker (1997) and
Sirianni et al. (2013), ensuring reliability and validity,
which have been verified through the literature. The
final version of the questionnaire consists of 30
questions. The questionnaire also includes
demographic variables such as gender, age, and
income, to control for potential confounding factors
that may interfere with the analysis of the main
effects. The purpose is to quantify respondents'
perceptions and behavioral attitudes toward the Nike
brand using a structured scale. An online self-
administered questionnaire survey was used as the
data collection method, distributed via an online
platform, and expanded through social media to
increase the sample coverage. A total of 325 valid
responses were collected.
5 DATA ANALYSIS RESULTS
The Cronbach's α coefficients for the data reliability
analysis all meet the standard of being greater than
0.7, indicating good data reliability (Table 1).
Table 1: Cronbach's Reliability Analysis.
Dimension
Number
of Items
Sample
Size
Cronbach's
α
Coefficient
Brand Personalit
y
10 325 0.921
Brand
Identification
3 325 0.724
Brand Trust 3 325 0.774
Social Media
Engagement
3 325 0.718
Brand-Cultural
Con
g
ruence
3 325 0.754
Brand Loyalt
y
5 325 0.827
The results of the KMO test and Bartlett's test
show that the KMO value is 0.964 > 0.7 and Bartlett's
sphericity test (p < 0.05) indicates high validity,
suggesting that factor analysis can be performed
(Table 2).
Table 2: KMO Test and Bartlett's Test
Bartlett's Sphericity Test
KMO Value 0.964
Approximate
Chi-S
q
uare
4472.612
df 351
P 0.000
Through regression analysis to test the main
effects, we find that competence and ruggedness, two
dimensions of brand personality, have a statistically
significant positive association with brand loyalty
(Table 3).
Table 3: Linear Regression Analysis Results(n=325).
Unstandardized
Coefficients
t p
B
Standard
Erro
r
Constant 1.277 0.174 7.352 0.000***
Sincerit
y
0.046 0.045 1.025 0.306
Excitement 0.051 0.046 1.114 0.266
Competence 0.158 0.047 3.360 0.001**
So
p
histication 0.097 0.046 2.134 0.034*
Ru
gg
edness 0.390 0.049 7.973 0.000***
R2 0.604
Adjusted R² 0.598
F F=97.427,p=0.000
D-W value 1.976
De
p
endent Variable: Brand Lo
y
alt
y
*
p
<0.05 **
p
<0.01 ***
p
<0.001
Through Bootstrap method for testing the indirect
effects, the results show that brand personality has a
significant positive predictive effect on brand
identification, brand trust, and brand loyalty. That is,
the stronger the brand personality, the higher the
consumers' brand identification, brand trust, and
brand loyalty. The examined brand‑related
The Impact of Brand Personality on Brand Loyalty and Its Indirect and Moderating Effects: An Empirical Study Based on Nike
391
constructs, personality, identification, and trust, each
demonstrates statistically significant positive
associations with loyalty outcomes (Table 4).
Table 4: Indirect Effects Regression Analysis.
Outc
ome
Vari
able
Predict
or
Variabl
e
Overall Fit Index
Regression
Coefficient
Significance
R R² F
stand
ard
B
t
Bran
d
Loya
lty
Brand
Person
ality
0.75
2
0.56
6
421.
057
0.75
2
20.5
2
Bran
d
Ident
ificat
ion
Brand
Person
ality
0.70
1
0.49
2
312.
27
0.70
1
17.6
71
Bran
d
Trust
Brand
Person
ality
0.81
5
0.66
4
317.
48
0.59
8
13.1
84
Brand
Identifi
cation
0.27
5
6.06
9
Bran
d
Loya
lty
Brand
Person
ality
0.82
7
0.68
4
231.
773
0.28
3
5.18
8
Brand
Identifi
cation
0.33
9
7.29
1
Brand
Trus
t
0.29
3
5.41
9
*p<0.05 **p<0.01 ***p<0.001
An examination of mediating mechanisms reveals
that indirect effects significantly contribute to the
relationship between brand personality and brand
loyalty. Brand identification emerges as the key route
through which brand personality enhances consumer
commitment. Moreover, brand trust acts as another
important mediator, with increased consumer
confidence reinforcing brand loyalty. Empirical
findings also suggest a comparatively weaker chain
mediation effect, in which brand personality
influences loyalty through a sequential process—first
by strengthening brand identification, which in turn
promotes trust (Table 5).
Table 5: Indirect Effects Path Analysis.
Path
Effec
t
Valu
e
Boot
strap
ped
Stan
dard
Erro
r
Boot
CI
Low
er
Limi
t
Boot
CI
Uppe
r
Limi
t
Relat
ive
Effe
ct
Size
Dire
ct
Path
Direct
Effect
0.26
8
0.05
2
0.16
6
0.37
37.6
4%
Medi
ating
Path
Total
Indirec
t Effect
0.44
4
0.05
4
0.33
2
0.54
6
62.3
6%
Ind1
Brand
Person
ality →
Brand
Identifi
cation
→
Brand
Loyalt
y
0.22
5
0.03
8
0.14
8
0.30
1
50.6
8%
Ind2
Brand
Person
ality →
Brand
Trust
→
Brand
Loyalt
y
0.16
6
0.03
7
0.09
4
0.23
9
37.3
9%
Ind3
Brand
Person
ality →
Brand
Identifi
cation
→
Brand
Trust
→
Brand
Loyalt
y
0.05
3
0.01
7
0.02
5
0.09
11.9
4%
An evaluation of the moderating influence
indicates that involvement with social media
platforms exerts a notably positive effect on
consumer allegiance to brands. Elevated levels of
social media interaction are associated with stronger
brand commitment among consumers. Nonetheless,
the interplay between brand personality and social
media engagement appears to have an insignificant
effect on brand loyalty. This suggests that the
mediating role of brand personality in linking social
media engagement to brand loyalty is limited, while
the direct contribution of social media engagement to
fostering brand loyalty is considerably more
pronounced (Table 6).
Table 6: Social Media Engagement - Moderating Effect
Model Coefficients
Coeffici
ent
Standar
d Erro
r
t p
Constant 4.965 0.048
102.6
64
0.000
***
Brand
Personalit
y
0.449 0.045 9.977
0.000
***
Social
Media
Engagement
0.37 0.045 8.234
0.000
***
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
392
Brand
Personality
* Social
Media
Engagement
0.009 0.027 0.323 0.747
R² 0.642
F 191.554
De
p
endent Variable: Brand Lo
y
alt
y
*
p
<0.05 **
p
<0.01 ***
p
<0.001
The examination of moderating variables reveals
that alignment between brand values and cultural
context exerts a significant positive influence on
consumer loyalty. Greater brand-cultural congruence
is linked to heightened levels of brand commitment.
However, the combined effect of brand personality
and brand-cultural congruence does not show a
meaningful impact on loyalty outcomes. This implies
that the indirect influence of cultural fit via brand
personality is relatively minor, whereas its direct
contribution to strengthening brand loyalty is
considerably more impactful (Table 7).
Table 7: Brand-Cultural Congruence - Moderating Effect
Model Coefficients.
Coeffici
ent
Standar
d Erro
r
t p
Constant 5.003 0.051
98.07
6
0.000
***
Brand
Personalit
y
0.387 0.051 7.547
0.000
***
Brand-
Cultural
Con
g
ruence
0.383 0.05 7.669
0.000
***
Brand
Personality
* Brand-
Cultural
Congruence
-0.023 0.026 -0.867 0.386
R² 0.639
F 189.53
De
p
endent Variable: Brand Lo
y
alt
y
*
p
<0.05 **
p
<0.01 ***
p
<0.001
6 DISCUSSION
The data analysis shows that competence
(professionalism, reliability) and ruggedness
(outdoor, strong image) in brand personality have a
significant direct positive impact on Nike's brand
loyalty. Companies can directly enhance consumer
loyalty by strengthening these two personality traits.
This result confirms the strategic value of brand
personality as a core element of brand differentiation.
The indirect effect analysis reveals that the chain
mediation mechanism involving brand identification
and brand trust is pivotal in connecting brand
personality to brand loyalty. Together, these
mediating pathways account for 62.36% of the total
effect, highlighting the critical role of the chain
mediation mechanism in influencing consumer
loyalty. This result supports the integrated framework
of Self-Congruity Theory and Signaling Theory:
consumers form emotional attachment through the
match between brand personality and self-concept
(identification) and reduce decision-making risks
through the predictability of brand behavior (trust),
which ultimately translates into long-term loyal
behavior. Additionally, while the direct effects of
social media engagement and brand-cultural
congruence are significant, their moderating effects
did not pass the test. A possible explanation is that
social media, as an information dissemination
channel, is more likely to amplify the perceived
intensity of brand personality (main effect) rather
than change the direction of the relationship between
personality and loyalty (moderating effect). Brand-
cultural congruence may indirectly influence loyalty
through brand identification rather than directly
moderating the main path.
7 CONCLUSION
This study constructed an integrated model of brand
personality, dual mediating variables (brand
identification/brand trust), and dual moderating
variables (social media engagement/brand-cultural
congruence), revealing the multi-level driving
mechanism of brand loyalty. The empirical results
show that brand personality explains brand loyalty
more effectively through the indirect paths
established by brand identification and brand trust
than through direct effects, providing a more detailed
explanation of the "brand personality - brand loyalty"
theoretical framework. At the same time, for sports
brands with a similar positioning to Nike, the study
clarified the core roles of competence and ruggedness
in brand personality, providing empirical evidence for
optimizing brand personality. Sports brands with the
same positioning as Nike should prioritize
strengthening the brand's competence (such as
technical expertise) and ruggedness (such as sports
spirit) images to directly enhance consumer loyalty.
Additionally, brands should strengthen consumer
brand identification through visual symbols, brand
stories, and other methods, while building brand trust
through consistent behavior (such as quality
commitments) to indirectly consolidate loyalty.
The Impact of Brand Personality on Brand Loyalty and Its Indirect and Moderating Effects: An Empirical Study Based on Nike
393

Although the moderating effects of social media
engagement and brand-cultural congruence were not
significant, their main effects suggest that brands still
need to frequently reach target groups on social media
and enhance personality perception intensity through
localization strategies (such as cultural symbol
integration). This study uses Nike as a single case,
and the generalizability of the conclusions needs to be
verified across multiple industries and brands. Cross-
sectional data struggles to capture dynamic
interactions between variables, so future research
could incorporate longitudinal studies. Moreover,
although Nike has broad influence in the sports brand
sector, its consumer base (mainly young users) and
product positioning (focused on mass sports) do not
cover all types of sports brands. For example, brands
focusing on skill-based sports (such as golf or
bowling) may have a different consumer age structure
and demand characteristics.
REFERENCES
Aaker, J. L., 1997. Dimensions of brand personality.
Journal of Marketing Research, 34(3), 347–356.
Alowaidi, A., Alhaelegy, Z. F., & Kadhim, M., 2024. Brand
personality drives loyalty: Insights from Iraq. Academic
Journal of Digital Economy and Stability.
Dick, A. S., & Basu, K., 1994. Customer loyalty: Toward
an integrated conceptual framework. Journal of the
Academy of Marketing Science, 22(2), 99-113.
Hudson, S., Huang, L., & Roth, M. S., 2020. The influence
of social media interactions on consumer-brand
relationships: A three-country study of brand
perceptions and marketing behaviors. Journal of
Retailing, 96(1), 81-98.
Islam, J. U., & Rahman, Z., 2016. The impact of online
brand community characteristics on customer
engagement: An application of Stimulus-Organism-
Response paradigm. Telematics and Informatics, 33(2),
470-488.
Kim, C. K., Han, D., & Park, S. B., 2001. The effect of
brand personality and brand identification on brand
loyalty: Applying the theory of social identification.
Japanese Psychological Research.
Kimpakorn, N., & Tocquer, G., 2010. Service brand equity
and employee brand commitment. Journal of Services
Marketing, 24(5), 378-388.
Mabkhot, H. A., & Salleh, S. M., 2017. The influence of
brand image and brand personality on brand loyalty,
mediating by brand trust: An empirical study. Jurnal
Pengurusan.
Manivel, R., 2024. Decoding customer engagement in the
sports shoe industry: A focus on brand loyalty and
customer satisfaction. SSRN Papers.
Muniz, K. M., & Marchetti, R. Z., 2012. Brand personality
dimensions in the Brazilian context. BAR-Brazilian
Administration Review.
Oliver, R. L., 1999. Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of
Marketing, 63(4_suppl1), 33-44.
Punniyamoorthy, M., Prasanna Mohan Raj, M., 2007. An
empirical model for brand loyalty measurement. J
Target Meas Anal Mark 15, 222–233 (2007).
Sirianni, N. J., et al., 2013. Branded service encounters:
Strategically aligning employee behavior with the
brand positioning. Journal of Marketing, 77(6), 108-
123.
Usakli, A., & Baloglu, S., 2011. Brand personality of tourist
destinations: An application of self-congruity
theory. Tourism Management, 32(1), 114-127.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
394
