
Integrating RPA in E-Commerce Live Streaming Sales: A Case Study
of YingDao RPA
Yezhuo Li
a
School of Economics, Shanxi University of Finance and Economics,030006, Taiyuan, China
Keywords: RPA, Live Streaming, E-Commerce, YingDao.
Abstract: With massive inflows of live-stream viewers, e-commerce enterprises face significant challenges in managing
vast data volumes through manual labor alone. In the current landscape of accelerated information iteration,
failure to promptly process critical data may expose live-streaming e-commerce businesses to financial losses
or severe operational setbacks. Consequently, there exists an urgent industry demand for technological
solutions capable of enhancing operational efficiency, reducing labor dependency, and refining workflow
precision. Robotic Process Automation (RPA), having undergone extensive maturation over years of
development, has demonstrated widespread applicability across multiple sectors, liberating substantial human
resources from repetitive tasks. This raises a pivotal question: Can RPA technology effectively empower
office operations in live-streaming e-commerce enterprises? This article selects YingDao RPA in China as
the research object, and through analyzing specific cases of providing technology to some live streaming e-
commerce enterprises, the author finds that RPA technology can replace some human resources in the process
of live streaming e-commerce office work, helping live streaming e-commerce enterprises improve office
efficiency, reduce costs and increase efficiency. The results of this study provide reference for the healthy
development of the e-commerce live streaming industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
The proliferation of mobile internet and the
accelerated advancement of 5G technology have
catalyzed the exponential growth of the live-
streaming e-commerce sector, which has solidified its
position as a core engine of China’s new consumption
era (Li, 2025). To enhance operational efficiency and
refine workflow precision, e-commerce enterprises
are increasingly seeking digital tools to augment
office operations. In response to the demand for
automated workflows, a proliferation of intelligent
software solutions has emerged. Among
these, Robotic Process Automation (RPA)—a
technology integrating automation and artificial
intelligence (AI) to deploy software robots or “digital
workers” for executing repetitive, rule-based business
processes—has gained prominence. RPA bots
operate by mimicking human-user actions through
preconfigured protocols, thereby automating
procedural tasks (Gao, 2020). Having evolved
through iterative advancements, RPA technology has
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-8841-4352
achieved widespread adoption across industries,
replacing labor-intensive manual operations,
liberating substantial human resources, and
significantly enhancing corporate operational
efficiency (Song and Li, 2022). This raises a critical
inquiry: Can RPA technology deliver operational
benefits to the nascent live-streaming e-commerce
sector?
YingDao RPA, a flagship RPA software brand
under Hangzhou Fork Intelligence Technology Co.,
Ltd., specializes in robotic process automation for
diverse sectors including e-commerce, finance,
internet services, academia, manufacturing, logistics,
and telecommunications. As a leading provider
serving over 10,000 enterprises, YingDao RPA holds
a pivotal position within the RPA technology
ecosystem. This study selects YingDao RPA as the
research subject, employing empirical case analysis
of its technical implementations for live-streaming e-
commerce enterprises. The findings aim to provide
actionable insights for stakeholders in the live-
streaming e-commerce industry, demonstrating how
290
Li, Y.
Integrating RPA in E-Commerce Live Streaming Sales: A Case Study of YingDao RPA.
DOI: 10.5220/0013842900004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 290-295
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
RPA integration can optimize workflows, reduce
operational redundancies, and foster scalable growth
(YingDao, 2025).
2 THE DEVELOPMENT OF
ROBOTIC PROCESS
AUTOMATION TECHNOLOGY
The evolutionary trajectory of Robotic Process
Automation (RPA) technology can be categorized
into four distinct developmental phases.
2.1 Assistive RPA
During this initial stage, RPA functioned as an
auxiliary tool to support manual operations, primarily
assisting human workers in basic data entry tasks.
2.2 Non-Assistive RPA
The subsequent phase witnessed the emergence of
non-assistive RPA, which aimed to achieve end-to-
end automation and virtual workforce tiering.
Technologies in this stage partially liberated human
labor by automating rule-based, repetitive workflows.
2.3 Autonomous RPA
Advancing further, autonomous RPA integrated
perceptual technologies to partially acquire external
knowledge, enabling the automated processing of
unstructured data within documents. This phase
marked a shift toward semi-intelligent automation
(Zhang and Yang, 2022).
2.4 Cognitive RPA
The current pinnacle of development lies in cognitive
RPA, which represents the future direction of the
technology (Ma et al., 2021). As show in Figure 1, by
leveraging modern technologies such as artificial
intelligence (AI), cognitive RPA transcends
procedural automation, achieving the capacity to
automate prolonged and intricate tasks through
adaptive learning, contextual analysis, and decision-
making emulation (Gao and Shi, 2024).
Figure 1: The evolutionary trajectory of RPA (Photo credit:
Original).
3 CURRENT DEVELOPMENT
STATUS AND CHALLENGES
OF LIVE-STREAMING E-
COMMERCE INDUSTRY
On October 11, 2024, the research findings of
the Blue Book on High-Quality Development of the
Live-Streaming E-Commerce Industry (2023–
2024) (hereinafter referred to as the "Blue Book")
were officially released in Shanghai, China. The Blue
Book reveals a sustained increase in the user base of
China’s live-streaming e-commerce sector. As
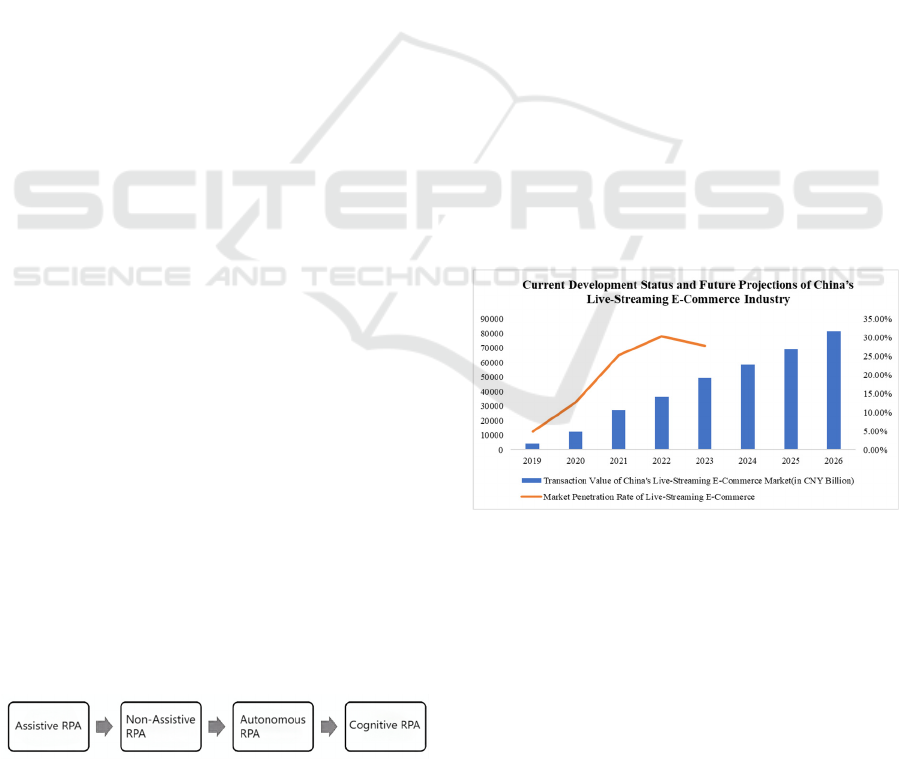
illustrated in Figure 2, the penetration rate of live-
streaming e-commerce surged from 4.9% in 2019 to
30.4% in 2022, reaching 37.8% in 2023—a year-on-
year growth of 24.3%. Meanwhile, the user scale
continued its upward trajectory, reaching 597 million
individuals by December 2023, accounting for 54.7%
of China’s total internet users and marking a 15.9%
annual increase, thereby demonstrating robust and
consistent growth. According to projections, the
transaction volume of China’s live-streaming e-
commerce industry is anticipated to exceed RMB 8
trillion by 2026. These metrics collectively indicate
that the live-streaming e-commerce sector will
remain a pivotal driver of economic activity,
sustaining its dynamic growth trajectory for the
foreseeable future (China News, 2024; Anonymous,
2024).
Figure 2: Current development status and future projections
of china’s live steaming E-commerce industry (Photo
credit: Original).
With the rapid development of the e-commerce
livestreaming industry, a series of challenges have
emerged across its operational chain. From the
supply-side perspective, e-commerce livestreaming
enterprises face escalating operational costs due to the
multi-platform deployment of brands and
discrepancies in platform-specific regulations.
During the price competition phase, disorderly
pricing and malicious competition among agents have
Integrating RPA in E-Commerce Live Streaming Sales: A Case Study of YingDao RPA
291

resulted in consumer rights issues arising from
discrepancies between advertised and actual
transaction prices. On the demand side, the volatility
of online trends creates significant obstacles in
identifying trending products and formulating
effective product selection strategies. The industry's
nascent growth has attracted numerous entrants with
limited operational experience, manifesting in two
primary dilemmas: the market exhibits a polarization
of talent distribution, where hosts demonstrate
varying levels of expertise, while top-tier influencers
command prohibitively high costs coupled with
stringent requirements for Return on Investment
(ROI) from livestreaming enterprises. Concurrently,
enterprises grapple with the substantial challenges
posed by massive order volumes during livestreaming
events. These systemic issues permeate all
operational phases of livestream commerce, and the
absence of effective solutions has hindered the
progress of numerous enterprises within this sector
(He, 2024).
4 THE APPLICATION OF
YINGDAO RPA IN THE E-
COMMERCE LIVE
YingDao RPA implements a cloud-based centralized
governance framework for automated task
orchestration through the creation, administration,
and monitoring of user-defined automated
workflows. Equipped with autonomous real-time
monitoring capabilities, the system dynamically
detects operational anomalies and system events,
executing predefined responses via embedded logical
processing modules. Furthermore, it incorporates
role-based access control mechanisms with audit
trails to ensure compliance in application ecosystems.
In livestream e-commerce contexts, YingDao RPA
enables multidimensional automation.
4.1 Product Lifecycle Management
The system facilitates cross-platform data
aggregation to monitor storefront performance and
merchandise sales metrics. Enterprises can automate
product listing optimizations through customizable
rule engines, including dynamic information updates
(titles, product imagery, inventory levels) and
algorithmic management of promotional campaigns
(automated enrollment, price adjustments, discount
configurations). This operational paradigm
significantly enhances procedural efficiency and data
integrity in product stewardship.
4.2 Merchandise Selection
Optimization
YingDao RPA employs public-domain platform
crawlers (Kuaishou, Douyin, T-mall, Xiaohongshu)
to harvest trending product metadata, subsequently
transforming raw datasets into interactive data
visualization dashboards via GUI-based analytics.
This methodological innovation resolves the endemic
challenge of cross-platform data fragmentation,
empowering enterprises to refine resource allocation
strategies and capitalize on emergent consumption
trends through holistic market insights.
4.3 Price Governance Mechanism
The platform institutionalizes a tripartite price control
protocol:
Price monitoring: Automated cross-platform price
surveillance via mobile shopping interfaces.
Documentation: Algorithmic evidence
preservation through price benchmarking and
screenshot archiving.
Formal notification: Auto-generated pricing
violation reports (structured by store identity,
transaction price, timestamp) dispatched to non-
compliant merchants.
This systematic approach effectively mitigates
pricing discordance caused by malicious markup
practices.
4.4 KOL Management Ecosystem
As the operational linchpin of livestream commerce,
Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) selection critically
determines brand amplification efficacy and sales-
conversion synergies. YinDao RPA constructs talent
databases through native APIs or third-party
analytics, automatically harvesting KOL
performance metrics (e.g., Xingtu backend data)
across predefined dimensions. Enterprises execute
targeted KOL screening via parametric filters within
unified interfaces. Additionally, the platform
pioneers unmanned livestreaming solutions through
RPA-driven operational takeover, achieving 72%
reduction in human resource expenditures for live
room management.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
292

5 THE OPERATIONAL
EFFECTIVENESS OF
YINGDAO RPA IN LIVE
STREAMING E-COMMERCE
INDUSTRY
YinDao RPA, as a leading provider of Robotic
Process Automation (RPA) solutions, addresses
critical pain points in the e-commerce livestreaming
industry through systematic technological
interventions.
5.1 Unified Cross-Platform Data
Integration Framework
Emerging livestream e-commerce enterprises face
operational complexities stemming from multi-
platform deployment, including fragmented data
acquisition, decentralized resource allocation (e.g.,
advertising budgets), and labor-intensive cross-
platform management. Manual processes prove
inadequate for real-time synchronization given the
exponential growth of daily content output (e.g., 300%
YoY increase in SKU updates across major
platforms).
Gongfu Biotech (Chongqing), a vertically
integrated biotechnology enterprise specializing in
cosmetic innovations (R&D, production, distribution),
exemplifies this paradigm. By deploying YingDao
RPA-driven solutions, Gongfu achieved:
(1) Algorithmic data harvesting: Automated
extraction of advertising metrics, live stream analytic
(viewership, user engagement), and conversion rates
across platforms.
(2) End-to-end data integration: Systemic
embedding of operational intelligence into business
workflows.
(3) Quantifiable outcomes: The achievements are
mainly reflected in three aspects. Firstly, more than
520 automated applications have been deployed;
Secondly, the accumulated operating hours are over
12000; The third is to save 7800-person days of
human resources.
Luo Weicai, Chief Information Officer of Gongfu
Cosmetics, emphasized: "YinDao RPA has catalyzed
operational metamorphosis through three strategic
axes: (1) automated business intelligence acquisition
and analytics, (2) procedural optimization via robotic
task execution, and (3) predictive monitoring systems.
This tripartite framework has generated substantial
temporal and labor cost efficiencies (40% reduction
in campaign management overhead), enabling
strategic reallocation of resources toward core
competency development and sustainable growth."
5.2 Automated Price Monitoring to
Prevent Malicious Bidding
Livestream e-commerce in the beauty category has
gained immense popularity among modern
audiences. In January 2025, Douyin platform's GMV
(Gross Merchandise Value) for this category showed
a 6.37% year-on-year increase. On Taotian platform,
the beauty sector achieved a total GMV of 16.394
billion yuan in January, while Kuaishou E-commerce
witnessed a 58% year-on-year growth in brands
exceeding 100 million-yuan sales in 2024. These
figures demonstrate the robust growth momentum of
beauty livestream commerce across major platforms.
As a category with tremendous growth potential, the
beauty sector faces increasingly severe price
disruption and disorder due to numerous merchants
vying for market entry.
Xiabao, a full-channel marketing service provider
specializing in beauty and personal care products,
manages multiple beauty brands. Wang Jiachao,
Manager of Xiabao's Information Management
Department, stated that beauty brands are particularly
vulnerable to parallel imports and counterfeit
products. Excessively low prices from unofficial
channels can divert customers, damaging both brand
pricing systems and distributor trust. Therefore,
unified price control remains an essential task for
every brand.
After implementing Yingdao RPA, as shown in
the diagram, Xiabao can automatically access
multiple pre-registered e-commerce platform
accounts containing different product links through
RPA programs. By simply proceeding to checkout
immediately, the system batch-collects final
consumer prices for price violation verification. Post-
implementation, the RPA robots complete 3-5 daily
cycles of price monitoring, each requiring only about
40 minutes - reducing the time by over 50% compared
to manual operations. This replaces the previous
maximum of one manual daily cycle that handled
price inspections for 200 links across multiple
platforms. The automated solution not only enhances
efficiency, frequency, and accuracy but also enables
scheduled operations, including random price checks
during late-night hours when manual monitoring
proves difficult. This comprehensive approach
maximizes brand protection against price chaos.
Integrating RPA in E-Commerce Live Streaming Sales: A Case Study of YingDao RPA
293
5.3 Combined Deployment of Virtual
and Human Hosts to Reduce Time
and Operational Costs
For emerging e-commerce live streamers or
enterprises lacking established audience bases,
human-hosted livestreams present challenges of time
consumption, high costs, and low efficiency.
Unmanned livestreaming utilizing RPA virtual hosts
effectively liberates human resources, enabling teams
to focus on user conversion during traffic peaks.
Bai Xiao T, an IP-oriented T-shirt brand under
Thumb Wardrobe (Zhejiang) Apparel Technology
Co., Ltd., was established in 2019 in Ningbo,
Zhejiang Province. It represents one of China's few
apparel brands successfully implementing private
domain strategies and new retail positioning.
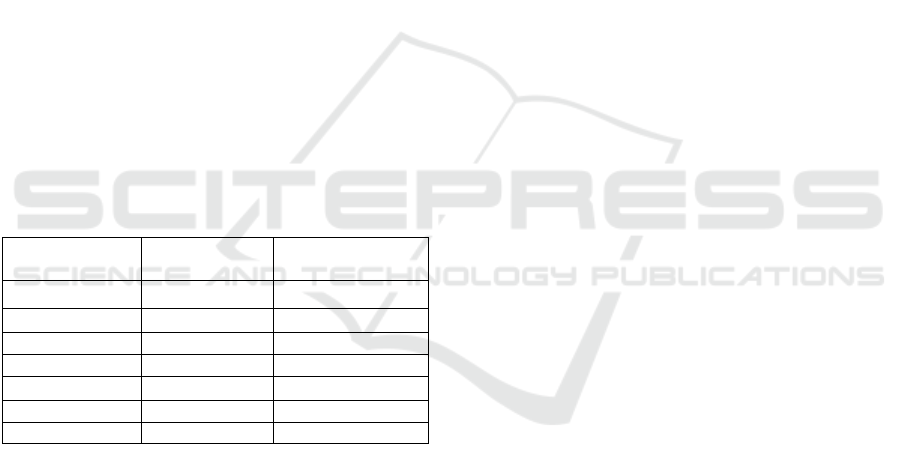
By employing Yingdao RPA robots with
preconfigured templates (see Table 1), the system
automatically recommends products, records product
explanations, and responds to viewer comments,
achieving fully unmanned livestream operation.
Furthermore, through Yingdao's AI Power product,
the RPA robots utilize artificial intelligence search
engines to directly access corporate knowledge bases,
delivering query results within 1 second.
Table1: Pre-prepared forms for operation
Product ID
Top Placement
Time
Top Placement
Termination time
100002834556 310 560
100002834557 680 990
100002834558 1170 1395
100002834559 1585 2320
100002834560 2430 2630
100002834561 2620 3210
En
d
4300 3550
Through continuous optimization of its
unattended live streaming system, the company Bai
Xiao T has successfully liberated two personnel from
repetitive tasks, enabling 24/7 cyclical broadcasting.
Empirical data demonstrates that this automated
solution achieves approximately 50% of the
conversion effectiveness compared to human-hosted
live streams, generating sales revenue ranging from
100,000 to 250,000 yuan. This technological
implementation has realized optimal traffic
monetization while maintaining operational costs at
zero expenditure level, particularly noteworthy being
its breakthrough in generating 100,000-yuan sales
revenue without incremental cost investment.
6 CONCLUSIONS
By analyzing specific cases of technical cooperation
between YinDao RPA and relevant live-streaming e-
commerce enterprises, this paper reveals the
significant application value of RPA technology in
live-streaming e-commerce. Data indicates that RPA
technology can assist live-streaming e-commerce
enterprises in reducing costs and enhancing
efficiency. In specific operational scenarios, these
enterprises can effectively utilize RPA technology to
replace manual operations, thereby decreasing human
resource expenditure while improving office
efficiency and refining work details. The author
believes that in this era of rapid e-commerce
development, RPA technology will gain more
extensive and comprehensive applications in
emerging live-streaming e-commerce enterprises and
other industries, with its potential requiring continued
exploration.
This study solely focuses on YinDao RPA and its
cooperative enterprises as research subjects, resulting
in relatively limited case selection. Moreover, the
paper does not address RPA's role in other domains
of live-streaming e-commerce, nor does it examine
enterprises that achieved insignificant results or even
experienced performance regression through RPA
implementation. Future research should prioritize
these aspects, incorporating analyses of different
RPA technology providers and their corresponding
enterprises.
REFERENCES
Anonymous. (2024). Livestreaming E-commerce: The
Development Path of Quality-Driven Livestreaming.
People’s Daily,014.
China, News. (2024). Latest Annual Report: China's live st
reaming e-commerce industry is booming and undergo
ing profound changes. Retrieved from https://www.chi
nanews.com.cn/cj/2024/10-11/10299803.shtml
Gao, Y. (2020). RPA Financial Robots: Technical Features
and Practical Applications, Light and Textile Industry
and Technology, 49(06), 98+103.
Gao, Y. C., & Shi, Q. (2023). RPA in E-commerce
Platforms: Application Analysis, Straits Science and
Technology and Industry, 36(06), 86-89.
He, S. Y. (2024). Analysis of the impact of e-commerce live
streaming sales on consumer behaviour. Marketing of
time-honored brands, (24), 62-64
Li, X. D. (2025). 5G-Advanced × AI: The Convergence and
Collaboration Between Communication and
Intelligence, People’s Posts & Telecommunications
Press,003.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
294

Ma, X. H., Zhou, Z. M., & Wang K. (2021). RPA in
Financial Shared Services Organizations: Application
Research, China Chief Accountant, (09), 39-42.
Song, H. & Li, X. (2022). RPA Application: Challenges and
Solutions, China Collective Economy, (02), 158-159.
YingDao. (2025). Retrieved from https://www.yingdao.co
m/,2025
Zhang, Y. C. & Yang, Y. (2022). RPA System in
Commercial Banks: Application Research, China
Financial Computer, (02),61-65.
Integrating RPA in E-Commerce Live Streaming Sales: A Case Study of YingDao RPA
295
