
Research on the Path and Effectiveness of Large Model Empowering
Tax Collection and Administration
Siyu Chen
School of public finance and taxation, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, Wuhan, 430073, P.R.China
Keywords: Large Model, Tax Collection and Administration, Empowering path, Collection and Administration
Effectiveness.
Abstract: The ongoing wave of digitalization has resulted in an unprecedented surge in both the volume and
complexity of tax data, thereby presenting significant challenges to conventional tax administration models.
This research explores the potential of large models as a transformative tool for tax governance. We delve
into the technical capabilities of large models, examining their application in critical areas such as data
processing,risk stratification,and the development of early warning systems. Furthermore, we investigate
their utility in enhancing taxpayer services. The integration of large model into tax operations promises to
substantially improve the efficiency of tax collection and administration. This approach can also strengthen
the data-driven foundation of decision-making processes and elevate taxpayer service satisfaction.
Ultimately, the adoption of large models represents a pivotal step towards the modernization and
optimization of tax collection and administration. Tax administration departments should continuously
upgrade their technological infrastructure, strengthen data management, and simultaneously enhance tax
personnel's understanding and application capabilities of large models to broaden the application scenarios
of large models, thereby achieving a qualitative leap in tax administration.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Background and
Significance
The digital transformation presents significant
challenges for tax administration. The exponential
growth of tax data, driven by increasingly frequent
economic activities and heightened digitalization,
encompasses a vast array of taxpayer information.
Consequently, tax authorities must address the
effective collection, organization, analysis,and
utilization of this data. Concurrently,the complexity
of tax operations is escalating, with the emergence
of novel business models and emerging industries,
rendering traditional tax administration approaches
inadequate.
The advent of large model technology represents
a significant advancement in artificial intelligence,
offering novel opportunities for the modernization of
tax administration. Large model possess robust
capabilities in language comprehension, generation,
and knowledge inference, enabling in-depth analysis
and extraction of insights from extensive tax
datasets. This facilitates the precise profiling of
taxpayers and the proactive identification of
potential risks. Furthermore, through natural
language processing, large model can power
intelligent advisory services and automate tax-
related processes, thereby enhancing the efficiency
and quality of taxpayer services. Consequently,
investigating the application of large model in tax
administration holds substantial theoretical and
practical significance.
1.2 Literature Review
With the widespread application of large model
technology across various domains, its exploration
within the domain of taxation has intensified.
Currently, numerous scholars are directing their
attention towards integrating artificial intelligence
technologies, such as those based on natural
language processing, into tax administration
operations.
In the realm of tax administration digitalization,
research indicates a significant role for artificial
Chen, S.
Research on the Path and Effectiveness of Large Model Empowering Tax Collection and Administration.
DOI: 10.5220/0013842300004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 249-254
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
249

intelligence (AI). Ni et al. (2021) posit that AI aids
in the digital transformation of tax management.
Yang and Yu (2023) suggest that the application of
natural language large model (LLM) technology can
enhance intelligent auditing, services, and decision-
making, thereby improving the efficiency of tax
operations. The Shenzhen Municipal Tax Bureau
research team (2023) has explored and proposed
typical application scenarios for AIGC products in
the tax domain. Chen et al. (2024) investigated the
application of LLMs in tax supervision,achieving
intelligent reading of non-resident tax
contracts,review of foreign payment filings, and risk
feedback functionalities. Zhou et al. (2025) explore
the advancement of MM-LLMs in tax collection and
management,significantly improving the accuracy of
tax data analysis and prediction, the level of tax risk
identification and management,and the quality of tax
consultation and services. Chen (2024) found that
EU member states have been early adopters of AI in
tax administration, focusing on tax risk management
and accelerating the development of taxpayer
services. South Korean researchers Y. H. Gu et al.
(2022) proposed the KTL-BERT pre-trained
language model, capable of automatically
classifying five types of tax issues. Y. Zhong et al.
(2024) introduced an LLM for intelligent tax
decision-making,integrating LLMs with domain-
specific databases and knowledge bases to enhance
the professionalism and timeliness of model
responses. Rahman, Sharifur et al. (2024) explore
how AI technologies optimize tax compliance, fraud
detection,and tax administration in modern tax
management. Giovanna Di Marzo Serugendo et al.
(2024) propose the use of AI-driven intelligent
document management systems to streamline tax
document management, with LLM further
enhancing optimization.
2 OVERVIEW OF LARGE
MODEL TECHNOLOGY
2.1 Fundamental Concepts and
Principles of Large Model
Large Models,also referred to as Foundation
Models,are characterized by their extensive
parameterization and intricate architecture,enabling
them to process vast datasets and execute complex
tasks across domains such as natural language
processing, computer vision, and speech recognition.
The Transformer architecture constitutes a core
principle of large model, departing from
conventional recurrent neural network structures and
integrating self-attention mechanisms. This
innovation allows models to effectively capture
dependencies between different positions within
sequential data, thereby significantly enhancing
computational efficiency and parallel processing
capabilities.
2.2 Common Types and
Characteristics of Large Model
2.2.1 Large Language Model
Large Language Models are a category of large
models within the field of Natural Language
Processing (NLP), typically employed for
processing textual data and understanding natural
language. The primary characteristic of these large
models is their training on extensive corpora to learn
the grammatical, semantic, and contextual rules of
natural language, exemplified by models such as
Wenxin Yiyan. In the domain of tax
administration,language large models can be utilized
to comprehend and process tax policy
documents,taxpayer inquiry texts, etc. Through the
study of a vast amount of tax-related text, these
models can accurately extract key information,
respond to taxpayer inquiries, and assist tax
personnel in policy interpretation and administrative
decision-making.
2.2.2 Vision Large Model
Vision Large Models (VLMs) represent expansive
models within the computer vision (CV)
domain,primarily utilized for image processing and
analysis. These models, trained on extensive image
datasets,facilitate various visual tasks, including
image classification, object detection, and facial
recognition, exemplified by models like INTERN
(SenseTime). In tax administration, the direct
application of VLMs is limited, yet they possess
potential in scenarios such as invoice image
recognition, where they can extract key information
to aid in tax auditing.
2.2.3 Multimodal Large Language Model
Multimodal Large Language Models (MM-LLMs)
are sophisticated models capable of processing
diverse data types, including text, images, and audio.
These models integrate Natural Language
Processing (NLP) and CV capabilities to
comprehensively understand and analyze
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
250

multimodal information. This enables a more
holistic comprehension and processing of complex
data. For instance, intelligent customer service
systems can simultaneously handle text and voice
data,enabling more natural interactions. Within tax
administration, MM-LLMs can integrate taxpayers'
textual declaration information with associated
image and video evidence, facilitating more
comprehensive administrative analysis. However,
the application of MM-LLMs in this domain is
currently in the exploratory phase.
3 EMPOWERING PATH OF
LARGE MODEL IN TAX
ADMINISTRATION
3.1 Data Processing and Analysis Path
Within the domain of tax administration, the sources
of data are extensive and structurally complex.
Large models can leverage their superior capabilities
to efficiently clean, integrate, and analyze multi-
source heterogeneous tax data, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
Initially,when tax data presents challenges such
as format errors, duplicate entries, missing
values,and outliers, large models can employ natural
language processing and machine learning
techniques for intelligent data cleansing.
Simultaneously, these models can analyze data
patterns to automatically populate missing values or
eliminate redundant records based on logical data
relationships, thereby enhancing data quality and
consistency. Subsequently, large language models
facilitate seamless data integration by overcoming
barriers between diverse tax data sources. Tax data
originates from various systems, including tax filing
systems,invoice management systems, and third-
party data platforms (e.g. banks,market regulatory
authorities), each with varying formats and
structures. Large models leverage their robust
semantic understanding capabilities to standardize
data from different sources,linking data of the same
entities (e.g.taxpayers,tax types). Ultimately,by
conducting in-depth analysis of the
integrated,extensive data, large models can uncover
hidden correlations, providing a comprehensive data
foundation for subsequent analyses.
Within the digitalization transformation process,
Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs (HMRC) has
proactively integrated large model technology to
revolutionize tax administration, thereby enhancing
efficiency and accuracy. Since 2015, HMRC has
established digital tax accounts, consolidating years
of tax filing data, taxpayer historical records,and
relevant tax regulations to construct a
comprehensive dataset for Large Model training.
Within the context of personal income tax return
audits, the previous manual review of extensive
personal income tax filings was time-consuming and
prone to errors. The implementation of large models
enables rapid processing of vast filing data.
Furthermore, large model analyze taxpayer income,
deductions, and tax reliefs to automatically identify
potential errors or anomalies in filings, thereby
alerting tax officials for focused attention.
Figure 1: Pathway of Large Models Empowering Data Processing and Analysis.
Research on the Path and Effectiveness of Large Model Empowering Tax Collection and Administration
251
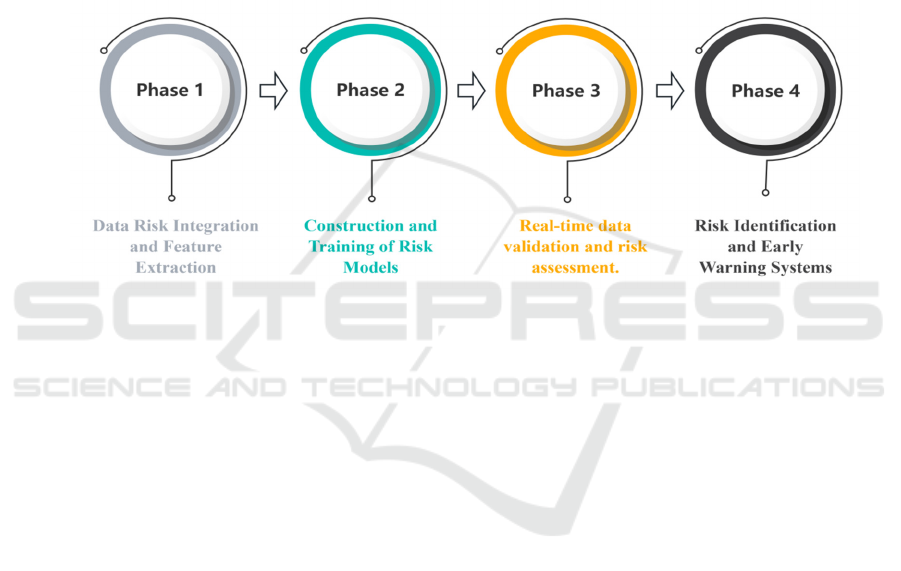
3.2 Risk Identification and Early
Warning Path
Following data processing and analysis, large
models can construct tax risk assessment models to
monitor business operations and tax data in real-
time, enabling precise risk alerts. This capability
provides robust support for tax administration, as
illustrated in Figure 2.
Large models automatically select and combine
feature variables related to tax risk from processed
and analyzed data, constructing an effective risk
assessment indicator system. Tax authorities
transmit the latest business operation and tax data of
enterprises to the large model risk assessment
system in real-time. The large models then
calculates the risk score of the enterprise based on
the trained risk assessment model. When the risk
score exceeds a predefined threshold, an automatic
alert mechanism is triggered. The system generates a
detailed risk alert report, specifying the risk type,
severity, and potentially involved specific business
and transactions, providing tax personnel with
precise risk clues.
Figure 2: Pathway of Large Models Empowering Tax Risk Identification and Alert Systems.
Currently,the Hubei Provincial Tax Service is
piloting the integration of large models for
outbound payment management. During the
processing of an outbound payment filing for a
specific enterprise, the large model swiftly analyzed
the contract documentation and identified that the
stipulated technical service fees significantly
exceeded prevailing market rates, coupled with
anomalous payment methods. Following risk
stratification, the case was classified as high-risk,
prompting the immediate dissemination of an alert.
Tax administrators, upon receiving the
alert,promptly initiated an investigation, which
revealed that the enterprise was engaged in tax
evasion through the artificial inflation of technical
service fees to facilitate the offshore transfer of
profits. This intervention successfully mitigated tax
revenue losses and effectively averted tax risks.
3.3 Optimizing Taxpayer Service
Pathways
Large models can revolutionize taxpayer services by
enabling intelligent consultation and personalized
service delivery, thereby significantly enhancing
taxpayer satisfaction. The "Smart Home Tax"
system implemented by the Korean National Tax
Service serves as a prime example. Leveraging large
model technology, this system integrates data
collection and analysis, natural language processing,
personalized service customization, and continuous
learning and optimization. This approach provides
taxpayers with tailored tax advisory services, setting
a significant precedent for optimizing taxpayer
services and demonstrating the substantial potential
and unique application of large model in this
domain.
As illustrated in Figure 3, large models construct
extensive tax knowledge graphs by integrating
diverse tax policies, procedural guidelines, and
frequently asked questions. When taxpayers submit
inquiries through online platforms or mobile
applications, the large model employs Natural
Language Processing (NLP) to interpret the query's
intent and semantics. For instance, if a taxpayer
asks,"What are the latest income tax incentives for
small and micro-enterprises?" the large model can
promptly retrieve relevant policy information and
respond in accessible language, potentially including
details on eligibility criteria and filing procedures.
Furthermore, through in-depth analysis of taxpayer
data,large model offer personalized tax advisory
services. For newly registered businesses, the large
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
252
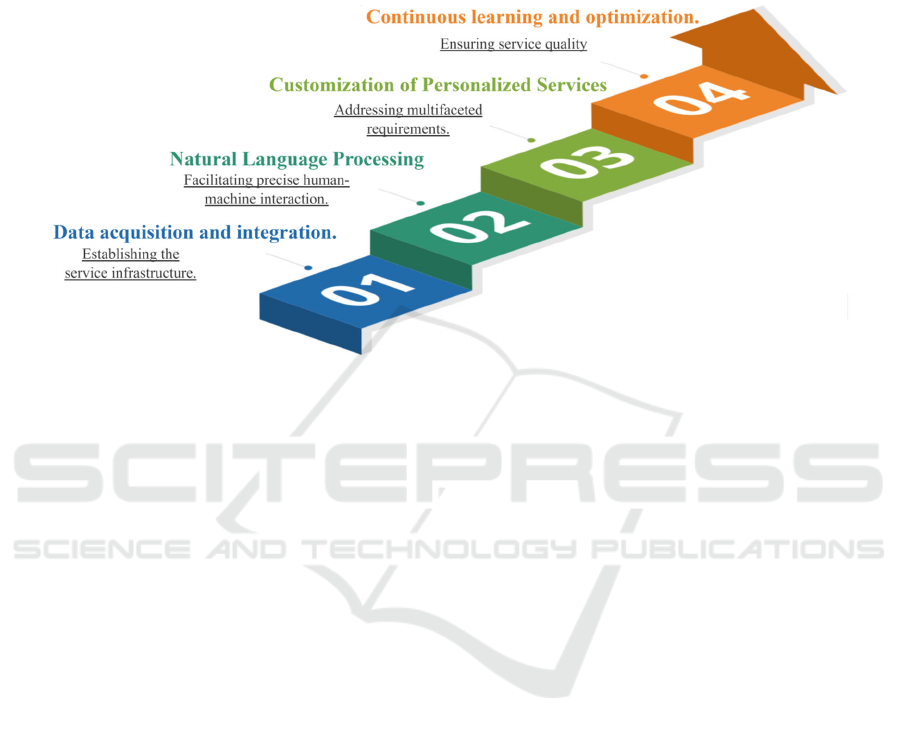
model proactively provides information on initial tax
registration processes and applicable tax incentives
based on industry and operational scale, facilitating
their rapid understanding of tax-related matters. The
large model also refines its recommendations based
on taxpayers' past inquiries and behavioral
preferences. To ensure the accuracy and
effectiveness of tax advisory services, tax authorities
regularly update the large model with new tax
policies, legislative revisions, and practical case
studies, enabling continuous learning and adaptation.
Figure 3: Pathways for Optimizing Tax Service Delivery through Large Models.
4 OPTIMIZATION OF TAX
ADMINISTRATION
EFFICIENCY THROUGH
LARGE MODELS
4.1 Enhancing Administrative
Efficiency
Traditional tax administration processes involve the
collection,organization, and analysis of vast datasets.
Manual processing is not only time-consuming and
labor-intensive but also prone to errors. The
integration of large model technology facilitates full-
process automation and intelligence. In the data
acquisition phase, large model can seamlessly
integrate with various governmental systems and
enterprise financial software to acquire taxpayers'
operational data, financial statements, and invoice
information in real-time and in batches, thereby
eliminating data silos and preventing redundant data
entry. During the selection of tax audit cases, large
model employ machine learning algorithms to
rapidly scan and filter tens of thousands of enterprise
data points, accurately identifying high-risk entities.
This significantly reduces case selection time,
enabling auditors to conduct targeted investigations.
In the tax collection phase, automated calculations
and intelligent comparisons ensure the accuracy of
tax calculations and expedite the collection process,
leading to an exponential increase in administrative
efficiency.
4.2 Strengthening the Scientific Basis
of Decision-Making
The formulation of tax policies and the allocation of
tax administration resources necessitate precise data
analysis and forecasting. Large models ,leveraging
their robust data mining and deep analytical
capabilities, can provide a solid foundation for
decision-making. By comprehensively analyzing
macroeconomic data,industry trends, and historical
tax data,large models can forecast the impacts of
various tax policy adjustments on fiscal revenue,
economic growth, and enterprise development,
thereby assisting tax authorities in formulating
scientifically sound tax policies. In terms of resource
allocation for tax administration, large model
analyze the distribution of tax risks across different
regions,industries,and enterprise sizes. This analysis
provides quantitative evidence for tax authorities to
rationally allocate human and material resources,
thereby avoiding resource waste, optimizing the
allocation of tax administration resources,and
enhancing overall tax administration efficiency.
Research on the Path and Effectiveness of Large Model Empowering Tax Collection and Administration
253

4.3 Enhancing Taxpayer Service
Satisfaction
Taxpayer service constitutes a critical component of
tax administration, and large models offer
significant advantages in optimizing these services.
Taking advantage of natural language processing
technology, large models can function as intelligent
virtual assistants, providing 24/7 support to
taxpayers. These systems can address a wide array
of tax-related inquiries, including policy
interpretations, procedural guidance, and assistance
with invoice generation, delivering prompt and
accurate responses, thereby minimizing taxpayer
wait times. Furthermore, large models facilitate
personalized services by analyzing taxpayer
data,such as industry specifics, operational scale,and
tax compliance history. This enables the tailored
dissemination of relevant tax incentives and
procedural reminders, thus assisting taxpayers in
maximizing policy benefits, reducing tax liabilities,
and improving overall satisfaction. This approach
fosters a positive tax administration environment.
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion,this study provides an in-depth
analysis of the pathways and effectiveness of large
models in empowering tax administration.
Leveraging their robust language comprehension,
learning capabilities, and data processing abilities,
large models offer novel approaches to tax
administration in areas such as data processing, risk
assessment, and the optimization of taxpayer
services. This leads to significant improvements in
administrative efficiency, the scientific basis of
decision-making, and taxpayer service satisfaction.
This is of great significance for promoting the
intelligent and modern development of tax
administration. Tax administration departments
should continuously upgrade their technical
infrastructure, strengthen data management, enhance
tax personnel's understanding and application
capabilities of large models and expanding the
application scenarios of it, so that can achieve a
qualitative leap in tax administration.
However, this study also has certain limitations,
such as the lack of discussion on the potential risks
and countermeasures of large models applications in
tax administration pathways, as well as the
deficiency in research on specific practical cases of
integrating large model technology in different
countries.
Looking ahead,with continuous technological
innovation, the application prospects of large models
in the field of tax administration will be even
broader. We anticipate more diversified research and
practices to further explore the potential of large
models, improve the tax administration system,and
contribute to the development of the tax cause.
REFERENCES
Chen, F., Sun, K. 2024. Application of Natural Language
Large Models in Tax Supervision: Taking the Review
of Non-Resident Tax Contracts as an Example. Tax
Economics Research, 29(03), 38-46.
Chen, J. 2024. Comparative Analysis of the Application of
Artificial Intelligence in Tax Administration in EU
Member States. International Taxation, (04), 49-54.
Di Marzo, Serugendo, G., Cappelli, M. A., Falquet, G.,
Métral, C., Wade, A., Ghadfi, S., Cutting-Decelle, A.-
F., Caselli, A., Cutting, G. 2024. Streamlining Tax and
Administrative Document Management with AI-
Powered Intelligent Document Management System.
Information, 15(8), 461.
Gu, Y. H., Piao, X., Yin, H., Jin, D., Zheng R., Yoo, S. J.
2022. Domain-Specific Language Model Pre-Training
for Korean Tax Law Classification, in IEEE Access,
10, 46342-46353.
Moore, R., Lopes, J., 1999. Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. SCITEPRESS.
Ni, J., Li, Y., Zhou, R. 2021. Strategies for Digital
Transformation of Tax Administration with Artificial
Intelligence. Tax Research, (04), 92-96.
Rahman, S., Khan, R., Sirazy, Md, Das, R. 2024. An
Exploration of Artificial Intelligence Techniques for
Optimizing Tax Compliance, Fraud Detection, and
Revenue Collection in Modern Tax Administrations.
56-80.
Shenzhen Municipal Tax Bureau Research Group, Li,W.,
Wang, X. 2023. Reflections and Suggestions on the
Application of Generative Artificial Intelligence
Represented by ChatGPT in the Tax Field. Tax Research,
(06), 5-9.
Smith, J., 1998. The book, The publishing company.
London, 2
nd
edition.
Yang, S., Yu, L. 2023. Opportunities and Challenges of
Generative Artificial Intelligence Represented by
ChatGPT for Tax Administration. Tax Research, (06),
16-20.
Zhong, Y., Wong, D., Lan, K. 2024. Tax Intelligent
Decision-Making Language Model, in IEEE Access,
12, 146202-146212.
Zhou, Y., Mao, Y., Chen, L. 2025. Modernization of Tax
Collection and Administration: Innovative Application
and Exploration of MM-LLMs. Journal of Southeast
University (Philosophy and Social Science Edition),
27(01), 65-73+151.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
254
