
ERP System Facilitates Digital Transformation in New Energy
Vehicle Enterprises: A Case Study of Xiaomi Automobile Factory
Xin Shen
a
School of Business Administration and Tourism Management, Yunnan University,
East Outer Ring Road, Chenggong District, Kunming 650500, China
Keywords: ERP System, Digital Transformation, New Energy Vehicles, Xiaomi Automobile Factory.
Abstract: In the era of digital economy, the new energy vehicle (NEV) industry is facing challenges from traditional
manufacturing models, such as low efficiency, high costs, and insufficient flexibility, which urgently require
the adoption of advanced digital technologies for digital transformation to enhance competitiveness. This
paper takes Xiaomi Automobile Factory as an example to explore the critical role of enterprise resource
planning (ERP) system in the digital transformation of NEV enterprises. Through case analysis, combined
with the practical application of ERP system in Xiaomi's core operational areas— supply chain, finance,
production, and sales—the study reveals that ERP system supports Xiaomi's "tripartite integration" digital
transformation framework. Specifically, ERP system have significantly optimized supply chain collaboration
efficiency, reduced procurement and inventory costs, established a comprehensive financial system and
intelligent production planning, while improving customer service accuracy and market responsiveness. By
analyzing the successful implementation of the ERP system at Xiaomi Automobile Factory, this research
provides valuable insights for the digital transformation of other NEV enterprises, thereby promoting the
development and innovation of the NEV industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the digital economy era, the significance of
enterprise digital transformation has become
increasingly prominent, particularly for the
manufacturing sector, where it has emerged as a core
driver for enhancing competitiveness. Propelled by
energy conservation/emission reduction mandates
and the wave of intelligent manufacturing, the
automotive industry—a pillar of national
economies—is undergoing a paradigm shift from
"traditional manufacturing" to "smart manufacturing"
(Xiao, Cao, & Xia, 2024). Within this transition, new
energy vehicles (NEVs) have emerged as a disruptive
force, rapidly capturing market share. Meanwhile,
traditional automakers constrained by rigid assembly
line processes—plagued by high costs, low efficiency,
and operational inflexibility—struggle to adapt to the
NEV market's demands for personalization and
sustainability (Yao, 2024). Against this backdrop,
enterprise resource planning (ERP) system has
proven instrumental in driving digital transformation
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-0126-5551
for NEV enterprises. These systems inject dynamism
into organizational restructuring by pursuing three
strategic objectives: efficiency enhancement, quality
optimization, and ecosystem collaboration. Through
holistic reinvention of automotive supply chains,
financial operations, production systems, and beyond,
ERP implementation represents an essential pathway
for overcoming industry bottlenecks and achieving
sustainable development (Tang, 2024).
As a representative case of "cross-boundary
vehicle manufacturing," Xiaomi Automobile Factory
has positioned digital transformation as its strategic
core. Utilizing the SAP S/4HANA Cloud ERP system
as a critical tool, the company has efficiently
integrated supply chain, financial, and production
processes, achieving the goals of cost reduction and
efficiency improvement. This initiative demonstrates
unique research value and practical significance in the
field of intelligent manufacturing. Therefore, this
paper selects Xiaomi Automobile Factory as the
research subject. The study primarily employs case
analysis to: (1) Track and analyze the implementation
Shen, X.
ERP System Facilitates Digital Transformation in New Energy Vehicle Enterprises: A Case Study of Xiaomi Automobile Factory.
DOI: 10.5220/0013840700004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 169-174
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
169
process of the ERP system at Xiaomi Automobile
Factory; (2) Collect relevant data to evaluate the
operational benefits of the ERP system; (3)
Investigate the pathways and value creation
mechanisms of its digital transformation.
Through this approach, the research aims to
elucidate the critical role of ERP system in Xiaomi
Automobile Factory’s digital transformation. The
findings are expected to provide strategic references
for other new energy vehicle (NEV) enterprises and
contribute to strengthening the competitive position
of China’s automotive industry in the global market.
2 ERP MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
The ERP system is a highly integrated information
management framework designed to consolidate and
manage core business processes and resources across
various organizational departments through a unified
platform. Typically, ERP system integrates
functional modules such as supply chain
management, finance, production, and sales
operations into a real-time data sharing and
processing platform. This integrated management
system eliminates information silos between
departments through data consolidation, enabling
real-time organizational collaboration and providing
decision-making support. Furthermore, ERP system
facilitates continuous monitoring and analytical
reporting of enterprise operations, allowing
management to promptly identify operational
challenges and opportunities. Effective
implementation of ERP system can significantly
enhance organizational management efficiency and
operational performance, playing a crucial role in
data synchronization, resource allocation
optimization, and risk mitigation, thereby
strengthening corporate competitiveness in the
marketplace (Bao, 2024).
3 APPLICATION OF ERP
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN
XIAOMI AUTOMOBILE
FACTORY
Positioning digital transformation as a core strategic
initiative, Xiaomi Automobile has established an
integrated tripartite digital transformation framework
encompassing a centralized data platform, cloud-
based architecture, and smart manufacturing systems,
with the ERP system serving as a pivotal component.
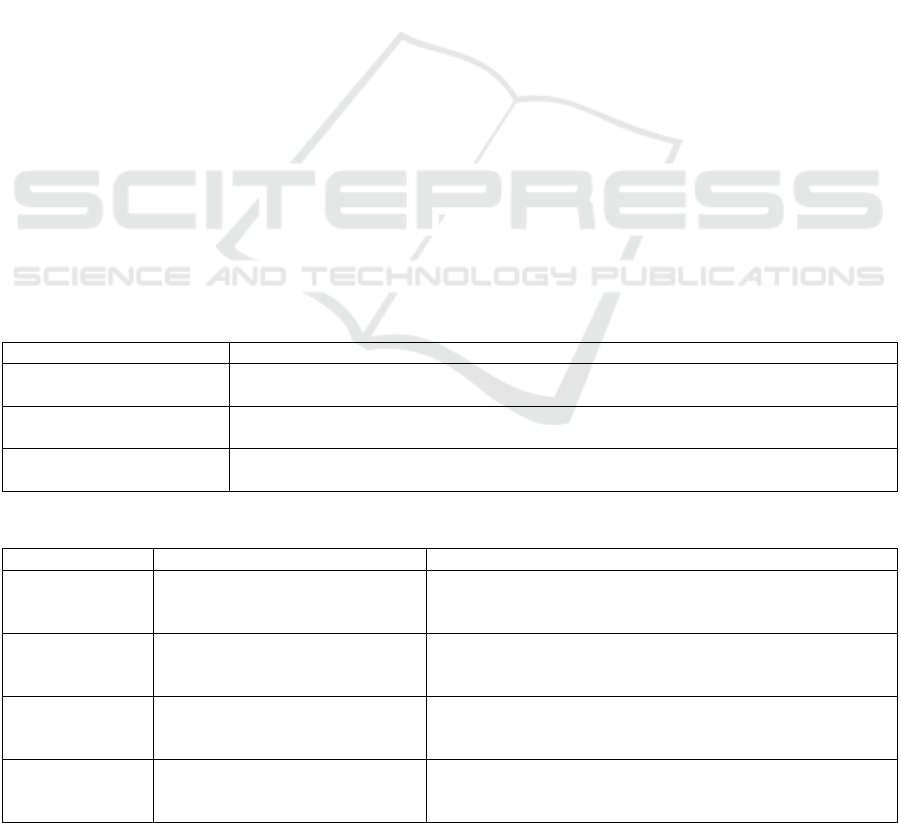
As detailed in Table 1, the ERP system demonstrates
critical functional alignments with Xiaomi's digital
transformation architecture. The projected
implementation timeline of the ERP system in
Xiaomi's automotive production facilities is
systematically outlined in Table 2 (ERPYUAN,
2024).
Table 1: Integration of ERP system with Xiaomi Automobile's digital transformation framework.
Com
p
onent Functional Im
p
lementation
Centralized Data Platform
Unified collection, storage, and analysis of enterprise-wide operational data to support
cross-de
p
artmental business decision-makin
g
Cloud Architecture
Implementation of SAP S/4HANA Cloud establishes flexible, scalable, and easily
deployable IT infrastructure that accommodates rapid business expansion
Smart Manufacturing
ERP-MES integration (e.g., with JianDaoYun MES) facilitates digital transformation and
intelligent automation of production processes
Table 2: Projected implementation timeline of ERP system in Xiaomi Automotive.
Yea
r
Phase Key Activities
2021
Planning & Requirements
Analysis
• March project initiation
• ERP strategic alignment
• Cross-functional re
q
uirements ma
pp
in
g
2022 Development & Testing
• Soft tooling vehicle completion
• ERP-enabled supply chain coordination
• Production simulation validation
2023 Mass Production Readiness
• ERP-driven production scheduling
• AI-powered quality control integration
• Automated order management deployment
2024 Commercialization & Delivery
• ERP-channel integration (sales networks)
• Real-time customer order tracking
• Post-sales service digitization
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
170

3.1 Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) refers to the
systematic coordination of suppliers, manufacturers,
and distribution facilities to optimize manufacturing,
logistics, distribution, and retail operations,
encompassing the complete cycle from raw material
procurement to finished product delivery. By
implementing ERP systems to facilitate intelligent
supply chain optimization, Xiaomi Automobile
achieves cost efficiency while maximizing
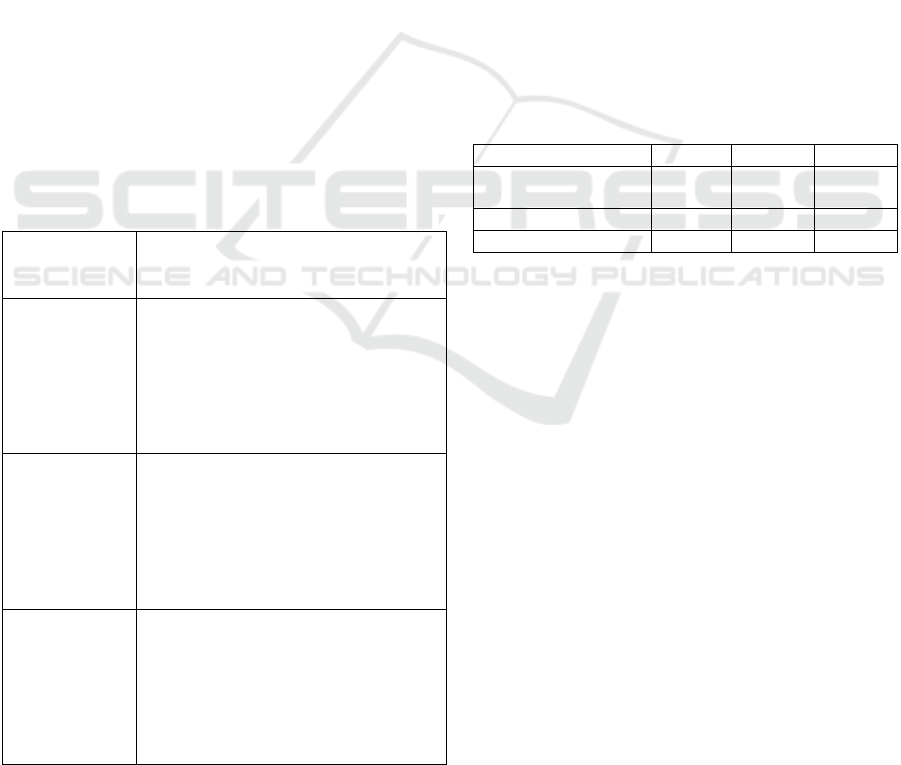
operational returns. The specific applications of the
ERP system in supply chain management at Xiaomi
Automobile's manufacturing facilities are detailed in
Table 3 (Pei, 2023).
Table 3: ERP system applications in supply Chain management.
Components Implementation
Supplier Management
Centralized management of supplier information including qualifications, performance
evaluation, and contract administration, eliminating information silos to ensure supply chain
stabilit
y
and reliabilit
y
procurement
Automated purchase order generation reduces manual operations, shortens procurement cycles,
and lowers purchasing costs
Inventory Control
Real-time inventory monitoring with stock alerts and automated replenishment functions
enhances inventor
y
turnover rates and reduces holdin
g
costs
Logistics
Integration of logistics information achieves process transparency, improving supply chain
efficienc
y
and o
p
erational a
g
ilit
y
3.2 Financial Management
The ERP system at Xiaomi Automobile enables
comprehensive financial management spanning from
accounting operations to analytical processes.
Through ERP implementation, financial data is
systematically recorded, accounting procedures
standardized, and a unified control framework
established. By adopting an integrated end-to-end
management system, financial personnel transition
from manual bookkeeping to a centralized model
focusing on fund management, financial reporting,
and regulatory compliance. This ERP-driven
transformation optimizes financial system
functionalities through enhanced data transparency
and operational efficiency, ultimately elevating
financial governance capabilities and strategic
decision-making proficiency (Han, 2024).
3.3 Production Manufacturing
Automobiles represent highly sophisticated industrial
products, where the manufacturing process
constitutes the pivotal phase for Xiaomi Automobile's
transition from conceptual design to mass production.
This stage directly impacts core competitiveness, cost
structure optimization, and market performance
metrics. By implementing digitalized and intelligent
manufacturing systems through innovative
technological integration, Xiaomi achieves
accelerated production scaling while maintaining
stringent quality assurance and safety compliance
protocols, thereby establishing a sustainable presence
in the global new energy vehicle market (Wang,
2024). The specific applications of the ERP system in
Xiaomi Automobile's production manufacturing
processes are systematically detailed in Table 4.
Table 4: ERP system applications in production manufacturing.
Production Process Components ERP System Implementation
Production Planning
ERP automatically generates production schedules based on market demand
analysis, order portfolios, and inventory profiles to ensure optimal resource
allocation
Production Progress Management
Real-time monitoring of manufacturing workflows through ERP enables prompt
anomaly resolution and strict schedule adherence
Quality Control
ERP-integrated quality management modules enforce end-to-end traceability from
raw material inspections to finished product testing, ensuring compliance with
QA/QC standards
ERP System Facilitates Digital Transformation in New Energy Vehicle Enterprises: A Case Study of Xiaomi Automobile Factory
171
3.4 Sales & Customer Relationship
Management
The sales and customer engagement process
significantly contribute to Xiaomi Automobile's
market value realization, directly influencing brand
appeal, customer retention rates, and sustainable
growth. By leveraging online-offline integrated sales
channels, transparent pricing strategies, and data-
driven order management systems, Xiaomi efficiently
engages target consumers while establishing trust.
Capitalizing on its intelligent ecosystem
advantages—including vehicle-infotainment
connectivity and user profiling analytics—the
company delivers personalized services and full
lifecycle experiences encompassing test drives,
delivery, after-sales support, and over-the-air (OTA)
updates. This approach not only strengthens customer
loyalty but also drives product innovation through
user feedback mechanisms, ultimately achieving
sales breakthroughs and brand differentiation in the
competitive new energy vehicle market. The ERP
system's applications in post-delivery customer
relationship management at Xiaomi Automobile are
detailed in Table 5 (Wang, 2024).
Table 5: ERP system applications in customer relationship
management.
CRM
Components
ERP System Implementation
Sales Channel
Integration
ERP unifies online-offline sales
channels with advanced data analytics
capabilities, enabling statistical analysis
of sales performance to inform strategy
formulation
Customer
Service
ERP delivers full lifecycle service
management through comprehensive
tracking of customer profiles and
requirements, facilitating personalized
offerings that enhance satisfaction and
loyalty rates
Order
Management
ERP enables end-to-end order
processing from reception to fulfillment,
ensuring operational efficiency and
delivery accuracy
4 BENEFITS OF ERP SYSTEM
IMPLEMENTATION AT
XIAOMI AUTOMOBILE
FACTORY
4.1 Cost Optimization & Efficiency
Enhancement
4.1.1 Reduction in Supply Chain,
Procurement, and Production Costs
Post-ERP implementation at Xiaomi Automobile's
manufacturing facilities, significant cost reductions
across supply chain operations, procurement
activities, and production processes have been
substantiated through recent financial disclosures, as
evidenced by empirical data from authoritative
sources (Daily Economic News, 2025; Wen, 2024; Lü,
2024). These cost-saving achievements are
systematically quantified in Table 6.
Table 6: Financial performance metrics of Xiaomi
Automobile.
Ite
m
2024Q2 2024Q3 2024Q4
Operating Revenue
(
Billion
)
64 97 167
Net Loss
(
billion
)
18 15 7
Gross Mar
g
in
(
%
)
15.4 17.1 18.5
Gross margin, a critical indicator of corporate
profitability, has remained at elevated levels for
Xiaomi Automobile since product launch. In Q4 2024,
the company achieved a gross margin of 18.5%,
significantly outperforming the industry average of
4.6%. Concurrently, quarterly operating revenue
demonstrated 72% sequential growth while net losses
continued to contract. Notably, these financial
improvements occurred during Xiaomi Automobile's
capital-intensive expansion phase, collectively
demonstrating exceptional operational efficiency that
suggests imminent profitability transition.
4.1.2 Operational Efficiency Improvement
Through Automation
The integration of ERP with Manufacturing
Execution Systems (MES) enables automated
purchase order generation and real-time monitoring
of equipment status and workflow processes. This
digital management framework replaces manual
supervision, reducing human intervention while
minimizing operational errors, thereby enhancing
both customer satisfaction and production efficiency.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
172

Although Xiaomi Automobile has not disclosed
specific metrics in this domain, industry
benchmarking data from Foton Motor's new energy
vehicle division reveals that ERP-MES integration
achieved a 10% improvement in order fulfillment
rates and 5% production efficiency gains,
demonstrating optimized resource utilization and
output maximization (China Listed Companies
Association, 2024).
Regarding financial operations, the ERP system
establishes a comprehensive financial analysis
framework that improves accounting efficiency and
accuracy. While Xiaomi Automobile has not released
quantitative evidence, Foton Motor's implementation
of its SuperTruck ERP system developed multi-
dimensional cost analysis models. Post-
implementation, their financial cost accounting
efficiency improved significantly, reducing monthly
closing cycles from 3 days to 1 day, with vehicle
standard cost accounting accuracy reaching 99% -
foundational enhancements for profitability
optimization (China Listed Companies Association,
2024).
4.2 Quality Enhancement & Process
Acceleration
4.2.1 Product Quality Improvement &
Defect Rate Reduction
The ERP system facilitates quality control by
replacing manual visual inspections with AI-powered
defect detection systems. Through real-time analysis
of production data, high-precision anomaly
identification is achieved, enabling proactive
mitigation of potential quality issues and elevating
defect-free rates to industry-leading benchmarks.
Concurrently, the ERP system implements
dynamic supplier evaluation protocols to eliminate
underperforming vendors, thereby optimizing
component procurement quality. For instance, the
stable supply partnership with Contemporary
Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) ensures
consistent reliability of battery systems (Wang,
2024).
4.2.2 R&D-Production Cycle Compression
The ERP system integrates data flows between
Xiaomi Automobile Factory's R&D division (3,400-
member team) and manufacturing operations,
enabling real-time synchronization of design
blueprints, bill of materials (BOM), and production
scheduling. This digital thread eliminates operational
latency and resource waste. While quantitative cycle
metrics remain undisclosed, industry validation exists
through premium automakers like BMW AG, which
leverages analogous ERP solutions to achieve
seamless order-to-production integration and rapid
customization response capabilities.
Through ERP-optimized dual-shift operations at
the Beijing Yizhuang Factory, post-July 2024
production line upgrades doubled per-shift capacity.
Delivery cycles were compressed from 25-28 weeks
to under 20 weeks, with annual delivery targets
elevated from 100,000 to 135,000 units in 2024.
Concurrently, capacity utilization rates improved,
while economies of scale effectively diluted per-unit
R&D and manufacturing costs.
5 CONCLUSION
This study explores the application of ERP
management systems in Xiaomi Automobile's
manufacturing operations and their associated
benefits, revealing the critical role ERP systems play
in the digital transformation of new energy vehicle
enterprises. Through case analysis, it demonstrates
that ERP systems significantly enhance operational
efficiency and reduce production costs by integrating
core processes across supply chain management,
financial operations, production planning, and sales.
Key outcomes include optimized supply chain
collaboration, standardized financial workflows,
intelligent production scheduling, and personalized
customer service. The implementation of ERP
systems has driven Xiaomi's digital transformation,
enabling the achievement of cost reduction,
efficiency improvement, quality enhancement, and
accelerated production timelines. These
advancements have supported rapid sales growth in a
highly competitive market. The findings indicate that
Xiaomi's successful practices provide valuable
insights for digital transformation initiatives in the
new energy vehicle industry. As artificial intelligence
(AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain
technologies continue to evolve, the functional scope
of ERP systems will expand further. These systems
not only help enterprises eliminate information silos
but also optimize resource allocation and operational
processes through data-driven decision-making. For
other new energy vehicle companies pursuing ERP-
enabled digital transformation, it is recommended to
prioritize alignment between system capabilities and
business requirements, strengthen cross-departmental
collaboration, and actively explore open ecosystem
partnerships. Such strategic measures will ensure
ERP System Facilitates Digital Transformation in New Energy Vehicle Enterprises: A Case Study of Xiaomi Automobile Factory
173

sustainable development amid the dual trends of
green energy adoption and intelligent digitalization,
injecting innovation momentum into the automotive
industry's ongoing transformation.
While this research systematically examines the
role of ERP systems in Xiaomi Automotive's digital
transformation, several methodological limitations
warrant acknowledgment. The single-case study
design, focused on one enterprise, restricts the
generalizability of conclusions, necessitating further
validation through comparative multi-case analyses.
Additionally, limited access to Xiaomi's operational
specifics—such as ERP implementation timelines
and financial reconciliation efficiency—has required
reliance on inferential reasoning and hypothetical
assumptions derived from disclosures by peer
enterprises, potentially affecting analytical precision.
Furthermore, the constrained research timeframe
precluded assessment of ERP systems' long-term
strategic impacts on Xiaomi Automotive.
Future research directions include extending the
observation window to evaluate ERP's sustained
organizational influence, systematically monitoring
Xiaomi's official disclosures to collect operational
datasets, and refining implementation benefit
analyses to enhance scholarly rigor. Comparative
investigations across NEV manufacturers of varying
scales will empirically validate ERP systems'
adaptability in automotive digital transformation
initiatives, while cross-industry benchmarking could
reveal sector-specific optimization pathways. These
efforts will advance theoretical frameworks for
intelligent manufacturing ecosystems while
informing practical strategies for Industry 4.0
adoption.
REFERENCES
Bao, H. J. (2024). Research on ERP system applications in
group corporate management. Modern
Marketing (Early Issues), (11), 127-129.
China Listed Companies Association. (2024). Foton Moto
r’s end-to-end process innovation: A benchmark case f
or digital transformation, https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/
g9qy5snedGQEr4BBh82EAg, last accessed 2025/3/24.
Daily Economic News. (2025). Lei Jun: Xiaomi reports
historic revenue of CNY 365.9 billion in 2024, with
automotive division contributing CNY 32.1 billion,
https://finance.eastmoney.com/a/20250318334895256
9.html, last accessed 2025/3/24.
ERPYUAN. (2024). Xiaomi Automobile: Digital transform
ation practices centered on ERP systems, https://mp.w
eixin.qq.com/s/VfFB-Lg5QgaTR6zgIYmxHQ.ls, last a
ccessed 2025/3/24.
Han, S. S. (2024). Innovation in corporate financial
management models under digital
transformation. Modern Marketing (Late Issues), (11),
104-106.
Lü, Q. (2024). Xiaomi Automotive narrows Q3 loss to CNY
1.5 billion, forecasts fastest growth in EV sector for
2025. First Financial Daily, A09.
Pei, X. (2023). Optimization strategies for enterprise
supply chain management in the new era. Business 2.0,
(31), 14-16.
Tang, D. B. (2024). Cost control challenges and
countermeasures for new energy enterprises based on
ERP systems: A case study of Company Y. China
Management Informatization, 27(24), 107-109.
Wang, W. Z. (2024). Intelligent manufacturing as a catalyst
for new productive forces: Leading the modernization
of industrial systems. Contemporary Economic
Research, (2), 105-115.
Wang, X. W. (2024). Inside Xiaomi’s SU7 production hub:
700+ robots enable 76-second vehicle assembly
cycle. Securities Times, A04.
Wen, T. (2024). Xiaomi achieves record Q2 revenue with
smart EV debut. Shanghai Securities News, p. A07.
Xiao, J. H., Cao, W. H., & Xia, Z. H. (2024). Adaptive
transformation in digitalization of manufacturing
enterprises: Dual pathways of leapfrogging and
capability-building. China Industrial Economics, (12),
136-154.
Yao, Y. (2024). Pathways for digital economy-driven
transformation and upgrading of the new energy
vehicle industry. China Management Informatization,
27(14), 120-122.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
174
