
Place Recognition Using Bag of Semantic and Visual Words from
Equirectangular Images
Mar
´
ıa Flores
a
, Marc Fabregat-Ja
´
en
b
, Juan Jos
´
e Cabrera
c
, Adri
´
an Peidr
´
o
d
,
David Valiente
e
and Luis Pay
´
a
f
Engineering Research Institute of Elche (I3E), Miguel Hern
´
andez University, Avda. de la Universidad, s/, 03202, Elche,
Alicante, Spain
fl
Keywords:
Place Recognition, Equirectangular Images, Semantic Information, Bag of Visual Words.
Abstract:
Place recognition has a crucial relevance in some tasks of mobile robot navigation. For example, it is used
for the detection of loop-closure or for estimating the position of a mobile robot along a route in a known
environment. If place recognition is based on visual information, it can be approached as an image retrieval
problem. The Bag of Visual Words technique can be used for image retrieval. Image retrieval is based on
an image representation (for example, a vector) that contains relevant visual information. In this paper, two
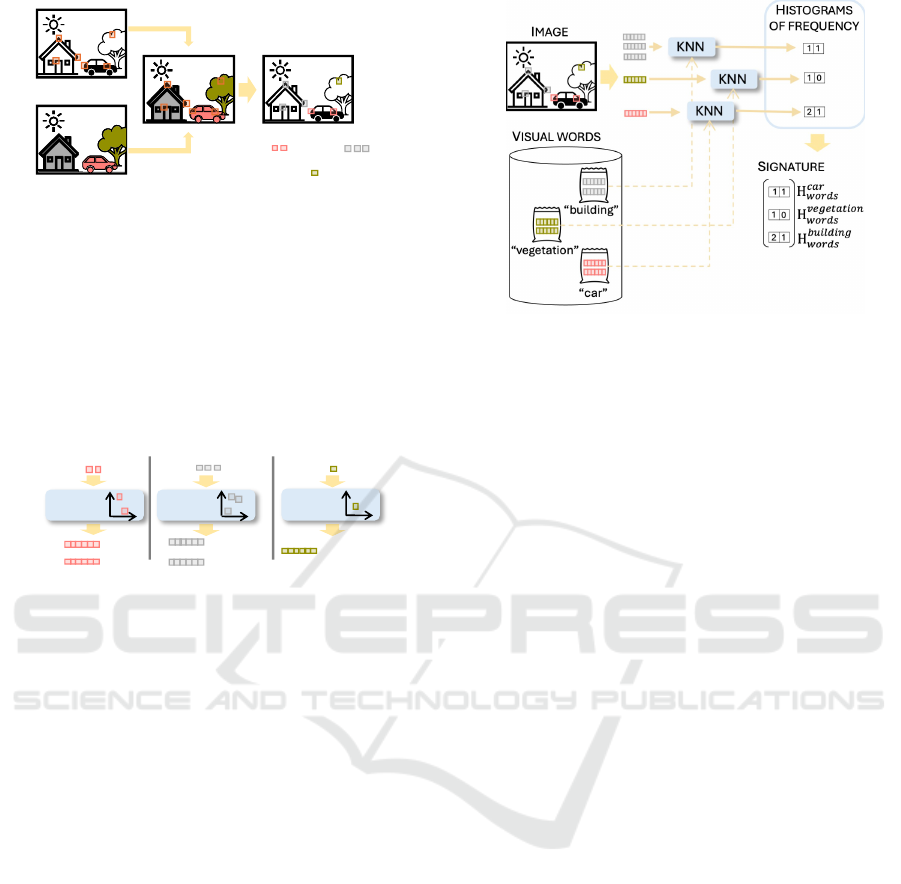
image signatures are proposed. Both are based on semantic and visual information. A bag of visual words
is created for each semantic class. Local feature descriptors are classified according to the projection of their
associated point on a segmented semantic map. On the one hand, the image signature is composed of a set
of histograms where each cell encodes the frequency with which a visual word appears in the image. On the
other hand, the image signature is composed of a set of vectors where each cell encodes the sum of the cosine
distance between the visual word and the nearest extracted features.
1 INTRODUCTION
A mobile robot can navigate autonomously in a pri-
ori unknown environment or, by contrast, in a known
environment. In the first situation, the mobile robot
must solve the Simultaneous Localization And Map-
ping (SLAM) problem. This means that the mobile
robot builds a map of the environment and simul-
taneously estimates its position within the map dur-
ing navigation. In visual SLAM, the accuracy of the
map and localization can be improved by identifying
a previously visited location (Loop Closure Detection
module). In the second situation, the map is already
available in advance, and the mobile robot must esti-
mate its actual position within this map. In this con-
text, the mobile robot can locate itself if it is able to
identify its current surroundings on the stored topo-
logical map.
Place recognition is a computer vision task in
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1117-0868
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-4327-0900
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7141-7802
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4565-496X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2245-0542
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3045-4316
which, given an image, its location is identified by
querying the locations of images which belong to
the same place in a large geotagged database (Zeng
et al., 2018). It is commonly posed as an image
retrieval task. Image retrieval techniques can be
grouped into the following: Text-Based Image Re-
trieval (TBIR) and Content-Based Image Retrieval
(CBIR). The main difference between both is that the
search for images similar to a given query from a large
database is based on their visual content (CBIR) or
on the textual data (metadata) associated with the im-
age. The CBIR is based on three key components: se-
lection, extraction, and representation of features. A
comprehensive survey of this is presented by Srivas-
tava et al. (2023). Similarly, Li et al. (2021) provide
another survey of the fast advances and applications
of theories and algorithms, focusing on those within
the period from 2009 to 2019.
In place recognition, an important issue is the sen-
sors on board the mobile robot, since they provide
information about its surrounding, and its location
is identified by analysing this captured information.
Some well-recognized types of sensors used in place
recognition are vision (Wang et al., 2018; Xu et al.,
2019; Alfaro et al., 2024) and LiDAR systems (Cabr-
166
Flores, M., Fabregat-Jaén, M., Cabrera, J. J., Peidró, A., Valiente, D. and Payá, L.
Place Recognition Using Bag of Semantic and Visual Words from Equirectangular Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0013838000003982
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2025) - Volume 2, pages 166-174
ISBN: 978-989-758-770-2; ISSN: 2184-2809
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

era et al., 2024; Vilella-Cantos et al., 2025).
This work focuses on solving place recognition
using visual information captured in images. An im-
portant feature of images is the rich information they
provide about the environment in which they were
taken. In mobile robotics, the field of view of the vi-
sion system is relevant, since, for example, the wider
the field of view, the fewer images are needed to cre-
ate a map.
The present work is based on (Ouni et al., 2022).
The authors propose three image signatures in order
to resolve the image retrieval task. Focusing specif-
ically on the type of signature that combines visual
features and semantic information in (Ouni et al.,
2022), this paper evaluates its behaviour for place
recognition and in images with a wider field of view
such as equirectangular images. This signature is an
NxM matrix where N is the number of classes and M
is the size of the visual descriptor. The procedure con-
sists in extracting local feature points and a semantic
segmented map, the points will be classified accord-
ing to their projection on such map so that a semantic
label is assigned. In this way, there are different clus-
ters (one per semantic class) composed of visual de-
scriptors. Each row of the image signature will be the
centroid of each of these clusters. However, it may
happen that a class has a completely different visual
appearance. For this reason, we propose to create a
bag of visual words for each semantic class instead of
a class being represented by a unique visual descrip-
tor.
The contributions of this work are as follows:
1. An image signature in which semantic and visual
information is merged. Each semantic category
will have a bag of visual words that will be used
to obtain a frequency histogram. The signature
will be the concatenation of all these histograms.
2. The frequency histograms of the previous sig-
nature are replaced by one-dimensional vectors,
where each bin represents the sum of the cosine
distances to each visual word. In other words, im-
age encoding is based on distance instead of fre-
quency.
3. The above image signatures and one of the pro-
posal in (Ouni et al., 2022) (BoSW) are compared
for place recognition in an outdoor environment.
We want to clarify that we have only evaluated the
image signature that the authors describe in Sec-
tion 3.1 (denominated BoSW) of their paper, not
their full global framework for CBIR.
4. These image signatures are evaluated in image
retrieval when images are distorted, such as in
equirectangular images.
5. The influence of the type of distance on the Near-
est Neighbour search in the image encoding step
is studied.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section 2, some image retrieval techniques
proposed in the literature are presented. Section 3 de-
scribes the different parts of the algorithm employed
to solve image retrieval in this paper. Section 4 is
focused on the experimental part, the database used,
and the analytical metrics are described. The results
obtained from the experiments are presented and dis-
cussed in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 presents the
conclusions.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Image Retrieval
In image retrieval, there are approaches based on bag
of visual words. Mansoori et al. (2013) focus on the
feature extraction stage and propose to incorporate
colour information (hue descriptor) in descriptor fea-
tures (SIFT) of the images.
In terms of works that propose combining se-
mantic information and local visual features, Ouni
et al. (2022) present three procedures in order to con-
struct the image signatures using semantic informa-
tion. Amongst the three signature, only two combine
these two types of information, the other is based on
semantic information only. One year later, Ouni et al.
(2023) proposed two additional types of signatures.
The first of these integrates at the same time the se-
mantic proportions of objects and their spatial posi-
tions. Meanwhile the second one builds a semantic
bag of visual phrase (i.e. a set of words linked to-
gether) by combining the visual vocabulary with se-
mantic information. In this case, the image signature
is an upper triangular matrix whose height and width
are equal to the number of visual words in the code-
book.
As with other computer vision tasks, the use of
convolutional neural network-based architectures has
increased in popularity over the last decade. Rani
et al. (2025) propose a separable convolutional neu-
ral networks-based framework. This contribution
reduces the computational complexity in terms of
a number of convolutional operations and hyper-
parameters. Forcen et al. (2020) present a new rep-
resentation of co-occurrences from deep convolu-
tional features which is combined with the feature
map in order to improve the image representation.
Dubey (2022) presents a comprehensive survey of
deep learning-based progress over the last decade.
Place Recognition Using Bag of Semantic and Visual Words from Equirectangular Images
167

EXTRACT
FEATURES
DATABASE
VISUAL VOCABULARY
CREATION
SIGNATURE
CONSTRUCTION
Section 3.1
Section 3.2
Section 3.3
Figure 1: The visual bag of visual words framework: given a set of images (database), feature extraction is performed for all
these images (Section 3.1). From all the features, the visual vocabulary is created (Section 3.2). Then, the signature of each
image is built using the visual words that compose the vocabulary (Section 3.3).
3 SEMANTIC AND VISUAL BAG
OF WORDS
In this work, a hierarchical bag of words is used to
solve the localization problem in the navigation of a
mobile robot. This hierarchical bag of words is com-
posed of two levels. The higher level is based on se-
mantic information, while the lower level is supported
by visual information.
As it has been mentioned, the bag of visual words
method involves creating a vocabulary which is com-
posed of representative visual words that are the re-
sults of clustering the visual descriptors extracted in
an image.
The bag of visual words technique consists of the
extraction of visual features which are then clustered
in order to create a set of visual words (vocabulary or
codebook). After that, each image is represented by a
signature that encodes the frequency with which each
visual word appears in the image. These components
are shown in Figure 1, and described in detail within
the following sections.
3.1 Feature Extraction
In this work, the features used are the result of com-
bining local feature descriptors (see Section 3.1.1)
and semantic information (see Section 3.1.2). Both
processes are carried out in parallel as shown in Fig-
ure 2.
SEMANTIC
SEGMENTATION
MODEL
LOCAL FEATURE
EXTRACTION
DESCRIPTION
Figure 2: The upper part of the figure corresponds to the ex-
traction of local features (points and its feature descriptors,
Section 3.1.1). On the other hand, the bottom part of the
figure corresponds to the extraction of semantic segmented
map using a semantic segmentation model (Section 3.1.2).
3.1.1 Local Features
This stage is divided into two steps. Firstly, the dis-
tinctive local points are identified for each image in
the database. This step is known as local feature ex-
traction. These points can be corners, edges or blobs.
Secondly, the extracted local points are represented
by a feature descriptor that extracts visual features of
its neighbourhood.
There are several techniques for this purpose, such
as SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) (Lowe,
2004), SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features) (Bay
et al., 2006) and ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated
BRIEF) (Rublee et al., 2011).
3.1.2 Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation is a technique that aims to as-
sign a semantic class to each pixel in the image.
Although the diagram presented in Figure 2 shows
a block corresponding to the extraction of the seman-
tic segmentation map using a semantic segmentation
model, it is important to note that this step is not car-
ried out in this work, as the semantic segmentation
maps have been previously generated and are part of
the dataset, as it will explained in Section 4.1.
3.1.3 Fusion of Semantic and Visual Information
A semantic segmentation map and a set of local points
with their corresponding feature descriptors are avail-
able for each image. The goal is to have a semantic
label associated to each local feature descriptor. For
that end, given a local point, its coordinates are em-
ployed to extract the semantic label encoded in the
map at this pixel. This label is then assigned to the
feature descriptor of this local point.
At the end of this step, the visual descriptors have
been classified into different semantic categories.
3.2 Visual Vocabulary Creation
In a bag of visual words algorithm, visual feature de-
scriptors extracted from all images in the database are
grouped into k clusters based on their similarity. This
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
168
“car”
“vegetation”
“building”
Figure 3: The local points detected are projected on the se-
mantic segmented map to obtain its semantic label.
stage requires the use of a clustering algorithm such
as k-means. This is followed by the creation of the
visual vocabulary. The visual words are the centroids
of the clusters and the size of the vocabulary is equal
to the number of clusters (k).
In this work, no visual vocabulary is created for
all extracted feature descriptors, but a single one is
generated for each semantic category.
“car”
“vegetation”
“building”
Kmeans
Kmeans
Kmeans
𝑤
1
𝑐𝑎𝑟
𝑤
1
𝑏𝑢𝑖𝑙𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔
𝑤
1
𝑣𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
𝑤
2
𝑐𝑎𝑟
𝑤
2
𝑏𝑢𝑖𝑙𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔
Figure 4: A bag of k visual words is created for each seman-
tic class. Given a set of local feature descriptors classified
as class i (e.g. car), a k-means algorithm is used to assemble
these descriptors into k clusters (e.g. two) and to extract the
centroids of each one. These centroids are the visual words
of this class (w
class
i
j
j = 1, ..., k).
3.3 Signature Construction
In a bag of visual words algorithm, each image is rep-
resented by a one-dimensional vector with a length
equal to the number of visual words (vocabulary size)
where each element encodes the number of times each
visual word appears in the image. In other words, the
signature is a histogram of the frequencies of visual
words.
In this work, there is not a unique bag of visual
words, but a bag of visual words for each semantic
category. Then, if the number of semantic categories
to be considered is N, the signature is a set of N fre-
quency histograms. It will be identified in the experi-
mental section (Section 5) as BoSVW.
In addition, we propose replacing the frequency
histogram with a vector in which each cell encodes
the sum of the cosine distance between the local fea-
tures and the visual word. It will be identified in the
experimental section (Section 5) as BoSVW*.
Figure 5: Once the feature descriptors have been divided
into different groups based on the semantic information, a K
nearest neighbour algorithm is used to find the most similar
visual word with the same semantic class. After obtaining
a histogram for each semantic group, the signature is con-
structed.
4 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
In this section, the visual localization problem is
solved using several configurations of bag of visual
words method. The main purpose is to evaluate these
configurations and select the one that provides the
best results. It is important to note that the full
content-based image retrieval algorithm proposed by
Ouni et al. (2022) has not been implemented. Only
the signature construction module explained in Sec-
tion 3.1 of (Ouni et al., 2022) was implemented in our
framework. It will be identified in the experimental
section (Section 5) as BoSW. Table 1 shows a brief
definition of each of these configurations, their IDs
used in Section 5 and a brief description of the image
signature.
The images used are equirectangular (more infor-
mation on the dataset is given in Section 4.1) in or-
der to evaluate these methods also for this type of im-
ages, since spherical images present some benefits in
mobile robot navigation (such as their wide field of
view).
The algorithm executed in all four cases is the
same except for the encoding image part, where the
procedure is different for each type of signature (or
distance for BoSVW). In all four cases, the measure
chosen to compare the signatures of the query im-
age and those in the database is the cosine distance.
Since these are two-dimensional image signatures in
all four cases, the rows are concatenated to obtain a
one-dimensional vector. After that, the vector is nor-
malized using L1. The cosine distance is then calcu-
lated, as indicated, in order to obtain the most similar
Place Recognition Using Bag of Semantic and Visual Words from Equirectangular Images
169
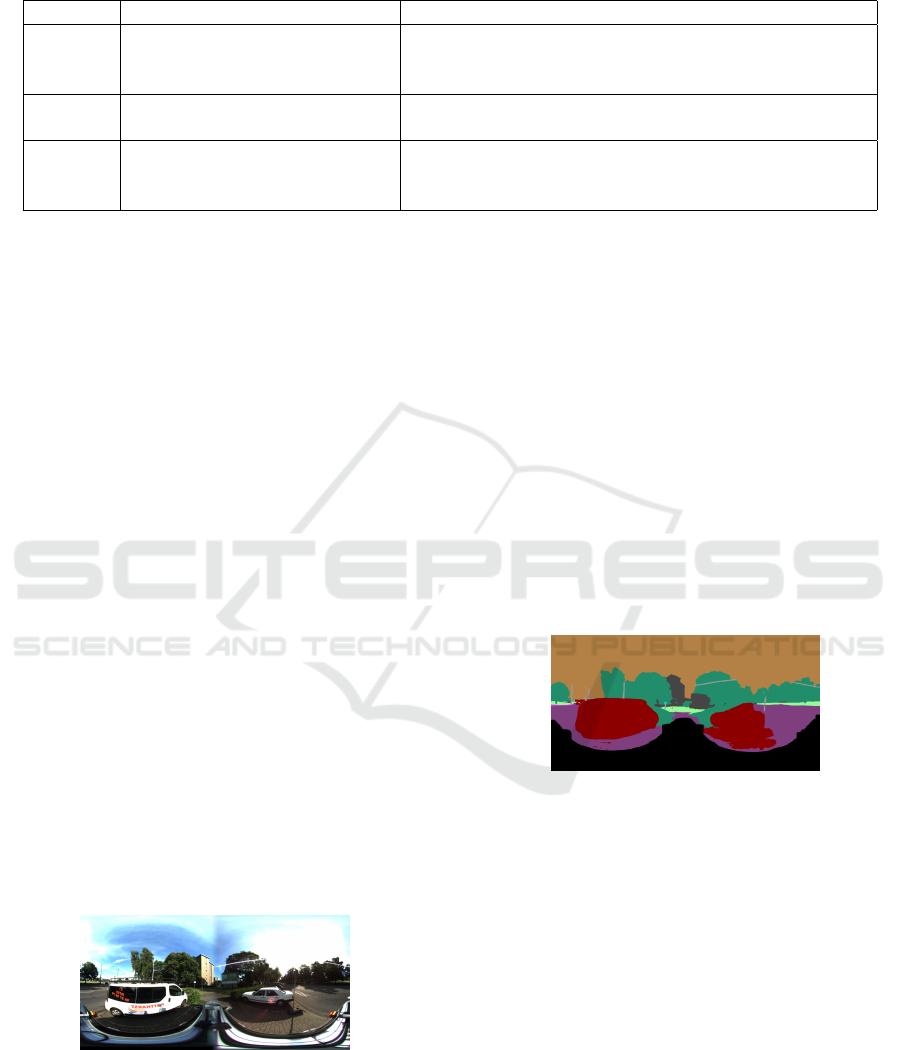
Table 1: The different configurations of the bag of words method that are evaluated. The first column shows the ID used for
each configuration when displaying the results, while the third column describes the signature of each.
ID Method Signature
BoSW Bag of Semantic Words (Ouni
et al., 2022)
MxN matrix where the width N corresponds to the size
of the visual descriptor and the height M corresponds to
the number of semantic classes.
BoSVW Bag of Semantic Visual Words A set of M (number of semantic classes) one-dimensional
frequency histograms with a length equal to K.
BoSVW* Bag of Semantic Visual Words
(no frequency).
A set of M (number of semantic classes) one-dimensional
vectors with a length equal to K where each bin is the sum
of the cosine distances instead of the count.
image (retrieved image) in the database based on this.
All signatures have in common that they use visual
information. In this work, ORB (Rublee et al., 2011)
has been chosen to obtain the local points and their
corresponding feature descriptors.
In the cases of BoSVW and BoSVW*, the vocab-
ulary size (k) is initially fixed for all semantic classes
and its value is 10. If any semantic class has a number
of feature descriptors less than 10, then the vocabu-
lary size of this class is equal to the number of feature
descriptors.
4.1 Dataset
The dataset employed in this paper is KITTI-360
(Liao et al., 2023). For the image collection, the au-
thors equipped a station wagon with two fisheye cam-
era positioned to each side. Both fisheye cameras
have 180 degrees of field of view so that a full view
of the scene is captured.
Before carrying out the experiments, each pair of
fisheye images was converted into a single equirect-
angular image. For that, the calibration provided
in the dataset is used to convert each fisheye image
into equirectangular (fisheye image projection to unit
sphere). Then, a polynomial transformation proposed
by Flores et al. (2024) is used to align both equirect-
angular images. Figure 6 shows an example (equirect-
angular image) after performing this process.
Figure 6: An equirectangular image generated from a pair
of fisheye images of the KITTI-360 dataset (Liao et al.,
2023).
The dataset of images has been divided into two
subsets: database and query. For the first subset, an
image was selected every 10 meters of the trajectory,
taking the first captured image as the starting image.
Thus, the database consists of a total of 791 images.
The images of the dataset not selected have been con-
sidered as query images. This means that 9723 im-
ages constitute the query set.
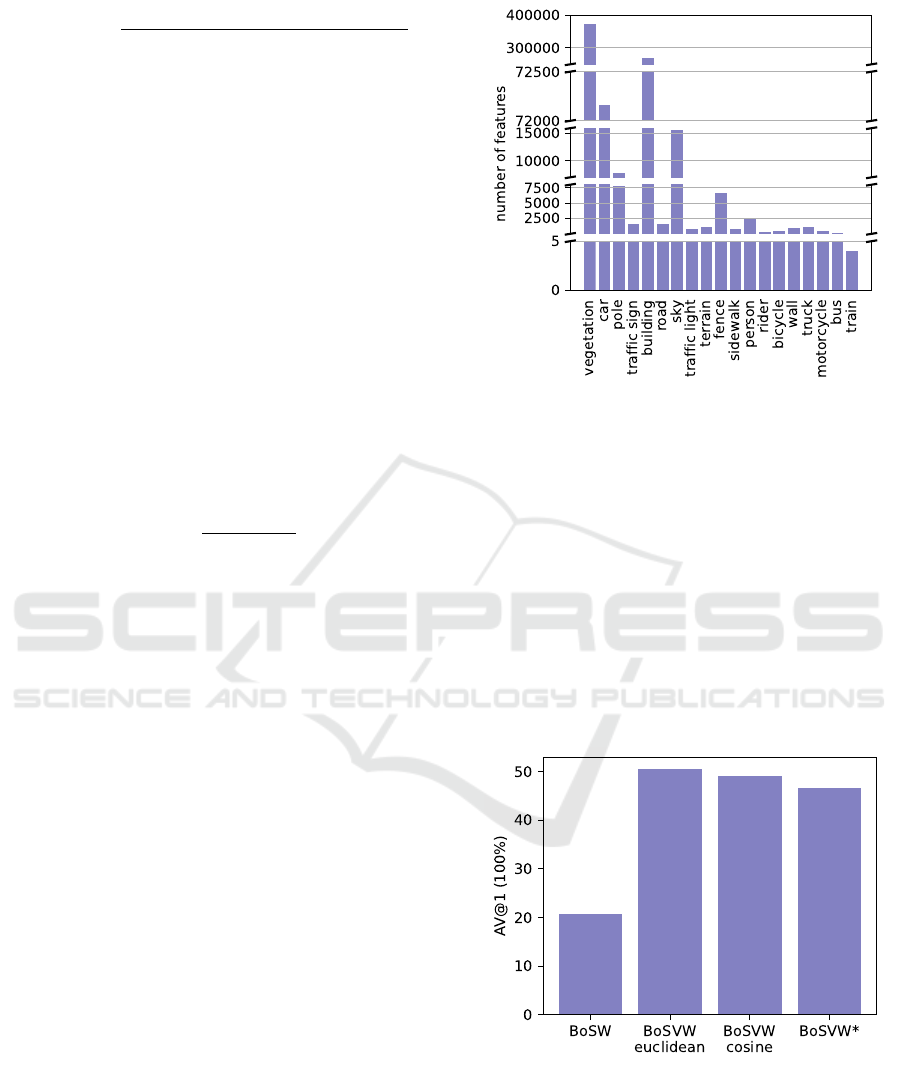
As mentioned above, the semantic segmentation
maps were not obtained during the running process
(obtained beforehand). The semantic segmentation
model employed for this purpose is SegFormer (Xie
et al., 2021). A semantic segmented map can be vi-
sualized in Figure 7. Due to the fact that it is a 380
vision system, part of the station wagon appears in the
image. However, it is not part of the scene so it has
been labelled as unlabelled (black pixels in Figure 7),
and this class has not been taken into account for the
image signature construction.
Figure 7: The semantic segmentation map of the image
shown in Figure 6. It was generated using SegFormer (Xie
et al., 2021).
4.2 Evaluation Protocol
4.2.1 Distance Difference
The distances between the query image (q) and the
retrieved image (r) will be analysed. Then, given
a query image captured at position XY Z
q
, the im-
age retrieval algorithm is executed, which returns the
database image most similar to the query image (i.e.
retrieved image). The retrieved image was acquired at
XY Z
r
. Both positions (XY Z
q
and XY Z
r
) are extracted
from the pose file provided by the dataset. The dis-
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
170
tance units are meters and are calculated as follows:
dist
q−r
=
q
(X
q
− X
r
)
2
+ (Y
q
−Y
r
)
2
+ (Z
q
− Z
r
)
2
(1)
4.2.2 Average Recall (AR) at 1
For each query image, a retrieved image is recovered
from the database after applying the image retrieval
method. Since the dataset provides the poses in which
all images were captured, after acquiring the retrieved
image, the distance between the pose of the retrieved
image and the query image (dist
q−r
) is calculated us-
ing equation (1).
If the distance is lower than 20 meters, the recall
for this query image (I
q
i
) is one. Otherwise, the recall
will be zero.
R@1
q
i
=
1 if dist
q−r
< 20meters
0 if dist
q−r
≥ 20meters
(2)
The evaluation measure is the average value of all
recall values after executing the method for all query
images (n images):
AR@1(%) =
∑
n
i=1
R@1
q
i
n
· 100 (3)
5 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
5.1 BoSVW: Feature Extraction in the
Database
To create the vocabulary, it is important to extract fea-
tures. In this section, we analyse the visual features
extracted from the images in the database, specifically
how many are associated with each of the semantic
classes. This can be observed in Figure 8 by means
of a graph chart, where the height of each bar repre-
sent the number of visual features that are classified
for each semantic class.
As it can be seen, the semantic class with the high-
est number of features is ”vegetation”, with a total of
374321. In contrast, ”train” is the class with the low-
est number, a total of 4. Other semantic classes with
a high number of associated local features are ”build-
ing”, ”car” and ”sky”, in that order.
5.2 Comparison and Evaluation
This section compares the different image signatures
presented in Table 1 using the evaluation protocols de-
scribed in Section 4.2. For the case of BoSVW, two
experiments have been carried out. The first exper-
iment used the Euclidean distance to create the his-
togram (i.e. during the K Nearest Neighbour process).
Figure 8: Number of ORB local features (y-axis) for each
semantic class (x-axis).
The second experiment uses the cosine distance. The
aim is to determine whether it has an influence on the
results.
5.2.1 Evaluation in Terms of Average Recall at 1
First, the different bag of words methods mentioned
above (see Table 1) are evaluated in terms of Average
Recall at 1 (AR@1). The results are shown by means
of bar graphs which can be observed in Figure 9. Each
bar indicates the AR@1 achieved for each signature
type.
Figure 9: Results of Average Recall at 1 (AR@1) calculated
after using the four image signatures evaluated.
With regard to the results shown in this figure,
the value of AR@1 for the BoSW method is equal
to 20.806, for BoSVW using the Euclidean distance
it is equal to 50.417, meanwhile using the cosine dis-
tance the value is 49.069, and for BoSW* it is equal
Place Recognition Using Bag of Semantic and Visual Words from Equirectangular Images
171
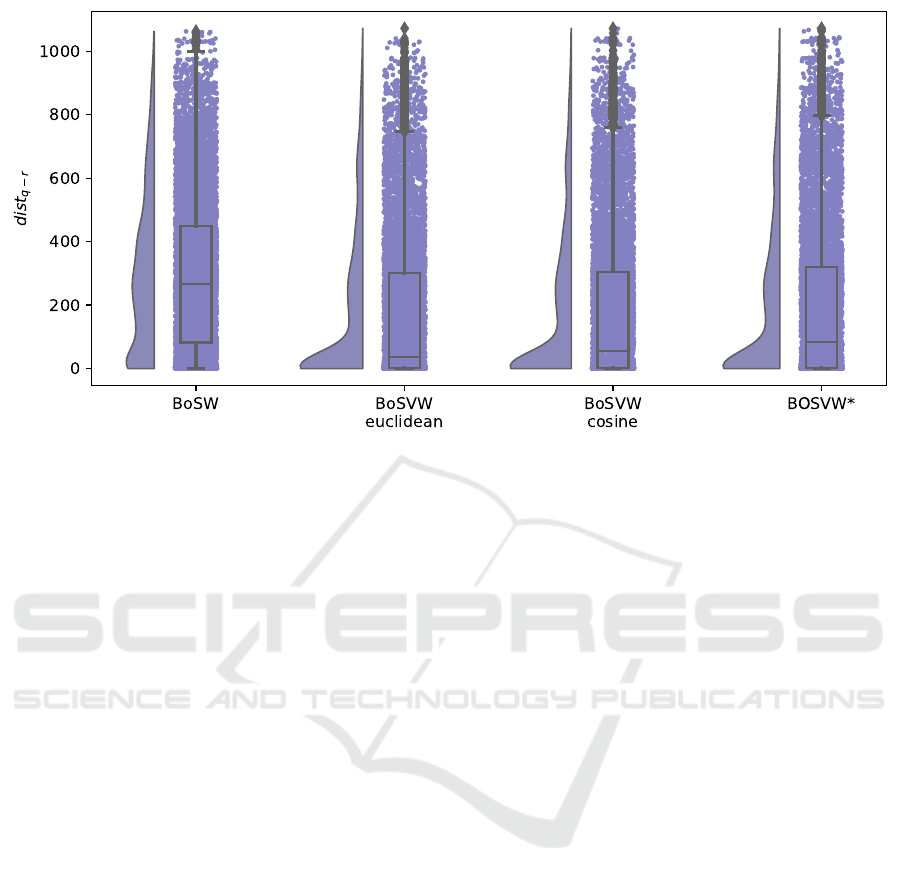
Figure 10: The distance between the position of the query image and the retrieved image using the different signatures.
to 46.529. As can be seen, a higher value of re-
call in place recognition is achieved for BoSVW vari-
ations than for BoSW. The results show that using
frequency (BoSVW) instead of distance (BoSVW*)
achieves better results. In terms of the distance to find
the visual words, the Euclidean distance provides bet-
ter results than the cosine distance.
In summary, we propose two image signatures
(BoSVW and BoSW*) in which each semantic cate-
gory has its own associated bag of visual words from
which its descriptor will be obtained, rather than the
descriptor being a single visual descriptor (BoSW).
The main objective of this paper is to solve the local-
ization problem by means of place recognition. Ac-
cording to this initial evaluation, the image signatures
we propose increase the AR@1 value when they are
used to address image retrieval in a set of images from
the same environment (a trajectory followed by a mo-
bile robot). In other words, the proposed image signa-
tures improve the capability of the algorithm to return
an image of the database with a distance of less than
20 metres from the query image on more times.
5.2.2 Evaluation in Terms of Distance Difference
Second, the different methods are also evaluated in
terms of distance difference in meters. For this pur-
pose, the distance in meters between each query im-
age in the query set (9723 images) and its retrieved
image is calculated using (1). For each type of sig-
nature, all of these 9723 distances are displayed us-
ing rain cloud plots, which help to analyse the dis-
tribution of distances as probability density, and at
the same time, key summary statistics (such as me-
dian and quartiles) can be visualized. This graph can
be seen in Figure 10. It is important to note that the
database set is made up of an image every 10 meters
on the trajectory (see Section 4.1). Then, the range of
Euclidean position distances between the query im-
ages and the nearest database images (ground truth) is
between 0 and 5 meters. Therefore, the committed lo-
calization error is considerable in the cases (points in
the graph) where the distance between the query im-
age and the retrieved image (dist
q−r
) is much greater
than 5 meters.
At first view, we can see that, for all four types
of signatures, the highest concentration of points is
found on distances below 100 metres approximately.
In addition to this, it is clear that the three types of
BoSVW have a higher peak than BoSW in this inter-
val. As for the box plots, BoSW has a higher median
value (around 265 meters) than the other three image
signatures. Also, the lower whisker of the BoSW box-
plot has a longer distance compared to the others. Fo-
cusing on BoVW types, the results are better when
using the frequency histogram, the median value is
around 36 metres when the distance is Euclidean and
around 55 metres when it is cosine. However, the me-
dian value is around 84 metres when using the vector
representing the sum of the cosine distance to the vi-
sual words.
In this section, the image signatures have not been
evaluated only on the condition of finding the most
similar one within a ratio, as in the previous eval-
uation, but rather all distances are shown after run-
ning the image retrieval algorithm for all query im-
ages. It for each signature. Taking these results into
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
172

account, the proposed signatures most frequently re-
turn as the most similar image from the database that
is in a closer position to the query image, achieving a
more refined localization.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The main objective of this work is to solve the task
of place recognition for a mobile robot navigating in
a known outdoor environment. The method used for
this is image retrieval using equirectangular images
as input. Image retrieval relies on the fact that images
are represented in a way that their significant features
are described (image signature).
In relation to this, three types of image signatures
are evaluated and compared in this work for place
recognition, when a mobile robot navigates a trajec-
tory in a previously visited environment. All the im-
plemented signatures combine semantic and visual in-
formation. The first one (i.e. BoSW) was proposed by
Ouni et al. (2022) whereas the other two variations are
proposed in this paper (i.e. BoSVW and BoSVW*).
The BoSW image signature is a matrix in which each
row is the centroid of a set of visual feature descrip-
tors belonging to the same semantic class. The num-
ber of rows is equal to the number of semantic classes
and the number of columns is equal to the size of the
local visual feature. In the case of BoSVW the rows
are histogram of frequency of visual words.
After the experiments, the results in terms of recall
at one determine that BoSVW using the Euclidean
distance during the image encoding step provides the
highest value. In contrast, the lowest recall value
is achieved using BoSW. Apart from this evaluation
measure, the distances between the position of the
query image and the position of the image retrieved
by the method using each image signature is also anal-
ysed. The use of a Euclidean distance achieves a
lower distance in more times than the cosine distance
for BoSVW.
Therefore, it can be concluded that creating a bag
of visual words for each semantic category, such as
proposed in this paper, rather than a single visual de-
scriptor, improves the results on the problem of place
recognition. Additionally, if each category is repre-
sented by a frequency histogram, the localization is
more accurate than using a vector that encodes dis-
tances.
In summary, the evaluations show that the imple-
mentation of the proposed signatures in an image re-
trieval algorithm for place recognition provides better
results.
In this work, only image signatures that merge se-
mantic and visual information have been evaluated
and compared to solve the place recognition. Taking
it into account, we propose as a future work to extend
this comparative evaluation to other algorithms (such
as these that use only visual information). In the same
line, other possible future work can be study these
signatures using other local features, both using tra-
ditional extraction methods and Deep Learning meth-
ods. Finally, other future work could be to research
whether the proposed signatures can be improved by
finding the optimal value of clusters for each vocabu-
lary size in each category, rather than this parameter
being fixed for all semantic categories as it is in this
work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research work is part of a project funded by
”AYUDAS A LA INVESTIGACI
´
ON 2025 DEL
VICERRECTORADO DE INVESTIGACI
´
ON Y
TRANSFERENCIA” of the Miguel Hern
´
andez Uni-
versity and part of the project PID2023-149575OB-
I00 funded by MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033
and by FEDER, UE. It is also part of the project
CIPROM/2024/8 funded by Generalitat Valenciana
and part of the project CIAICO/2023/193 funded by
Generalitat Valenciana.
REFERENCES
Alfaro, M., Cabrera, J., Jim
´
enez, L., Reinoso, O., and Pay
´
a,
L. (2024). Triplet Neural Networks for the Visual
Localization of Mobile Robots:. In Proceedings of
the 21st International Conference on Informatics in
Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 125–132,
Porto, Portugal. SCITEPRESS - Science and Technol-
ogy Publications.
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L. (2006). SURF:
Speeded Up Robust Features. In Leonardis, A.,
Bischof, H., and Pinz, A., editors, Computer Vision
– ECCV 2006, pages 404–417, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer.
Cabrera, J. J., Santo, A., Gil, A., Viegas, C., and Pay
´
a,
L. (2024). MinkUNeXt: Point Cloud-based Large-
scale Place Recognition using 3D Sparse Convolu-
tions. arXiv:2403.07593.
Dubey, S. R. (2022). A Decade Survey of Content Based
Image Retrieval Using Deep Learning. IEEE Trans-
actions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,
32(5):2687–2704.
Flores, M., Valiente, D., Peidr
´
o, A., Reinoso, O., and Pay
´
a,
L. (2024). Generating a full spherical view by mod-
eling the relation between two fisheye images. The
Visual Computer, 40(10):7107–7132.
Place Recognition Using Bag of Semantic and Visual Words from Equirectangular Images
173

Forcen, J. I., Pagola, M., Barrenechea, E., and Bustince,
H. (2020). Co-occurrence of deep convolutional fea-
tures for image search. Image and Vision Computing,
97:103909.
Li, X., Yang, J., and Ma, J. (2021). Recent developments of
content-based image retrieval (CBIR). Neurocomput-
ing, 452:675–689.
Liao, Y., Xie, J., and Geiger, A. (2023). KITTI-360: A
Novel Dataset and Benchmarks for Urban Scene Un-
derstanding in 2D and 3D. IEEE Transactions on Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45(3):3292–
3310.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive Image Features from Scale-
Invariant Keypoints. International Journal of Com-
puter Vision, 60(2):91–110.
Mansoori, N. S., Nejati, M., Razzaghi, P., and Samavi, S.
(2013). Bag of visual words approach for image re-
trieval using color information. In 2013 21st Iranian
Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), pages
1–6. ISSN: 2164-7054.
Ouni, A., Chateau, T., Royer, E., Chevaldonn
´
e, M., and
Dhome, M. (2023). An efficient ir approach based
semantic segmentation. Multimedia Tools and Appli-
cations, 82(7):10145–10163.
Ouni, A., Royer, E., Chevaldonn
´
e, M., and Dhome, M.
(2022). Leveraging semantic segmentation for hybrid
image retrieval methods. Neural Computing and Ap-
plications, 34(24):21519–21537.
Rani, S., Kasana, G., and Batra, S. (2025). An efficient con-
tent based image retrieval framework using separable
CNNs. Cluster Computing, 28(1):56.
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., and Bradski, G.
(2011). ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or
SURF. In 2011 International Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 2564–2571. ISSN: 2380-7504.
Srivastava, D., Singh, S. S., Rajitha, B., Verma, M., Kaur,
M., and Lee, H.-N. (2023). Content-Based Image Re-
trieval: A Survey on Local and Global Features Selec-
tion, Extraction, Representation, and Evaluation Pa-
rameters. IEEE Access, 11:95410–95431.
Vilella-Cantos, J., Cabrera, J. J., Pay
´
a, L., Ballesta, M., and
Valiente, D. (2025). MinkUNeXt-SI: Improving point
cloud-based place recognition including spherical co-
ordinates and LiDAR intensity. arXiv:2505.17591.
Wang, T.-H., Huang, H.-J., Lin, J.-T., Hu, C.-W.,
Zeng, K.-H., and Sun, M. (2018). Omnidirectional
CNN for Visual Place Recognition and Navigation.
arXiv:1803.04228.
Xie, E., Wang, W., Yu, Z., Anandkumar, A., Alvarez, J. M.,
and Luo, P. (2021). Segformer: Simple and efficient
design for semantic segmentation with transformers.
Advances in neural information processing systems,
34:12077–12090.
Xu, S., Chou, W., and Dong, H. (2019). A Robust Indoor
Localization System Integrating Visual Localization
Aided by CNN-Based Image Retrieval with Monte
Carlo Localization. Sensors, 19(2):249.
Zeng, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Chen, Y., and Zhu, C. (2018).
Place Recognition: An Overview of Vision Perspec-
tive. Applied Sciences, 8(11):2257.
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
174
