
Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate Value Creation: A
Case of Airbus
Mingwu Han
a
Surrey International Institute, Dongbei University of Finance and Economics,217 Jianshan Street, Dalian 116025, China
Keywords: Digital Transformation, Value Creation, Aviation Manufacturing, Technological Empowerment, Business
Model.
Abstract: In the context of the global digital economy, digital transformation has become the core path for enterprises
to break through the traditional value boundary and build new competitiveness. This paper takes Airbus as
the research object to explore the impact mechanism of digital transformation on the value creation of aviation
manufacturing enterprises. Through case studies and literature research, it is found that Airbus has
reconfigured its value chain by integrating technologies such as digital twins and the industrial Internet of
Things. This integration significantly enhances its R&D agility and production efficiency and drives the
company's expansion from equipment manufacturing to service ecology. The findings indicate that digital
transformation enables cross-chain collaboration, optimizes resource allocation, and reshapes competitive
barriers through technological empowerment, the core of which lies in the systematic reconfiguration of
business processes and business models and the transformation of technological value into commercial
benefits. The practice of Airbus demonstrates that enterprises need to be customer demand-oriented, balancing
technological innovation and ecological synergy. This provides theoretical references for the systemic impact
of the digital transformation value chain, injecting sustainable growth momentum into the core industry chain,
and providing replicable strategic paths for high-end manufacturing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Under the wave of global digital economy, digital
transformation has become an important engine for
sustained global economic growth. Digital
transformation is a strategic process of reconfiguring
the core architecture of an enterprise through the
integration of digital technologies, the essence of
which is to develop a market-driven capacity for
continuous and rapid innovation through the
systematic optimisation of production processes,
technologies and operations (Westerman, G et al,
2014). Therefore, enterprise digital transformation
has become a key way to improve the core
competitiveness of enterprises. According to
McKinsey & Company's 2023 report on the
digitisation of the global manufacturing industry,
although more than two thirds of manufacturing
enterprises have begun to implement a digital
strategy, less than 20 per cent of them have achieved
financial efficiency gains through the vertical
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-0560-2777
integration of core technologies (McKinsey &
Company, 2023). In the field of aviation
manufacturing, digital transformation not only
implies the intelligence of the production process and
the specialisation of the management mode, but also
involves the reconstruction of the value distribution
matrix of the industrial chain, as well as the in-depth
optimisation of the efficiency of research and
development and financial efficiency, and the
enhancement of user satisfaction, thus forming a new
transmission mechanism between technological
inputs and capital returns. As one of the two giants in
the global aviation manufacturing industry, Airbus
occupies an important position in the global market.
Since 2017, Airbus has been comprehensively
promoting digital transformation, covering a number
of cutting-edge fields including smart manufacturing,
artificial intelligence, quantum technology, etc., and
is gradually building up a full-chain digital ecosystem
from design to service. According to Airbus's annual
report for 2023 (Airbus, 2024), Airbus's full-year
102
Han, M.
Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate Value Creation: A Case of Airbus.
DOI: 10.5220/0013834300004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 102-109
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
revenue reached 65.4 billion euros, with digital
transformation-related projects contributing about
12% of profit growth, which is representative of its
effectiveness (Airbus, 2024). In addition, existing
research on digital transformation in the aerospace
manufacturing industry is still insufficiently
analysed. Most of the cases only focus on local
technology application, and lack of systematic
research on the synergistic mechanism of the whole
industry chain. AlNuaimi, B. K. et al (2022) stated
that current digital innovation focuses more on
technological tools than on systematic business
model and organisational reconfiguration, which
leads to a disconnect between technological inputs
and corporate strategy. There is a significant lack of
research on the correlation between value creation
and financial metrics. Given that most existing
research focuses on a single technology application
and lacks a systematic exploration of the impact of
digital transformation across the value chain, there is
an urgent need to explore this issue through case
studies. Therefore, this paper takes Airbus as the
research object, adopts the method of combining case
analysis and literature research, and through
systematically sorting out the motives and pathways
of Airbus' digital transformation and its specific
mechanism of value creation, it aims to reveal the
internal logic of the synergy between digital
technological empowerment and corporate strategy,
and to provide a double inspiration for the theoretical
construction and practical application. By analysing
its digital transformation system and approach, and
studying the impact and effect of transformation on
enterprise value creation, it provides certain
inspiration and reference for the aviation
manufacturing industry and similar enterprises to
achieve digital transformation and healthy operation.
2 THE DRIVERS OF AIRBUS'
DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
2.1 Company Overview
Founded in December 1970 in France, Airbus is the
world's leading civil aircraft manufacturer and
Europe's largest aerospace company. In 2024, Airbus
was ranked 183rd on the Fortune 500 list with
revenues of $70.751 billion (Fortune, 2024). Its
business covers aircraft design, manufacturing,
supply chain management, customer service, etc., and
its influence on the industry is significant. Airbus has
set as its development goal to create a new chapter in
sustainable aerospace and to commit to building a
safe and harmonious world. By the beginning of
2024, Airbus had 147,893 employees and assets
totaling US$131.2 billion (Airbus, 2024). Airbus has
more than 180 locations in more than 150 countries
and territories and is supported by 18,000 direct
suppliers around the world, covering most of the
world (Airbus, 2024).
In addition, Airbus is committed to leading the
transformation and modernization of the aerospace
industry to drive its continued growth. Since 2017,
Airbus has been relying on advanced digital
technologies to completely revolutionize the way it
designs, manufactures, and operates its products
(Airbus, 2024). This digital transformation extends to
all levels of the company's operations, driving
innovation and excellence throughout the ecosystem.
The company is also actively promoting the use of
digital tools to streamline workflows, increase
efficiency, and completely transform traditional
production methods. After the transformation, Airbus
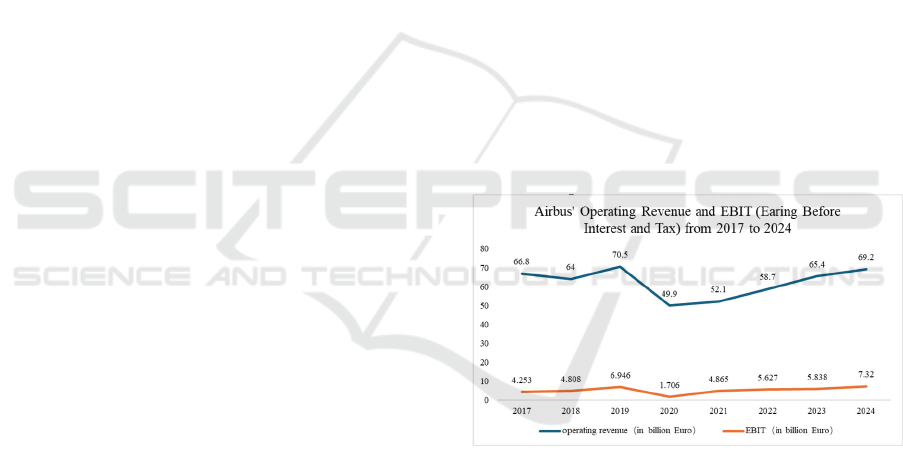
is doing well. According to the relevant data in Figure
1, although the company's operating performance
declined in 2020 due to the impact of the epidemic
and the global economic slowdown, it recovered
quickly after the epidemic and showed a continuous
and stable upward trend.
Figure 1: Airbus' operating revenue and EBIT (earing
before interest and tax) from 2017 to 2024 (Airbus, 2024).
2.2 Airbus Digital Transformation
Motivation
2.2.1 Industry Competition
Global competition in the aviation manufacturing
industry has expanded from individual product
performance to digital service capabilities across the
value chain. According to Boeing's forecast, the size
of the global aviation services market will exceed $14
trillion by 2041, prompting Airbus to accelerate its
digital transformation to compete in emerging
markets (Boeing, 2022). For example, by building the
Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate Value Creation: A Case of Airbus
103
Skywise platform, Airbus has achieved real-time
monitoring of globally connected aircraft, increasing
predictive maintenance accuracy to 98 percent and
helping airlines reduce unscheduled downtime by a
quarter (Boeing, 2022). This strategy not only
consolidates Airbus' strength in aircraft
manufacturing but also extends its business
boundaries into a high value-added digital services
ecosystem.
2.2.2 Technological Innovation
Industry 4.0 and artificial intelligence technology are
driving innovation in the manufacturing process. The
wave of industrial digitalization has led to the
transformation of the manufacturing process system.
Through the integration and application of Industrial
Internet of Things and artificial intelligence
technology, Airbus has realized the integration of
cross-factory data chains and the intelligent iteration
of production processes. It has significantly improved
the efficiency of supply chain collaboration and the
precision of composite material processing and built
a differentiated technological competitive advantage.
The digital factory can increase the efficiency of
aircraft assembly by 30% and reduce the quality
defect rate by 40%. It also proves that digital
innovation contributes significantly to productivity
improvements (Airbus, 2024).
2.2.3 Market Demand
Global air travel demand continues to recover in the
post-epidemic era, with total airport passenger traffic
expected to return to pre-epidemic levels by the end
of 2023 (Qianqian Pendulum & Li Zhi, 2022). As a
result, customer demand for lead time and
customization has increased. For example, Airbus
launched its "Digital Twin First" strategy to increase
the response time for customized configurations to
within 72 hours on the A220 program, directly
supporting its premium terms in the competition for
orders from Qatar Airways (Airbus, 2024). Market
demand has thus redefined digital technology and
opened a new chapter in the application of digital
transformation to manufacturing processes and
technologies.
2.2.4 Policy Compliance
In response to the European Union's (EU)
sustainability needs to implement the EU's Clean
Skies 2.0 framework (2021-2027), which sets dual
targets for airframe weight reduction and carbon
emissions, Airbus has been prompted to increase the
proportion of its investment in Digital Thread
technology (European Commission, 2018). The
European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) has
mandated that aircraft manufacturers reduce fuel
consumption by 50% by 2035, as outlined in the 2050
Aviation Carbon Neutral Roadmap (Royal, N. L. R.,
& Economics, 2024). Airbus is relying on digital twin
technology to complete the ZEROe hydrogen-
powered aircraft program, accelerating its goal of
commercializing a zero-carbon aircraft by 2050
(Sacchi, R. et al., 2023). Consequently, a strategic
alignment of digital transformation to support the EU
aviation emissions reduction milestones is imminent.
3 PATHWAYS AND
MECHANISMS FOR AIRBUS'
DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
3.1 Airbus Digital Transformation
Pathway
Airbus is using digital technologies to revolutionize
the way it designs, produces, and operates its products
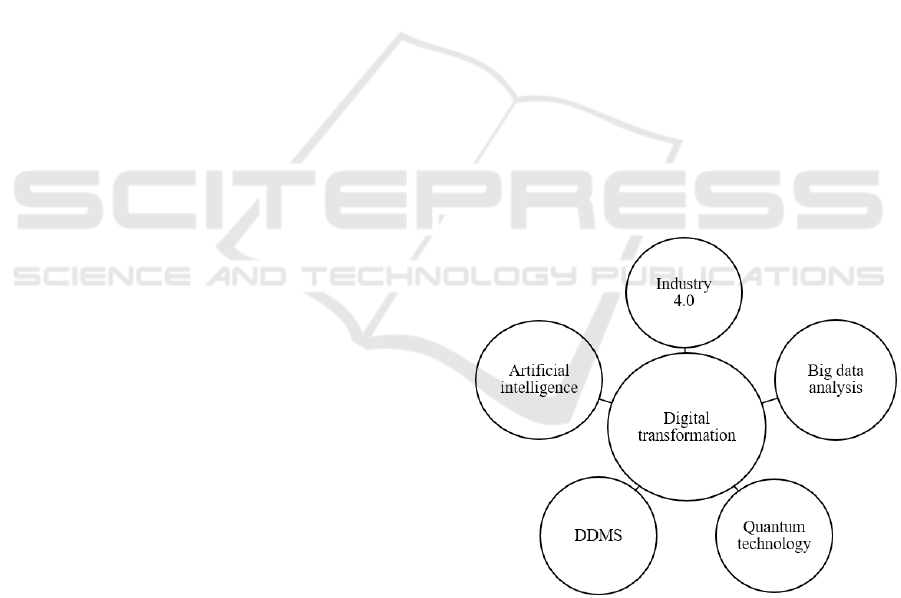
(Airbus, 2024). As shown in Figure 2, its digital
transformation encompasses the following five
different aspects of the pathway.
Figure 2: Airbus digital transformation relationship map
(Airbus, 2024).
3.1.1 Industry 4.0
Changing market demands and customer
expectations are profoundly affecting aircraft design
and manufacturing. Airbus is following the pace of
Industry 4.0 and exploring advanced manufacturing
technologies. It is Applied the latest advanced
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
104

manufacturing technology achievements, such as
robotics, virtual reality, digitalization, and 3D
printing, to the factory of the future, to promote the
industrial ecology towards intelligence and
digitalization, and to fully open the path of digital
transformation of the product lifecycle (Sigov, A.et
al, 2022).
3.1.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is at the heart of future technologies and has a
profound impact on all areas of society. For Airbus, it
is the key to competitive advantage. The Skywise
platform, which relies on AI technology to identify
potential problems and delays in a timely manner, is
an innovation that is disrupting the aviation industry.
The platform enables connectivity capabilities to ease
real-time information propagation within the airline’s
digital ecosystem, applying AI and Machine Learning
(ML) engineering to advance predictive and health
monitoring (Bernard & Hoffmann, 2023). AI is
therefore fully integrated into corporate governance
to ensure responsible and sustainable technological
development.
3.1.3 Quantum Technology
Quantum technology has the potential to transform
the way aircraft are built and flown. Airbus fully
recognizes the importance of this technology in
enhancing the performance of its products and
services and is using it to address complex aerospace
challenges.
3.1.4 Digital Design, Manufacturing, and
Services (DDMS)
The DDMS initiative, shown in Figure 3, uses end-to-
end digital methods and tools to optimize business
processes. The goal is to increase the capability
readiness level (CRL) of various modeling and
simulation functions, including multidisciplinary
analysis and optimization (MDAO) capabilities
(Sarda, N. et al., 2023). In addition, Airbus' use of the
Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE platform
provides digital continuity from design to operations,
enabling Airbus to achieve enterprise-wide digital
design, manufacturing, and services (Courtney, M,
2015). This results in lower costs, faster time to
market, and meets the high standards of quality,
safety, and environmental performance demanded by
customers (Courtney, M ,2015).
Figure 3: Airbus DDMS programme core processes and
tools framework diagram (Airbus, 2024).
3.1.5 Big Data Analytics
Making the right business decisions depends on big
data analytics and insights. Airbus deals with
complex, unstructured data and uses advanced
analytics to ensure that the right information is
available to the right people at the right time to make
decisions.
3.2 Mechanisms for Airbus Digital
Transformation
The essence of Airbus' digital transformation is to
reconstruct the value creation system of the aviation
manufacturing industry by means of digital
capabilities. This transformation is evident in a
sequential progression from the innovation of
technical tools to the enhancement of the industrial
ecosystem. Through the in-depth integration of digital
technology and aviation manufacturing elements,
Airbus has built a value-added network throughout
the entire life cycle of its products, forming a new
type of competitiveness with “digital continuity” at its
core. Therefore, Airbus' digital transformation is
based on a three-dimensional value chain system of
“digital twin, intelligent manufacturing and
ecological synergy” (Figure 4).
Figure 4: The three-dimensional value chain system of
“Digital Twin - Intelligent Manufacturing - Eco-
Collaboration” (Photo credit: Original).
At the level of the underlying technical
architecture, digital twin technology constitutes the
cornerstone of transformation. Airbus has extended
the two-way connection between physical aircraft and
Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate Value Creation: A Case of Airbus
105

virtual models to the whole process of R&D,
manufacturing, and operation, and most of the design
verification process has been moved to the digital
space. The A350XWB pro
ject has used the
multidisciplinary collaborative simulation system to
compress the development cycle of the prototype by
up to 25%, which is a breakthrough marking the
transformation of the aviation product R&D
paradigm from physical iteration to virtual
verification (Airbus, 2024). This innovative model of
blending the real and the virtual has reduced the R&D
cost of a single aircraft by $760 million and
empowered the product to respond quickly to market
demands (Airbus, 2024).
Midstream manufacturing system innovation
focuses on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to
reconfigure the logic of production. The ‘factories of
the future’ in Hamburg and Toulouse are
interconnected with more than 3,500 intelligent
devices, capturing more than 28,000 production data
streams in real time and building a dynamic
scheduling system with autonomous decision-making
capabilities (Airbus, 2024). Relying on this system,
the total assembly efficiency of the A320 series has
increased by 30 percent, setting a new industry record
of one narrow-body airliner off the production line
every minute (Airbus, 2024). This flexible production
capacity supports Airbus in winning aircraft orders.
At the top of value creation, Airbus is breaking
through the traditional boundaries of hardware sales
to build a new data-driven service ecosystem. Its
Skywise aviation big data platform has accessed real-
time flight data from 12,000 aircraft worldwide and
developed nine types of service products, including
predictive maintenance and fuel efficiency
optimization. Through subscription models such as
‘pay by the hour,’ the company's digital service
revenue will reach 1.9 billion euros in 2022 (Airbus,
2024).
The deeper significance of Airbus' digital
transformation lies in breaking down the physical
boundaries of traditional aircraft manufacturing
through digital continuity. This practice provides a
triple revelation for the global high-end equipment
manufacturing industry: the digital main line through
is the technical premise of realizing the optimization
of the whole value chain, data assetization is the key
lever to break through the industrial value ceiling, and
open ecological synergy is the strategic choice to
cope with the challenges of the complex market.
The transformation drive mechanism is shown in
Figure 5:
Figure 5: Airbus digital transformation mechanisms map
(Photo credit: Original).
4 ANALYSES OF THE IMPACT
OF DIGITAL
TRANSFORMATION ON
VALUE CREATION
4.1 R&D Efficiency and Costs
Airbus has gradually restructured its R&D system
recently and consolidated its technological barriers
with digital transformation at its core. Figure 6 shows
that from 2017 to 2023, its R&D expenditure will
increase from 3.68 billion euros to 4.83 billion euros,
and its investment intensity (R&D expenditure as a
proportion of operating revenue) will remain stable at
5-6 percent and gradually increase to more than 7
percent, which is significantly higher than the average
level of the aviation manufacturing industry. This
continuous investment and the deep integration of
digital tools have created synergies: the introduction
of the ‘digital twin’ technology in 2017 has enabled
the design verification cycle of the A320 family of
models to be compressed from 33 months in the
traditional model to 24 months in 2023, resulting in
significantly faster R&D efficiency and delivery
(Airbus 2024). The efficiency gains also extend to
production and delivery. In addition, the average
aircraft delivery cycle has also been reduced from 33
months in 2017 to 24 months in 2023, according to
the data, with digitalized assembly lines and
predictive maintenance systems driving a return to
pre-outbreak levels of capacity and delivery numbers.
Airbus has demonstrated that its R&D investment
is not simply a matter of scaling up but of digitization
to achieve ‘precision efficiency.’ This model
strengthens short-term resilience (rapid recovery in
operating income and cash flow) and lays the
foundation for long-term technological leadership.
According to the Airbus website, the proportion of
digital technology-related patents has exceeded 25%
(Airbus, 2024). This value creation logic of data-
driven efficiency is reshaping the competitive
paradigm of aviation manufacturing.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
106
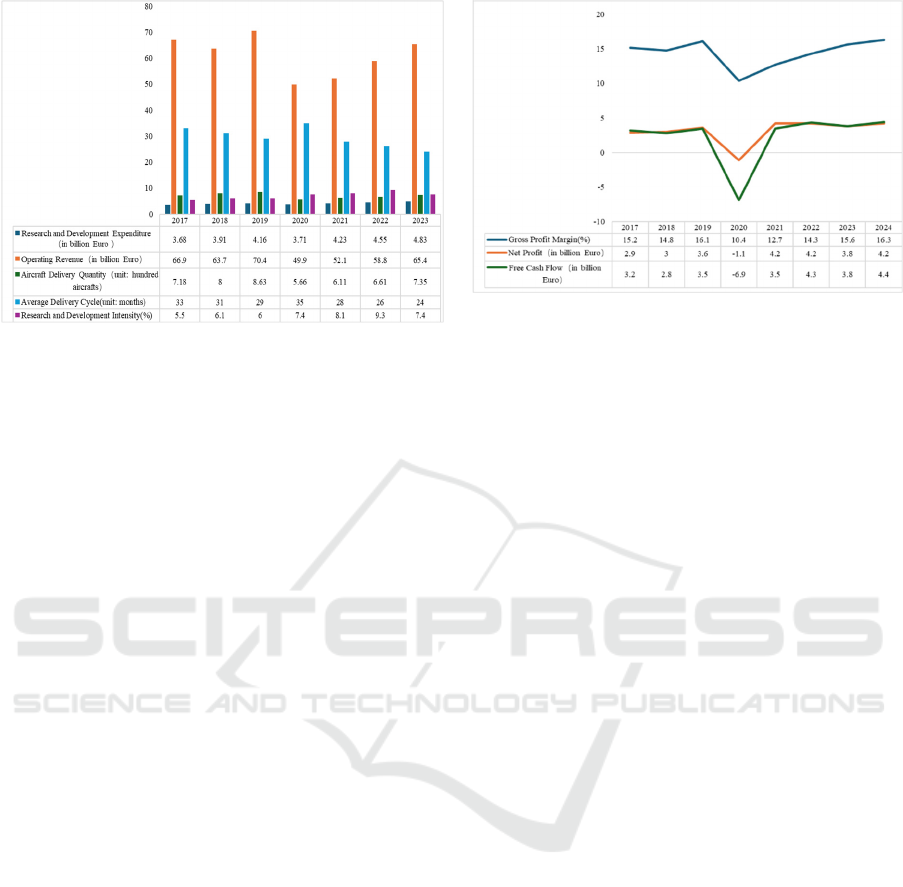
Figure 6: Airbus data on R&D efficiency and costs (Airbus,
2024).
4.2 Operations and Financial
Performance
The movement of Airbus' gross margin and net profit
confirms its ability to balance external shocks and
management efficiency. As shown in Figure 7,
Airbus' gross margin stabilized at 14-16% in 2017-
2019 on the strength of delivery of high-value-added
models such as the A350 and supply chain synergies.
2020 saw its gross margin plummet to an all-time low
of 10.4% on the back of major factors such as
epidemic shocks and idle capacity, as well as a 40%
increase in the cost of raw materials such as titanium
alloys. However, after 2021, through the
strengthening of supply chain resilience and digital
transformation of production, its operating capacity
improved significantly, and its gross margin
rebounded to 15.6% in 2023, reaching the pre-
epidemic level.
In contrast to the volatility in gross margins, net
profit and free cash flow have shown more resilience
and positive development, stabilizing at around €3
billion in the pre-epidemic period. Despite a severe
shock in 2020, when both were negative, an all-time
low, they turned positive instantly a year later and
recovered quickly to grow to record highs of over €4
billion from 2022 onwards. This phenomenon reflects
the fact that digital transformation is driving Airbus
to be a thriving and resilient company and a source of
value creation for the company. At the same time, it
is a sign that the company's digital transformation
strategy is paying off.
Figure 7: Airbus data on operations (Airbus, 2024).
4.3 Customer Satisfaction
Digital transformation significantly improves
customer satisfaction by building a proactive service
system, and predictive maintenance and full-process
optimization form a closed loop of value. The
Skywise system deployed by Airbus, based on the
analysis of real-time data of 7,000 aircrafts
worldwide, achieves 92% fault prediction accuracy,
enabling the airline to reduce unplanned downtime by
30%, increase on-time performance by 23%, and
increase customer retention rate by 15% (Airbus,
2024). The upgraded service efficiency is further
reflected in the digital delivery system: the e-signing
process is 70% faster, and the delivery cycle time is
22% shorter, driving incremental orders of €460
million from airlines in 2024 (Airbus, 2024). With a
spontaneous overall satisfaction index of 84.9
percent, Airbus has an advantage in terms of fleet
versatility, operational flexibility, training
requirements, etc., and the A320's cabin comfort and
width are better than that of Boeing's 737 model
(Flight School USA ,2024). As a result, the digital
service network established by Airbus is restructuring
the customer value model of the aviation
manufacturing industry through accurate insights and
rapid response.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The practice of Airbus shows that the digital
transformation strategy through the dual path of
technological empowerment and ecological
reconstruction has profoundly reshaped the logic of
value creation in the aviation manufacturing industry.
At the technological level, the deep integration of
digital twins, the Industrial Internet of Things, and
artificial intelligence has promoted the improvement
Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate Value Creation: A Case of Airbus
107

of R&D efficiency, production process optimization,
and service model innovation, forming a
differentiated competitive chain of ‘accurate R&D -
agile manufacturing - data-driven service’; on the
ecological level, digital transformation has broken the
industrial boundaries and built a new competitive
chain based on data assets and services. On the
ecological level, digital transformation has broken the
industrial boundaries, built a value network with data
assets as the core and multi-party collaboration, and
promoted the transformation of enterprises from
traditional equipment suppliers to comprehensive
service providers.
In summary, the application of digital tools has
the potential to drive value creation by improving
operational efficiency and financial resilience.
Furthermore, these tools can provide long-term power
for enterprises by upgrading customer experience,
sharing ecological value, and building strategic
barriers. The case of Airbus demonstrates that the
logic of digital transformation empowering enterprise
value creation is not purely a superimposition of
technology but rather lies in the systematic
reconstruction of business processes and optimization
of the resource allocation model, which ultimately
realizes the transformation of technological dividends
into sustainable business value. Its experience reveals
that digital transformation is a systematic innovation
of strategic thinking and business model, and
enterprises need to be based on long-term value
objectives, take customer demand as the traction, and
deeply integrate digital capabilities into the core value
chain so as to seize the first opportunity in the
industrial change.
Despite the systematic exploration of the impact
of digital transformation on value creation, as
exemplified by the Airbus case study, the study is not
without its limitations. Firstly, the research focuses on
top enterprises that have specificity. As a result, the
research conclusions lack universality for small and
medium-sized enterprises. Secondly, the long-term
economic effects and social impacts (e.g., changes in
the employment structure, technological and ethical
risks) of digital transformation have not yet been
sufficiently discussed. Thirdly, there is insufficient
empirical analysis of the value transformation paths
of quantum computing and other technologies. In the
future, it is necessary to expand the research on the
transformation paths of enterprises in multiple
industries and of different scales and, at the same
time, pay attention to the impact of technological
iteration on the governance model of the industrial
chain, as well as the synergistic mechanism between
digital transformation and the goal of carbon
neutrality. The purpose of this theoretical research is
to provide support for the construction of a more
inclusive and sustainable transformation paradigm.
REFERENCES
Airbus. (2024). Financial results (2017-2024), Airbus Offi
cial Website, https://www.airbus.com/en/investors/fina
ncial-results,last accessed 2025/3/20.
Airbus. (2024). Digital transformation, Airbus Official
Website, https://www.airbus.com/en/innovation/digital
-transformation,last accessed 2025/3/20.
AlNuaimi, B. K., Singh, S. K., Ren, S., Budhwar, P., &
Vorobyev, D. (2022). Mastering digital
transformation: The nexus between leadership, agility,
and digital strategy. Journal of Business Research, 145,
636-648.
Bai, Q. Q., & Li, Z. (2022). Houyiqing shiqi duo jichang
lüke tunuliang fenlei yuce [Classification prediction of
multi-airport passenger throughput in the post-
epidemic period]. Journal of Transportation
Technology and Economy, 24(6), 9–15.
Bernard, W., & Hoffmann, A. (2023). SKYWISE-Big data
platform as a foundation of airlines predictive and
health monitoring. In PHM Society Asia-Pacific
Conference, 4 (1).
Boeing. (2022). Commercial Market Outlook 2022. Retrie
ved from https://www.boeing.com/commercial/market
/commercial-market-outlook/,last accessed 2025/3/20.
Courtney, M. (2015). The future of flight is
green. Engineering & Technology, 10(6), 38.
European Commission. (2018, April 17). Clean Sky 2 - the
largest research programme for aviation ever launche
d in Europe. Projects. https://projects.research-and-inn
ovation.ec.europa.eu/en/projects/success-stories/all/cle
an-sky-2-largest-research-programme-aviation-ever-la
unched-europe,last accessed 2025/3/20.
Flight School USA. (2024). Operator feedback analysis: B
oeing vs. Airbus customer satisfaction. Flight School U
SA. https://www.flightschoolusa.com/zh-CN/%E6%B
3%A2%E9%9F%B3%E4%B8%8E%E7%A9%BA%E
5%AE%A2/#operator-feedback-analysis-boeing-vs-air
bus-customer-satisfaction, last accessed 2025/3/20.
Fortune. (2024). Global 500 rankings 2024. Fortune
Magazine, 2024(8), 56-73.
McKinsey & Company. (2023). Digital transformation in
global aviation manufacturing: Challenges and
opportunities. Aviation Technology Review, 47(3), 45-
60.
Grande, R., & Tang, H. K. (2023). Emerging digital
technologies in the workplace. 3d printing, work
organization and job quality at the airbus spain case
study. International Journal of Innovation &
Technology Management, 20(6).
Sacchi, R., Becattini, V., Gabrielli, P., Cox, B.,
Dirnaichner, A., Bauer, C., & Mazzotti, M. (2023).
How to make climate-neutral aviation fly. Nature
Communications, 14(1), 3989.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
108

Sarda, N., Estanguet, R., & Ernadote, D. (2023, June).
Model-based approach to support Multi-Disciplinary
Analysis and Optimization capability governance at
enterprise level: preliminary results. In 2023 18th
Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference
(SoSe) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Sigov, A., Ratkin, L., Ivanov, L. A., & Xu, L. D. (2022).
Emerging enabling technologies for industry 4.0 and
beyond. Information Systems Frontiers, 1-11.
Westerman, G., Bonnet, D., & McAfee, A. (2014). Leading
digital: Turning technology into business
transformation. Harvard Business Press.
Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate Value Creation: A Case of Airbus
109
