
The Puzzle of Stock Premium in Western Market and Its
Enlightenment to Chinese Market
Yuchuan Zhou
a
International College, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, 169 Shuanggang East Street, Nanchang, China
Keywords: Puzzle of Stock Premium, Behavioural Finance, Western and Chinese Market.
Abstract: The mystery of stock premium has been a curious issue for nearly a hundred years. This study discusses the
origin of the puzzle of stock premium, the progress of western research and Its Enlightenment to China's
capital market. The mystery of stock premium comes from Mehra and Prescott's research in 1985, which
refers to the phenomenon that the real return of stocks is much higher than the risk-free interest rate, which is
difficult to explain by the traditional CAPM model. Behavioural finance provides new explanations from the
perspective of psychological bias and emotion, such as prospect theory, disposition effect, over trading. This
paper analyses the causes of stock premium, including investor behaviour, market volatility, information
asymmetry and so on, and points out its enlightenment to China's capital market, such as controlling inflation,
reducing policy intervention, strengthening market supervision and information disclosure transparency.
These results provide a useful reference for improving the institutional design and policy making of China's
capital market, and promotes its healthy development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The puzzle of stock premium was an important point
put forward by Mehra and Prescott in 1985. By
analysing the stock market data of the US S&P 500
index from 1889 to 1978 (Zhou, 2013), they found
that the stock yield was about 7%, while the Treasury
bond yield, that is, the risk-free bond yield, was about
1% in the same period (Zhu & Zheng, 2013). The
stock yield and the risk-free bond yield form the
equity premium. However, under the traditional
financial model, the phenomenon of equity premium
cannot be explained, which leads to the view of "the
puzzle of stock premium".
In the western market, the research on the puzzle
of stock premium has experienced several stages of
development. Early studies mainly focused on the
classical capital asset pricing model (CAPM), trying
to explain the stock premium phenomenon by
improving the model assumptions. However, with the
in-depth study, scholars gradually realized that it was
difficult to fully explain the causes of stock premium
only by traditional models, and then introduced the
multi-dimensional theoretical framework of
behavioural finance, macroeconomic factors, market
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-2772-685X
friction and so on (Zheng & Xiao, 2013). For example,
Barberis et al. introduced the prospect theory into the
asset pricing model to explore the impact of investors'
bounded rationality on the stock premium (Barberis
et al., 2001).
With the continuous development of the global
financial market, China's capital market is also
gradually maturing, and China's influence on the
international stock market and economy is growing
(Shao, 2008). It is of great theoretical and practical
significance for China to study the mystery of stock
premium. This paper will first review the origin of the
puzzle of stock premium and its research progress in
the west, then analyse the causes of the puzzle of
stock premium, and finally put forward policy
suggestions and future research directions for the
development of China's capital market. Through the
in-depth study of the puzzle of stock premium, one
can not only better understand the relationship
between risk and return in the financial market, but
also provide a useful reference for improving the
institutional design and policy-making of China's
capital market, so as to promote the healthy
development of China's capital market and enhance
82
Zhou, Y.
The Puzzle of Stock Premium in Western Market and Its Enlightenment to Chinese Market.
DOI: 10.5220/0013833100004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 82-86
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
its position in the global financial system (Zhao & Hu,
1999).
2 BACKGROUNDS
2.1 Traditional Finance
Mehra and Prescott first put forward the puzzle of
stock premium in 1985, i.e., the real rate of return of
stocks is much higher than the risk-free interest rate
(Mehra & Prescott, 1985). Traditional finance uses
capital asset pricing model (CAPM) to explain the
phenomenon of stock premium. The CAPM model
was proposed by Sharpe in 1964. It believes that the
expected return of assets is proportional to its
systematic risk (β value). However, CAPM model
assumes that the market is completely efficient and
investors are rational, which is quite different from
the behaviour of investors in the actual market
(Sharpe 1964). It is difficult to explain this
phenomenon with a reasonable risk aversion
coefficient. Mehra and Prescott pointed out that to
explain the stock premium, investors' risk aversion
coefficient needs to be as high as 30 to 40, which is
in contradiction with the risk aversion coefficient of
about 1 observed in reality. Some typical results are
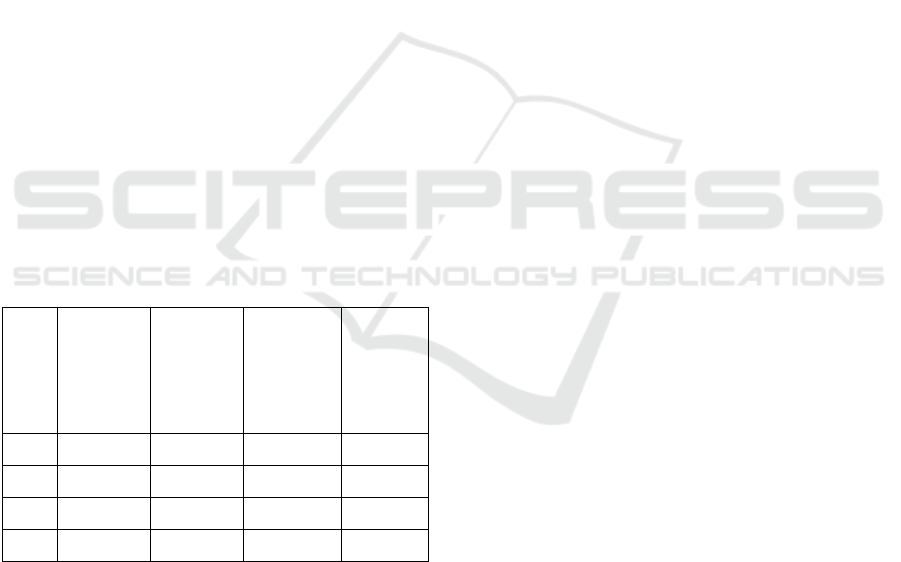
shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Comparison between CAPM model prediction and
actual rate of return.
β Risk free
interest
rate
Market
rate of
return
CAPM
forecast
rate of
return
Actual
rate of
return
0.5 2% 8% 5% 6.5%
1.0 2% 8% 8% 9.2%
1.5 2% 8% 11% 12.8%
2.0 2% 8% 14% 15.5%
Data source: risk free interest rate: fed economic data (Fred).
Market return: S&P 500 index historical data (CRSP).
Actual rate of return: Based on historical stock portfolio
(CRSP)
2.2 Behavioural Finance
The rise of behavioural finance provides a new
perspective to explain the mystery of stock premium.
Behavioural finance believes that the behaviour of
investors is affected by psychological bias and
emotion, which leads to the market is not always
effective. The explanation mainly focuses on the
psychological bias of investors. The disappointment
aversion theory explains investors' behaviour of
reducing holdings due to the volatility of stock returns
by introducing the disappointment aversion
coefficient and reference level; Barberis and Huang
pointed out in 2007 that incorporating loss aversion
and a narrow framework into the traditional utility
function can generate. Higher stock premiums and
lower risk-free interest rates at the same time, even
when consumption growth is stable and the
correlation with the stock market is weak (Barberis,
et al., 2001). Based on the prospect theory, the short-
term loss aversion theory points out that investors
magnify short-term loss perception due to frequent
portfolio evaluation, which requires a higher stock
premium to compensate for psychological costs
(Benartzi, 1995). These theories reveal the
phenomenon of stock premium that cannot be
explained by traditional finance from the perspective
of behaviour.
2.3 Empirical Analysis
Prospect theory, proposed by Kahneman and Tversky,
emphasizes that investors' perception of loss and
return is nonlinear, and their sensitivity to loss is
higher than that of return. Barberis, Huang and Santos
applied the prospect theory to the asset pricing model
in 2001, assuming that investors' sensitivity to loss is
higher than income, and the degree of risk aversion
will change with the change of investment results
(Barberis et al., 2001). This framework can explain
the historical data of stock premium.
Utility function is used to describe the risk
preference of investors in behavioural finance. The
traditional utility function assumes that investors are
risk neutral, while behavioural finance introduces the
concept of loss aversion and modifies the form of
utility function (Mehra & Prescott, 1985).
3 REASONS
3.1 Disposal Effect
The disposition effect was first proposed by Shefrin
and Statman in 1985, pointing out that investors tend
to sell profitable stocks too early and hold loss stocks
too long (Shefrin & Statman, 1985). The existence of
disposal effect shows that investors are affected by
psychological bias in the decision-making process,
especially the aversion to losses and the premature
realization of profits.
The Puzzle of Stock Premium in Western Market and Its Enlightenment to Chinese Market
83
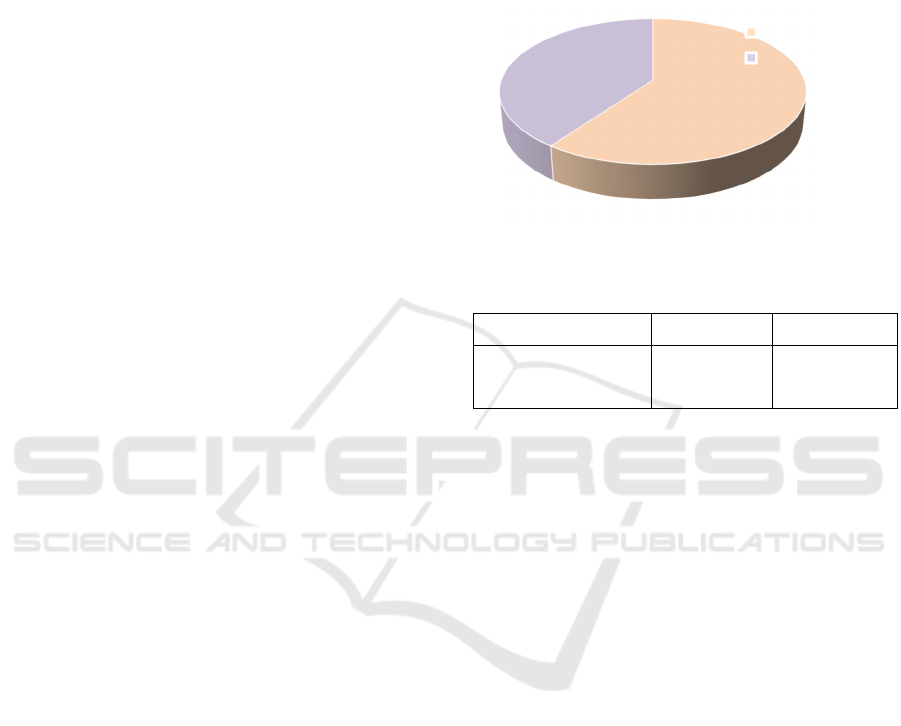
Odean analysed the trading data of individual
investors in 1998 and found that the probability of
investors selling profitable stocks was significantly
higher than that of selling loss stocks (as shown in
Figure 1). This finding supports the existence of
disposition effect and shows that investors are
significantly affected by psychological bias in the
decision-making process (Odean, 1998). Feng and
Seasholes found that Chinese investors also showed
significant disposition effect through the study of
Chinese stock market in 2005. Their research also
found that experienced investors are less affected by
the disposal effect than novice investors, indicating
that investors can reduce the impact of psychological
bias through learning and experience (Feng &
Seasholes, 2005).
Over trading refers to the phenomenon that
investors buy and sell stocks frequently, resulting in
increased transaction costs and decreased net return.
This behaviour is usually driven by overconfidence
and over optimism. Barber and Odean found in 2000
that the annualized rate of return of over traded
investors was significantly lower than the market
average. Their research also shows that male
investors are more likely to show overconfidence than
female investors, leading to higher trading frequency
(Barber & Odean, 2000).
Attention driven trading means that investors tend
to buy stocks that attract their attention, and these
stocks may not have good fundamentals. This
behaviour is usually driven by media reports,
advertisements or other external information sources.
Hirshleifer et al. Found in 2011 that media reports
increased the trading volume and volatility of stocks.
Seen from Table 2, their research shows that when
faced with a large amount of information, investors
may rely on simple clues (such as stock names or
recent performance) to make decisions (Hirshleifer et
al, 2011).
Emotion driven trading means that investors'
decisions are affected by emotional fluctuations,
resulting in excessive buying when market sentiment
is high and excessive selling when market sentiment
is low. Such behaviour is usually driven by
psychological factors such as market sentiment and
herding. Baker and Wurgler found in 2006 that
market sentiment has an impact on stock returns.
Their research shows that investors may be overly
optimistic when the mood is high, and may be overly
pessimistic when the mood is low (Baker & Wurgler,
2006). Inadequate diversification of investment
portfolio means that investors fail to fully diversify
investment risks, resulting in unnecessary risks. This
behaviour is usually driven by psychological factors
such as local preference and industry concentration.
French and Poterba found in 1991 that investors
generally have local preferences, leading to the lack
of internationalization of the portfolio. Their research
shows that investors may underestimate some risks,
resulting in insufficient diversification of the
portfolio (French & Poterba, 1991).
Figure 1: Stock type (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Table 2: This caption has one line so it is centered.
Male Female
Annual average
transaction frequency
80% 50%
3.2 Market
Market volatility refers to the volatility of stock prices,
which is usually measured by standard deviation.
High market volatility may lead investors to demand
higher risk premium. Campbell and Shiller found in
1988 that there was a significant correlation between
market volatility and stock premium. Their research
shows that high market volatility may lead investors
to demand higher returns to compensate for risks
(Campbell & Shiller, 1988).
Information asymmetry refers to the fact that
different participants in the market have different
amounts of information, which leads to investors'
inaccurate risk assessment of stocks, thus requiring
higher returns. Grossman and Stiglitz pointed out in
1980 that information asymmetry is one of the
important reasons for market failure. Their research
shows that information asymmetry may cause the
market price to deviate from its true value (Grossman
& Stiglitz, 1980).
4 ENLIGHTENMENTS TO
CHINA
Hyperinflation will severely hit the national debt
market and the stock market. Holders of government
60%
40%
Profitable stock
Loss stock
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
84

bonds may sell government bonds in the event of
inflation, leading to a decline in the price of
government bonds. At the same time, inflation may
lead to the bubble of the stock market and eventually
lead to the bursting of the economic bubble, as shown
by the bursting of the economic bubble in Japan in the
1980s (Zhao & Hu, 1999). In order to promote the
healthy development of the capital market, one must
strictly control the inflation rate and ensure the
stability of the national debt and stock markets.
The time-varying parameters and statistics show
that there are limitations in the application of
consumption-based asset pricing model in China's
stock market. China's stock market is often referred
to as a "policy market". For example, the increase in
stamp duty on May 30th, 2007 led to a sharp decline
in the stock market. Such policy intervention has
increased market instability and intensified
speculation. In order to improve this situation, the
management should reduce direct intervention,
strengthen market supervision, crack down on
manipulation, improve the regulatory system,
improve the transparency of information disclosure,
and increase the punishment for violations. Through
these measures, China's stock market will gradually
mature, making the model introduced from abroad
more practical (Song, 2008).
The calculation of stock premium depends on
historical data, which may not accurately predict the
future market performance. In addition, the risk-free
interest rate (e.g., treasury bond interest rate) used to
calculate the stock premium also has risks, and the
difference of treasury bond interest rate in different
periods may affect the calculation results. Due to the
particularity of the Chinese market, the Chinese stock
market has existed for a short time, and the policy
intervention is frequent, and the investor structure is
different.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Since Mehra and Prescott proposed the mystery of
stock premium in 1985, it has aroused extensive and
in-depth discussion in the field of western financial
research. The CAPM model of traditional finance is
limited by the assumptions of its fully efficient
market and rational investors, and it is difficult to
reasonably explain the phenomenon that the real rate
of return of stocks is much higher than the risk-free
interest rate. The rise of behavioural finance provides
a new perspective for solving the mystery of stock
premium from the perspective of psychological bias,
such as disappointment aversion theory, prospect
theory, loss aversion and so on, which enables us to
have a deeper understanding of investor behaviour
and market phenomenon.
From the perspective of the causes of stock
premium, investors themselves have a variety of
irrational behaviours, such as disposal effect,
excessive trading, attention driven trading, emotion
driven trading and insufficient portfolio dispersion.
These behaviours are not only affected by
psychological factors, but also significantly affect the
return on investment in the market. At the same time,
the volatility and information asymmetry at the
market level make investors face higher risks and
demand higher returns, which together contribute to
the phenomenon of stock premium.
For China's capital market, the study of the puzzle
of stock premium has important theoretical and
practical significance. Theoretically, it helps us
understand the complex relationship between risk and
return in financial markets; In practice, it provides a
reference for the system design and policy making of
the capital market. On the one hand, controlling the
inflation rate is the key to stabilizing the national debt
and stock market, and the damage of hyperinflation to
the financial market should not be underestimated.
On the other hand, the policy management should
reduce direct intervention in the market, avoid
increasing market instability and speculation, and
instead strengthen market supervision, improve the
regulatory system, improve the transparency of
information disclosure, and severely crack down on
market manipulation and other violations, so as to
promote the maturity and healthy development of
China's stock market, so that international advanced
financial models can better play a role in the Chinese
market.
However, there are some limitations in the study
of the puzzle of stock premium. On the one hand, its
calculation relies on historical data, which makes it
difficult to accurately predict the future market trend,
and the selection of risk-free interest rates and term
differences will affect the calculation results. On the
other hand, the Chinese market has its particularity,
such as short development time, frequent policy
intervention, unique investor structure, etc., which
makes it necessary to be cautious when learning from
western research results. Future research should focus
on how to combine the characteristics of the Chinese
market and the development technology of artificial
intelligence, build a more practical theoretical model,
and deeply analyse the phenomenon of stock
premium, so as to provide more powerful theoretical
support for the long-term development of China's
capital market. This study will help to explore the
The Puzzle of Stock Premium in Western Market and Its Enlightenment to Chinese Market
85

causes of the mystery of stock premium and provide
a better reference for the development of China's
stock market.
REFERENCES
Baker, M., Wurgler, J., 2006. Investor sentiment and the
cross-section of stock returns. Journal of Finance,
61(4), 1645-1680.
Barber, B. M., Odean, T., 2000. Trading is hazardous to
your wealth: The common stock investment
performance of individual investors. Journal of
Finance, 55(2), 773-806.
Barberis, N., Huang, M., Santos, T., 2001. Prospect Theory
and Asset Prices. The Quarterly Journal of Economics,
1162.
Benartzi, T., 1995. Myopic Loss Aversion and the Equity
Premium Puzzle. The Quarterly Journal of Economics,
2(1), 73-92.
Campbell, J. Y., Shiller, R. J., 1988. Stock prices, earnings,
and expected dividends. Journal of Finance, 43(3),
661-676.
Feng, L., Seasholes, M. S., 2005. Do investor sophistication
and trading experience eliminate behavioral biases in
financial markets. Review of Finance, 9(3), 305-351.
French, K. R., Poterba, J. M., 1991. Investor diversification
and international equity markets. American Economic
Review, 81(2), 222-226.
Grossman, S. J., Stiglitz, J. E., 1980. On the impossibility
of informationally efficient markets. American
Economic Review, 70(3), 393-408.
Hirshleifer, D., Lim, S. S., Teoh, S. H., 2011. Limited
investor attention and stock market misreactions to
accounting information. Review of Asset Pricing
Studies, 1(1), 35-73.
Mehra, R., Prescott, E. C., 1985. The equity premium: A
puzzle. Journal of Monetary Economics, 15(2), 145-
161.
Odean, T., 1998. Are investors reluctant to realize their
losses. Journal of Finance, 53(5), 1775-1798.
Shao L., 2008.An empirical analysis of the puzzle of equity
premium in China. Qingdao University.
Sharpe, W. F., 1964. Capital asset prices: A theory of
market equilibrium under conditions of risk. Journal of
Finance, 19(3), 425-442.
Shefrin, H., Statman, M., 1985. The disposition to sell
winners too early and ride losers too long: Theory and
evidence. Journal of Finance, 40(3), 777-790.
Song, N., 2008. An analysis of the puzzle of equity
premium in China's stock market. Huazhong University
of science and technology.
Zhao, L., Hu, Y., 1999. The puzzle of western stock
premium and the steady development of China's capital
market. Journal of Qingdao Ocean University, 1, 67-
71+50.
Zheng, X., Xiao, Y., 2013. Review of equity risk premium
theory Based on C-CAPM model. Journal of Guizhou
University of Finance and Economics, 6, 42-47.
Zhou, H., 2013 The puzzle of equity premium in China: An
analytical perspective of behavioural finance. Liaoning
University.
Zhu, K., Zheng, S., 2013. Prospect theory and an
explanation of stock premium -- An Empirical Analysis
Based on China's securities market. Journal of
Southwest Agricultural University (Social Science
Edition), 11(11), 22-26.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
86
