
Practical Research on the Inclusion of Data Assets of Data-Driven
Intelligent Enterprises in Financial Statements: Taking "Merit
Interactive" as an Example
Yuer Chen
a
Business School, Dalian University of Foreign Languages, Longtou Street, Lüshunkou District, Dalian, China
Keywords: Data Assets, Current Situation of Inclusion in Financial Statements, Merit Interactive, Economic
Consequences.
Abstract: The inclusion of data assets in financial statements is a crucial step in the digital transformation of enterprises.
It makes the value of data explicit, which is conducive to in-depth exploration and utilization. However,
existing research mainly stays at the theoretical level, lacking practical cases of implementation in enterprises,
and there is a problem of disconnection between theory and practice. Taking Merit Interactive as an example,
this paper uses the longitudinal single-case study method and the literature research method to study the
financial reports of this enterprise in the first three quarters of 2024. The study finds that the inclusion of data
assets in financial statements not only helps Merit Interactive turn losses into profits, but also has a positive
impact on the market value of the company. According to the study, promoting the inclusion of data assets of
data-driven intelligent enterprises in financial statements is conducive to making the value of their data
resources explicit. This paper attempts to explore the possible economic consequences of including data assets
in financial statements for data-driven intelligent enterprises, and provides empirical references for enterprises
to better realize the explicit manifestation of data assets.
1 INTRODUCTION
The digital economy is increasingly becoming a key
force in reorganizing global factor resources,
reshaping the global economic structure, and
changing the global competition pattern. As a core
production factor, data is of positive significance for
promoting the optimization of resource allocation and
facilitating the upgrading of the industrial structure
(Liu Liyan and Sun Yue, 2025). In order to unlock the
potential of data factors and strengthen, optimize, and
expand the digital economy, in 2022, the Central
Comprehensively Deepening Reforms Commission
adopted the "Twenty Provisions on Data", exploring
a new model for including data assets in financial
statements (Lv Meng et al., 2024). On August 21,
2023, the Ministry of Finance issued the "Interim
Provisions on the Accounting Treatment Related to
Enterprises' Data Resources", which marked that it
was "imperative" for data assets to be included in
financial statements in China. In September of the
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-2263-9972
same year, the China Association of Assets
Appraisers formulated the "Guiding Opinions on the
Appraisal of Data Assets". The introduction of the
above policies has made the inclusion of data assets
in financial statements more feasible.
Domestic A-share listed companies have
responded to national policies and carried out
preliminary explorations on including data assets in
financial statements. The financial data of the third-
quarter reports in 2024 show that among A-share
listed companies, the number of companies that have
included data assets in their financial statements has
reached 55, and the total amount included has
increased to 1.512 billion yuan (SAIF, 2025). From
the perspective of enterprises, the recognition and
inclusion of data assets in financial statements can
more truthfully and comprehensively reflect the asset
status of enterprises (Zhang Xinmin and Jin Ying,
2022). At the same time, inclusion in financial
statements can promote the transformation of data
from a cost center to a value center, enhance data
Chen, Y.
Practical Research on the Inclusion of Data Assets of Data-Driven Intelligent Enterprises in Financial Statements: Taking "Merit Interactive" as an Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0013832500004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 49-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
49

competitive advantages, and provide a basis for the
trading, pledging, and investment of data assets (Xie
Kang et al., 2020). However, due to the limitations of
enterprises' data management awareness and
capabilities, as well as the lack of relevant laws and
accounting rules, listed companies that present data
assets in the form of accounting items and
monetization and actively disclose information
account for less than 3% of the total market. The
massive amounts of data owned by most enterprises
have not yet become a source of value for production
and development (Cleveland H., 1982).
Considering that Merit Interactive Company
included data assets in its financial statements
relatively early, this paper takes Merit Interactive
Company as the research object, adopts the
longitudinal single-case study method and the
literature research method, and studies its financial
reports for the first three quarters of 2024. It explores
the practice of the accounting treatment and
disclosure of its data assets, and further discusses the
possible economic consequences. This study aims to
make contributions in two aspects: On the one hand,
it acquires and refines the application practices of the
businesses related to enterprises' data assets; on the
other hand, it explores and analyzes the possible
economic consequences that the inclusion of data
assets in financial statements may bring to data-
driven intelligent enterprises, so as to help enterprises
make the value of data assets explicit and enhance
their data competitiveness.
2 THE BUSINESS SITUATION OF
MERIT INTERACTIVE'S DATA
RESOURCES
2.1 The Formation Methods and
Application Scenarios of Data
Assets
The formation methods of data assets: Firstly, the
original data mainly comes from the company's
developer services. The accumulated data resources
are legally collected on the premise of users'
authorized consent, forming the original data of
relevant data resources, including device information,
network information, scenario information, APP
characteristics, etc. As of the first half of 2024, the
cumulative installation volume of the company's
software development kit (SDK) has exceeded 110
billion, the cumulative installation volume of the
software development kit (SDK) for smart Internet of
Things (IoT) devices has exceeded 370 million, and
the number of daily active independent devices (with
duplicates removed) of the SDK has exceeded 400
million. Secondly, a dedicated data team conducts in-
depth insights and governance on the data,
accumulating profound data assets and ensuring the
accuracy and effectiveness of the data. After data
governance and mining, more than 7,000 types of
data tags have been formed, and the cumulative
number of characteristic parameters directly involved
in calculations exceeds 200 million. Thirdly, the self-
developed data intelligent operating system (DiOS) is
used to process and govern the data, realizing the
collection of data, asset management, and integrated
application management. The generated data
products will be regularly iterated and optimized
(SAIF, 2024).
There are two types of application scenarios:
Firstly, the company utilizes data resources to provide
professional push solutions for mobile application
developers, including services such as message push
SDK and user operation platform SDK. Secondly,
relying on data resources, the company has developed
data intelligence applications for different industries,
such as intelligent transportation, medical and health
care, etc., and also provides data support for brand
marketing, public governance, etc. In addition, the
company is actively exploring the combination of
data resources with new technologies such as
artificial intelligence. For example, it has accessed
large models like ChatGPT and developed
applications of large models for vertical scenarios.
2.2 The Business Model of Data
Resources
The company's business logic is divided into three
layers (D-M-P, Data-Machine-People): The bottom
layer "D" refers to data accumulation. Based on the
data accumulated in developer services and in-depth
insights into massive dynamic data, the company
continuously provides data support for top-level
businesses. The middle layer "M" refers to data
governance. The company has created a data
intelligent operating system (DiOS), which can
collect and gather data, manage it as assets, and
conduct refined processing, and then provide the
upper-level business systems with the ability of data
services. The upper layer "P" refers to data
application. Combining data models with industry
understanding, the company has created productized
and large-scale profit-making data intelligent
applications in the fields of commercial services and
public services.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
50
3 THE OVERALL SITUATION OF
MERIT INTERACTIVE'S
INCLUSION OF DATA ASSETS
IN FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
3.1 Inclusion of Data Resources in the
"Intangible Assets" Account
As of September 30, 2024, the carrying value of the
company's data resources at the end of the period was
32,840,600 yuan. Among the three ways of obtaining
intangible assets of data resources, the intangible
assets of data resources that Merit Interactive has
currently included in the financial statements are all
obtained through self-research and development, and
there is currently no involvement in acquisition
through external purchase or other means (Zou
Zhaoju, 2017). The company's data resources are
measured using the cost method as shown in Table 1.
Considering that the timeliness of data resources
generally decreases year by year, the accelerated
depreciation and amortization method is used for
amortization. Through a comprehensive analysis of
the historical data of the past three years, the
amortization period is confirmed to be 5 years.
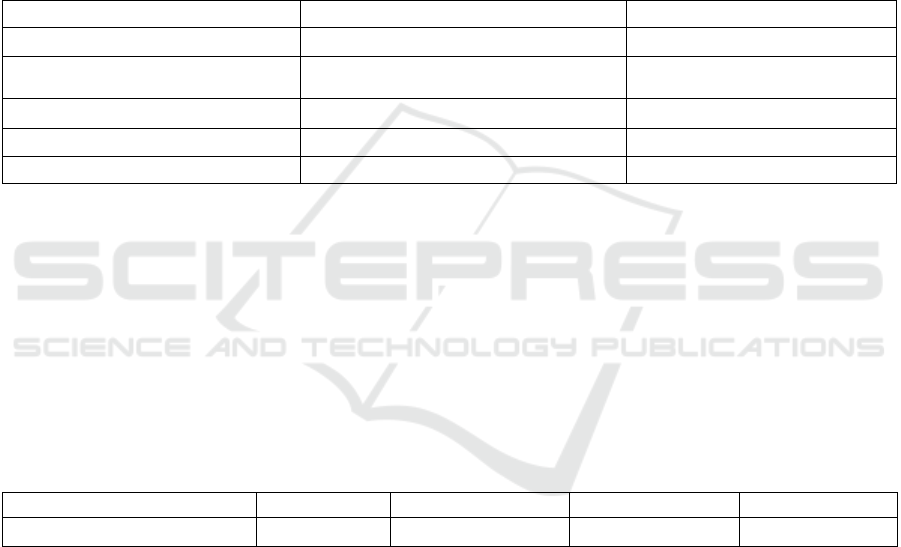
Table 1: Useful Life and Amortization Method of Merit Interactive's Data Resources.
Project Useful Life and Its Determination Basis Amortization Method
Land Use Right The land use term (50 years) Straight - line Method
Asset Groups Such as Copyrights,
Patents, and Trademarks
10 years Straight - line Method
Management Software 5 years Straight - line Method
Self - developed Operating System 5 years Straight - line Method
Data Resources 5 years Accelerated Amortization Method
Data Source: Merit Interactive's Financial Report (Juchao Information, 2024)
3.2 The Situation of Including Data
Assets in Financial Statements in
the First Three Quarters of 2024
and Comparative Analysis
As shown in Table 2, in the third - quarter report of
2024, the intangible assets of Merit Interactive were
187.62 million yuan, including 32.8406 million yuan
of data resources, accounting for 17.50%. In the semi
- annual report of 2024, the intangible assets of Merit
Interactive were 183.0774 million yuan, including
23.3331 million yuan of data resources, accounting
for 12.75%. In the first quarter of 2024, Merit
Interactive included data resources in the financial
statements for the first time. As of March 31, the
company's intangible assets were 177.7344 million
yuan, including 12.8369 million yuan of data
resources, accounting for 7.22%.
Table 2: The Situation of Merit Interactive's Inclusion of Data Resources in Financial Statements (Unit: Yuan)
Intangible Assets 167,569,605.07 177,734,449.71 183,077,447.89 187,620,034.26
Among which: Data Resources
—
12,836,884.11 23,333,053.90 32,840,611.29
Data source: The financial report of Merit Interactive (Juchao Information, 2024)
3.3 Overview of the Impact of
Including Data Assets in Financial
Statements on the Company's
Profits
As shown in Table 3, as of September 30, 2024, the
company's total operating revenue was 333 million
yuan, an increase of 7.5%; the net profit was 5.9189
million yuan, an increase of 88%. The impact of
including data resources in the financial statements on
the net profit was 32.8406 million yuan, and the profit
margin was 1.78%. If the data resources had not been
included in the financial statements, the net profit
should have been -26.9217 million yuan, and the
profit margin would have been -8.08%. It can be seen
that the inclusion of data resources in the financial
statements helped the company turn losses into
profits.
Practical Research on the Inclusion of Data Assets of Data-Driven Intelligent Enterprises in Financial Statements: Taking "Merit Interactive"
as an Example
51
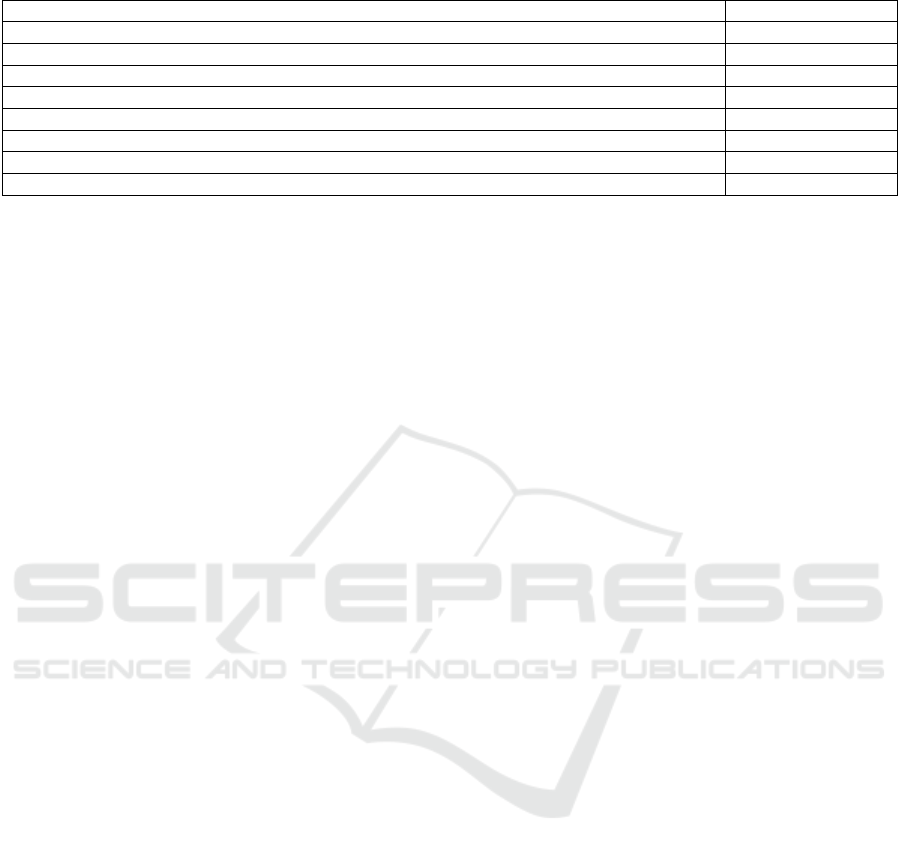
Table 3: The Impact of Including Data Assets in Financial Statements on Merit Interactive.
Com
p
an
y
Merit Interactive
Account for Inclusion in Financial Statements Intan
g
ible Assets
Total Amount of Data Resources Included in Financial Statements
(
Yuan
)
32,840,611.29
Asset-Liability Ratio 9.77%
Asset-Liability Ratio (Estimated) if Data Resources are not Included in Financial Statements 10.90%
Decrease in Asset-Liability Ratio after Including Data Resources in Financial Statements 1.13%
Profit Mar
g
in 1.78%
Profit Mar
g
in
(
Estimated
)
if Data Resources are not Included in Financial Statements -8.08%
Increase in Com
p
an
y
's Profit Mar
g
in after Includin
g
Data Resources in Financial Statements 9.86%
Data source: The financial report of Merit Interactive (Juchao Information, 2024)
The asset-liability ratio (estimated) when data
resources are not included in the financial statements
is equal to the total liabilities divided by (total assets
minus the total amount of data resources included in
the financial statements). The decrease in the asset-
liability ratio after including data resources in the
financial statements is equal to the asset-liability ratio
(estimated) when data resources are not included in
the financial statements minus the actual asset-
liability ratio. The profit margin (estimated) when
data resources are not included in the financial
statements is equal to (net profit minus the total
amount of data resources included in the financial
statements) divided by the total revenue. The increase
in the net profit margin after including data resources
in the financial statements is equal to the net profit
margin minus the profit margin (estimated) when data
resources are not included in the financial statements.
4 THE IMPACT OF INCLUDING
DATA RESOURCES IN
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS ON
THE FINANCIAL
PERFORMANCE AND
MARKET VALUE OF MERIT
INTERACTIVE
The financial information disclosed in Merit
Interactive's semi-annual report is more detailed than
that in the third-quarter report, making it more
suitable for the analysis of the company's financial
situation due to the inclusion of data assets in
financial statements. Based on this, this chapter
mainly explores the economic consequences and the
impact on the market value of the company caused by
the inclusion of data assets in financial statements by
obtaining and analyzing the data from Merit
Interactive's semi-annual report.
4.1 Analysis of the Financial
Performance Generated by
Including Data Resources in
Financial Statements
4.1.1 Analysis from the Changes in
Financial Statement Data
Firstly, this paper focuses on analyzing the changes in
the balance sheet before and after the inclusion of data
assets in financial statements. Before inclusion, there
were no accounts related to data assets in the
enterprise's balance sheet. After inclusion, data assets
that meet the recognition criteria of intangible assets
are recorded in the balance sheet. As shown in Table
4, the recognition of data assets leads to a
corresponding increase of 23,333,100 yuan in the
carrying value of intangible assets (after deducting
the amortization amount of the current year). At the
same time, since the data assets that were originally
expensed are recognized as intangible assets after
being included in the financial statements, the total
profit increases by 23,333,100 yuan. The intangible
assets formed by data assets in the current period are
amortized using the accelerated amortization method
over 5 years, and the deferred income tax assets
formed by the straight-line amortization of taxes over
10 years increase by 121,600 yuan. The
reclassification of research and development
expenses to data assets leads to a reduction of
4,024,000 yuan in the additional deduction of
research and development expenses. As a result, the
income tax payable (reflected in taxes payable)
increases by 7,645,600 yuan in a comprehensive
manner.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
52
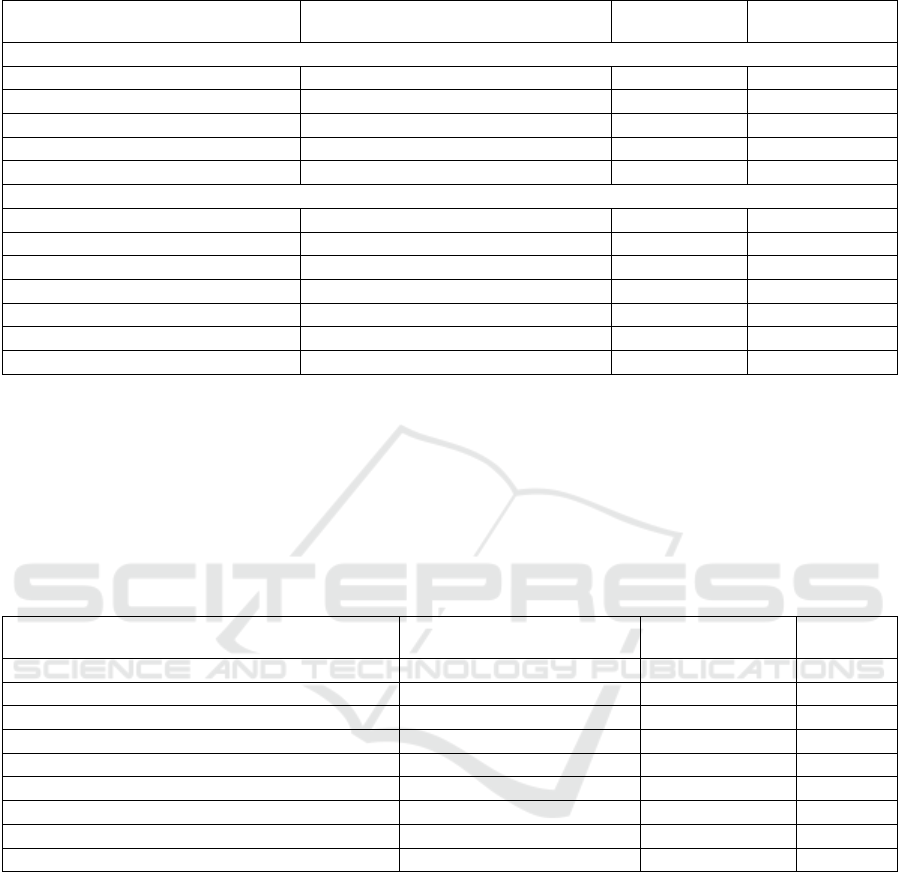
Table 4: Simplified Balance Sheets before and after the Inclusion of Data Assets in Financial Statements (Unit: Yuan)
Project
Before Inclusion (Estimated)
June 30, 2024
After Inclusion
June 30, 2024
Difference
Assets
Total Current Assets 70,058.66 70,058.66 0.00
Deferred Income Tax Assets 4,783.08 4,795.24 12.16
Intangible Assets 15,974.43 18,307.74 2,333.31
Total Non-current Assets 111,779.77 114,125.24 2,345.47
Total Assets 181,838.43 184,183.90 2,345.47
Liabilities and Owner's Equity
Taxes Payable 4,270,963.91 4,271,728.47 764.56
Total Current Liabilities 13,766.06 14,530.62 764.56
Total Non-current Liabilities 1,082.03 1,082.03 0.00
Total Liabilities 14,848.10 15,612.66 764.56
Undistributed Profits 46,310.92 47,891.83 1580.91
Total Owner's Equity 166,990.33 168,571.24 1580.91
Total Liabilities and Owner's Equity 181,838.43 184,183.90 2345.47
Secondly, analyze the changes in the income
statement before and after the inclusion of data assets
in the financial statements. Before the inclusion, the
enterprise accounted for the expenditures related to
data assets as expenses. After the inclusion, the
enterprise capitalized the expenditures that met the
asset recognition criteria. As can be seen from Table
5, the research and development expenses decreased
by 23,333,100 yuan. Due to the adjustment for
inclusion in the financial statements, the total profit
and net profit of the enterprise in the current period
increased significantly. Meanwhile, the income tax
expense also increased significantly, with an increase
of 6,999,900 yuan.
Table 5: Simplified Income Statements before and after the Inclusion of Data Assets in Financial Statements (Unit: Yuan)
Project
Before Inclusion (Estimated)
June 30, 2024
After Inclusion
June 30, 2024
Difference
Business Revenue 21,701.84 21,701.84 0.00
Less: Cost of Business Operations 4,867.24 4,867.24 0.00
Research and Development Expenses 8,393.37 6,060.06 -2,333.31
Other Expenses 10,207.31 10,207.31 0.00
Operating Profit (Loss is filled with the “-” sign) -1,766.08 567.23 2,333.31
Less: Non-operating Expenses 266.41 266.41 0.00
Total Profit (Total Loss is filled with the “-” sign) -2,032.49 300.82 2,333.31
Less: Income Tax Expenses -886.42 -226.39 660.03
Net Profit (Net Loss is filled with the “-” sign) -1,146.07 527.21 1,673.28
Finally, regarding the cash flow statement, the
inclusion of an enterprise's data assets in the financial
statements mainly affects the cash flow from
investing activities and the cash flow from operating
activities. Due to the increase in intangible assets of
data resources after inclusion, the item of "Cash paid
for the acquisition of fixed assets, intangible assets
and other long-term assets" increased by 23,333,100
yuan. At the same time, the cash payments for
operating activities (expenditures in the items of
"Cash paid to and on behalf of employees" and "Cash
paid for other operating activities") that were
originally included in the operating costs or research
and development expenses before inclusion
decreased by 23,333,100 yuan correspondingly. The
specific differences are shown in Table 6.
Practical Research on the Inclusion of Data Assets of Data-Driven Intelligent Enterprises in Financial Statements: Taking "Merit Interactive"
as an Example
53
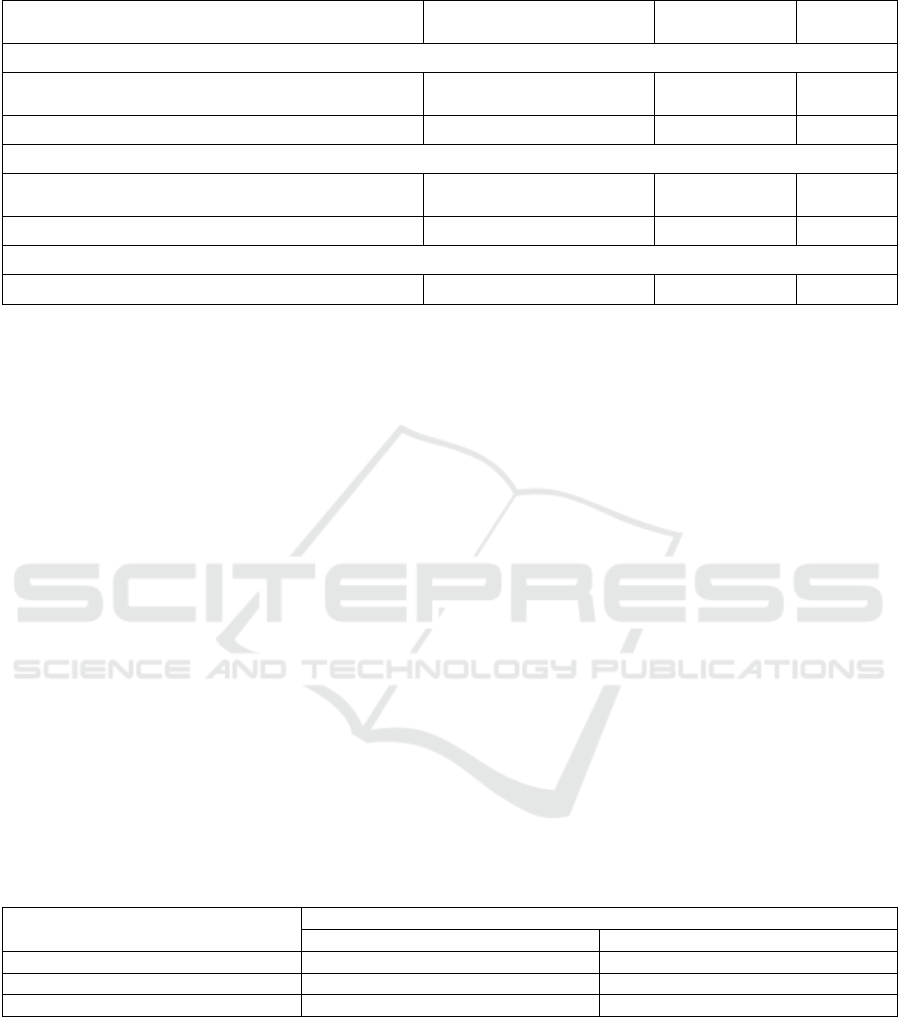
Table 6: Simplified Cash Flow Statements before and after the Inclusion of Data Assets in Financial Statements (Unit: Yuan)
Project
Before Inclusion (Estimated)
June 30, 2024
After Inclusion
June 30, 2024
Difference
I. Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
Cash paid to and on behalf of employees and cash paid
for other operating activities
24,446.30 22,112.99 -2,333.31
Net cash flows from operating activities -9,676.17 -7,342.86 2,333.31
II. Cash Flows from Investing Activities:
Cash paid for the acquisition of fixed assets, intangible
assets and other lon
g
-term assets
2,091.26 4,424.57 2,333.31
Net cash flows from investing activities 9,264.38 6,931.07 -2,333.31
III. Cash Flows from Financing Activities:
Net cash flows from financing activities -14,612.02 -14,612.02 0.00
4.1.2 Comparative Analysis of Financial
Indicators Before and after the
Inclusion of Data Assets in Financial
Statements
Based on the above financial statements, this paper
calculates the key financial indicators before and after
the inclusion of data assets in financial statements,
including the current ratio, asset-liability ratio, return
on net assets, and gross profit margin, as shown in
Table 7. Through the comparative analysis of the
inclusion process and key indicators, the main
changes brought about by the inclusion of data assets
in financial statements are as follows: (1) The
inclusion leads to an increase in income tax expenses,
an increase in current liabilities such as taxes payable.
The increase in current liabilities is greater than that
of current assets, resulting in a decrease in the current
ratio; (2) The increase in total assets is caused by the
increase in intangible assets. However, due to the
increase in taxes payable and other factors, the change
range of liabilities before and after is greater than that
of assets, resulting in an increase in the asset-liability
ratio; (3) After data resources form intangible assets,
they need to be amortized according to the estimated
useful life. Although the inclusion of some expensed
data assets in the balance sheet in the current year of
inclusion leads to a decrease in current costs or
expenses, the amortization of intangible assets of data
resources in subsequent years will be included in the
current costs or expenses again until the intangible
assets are finally disposed of or scrapped. That is, the
inclusion may lead to a time difference in the
recognition of an enterprise's costs or expenses,
showing a pattern of being low first and then high; (4)
Assuming that the enterprise's revenue is stable, since
data assets are transformed from being expensed to
being capitalized, the costs or expenses included in
the current period are low first and then high,
enabling the profit to turn from loss to profit, and at
the same time showing a state of being high first and
then low. The gross profit margin and return on net
assets will also show a state of being high first and
then low; (5) Due to the change of profit being high
first and then low, it may lead to income tax also
showing a pattern of being high first and then low.
Table 7: Key Financial Indicators of Merit Interactive before and after the Inclusion of Data Assets in Financial Statements.
Indicator
June 30, 2024
Before Inclusion (Estimated) After Inclusion
Current Ratio 5.09 4.82
Asset-Liability Ratio (%) 8.17 8.48
Net Profit Rate
(
%
)
-5.28 2.43
4.2 The Impact of Including Data
Resources in Financial Statements
on Market Value
Based on the study of the impact of including data
assets in financial statements on the important
financial indicators of Merit Interactive, this paper
further explores whether, on the basis of improving
some financial indicators of the enterprise, it will
have an impact on the enterprise's market value or
stock price. Due to the influence of multiple factors
such as the stock market being affected by many
factors, it is difficult to evaluate the impact of
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
54

including data assets in financial statements on the
stock price or market value based on a single
hypothesis. At the same time, the annual income and
profits of many enterprises are not smoothly
distributed over the four quarters, and the estimation
based on semi-annual financial data and the
company's price-to-earnings ratio (PE) has relatively
low reference value, so it is not adopted for the time
being. Therefore, this paper only calculates the
theoretical impact of including data assets in financial
statements on the market value of the listed company
by multiplying the increased value of assets brought
about by including data assets in financial statements
by the company's price-to-book ratio (PB) (Dong
Dongming, 2015). According to the calculation of the
marginal market value increment brought by
including data resources in financial statements
estimated by PB (see Table 8), the theoretical market
value increment brought to Merit Interactive by
including data assets in financial statements exceeds
1% of the company's market value.
Table 8: The Theoretical Marginal Impact on Market Value Brought by the Inclusion of Data Resources in Financial
Statements Estimated According to Merit Interactive's PB.
Company
Account for
Inclusion in
Financial
Statements
Total Amount of Data
Resources Included in
Financial Statements
(Yuan)
Average
PB Value
Marginal
Impact on
Market
Value
Proportion of Market
Value Impacted by
Data Assets to Total
Market Value
Merit Interactive Intan
g
ible Assets 23,333,054 2.38 55,431,474 1.57%
5 CONCLUSION
By analyzing the situation of Merit Interactive's
inclusion of data assets in financial statements, this
paper draws the conclusion that promoting the
inclusion of data assets in financial statements by data
- driven intelligent enterprises is conducive to making
the value of their data resources explicit. Firstly, this
paper uses the literature research method to explore
the formation methods and application scenarios of
Merit Interactive's data resources. At the same time,
it analyzes the current situation of Merit Interactive's
inclusion of data assets in financial statements
through the longitudinal single - case study method.
Furthermore, through a simulation analysis before
and after the inclusion of data assets in financial
statements, it examines the changes in financial
statements, the changes in key financial indicators,
and the impact on the company's market value. It is
found that the inclusion of data assets in financial
statements not only helps Merit Interactive turn losses
into profits but also has a positive impact on the
company's market value. However, it should be noted
that when data resources are transferred into
intangible assets, there may be impairment and
amortization, which will, to a certain extent, lead to
risks such as an increase in the later - stage asset -
liability ratio and a decrease in the return on net
assets. This research shows that the inclusion of data
assets in financial statements is not only an innovative
tool for enterprise value management but also a
systematic breakthrough in the in - depth
development of the digital economy. Enterprises need
to adopt a trinity strategy of organizational change
(such as establishing a data asset management
committee), technological enablement (deploying an
intelligent financial system), and ecological
collaboration (participating in the formulation of
industry standards) to achieve a dynamic balance
between the release of data factor value and financial
soundness.
This paper adopts a single - case study method,
which, to some extent, limits the general applicability
and extrapolation of the research results. Meanwhile,
there are certain subjective biases in the process of
case selection, data collection, and analysis, which
have a certain impact on the objective accuracy of the
research results. In the future, it is necessary to further
explore the impact of the data rights confirmation
mechanism on accounting recognition and the
compound value measurement model of data assets
under multi - scenario collaboration. It is
recommended to expand cross - industry comparative
research, especially paying attention to the
differential practices of ToB platform - based and
ToC service - based enterprises in the accounting
treatment of data assets, so as to provide a basis for
constructing a universal theoretical framework.
REFERENCES
Cleveland, H. (1982). Information as a resource. Futurist,
16(6), 34 - 39.
Practical Research on the Inclusion of Data Assets of Data-Driven Intelligent Enterprises in Financial Statements: Taking "Merit Interactive"
as an Example
55

Dong, D. M. (2015). Research on the influencing factors of
the price - to - book ratio of listed companies, Beijing
Jiaotong University.
Juchao Information. (2024). Merit Interactive's Semi -
annual Financial Report 2024.
https://file.finance.sina.com.cn/211.154.219.97:9494/
MRGG/CNSESZ_STOCK/2024/2024-8/2024-08-
27/10415502.PDF
Liu, L. Y., & Sun, Y. (2025). Practical research on the
inclusion of enterprise data assets in financial
statements: Taking "Flush" as an example. Friends of
Accounting, (01), 21 - 28.
Lv, M., Zhao, L. F., & Zhong, Y. C. (2024). A preliminary
exploration of the value effect and economic
consequences of including data assets in financial
statements. Management Review, 36(12), 47 - 59.
SAIF. (2024). Tracking Report on the Inclusion of Chinese
Enterprises' Data Assets in Financial Statements.
https://www.saif.sjtu.edu.cn/show-107-6480.html
SAIF. (2025). Tracking Report on the Inclusion of Chinese
Enterprises' Data Assets in Financial Statements.
https://www.saif.sjtu.edu.cn/show-107-6539.html
Xie, K., Xia, Z. H., & Xiao, J. H. (2020). The enterprise
realization mechanism for big data to become a real
production factor: From the perspective of product
innovation. China Industrial Economics, (05), 42 - 60.
Zhang, X. M., & Jin, Y. (2022). The reconstruction of the
balance sheet: A study based on the behavior of
enterprises in the digital economy era. Management
World, 38(9), 157 - 175.
Zou, Z. J. (2017). Discrimination of the asset attributes of
enterprise big data. Friends of Accounting, (12), 7 - 12.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
56
