
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language
Models
Aishan Maoliniyazi
1 a
, Chaohong Ma
2 b
, Xiaofeng Meng
1 c
and Bingbing Xu
1 d
1
Renmin University of China, Beijing, China
2
HEBEI Normal University, Shijiazhuang, China
Keywords:
Personal Knowledge, Knowledge Graph Construction, Large Language Models.
Abstract:
The growing volume of digital information requires effective Personal Knowledge Management. Personal
Knowledge Graphs (PKGs), which model knowledge as connected entities and relationships, show potential.
Chats or natural voice conversations contain abundant context information about users’ thoughts and pref-
erences, which is beneficial for constructing PKGs. However, constructing PKGs from unstructured natural
conversations is still challenging. The main obstacle comes from two aspects: inherently complex and context-
dependent conversations. In this paper, we present PROM, a novel framework of personal knowledge graph
construction with LLMs. PROM effectively constructs PKGs from natural conversations. Particularly, PROM
constructs PKGs with rich knowledge information, preserves context information for knowledge provenance,
and fuses different kinds of contexts for structural and semantic coherence. Specifically, PROM constructs
knowledge triples (subject, predicate, object) from conversational text and integrates them into a coherent
PKG with the help of LLMs. We propose a multi-strategy knowledge fusion technique to resolve conflicts
and unify information from different sources for structural and semantic consistency. Moreover, we design
an API proxy engine to facilitate consistent knowledge extraction from different LLM backends. The proxy
system is flexible and cost-effective. It can adapt different triple extraction strategies from LLMs and unify the
results with a knowledge fusion strategy. We evaluate PROM in different scenarios. The experiments show
that PROM is able to construct comprehensive and context-aware PKGs from unstructured conversations and
can support personal knowledge discovery.
1 INTRODUCTION
The proliferation of digital information has made
effective Personal Knowledge Management (PKM)
systems highly desirable (Apshvalka and Wendorff,
2005). Individuals are constantly confronted with
streams of information from diverse sources, includ-
ing emails, messages, documents, and social net-
works. Much of this valuable information originates
from naturally occurring conversational data, such as
transcripts and voice calls (Fu et al., 2020). To cope
with this data deluge, there is a critical need for ef-
fective techniques to automatically manage, distill,
and access relevant knowledge tailored to both per-
sonal needs and specific contexts. Personal Knowl-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-1376-6701
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6168-4771
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7889-2120
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-5253-7338
edge Graphs (PKGs), which model entities as nodes
and relations as edges, offer a particularly promising
approach for this task, enabling efficient knowledge
discovery and personalized insights.
Traditional methods for knowledge graph con-
struction, typically reliant on rule-based or statistical
machine learning approaches (Paulheim, 2017), of-
ten demand significant manual labor for feature label-
ing and rule design. This inherent limitation hinders
their scalability across various personal knowledge
domains and contexts. Furthermore, these methods
prove less effective when confronted with the highly
ambiguous and context-dependent natural language
found in conversations (Liu et al., 2020), rendering
them less applicable for dynamic, personalized sce-
narios. Traditional PKG methods rely on manual tem-
plates/ontologies, which makes it difficult to handle
unstructured conversations and lack privacy aware-
ness mechanisms.
The recent advent of Large Language Models
Maoliniyazi, A., Ma, C., Meng, X. and Xu, B.
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0013830900004000
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2025) - Volume 2: KEOD and KMIS, pages
301-312
ISBN: 978-989-758-769-6; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
301

(LLMs) has opened new avenues for automated
knowledge graph construction (Yao et al., 2019).
Pre-trained on massive text corpora, LLMs demon-
strate remarkable capabilities in understanding natu-
ral language nuances, resolving ambiguities, and per-
forming complex reasoning tasks (OpenAI, 2023).
These strengths make them exceptionally well-suited
for extracting structured knowledge from unstruc-
tured conversational data and constructing coherent
PKGs. While several studies have explored LLMs
for knowledge graph completion and entity link-
ing (Cheng et al., 2023), constructing and maintain-
ing PKGs specifically from conversational data using
LLMs poses unique challenges. These include pre-
serving complex conversational context, effectively
fusing knowledge from heterogeneous sources, and
adapting to users’ evolving knowledge preferences.
Effectively addressing these challenges is essential to
fully harnessing the potential of LLMs in personal
knowledge management.
To address these challenges, this paper proposes
PROM, a novel framework for personal knowl-
edge graph construction with LLMs. PROM effi-
ciently constructs PKGs directly from natural conver-
sations, specifically emphasizing context preservation
and seamless knowledge fusion to enhance personal
knowledge management.
Our framework incorporates several key designs:
First, an API Proxy Engine facilitates robust inter-
action with LLMs, preserving the utility of the orig-
inal API and enabling consistent access to conversa-
tional data. Second, a Knowledge Extraction mod-
ule leverages the few-shot learning capabilities of
LLMs to extract structured knowledge in the form of
triples (subject, predicate, object) from unstructured
conversational text. This approach minimizes reliance
on extensive fine-tuning and adapts to diverse con-
versational styles. Third, Knowledge Fusion imple-
ments a multi-strategy approach to resolve conflict-
ing information and consolidate knowledge from het-
erogeneous conversational sources, utilizing semantic
similarity metrics and rule-based conflict resolution to
ensure consistency and completeness.
Building on these designs, we develop a compre-
hensive framework that leverages prompt-engineered
LLMs and graph databases to enable efficient PKG
construction. Comprehensive experiments demon-
strate PROM’s superiority in real-world personal
knowledge management scenarios, highlighting its
effectiveness, adaptability, and generalizability.
The main contributions of this work are summa-
rized as follows:
• We propose PROM, a novel framework for con-
structing personal knowledge graphs from conver-
sational data, leveraging the power of LLMs to
achieve scalability, adaptability, and minimal fine-
tuning.
• We develop an API Proxy Engine that enables
consistent knowledge extraction across different
LLM backends, facilitating future expansion to
include new and improved LLMs as they become
available.
• We design a knowledge extraction module that
employs prompt engineering with few-shot learn-
ing to increase extraction accuracy and reduce re-
liance on labeled data for triple extraction.
• We introduce a multi-strategy knowledge fu-
sion mechanism that enhances graph connectiv-
ity and coherence by intelligently integrating in-
formation from diverse sources and conversation
types, resolving conflicts using heuristics, confi-
dence scores, and optional user input.
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows: Section 2 reviews the related work. Section 3
details our PROM framework. Section 4 presents the
experimental setup and evaluation methodology. The
experimental results and discussion are provided in
Section 5. We conclude the paper in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
Personal Knowledge Graph (PKG) construction is
a burgeoning area focused on organizing an indi-
vidual’s unique knowledge, preferences, and experi-
ences to facilitate personalized information manage-
ment. Extensive research highlights the diverse appli-
cations of PKG across fields like health, finance, edu-
cation, and general research (Chakraborty and Sanyal,
2023). These efforts often detail various construc-
tion methodologies, including those leveraging user-
generated content, system-stored data, and hybrid ap-
proaches. The construction of PKG in this area lever-
ages both traditional and deep learning-based strate-
gies, spanning multiple domains, such as education,
business, and healthcare. We next discuss the PKGs’
construction approaches from traditional and deep
learning-based aspects.
Traditional PKG Construction Methods. Early
approaches often relied on rule-based or crowd-
sourced systems. For example, the teaching system
in (Weng et al., 2020) used crowdsourcing and re-
verse captcha to build hierarchical graphs with user
collaboration. In minority languages, (Sun and Zhu,
2016) used SVM and template-based extraction for
Tibetan knowledge, supporting question answering.
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
302

In domain-specific applications, (Yu et al., 2020) pro-
posed the Tax Knowledge Graph for modeling U.S.
and Canadian tax rules. (Vassiliou et al., 2024) intro-
duced iSummary, which creates personalized graph
summaries by analyzing query logs.
Deep Learning-Based PKG Construction
Methods. Several methods leverage advanced
deep-learning architectures to construct PKG. For
example, (Jiang et al., 2019) introduced AttKGCN,
which uses attribute-aware GCNs for person re-
identification. In healthcare, (Shirai et al., 2021)
reviewed challenges in Personal Health Knowledge
Graphs (PHKGs), while (Seneviratne et al., 2021)
proposed a semantic dietary knowledge model for
personalized recommendations.
Recent works explore LLMs for graph construc-
tion. (C¸
¨
opl
¨
u et al., 2024) leveraged LLMs with
ontologies to capture personal information. (Yang
et al., 2021) proposed TrigNet, a tripartite graph us-
ing psycholinguistic features for personality detec-
tion. (Kuculo, 2023) focused on event-centric knowl-
edge graphs using transformer-based extraction.
Although these efforts are valuable, most do not
fully exploit LLMs for dynamic, context-aware PKG
construction from natural conversations. This work
addresses challenges by proposing a framework for
PKGs with strong context preservation and knowl-
edge fusion capabilities.
3 THE FRAMEWORK
In this section, we first present an overview of PROM
and then detail each component.
3.1 PROM Overview
As depicted in Fig. 1, PROM consists of three main
components: the API Proxy Engine, Knowledge
Extraction, and Knowledge Fusion. The API Proxy
Engine uses a Forward API to retrieve and collect
conversation data from the user applications (e.g.,
ChatBox, Zotero). It supports batch and streaming
data from various sources, including text documents,
APIs, and direct user input. Next, the Knowledge
Extraction identifies and extracts conception, entity,
relation, and triplet using a hybrid and fallback
approach that combines LLM-based methods with
rule-based techniques. Subsequently, the Knowledge
Fusion module refines the extracted knowledge
through entity resolution, merging strategies, re-
lationship discovery, and triplet inference. This
module also systematically addresses inconsisten-
cies, removes duplicates, and completes missing
relations through knowledge correction to ensure
high-quality PKGs. It also provides insight through
entity, relation, and triplet analysis. Finally, the
resulting PKGs are stored in the Knowledge Storage.
3.2 API Proxy Engine
Personal data is distributed across various applica-
tions in different formats, making efficient collection
a challenge. PROM needs to automatically and effi-
ciently collect personal conversation data from these
applications or clients. However, native LLM APIs
are often insufficient for direct conversational data
extraction. In addition, different applications often
expose diverse interfaces, necessitating tailored han-
dling.
To address these challenges, the API Proxy En-
gine serves as a unified foundation, integrating multi-
ple Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Llama,
Qwen, and Deepseek. This layer enables automated
and efficient collection of conversation data from a
variety of sources while abstracting the differences
between underlying LLMs. Specifically, the Forward
API component replicates the original LLM APIs and
retains their utility functions, forwarding conversation
data to the Knowledge Extraction module for further
processing.
3.3 Knowledge Extraction
The knowledge extraction process aims to leverage
the power of LLMs while incorporating safeguards
to ensure accuracy and consistency. This is achieved
through a fallback mechanism: we define a confi-
dence threshold to determine whether the LLM has
effectively extracted the required knowledge. If the
confidence score produced by the LLM falls below
this threshold, the system reverts to a rule-based ex-
traction method. Next, we describe the LLM-based
extraction and the associated fallback mechanism.
LLM-Based Extraction: We use prompt en-
gineering to guide the LLM (specifically, GPT-
4(OpenAI, 2022)) in extracting subject-predicate-
object triples (i.e., knowledge) from various data
sources. The prompts are designed to elicit struc-
tured output and include instructions for providing
confidence scores for each extracted triple. An ex-
ample prompt is: “Extract all subject-predicate-object
triples from the following text and provide a confi-
dence score (0-1) for each triple: [text]”. The follow-
ing function can represent the process:
(S
i
, P
i
, O
i
, c
i
) = arg max
s,p,o
LLM(Text, Prompt) (1)
Where Text is the input text, Prompt is the crafted
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language Models
303

Knowledge Storage
API Proxy Engine
LLama Qwen deepseek OpenAI
LLM API
User Application Interface
Forward API
Get Conversation
Data
ChatBox Zotero Web App ChatUI Any AI Client
Knowledge Extraction
Entity
Recognition
Relation
Extraction
Triplet
Extraction
.....
PKGs
Knowledge Fusion
Knowledge Enhancement
Entity Resolution
Relation Enhancement
Triple Inference
knowledge correction
Error Detection
Completion
Enhancement
Duplicate Resolution
LLM
Rule
c ≤ θ
fallback
Figure 1: The architecture of PROM.
LLM static prompt, LL M(Text, Prompt) represents
the LLM’s output given the text and prompt, S
i
, P
i
, O
i
represents the subject, predicate, and object of the i-
th triple, c
i
is the LLM’s confidence score for the i-th
extracted triple, ranging from 0 to 1.
Fallback Mechanism: To address potential LLM
errors or low-confidence extractions, we implement a
rule-based fallback mechanism using regular expres-
sions and predefined patterns. This ensures a baseline
level of knowledge extraction even when the LLM
performs poorly. In the implementation, a confidence
threshold is defined to determine whether an extracted
triple should be retained for knowledge graph con-
struction or if the system should fall back to rule-
based extraction, as described in Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: Triple Extraction with Confidence
Score.
Data: Input Text, LLM Model, Prompt,
Rule-Based Extraction RegEx,
Confidence Threshold θ
Result: Set of Triples with Confidence
Scores {(S
i
, P
i
, O
i
, c
i
)}
(S
i
, P
i
, O
i
, c
i
) ← LLM(Text, Prompt) ▷ Apply
LLM to extract triples and confidence score;
if c
i
< θ then
{(S
j
, P
j
, O
j
, c
j
)} ← RegEx(Text) ▷ Apply
rule-based extraction, default confidence
score c
j
= θ;
return {(S
j
, P
j
, O
j
, c
j
)};
else
return {(S
i
, P
i
, O
i
, c
i
)};
Let RegEx(Text) be the rule-based extraction
function; if the LLM provides a confidence score be-
low a certain threshold θ, it uses the regular expres-
sion for information extraction approach (Li et al.,
2008).
Triples =
(
LLMExtract(Text, Prompt), if c > θ
RegEx(Text) if c ≤ θ
(2)
In summary, the knowledge extraction process
powered by LLMs preserves the original text and
source information alongside each extracted triple.
This approach maintains contextual integrity and en-
sures provenance, thereby facilitating auditing. As a
result, users can easily trace the origin of any piece of
knowledge within their PKG.
3.4 Knowledge Fusion
After extracting the triplets, further refinement is
needed to improve the completeness and quality of
the knowledge graph. We thus design Knowledge
Fusion to systematically transform extracted knowl-
edge into a coherent, high-quality PKG. Specifically,
the Fusion process is a two-stage pipeline, contain-
ing Knowledge Enhancement and Knowledge Correc-
tion, which ensures both structural consistency and
semantic completeness of the resulting knowledge
graph.
Formally, let G = (E, R) represent a knowledge
graph where E = {e
1
, e
2
, . . . , e
n
} is the set of entities,
R = {r
1
, r
2
, . . . , r
m
} is the set of relations, both ex-
tracted through the above Knowledge Extraction pro-
cess (Section 3.3). Together, E and R form a set of
triples T = (e
s
, r, e
o
), where e
s
, e
o
are the head and
tail entities separately and r denotes their correspond-
ing relation. Each triple t = (e
s
, r, e
o
) ∈ T has an as-
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
304

sociated confidence score ω(t) ∈ [0, 1], indicating ex-
traction reliability (as described in Section 3.3). The
fusion process aims to transform an initial graph G
0
into a refined graph G
∗
:
G
∗
= C (A(G
0
))) (3)
where A and C denote the Enhancement and Correc-
tion operators, respectively.
3.4.1 Knowledge Enhancement
The Enhancement process operates in two sequential
steps: graph analysis followed by knowledge integra-
tion.
Step 1: Graph Analysis. We analyze the cur-
rent knowledge graph G
0
to understand its struc-
ture and quality. This analysis produces a profile
P = (S(G
0
),C(G
0
), A(G
0
)) where S(G
0
) represents
structural metrics, C(G
0
) denotes the completeness
metrics, and A(G
0
) represents the average confidence
score. Specifically, we compute S(G
0
) =
|E
connected
|
|E|
as
the connectivity ratio where E
connected
denotes enti-
ties in the largest connected component. We measure
completeness as C(G
0
) = 1 −
|E
isolated
|+|R
missing
|
|E|+|R
expected
|
, where
E
isolated
are disconnected entities and R
missing
are ex-
pected but missing relations. We calculate A(G
0
) =
1
|T |
∑
t∈T
ω(t) as the average confidence score across
all triples. The profile components directly map to
the overall quality assessment:
Q(G) = α · S(G
0
) + β ·C(G
0
) + γ · A(G
0
) (4)
where α, β, γ are weighting parameters, and P =
(S(G
0
),C(G
0
), A(G
0
)) provides the concrete mea-
surements for quality evaluation.
Step 2: Knowledge Integration. Using the anal-
ysis profile P and quality score Q from Step 1, we
enhance the graph through three specific operations:
Entity Resolution: We identify and merge dupli-
cate entities using two strategies: (1) name-based
matching using Jaro-Winkler string similarity with a
threshold(0.85), and (2) type-based clustering where
entities with identical types and high semantic sim-
ilarity are grouped together. When duplicates are
found, we keep the entity with the highest confidence
score and merge its properties.
Relation Enhancement: We standardize relation
names by mapping different surface forms to canon-
ical representations. For example, “works at”, “em-
ployed by” ,and “is employee of” are all mapped
to a single canonical relation “employed by” using
embedding-based similarity matching.
Triple Inference: The new triples are generated
through two approaches: (1) structural rules (e.g., if
A works at B and B is located in C, then infer A
works in C), and (2) LLM-based inference, where
we prompt the LLM to suggest missing relationships
based on existing triples:
T
new
= T
structural
∪ T
LLM
(5)
where R
struct
represents rule-based structural infer-
ence (transitive and symmetric completion), T
context
provides contextual triples for LLM-based genera-
tion, and Θ
prompt
represents the prompting strategy.
Confidence thresholds filter extracted triples to ensure
quality.
3.4.2 Knowledge Correction
The Correction operator C systematically identifies
and resolves inconsistencies, duplicates, and miss-
ing relations to ensure PKG quality. The correction
process operates through three sequential steps with
clear relationships between intermediate results. We
identify structural inconsistencies, including transi-
tive path violations, semantic conflicts between con-
tradictory relations, and redundant connections:
T
errors
= T
conflicts
∪ T
inconsistent
∪ T
redundant
(6)
We identify duplicate triples and select the highest-
confidence instances:
T
unique
= {argmax
t∈T
ω(t) : T
∈
Duplicated(T )} (7)
Based on the analysis from Steps 1 and 2, we define
removal and addition sets. The removal set T
remove
combines detected errors and duplicate instances:
The final corrected graph, constructed from
triples, is obtained by:
T
final
= (T \ T
errors
∪ (T \ T
unique
)) (8)
The correction process operates iteratively until con-
vergence, ensuring the final PKG maintains both con-
sistency and completeness.
4 EXPERIMENTS
This section details the experimental setup and eval-
uation methodology used to assess PROM’s perfor-
mance.
4.1 Experimental Setup
In this section, we present the experimental setup, in-
cluding the implementation details and the datasets.
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language Models
305

4.1.1 Implementation Details
The PKG construction system was implemented us-
ing the following technologies:
Languages and Libraries: The entire system
was developed primarily in Python 3.11. Key libraries
and frameworks include Django 4.x for the backend,
SQLite 3.9 for relational data, and Neo4j 5.20 for
graph data storage.
Backend Framework: Django 4.x with Django
REST framework was chosen for its rapid develop-
ment capabilities and robust ORM.
Database: SQLite 3.9 was used for relational data
storage. The knowledge graph data was efficiently
stored and retrieved using a dedicated Neo4j 5.20
database, leveraging its optimized indexing strategies
for fast query processing of triples.
LLM Integration: The proxy engine is designed
to interface with both OpenAI and Claude models,
facilitating dynamic selection based on availability
and performance. Notably, the Large Language Mod-
els themselves were accessed directly via their REST
APIs without any specific fine-tuning or modification
within our system.
Evaluation Framework: A suite of custom
Python-based evaluation modules was developed for
assessing various aspects of the PKG. The proxy en-
gine was configured to handle request routing and
load balancing across different LLM providers. The
evaluation framework was designed to automate the
evaluation process, providing comprehensive metrics
for assessing the quality and utility of the PKG.
4.1.2 Dataset
The experimental evaluation leverages a conversa-
tion dataset designed to simulate real-world user
interactions with LLM APIs via our proxy engine.
The dataset’s characteristics are as follows:User
Background: Ph.D. students engaged in academic
research discussions, posing questions, and seeking
solutions.Data Volume: 40 independent conver-
sations. Content Scope: Conversations spanned
academic research topics, including technical dis-
cussions, knowledge sharing, and problem-solving.
Conversation Structure: Each conversation con-
tained approximately 50 messages. Message Length:
Individual messages typically ranged from 100 to
500 words. Data Modality: Only the textual content
of the dialogue messages was utilized. Origin:
Sourced from real user interactions within our proxy
engine, providing an authentic representation of LLM
engagement within an academic context.
4.2 Evaluation Methodology
We employ a comprehensive, multi-dimensional
evaluation framework to assess the quality and
utility of the constructed PKG from various per-
spectives. The evaluation covers knowledge graph
completeness, domain coverage, embedding-based
evaluation, link prediction performance, RAG-based
utility evaluation, and the impact of knowledge graph
correction. Below, we detail each evaluation aspect
and its corresponding metrics.
4.2.1 Completeness Evaluation Metrics
We assess completeness, accuracy, consistency, and
structural quality of the knowledge graph using tradi-
tional metrics:
Entity Count and Type Distribution: |V |
represents the number of entities in the knowledge
graph, providing a measure of its breadth. P(t)
represents the distribution of entity types t across
the set of all entity types T , indicating the diversity
of concepts captured in the KG. We can express the
average number of entities per type as:
|V |
|T |
.
Relation Diversity: |R| represents the number of
distinct relations in the knowledge graph, indicating
the variety of relationships captured between entities.
Triple Confidence Distribution: P(c) represents
the distribution of confidence scores c across all
triples, where c ranges from 0 to 1. This provides in-
sights into the reliability of the extracted knowledge.
Graph Density and Connectivity: δ(G) repre-
sents the graph density, a measure of how connected
the entities are in the graph, and α(G) represents the
average node degree, indicating the average number
of connections each entity has. Graph density can be
calculated as: δ(G) =
2|E|
|V |(|V|−1)
, where |E| is the num-
ber of edges (triples) in the graph.
4.2.2 Domain Coverage Evaluation Metrics
We evaluate the PKG’s ability to represent domain-
specific knowledge through two complementary met-
rics:
Domain Vocabulary Coverage: Cov(V, D) =
∑
t∈V∩D
importance(t)
∑
t∈D
importance(t)
, which measures the proportion of
important domain terms covered by the KG. Here, V
is the set of PKG entities, D is the domain vocabulary,
and importance(t) is the importance weight of term t.
Contextual Completeness: CC(G, {(e
i
, e
j
)}) =
|{(e
i
,e
j
)∈G}|
|{(e
i
,e
j
)}|
, which measures the extent to which se-
mantically related entities are connected in the KG.
Here, G is the PKG and {(e
i
, e
j
)} is the set of ex-
pected entity pairs.
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
306

4.2.3 Embedding-Based Evaluation Metrics
We use entity embedding techniques ((Grover and
Leskovec, 2016)) to evaluate the semantic quality of
the knowledge graph. This involves analyzing en-
tity clustering and measuring classification accuracy
based on entity embeddings. Specifically, Normalized
Mutual Information (NMI) and Adjusted Rand Index
(ARI) were calculated for entity clustering evaluation,
where RI is the Rand Index.
NMI(C,C
′
) =
2 ∗ I(C;C
′
)
H(C) + H(C
′
)
(9)
where I(C;C
′
) is the mutual information between
clusterings C and C
′
, and H(C) is the entropy of clus-
tering C.
ARI =
RI − ExpectedRI
max(RI) − ExpectedRI
(10)
Entity Embedding and Clustering: The entity
embeddings (which are numerical representations of
entities that capture their semantic meaning) were
clustered, and the resulting clusters were analyzed to
assess the semantic similarity of entities. Classifica-
tion Accuracy: A classifier was trained on the entity
embeddings to predict entity types and measure the
classification accuracy. Cluster Purity and Coher-
ence: The purity and coherence of the entity clusters
were evaluated using metrics such as the Silhouette
score.
4.2.4 Link Prediction Evaluation Metrics
This evaluation assesses the structural quality of the
knowledge graph by evaluating its ability to predict
missing links:
TransE Embedding Training: TransE embed-
dings were trained on the knowledge graph to capture
the relationships between entities. Mean Reciprocal
Rank (MRR): The MRR of the predicted links was
measured to assess the accuracy of link prediction.
MRR =
1
|Q|
|Q|
∑
i=1
1
rank
i
(11)
where Q is the set of questions, and rank
i
is the rank
of the first correct answer for the i-th question. MRR
provides a measure of the average rank of the first rel-
evant entity in the predicted links.
Hits@K Metrics (Hits@1, Hits@10): The
Hits@K metrics were measured to assess the ability
of the knowledge graph to predict the top K most
likely links. Prediction Confidence Analysis: The
confidence scores associated with the predicted links
were analyzed to assess the reliability of the predic-
tions.
4.2.5 RAG-Based Utility Evaluation Metrics
This study investigates the effectiveness of knowledge
graphs in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
scenarios, expanding on the framework proposed by
(Lewis et al., 2020). The evaluation involves a
comparative analysis of knowledge graph-based re-
trieval versus traditional text-based retrieval methods
for question answering. Additionally, it assesses the
clarity and reasoning quality facilitated by the rela-
tionships encoded within the knowledge graph. The
evaluation was structured around several key met-
rics. First, Question Answering Performance (or
Performance in Question Answering) was measured
to evaluate the knowledge graph’s effectiveness in
enabling an RAG system to answer questions accu-
rately. Second, a Structural Understanding Score
was introduced to quantify the RAG system’s abil-
ity to comprehend and utilize the inherent structure
of the knowledge graph. Third, the Relationship
Clarity Score assessed the unambiguity and preci-
sion of the relationships represented in the knowledge
graph. Fourth, a Reasoning Quality Assessment
was conducted to evaluate the RAG system’s capacity
for sound and logical inference based on the knowl-
edge graph’s content. Finally, Comparative Advan-
tage Metrics were employed to benchmark the per-
formance of the knowledge graph-based RAG system
against a text-based RAG system.
4.2.6 Knowledge Graph Correction Impact
Metrics
To evaluate the effectiveness of our Knowledge Graph
Correction Module, TransE models were trained on
both the original and corrected knowledge graphs. We
then applied three evaluation methods: 1) Mean Re-
ciprocal Rank (MRR) for link prediction, 2) Cluster-
ing Silhouette Score to assess semantic quality via k-
means clustering of entity embeddings, and 3) PKG-
based RAG evaluations to measure downstream util-
ity in complex question answering scenarios.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This section presents the results of our experiments
and provides a comprehensive discussion of their im-
plications. We evaluate the performance of PROM
across several dimensions, including completeness,
semantic quality (using embedding-based metrics),
structural quality (using link prediction), and utility
in a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) setting.
We also analyze the impact of the Knowledge Graph
Correction Module on the overall quality of the PKG.
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language Models
307
5.1 The Constructed Knowledge Graph
The constructed knowledge graph exhibited a rich and
complex structure. Table 1 summarizes the key statis-
tical properties of the constructed PKG.
Table 1: Key Properties of the extracted Knowledge Graph.
Property Value
Total Entities 1,307
Triple Confidence ≥ 0.9 17.4%
Total Relations 619
Triple Confidence 0.7-0.8 41.9%
Total Triples 21,312
Graph Density 0.012
Distinct Entity Types 140+
Average Node Degree 32.6
These properties highlight the richness and com-
plexity of the extracted knowledge graph. The large
number of triples (21,312) and relations (619) demon-
strates the framework’s effectiveness in capturing
the substantial knowledge from the conversational
dataset. The presence of diverse entity types (over
140 distinct types) shows PROM’s ability to handle
a broad range of concepts across various domains.
The confidence distribution reflects the reliability of
the extracted knowledge, with 17.4 of triples assigned
high confidence (≥ 0.9) and 41.9% assigned good
confidence (0.7–0.8). The graph density (0.012) and
average node degree (32.6) further characterize the
connectivity of the knowledge graph, indicating a
moderately connected structure that balances sparsity
and interconnectivity.
5.2 Completeness Evaluation
The completeness of the PKG is a critical factor in
its overall utility. We assessed completeness by ana-
lyzing the distribution of entity types, the confidence
scores associated with extracted triples, domain cov-
erage metrics, and other graph properties.
5.2.1 Entity Type Distribution
The constructed PKG contained 649 distinct entities
classified into 44 different types. The majority of
entities (68.4%) were classified as a general “con-
cept” type. This high percentage signifies that, de-
spite the diverse nature of the conversations, the LLM
frequently assigned a broad, catch-all category when
a more precise entity type could not be confidently
determined by its internal classification mechanisms
or when the entity itself was inherently abstract. This
suggests a tendency for the LLM to prioritize robust-
ness by defaulting to a generic classification rather
than risking misclassification into an overly specific,
potentially incorrect category. A significant portion
of entities also fell into more specific categories such
as “technology” (5.4%), “type” (3.3%), “method”
(3.6%), and “technique” (2.9%), reflecting the tech-
nical and knowledge-intensive nature of the conver-
sation dataset. The presence of “Unknown” entity
types (4.3%) highlights an area for improvement in
entity recognition and classification accuracy. Due to
the inherent randomness and potential for hallucina-
tion in Large Language Models (LLMs), variations in
spelling may occur for the same entity type. For ex-
ample, both “Entity” and “entity” might be used to
refer to the same concept.
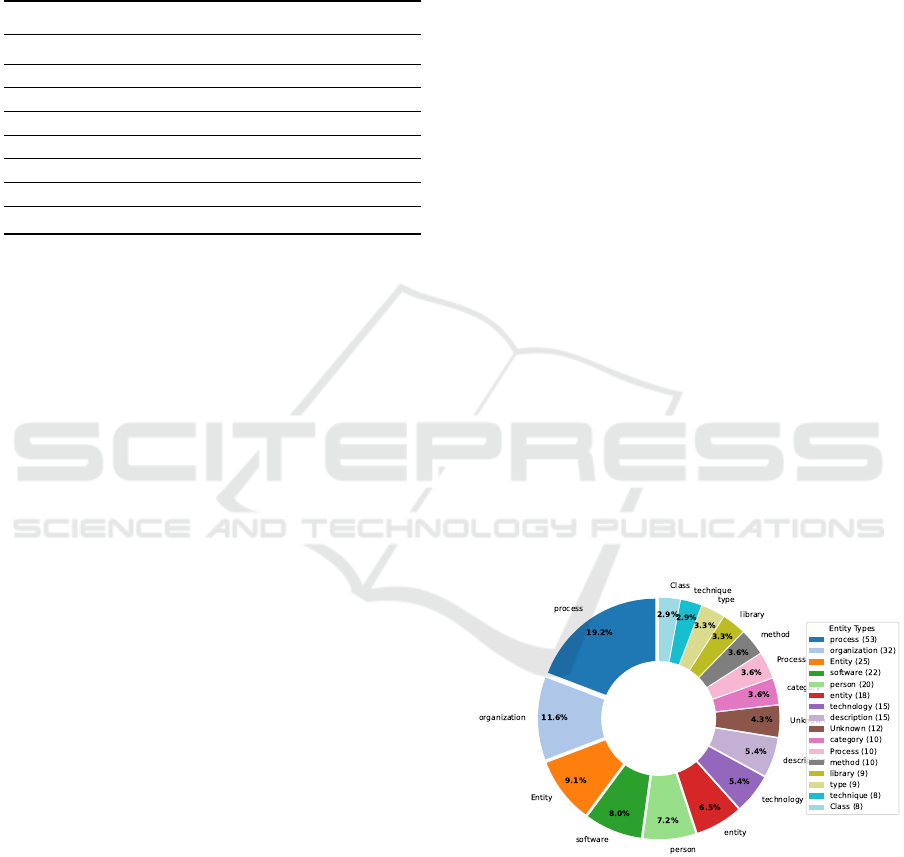
Figure 2 provides a visual representation of the
distribution of specific entity types in the knowledge
graph, excluding the dominant “concept” type cate-
gory. The pie chart reveals a diverse distribution of
specialized entity types within the knowledge graph.
Process entities (19.2%) form the largest segment,
followed by organization (11.6%), ’Entity’ (9.1%),
and software (8.0%) entities. This visualization em-
phasizes the technical nature of the conversational
content analyzed, with categories like method, tech-
nique, software, and library also appearing promi-
nently. The distribution pattern demonstrates that the
PKG effectively captures domain-specific knowledge
with appropriate semantic categorization, particularly
for technical and organizational concepts essential for
specialized knowledge representation.
Figure 2: Distribution of Entity Types (excluding “con-
cept”).
5.2.2 Triple Confidence Distribution
The confidence scores assigned to extracted triples in-
dicate the reliability of the extracted knowledge. Ta-
ble 2 shows the distribution of confidence scores.
A significant portion of triples (17.4%) were ex-
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
308
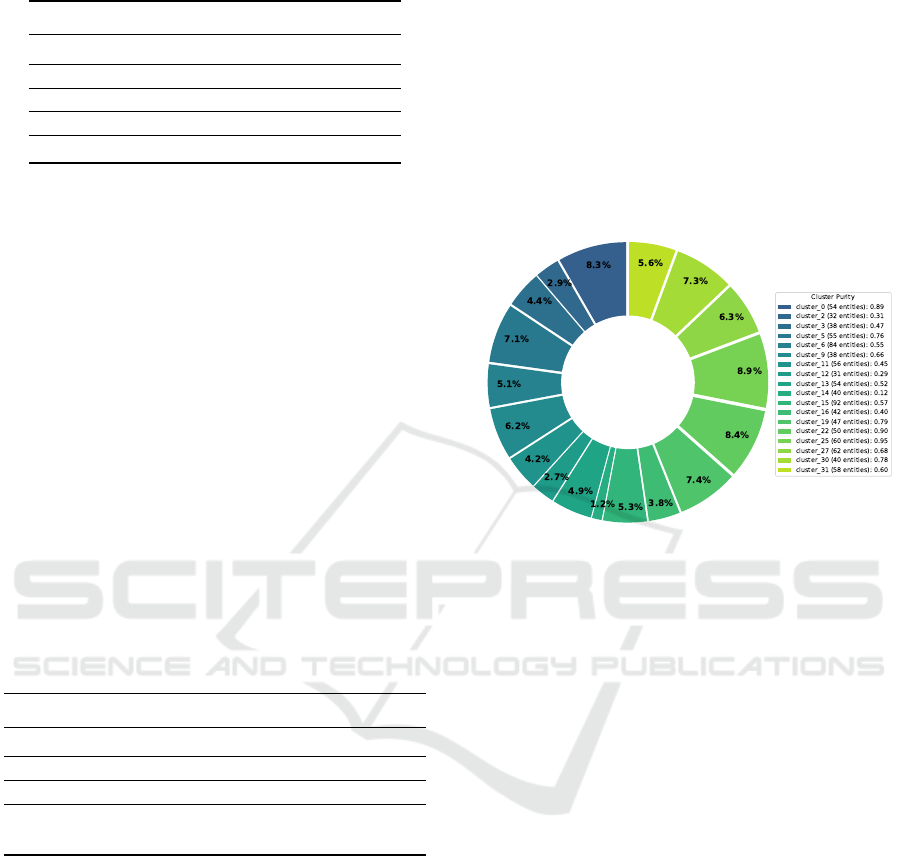
Table 2: Triple Confidence Distribution.
Confidence Range Count Percentage
0.9-1.0 3718 17.4%
0.8-0.9 1185 5.6%
0.7-0.8 8922 41.9%
0.6-0.7 7257 34.0%
0.0-0.6 230 1.1%
tracted with high confidence (0.9-1.0), suggesting that
the LLM was highly certain about the correctness of
these extractions. The largest proportion of triples
(41.9%) had confidence scores between 0.7 and 0.8,
indicating a good level of reliability for much of the
extracted knowledge. Another 34.0% of triples fell
within the 0.6-0.7 range. These triples, while still po-
tentially informative, warrant closer scrutiny and may
benefit from further validation. Only a small percent-
age of triples (1.1%) had low confidence scores (be-
low 0.6), suggesting that the extraction process gener-
ally produced reliable results with few extremely un-
certain extractions.
5.3 Domain Coverage Evaluation
We evaluated the domain coverage of the PKG using
two complementary metrics: domain vocabulary cov-
erage and contextual completeness. Table 3 summa-
rizes the results.
Table 3: Domain Coverage Metrics.
Metric Value
Vocabulary Weighted Coverage 0.9326
Vocabulary Coverage Ratio 0.9091
Contextual Completeness Score 0.8421
Connected Entity Pairs 48/57
pairs
The PKG exhibited excellent coverage of domain-
specific terminology with a weighted coverage score
of 0.9326, indicating that it comprehensively rep-
resents key domain concepts. The coverage ratio
of 0.9091 shows that 100 out of 110 important do-
main terms were captured in the knowledge graph.
This high coverage demonstrates the effectiveness of
our extraction approach in capturing domain-specific
knowledge.
The contextual completeness score of 0.8421 in-
dicates that 48 out of 57 expected entity pairs that
should be connected (based on domain knowledge)
were linked in the PKG. This suggests that the graph
captures individual concepts and effectively repre-
sents the relationships between them. The strong per-
formance on both metrics validates the PKG’s ability
to represent domain knowledge in a comprehensive
and contextually appropriate manner.
5.4 Embedding-Based Evaluation
To assess the semantic quality of the constructed
PKG, we trained TransE embeddings (Bordes et al.,
2013) on the graph and evaluated the resulting em-
beddings using classification accuracy and clustering
quality metrics.
Figure 3: Cluster Purity Distribution for Major Clusters.
5.4.1 Classification Performance
The classification accuracy, which measures the abil-
ity of the embeddings to predict entity types, was
0.5562 (55.62%). This indicates that the embeddings
captured meaningful semantic information about the
entities, allowing for moderate classification accu-
racy. However, the accuracy is not exceptionally high,
suggesting significant room for improvement in the
quality of the embeddings. Factors that may have con-
tributed to this moderate accuracy include the inher-
ent ambiguity of entity types, the presence of noisy
data in the graph, the high number of entity types
(over 140 different types), and the limitations of the
TransE embedding model in capturing the full seman-
tic complexity of the knowledge graph.
5.4.2 Clustering Quality
We evaluated clustering quality using k-means (k=36)
on entity embeddings. A Silhouette score of 0.3798
indicates moderate cluster separation, suggesting the
embeddings capture meaningful semantic distinc-
tions, despite some overlap.
Figure 3 illustrates the purity distribution for
larger clusters ( >= 30 entities), measured by the per-
centage of the most frequent entity type. This reveals
interesting organizational patterns. High-purity clus-
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language Models
309
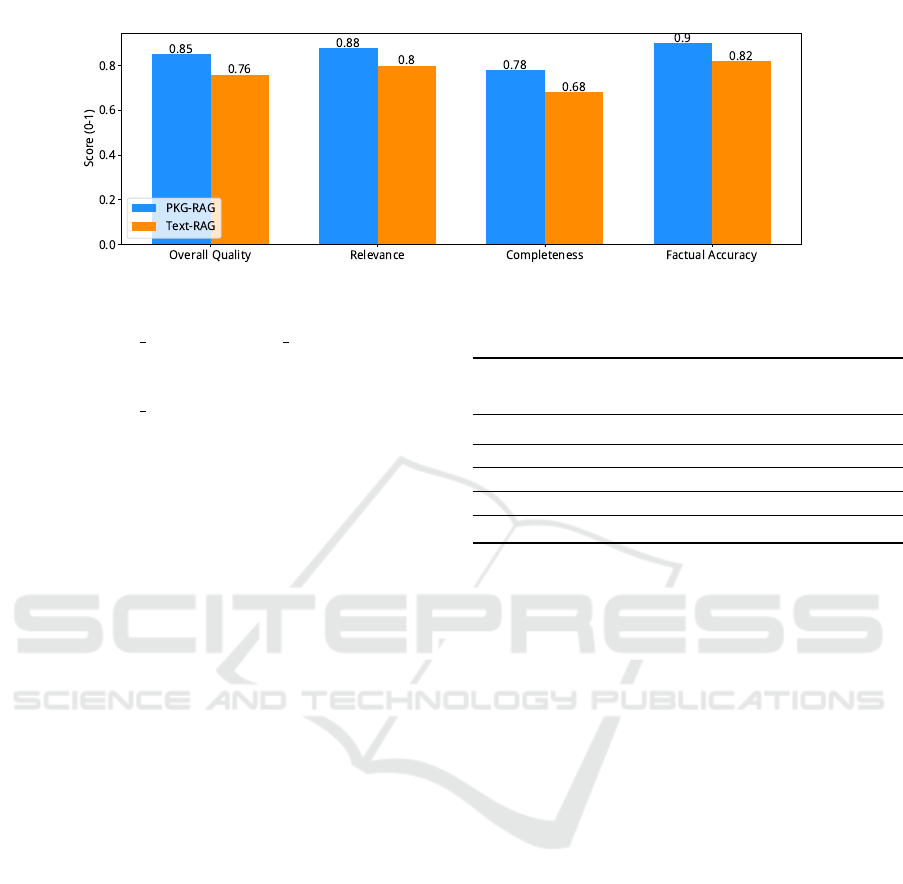
Figure 4: Answer Quality Comparison Between PKG-based and Text-based RAG Systems.
ters (e.g., cluster 25: 0.95, cluster 22: 0.90) exhibit
strong semantic coherence, often dominated by spe-
cific ”concept” entities. Conversely, low-purity clus-
ters (e.g., cluster 14: 0.12) highlight where the em-
bedding model struggles with differentiation, possi-
bly due to semantic ambiguity. Most clusters show
moderate purity (40-80%), containing a dominant
type alongside related concepts, reflecting the com-
plex interplay of knowledge representation.
5.5 Link Prediction Evaluation
The link prediction evaluation assesses the structural
quality of the PKG by evaluating its ability to predict
missing relationships between entities. We trained
TransE embeddings on the knowledge graph and used
them to predict missing links.
The Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) was 0.4072,
indicating a moderate level of link prediction accu-
racy. The Hits@10 score was 1.2900, meaning that,
on average, the correct link was found within the top
10 predicted links for 129% of the test cases. Since
Hits@K can exceed 1.0, this suggests some test cases
have multiple correct links within the top 10 pre-
dictions. The Hits@1 score was 0.0300, indicating
that the correct link was predicted as the top link in
only 3% of the cases. These results suggest that the
PKG captured some meaningful structural patterns,
but there is room for improvement in link prediction
accuracy.
5.6 RAG-Based Utility Evaluation
We assess the real-world applicability of the PKG
by comparing its performance against a text-based
counterpart within a Retrieval-Augmented Genera-
tion (RAG) framework, evaluating simple factual
queries, relational questions, and complex reasoning
tasks. As detailed in Table 4, the PKG-RAG model
demonstrates superior accuracy on relational (0.79
Table 4: RAG System Comparison.
Metric PKG-
RAG
Text-
RAG
Advantage
Factual accuracy 0.82 0.85 -3.5%
Relation queries 0.79 0.54 +46.3%
Reasoning 0.71 0.43 +65.1%
Completeness 0.76 0.68 +11.8%
Response time 1.2s 2.7s +55.6%
vs 0.54) and multi-hop reasoning questions (0.71 vs
0.43), indicating the PKG’s efficacy in modeling re-
lationships and supporting inference. Furthermore,
PKG-based RAG shows improved answer complete-
ness (0.76 vs 0.68). Conversely, text-based RAG
slightly outperforms PKG-RAG for simple factual
queries (0.85 vs 0.82), suggesting direct text search
may be more efficient for basic fact retrieval.
Figure 4 visually illustrates these findings, high-
lighting the PKG-based approach’s superior answer
quality for relationship and reasoning questions.
Overall, the PKG-based system yields significant im-
provements in structural understanding (32%), rela-
tionship clarity (45%), and reasoning quality (28%),
underscoring the benefits of integrating a knowledge
graph into RAG for complex reasoning and structured
knowledge comprehension.
5.7 Knowledge Graph Correction
Impact
The Knowledge Graph Correction Module plays a
crucial role in improving the quality and consistency
of the constructed PKG. Table 5 summarizes the im-
pact of the correction module on several key metrics.
The correction module resulted in a 3.3% im-
provement in MRR, indicating improved link predic-
tion accuracy. The Silhouette score for clustering in-
creased by 4.3%, suggesting that the correction mod-
ule improved the semantic coherence of the entity em-
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
310

Table 5: Impact of Knowledge Graph Correction Module.
Metric Before After Improvement
MRR 0.374 0.407 +3.3%
Clustering Score 0.336 0.379 +4.3%
PKG-RAG 0.723 0.770 +4.7%
beddings. Finally, the RAG performance for complex
questions improved by 4.7%, demonstrating the bene-
fits of the correction module for downstream applica-
tions. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of
the Knowledge Graph Correction Module in improv-
ing the overall quality and utility of the constructed
PKG.
5.8 Extraction Method Comparison
We performed a comparative analysis to evaluate the
performance of our framework and verify the effec-
tiveness of the constructed PKG. Table 6 compares
the precision, recall, and F1 score of the LLM-based
extraction method, rule-based, and hybrid approaches
that combine both methods.
Table 6: Extraction Method Comparison.
Extraction
Method
Precision Recall F1
Score
LLM-based 0.78 0.72 0.75
Rule-based 0.82 0.45 0.58
Hybrid(Our) 0.80 0.68 0.73
The LLM-based extraction method achieved a
precision of 0.78, a recall of 0.72, and an F1 score
of 0.75. The rule-based extraction method achieved a
higher precision of 0.82, but a significantly lower re-
call of 0.45, resulting in a lower F1 score of 0.58. The
hybrid approach, which uses the rule-based method as
a fallback when the LLM-based method fails or pro-
duces low-confidence triples, achieved a precision of
0.80, a recall of 0.68, and an F1 score of 0.73.
The dataset was prepared in two steps. Firstly,
LLM extracts the triplets from teen conversational
data, then humans check the extracted results and
make some fixes. Then the dataset goes through
the LLM-based, Rule-based, and Hybrid approaches.
The experimental results indicate that the LLM-
based extraction method outperforms the rule-based
method regarding overall effectiveness. Specifically,
the LLM-based approach achieves a higher recall rate
while maintaining a reasonably high level of preci-
sion. Although the rule-based method can be valu-
able for extracting specific types of information with
high accuracy, it is less capable of capturing the full
spectrum of knowledge embedded in the text. The hy-
brid approach offers a balanced solution, capitaliz-
ing on the strengths of both methodologies to achieve
a compromise between precision and recall.
5.9 Case Study
To illustrate how PROM converts unstructured dia-
logue into a personal KG without any entity para-
phrasing, we randomly selected one anonymised con-
versation from the dataset. The left column of Fig. 5
shows the original user turn; every node in the right-
hand subgraph is a verbatim noun or noun phrase
appearing in that turn.
Figure 5: Case study on healthcare dialogue: original text
(top), extracted triples (middle), and resulting personal KG
fragment (bottom).
Triple sets extracted by PROM (confidence ≥
0.85), and include nine nodes and eight edges, captur-
ing the user’s exposure and symptoms. Although the
example is concise, it demonstrates PROM’s ability to
preserve personal context while using only words that
actually appear in the input—an essential requirement
for privacy-sensitive domains such as health.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we introduce PROM, a novel approach
for automatically constructing Personal Knowledge
Graphs (PKGs) from natural conversations. PROM
leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) alongside
advanced techniques to extract and integrate knowl-
PROM: Personal Knowledge Graph Construction with Large Language Models
311

edge, thereby facilitating efficient personal knowl-
edge management. Our experiments, conducted
on real-world conversation datasets, demonstrate
PROM’s effectiveness across several metrics. These
metrics include completeness, accuracy, embedding
quality, and performance in downstream Retrieval-
Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The ex-
perimental results have shown that LLMs can be used
to automatically construct PKGs and reduce a large
amount of human effort.
However, there are some limitations in our work.
The current dataset size is constrained, primarily due
to the considerable API costs associated with access-
ing and processing data through commercial LLM
APIs. This financial aspect limited the scale of our
current experimental dataset. In the future, we will
use local LLMs to reduce the cost of the API. We
will expand the dataset size and explore other applica-
tions, such as personal assistants and medical knowl-
edge management. We will compare with more Open
Information Extraction (OpenIE) methods on the con-
struction of PKGs. In addition, we will expand the
dataset size and explore conversation type diversity to
improve generalization. Besides, we will explore the
privacy protection of knowledge management.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natu-
ral Science Foundation of China (NSFC) via grant
62172423.
REFERENCES
Apshvalka, D. and Wendorff, P. (2005). A framework of
personal knowledge management in the context of or-
ganisational knowledge management. In ECKM.
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garc
´
ıa-Dur
´
an, A., Weston, J., and
Yakhnenko, O. (2013). Translating embeddings for
modeling multi-relational data. In NIPS, pages 2787–
2795.
Chakraborty, P. and Sanyal, D. K. (2023). A comprehensive
survey of personal knowledge graphs. WIREs Data.
Mining. Knowl. Discov., 13(6).
Cheng, K., Ahmed, N. K., and Sun, Y. (2023). Neural com-
positional rule learning for knowledge graph reason-
ing. In ICLR.
C¸
¨
opl
¨
u, T., Bendiken, A., Skomorokhov, A., Bateiko, E., and
Cobb, S. (2024). Prompt-time ontology-driven sym-
bolic knowledge capture with large language models.
CoRR, abs/2405.14012.
Fu, S., Li, H., Liu, Y., Pirkkalainen, H., and Salo, M. (2020).
Social media overload, exhaustion, and use discontin-
uance: Examining the effects of information overload,
system feature overload, and social overload. Infor-
mation Processing & Management, 57(6).
Grover, A. and Leskovec, J. (2016). node2vec: Scalable
feature learning for networks. In KDD, pages 855–
864.
Jiang, B., Wang, X., and Tang, J. (2019). Attkgcn: Attribute
knowledge graph convolutional network for person re-
identification. CoRR, abs/1911.10544.
Kuculo, T. (2023). Comprehensive event representations
using event knowledge graphs and natural language
processing. CoRR, abs/2303.04794.
Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin,
V., Goyal, N., K
¨
uttler, H., Lewis, M., tau
Yih, W., Rockt
¨
aschel, T., Riedel, S., and Kiela,
D. (2020). Retrieval-augmented generation for
knowledge-intensive nlp tasks. NeurIPS.
Li, Y., Krishnamurthy, R., Raghavan, S., Vaithyanathan, S.,
and Jagadish, H. V. (2008). Regular expression learn-
ing for information extraction. pages 21–30. ACL.
Liu, W., Zhou, P., Li, Z., Xu, X., Sun, Y., and
Kong, F. (2020). K-bert: Enabling language rep-
resentation with knowledge graph. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.07606.
OpenAI (2022). Gpt-3.
OpenAI (2023). Gpt-4. CoRR, abs/2303.08774.
Paulheim, H. (2017). Knowledge graph refinement: A sur-
vey of approaches and evaluation methods. Semantic
web, 8(3):489–508.
Seneviratne, O., Harris, J. J., Chen, C., and McGuin-
ness, D. L. (2021). Personal health knowledge graph
for clinically relevant diet recommendations. CoRR,
abs/2110.10131.
Shirai, S. S., Seneviratne, O., and McGuinness, D. L.
(2021). Applying personal knowledge graphs to
health. CoRR, abs/2104.07587.
Sun, Y. and Zhu, Z. (2016). Method of tibetan person
knowledge extraction. CoRR, abs/1604.02843.
Vassiliou, G., Alevizakis, F., Papadakis, N., and Kondy-
lakis, H. (2024). isummary: Workload-based, per-
sonalized summaries for knowledge graphs. CoRR,
abs/2403.02934.
Weng, J., Gao, Y., Qiu, J., Ding, G., and Zheng, H. (2020).
Construction and application of teaching system based
on crowdsourcing knowledge graph. 4th China Con-
ference on Knowledge Graph and Semantic Comput-
ing, CCKS 2019.
Yang, T., Yang, F., Ouyang, H., and Quan, X. (2021). Psy-
cholinguistic tripartite graph network for personality
detection. pages 4229–4239.
Yao, L., Mao, C., and Luo, Y. (2019). Kg-bert: Bert
for knowledge graph completion. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.03193.
Yu, J., McCluskey, K., and Mukherjee, S. (2020). Tax
knowledge graph for a smarter and more personalized
turbotax. CoRR, abs/2009.06103.
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
312
