
Application of Planned Behaviour Theory in Chinese Market
Yixin Dong
a
Qingdao Innovation School of Qingdao Experimental High School Education Group,69 Shuoyang Road, Qingdao, China
Keywords: Theory of Planned Behaviour, Cultural Differences, Foreign Exchange Market, Investment Decision,
Behavioural Preference.
Abstract: The Theory of Planned Behaviour, as a famous theory used to predict behaviour, also takes part in Chinese
economic market. This study aims to explore the application of TPB theory in specific research aspects such
as Chinese stock market, fund investment and personal finance and analyse the influencing factors and
mechanisms of specific research variables such as investor sentiment, risk appetite and investment decision.
This essay begins with the introduction of basic definition of TPB theory and connect them with investment
decision and actual behaviour. Furthermore, this research explores and lists the limitation of TPB theory and
provide future solution eventually. This research improves the universality and flexibility of its findings,
guaranteeing their application in distinct culture and policy contexts by including the surveys from other
countries. Ultimately, the significance and future expectations of theory and practice are discussed, expanding
the application of TPB theory with other fields. These results help to deepen the understanding of investor
behaviour and provide theoretical basis for financial institutions to formulate marketing strategies and investor
education programs.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the financial market which full of uncertainty, the
decision-making behaviour of investors directly
influents asset prices and market efficiency.
Traditional financial theory assumes that investors
are perfectly rational and can make optimal decisions
based on diverse available information. However,
more and more empirical studies show that investor
behaviour often deviates from rational expectations,
showing various cognitive biases and emotional
characteristics.
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB), which
proposed by Icek Ajzen in 1991, is an important
theoretical framework for explaining and predicting
human behaviour in the field of social psychology
(Ajzen & Driver, 1992). TPB theory is a variant of
Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), which mentioned
by Ajzen and Fishbein, means that an individual's
behavioural intention for a particular behavioural
preference is influenced by the subjective norms of
whether the individual agrees with the attitude and
whether others support it. Although TRA has
considerable explanatory power for the behaviour
decision-making process, it is still limited (Hassan et
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-0718-329X
al., 2015). In reality, many behaviours are not
completely controlled by one's own will. Therefore,
Azen made improvements based on TRA and
proposed the TPB. The biggest difference between
planned behaviour theory and rational behaviour
theory is that planned behaviour theory overcomes
the limitation that rational behaviour theory cannot
reasonably explain behaviours that are not completely
controlled by will, and adds PBC (perceived control
belief) variables representing other irrational factors
into the original theoretical framework. Form TPB.
Therefore, when analysing behavioural intention and
actual behaviour, planned behaviour theory is
influenced not only by attitude and subjective norm,
but also by perception of behavioural control.
2 DEFINITIONS OF TPB
THEORY
Traditional TPB has focused primarily on cognitive
factors (attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived
behavioural control), but in recent years research has
begun to incorporate affective factors into models. To
be specific, an individual's emotional echoes to an
Dong, Y.
Application of Planned Behaviour Theory in Chinese Market.
DOI: 10.5220/0013829500004719
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics (ICEML 2025), pages 5-9
ISBN: 978-989-758-775-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
5
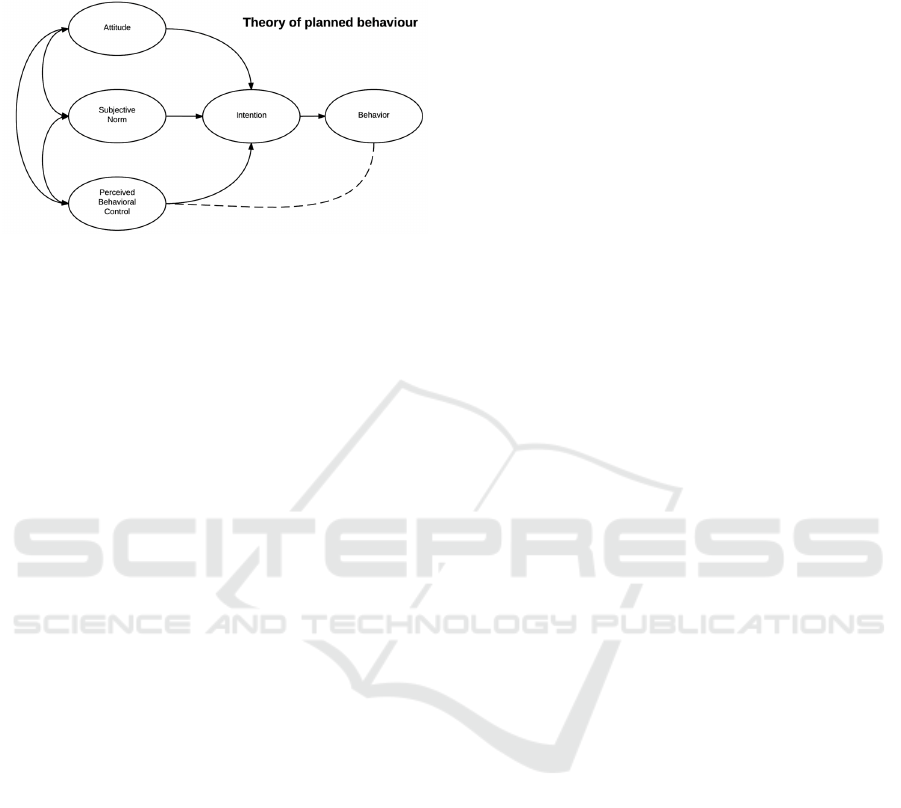
action may significantly influences behavioural intent
and actual behaviour. The research framework of this
theory is shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: Key Component (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Nowadays, TPB theory is applicated increasingly
in investment field in order to explain and predict
decision-making behaviour of investors. Compared to
traditional financial theory, TPB theory can better
clarify the irrational components of investor
behaviour, such as herd behaviour, overconfidence
and loss aversion (Ajzen, 2020). TPB believes that
behavioral intention is the result of attitude,
subjective norm and perceived behavioral control,
and behavioral intention is a key factor in predicting
actual behaviour. TPB theory provides a new way to
understand market anomalies, formulate investment
strategies and educate investors by analysing
investors' behaviour attitudes, subjective norms and
perceived behaviour control (Lacasse et al., 2024).
3 THE INFLUENCE OF TPB
THEORY IN CHINA'S
INVESTMENT DECISION
TPB theory has a reflective influence on the decision-
making mode of Chinese investors. Investors are able
to evaluate their own decision-making process more
completely by introducing concepts such as attitudes,
subjective norms, and perceived behavioural control.
For instance, in stock investment decisions, TPB
theory can help investors identify and correct
cognitive biases such as overconfidence and herding.
In the aspect of risk management, the application
of TPB theory has also achieved significant results.
TPB theory can help investors formulate and improve
more reasonable risk control strategies through
developing investors' awareness of their own control
ability. However, the common risk aversion tendency
of Chinese investors might influence the application
effect of TPB theory, which needs to be adjusted and
optimized in practice (Kobbeltved & Wolff, 2009).
4 THE INFLUENCE OF
CULTURAL DIFFERENCES ON
THE APPLICATION OF TPB
THEORY
Diverse Cross-cultural have slightly different
responding norms into the theory of planned
behaviour. The characteristics of Chinese culture
have exerted an important impact on the application
of TPB theory. Collectivist tendencies are a
prominent feature of Chinese culture, which can
make investors more susceptible to social norms and
the opinions of others, thus influencing their
investment decisions. To be specific, in the stock
market, Chinese investors may be more inclined to
follow "expert" opinions or popular choices, a pattern
of behaviour that requires special concern according
to the framework of TPB theory.
Risk aversion is another important characteristic
of Chinese investors. This cultural tendency may
influence investors' assessment of risk perception and
control ability, thus affecting the application effect of
TPB theory (Morren & Grinstein, 2021). In practice,
it is necessary to adapt the theory to the risk appetite
of Chinese investors in order to improve the
applicability and prediction accuracy of TPB theory.
5 THE APPLICATION OF TPB
THEORY IN CHINA'S
FOREIGN EXCHANGE
MARKET
The uniqueness and complexity of China's foreign
exchange market provide ample research scenarios
for the application of TPB theory. TPB theory shows
significant advantages in forex market forecasting,
which can more accurately predict exchange rate
inclinations and market fluctuations by analysing
investors' attitudes, subjective norms and perceived
behaviour control. Considering the sensitivity of
Chinese investors to policy changes and herd
mentality can improve the accuracy of prediction
when studying the movement of RMB exchange rate.
Based on the theory of Planned behaviour (TPB),
this paper applies it to the study of investors' socially
responsible investing (SRI) behaviour in Chinese
stock market, and discusses the influence of various
factors and extended variables in the TPB model on
investors' SRI intentions and behaviours (Zhang &
Huang, 2024). Despite stock market and forex market,
TPB theory also plays an important role in the real
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
6
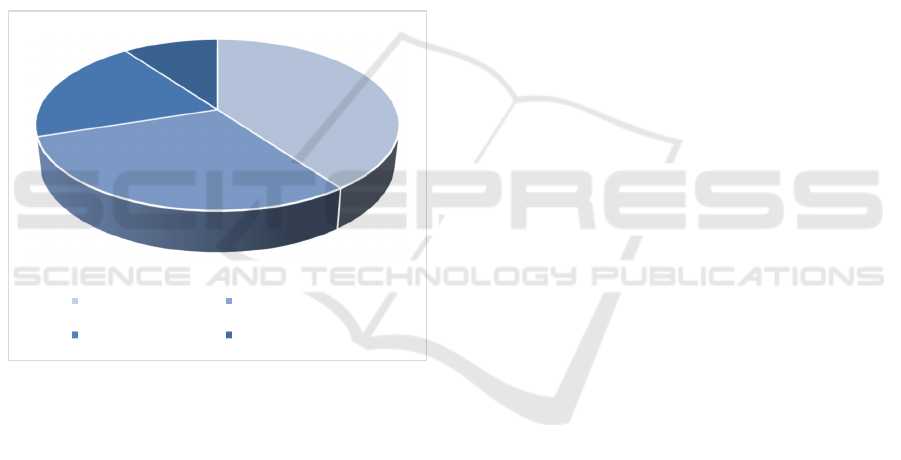
estate market as depicted in Fig. 2. Yanz concluded
in 2024 that the real estate decision affected by
combining the TPB theory with the specific factors,
puts forward the influence of attitude on the purchase
intention (Yanz & Ming, 2024). According to Yanz,
TPB theory helps to fully understand the
psychological and social factors in the decision-
making process of real estate consumers.
However, the application of TPB theory in
China's foreign exchange market also faces some
challenges. China's foreign exchange market is
subject to strict regulation and policy influences,
which can lead to a deviation between investors'
perceived behavioral control and their actual control
ability. In addition, the decision-making process of
Chinese investors may be influenced by traditional
culture and collectivist thinking, which require
special consideration while applying TPB theory.
Figure 2: The application ratio of TPB theory in different
investment fields in China (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
6 LIMITATIONS
Although TPB theory has significant value in
explaining and predicting investment behaviour, it
also has some limitations in its practical application.
These limitations might impress its explanatory
power and predictive accuracy, especially in the
complex Chinese market environment.
Firstly, TPB theory principally focuses on logical
inference, but ignores the influence of external
environmental factors on behaviour. China's
investment market is greatly affected by policies such
as government regulation and monetary policy
changes. These external factors may significantly
affect investor behaviour, but TPB theory does not
directly include these variables. For instance, in real
estate investment, the government's purchase
restriction policy may directly change the behaviour
of investors, and TPB theory is difficult to fully
explain such policy-driven behaviour changes
(Hemavathy Ramasubbian, 2018). Not only China,
but also other developing counties particularly India,
where development of the real estate industry is late,
and attitude is the most important factor affecting the
investment intention of this large population of
individual real estate investors (Singh, 2024).
Furthermore, TPB theory originated in a Western
cultural context, and its core assumptions may not be
fully applicable to markets with collectivist cultural
backgrounds such as China. Chinese investors
generally have a strong tendency of collectivism and
high-risk aversion, and these cultural factors may
significantly correspond to their attitudes, subjective
norms and perceived behaviour control, but TPB
theory does not fully consider these cultural
differences. For instance, Chinese investors tend to
rely more on social norms such as the opinions of
friends and family or expert advice, and TPB theory
may underestimate the importance of such social
effects.
Secondly, TPB theory is limited explanatory
power to dynamic behaviour because it primarily
focuses on behavioral intention at a certain point in
time, but investment behaviour is often dynamic and
impacted by a variety of factors for a long time. The
attitude and behaviour of investors may change over
time, during market fluctuations or economic cycles,
and TPB theory is difficult to capture such kinds of
dynamic changes. Hence, investors' risk appetite may
change significantly after a stock market crash, but
TPB theory cannot directly explain such long-term
behavioral changes.
Thirdly, the measurement of perceived behaviour
control is finite. The "perceived behavioral control"
in TPB theory depends on the subjective judgment of
the individual, but the subjective judgment may be
deviated from the actual control ability (Sniehotta,
Presseau, 2013). Chinese investors may overestimate
or underestimate their ability to control, when
participating in high-risk investments such as peer-to-
peer lending or digital currencies. As a result, this bias
may lead to inaccurate prediction results from TPB
theory. At the same time, TPB theory assumes that
individuals are rational, but in actual investment
behaviour, emotions and irrational factors may have
an important impact on decision-making. Chinese
investors generally have irrational behaviours such as
"chasing up and killing down" and "herding effect",
which are difficult to be fully explained by TPB
stock market forex market
real estate market other market
Application of Planned Behaviour Theory in Chinese Market
7

theory. To be specific, during a stock market bubble,
investors' emotions may dominate their decisions,
and TPB theory cannot directly incorporate sentiment
variables. Change Theories Collection refers that
humans sometimes act emotionally and are not
entirely rational, which makes the rational
assumption of the theory controversial. In addition,
the attitude and behaviours of Chinese investors may
be influenced by social expectation bias, which is a
deviation may lead to inaccurate analysis results of
TPB theory.
TPB theory is of great value in explaining and
predicting investment behaviours, but its limitations
should not be ignored. In the application of the
Chinese market, TPB theory needs to be adjusted and
optimized in combination with localization
characteristics, such as incorporating external
environmental factors, considering cultural
differences, and introducing emotional variables.
Future studies can try to combine TPB theory with
other theories such as behavioral finance and cultural
psychology to improve its explanatory power and
prediction accuracy.
7 PROSPECTS
TPB theory has shown great value in explaining and
predicting investor behaviours, but its application in
the Chinese market still has limitations, and future
research needs to be further explored in the following
directions. TPB theory needs to be combined with
behavioral finance, cultural psychology and other
disciplines to make up for its neglect of emotional
factors and external environment. For example, the
introduction of emotional variables can enhance the
explanatory power of irrational behaviours, while the
framework combined with behavioral finance can
more comprehensively analyse decision changes in
dynamic markets. The collectivist culture and risk
aversion tendency of Chinese market significantly
affect investors' subjective norms and perceived
behaviour control. Future studies need to incorporate
cultural dimensions and traditional values into the
TPB model and develop localized measurement tools
to enhance the applicability of the theory in cross-
cultural scenarios. China's financial market is subject
to strong policy intervention, and these external
factors may weaken the correlation between
perceived behavioral control and actual ability. The
future model should include policy variables to
analyse how they adjust the relationship between
three factors to better fit the realistic scenario.
8 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, TPB theory is of great value in
explaining and predicting investment behaviour, but
it needs to consider the influence of cultural
differences and external environmental factors in its
application in the Chinese market. This article
discussed the key component and fundamental
significance of TPB theory through summarizing
experiments and studies. Even though TPB theory is
one of the primary prediction theories, it has
subjective limitation. The application prospect of
TPB theory will be broader by combining the
characteristics of localization with other theories.
Overall, this research not only responses to previous
studies, but also provides profound collection and
analysis on the relationship between behaviour and
TPB theory, contributing precious insights to the
fields of Chinese market.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I., 2020. The theory of planned behavior: Frequently
asked questions. Human behavior and emerging
technologies, 2(4), 314-324.
Ajzen, I., Driver, B. L., 1992. Application of the theory of
planned behavior to leisure choice. Journal of leisure
research, 24(3), 207-224.
Hassan, L. M., Shiu, E., Parry, S., 2015. Addressing the
cross
‐
country applicability of the theory of planned
behaviour (TPB): A structured review of multi
‐
country TPB studies. Journal of Consumer Behaviour,
15(1), 72–86.
Kobbeltved, T., Wolff, K., 2009. The Risk-as-feelings
hypothesis in a Theory-of-planned-behaviour
perspective. Judgment and Decision Making, 4(7),
567–586.
Lacasse, H., Buzas, J., Kolodinsky, J., Mark, T., Hill, R.,
Snell, W., Darby, H., 2024. Determinants of behavior
towards hemp-based products: an application of the
theory of planned behavior. British Food Journal,
126(13), 394-414.
Morren, M., Grinstein, A., 2021. The cross-cultural
challenges of integrating personal norms into the
Theory of Planned Behavior: A meta-analytic
structural equation modeling (MASEM) approach.
Journal of Environmental Psychology, 75, 101593.
Singh, A., Kumar, S., Goel, U., Johri, A., 2024. Predictors
of investment intention in real estate: Extending the
theory of planned behavior. International Journal of
Strategic Property Management, 28(6), 349–368.
Sniehotta, F. F., Presseau, J., Araújo-Soares, V., 2013. Time
to retire the theory of planned behaviour. Health
Psychology Review, 8(1), 1–7.
ICEML 2025 - International Conference on E-commerce and Modern Logistics
8

Yanz, Y., Ming, C. W., 2024. Understanding Consumer
Decision-Making in Real Estate: An Integrative
Analysis using the Theory of Planned Behavior. Journal
of Digitainability Realism & Mastery (DREAM),
3(08), 33–46.
Zhang, X., Huang, C., 2024. Investor characteristics,
intention toward socially responsible investment (SRI),
and SRI behavior in Chinese stock market: The
moderating role of risk propensity. Heliyon, 10(14),
e34230.
Application of Planned Behaviour Theory in Chinese Market
9
