
Research on the Current Situation of Intergenerational Income Flow
and Its Influencing Mechanism
Yuexia Zhang
a
Institute of Quantitative Economics and Statistics, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, 361021, China
Keywords: Intergenerational Mobility, Influencing Mechanism, Multiple Linear Regression.
Abstract: As socialism with Chinese characteristics enters a new era, further deepening reform requires breaking
through the barriers of solidified interests. It is essential to analyze the current situation of inter-generational
income flow, explore the causes of inter-generational income flow. The research first consulted the population
of each administrative region of Xiamen City through the seventh population census data, conducted multi-
stage sampling. It conducted a qualitative and quantitative investigation of the existing state of
intergenerational income flow using a questionnaire survey. Thus, three features of the current state of
intergenerational income flow were obtained: Parents' assistance in children's growth, education and
employment, individuals' views on intergenerational income flow, and their cognition of income comparison.
Then, based on the multiple linear regression model, the influence mechanism of the child income is analyzed.
Additionally, the income elasticity across generations is determined. The findings indicate that the study's
contents have a favorable effect on the offspring's intergenerational income.
1 INTRODUCTION
The primary focus of social mobility research is
intergenerational mobility. Intergenerational income
mobility (IIM) refers to the relationship or elasticity
of children's income to that of their parents. The
situation can reflect the basic order and opportunity
structure of the society as well as the relationship
model between different classes, so it has been paid
much attention.
IIM was mainly studied about human capital
(Becker & Thomes, 1979). At first, in order to
accurately measure IIM, many scholars studied
temporary income bias. Life cycle bias and co-
resident sample bias are used to correct
intergenerational mobility.
To address the issue of temporary income bias,
combined with the theory of permanent income and
reduced the bias caused by short-term fluctuations by
taking the average years of the current income of the
parents as the proxy variable of permanent income
(Solon et al., 1992). Bjorklund corrected the upward
bias of intergenerational income elasticity based on
Solon by using the father's years of education and
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-1690-2745
occupation as instrumental variables (Bjorklund et al.,
1997). About the correction of life cycle bias, Haier
found that the actual income in the early 30s and mid-
40s was used to estimate the minimum bias and was
most suitable for estimating the average income close
to the lifetime (Haider et al., 2006). Co-living sample
selection bias, that is, co-living sample in the same
family can easily lead to high estimation of
intergenerational income elasticity. At present, the
proportion of parents living with their children in
China is gradually declining, and most of the existing
databases conduct unified surveys based on the family
level, which is easy to lead to the situation of
respondents asking more questions than answers,
resulting in large intra-sample bias.
Based on gradually improving the correction of
the bias of income indicators, Dahl proposed to use
the correlation coefficient of intergenerational income
rank as a new measurement index to describe the
intergenerational income relationship (Dahl et al.,
2008). C&H introduced quantile regression of
instrumental variables to further eliminate its bias
(Chernozhukov & Hansen, 2008). Zhang deeply
discussed the impact of education level on the
Zhang, Y.
Research on the Current Situation of Intergenerational Income Flow and Its Influencing Mechanism.
DOI: 10.5220/0013829400004708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy (IAMPA 2025), pages 557-566
ISBN: 978-989-758-774-0
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
557

intergenerational transmission of relative poverty in
rural families (Zhang, 2024). Wang sorted out and
summarized the research results on intergenerational
income mobility (Wang Shanshan, 2023). Levi found
that the ability of education to regulate inter-
generational mobility is limited (Levi, 2018), just as
Chen thought that the expansion of higher education
has reduced its value (Chen, 2023). Shu demonstrated
how the opening up and restructuring of the economic
system have undermined the value transformation of
education (Shu, 2022).
Through questionnaire design and investigation,
the paper carries out factor analysis after data
differentiation analysis, reliability analysis and
validity analysis, and explores the causes of inter-
generational income flow by analyzing the current
situation (CS) of inter-generational income flow and
multiple linear regression model, and puts forward
constructive suggestions.
2 INVESTIGATION METHOD
2.1 Questionnaire Survey Method
The research group conducted two questionnaire
surveys, namely pre-survey and formal survey. The
questionnaire was randomly sampled and distributed
using the questionnaire star platform. After clearing
the faulty surveys, the pre-investigation yielded 62
valid questionnaires, while the official investigation
yielded 150 valid questionnaires.
The questionnaire used in this survey is set into
three sections: the basic information of the
respondents, the situation of the respondents' parents,
and the factors affecting the intergenerational income
flow.
2.1.1 Questionnaire Content Design
In the first step, it determines the topic direction
according to the research content: analysis of the CS
of intergenerational income flow and its influence
mechanism. In the second step, it consulted relevant
literature and books according to the direction of topic
selection, carried out field investigation in Xiamen,
collected relevant information, and further
understood the relevant situation. The third step is to
design different types of questions according to the
situation of field investigation and enrich the contents
of the questionnaire.
2.1.2 Modification and Improvement of the
Questionnaire
After the questionnaire was designed and completed,
the content, wording, format and sequence of the
questionnaire were analyzed several times, and the
questionnaire was adjusted and modified to make it
more concise and substantial, to better obtain the
information needed for the survey.
2.2 Multi-Stage Sampling
This research group adopts multi-stage sampling, and
the sampling process is carried out in stages. Different
sampling methods are used in each stage, that is,
various sampling methods are combined to consider
not only the sample representativeness, but also the
manpower required and the total cost incurred in
issuing questionnaires.
3 SURVEY DATA ANALYSIS
3.1 Differentiation Analysis
The primary purpose of item analysis is to delete
items with low differentiation degree. After
recovering the pre-survey questionnaire, the research
team first selects effective questionnaires and
analyzes the differentiation degree of scale items in
the questionnaire. The purpose is to study whether the
data can effectively distinguish between high and low
levels, to evaluate the quality of a specific item. The
total scores of all respondents were ranked in high
order. From the analysis results, it can be seen that the
score of the high group is above 42 points, and the
score of the low group is below 25 points. The test
results of 10 items in the scale are all significant
(P<0.05). The final result shows that all items in the
scale have differentiation and can identify different
interviewees.
3.2 Reliability Analysis
Reliability analysis is to prove the reliability of the
research sample data through analysis, which can be
divided into four categories:
coefficient,
broken half reliability, duplicate reliability and retest
reliability. Since multiple measurements were not
made in this pre-survey, the internal uniform
convergence coefficient
was adopted to
test the reliability of the data in consideration of the
reliability analysis. The calculation formula of the
coefficient is shown:
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
558
2
1
2
1
1
k
i
i
p
S
k
kS
α
=
=−
−
(1)
Where
is the total number of questions in the
scale,
denotes the
𝑖
th in-question variance, and
is the variance of the total score of all items. The
coefficient
evaluates the internal
consistency of the scores of each survey item in the
scale question. Generally speaking, the coefficient
is best above 0.8, and 0.7-0.8 is an
acceptable range. If the coefficient is below 0.6, the
scale needs to be reconsidered.
The questionnaire was divided into five
dimensions: health status, education concept, CS
view, income comparison, and family help, and the
coefficients
were calculated by SPSS
analysis software to judge their reliability level. The
output is shown in Table 1.
Table 1:
Pre-survey Coefficients
Dimensions
Coefficient
Number of terms Evaluation result
Health status 0.838 2 Good reliability
Educational concept 0.712 2 Good credibility
Status quo view 0.776 2 Reliability is good
Income comparison 0.844 2 Good reliability
Home help 0.719 2 Good reliability
Scale overall 0.821 10 Good reliability
3.3 Validity Analysis (VA)
VA is to continue to analyze the validity of the item
after completing the reliability analysis. There are
many kinds of VA, and the VA of the pre-survey
questionnaire can usually be divided into content VA
and structural VA. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA)
and confirmatory factor (CFA) were used to analyze
the validity of the questions.
Firstly, the EFA was carried out, which was a
cyclic exploration process. The research group used
Bartlett sphericity (BS) test and KMO test on the
scale, the purpose of which was to test whether the
questionnaire items and factors had a good
correspondence.
For BS test, check whether its value is less than
0.05. If the value is less than 0.05, it means that BS
test is passed. For KMO test, check whether its KMO
value is greater than 0.6, if the KMO value is greater
than 0.6, it indicates that it is suitable for exploratory
factor analysis, and the larger the value, the better.
The output results of SPSS are shown in Table 2:
Table 2: Pre-investigated KMO and BS tests
Adequacy test KMO test 0.831
BS test
Approximate Chi-square 1335.116
Degrees of Freedom 378
value
0.000
As can be seen from Table 2, KMO value is 0.831
and BS test value
is less than 0.05, which is
significant, indicating that the questionnaire scale is
suitable for factor analysis.
When factor extraction was carried out by the
principal component analysis method, the number of
factors to be extracted was set to 5 due to the research
dimensions of 5 when designing the scale, and the
results were rotated by variance orthogonal. At the
same time, the display format of factor load
coefficients was set to form a matrix according to the
order of size, and variables with load coefficients less
Research on the Current Situation of Intergenerational Income Flow and Its Influencing Mechanism
559

than 0.4 were excluded. The variables
with higher load on the same factor are grouped
together, so as to better observe the corresponding
relationship between factors and items and get a
conclusion. The output result of total variance
interpretation is shown in T
able 3, and the factor load matrix obtained after
orthogonal rotation is shown in Table 4:
Table 3: Total variance interpretation table
Compon
ents
Initial eigenvalues
Extract the sum of squares of
loads
Rotate the load sum of squares
total
Variance
(%)
Cumula
tive (%)
Total
Variance
(%)
Cumulati
ve (%)
Total
Varianc
e (%)
Cumulativ
e (%)
1 10.015 35.766 35.766 10.015 35.766 35.766 5.15 18.392 18.392
2 2.6 9.285 45.052 2.6 9.285 45.052 3.298 11.779 30.171
3 2.347 8.382 53.434 2.347 8.382 53.434 3.294 11.763 41.934
4 1.654 5.906 59.34 1.654 5.906 59.34 2.922 10.437 52.371
5 1.262 4.508 74.054 1.262 4.508 74.054 1.41 5.035 74.054
Table 4: Composition matrix after rotation
Ingredients
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Mental health status 0.666
Physical health 0.791
The degree to which an individual
values education
0.784
The degree to which one's parents
value education
0.693
Agree that "a poor family cannot
produce a noble son"
0.602
"Knowledge changes destiny" 0.865
Income versus peers 0.622
Compare your income to that of your
parents
0.853
The extent to which the income gap is
influenced by the family
0.838
The extent to which parents help with
employment
0.699
According to the requirement of factor load in
factor analysis, if the total variation rate of principal
factor explanation is greater than 60% and the factor
load is greater than 0.6, then the structural validity is
good. From the observation of Table 3, it can be seen
that the accumulated variance explanation rate of the
five factors extracted is 74.054%, and the factor load
of the 10 indicators studied is greater than 0.6,
indicating that the factors can extract the information
of each item well, and the convergent and
discriminative validity of the scale meet the relevant
requirements. Further observe the rotation component
matrix in Table 4. The corresponding relationship
between the five factors extracted and the items was
consistent with the expectation.
3.4 Formal Questionnaire Data
Processing and Testing
This data review primarily uses a manual format that
is broken down into two phases: The first step is to
confirm the questionnaire's thoroughness by
reviewing it soon after the survey, correctness, and
consistency. Considering that the survey subjects
come from all walks of life and have different
educational backgrounds, whether the questionnaire
content is clear and easy to understand is also the key
to consider; In the second stage, I audited all
questionnaires after completing all questionnaire
distribution tasks, to ensure the consistency of
processing methods. After first examination, 849 of
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
560
the 886 questionnaires that were distributed for this
study were recovered, yielding a 95.8% recovery rate.
After finishing the questionnaire, the specific
coding method was as follows: the question number
was set as Q1, Q2, Q3…. The function of calculating
variables refers to a mathematical transformation that
deals with the items in the questionnaire. This
function is usually used in two situations in
questionnaire research, namely, variable production
and variable processing. The four items Q10, Q26,
Q27, Q28, and Q29 were respectively calculated and
the data columns generated were named as "health
level", "education concept", "CS view", "income
comparison" and "family help".
For missing, duplicate, incomplete and other
questionnaire data, data cleaning, for a small number
of missing values will be replaced by the mean of the
same category, and for a large number of missing
values of the questionnaire will not be investigated
and analyzed, that is, scrapped.
3.5 Data Inspection
3.5.1 Random Run Test
Random run test uses the run to construct the Z
statistic and gives the corresponding associated
probability value according to the normal distribution
table. The test results were shown in Table 5, all
values were greater than 0.05, and the null hypothesis
was not rejected. Therefore, the questionnaire
samples could be considered as random samples and
could be analyzed in the following data.
Table 5: Run test table
Fitness Level
Educational
perception
Z -0.711 0.512
value
0.477 0.608
3.5.2 Reliability Test
The test method and process of the reliability of the
formal questionnaire are the same as those of the pre-
survey, and the results show that the
coefficients at all levels are shown in Table 5.
Table 6:
The coefficients of the formal survey
Dimensions
Coefficient
Number of terms Evaluation results
Health status 0.838 2 Good reliability
Educational concept 0.712 2 Good credibility
Status quo view 0.776 2 Reliability is good
Income comparison 0.844 2 Good reliability
Home help 0.719 2 Good reliability
Scale ensemble 0.821 10 Good reliability
The results show that the
coefficients of all dimensions are greater than 0.7, and
the
coefficient of the scale as a whole is
0.821, which indicates that the internal consistency of
the questionnaire is good, and the scientific and
rational design of the questionnaire structure and
questions meet the requirements of market research
and analysis in this line.
3.5.3 Validity Test
The concept and basic theory of questionnaire
validity test have been mentioned in the pre-survey
data analysis, so it will not be repeated. In the same
process as the pre-survey validity test, KMO test and
BS test are first performed. The calculated KMO
value is 0.893 and greater than 0.7, and the
corresponding
value of BS test is less than 0.05, as
shown in Table 7.
TABLE7. Formal investigation of KMO and BS test
Adequacy test KMO test 0.893
Approximate Chi-
square
2893.846
Degrees of
Freedom
378
value
0.000
Research on the Current Situation of Intergenerational Income Flow and Its Influencing Mechanism
561
4 CURRENT ANALYSIS OF
INTERGENERATIONAL
INCOME FLOWS
Through the analysis of parents' help in children's
growth, education and employment, individuals'
views on intergenerational income flow and their own
cognition of income comparison, the main direction
of this investigation is determined.
4.1 The Analysis of Parents' Help to
Their Children
4.1.1 The Help Parents Provide to Their
Children's Development
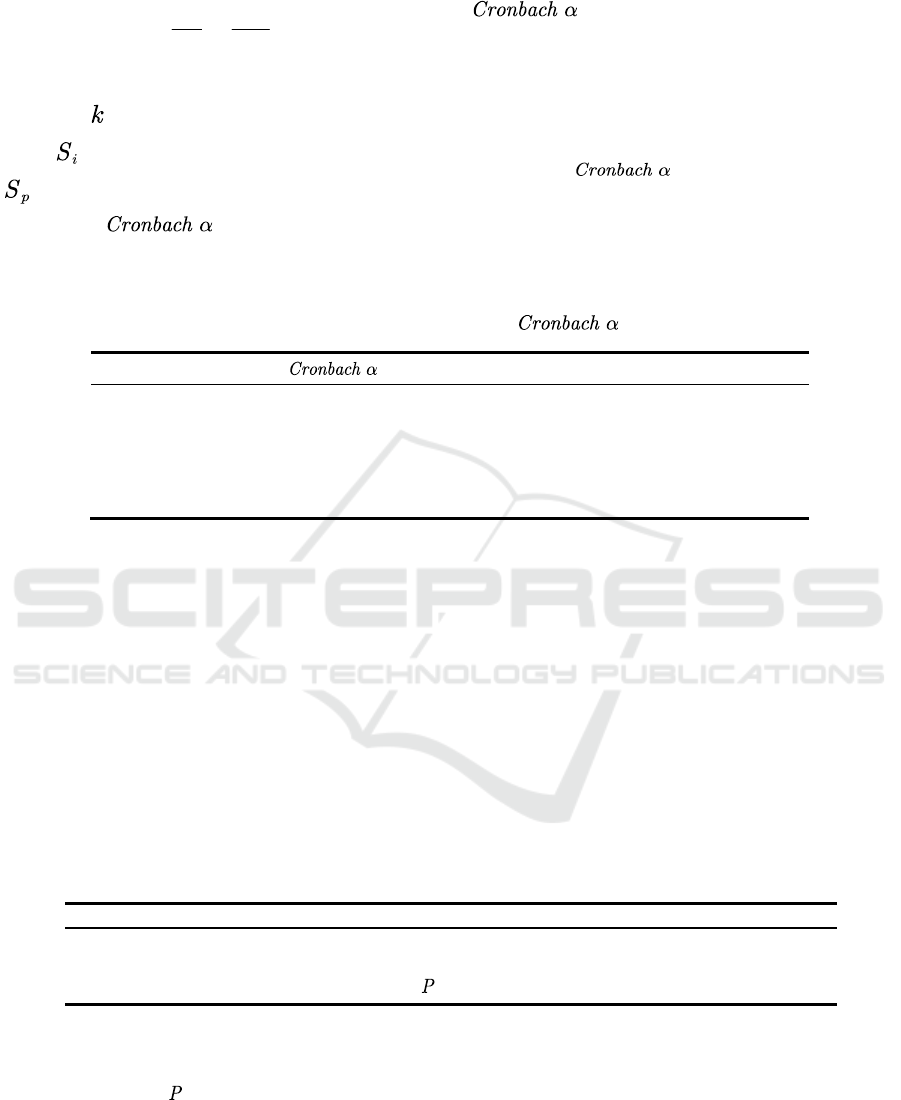
Figure 1: Parents' assistance in the development of their children (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
First of all, the article surveyed the help provided by
parents in the growth of their children, as shown in
Figure 1. Among the surveyed people, the help
received from parents comes from many aspects,
including economic, educational, spiritual, physical,
and other aspects, and is not limited to financial
support, which shows that in today's society, parents
take into account the cultivation of their children in
many aspects. At all levels of the survey, almost all
respondents agreed that they get good health from
their parents, while more than half of respondents
acknowledged that they get good company, adequate
financial support and good family education.
4.1.2 Parents' Help with Their Children's
Education
Figure 1: Parents' help with their children's education (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Secondly, the research team made statistics on the
help provided by parents in the child's education. As
shown in Figure 2, almost all of the respondents'
parents provide for their basic education in school,
which is consistent with our cognition. In addition,
more than half of the respondents, 68.67% and
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
562
57.36%, pay for school choice and cultivate their
children's good study habits, respectively. At the
same time, 46.53% of the respondents said that their
parents would provide the expenses for after-school
tutoring classes. Therefore, the cultivation of their
children is profound and multi-faceted.
4.2 Individuals' Views on
Intergenerational Income Flows
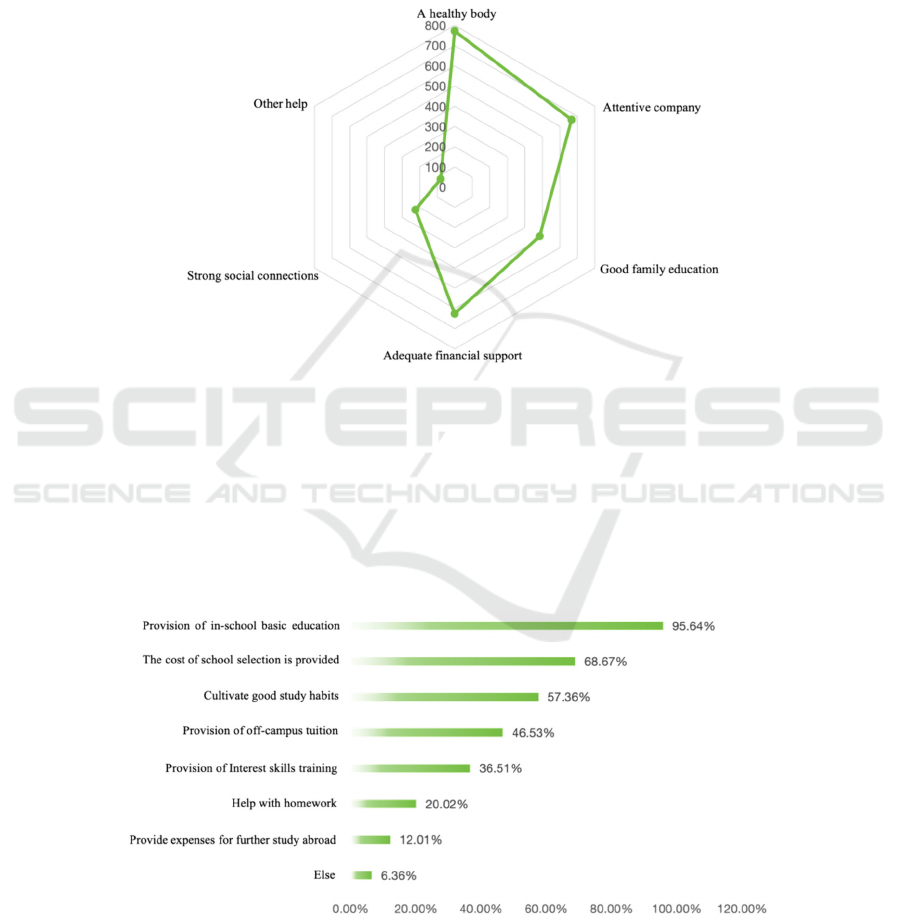
Figure 2: Individuals' views on intergenerational income flows (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
As is shown in Figure 3, more than 75% of the people
surveyed agree with the idea that knowledge can
change their fate, while only 8% disagree with it. It
can be seen that with the development of The Times,
more than enough people have felt the power of
knowledge and the influence on their fate. The
number of people who agree with the view that a poor
family rarely produces a good son is nearly 54%,
more than half, only 23% of the people have a
pessimistic attitude towards the current era, and think
that a person's success is relatively closely related to
their birth.
4.3 The Cognition of One's Income
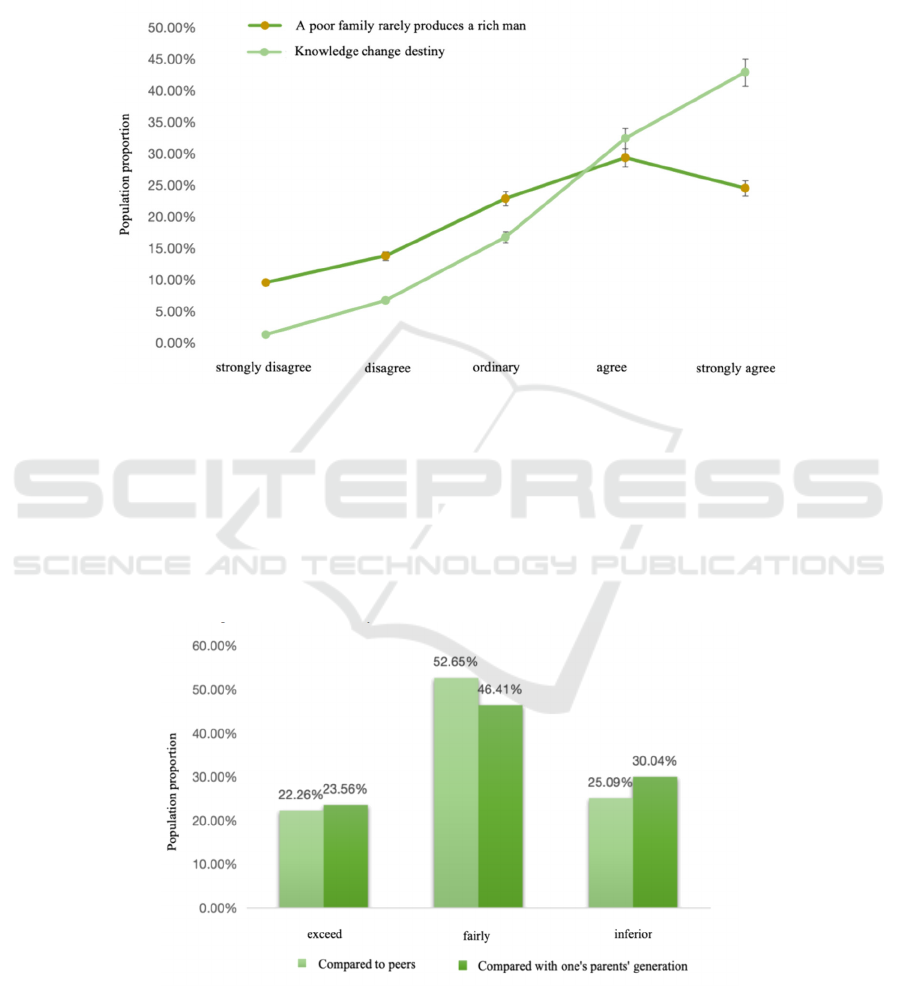
Figure 3: Individual's own income comparison cognition (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
As can be seen from Figure 4, about half of the
people think that their income is similar to that of their
parents and peers, and about 25% of the people think
that they are above or below the level of their peers.
Currently, 24% of people think their income is higher
than that of their parents' generation, 30% think it is
Research on the Current Situation of Intergenerational Income Flow and Its Influencing Mechanism
563

lower than that of their parents' generation, and 46%
of people think their income is the same as that of
their parents' generation. Their parents are still the
breadwinner of their families, and they are gradually
bearing the burden of family income. The income of
the whole society is also at a relatively healthy and
stable level.
5 ANALYSIS OF INFLUENCING
FACTORS OF CHILD INCOME
BASED ON MULTIPLE LINEAR
REGRESSION MODEL
Through descriptive statistics, it has a certain
understanding and cognition of the CS of
intergenerational mobility in today's society. In order
to better study the mechanism of intergenerational
income mobility, it first analyzes the influencing
factors of children's income, and select a OLS model
to carry out multiple linear regression of children's
income.
5.1 Model Selection
In the regression prediction of child income, the
logarithm of child income is selected as the dependent
variable, and the dependent variable is calculated by
logarithmic processing of Q8, which is the
quantitative data. Therefore, the multiple linear
regression model is selected to analyze various
factors affecting the child income.
5.2 Variable Setting
In this model construction, six indicators such as
"personal basic information", "parents' basic
information", "education concept", "CS view",
"income comparison" and "family help" are selected
for measurement, and 21 characteristics, including
age, gender, and educational background, are broken
down into these six indications, which are set as
as independent variables that may
affect children's income.
5.3 Model Construction
When multiple linear regression is carried out, the
complete multicollinearity problem of the data will be
detected automatically, and the output results are
shown in Table 8.
Table 8:
OLS regression results
Variables Child income pair value
Father's income pair
value
0.25
***
(0.018)
Maternal income pair
value
0.15
**
(0.013)
Children's years of
schooling
0.031
***
(0.010)
Sex
-0.139
***
(0.021)
Age
0.191
***
(0.048)
Whether reading
0.468
***
(0.085)
Health status
0.030
*
(0.012)
Household registration
status
0.021
(0.032)
Father's years of
education
0.100
**
(0.013)
Years of schooling for
mothers
0.008
***
(0.016)
Real estate per capita
0.229
***
(0.040)
Human capital input
0.394
***
(0.056)
The degree to which
families value education
0.239
***
(0.047)
Perceptions of
intergenerational mobility
0.143
(0.197)
Perceptions of one's own
income
0.179
(0.211)
Degree of subjective
perception of family help
0.012 *
(0.114)
Constant term
4.093
***
(0.693)
Observed value 849
0.798
Note: "***", "**", and "*" indicate significant at 1%, 5%,
and 10% significance levels, respectively; () inside is
clustering standard error.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
564

5.4 Model Test
For regression models, the homoscedasticity
hypothesis
which
is considered to occur if it occurs that the
variance
of the random error term is no longer constant for
different sample points. In the significance test of a
variable, the
statistic:
()
221
ˆ
ˆˆ
(0,1,2,,)
ˆ
()
jj jj jjj
j
uujj
tjk
Se
cXX
ββ ββ β β
β
σσ
−
−− −
=== =
(2)
Contains the common
2
u
σ
variance of the random
error terms. If heteroscedasticity is present and the
t
statistic is still calculated according to the formula
used in the case of homoscedasticity, the
t
statistic
will be distorted, thus invalidating the
t
test. In short,
heteroscedasticity affects whether the inference is
valid and will reduce the efficiency of the estimation,
so it tests the heteroscedasticity of the regression
model.
The difference between the two can be used to
quantify conditional heteroscedasticity because under
conditional homoscedasticity, the robust standard
error is reduced to the common standard error.
Examining if the robust standard error and the
ordinary standard error are comparable is the informal
approach. This concept is the foundation of the White
test, which White first presented in 1980.
White test has the advantage of testing any form
of heteroscedasticity and is widely applicable.
Therefore, White test is carried out on the established
multiple linear regression model, and the output is as
follows:
.
The null hypothesis is that the disturbance term does
not exist heteroscedasticity, because the
value is
greater than 0.05, so the null hypothesis is not
rejected, there is no evidence that the disturbance
term exists heteroscedasticity, that is, it is considered
that there is no heteroscedasticity.
Multicollinearity diagnosis can be based on the
Variance Inflation Factor (VIF). A common guideline
is that if VIF>0, the regression equation is considered
to have severe multicollinearity. By using Stata or
other econometric software, if the results show
VIF<0, it generally concludes that the model does not
exhibit serious multicollinearity.
5.5 Analysis of Results
The model's independent variables all pass the
significance test, suggesting that each of them
influences the dependent variable. Meanwhile, when
the regression coefficient of the independent
variable is greater than 0, it indicates that it has a
positive effect on the dependent variable, and vice
versa. According to the obtained
regression
results, the following conclusions can be drawn:
In contrast to the distribution of intergenerational
income elasticity between 0.3 and 0.5 in earlier
studies, the estimated results of the parental income
pair value and the individual income pair value are
significantly positive at the 1% level, with
intergenerational income elasticity values of 0.15 and
0.25, respectively. The possible reasons are as
follows: The data selected in this paper are all current
data, which may lead to the possibility of downward
bias in the results. Therefore, the intergenerational
income elasticity obtained in this paper is relatively
small.
The regression coefficient of gender on individual
income is significantly negative, indicating that
women are in a relatively weaker position than men
in the labor market, and therefore may be in a lower
income level than men. This is consistent with the
reality, which is also one of the urgent problems to be
solved.
Personal income rises with age and with
increasing academic degrees, according to the
regression results of age and years of schooling,
which are statistically positive at the 1% significance
level. Family education and support are crucial for the
rise of personal income, as seen by the significantly
positive regression results of family emphasis on
education and family assistance to individual income
at the significant levels of 1% and 10%, respectively.
The regression coefficients of personal income on
health, education, and per capita household property
are significantly positive. The reasons may be as
follows: First, having a healthy body can more
effectively exert the value created by the body in the
work, and thus obtain higher personal income. At the
same time, parents can reduce the expenditure on
medical care for their children, to reduce the degree
of dependence of children on their parents; Secondly,
in the case of non-schooling, individuals can replace
more valuable work experience and income through
the opportunity cost of non-schooling, to reduce their
dependence on parents.
Research on the Current Situation of Intergenerational Income Flow and Its Influencing Mechanism
565

6 CONCLUSION
The data analysis of the comprehensive questionnaire
survey shows that there are discussions about
intergenerational mobility on the Internet, and most
of them hold a positive attitude towards future
development after rational thinking about the social
status quo. At the same time, the help provided by
parents in the growth, education and employment of
their children cannot be ignored. To better study the
mechanism of intergenerational income flow, the
research team first conducted a regression analysis on
the influencing factors of child income, and found
that parental income, gender, age, years of education,
health level, whether they are studying or not, and real
estate per capita of the family have significant effects
on child income.
Regression analysis shows that among education
parameters, the number of years of education has a
substantial positive effect on children's income.
Applying the model of intergenerational income, it is
necessary to strengthen the investment of public
education resources, especially public education
resources. And promote the dynamic balance of high-
quality education resources, so as to improve the level
of intergenerational income mobility of the whole
society.
From the above analysis, we have reason to
believe that higher education needs to further
strengthen the adaptation to the market, that is, to
explore the market demand with The Times. For
example, strengthen technical training and practical
courses, to improve the quality of technical ability.
According to the results of the moderated
mediation model, the intergenerational income
elasticity of families with good educational ideas is
lower. Adhere to the good family education concept,
cultivate more excellent children. "Strict" as the first,
seize the children's learning critical period; Cultivate
independent consciousness, so that children do not
have dependent thoughts; Pay attention to children's
growth, communicate with them more, guide children
correctly; Home and school contact, maintain
consistency, support together.
REFERENCES
Becker, G.S. and Tomes, N. (1979). An Equilibrium Theory
of the Distribution of Income and Intergenerational
Mobility. The Journal of Political Pa, 87(6), 1153-1189.
Solon, G. (1992). Intergenerational Income Mobility in the
United States. American Economic Review, 82(3), 393-
408.
Bjorklund, A. and Jantti, M. (1997). Intergenerational
Income Mobility in Sweden Compared to the United
States. American Economic Review, 87(5), 1009-1018.
Haider, S.J. and Solon, G. (2006). Life-Cycle Variation in
the Association between Current and Lifetime Earnings.
American Economic Review, 96(6), 1308-1320.
Dahl, M.W. and De Leire, T. (2008). The Association
Between Children's Earnings and Fathers' Lifetime
Earnings: Estimates Using Administrative Data.
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Institute for
Research on Poverty.
Chernozhukov, V. and Hansen, C. (2007). Instrumental
Variable Quantile Regression: A Robust Inference
Approach. Journal of Econometrics, 142(1), 379-398.
Zhang, M. (2024). Research on Blocking Intergenerational
Transmission of Relative Poverty in Rural Families
Through Education. Huazhong Agricultural University.
Wang, S. (2023). Education Research on the Influence of
Intergenerational Income Mobility in China. Henan
Finance and Economics University of Political Science
and Law.
Levi, G.G., Limor, G. and A.M.S. (2018). Intergenerational
Mobility and the Effects of Parental Education, Time
Investment, and Income on Children’s Educational
Attainment. Review, 100(3).
Chen, C. (2023). Precise Poverty Alleviation and
Intergenerational Mobility in China. Taylor and Francis.
Shu, W., Xiao, Y., Kuo, Z. et al. (2022). How Does
Education Affect Intergenerational Income Mobility in
Chinese Society? Review of Development Economics,
26(2), 774-792.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
566
