
Statistical Insights into the Influence of Music on Mental Health
Xinyi Zhang
a
School of Management, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200433, China
Keywords: Logistic Regression, Mental Health, Music, Machine Learning.
Abstract: Mental Health has recently become a heated topic among the public, ranging from biologists seeking for
pathological cause to psychologists who attempts to improve the dilemma. In this paper, a comprehensive set
of methods such as descriptive analysis, logistic regression, random forest and XGBoost will be adopted to
analyse the dataset from Kaggle and establish the relationship between music and mental health as well, with
an aim to provide some evidence on the effect of music therapy, an emerging curing method. By comparing
the figure of the Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), it can be concluded that logistic regression performs the
best among these models in predicting mental health states. Nevertheless, the actual figures of RMSE still
suggest room for improvement. For future related experiments, significant improvements can be done by
increasing the volume of samples, perfecting data filtration, adding more variables and further refining
parameters of the model. After all, this research provides empirical evidence for the application of music
therapy by using statistical models while at the same time offering keen insights for further improvements.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the public’s awareness of personal
well-being is gradually increasing, frequently
accepting the transformation to healthy lifestyles.
While physical health has remained necessary, as
evidenced by growing attention paid on exercise and
nutrition, it is generally acknowledged that
psychological health issues need to be highly valued
as well. Among all the people agonizing over mental
problems, it is the adolescents that suffer the most.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reported in
2021 that one in seven individuals aged between 10
to 19 suffered from a mental disorder. In addition,
statistics indicate that there is a rising prevalence of
mental health issues in the current generation of
adolescents (often referred to as “Generation Z”)
falling victim to a “mental health crisis” (Borg et al.,
2024). Contributing factors proposed range from
social media misuse to enhanced tension arisen from
adapting to novel academic situations (Chen, 2024).
There are varied types of psychological disorders
such as depression, anxiety, somatization and
interpersonal sensitivity (Wang, 2023). These
symptoms partly account for poor academic
performance, severe insomnia and even disability in
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-7040-5647
daily activities (Yang et al., 2025). Given the severe
consequences, addressing adolescents’ mental health
has become researchers’ critical focus.
Currently, researchers have explored various
effective strategies to alleviate psychological issue
suffering, with workshops and psychological
counselling been more frequently implemented from
primary schools to universities. Scientists also
proposed the possibility to use artificial intelligence
models to predict psychiatric risk with an aim of
better precaution (Hill et al., 2025). Besides this,
based on previously published samples, psychologists
have established Positive Mental Health (PMH) Scale
for middle school students, enabling teenagers to
evaluate their mental states by themselves (Han et al.,
2025).
Among all the emerging therapeutic approaches,
music therapy, which differs from traditional curing
methods, has gained attention among both musicians
and psychologists. To be more specific, music
composition and group music-making, music
medication and music-based self-care are all
considered effective intervention strategies (He et al.,
2024). The preliminary practice of music therapy is
initiated in several colleges. Students who participate
in the practice are given tailored immersive
Zhang, X.
Statistical Insights into the Influence of Music on Mental Health.
DOI: 10.5220/0013826900004708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy (IAMPA 2025), pages 413-418
ISBN: 978-989-758-774-0
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
413

experience according to their psychological state
assessment in advance (Hu, 2024). Biology
researchers also give insights of the mechanism of
music therapy. Furthermore, studies have identified
that pop fans exhibit fewer depressive symptoms,
while all-out rock fans behaved the worst in personal
well-being (Bogt et al., 2021). Based on the vocal
communication theory (VST), humans perceive tones
in different ways depending on the behavioral
significance in vocal communication (Bowling,
2023). This theory provided biological basis for
applying specific music to patients with different
symptoms.
While a majority of existing studies merely focus
on case studies and additional biological theories, this
research will provide empirical evidence in the
correlation between exposure to music and
adolescents’ mental health states through big data and
statistical methods. This research aims to provide
empirical evidence on the influence of different types
of music on adolescents’ mental health through the
use of statistics. Methods of the study include
descriptive analysis, correlation analysis, decision
tree and multiple linear regression. In addition, the
study will further compare the performance by
indexes such as confusing matrix and mean squared
error (MSE). Data used in the study is found on
Kaggle. By quantifying the association between
music exposure and psychology states, the study
seeks to establish some scientific evidence for the
application of music therapy in adolescents’ mental
disorder interventions.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Data Source
The data utilized in the research is obtained from the
Kaggle website, specifically the “Music & Mental
Health Survey Results”. The data collection process
was carried out via a Google Form in 2022, with no
restrictions of respondents’ age or location.
Furthermore, it has been downloaded around 31.7
thousand times and has won the usability score of
10.00, indicating high data quality. The dataset is in
.csv format.
From the overall dataset, a variety of factors
relating to music and mental health can be observed.
Such diversity in variable selection facilitates
comprehensive analysis in the research.
2.2 Variable Selection and Description
This dataset as a whole contains observations and 33
variables. In order to clarify the influence of music on
individuals’ mental health, irrelevant columns such as
“timestamp” and “Permissions” are filtered out. For
data analysis, there will eventually be 31 columns.
After further filtering steps, 12 out of all 31 variables
are the most relevant, clustered to two types,
“Numeric” and “Categorial”, and the terms and
explanations of each variable are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Variable Description
Ter
m
T
yp
e Ex
p
lanation
A
g
e Numeric The a
g
e of res
p
ondents, ran
g
in
g
from10 to 25
Hours per da
y
Numeric Hours per day spent in listening to music
While workin
g
Cate
g
orial Whether res
p
ondents listen to music while workin
g
, 1 for
y
es, 0 for no
Instrumentalist Categorial Whether respondents are able to play an instrument, 1 for yes, 0 for no
Com
p
ose
r
Cate
g
orial Whether res
p
ondents can com
p
ose music themselves, 1 for
y
es, 0 for no
Fav genre
BPM
Anxiety
Depression
Insomnia
OCD
Music effects
Categorial
Numeric
Numeric
Numeric
Numeric
Numeric
Categorial
Respondents’ favorite or top genre
Beats per minute of respondents’ favorite genres
Self-reported anxiety, on a scale of 0-10
Self-reported depression, on a scale of 0-10
Self-reported insomnia, on a scale of 0-10
Self-reported OCS, on a scale of 0-10
Whether music improve or worsen respondents’ mental health
conditions, 1 for im
p
rove, 0 for no effect, -1 for worsen
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
414
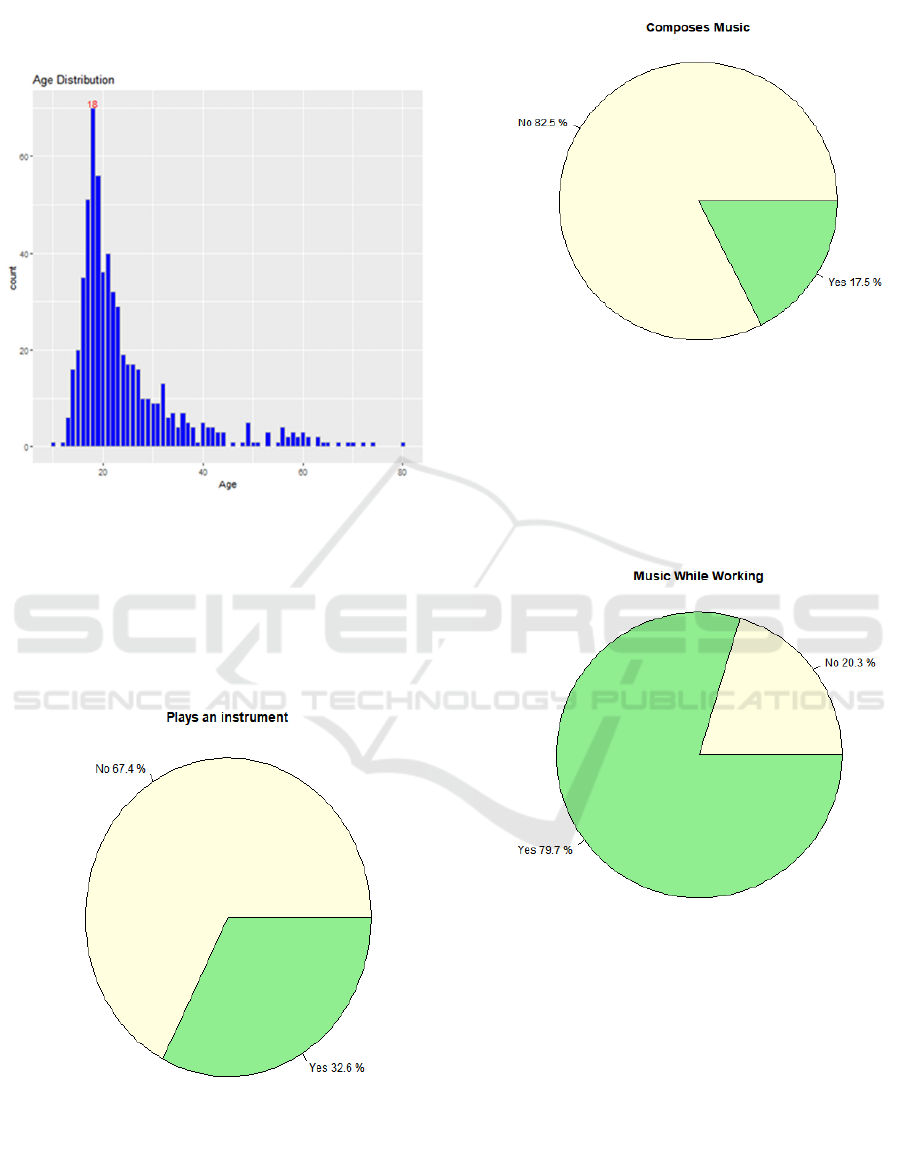
Graphs indicating the features of the dataset are
shown below.
Figure 1: The Histogram of Age Distribution (Picture
credit: original)
From figure 1, it can be concluded that the average
age of the respondents is 25.21, the maximum and
minimum figure of which is 89 and 10 respectively.
The graph depicts a right skewed distribution and
respondents with an age of 18 have the most counts.
Figure 2: Pie Chart of Whether Respondents Play an
Instrument (Picture credit: original)
Figure 3: Pie Chart of Whether Respondents Compose
Music (Picture credit: original)
Figure 4: Pie Chart of Whether Respondents Listen to
Music While Working (Picture credit: original)
Figure 2 indicates that 32.6% of the interviewees play
an instrument besides listening to music. Only a slight
17.5% of them can compose music themselves,
according to figure 3. However, as indicated by figure
4, a high percentage of 79.7% claim that they listen to
music while working.
Statistical Insights into the Influence of Music on Mental Health
415
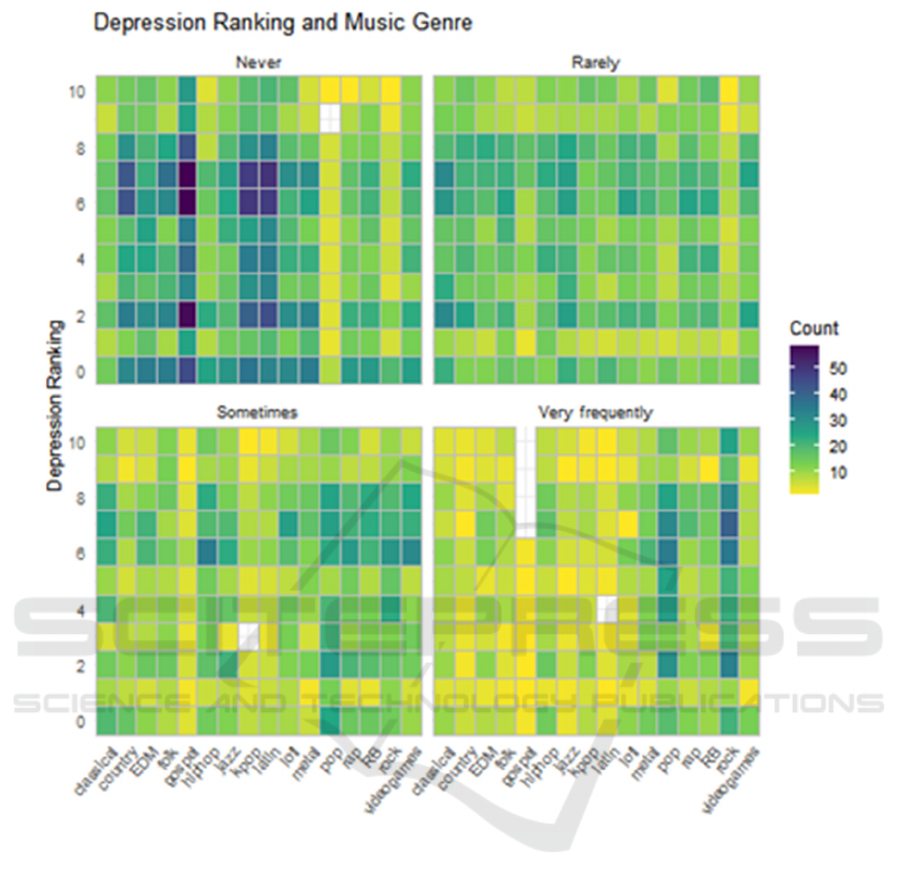
Figure 5: Heatmaps of Music Genres and Mental Health States of depression (Picture credit: original)
Additionally, the color gradient of the heatmap in
figure 5 indicates different figures regarding the
match between favorite and level of mental health.
Nevertheless, there are no clear and strong patterns
uniformly emerging in four types of mental health
issues. A more complicated relationship needs to be
determined.
2.3 Methods Introduction
The paper combines statistical methods and machine
learning methods, including descriptive analysis,
logistic regression, random forests and decision tree.
Firstly, descriptive analysis provides an elementary
summary of the whole dataset and visualizes variable
features. For numerical variables such as “age”,
histograms are adopted to provide data distribution.
For binary and multiple categorial variables such as
“While working”, “Primary streaming service”, etc.,
pie charts are adopted. Additionally, heatmaps
explore the relationship between two variables.
Secondly, logistic regression model is utilized to
predict the influence of music-related indexes on
different mental health conditions, given a certain
trained dataset and a test dataset with a proportion of
8:2. To facilitate logistic regression, the data related
to the level of different mental health states are
divided into two groups, 1 for the figure over 4, and 0
for the else. The article used confusion matrix to
present figures of false positive (type I error) and false
negative (type II errors) and the accuracy of the
logistic regression model. Thirdly, the random forest
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
416
classifier builds multiple decision trees to determine
feature importance. XGBoost, a gradient-boosting
library, iteratively improve the model by fitting the
residuals of previous ones. In every iteration, the
model adopts decision tree as its basic learners.
Generally, the three methods’ performance is
assessed using RMSE to propose a better strategy for
a specific dataset. R and Python are employed for
programming.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Model Results
The visualized results of confusion matrix using
logistic regression and XGBoost and the graph
indicating feature importance are depicted below.
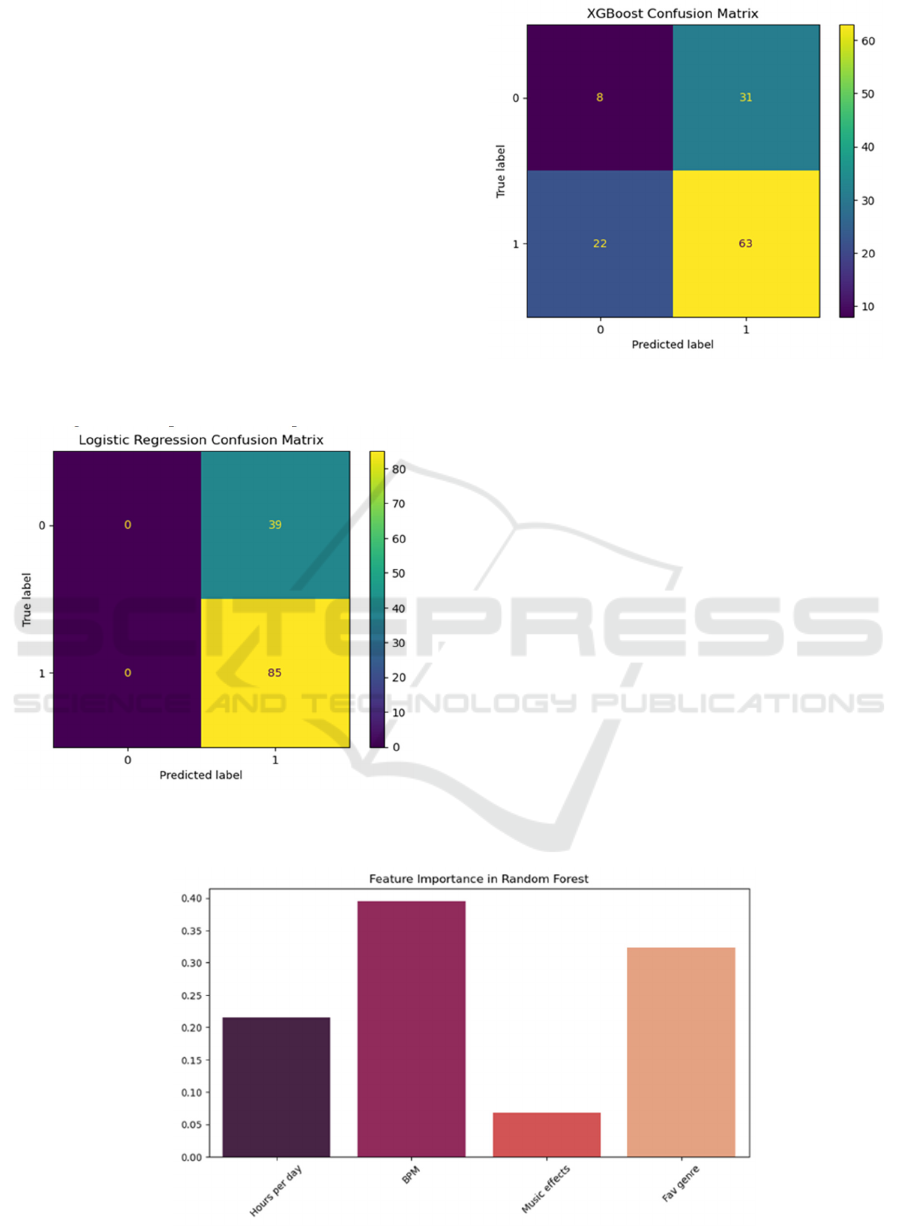
Figure 6: Confusion Matrix of Logistic Regression
Regarding Anxiety (Picture credit: original)
Figure 7: Confusion Matrix of Logistic Regression and
XGBoost Regarding Anxiety (Picture credit: original)
From figure 6 and 7, for anxiety prediction, the
number of samples with a true label of 0 but predicted
label of 1 is 39, and the number of samples with a true
label of 1 and a predicted label of 0 is 0. The figure of
correctly predicted cases is 85. On the other hand, the
XGBoost model possesses 63 cases of true positives,
8 false negatives, 22 true negatives and 31 false
positives. It can be concluded that XGBoost performs
overall better than logistic regression, but stull with
an imperfect performance.
Cases of true positives, false negatives, true
negatives and false positives regarding logistic
regression model for the other three type of mental
health statuses are (59,9,10,46), (8,63,42,11),
(1,91,31,1) respectively, as shown in figure 6, figure
7 and figure 8. Those for XGBoost are (36,20,33,35),
(14,57,36,17), (1,75,31,17) respectively.
Figure 8: Feature Importance of Random Forest (Picture credit: original)
Statistical Insights into the Influence of Music on Mental Health
417

Figure 8 is the feature importance graph of random
forest depicts that “BPM” (beats per minute) occupies
the highest importance in affecting music listeners’
mental health states. “Fav genre” (favorite genre)
ranks the second and “Hours per day” has a moderate
effect. “Music effects” (self-analyzed music effects
on individual mental health states) contributes the
least to predicting mental health conditions using
random forest.
3.2 Compare Results
Based on table 2, which shows the RMSE value for
each model and for each category of mental health
issues, logistic regression generally outperforms
random forest and XGBoost since it has relatively
low RMSEs among all four mental health states,
indicating a more accurate prediction ability.
Nevertheless, the logistic regression model is never
without room for improvement.
Table 2: RMSE values for all three models regarding four mental health states
RMSE Anxiet
y
De
p
ression Insomnia OCD
Logistic Regression 0.5608 0.6720 0.6538 0.5080
Random Forest 0.6720 0.7184 0.6660 0.5820
XGBoost 0.6538 0.7405 0.6538 0.6222
4 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, although the percentages of false
predictions are not so significant in terms of both
logistic regression and XGBoost, the RMSE figure is
not good enough. Overall, the paper partly
demonstrates the influence of music on mental health,
with beats per minute (BPM) affecting the most.
Nevertheless, the research might be more convincing
if the RMSE values are lower than 0.1. For future
improvement, the reason of the relatively bad
performance must be determined. Poor data quality is
the culprit of underperformance since the self-
assessment of mental health indicators might deviate
due to subjective factors and inconsistent criteria,
which will affect the effectiveness of the dataset. Also
the lack of restrictions in data collection may also lead
to some noise. In addition, the model itself should be
modified by adjusting the parameters and considering
probable other complicated relationship between
music and mental health states rather than splitting
the level into two groups. Last but not least, other
variables such as the time period of listening to music
in a day are not taken into consideration. These
factors may also affect people’s mental health status.
In conclusion, while the performance of the proposed
model does not meet researcher’s expectation, it does
provide some insights into the relationship between
music and mental health, and at the same time paves
the way for future optimization.
REFERENCES
Bogt, T. T., Hale, W. W. Becht, A. 2021. Wild Years: Rock
Music, Problem Behaviors and Mental Well-being in
Adolescence and Young Adulthood. J Youth, 50, 2487-
2500.
Borg, M. E., Heffer, T. Willoughby, T. 2024. Generational
Shifts in Adolescent Mental Health: A Longitudinal
Time-Lag Study. J. Youth Adolescence, 1-12.
Bowling, D. L. 2023. Biological Principles for Music and
Mental Health. Transl Psychiatry, 13, 374.
Chen, L. F. 2024. Analysis on the Construction Path of
College Students' Mental Health Education and
Guidance Mechanism in the New Media Era. News
Research Guide, 15 (01), 148-150.
Han, Y., Yang, Y., Shentu, M. L., et al. 2025. Positive
Mental Health (PMH) Scale for Middle School
Students: Structure and Measure. Journal of Peking
University (Natural Science), 61(01), 166-172.
He, Q., Attan, S. A., Zhang, J. et al. 2024. Evaluating Music
Education Interventions for Mental Health in Chinese
University Student: a Dual Fuzzy Analytic Method. Sci
Rep, 14, 19727.
Hill, E. D., Kashyap, P., Raffanello, E. et al. 2025.
Prediction of Mental Health Risk in Adolescents. Nat
Med, 1-7.
Hu, P. Y. 2024. Application of Music Therapy in College
Students' Mental Health Education. Education Science
& Culture Magazine, 18, 184-188.
Wang, L. 2023. Exploring the Influence of Music
Education on the Development of College Mental
Health based on Big Data. Soft Comput. 27, 17213-
17229.
Yang, Y. Q., Huang, J., Lin, Z. X., et al. 2025. Mental
Health Literary and its Relationship with Symptoms of
Depression, Anxiety, and Insomnia in Young Adults.
Chinese Mental Health Journal, 4, 344-349.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
418
