
Research on the Influencing Factors of Chinese Healthcare Resource
Allocation Problems Based on Principal Component Analysis
Bingzhang Wang
College of Mathematics and Systems Science, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, Shandong,
266590, China
Keywords: Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Z-score Standardization, KMO and Bartlett's Tests.
Abstract: With the development of the social economy and the people's need for a better life, more and more people
begin to pay attention to physical health. Consequently, the judicious allocation of healthcare resources has
become paramount. This study utilizes 2022 healthcare indicator data from various regions of China. Before
analysis, the data underwent Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) and Bartlett's tests to confirm its suitability.
Subsequently, a principal component analysis (PCA) was employed to construct a comprehensive evaluation
model, facilitating an investigation into the allocation of healthcare resources across different regions. The
findings revealed that factors such as population, economic conditions, and healthcare supply all positively
influence the allocation of medical resources. Ultimately, this research aims to inform the development of a
high-quality and efficient healthcare service system in China. Furthermore, it seeks to contribute to resource
sharing among regions, reduce healthcare disparities, and ensure equitable access to medical care across all
areas of China.
1 INTRODUCTION
The proper distribution of medical resources is related
to the health of the people and the overall promotion
of the construction of a healthy China (Liu, & Zhao,
2024). With the rapid socioeconomic development
and accelerated population aging in China, the
demand for high-quality medical services among the
populace is increasing. However, significant are the
disparities observed nowadays in health resource
distribution across various regions. This makes the
current allocation of medical and health resources in
China still present an unfair situation of the dualistic
structure system of urban and rural area (Dai et al.,
2023).
Research on healthcare resource allocation has
gained significant attention in recent years, leading to
a proliferation of relevant studies. For instance,
Zheng et al. (2018) applied principal component
analysis to evaluate healthcare resource allocation,
finding significant improvements over the past
decade in service provision, utilization, and care
delivery. Li (2023) applied factor analysis to show
that there are regional differences in the rationality of
medical resource allocation in China, and the overall
situation is poor, with only a few provinces in a state
of balanced supply and demand. Liu et al. (2024) used
a three-stage DEA-Tobit model to analyze the
efficiency of healthcare resource allocation and its
influencing factors. The analysis concluded that there
are obvious differences in the allocation of health
resources in various regions. Therefore, in-depth
research on the allocation of medical and health
resources is important.
This study employs principal component analysis,
which explores the factors influencing healthcare
resource distribution. The findings aim to provide a
scientific basis for optimizing government financial
investment structures and guiding the allocation of
high-quality resources to lower-level healthcare
facilities.
2 METHOD
2.1 Data Sources and Indicator
Selection
The data indicators for this study were obtained from
China Statistical Yearbook (2023), China Health
Statistics Yearbook (2023), and the National Bureau
of Statistics of China. These indicators were
Wang, B.
Research on the Influencing Factors of Chinese Healthcare Resource Allocation Problems Based on Principal Component Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0013826500004708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy (IAMPA 2025), pages 391-396
ISBN: 978-989-758-774-0
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
391
integrated to create the dataset required for this
analysis, as presented in Table 1. Due to data
collection limitations, the regions of Macau, Hong
Kong and Taiwan were excluded from the scope of
this research. In this paper, the 31 provinces,
municipalities and autonomous regions of Mainland
China were categorized into three major regions: the
eastern region, the central region and the western
region.
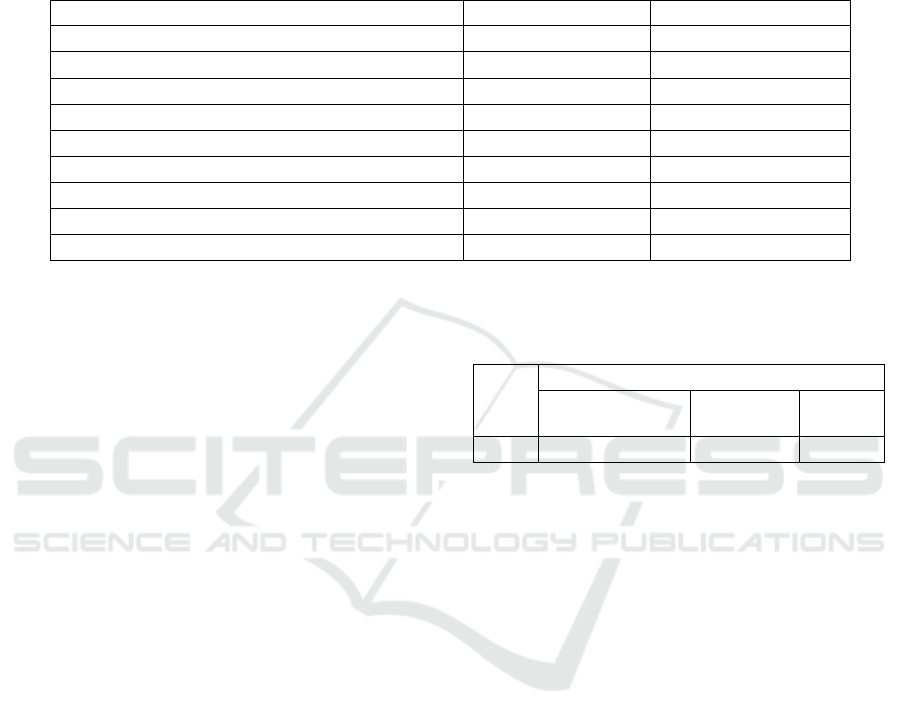
Table 1: Description of Indicator Symbols
Name of the Indicator Unit of the Indicator Symbols of the Indicator
Population of the regions Ten Thousand People
x
Number of public hospitals per region PCS
x
The capability of hospital beds per 10,000 populations PCS
x
Health technicians per 10,000 population Person
x
Registered nurses per 10,000 population Person
x
Hospital bed occupancy rate by region %
x
Expenditures on health care by local finances Hundred Million Yuan
x
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Hundred Million Yuan
x
Per Capita Disposable Income Yuan
x
2.2 Method Introduction
Principal Component Analysis, a technique for
reducing dimensionality, stands as PCA commonly
that reconstructs the original variables into
uncorrelated principal components by linear
combination. The advantage of using this method is
that it simplifies analysis complexity by removing
redundant data and extracting key features. It also
maximizes the preservation of the original data
structure, further simplifying the data analysis
process.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Data Preprocessing
In order to eliminate the difference in magnitude
between different feature indicators, it is necessary to
use Z-Score standardization to ensure that the
contribution of each existing data to the model results
is fair. After that, to verify the selected data's
suitability and effectiveness, employed were the
KMO and Bartlett's tests in this study. Shown in
Table 2 are the obtained results. Reaching 0.662 was
the KMO value, while the significance level p = 0.000
was observed. Thus, it can be seen that sufficiently
reliable are the measurement outcomes obtained
through these tests.
Table 2: The value of KMO and Bartlett's tests
KMO
Value
Bartlett's tests
Approximate Chi-
squared value
degrees of
freedom
significanc
e level
0.662 273.015 36 0.000
Indicator extraction
Following data validation and processing, PCA
was employed for feature extraction and subsequent
analysis. The results are presented in Tables 3.
Further analysis based on the data in Table 3.
Employing the Kaiser-Harris criterion, factors with
eigenvalues exceeding 1 were retained. This study
extracted three principal components using PCA. The
eigenvalue for Component 1 was found to be 3.844,
while Component 2 showed a value of 2.556. As for
Component 3, it was only 1.348. These three
components collectively accounted for 86.086% of
the variance. Overall, the information loss from the
original indicators was minimal, indicating a
satisfactory outcome from the PCA.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
392
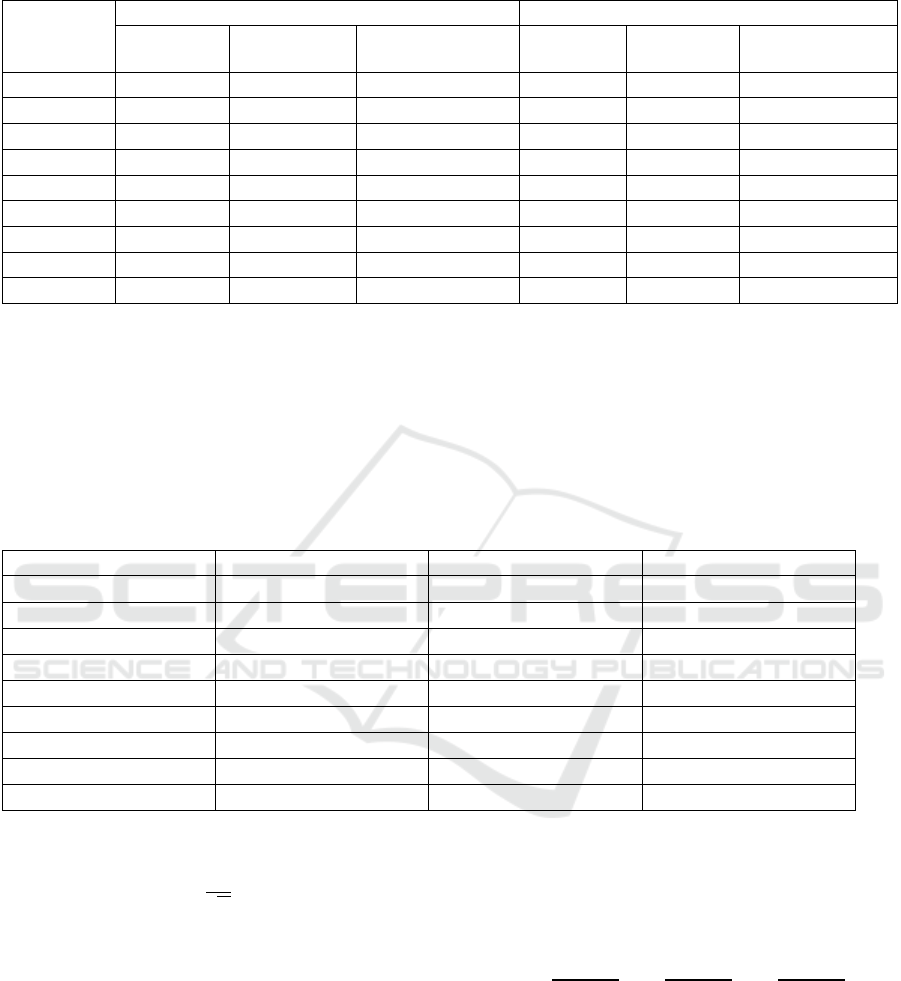
Table 3: Explained Variance
Component
Initial Eigenvalue Sum of Squares of the Factor Loadings
Initial
Eigenvalue
Percentage of
Variance
variance
contribution rate%
Total
Eigenvalue
Percentage
of variance
variance
contribution rate%
1 3.844 42.710 42.710 3.844 42.710 42.710
2 2.556 28.395 71.105 2.556 28.395 71.105
3 1.348 14.980 86.086 1.348 14.980 86.086
4 0.710 7.886 93.971
5 0.266 2.960 96.931
6 0.137 1.518 98.449
7 0.059 0.654 99.103
8 0.053 0.593 99.696
9 0.027 0.304 100.000
3.2 Principal Component Analysis
From Table 4 can be observed the component matrix,
which emerges after principal components extraction
procedures. This matrix elucidates the
correspondence between each indicator and the
extracted principal components. Employing an
absolute factor loading coefficient threshold of 0.5, it
observes that indicators x_1, x_2, x_6, x_7 and x_8
correspond to component 1; indicators x_4,x_5 and
x_9 correspond to component 2; and indicator x_3
corresponds to component 3. Consequently, the linear
combinations of the principal component factors can
be expressed as in equation (1).
Table 4: Component Matrix
Indicator Component 1 Component 2 Component 3
x
0.938 -0.271 0.063
x
0.759 -0.397 0.253
x
-0.036 -0.241 0.922
x
-0.059 0.911 0.209
x
0.098 0.858 0.439
x
0.652 0.191 0.215
x
0.969 0.065 -0.090
x
0.940 0.044 -0.203
x
0.354 0.811 -0.313
𝐹
=
∑
𝐴
∗𝑍𝑥
, (𝑖 = 1,2,3) (1)
𝐴
=
, (𝑖 = 1,2,3)
(2)
From equation (2) where 𝐴
denotes the
eigenvectors, 𝐵
represents the i-th column vector of
the component matrix for the three extracted principal
components, 𝐶
signifies the eigenvalues of the three
extracted principal components and 𝑍𝑥
is the
variable matrix after Z-score standardization of the
data for each province.
Substituting 𝐴
yields three linear combinations
of 𝐹
r e g a r d i n g 𝑍𝑥
. Subsequently, substituting the
𝑍𝑥
data into equation (1) allows for the derivation of
principal component scores for each province. This
process effectively transforms the initial nine
indicators into three composite indicators, 𝐹
, 𝐹
, and
𝐹
, which represent the allocation of regional
healthcare resources. To be more specific, a
comprehensive principal component evaluation
model is generated. The specific model is shown in
equation (3).
𝐹=
𝐹
+
𝐹
+
𝐹
(3)
By substituting the data for 𝐹
, 𝐹
, and 𝐹
into
equation (3), a comprehensive score (F) is calculated
for each province. The results of this analysis are
presented in Table 5. It shows the top regions for
medical resource allocation. Beijing ranks first,
followed by Guangdong Province and Zhejiang
Province. Conversely, Tibet Autonomous Region,
Qinghai Province, and Ningxia Hui Autonomous
Region, occupying the bottom three positions. These
Research on the Influencing Factors of Chinese Healthcare Resource Allocation Problems Based on Principal Component Analysis
393
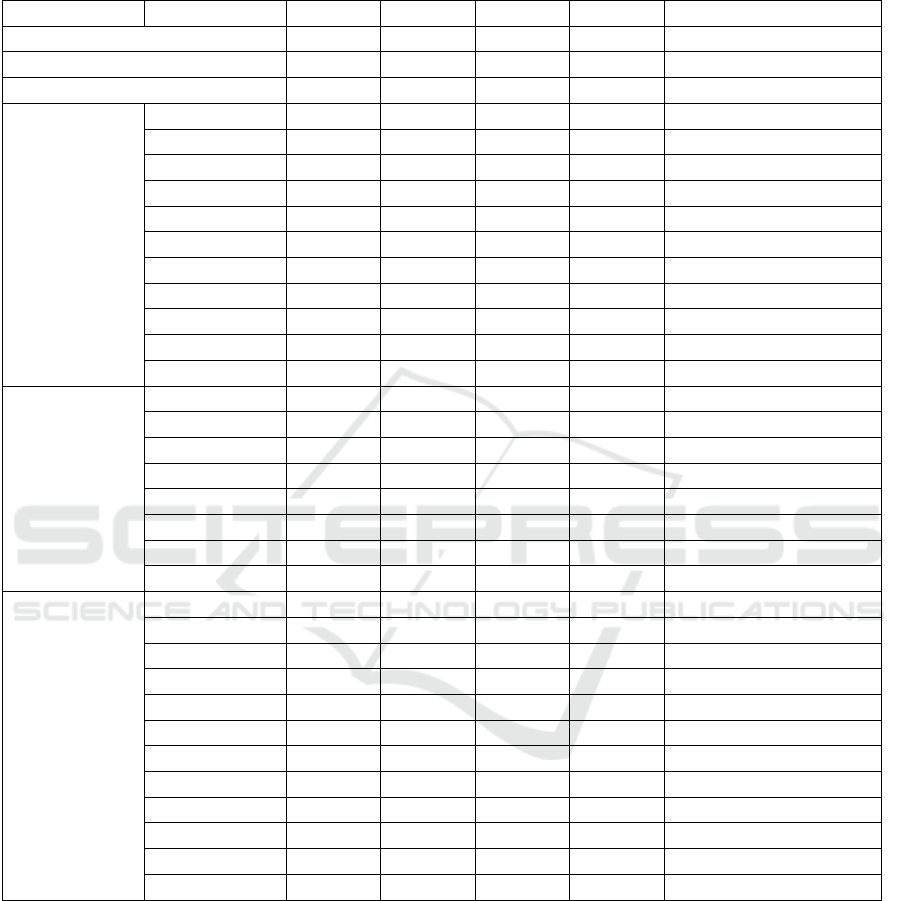
areas are all located in China's western part. All in all,
the result reveals that medical and health resources
are predominantly concentrated in the eastern region,
gradually decreasing as one moves westward.
Table 5: Region Comprehensive Score
Region Province
F
F
F
F Comprehensive Ranking
Eastern Region 0.999 0.875 -0.781 0.648 1
Central Region 0.065 -0.740 0.614 -0.105 2
Western Region -0.959 -0.309 0.306 -0.524 3
Eastern Region
Beijing -0.055 6.555 0.539 2.229 1
Tianjin -1.990 1.191 -2.061 -0.953 27
Hebei 1.125 -1.604 -0.370 -0.035 14
Shanghai 1.041 3.318 -0.591 1.508 5
Liaoning -0.780 -0.499 0.660 -0.437 19
Fujian 0.106 -0.332 -1.769 -0.365 18
Guangdong 5.207 -0.957 -2.546 1.825 2
Hainan -2.309 0.182 -0.873 -1.237 28
Jiangsu 3.242 0.399 -0.838 1.594 4
Zhejiang 2.403 1.888 -0.912 1.656 3
Shandong 2.996 -0.512 0.174 1.348 6
Central Region
Anhui 0.345 -0.761 0.117 -0.060 15
Jiangxi -0.134 -1.315 -0.399 -0.570 20
Heilongjiang -1.204 -1.192 1.347 -0.756 25
Henan 2.392 -1.319 1.029 0.931 8
Hubei 0.826 -0.456 0.811 0.400 10
Hunan 0.953 -0.750 1.262 0.445 9
Shanxi -0.814 -0.650 -0.233 -0.659 22
Jilin -1.847 0.528 0.981 -0.571 21
Western Region
Chongqing -0.663 -0.146 0.740 -0.248 17
Sichuan 2.305 -0.788 1.667 1.173 7
Guizhou -0.610 -0.359 1.363 -0.184 16
Yunnan 0.225 -0.045 1.072 0.283 12
Tibet -3.307 -2.091 -2.733 -2.806 31
Shaanxi -0.145 0.570 1.054 0.300 11
Gansu -1.680 -0.502 0.802 -0.860 26
Qinghai -2.792 -0.047 0.143 -1.376 30
Ningxia -2.598 0.564 -0.906 -1.261 29
Xinjiang -0.789 -0.938 0.100 -0.683 24
Inner Mongolia -1.534 0.267 -0.028 -0.678 23
Guangxi 0.084 -0.197 0.400 0.047 13
3.3 Discussion
Through the above analysis, it highlights uneven
medical resource allocation across China’s eastern,
central, and western regions, aligning with findings
by Liu (2023). And the Economic development levels
and demographic factors further shape this disparity,
corroborating research by Liu et al. (2024).
Based on the above research, this paper makes the
following recommendations:
The eastern region requires optimized healthcare
resource allocation to address its concentration in
urban hubs. It should be comprehensively evaluated
based on the coverage of existing primary care
organizations, the scope of the population served, and
other factors (Feng, 2019). And policies should
promote the coordinated, balanced and sustainable
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
394

development of medical resources within the region
(Guo, Li, &Wu, 2024). Furthermore, telemedicine
and routine expert consultations can further support
central, western, and less-developed regions,
enhancing overall healthcare quality. For example,
Peking University First Hospital has assisted many
county hospitals by sending experts. They have
promoted the development of local medical care.
As a bridge between east and west, the central
region should establish provincial healthcare centers
to integrate advanced eastern resources and
technologies, extending their benefits westward for
improved resource-sharing efficiency. Meanwhile,
through implementing a concurrent construction and
training approach can upgrade infrastructure and
elevate local medical capabilities. For instance, the
collaboration with the Second Affiliated Hospital of
Xi'an Jiaotong University to establish a national
regional medical center aims to leverage Xinjiang as
a base, radiate to the northwest and Central Asia, and
achieve coordinated development in regional
healthcare.
As health human resources are converging to
developed regions (Lei, Yan, Hu, Xi, &Xiao, 2023),
the western region needs policies incentivizing talent
mobility. The government needs to establish long
term retention mechanisms to attract skilled
professionals, measures to encourage experts to
relocate westward, and strategies to reduce local
talent outflow. As the same time, the government
should redistribute funds from developed to
underdeveloped provinces to balance regional
financial burdens (Li, Yang, &Chen, 2025). This
could equalize medical resource allocation.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on 2022 data encompassing population,
economic indicators, and healthcare supply, this
paper analyzes the factors influencing healthcare
resource allocation of China. Overall, the
comprehensive scores for the eastern region exceed
zero, indicating a positive trajectory for the future
development of healthcare resources. Conversely, the
central and western regions exhibit comprehensive
scores below zero, suggesting significant challenges
and slower progress in healthcare resource allocation.
Further analysis of F1, F2, and F3 reveals a notable
disparity in the F3 score for the eastern region
compared to other areas. This suggests a higher
population density in the eastern region, leading to a
sustained high demand for hospital beds and chronic
operational strain on healthcare facilities. However,
the eastern region maintains advantages in terms of
hospital quantity, quality of medical resources,
economic factors, and healthcare demand. In contrast,
the central and western regions, characterized by
lower population densities, experience significantly
reduced healthcare demand compared to the eastern
region. These regions also face lower government
economic investments, leading some areas to lagging
development and facing the challenge of
underutilized medical resources.
Based on these findings, The paper proposes
several recommendations. These recommendations
aim to provide a reference for the development of a
Healthy China. Implementing these policies can
facilitate resource sharing among regions, reduce
healthcare disparities, and ensure equitable access to
medical services for the population. Ultimately, the
goal is to establish a high-quality and efficient
healthcare service system, significantly improving
the health of the population and achieving the long-
term objective of building a healthy nation
commensurate with a modern socialist country.
REFERENCES
Dai, J., Zhou, Z., Yu, L., & He, Y., 2023. Analysis of the
regional differences and convergence of medical
resource allocation efficiency in rural China. China
Health Service Manage, 40(08), 616–621.
Feng, W., 2019. Research on the allocation of primary
medical resources in China under the background of
Healthy China strategy (Master’s Thesis, Jilin
University).
Guo, J., Li, H., & Wu, A., 2024. Status quo and equity of
healthcare resource allocation in China. Chinese Rural
Health Service Administration, 44(11), 769–775+781.
Lei, Z., Yan, W., Hu, W., Xi, N., & Xiao, J., 2023. Analysis
on the balance of primary health care resource
allocation in China. Journal of Nanjing Medical
University (Social Sciences), 23(05), 404–408.
Li, L., Yang, S., & Chen, Z., 2025. Spatio-temporal
evolution and trend prediction of the coordinated
development of medical resource allocation and
economic and social coupling. Chinese Health
Economics, 44(01), 40–46.
Li, Y., 2023. Study on the rationalization and the
influencing factors of medical resources allocation in
China (Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University).
Liu, H., Wang, L., Kou, L., Xia, X., Dong, Q., & He, X.,
2024. Study on allocative efficiency of primary medical
and health resources and influencing factors in China.
Soft Science of Health, 38(08), 53–57.
Liu, R., & Zhao, Y., 2024. Current status and optimization
research of municipal medical resource allocation.
Assets and Finances in Administration and Institution,
(03), 44–46.
Research on the Influencing Factors of Chinese Healthcare Resource Allocation Problems Based on Principal Component Analysis
395

Liu, Y., 2023. Allocation efficiency measurement of
primary health resources in China and policy
recommendations. Chinese Rural Health Service
Administration, 43(09), 644–649.
Zheng, H., Wu, J., Zhang, N., & Gao, S., 2018. Research on
balance of medical resource allocation under new
urbanization of Jiangsu Province based on principal
component analysis. Medicine and Society, 31(08), 8–
10+21.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
396
