
Research on the Dynamic Game in Consumer Choice Between Fuel
and Electric Vehicles
Junhao Wu
a
Rugao International Academy, Nantong, Jiangsu, 226500, China
Keywords: Dynamic Game, Consumer Choice, Fuel Vehicles, Electric Vehicles.
Abstract: This study uses a coordinated game model to analyze consumer behavior in the transition between fuel and
electric vehicles (EVs), emphasizing the synergistic role of government policy incentives, regional
infrastructure equity, and collective social norms in shaping market equilibrium. A comparative case study of
Norwegian EV dominance and Chinese subsidy-driven volatility shows that fragmented policies (e.g., sudden
subsidy cuts or uneven infrastructure investment) cannot break the tram sector’s dependence, while an
integrated strategy achieves a stable Nash equilibrium. Key findings highlight the environmental and
economic benefits of electric vehicles, including a 50% lifecycle reduction and long-term cost savings, but
also highlight ongoing challenges: the urban-rural tram infrastructure rate gap (12% coverage), the
unpredictability of post-subsidy market volatility (sales fell by 40% after subsidy cuts), and socio-geocultural
resistance (e.g., fossil fuel dependence in Texas). To address these issues, the study proposes a multi-
dimensional framework approach: phased subsidy cuts linked to market penetration thresholds centered on
government decision-making, decentralized solar charging networks for rural areas centered on infrastructure,
and behavior-based campaigns using social media and education based on popular social preferences.
Theoretically, this paper integrates Debreu’s dynamic equilibrium (analyzing subsidy phase-out thresholds)
with Buchanan’s coordination paradigm (for infrastructure-public preference alignment), providing a dual
lens to optimize policy timing and stakeholder incentives.
1 INTRODUCTION
The global transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is a
critical component of achieving carbon neutrality, yet
consumer adoption remains influenced by cost,
infrastructure, and cultural factors. As the world
enters a phase of rapid technological development,
the environmental hazards brought about by the
process of industrial modernization have become a
challenge for the entire globe. From the Paris
Agreement to carbon neutrality, the shift from
traditional fuels to electric and new energy sources
has made environmental protection a global priority.
Especially, Drive EV adoption is especially targeted
by Global carbon neutrality. From the consumer’s
perspective, their choices are still influenced by cost
differentials, infrastructure gaps, and cultural inertia.
For instance, Norway’s EV market share reached
about eighty percent (82%) in 2023 through tax
exemptions and charging networks, while Texas
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-3151-7166
retained 93% fossil fuel vehicles due to infrastructure
deficits and cultural resistance (IEA, 2023). These
reflect the different preferences of consumers in
various countries towards the oil and electric vehicle
market. In order to better understand the government
and society adjustments to the consumption market of
electric vehicles to study its influences on the
formation of Nash equilibrium and coordinated
games, this study examines how policy coordination
reshapes market equilibrium through a dynamic game
framework.
External psychological effect: Smith & Jones
(2021) identified a “bandwagon effect” where peer
preferences accelerate EV adoption. This
psychological effect of the trend toward popular
choices is seen as an important basis for guiding
consumers in their choices of electric vehicles.
Consumers may more readily accept car types that are
more popular with the public.
Wu, J.
Research on the Dynamic Game in Consumer Choice Between Fuel and Electric Vehicles.
DOI: 10.5220/0013814400004708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy (IAMPA 2025), pages 83-89
ISBN: 978-989-758-774-0
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
83

The guiding nature of government policy: Wang
et al. (2022) demonstrated that subsidies exceeding
$5,000 significantly increase EV adoption by
lowering upfront costs. This example shows that the
macro-control of government policies is a decisive
factor that cannot be ignored for the competitiveness
of the electric vehicle industry in the automotive
consumer market. The low market price of electric
vehicles after subsidies is a key reason for consumer
choice.
Infrastructure Impact: Lee (2023) highlighted a
strong correlation between charging density and
urban EV penetration. The completeness of basic
equipment is an important reason affecting
consumers’ choices of related products. This
indicates that the local availability of corresponding
basic supporting facilities, such as charging stations
for electric vehicles, is an important factor for local
consumers when choosing between petrol and electric
cars. It is an explanation of the regional influence on
the hybrid vehicle market.
Existing studies often isolate policy,
infrastructure, or social factors, neglecting their
synergistic impact on consumer behavior and market
equilibrium. Most scholars’ articles mainly study the
impact factors of a specific aspect on consumers’
choice judgments in the economic market. Such
research tends to overlook the cumulative effects
between different factors, resulting in conclusions
that lack flexibility, limit usability, and fail to analyse
the economy from both macro and micro perspectives.
Fragmented interventions fail to address systemic
path dependency. In reality, very few scholars analyse
consumers’ preferences for goods in the economic
market using multi-angle, multi-faceted, and multi-
factor research methods. As a result, objective
choices cannot be well reflected in consumers due to
the lack of relevant research analysis. As explained in
1.2, the influencing factors from the three different
aspects of society, government, and infrastructure
have not been unified and integrated into research,
resulting in the current research on the market
tendencies of oil and electric vehicles being overly
singular and lacking comprehensiveness, making the
analysis of the market insufficiently objective and
complete (Wang, et al., 2022; Lee, 2023; Zhang &
Ren, 2023).
In order to ensure the comprehensive availability
of the research, during the course of this study,
coordinated games will be regarded as the main
approach to researching consumer choices regarding
electric vehicles, thereby analysing the impact of
government, society, and infrastructure on consumer
choices through game theory concepts such as Nash
equilibrium. During the research process,
government variables such as subsidies and
restrictions will interact with social preferences for a
joint study. Additionally, actual data and conclusions
from previous literature will be used to verify the
authenticity of the results. The aim is to provide the
public with a more reasonable and economically
viable choice of electric vehicles through a relatively
objective and multi-faceted research outcome. This
study aims to provide a comprehensive understanding
of consumer preferences for EVs through a multi-
faceted analysis of government policies, social factors,
and infrastructure impacts.
2 CASE DESCRIPTION
2.1 China’s Subsidy-Driven Market
Transition
China’s phased subsidy policy initially boosted EV
adoption but faced challenges when subsidies were
reduced. To promote new energy industries, the
Chinese government implemented a phased subsidy
policy, such as the ’10 cities, 1000 vehicles’ plan,
which initially boosted EV adoption in the public
sector. However, the sudden reduction in subsidies
after the industry reached initial maturity led to a 40%
decline in EV sales. Since the reduction of subsidies
for electric vehicles in 2019, the total sales of the new
energy electric vehicle market have decreased by
40% compared to the past, which highlights the need
for stable coordination of the government to be an
important part of the vigorous development of the
electric vehicle industry (Ma et al., 2017).
2.2 Policy, Infrastructure, and Social
Preferences: A Comparative
Analysis of EV Adoption in Norway
and Texas
The contrasting cases of Norway and Texas illustrate
how policy coordination, infrastructure development,
and social preferences shape EV adoption outcomes.
Norway, a Nordic country, will account for more than
80% of the electric vehicle market in 2023 with
exemption from vehicle purchase tax, full subsidy for
national tram charging fees, and high-density tram
supporting systems, and has established an
environmental protection strategy with tram
transportation as the core of transportation (IEA,
2023, Lee, 2023). Through the Norwegian
government’s set of tram policy models, it is shown
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
84
that the coordinated investment in policy and
infrastructure has greatly accelerated the market
coverage of trams for fuel vehicles (IEA, 2023). In
contrast, The Texas state government’s lax, non-rigid
new energy vehicle promotion policy for electric car
companies and the resistance to the local deep fuel
vehicle culture has led to the fact that petroleum fuel
still accounts for the majority of transportation,
accounting for about 90% of the total number of
vehicles, as shown in Table 1 (IEA, 2023; Alkhathlan
& Javid, 2015).
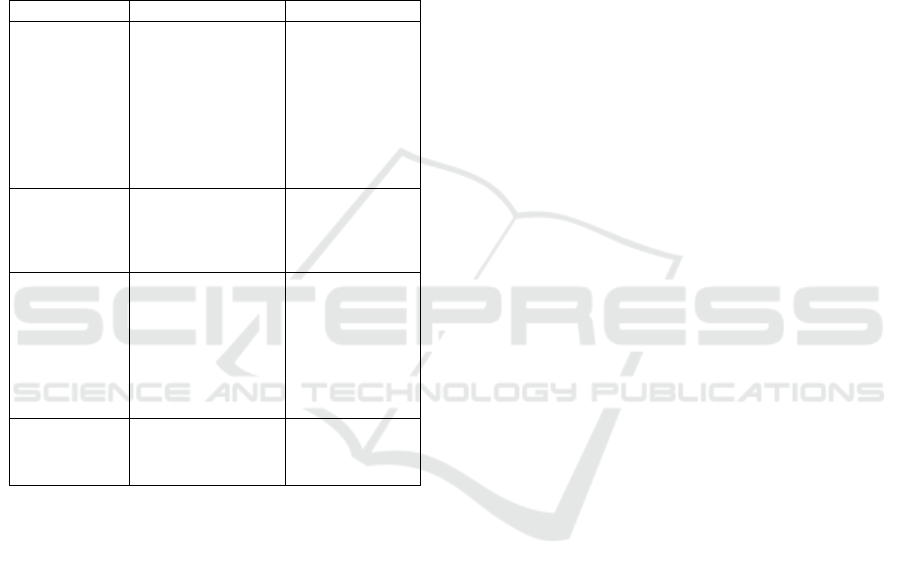
Table 1: Tram differentiation in Norway and Texas
Dimension Norway Texas, USA
Policy
coordination
Tax reductions,
infrastructure
investment, and
social
mobilisation are
proceeding on
three parallel
tracks.
Federal
subsidies are
isolated, and
local policies
are lacking.
Infrastructure
coverage
The density of
charging stations
is eight times that
of Texas.
Less than 5% of
charging piles
in rural areas
Social
preference
With a high degree
of environmental
recognition, EVs
have become
status symbols.
There is strong
cultural
resistance, and
fuel vehicles
are bound to the
values of
“freedom”.
Market
Results
EVs accounted for
82% of the total in
2023
Fuel vehicles
accounted for
93%.
Revelation: The Norwegian case indicates the
“triple synergy” of policy, infrastructure, and culture
is the core mechanism for breaking path dependence.
Conversely, the disjointed policies and lagging
infrastructure in Texas have led the market to be
locked into an inefficient equilibrium. The
contrasting cases of Norway and Texas highlight the
importance of coordinated policy, infrastructure, and
social engagement in driving EV adoption.
3 ANALYSIS ON THE PROBLEM
3.1 Positive Impacts
3.1.1 Significant Environmental Benefits of
Electric Vehicles
EVs provide significant environmental benefits
through reduced emissions and improved air quality.
EVs offer multi-faceted environmental benefits,
including reduced CO2 emissions, improved air
quality, and ecosystem optimization.
Life cycle emission reduction of lithium battery
raw materials: While the production of lithium-ion
batteries, the main fuel for electric vehicles, produces
5-10 tonnes of CO2, tram factories that are driven by
green energy production (such as Tesla’s Berlin
Gigafactory) can reduce carbon pollution emissions
by 40% by optimizing battery production (IPCC,
2022). In China, grid decarbonization policies (36%
of non-fossil energy by 2023) have resulted in a 60%
reduction in polluting gas emissions per kilometer
from electric vehicles compared to fuel-powered
vehicles (Yuan et al., 2015).
Local Pollution Control for Electric Vehicles:
According to the study, PM2.5 concentrations in
Beijing decreased from 80.6 μg/m³ (2015) to 38
μg/m³ (2023), with a 12% reduction in the proportion
related to transportation gas emissions (Zhang & Ren,
2023).
Ecological synergy of new energy use: With an
annual capacity of 150 kWh/m², the solar-integrated
charging station in Oslo balances basic energy
production with the protection of the ecological
environment of the land (IEA, 2023).
3.1.2 High Economic Efficiency Brought by
the Tram Industry
The advantages of the low cost of long-term tram
production and the spillover effect of tram industrial
production of electric vehicles have demonstrated
economic viability through consumer purchases,
savings, and macroeconomic transformation of the
automotive industry.
Consumer Cost Analysis: China’s EV ownership
costs (purchase + electricity + maintenance) total
18,000 over 10 years, 2218,000 over 10 years,
2223,000) (Ma et al., 2017).
Industrial Upgrading: Battery energy density
doubled from 150 Wh/kg (2015) to 300 Wh/kg (2023),
driving advancements in energy storage and drones
(Yang, 2024).
Employment and Trade: China’s electric vehicle
industry employs 1.5 million workers, and 60% of
that human resources are used in battery
manufacturing (Zhang & Ren, 2023). In 2023,
China’s total overseas exports of electric vehicles will
reach 1.2 million units, and China has reduced its
dependence on oil imports through the development
of new energy fuels and the export of electric vehicles
(Yang, 2024).
Research on the Dynamic Game in Consumer Choice Between Fuel and Electric Vehicles
85

3.2 Existing Challenges
The challenges in EV adoption stem from
infrastructure inequities, policy fluctuations, and
socio-cultural resistance.
3.2.1 Inequities in Infrastructure: Spatial
Distance Differences and Behavioral
Habit Disorders
Infrastructure inequities between urban and rural
areas deepen regional disparities in EV adoption.
Large disparities in social, urban, and rural
infrastructure exacerbate regional inequality in EV
use. For example, Norway’s high-density charging
network (8 stations per 100 km) contrasts sharply
with Texas’s sparse coverage (less than 5% in rural
areas), reflecting the impact of coordinated policy and
investment on EV adoption (IEA, 2023; Alkhathlan
& Javid, 2015). Charging Density: The same urban
tram chargers contain only one in ten (12%) in rural
areas (Lee, 2023). In China, this gap in coverage of
urban and rural tram infrastructure coincides with the
2.5:1 urban-rural income gap, so the regional
differences in tram infrastructure construction deepen
the commodity stratification of consumer groups.
Behavioral Inertia: Research shows that the
adoption rate of electric vehicles in Texas, USA, is
very low (7%), and this phenomenon of indifference
towards electric cars actually stems from the cultural
resistance to them in Texas, where fuel cars
symbolize “freedom” in the local culture (Alkhathlan
& Javid, 2015)
3.2.2 Government Policy Fluctuations:
Volatile Consumer Market
Environment and Uncertainty About
Popular Goods
Abrupt changes or enacted changes in government
policies can undermine consumers’ propensity to buy
and businesses’ earnings expectations.
Subsidy Rollback Effects: The Chinese
government’s 2022 reduction in subsidies for
domestic EVs led to a 40% decline in consumer
demand, highlighting the direct impact of policy
changes on purchasing decisions. This volatility
underscores the EV market’s dependence on
government support (Zhang & Ren, 2023).
Regulatory Fragmentation: Local governments in
Texas lack a standardized set of industrial fees for the
NEV industry, resulting in duplicate investment in
their domestic tram companies (IEA, 2023).
3.2.3 Socio-Cultural Lock-In: Identity
Politics and Path Dependency
Cultural narratives and institutional inertia hinder
transitions.
Symbolic Resistance (Subsidy repatriation effect):
In Texas, about seven in ten consumers (68%)
associate gasoline vehicles with their regional
identity (Texas residency) and resist the adoption of
electric vehicles with a regional fuel culture
(Alkhathlan & Javid, 2015)
Corporate Reluctance: Legacy automakers delay
EV R&D due to sunk costs in combustion engine
supply chains (Yang, 2024).
3.3 Extended Analysis: Dynamic Game
Perspective
3.3.1 Coordination Failure in Multi-
Stakeholder Systems
The absence of coordination among policymakers,
firms, and consumers leads to a suboptimal market
equilibrium.
Case: China’s Subsidy Rollback: The abrupt shift
in policy shifts has disrupted commodity supply
chains, just as battery makers faced a huge $2 billion
in stranded assets in response to a policy change in
2019 (Zhang & Ren, 2023).
Theoretical Framework: Using Debreu’s dynamic
equilibrium model, EV market stability requires
Ui(EV)=αPj(EV)+β(Si−Ci)Ui(EV)=αPj(EV)+β(Si−
Ci), where PjPj (peer adoption) and SiSi (policy
benefits) must align (Liu, 2006).
3.3.2 Technical-Level Upper Limit Lock-In
and Innovation-Level Breakthrough
Dilemma
Due to the information network, externalities of high-
paying technology positioning, and new energy
electric vehicles, the traditional technology of
automobile manufacturing occupies a dominant
position in the whole production.
Battery Standardization: Competing standards
(e.g., Tesla NACS vs. CCS) fragment the EV
charging network, increasing the long-term cost of
energy consumption by 15% for EV users (Lee, 2023).
Innovation Trade-offs: Hybrid electric vehicles
(HEVs), a power-driven vehicle type that optimizes
auxiliary fuel energy with electric energy, offer a
transitional advantage for electric substitution of
automotive fuels, but the existence of these hybrid
electric vehicles will extend the actual time to reach
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
86

the full electrification of automotive goods. In the
United States, government commodity subsidies for
HEVs crowd out production investment in EV
development (IEA, 2023).
4 SUGGESTIONS
4.1 Policy Stability Through Gradual
Subsidy Reform
4.1.1 Dynamic Subsidy Adjustment:
Aligning Policy with Market
Penetration
By learning from the Chinese government’s post-
2019 subsidy cuts for electric vehicles, the electric
vehicle market has experienced a period of cooling in
both production innovation and consumer intentions.
This is in contrast to the fact that the Norwegian
government’s incremental tax exemption adjustments
for electric vehicle consumers (e.g., a 5% reduction
per year) have maintained confidence in the purchase
of electric vehicles among mass consumers (IEA,
2023).
Adjustment based on market thresholds: Subsidy
levels should be tied to EV market penetration (e.g.,
reducing subsidies by 30% when EV share exceeds
10%), preventing market oversaturation (Yang, 2024).
Differentiated regulation of regional conditions:
Priority should be given to providing subsidies for
tram consumption and production in underdeveloped
regions (e.g., rural China in remote areas), and at the
same time, incentives for production and
consumption in urban markets saturated with tram
consumption should be phased out for a certain period
of time (Yang, 2024).
4.1.2 Transitioning from Purchase Subsidies
to R&D Incentives
China’s “subsidy-for-innovation” model redirected
$2.8 billion to battery R&D from 2020–2023,
boosting energy density by 25% (Yang, 2024).
Policy Tools: Production Tax Credit for Tram
Patents: The U.S. government provides a 15%
corporate tax deduction to companies with EV-
related patents, such as Tesla’s 4680 battery
technology (Yuan et al., 2015).
Public-Private R&D Funds: Norway’s $500
million Green Innovation Fund co-financed solid-
state battery projects with private firms (IEA, 2023).
4.2 Equity in Tram Infrastructure:
Bridging Geographical Space and
Social Class Gaps
There are 0.3 chargers per square kilometer in rural
China, compared to 2.1 in urban areas (Lee, 2023).
Solutions include:
A new mode of charging for electric vehicles with
distributed solar: Villages with low rainfall have
deployed off-grid solar power stations to reduce the
dependence of electric vehicle charging on the
traditional grid (Zhang & Ren, 2023). For example,
India’s solar microgrids in rural Maharashtra reduced
EV charging costs by 60% through daytime solar
storage, offering a replicable model for low-rainfall
regions.
Cross-Subsidy Mechanisms: Allocate 30% of
urban EV tax revenue to rural infrastructure, as
practiced in Germany’s Ladeinfrastrukturprogramm
(Lee, 2023).
Competing charging standards (e.g., CCS vs.
NACS) raise user costs by 18% (Lee, 2023). Unified
Protocols: Mandate ISO 15118-20 compliance for all
new installations, enabling “plug-and-charge”
interoperability (Lee, 2023). Data Transparency
Platforms: Launch national charging maps (e.g.,
Norway’s Elbilforeningen) to optimize station
utilization (IEA, 2023).
4.3 Behavioral Interventions in
Government: Using Social
Dynamics
4.3.1 Leveraging Social Influence
Mechanisms for EV Adoption
Norway’s EV owners’ Facebook groups increased
peer influence efficacy by 40%, accelerating adoption
(Smith & Jones, 2021).
Partnerships with well-known artists: Partnering
with environmentally conscious celebrities, such as
Eileen Gu, a famous Chinese skier, to promote the
electric vehicle industry through its vast social appeal
by using electric vehicles as a status symbol (Yang,
2024).
Gamified Policy Tools: China’s ‘Green Miles’
app rewards users with tax rebates (up to 5% of
annual vehicle tax) for sharing EV charging reviews,
achieving 1.2 million user engagements in 2023
(Smith & Jones, 2021).
Research on the Dynamic Game in Consumer Choice Between Fuel and Electric Vehicles
87

4.3.2 Education vs. Fossil Fuel Culture:
Curriculum-Based Interventions
Texas’s fossil fuel culture stems from its historical
dominance of regional oil supply. Mitigation
Strategies:
Government integration of electric vehicle policy
into school curricula: Norway’s STEM program has
added an enrichment curriculum on EV-related
technologies to 80% of Norwegian school curricula,
shaping a positive perception of electric vehicle
technology research among young people (IEA,
2023).
Community Tram Culture Workshop: Hold
similar electric vehicle test drive events in areas with
high environmental awareness that resist the
development of gasoline vehicles and subtly cultivate
environmental awareness of public trams, just like the
Eco Mobility Festival in Japan (Yuan et al., 2015).
4.4 Multi-Field Technology
Collaboration: Cross-Industry
Cooperation in Tram Development
Only 5% of lithium-ion batteries are recycled globally.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR):
According to the legal and regulatory requirements of
the European Union for battery manufacturing, car
manufacturers are required to recycle 95% of battery
materials, and the mandatory constraints of the law
are used to raise the awareness of social responsibility
of electric car producers so that battery safety is
basically guaranteed (Yang, 2024).
Blockchain traceability: The use of a distributed
ledger to track the life cycle of a battery makes the
number of ledgers public, greatly avoiding financial
fraud and reducing illegal dumping (Zhang & Ren,
2023). CATL’s blockchain platform tracks 100% of
battery raw materials, reducing illegal dumping
incidents by 75% in pilot provinces (Yang, 2024).
EVs can stabilize grids via vehicle-to-grid (V2G)
systems, yet adoption remains below 1% (Yuan et al.,
2015). Dynamic Pricing Incentives: Offer a 50%
discount on electricity for V2G participants during
peak hours (Yuan et al., 2015). Grid Upgrade
Subsidies: China’s State Grid allocated $1.2 billion to
V2G-compatible transformer upgrades in 2023 (Yang,
2024).
5 CONCLUSION
The paper’s research shows that the transition to
electric vehicles (EVs) in the transportation market is
not just a technological innovation or economic
challenge but a complex game of coordination. Nash
equilibrium in EV markets emerges only when
government policies, infrastructure equity, and social
preferences align.
Policy-infrastructure interdependence: The
success of tram penetration in Norway stems from the
Norwegian government’s policy tax exemption
subsidies and Norway’s dense infrastructure charging
network system, while the volatility of government
tram subsidies in China highlights the hidden risks of
policy intervention in the decentralized tram industry.
Dynamic influence of social and regional culture:
Regional cultural accumulation, such as the dominant
identity of fossil fuels in Texas or the green spirit of
Nordic Norway, is either an obstacle to the
development of electric cars or an accelerator of
electric variation and this dynamic cultural attribute
plays a role in reshaping consumer perceptions and
social preferences in the coordination game.
The research provides actionable strategies for
governments and industries: Dynamic Policy
Calibration: Gradual subsidy reductions paired with
R&D incentives can stabilize markets, as evidenced
by China’s battery innovation surge. Infrastructure
Justice: Solar-powered rural charging stations and
cross-regional subsidies can mitigate spatial
disparities. Behavioral Leverage: Social media
campaigns and educational programs, like Norway’s
STEM curricula, amplify peer effects and dismantle
cultural resistance.
While this study offers systemic insights, two
constraints warrant attention: Data scope: The
reliance on secondary data limits the analysis of
behavior at the micro level of coordinated games.
Future research can integrate original surveys to
capture consumers’ nuanced decisions.
Technological developments: The rapid development
of solid-state batteries and V2G systems is likely to
redefine the equilibrium in the electric vehicle market.
It is essential to keep track of these technological
innovations on a continuous basis. Forward-looking
comprehensive outlook: The transition to electric
vehicles is a typical microcosm of the broader
challenges of sustainable industrial transformation.
As the classical theory of dynamic equilibrium
postulates, stability does not come from isolated
interventions but from the continuous alignment of
rules, resources, and social values. Policymakers
must embrace this complexity if they move from
“locked-in” fossil fuel inertia to a resilient low-carbon
balance of electricity and new energy.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
88

REFERENCES
Alkhathlan, K., & Javid, M., 2015. Carbon emissions in
Saudi Arabia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy
Reviews, 48, 105–111.
IEA., 2023. Global EV Outlook 2023. International Energy
Agency.
IPCC., 2022. Climate Change Mitigation. Cambridge
University Press.
Lee, C., 2023. Infrastructure and EV
penetration. Transportation Research, 77(4), 55–67.
Liu, Y., 2006. Dynamic equilibrium and coordination
theories. Price Monthly, 9, 44–45.
Ma, S. C., et al., 2017. Evaluating vehicle purchase
restrictions in China. Energy Policy, 110, 609–618.
Smith, A., & Jones, B., 2021. Network effects in EV
adoption. Journal of Environmental Economics, 45(3),
112–125.
Wang, L., et al., 2022. Subsidy thresholds for EV market
transitions. Energy Policy, 88, 200–210.
Yang, X., 2024. A review of subsidy impacts on China’s
NEV industry. Internal Combustion Engine &
Parts, 24, 122–124.
Yuan, X., et al., 2015. NEV development for
sustainability. Renewable and Sustainable Energy
Reviews, 42, 298–305.
Zhang, M., & Ren, X., 2023. Policy volatility in China’s
EV market. Sustainability, 15(8), 3205.
Research on the Dynamic Game in Consumer Choice Between Fuel and Electric Vehicles
89
