
Research on the Influencing Factors of Depression in Young Students
Based on Binary Logit Regression
Xiaoyu Chen
a
Leicester International Institute, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221, China
Keywords: Binary Logit Regression, Depression in Young Students, Influence Factors.
Abstract: With the progress of time and economic development, the depression of young students deserves attention.
The study on the influencing factors of depression in this group is of great significance for prevention and
treatment. The objective of this study was to identify the underlying determinants of depression in young
students. First, this study used the Student Depression Analysis dataset for feature analysis and then combined
it with correlation analysis to identify the factors that have a significant impact on depression. Then, Binary
Logit Regression analysis is carried out on these data to further explore its influence mechanism, and the test
shows that the model has a good fitting effect of independent variables. The study found that academic and
economic pressure had a significant positive impact on depression in young students. Therefore, improving
these factors through schools can control depression and boost young students' mental health.
1 INTRODUCTION
The mental health problems of young students have
been paid more and more attention by researchers.
Depression is a kind of emotional disorder seen in
young students. It may cause persistent feelings of
sadness over an extended period and may even lead to
suicidal thoughts (Gao et al.,2020). Confusion and
uncertainty can also cause anxiety. More and more
students around the world are falling into depression
(Liu & Wang, 2024), with about 30% of college
students worldwide reporting depressive symptoms
(Fu et al., 2020). According to the World Health
Organization's Mental Health report released on 10
October 2024, it is estimated that one in seven people
aged 10-19 globally suffer from mental disorders,
representing 15 percent of the worldwide health
issues within this demographic. Depression, anxiety,
and behavioral disorders are among the primary
conditions contributing to disease and disability in
adolescents. In individuals aged 15 to 29, suicide
ranks as the third most common cause of mortality.
(World Health Organization, 2024).
According to the study by Gao et al (2020), the
prevalence rate of depression among Chinese college
students was 28.4% through meta-analysis. Among
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-1417-8200
them, non-freshmen students, ethnic minorities,
people with religious beliefs, and left-behind
childhood experience had a higher risk of depression,
while students with parents with higher education
levels had a lower risk of depression. Liu & Wang
(2024) found a significant negative correlation
between college satisfaction and the depression rate
of college students through the cross-lag model.
Cassady et al (2019) deduced the correlation between
academic anxiety and depression based on the
assessment of a wide range of neuroticism, and the
research results showed that the probability of college
students suffering from depression could be predicted
through the perception of academic pressure.
Qu et al (2024) began to explore the impact of
school education on students' depression, and the
study showed that age, gender, and experience of
abuse were risk factors for depressive symptoms,
while parent-child relationship and psychological
resilience were protective factors for depressive
symptoms. Khawaja & Duncanson's (2008) study
measured students' depression through the USDI
scale, which accurately identified the groups most in
need of help. Although existing studies have
discussed the prevalence of depression and its
influencing factors in college students from various
perspectives, the correlation among influencing
20
Chen, X.
Research on the Influencing Factors of Depression in Young Students Based on Binary Logit Regression.
DOI: 10.5220/0013813300004708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy (IAMPA 2025), pages 20-24
ISBN: 978-989-758-774-0
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
factors and the difference in their effects on
depression have not been discussed.
This study used the data set of depression among
young students, visualized the influencing factor data
set through feature distribution and correlation
analysis, and built a binary logistic regression model
with depression as a binary dependent variable,
aiming to identify the factors leading to depression
among students, and then designed intervention
strategies.
2 METHOD
The dataset used in this study included 16 factors
affecting depression in young students, with a total
sample size of 27,900 (Kaggle, 2024). This data
comes from the Kaggle website, and after testing, the
overall sample missing rate is close to zero, meeting
the strict data quality requirements. Among them,
age, academic stress, work stress, CGPA, learning
satisfaction, career contentment, study(work) hours,
and economic pressure were 8 numerical variables,
and gender, city, occupation, sleep duration, eating
habits, degree, suicidal thoughts, and family medical
history were 8 textual variables. The study's data set
has quantified academic stress, job stress, learning
satisfaction, job satisfaction, and financial stress into
numerical variables ranging from 0 to 5, with
increasing stress and satisfaction.
Binary logit regression models the probability
relationship between dependent and independent
variables using the Logit function, which is specially
used to deal with binary dependent variables. The
output result of this model is the probability of
depression, which can be effectively used to predict
depression. The argument variables in this study
include numerical type and fractal type, and the
binary logit regression can deal with both kinds of
argument variables. At the same time, the regression
coefficient of this model can represent the degree of
influence of independent variables on the probability
of depression. The model formula is as follows:
𝑙𝑜𝑔
= 𝛽
+ 𝛽
𝑋
+ ⋯+ 𝛽
𝑋
, (1)
where p is the probability that the dependent
variable is 1, 𝑋
,…,𝑋
are the independent variables
, 𝛽
,…,𝛽
are the regression coefficient of the
independent variables,𝛽
is the intercept term. The
model assumes that the dependent variable is binary
and conforms to Bernoulli distribution. The value of
the dependent variable obeys independence; There is
no multicollinearity between independent variables;
No normal value, etc.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Statistical Analysis of Depression in
Young Students
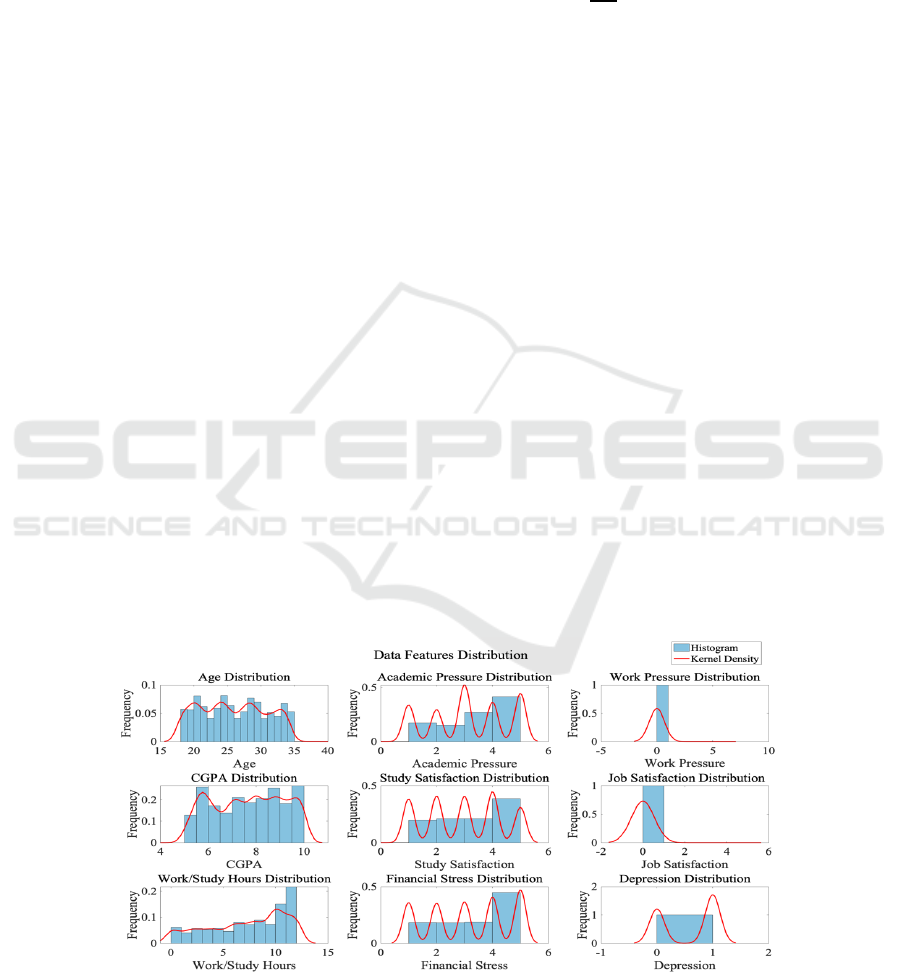
Figure 1 lists the results of descriptive statistics on the
characteristic distribution of independent variables
affecting students' depression. Figure 1 shows the
data distribution of age, academic pressure, job
pressure, CGPA, study satisfaction, job satisfaction,
study (work) hours, economic pressure, and whether
people suffer from depression, in order from left to
right. The horizontal coordinate represents the
numerical variable itself, and the vertical coordinate
represents the frequency of the numerical variable
under different values.
Figure 1: Characteristic distribution of numerical variables (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Research on the Influencing Factors of Depression in Young Students Based on Binary Logit Regression
21
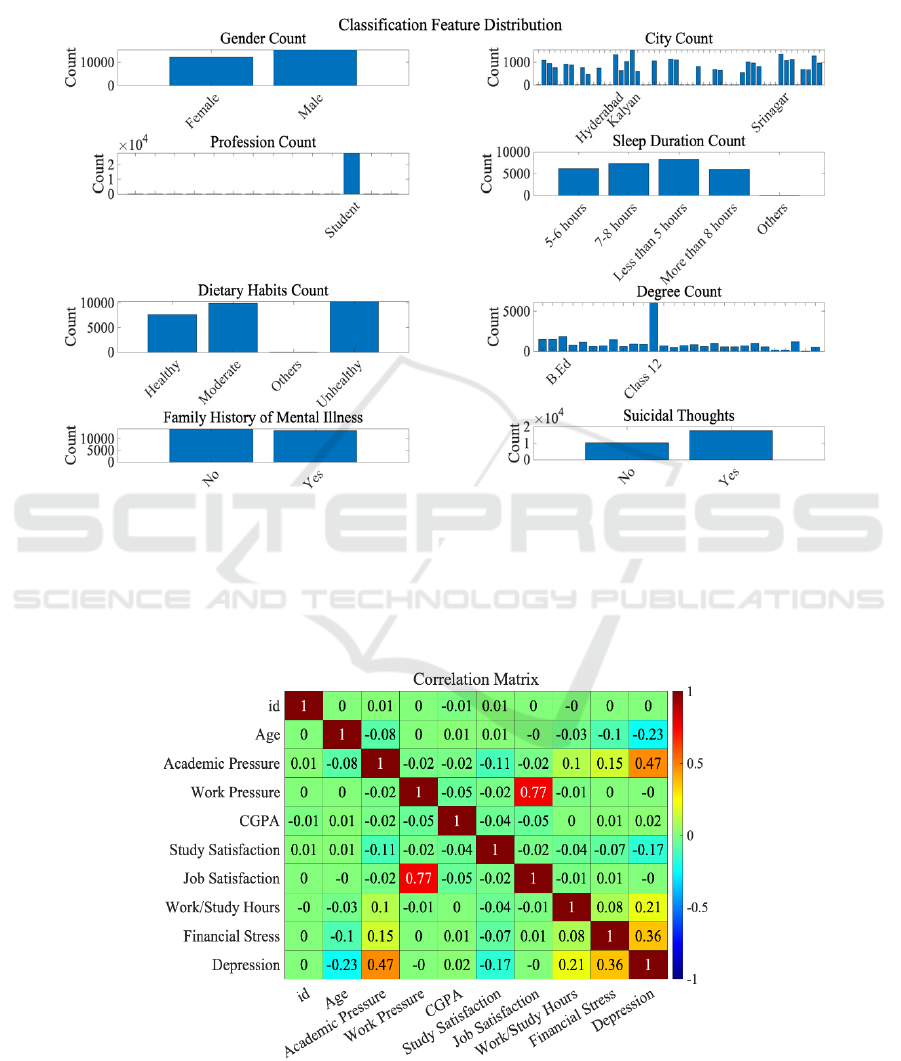
Figure 2 shows the characteristic distribution of
textual variables, namely, the data distribution of
gender, city, occupation, sleep duration, eating habits,
degree, family medical history, and suicidal thoughts.
The horizontal coordinate represents the textual
variable itself, and the vertical coordinate represents
the frequency of the textual variable.
Figure 2: Characteristic distribution of categorical variables (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Figure 3 lists the correlation coefficient matrix of
depression influencing factors obtained by correlation
analysis.
Figure 3: Correlation coefficient matrix of influencing factors of depression among young students (Photo/Picture credit:
Original).
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
22

As shown in Figure 3, the correlation between job
pressure and job satisfaction is the strongest, and
academic pressure and economic pressure are the
most significant factors affecting young students'
depression. Table 1 lists the data obtained from the
binary logit regression analysis and the related results
obtained from these data (Table 1).
Table 1: Summary of Results of Binary Logit Regression Analysis
Sum Re
g
ression coefficient Standard erro
r
z Wald
χ
2
p
OR
p
rice 95% CI
Age -0.111 0.004 -29.289 857.830 0.000 0.889 ~ 0.903
Academic Pressure 0.835 0.015 57.567 3314.000 0.000 2.241 ~ 2.372
CGPA 0.061 0.012 5.001 25.005 0.000 1.037 ~ 1.088
Stud
y
Satisfaction -0.240 0.013 -18.138 328.980 0.000 0.766 ~ 0.807
Work/Stud
y
Hours 0.116 0.005 23.868 569.680 0.000 1.112 ~ 1.134
Suicidal Thoughts 2.510 0.038 65.766 4325.200 0.000 11.409 ~ 13.249
Financial Stress 0.554 0.013 42.497 1806.000 0.000 1.696 ~ 1.784
Family Histor
y
0.243 0.036 6.805 46.303 0.000 1.188 ~ 1.367
interce
p
t -3.244 0.160 -20.227 409.130 0.000 0.029 ~ 0.053
As can be seen from Table 1, age, academic
pressure, CGPA, study satisfaction, work/study time,
suicidal thoughts, economic pressure, and family
history of mental illness were independent variables.
Binary Logit regression analysis was conducted with
depression as the dependent variable, and the model
formula was obtained as follows:
ln
= −3.244 − 0.111 × 𝐴𝑔𝑒 + 0.835 ×
𝐴𝑐𝑎𝑑𝑒𝑚𝑖𝑐 𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒+⋯+0.243×
𝐹𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑙𝑦 𝐻𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦 (2)
It can be seen from the data in the table that
academic pressure and economic pressure have a
significant positive impact on depression, and the OR
value of academic pressure is 2.241 ~ 2.372,
indicating that the probability of depression increases
by about 124% ~ 137% for every unit increase of
academic pressure. The OR value of economic stress
was 1.696-1.784, indicating that the probability of
depression increased by about 69.6% to 78.4% for
every unit increase in economic stress. Learning
satisfaction has a significant negative impact on
depression; its regression coefficient is -0.240, and
the OR value is 0.766 ~ 0.807, indicating that with
each unit increase in learning satisfaction, the
probability of depression decreased by about 19.3% ~
23.4%.
In this study, the binary Logistic regression model
was tested by likelihood ratio and pseudo-R2. The
result of the likelihood ratio test is p = 0.000, and the
result of the pseudo-R2 test is Nagelkerke R2 = 0.631.
Therefore, the model's eight independent variables
significantly predict young students' depression
levels, with excellent fit.
3.2 Discussion
The summary analysis suggests that it is necessary to
provide mental health services for this population,
regularly assess depressive symptoms, and develop
targeted depression prevention programs (Luo et
al.,2021). Academic and financial pressures
significantly increase the likelihood of depression;
age and study satisfaction hurt depression, and
gender, work pressure, and job satisfaction have no
significant impact on depression.
Therefore, schools and educational institutions
should reasonably set up courses and examination
arrangements, avoid over-squeezing students' energy
and time to put them in a long-term state of high
pressure and reduce students' academic pressure.
They can help college students develop a healthy
lifestyle with regular diet and exercise (Xiao et
al.,2022). The government and social organizations
should provide financial assistance to alleviate the
financial pressure on young students. Controlling the
significant factors affecting depression can
effectively reduce the incidence of depression and
improve the mental health level of young people. At
the same time, the study is limited in that traumatic
events that young students may experience, such as
bullying, are not taken into account in the general
influence factors, and these extreme events have a
strong influence on the development of depression in
students (World Health Organization, 2023). The
specific causes of depression of students at different
stages are different. For example, the study of Teng et
al. (2022) constructed a group portrait of doctoral
students with depression risk and found that
overwork, work-life imbalance, and poor
Research on the Influencing Factors of Depression in Young Students Based on Binary Logit Regression
23

relationships between supervisors and students are
typical characteristics of these doctoral students, and
the data in this study span a large age range.
4 CONCLUSION
In this study, a binary logit regression with depression
of young students as the dependent variable was used,
and age, academic pressure, CGPA, study
satisfaction, work/study hours, suicidal tendency,
economic pressure, and family history of mental
illness were used as the independent variables. The
relationship among the factors affecting the
depression of young students is discussed. By
analyzing a large number of depression data, a series
of statistical results are obtained. For example, job
pressure and job satisfaction have the strongest
correlation, and academic pressure and economic
pressure have a significant impact on young students'
depression.
The regression model based on this study can
make some recommendations for future treatment and
prevention. Professionals should seriously consider
these two factors when formulating strategies to deal
with depression and improve the learning and life
experience of young students by modifying education
and college-related policies to alleviate academic
pressure to reduce the outbreak rate of depression in
young students. At the same time, future research can
further explore other factors that may affect the
depression situation of young students to gain a more
comprehensive understanding of the mental health
status of young students.
REFERENCES
Cassady, J. C., Pierson, E. E., Starling, J. M., 2019.
Predicting student depression with measures of general
and academic anxieties. Front. Educ. 4, 11.
Fu, Z., Zhou, S., Burger, H., Bockting, C. L. H., Williams,
A. D., 2020. Psychological interventions for depression
in Chinese university students: a systematic review and
meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 262, 440-450.
Gao, L., Xie, Y., Jia, C., et al., 2020. Prevalence of
depression among Chinese university students: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 10,
15897.
Kaggle, 2024. Student depression dataset. Accessed
December 15, 2024.
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/hopesb/student-
depression-dataset/data
Khawaja, N. G., Duncanson, K., 2008. Using the University
Student Depression Inventory to investigate the effect
of demographic variables on students' depression. J.
Psychol. Couns. Sch. 18(2), 195-209.
Liu, X., Wang, J., 2024. Depression, anxiety, and student
satisfaction with university life among college students:
a cross-lagged study. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11,
1172.
Luo, W., Zhong, B.-L., Chiu, H. F.-K., 2021. Prevalence of
depressive symptoms among Chinese university
students amid the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci.
30, e31.
Qu, M., Yang, K., Ren, H., et al., 2024. The impact of
school education on depressive symptoms in Chinese
adolescents: a prospective longitudinal study. Int. J.
Ment. Health Addict. 22, 1582–1596.
Teng, C., Yang, C., Liu, Q., 2024. Utilizing AI technique to
identify depression risk among doctoral students. Sci.
Rep. 14, 31978.
World Health Organization, 2023. Depressive disorder.
Accessed March 31, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-
room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
World Health Organization, 2024. Adolescent mental
health. Accessed October 10, 2024.
https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-
sheets/detail/adolescent-mental-health
Xiao, P., Chen, L., Dong, X., Zhao, Z., Yu, J., Wang, D.,
Li, W., 2022. Anxiety, depression, and satisfaction with
life among college students in China: nine months after
initiation of the outbreak of COVID-19. Front.
Psychiatry 12, 777190.
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
24
