
Research on the User Behaviour Game Analysis of Social Network
Rumour Propagation Based on the Weibo
Hailan Lan
a
Chengdu No.7 High School International Department, Chengdu, Sichuan, 610095, China
Keywords: Social Media, Weibo Rumor Propagation, Game Theory, User Behavior, Multi-Group Game-Theoretic
Model.
Abstract: “Rumor propagation on social media poses significant challenges to public trust and social stability.” In
today’s digital world, rumour propagation on social media has posed significant challenges to public trust and
social stability. Weibo, China’s dominant social media platform, accelerates rumor propagation through its
openness and real-time features, leading to social panic, trust crises, and economic losses. This paper
innovatively develops a multi-group game-theoretic model that classifies users into spreaders, refuters, and
ordinary users, analyzing their payoff functions and strategic choices through Nash Equilibrium theory to
uncover the potential influence factors of rumor spread. The study demonstrates that algorithmic
recommendation mechanisms, users’ psychological characteristics, and the response efficiency of debunking
systems constitute the three pivotal factors affecting rumor propagation. Accordingly, we propose an
integrated solution framework: restructuring platform incentives to modify user payoffs, implementing media
literacy programs, enhancing rumor-refuting systems for rapid response, and recalibrating algorithms to
reduce misinformation exposure. This research not only extends the application of game theory in social
media studies but also establishes a theoretically grounded and practically viable approach for platform
governance, providing actionable insights for improving social media governance and mitigating the negative
impacts of rumors.
1 INTRODUCTION
As the social network develops by leaps and bounds,
Weibo, as one of the largest social media platforms in
China, has become a significant channel for
information dissemination. However, the democracy
of knowledge and resources also makes rumor
propagation easier. Until 2025.3.14, the Chinese
Internet rumor-refuting platform Weibo has released
13097 posts about clarifying rumors, which even
ignored the unfound rumors. The spread of fake
information can not only cause social panic but can
also severely harm commercial brands, government
credibility, and individuals’ reputations. For instance,
The cover of Hong Kong-based Next magazine said,
“Bawang causes cancer” and claimed the product
contained dioxane. The whole article was merely
based on “expert speculation” alone, and the listed
company with annual sales of HK $1.7 billion lost
HK $2.4 billion. Therefore, investigating the users’
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-1148-0999
behavior in rumor spreading on the internet,
especially from a multi-group game-theoretic
perspective, is of significant practical importance and
urgency.
This paper selects Weibo as an example and a
research object to analyze participants’ acting
strategies(e.g., spreading, refuting, silence) when
they face rumors based on a game theory. It can not
only provide an iconic example and theoretical
foundations for rumor control on general platforms
but also offers valuable insights for national
authorities and enterprises in formulating information
management strategies, showcasing crucial social and
commercial values.
In the field of online rumor propagation, many
scholars have already explored the topic from various
perspectives, for example:
Li, Ma, and Fang investigated the impact of
emotion types and intensity on rumor spreading,
Lan, H.
Research on the User Behaviour Game Analysis of Social Network Rumour Propagation Based on the Weibo.
DOI: 10.5220/0013803600004708
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy (IAMPA 2025), pages 5-11
ISBN: 978-989-758-774-0
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
5

finding negative feelings have a more significant
influence on the evolution of rumors. But, they
mainly focused on sentimental aspects, lacking the
overall strategy analysis (Li, Ma, and Fang, 2023).
Yi, Liu, and Wang proposed the Twin-SIR model
to analyze the unsatisfactory speed of clarifying
rumors and introduce a “rumor dispeller” to improve
it. But, they did not deeply consider the game-
theoretic aspects of participants’ strategies (Yi, Liu,
and Wang, 2021).
Li and Liu set up the ET game model to find an
equilibrium but did not combine it into empirical data,
particularly social media (Li and Liu, 2016).
Liu and Liu developed a tripartite evolutionary
game model based on game theory. This consists of
the insider, the media, and the government regulatory
agencies (Liu and Liu, 2021).
Liu, Wang and Ouyang modeled all online users
are represented as a node in one of five compartments.
The transition dynamics are obtained as a system of
ordinary differential equations, and the system is
described using an edge-based formulation (Liu,
Wang and Ouyang, 2022).
Although much research has been conducted on
rumor propagation on the internet, most studies focus
on dynamic models, sentimental factors, or
improvement of present rumour detection systems;
few scholars have deeply investigated the interaction
of users’ behaviour strategies and application in
reality from a game-theoretic perspective. This paper
aims to fill this gap by constructing a multi-group
game-theoretic model to analyse user behaviour and
its impact on rumour propagation.
In order to achieve this, filling this gap, the following
structure of this paper is presented:
Firstly, the establishment of a multi-group game-
theoretic model is completed, categorizing
participants into spreaders, refuters, and ordinary
users and analyzing their strategy choices (e.g.,
spreading, refuting, silence) and payoff functions,
which is based on the real data from Weibo.
Secondly, the Nash Equilibrium will be solved to
explore different behavior strategies under
equilibrium and their influence on rumor
transmission.
Thirdly, parameter analysis and sensitivity testing
are conducted to examine the specific effect of
different factors (e.g., spreading benefits, refuting
cost) on rumor spreading.
Finally, the rumor-preventing strategies based on
the results will be proposed to offer the theoretical
foundations for rumor control on social platforms.
2 CASE DESCRIPTION
2.1 Introduction of Weibo as a Typical
Social Media Platform
Weibo, as the counterpart of Twitter, is one of the
most prevailing social media platforms in China, with
over 605 million monthly active users until 2023. It
enable people around the world to communicate
instantly and easily, democratizing variable
information and updating users on current affairs.
With the characteristics of openness and frequent
interaction, Weibo has become a hotspot for both
legal information dissemination and the transmission
of rumors. This platform’s real-time nature and large
user base make it particularly vulnerable to the rapid
spread of fake news, which can lead to critical social
and economic consequences.
2.2 Overview of Rumor Propagation on
Weibo
As a common phenomenon on Weibo, rumor
propagation is often exaggerated by high user
engagement and fast dissemination speed. According
to the “2023 Weibo ‘We-Media’ Governance Report”,
until 2023, Weibo has already handled over 27000
rumors and over 428000 fake accounts. These rumors
cover a wide range of aspects, including medical
health, food security, and social science, influencing
people quietly.
2.3 Main Characteristics of Rumor
Propagation on Weibo
There are several predominant features of rumor:
Fast speed and large scale: Since Weibo is a real-
time platform with the convenience and availability
of vast information, with just a single click, rumors
can spread there at a rate never seen before. Within
hours, a single rumor can reach millions of users,
making it challenging to stop once it starts to spread.
Conformity of user behavior: People frequently
participate in rumor spreading on Weibo merely
because they are curious, afraid, or want to contribute
eye-catching content. Therefore, rumors are further
spread via the platform’s algorithm, which gives
priority to popular subjects.
Impact on society and economy: Rumors on
Weibo have the potential to cause social unrest, harm
to people’s reputations, and financial losses, along
with other not-mentioned negative consequences. For
instance, the “Bawang causes cancer” event, which
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
6

was mentioned before, has resulted in the loss of HK
$2.4 billion to the company.
According to the relevant research, the rumors
also tend to possess periodic spikes, different from the
single prominent sipes in terms of the temporal aspect,
illustrating the repeated characteristic of rumors; the
fake news is also inclined to form a “Bigfoot”
diffusion network rather than “Summize” diffusion
network, demonstrating the blindness and uni-
directivity of rumors (Kwon, Cha, Jung, Chen &
Wang, 2013). The spread of rumors on Weibo is a
complicated problem that presents serious difficulties
for the site and its users. Consequently, social media’s
dynamic nature necessitates ongoing efforts to
address this issue adequately.
3 ANALYSIS OF THE PROBLEM
3.1 Severe Influences of Rumor
Propagation
3.1.1 Social Panic and Trust Crisis
The rapid spread of rumors often leads to social unrest,
especially on prevailing social platforms like Weibo.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic in
2020, false information about the origin and treatment
of the virus spread widely on social media, resulting
in large-scale social panic and distrust in the
government and medical institutions (Bukhari, 2020).
Many people were already swayed by the rumors
when official sources tried to provide clarification,
which resulted in resistance and a skeptical attitude
towards official comments. Because it damages the
credibility of reliable sources and makes future
communication attempts more difficult, this crisis of
confidence may have long-term consequences. The
psychological impact of such rumors can also lead to
a breakdown in social cohesion, as individuals
become more suspicious of each other and less
willing to cooperate with authorities. These
declinations on government credibility not only
destabilize society but may also lead to public
resistance to official information, further
exacerbating the chaos in rumor dissemination.
3.1.2 Damage to Individual, Group, or
Brand Reputation
The blinded transmission of fake news can also cause
severe consequences to related people or brand
reputation. For instance, in 2022, there was a common
rumor that a “nurse was playing on her phone while
rescuing a child.” However, the nurse was actually
using her phone to call a doctor for help with the
rescue. The rumor-creators purposefully made up
false information to gather attention, which was
extremely deceptive, and took advantage of the
important roles that nurses and volunteers play in
preventing and controlling epidemics (Global Times,
2022). Despite the clarifications on the multi-
platforms, the impact of the rumor still exists and
even spreads. Such reputational damage not only
affects the short-term individuals’ mental health, the
credibility of medical workers, or the economic
interest of relevant corporations but may also have
long-term implications for their development. The
damage to reputation is often difficult to quantify but
can have lasting effects on both personal and
professional lives.
3.1.3 Fluctuation in Economy and Market
Rumor propagation can also trigger the whole
economy and market to become more unstable. Like
the “Bawang causes cancers” fake news, which is
mentioned before, a single false claim leads to a loss
of HK$2.4 billion for a listed company, causing
significant losses to investors. In addition to
disrupting businesses’ regular operations, this
economic volatility may also have an adverse impact
on the entire industry. In certain instances, rumors
may result in regulatory scrutiny, legal disputes, and
higher operating costs for businesses attempting to
repair the harm. The financial impact of rumors is not
restricted to specific businesses; it can also impact
entire sectors, causing wider economic instability.
This fake information about certain corporations can
lead to drastic fluctuations in stock prices and market
shares, undermining investor confidence and market
stability, resulting in a ripple effect on the entire
industry. In 2012, following political unrest in the
Maldives, a rumor spread claiming the country was
unsafe for tourists. Despite government clarifications,
the rumor led to massive cancellations of travel plans
and a sharp decline in hotel bookings. This incident
highlights the devastating impact of rumors on the
tourism industry, causing significant economic losses
for the Maldives in a short period.
3.1.4 Psychological Impact on Individuals
In addition to the negative social and economic
effects, rumors can have a significant psychological
effect on people. False information spreading can
make people anxious, stressed, and afraid,
particularly when it comes to health or personal safety.
For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic,
Research on the User Behaviour Game Analysis of Social Network Rumour Propagation Based on the Weibo
7

widespread panic and irrational behavior, including
hoarding medical supplies and avoiding healthcare
institutions, were caused by rumors about the virus’s
lethality and the efficacy of specific therapies
(Bukhari, 2020). Vulnerable groups, such as the
elderly or people with underlying mental health issues,
may be most affected psychologically. Rumors have
an emotional cost that can result in long-term
psychological stress that impairs a person’s general
well-being and quality of life. According to related
research, rumor-spreading behavior is also more
significantly influenced by negative emotions (e.g.,
anger and disappointment), as the recipient is more
likely to spread rumors to express emotions or seek
empathy. This type of emotion-driven
communication behavior is especially prevalent in
social networks, which exacerbates the further
transmission of fake news (Kim & Bock, 2011).
3.2 Problems of Rumor Propagation on
Weibo
3.2.1 Uncontrollability of Information
Dissemination
As an open social platform, Weibo’s speed and scale
of diverse information dissemination are difficult to
control. A single rumor can reach millions of users
within hours, and the platform’s algorithm further
accelerates its spread. Although Weibo has already
implemented measures such as content moderation
and rumor-debunking systems, its response speed and
coverage are still insufficient to defeat the rapid speed
of false information fully. The fact that a rumor may
have reached a large amount of users by the time it is
detected and addressed makes it difficult to control.
This uncontrollability is a serious problem since it
permits rumors to proliferate unchecked, causing
extensive harm before they can be successfully
challenged.
3.2.2 Complexity of User Behavior
Participants’ behaviors in rumor propagation are
varied, ranging from passive sharing driven by
curiosity or fear to active sharing driven by personal
interest. Some users may share rumors without
verifying their authenticity simply because the
content aligns with their beliefs or interests, while
others may actively broadcast incorrect information
to get attention, gain followers, or even profit
monetarily. According to related research, the variety
of user behavior depends on the user’s information
perception(e.g., Number of followers and social
network activity) and activity, individuals’
psychological aspect(e.g., Profit-seeking psychology
or Herd mentality), and the competitive mechanism
of rumor and anti-rumor information (Xiao, Chen,
Wei et al., 2019). Another research study also pointed
out that people who hesitate to join in the propagation
of rumors can even exacerbate their speed (Hu, Pan,
Hou and He, 2018). This complexity makes it
challenging to predict the motivations behind rumor
propagation, which, therefore, further increases the
difficulty of rumor control.
3.2.3 Limitations of Rumor-Refuting System
Despite the diverse measures taken by Weibo to deter
the dissemination of rumors, the limitation of its
rumor-refuting system still exists. According to
related research, the speed and scale of refuting
information are often less than the rumor itself, and
the former is more likely to be confined within the
scientific chamber without being exposed to a large
number of ordinary people, which results in limited
efficiency. Additionally, the results of the research
showed that some users have low trust in rumor-
refuting information and even resist it. This resistance
can be due to a variety of factors, including pre-
existing biases, distrust of official sources, or the
influence of echo chambers within social networks
(Zollo, Bessi, Del Vicario et al., 2017). In some cases,
debunking efforts may even have the opposite impact,
as users who are deeply invested in a particular rumor
may view the debunking as an attempt to suppress the
truth, leading to further resistance and skepticism.
3.2.4 Algorithmic Amplification of Rumors
The platform’s algorithm’s function in spreading
misleading information is one of the biggest obstacles
to regulating rumor propagation on Weibo. The
algorithm gives priority to content that receives a lot
of likes, shares, and comments. The algorithm is more
likely to promote rumors than true facts since rumors
frequently provoke powerful emotional responses. As
a result of this algorithmic bias, rumors spread more
quickly since they become more visible when more
people share them. Recording to a relevant research,
videos with a high level of involvement (likes,
comments, shares) are typically recommended by the
social media’s algorithm. The rumor may spread
more quickly if the algorithm pushes it to more users
and creates a lot of interaction, especially if the
information is controversial. Second, the algorithm
might distribute the item to more users faster if it is
produced when users are active, which would
accelerate the spread of the rumor. Additionally, users
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
8
still tended to employ algorithmic hashtags (such as
#fyp, #foryou) to boost visibility, even though the
study indicated that utilizing popular hashtags did not
directly enhance the number of video plays. The
algorithm may mistake the rumored content for
popular content and recommend it to additional
viewers if it utilizes these tags. Lastly, because people
don’t fully comprehend the algorithm, they try
different tactics to cater to it. Because of this
uncertainty, rumor content may be chosen by
algorithms and disseminated using a variety of tactics
(e.g., high interaction, contentious headlines, etc.)
(Klug, Qin, Evans and Kaufman, 2021). To solve this
problem, social media algorithms’ content
prioritization must be fundamentally rethought,
placing more weight on accuracy and dependability
than just engagement numbers.
4 SUGGESTIONS
4.1 Optimizing Platform Governance
Through Incentive Mechanisms
The rapid and large-scale spread of rumors on Weibo
stems from the platform’s open nature and
algorithmic amplification. To mitigate this, Weibo
should adopt a multi-layered governance approach by
using the multi-group game-theoretic model.
4.1.1 Construction of the Multi-Group
Game-Theoretic model
Participants: Spreaders, Refuters, and Ordinary users
Strategies: Spreaders: Spreading or Not Spreading;
Refuters: Refuting or Not Refuting; (P.S. Ordinary
users choose silence as the default strategy and do not
include it in the calculation of Nash Equilibrium.)
Parameter Setting:
Spreader’s payoff:
Successful spread: +B (social capital, e.g.,
increase the fan base).
Being refuted: −C (penalty, e.g., account
suspension).
Refuter’s payoff:
Successful refute: +R (platform reward).
Cost of refuting: −E (time effort).
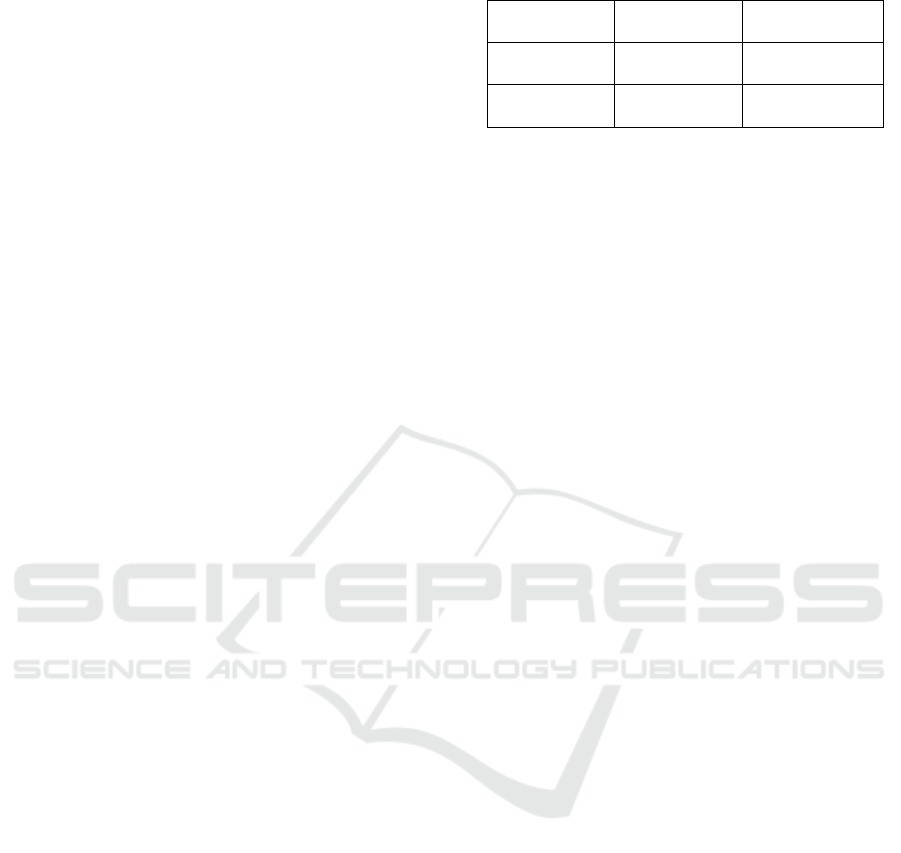
Construction of the matrix, as shown in Table:
Table 1: Payoff Matrix of Rumor Propagation Participants
Refuters:
Refuting
Refuters: Not
Refuting
Spreaders:
S
p
readin
g
(B-C, R-E) (B, 0)
Spreaders:
Not Spreading
(0, -E) (0, 0)
4.1.2 Calculation of Nash Equilibrium
From Spreaders’ perspective, firstly, suppose
Refuters choose “Refuting”, Spreaders will get (B –
C) for “Spreading”, and 0 for “Not Spreading”.
Therefore, their optimal strategy is to choose
“Spreading” if (B−C)> 0; otherwise, the optimal
strategy is to choose “Not Spreading”.
Secondly, suppose Refuters choose “Not
Refuting”, Spreaders will get B for “Spreading”, and
0 for “Not Spreading”. Therefore, their optimal
strategy is always choosing “Spreading” if B > 0.
From Refuters’ perspective, firstly, suppose
Spreaders choose “Spreading”, Refuter will gets (R –
E) for “Refuting”, and 0 for “Not Refuting”.
Therefore their optimal strategy is to choose
“Refuting” if (R – E) > 0; otherwise, the optimal
strategy is to choose “Not Refuting”.
Secondly, suppose Spreaders choose “Not
Spreading”, Refuters’ payoff is 0, regardless.
Therefore, their optimal strategy is always choosing
“Not Refuting” to save cost.
Consequently, we can conclude 2 Nash
Equilibrium from the analysis above:
Firstly, when B > 0 and (R-E) <= 0, Spreaders
choose “Spreading”, and Refuters choose “Not
Refuting”.
Secondly, when (B-C) <= 0 and (R-E) > 0,
Spreaders choose “Not Spreading”, and Refuters
choose “Refuting”.
4.1.3 Application in Real Cases
The game-theoretic model suggests that modifying
user payoffs can effectively reduce rumor
propagation. Therefore, Weibo should modify these
payoffs in its incentive structure to lessen the spread
of rumors:
Firstly, reducing the benefits of spreading rumors
(B). Applying algorithmic demotion to remove
unconfirmed content from recommendation feeds and
hot topics reduces its visibility. Additionally,
implementing account penalties such as temporarily
suspending or shadow-ban accounts that repeatedly
share false information decreases their influence.
Research on the User Behaviour Game Analysis of Social Network Rumour Propagation Based on the Weibo
9

Secondly, increasing the costs of spreading
rumors (C). Using Fact-Checking Alerts to
automatically flag suspected rumors with warnings
(e.g., “This post conflicts with verified reports”).
Thirdly, rewards for refuting(R) should be
boosted. Offering tangible benefits (e.g., badges,
monetization opportunities) to users who actively
debunk rumors. In addition, allowing credible
debunking accounts to earn advertisements’ revenue
or tipping. Also, amplifying official corrections to
prioritize posts from verified sources (e.g., health
agencies) in users’ feeds.
Lastly, the effort to debunk (E) should be lowered.
Establishing One-Click Fact-Checking, such as
integrating tools like reverse image search and AI-
generated summaries of debunking articles.
By applying these measures, users are more
inclined to stop spreading and even debunking rumors;
the detection of fake news can also develop by leaps
and bounds.
4.2 Enhancing Public Awareness and
Critical Thinking
To alleviate the amplification of rumors from herd
mentality, several measures should be implemented
to increase media literacy:
First of all, constructing the interactive pop-ups.
Show quick alerts (such as “Have you checked this
with reliable sources?”) when people try to share
content that hasn’t been validated.
Secondly, gamify rumor detection by introducing
quizzes that test users’ ability to identify
misinformation. For example, users can complete
interactive quizzes on spotting fake news, with top
scorers earning badges and rewards such as platform
credits or exclusive features.
Thirdly, collaborating with Educators. Platforms
should cooperate with schools to promote digital
literacy campaigns targeting younger users.
Through the implementation of these measures,
rumors can be eliminated from their roots.
4.3 Improving the Rumor-Refuting
System
The inefficiency of the current system is caused by
poor credibility and delays. Among the solutions are:
Firstly, implement fact-checking in real time. For
example, AI can be used to identify possible rumors,
closing the “detection gap quickly”.
Secondly, use transparent procedures: Make the
process of verifying assertions publicly available (e.g.,
“This was debunked using CDC data”).
Thirdly, it involves participation at the grassroots
level. Related authorities should train volunteers to
become “rumor detectors” to spot local false
information promptly.
Consequently, by using the above solutions, the
present rumor-refuting system of Weibo could be
improved and provide more efficient and useful
services to users.
4.4 Algorithmic Adjustments to Curb
Rumor Transmission
Since Weibo’s engagement-driven algorithm
unintentionally spreads rumors, the reformation
should involve the following measures:
Firstly, the platform should prioritize the accuracy
signals, like ranking content, by using “trust scores”
(e.g., past accuracy of the poster).
Secondly, add brief refutation tips before users
confirm that they want to share websites. (e.g., “Read
this debunking article before sharing?”).
Thirdly, construct user customization. Let users
filter out unverified topics or mute frequent rumor
spreaders.
Through these algorithmic adjustments, the
platform can significantly reduce the unintentional
spread of rumors.”
5 CONCLUSION
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of
rumor propagation on Weibo, identifying key factors
and proposing actionable solutions from a game-
theoretic perspective. The analysis identifies several
critical issues, including complex user motivations
such as herd mentality and profit-seeking. These
motivations stem from users’ pursuit of economic
benefits and social recognition. Additionally,
algorithmic amplification prioritizing viral but
unverified content and inefficiencies in the rumor-
refuting system (e.g., delayed responses, low
credibility) are also involved in these issues. By
constructing a multi-group game model, the research
categorizes participants into spreaders, refuters, and
ordinary users, analyzing their strategy choices based
on payoff functions. Nash Equilibrium solutions
reveal two scenarios: rumor outbreaks when refuting
costs exceed benefits and rumor suppression when
incentives align. Proposed suggestions include
redesigning platform incentives, enhancing public
media literacy, optimizing fact-checking mechanisms,
and algorithmic reforms. These suggestions are aimed
at reducing the spread of rumors by adjusting
IAMPA 2025 - The International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy
10

participants’ payoff and improving the efficiency of
refuting rumors.
This study offers practical and social value. For social
media platforms like Weibo, our findings suggest
actionable measures to mitigate rumor risks, such as
penalizing unverified content and rewarding
debunkers. These measures aim to adjust user payoffs,
improve debunking efficiency, and reduce rumor
propagation. Policymakers may leverage the model to
design regulations (e.g., penalty adjustments) to
disrupt the rumors that lead to harmful consequences.
Additionally, by advocating digital literacy programs,
the research contributes to regaining public trust and
social cohesion, addressing challenges caused by the
transmission of false information during significant
events like COVID-19.
A limitation lies in its reliance on secondary data (e.g.,
published reports), lacking primary user behavior
validation. Future studies could: (1) collaborate with
platforms to analyze user logs for precise parameter
calibration (e.g., quantifying “B” and “ R”); (2)
compare cross-cultural differences in rumor-
spreading strategies; (3) integrate sentiment analysis
to explore emotional drivers of equilibrium shifts.
Addressing these limitations will enhance the
practical applicability of academic findings.
REFERENCES
Bukhari, W. 2020. Role of social media in COVID-19
pandemic. The International Journal of Frontier
Sciences, 4(2), 59–60.
https://doi.org/10.37978/tijfs.v4i2.144
Global Times. 2022, July 18. Nurse checking her phone
while rescuing patient arouses controversy. Retrieved
March 19, 2025, from
https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202207/1270783.sht
ml
Hu, Y., Pan, Q., Hou, W., & He, M. 2018. Rumor spreading
model with the different attitudes towards rumors.
Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,
502, 331–344.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.02.096
Kim, J., & Bock, G. 2011. A study on the factors affecting
the behavior of spreading online rumors: focusing on
the rumor recipient’s emotions.
Klug, D., Qin, Y., Evans, M., & Kaufman, G. 2021. Trick
and please: A mixed-method study on user assumptions
about the TikTok algorithm. In Proceedings of the 13th
ACM Web Science Conference 2021 (WebSci’ 21) (pp.
84–92). Association for Computing Machinery.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3447535.3462512
Kwon, S., Cha, M., Jung, K., Chen, W., & Wang, Y. (2013,
December). Prominent features of rumor propagation in
online social media. In 2013 IEEE 13th International
Conference on Data Mining (ICDM) (pp. 1103–1108).
IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2013.61
Li, M., & Liu, F. 2016, January. Game theory-based
network rumor spreading model. In 2016 International
Conference on Network and Information Systems for
Computers (ICNISC) (pp. 89–94). IEEE.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNISC.2016.029
Li, Y., Ma, J., Fang, F., & Jiang, Y. 2023. How emotion
type and intensity affect rumor spreading. International
Journal of Modern Physics C, 34(6).
https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183123500833
Liu, C., & Liu, F. 2021, October. Tripartite evolutionary
game analysis of online rumor supervision based on
stakeholder theory. In 2021 IEEE 5th Information
Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation
Control Conference (ITNEC) (pp. 580–583). IEEE.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ITNEC52019.2021.9586906
Liu, W., Wang, J., & Ouyang, Y. 2022. Rumor transmission
in online social networks under Nash equilibrium of a
psychological decision game. Networks and Spatial
Economics, 22, 831–854.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-022-09574-9
Xiao, Y., Chen, D., Wei, S., et al. 2019. Rumor propagation
dynamic model based on evolutionary game and anti-
rumor. Nonlinear Dynamics, 95, 523–539.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4579-1
Yi, J., Liu, P., Wang, Z., & L, W. 2021. Research on twin-
SIR rumor spreading model in online social network.
Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems: Applications in
Engineering and Technology, 40(4), 5863–5874.
https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-189426
Zollo, F., Bessi, A., Del Vicario, M., Scala, A., Caldarelli,
G., Shekhtman, L., Havlin, S., & Quattrociocchi, W.
2017, July 24. Debunking in a world of tribes. PLOS
ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181821
Research on the User Behaviour Game Analysis of Social Network Rumour Propagation Based on the Weibo
11
