
Toolchain for Dataset Description with Contextual Recommendation
from Machine-Actionable Data Management Plans
Mohamed-Anis Koubaa
1 a
, Nan Liu
1 b
, Fabia Martens
1 c
, Andreas Schmidt
1,2 d
,
Karl-Uwe Stucky
1 e
and Wolfgang S
¨
uß
1 f
1
Institute for Automation and Applied Informatics, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany
2
University of Applied Sciences, Karlsruhe, Germany
Keywords:
Research Data Management, Metadata, Automated Metadata Generation, Metadata Suggestions, Data
Description, FAIR Principles, RDMO, Data Management Plans, Ontologies, Semantic Web, Scientific Data,
Metadata Quality, Metadata Consistency, Digital Repositories, Information Systems, Knowledge Graphs.
Abstract:
By harnessing the power of interconnected research project information, this position paper introduces a novel
system designed to automate and enhance the metadata description process for research data. The system
effectively leverages existing structured data from RDMO (Research Data Management Organiser), drawing
insights from research projects, measurement equipment, sensors, and simulations to provide context-aware
suggestions for metadata fields. We argue that this system significantly reduces the manual burden on re-
searchers, improves the quality and consistency of metadata, and ultimately champions the FAIR principles
(Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) for all research data.
1 INTRODUCTION
The energy sector, with its foundation in long-
standing infrastructure and siloed data systems, faces
a monumental task in integrating disparate datasets
that are crucial for innovation and resilience. As
we shift towards decentralised energy production and
smart consumption, the challenge of managing re-
search data across these heterogeneous environments
becomes acute. High-quality, semantically rich meta-
data is not merely a best practice; it is the fundamen-
tal enabler of interoperability, bridging the gaps be-
tween legacy systems, new technologies, and multi-
stakeholder collaboration to drive the energy transi-
tion forward.
The process of creating metadata is largely man-
ual, time-consuming, and, unfortunately, prone to er-
rors. Researchers often spend considerable effort on
this administrative task, diverting valuable time and
resources away from their primary research activities.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8552-2008
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-8768-7072
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-2890-430X
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9911-5881
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0065-0762
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2785-7736
This manual effort frequently leads to inconsistency
and significant variability in metadata quality across
different datasets, projects, and even within the same
research group. Consequently, a critical problem
arises: a widespread lack of semantic interoperabil-
ity (Borgman, 2016). Without a common, machine-
readable understanding of the terms and concepts
used to describe data, it becomes exceedingly dif-
ficult to integrate, compare, or reuse datasets effec-
tively, even when they originate from related studies
(Sasse et al., 2022). Ultimately, the burden on re-
searchers associated with this cumbersome, manual
metadata creation process not only impacts the qual-
ity of the metadata itself but also detracts significantly
from core scientific discovery.
Many research institutions have already made sig-
nificant investments in tools like Research Data Man-
agement Organiser (RDMO) (Anders et al., 2024)
to facilitate good research practices, particularly in
the creation and management of Data Management
Plans (DMPs). RDMO excels at guiding researchers
through the planning phase, prompting them to artic-
ulate crucial aspects such as data types, storage so-
lutions, access policies, and long-term preservation
strategies well in advance of data collection (Anders
et al., 2024). However, a persistent challenge re-
mains: the valuable, structured information metic-
506
Koubaa, M.-A., Liu, N., Martens, F., Schmidt, A., Stucky, K.-U. and Süß, W.
Toolchain for Dataset Description with Contextual Recommendation from Machine-Actionable Data Management Plans.
DOI: 10.5220/0013786300004000
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2025) - Volume 2: KEOD and KMIS, pages
506-513
ISBN: 978-989-758-769-6; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

ulously documented within these DMPs often be-
comes siloed from the actual, hands-on data descrip-
tion phase. While a DMP outlines how data should
be managed, the practical application of this planning
– the creation of comprehensive metadata for the data
itself – frequently reverts to a separate, often man-
ual, process. This disconnection means that the rich
contextual information captured during the planning
stage is not automatically leveraged when the research
data is ultimately prepared for sharing, archiving, or
publication, leading to redundant efforts and potential
inconsistencies.
Our proposed system seamlessly integrates the
structured project and resource information that al-
ready resides within RDMO and offers a robust and
transformative solution. It tackles these pervasive
metadata challenges by utilising advanced seman-
tic reasoning capabilities. This innovative approach
promises to foster a significantly more efficient and
demonstrably higher-quality research data description
process, ultimately accelerating scientific discovery
and enhancing data reusability.
2 THE CURRENT LANDSCAPE
AND GAPS
While the idea of enriching datasets with descriptive
metadata is not new, many current metadata tools, es-
pecially those widely used in research, have signifi-
cant drawbacks. These limitations contribute to the
persistent challenges in managing research data.
2.1 Limitations of Current Metadata
Tools
To guide data providers in linking metadata to their
actual data, generic forms and templates are a stan-
dard tool. However, despite offering a basic struc-
ture, these tools frequently lack the necessary speci-
ficity and flexibility to capture the rich, nuanced con-
text inherent in diverse scientific data. This forces
researchers to manually enter information, often via
free-text descriptions, which ultimately results in in-
consistencies and ambiguities in the metadata.
Furthermore, these tools frequently suffer from a
lack of contextual awareness. They operate as a stand-
alone data entry systems, which is disconnected from
the broader research ecosystem. They do not inher-
ently ”know” about the project’s funding details, the
precise specifications of the sensor that generated the
data, or the parameters of the simulation software
used, even if such information is meticulously doc-
umented elsewhere. This forces researchers to heav-
ily rely on manual input, not just for the data itself,
but for re-entering or re-interpreting information that
already exists in other structured formats. The ab-
sence of automated linkages and intelligent sugges-
tions means the burden of connecting disparate pieces
of information falls squarely on the individual re-
searcher, perpetuating the inefficiencies and quality
issues previously identified.
Provenance data captured during workflow execu-
tion offers a rich source for ”Provenance” and ”Con-
text” metadata in dataset publication (Alper et al.,
2013). However, directly using this raw data can in-
advertently expose internal operational details, which
are irrelevant and potentially confusing to data con-
sumers. Modern data orchestrators and sequencers,
such as Dagster, solve this by providing a more
declarative and curated approach, offering a higher-
level view of data lineage and semantic context tai-
lored for external consumption.
2.2 Efforts Towards
Machine-Actionable DMPs
The Research Data Alliance (RDA) is a key player in
making efforts to generate a common understanding
for machine-actionable DMPs, which are very helpful
for the automation of annotation processes. Specif-
ically, the RDA Common Application Programming
Interface (API) for machine-actionable Data Man-
agement Plans Working Group is actively developing
this API specification.
This project is built on the foundation of these
advancements and aligns with established principles
for machine-actionable DMPs, outlined in (Miksa
et al., 2019). Specifically, the following principles are
implicitly integrated as foundational system require-
ments for the present work:
Principle 1. Integrate DMPs with the workflows of
all stakeholders in the research data ecosystem
Principle 3. Make policies (also) for machines, not
just for people
Principle 5. Use Persistent Identifiers (PIDs) and
controlled vocabularies
Principle 6. Follow a common data model for
maDMPs
Principle 8. Support data management evaluation
and monitoring
Principle 9. Make DMPs updatable, living, ver-
sioned documents
Principle 10. Make DMPs publicly available
Toolchain for Dataset Description with Contextual Recommendation from Machine-Actionable Data Management Plans
507

2.3 Energy-Domain Specific Tools
In the specific context of the energy sector, no-
table efforts are underway to streamline meta-
data creation. The Open Energy Platform (OEP)
(openenergyplatform.org), for example, provides a
web-based metadata wizard designed to guide users
through the process of describing their energy-related
datasets. This wizard is an important step forward
as it simplifies metadata entry, enforcing a specific
metadata standard (OEMetadata, which is built on
Frictionless Data Package specifications and aligns
with Findable, Accessible, Interoperable & Reusable
(FAIR) principles) and assisting users in providing
crucial context for their data. It also integrates
with the Open Energy Ontology (OEO) introduced in
(Booshehri et al., 2021), enabling semantic annota-
tion of data and enhancing findability.
However, while the OEP’s wizard brings signifi-
cant improvements upon generic forms by providing
a structured, domain-specific approach, it still primar-
ily relies on the researcher’s direct manual input into
many of its fields. It guides what information to pro-
vide, but is not able to suggest values for those fields.
A researcher might still need to manually re-enter
project titles, funding details, or sensor calibration pa-
rameters, even if these were already documented in an
RDMO Data Management Plan or an internal lab in-
ventory system. This shows a potential area where
the already upstream captured information is not au-
tomatically leveraged, necessitating redundant efforts
and potentially leading to inconsistencies if the man-
ual entry differs from the details of DMP.
Apart from the Open Energy Platform’s metadata
wizard, other initiatives directly address energy data
sharing. EnergySHR (https://energyshr.nl) as an ex-
ample serves as a specialised platform explicitly de-
signed for energy dataset sharing and communica-
tions, particularly focusing on researchers working on
AI and data-driven solutions for the energy transition.
While EnergySHR and similar platforms are cru-
cial for breaking down data silos and fostering col-
laborative research by providing the infrastructure for
data exchange, their primary focus often lies on the
sharing mechanism and access control rather than the
initial automated generation or intelligent suggestion
of comprehensive metadata.
2.4 RDMO’s Role and Limitations in
Isolation
While RDMO has established itself as an indispens-
able tool for many institutions by enabling the struc-
tured creation and systematic collection of informa-
tion for DMPs (Mozgova et al., 2022), a signifi-
cant gap persists between this detailed planning phase
(DMPs creation) and the subsequent practical meta-
data application during the actual data description
process (Windeck et al., 2024). The structured de-
tails about a project, the specific measurement equip-
ment used, the characteristics of sensors, or the pa-
rameters of simulations — all recorded in RDMO —
are frequently not used for the subsequent task of cre-
ating descriptive metadata for the research output it-
self. When preparing data for publication, sharing, or
long-term archiving, researchers often resort to man-
ually re-entering or re-interpreting the same informa-
tion into separate metadata forms or schemas. This
disconnection causes redundant work, risks inconsis-
tencies, and isolates valuable context within the DMP,
as planning details are not automatically used to en-
hance the final metadata, reducing the efficiency and
quality benefits intended by RDMO.
2.5 Addressing the Gaps
Simple, static metadata forms, while offering a basic
framework, prove insufficient for truly effective re-
search data description in today’s complex scientific
landscape. For instance, on the OEP, the vast ma-
jority of tables lack semantic annotations at both the
subject and fields’ descriptions, with only 23% pos-
sessing such terms. Their fundamental limitation lies
in their passive nature.
To overcome these identified gaps, intelligent,
context-aware suggestions are not just beneficial, but
necessary. This shifts the researcher’s role from labo-
rious data entry to efficient validation and refinement,
dramatically increasing the speed, accuracy, and rich-
ness of metadata, thereby making data truly FAIR
and unlocking its full potential for future scientific in-
quiry. See Table 1.
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM:
AUTOMATED METADATA
SUGGESTION
At its core, the proposed system introduces a trans-
formative approach to metadata creation: it leverages
the already captured rich and structured data within
RDMO – specifically regarding research projects,
measurement equipment, sensors, and simulations –
and combines it with robust semantic knowledge to
automatically generate intelligent suggestions for var-
ious metadata fields. This fundamental concept aims
to move beyond manual input, providing researchers
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
508
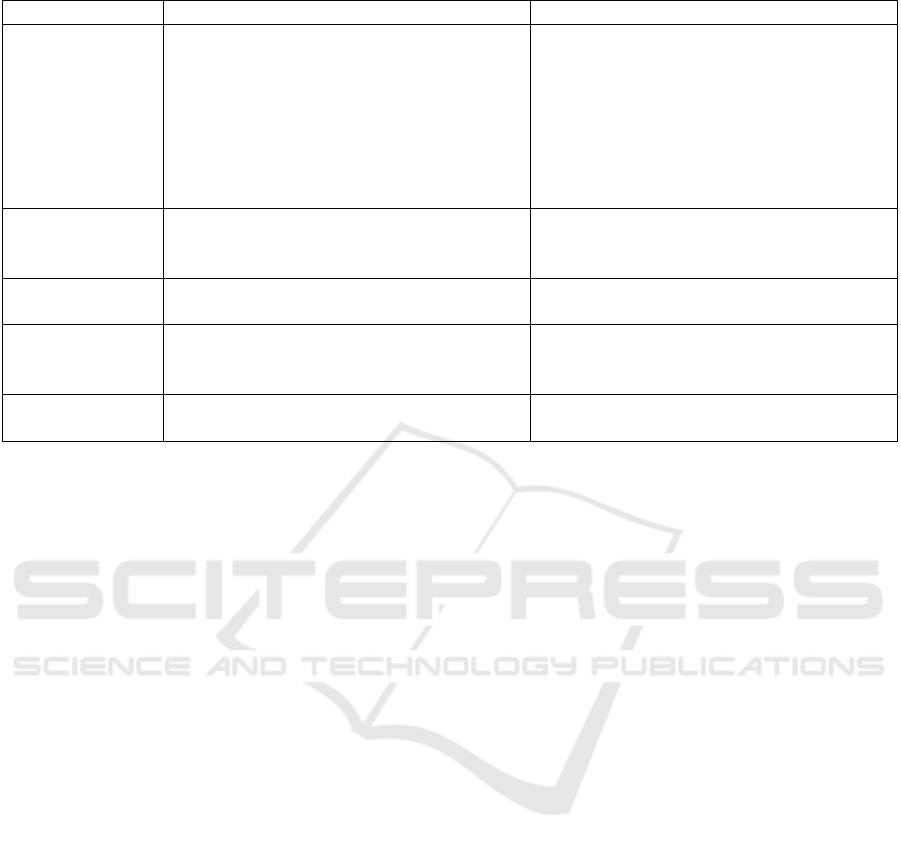
Table 1: Comparison of current tools and the proposed system.
Criteria Current Tools Proposed System
Functionality
and Automation
Manual metadata entry, often in generic
templates and in free-text; prone to (hu-
man) error and inconsistencies
Collects information from external sources
and provides suggestions. Uses existing
knowledge from various sources, domain-
specific semantics, consistency with pre-
existing plans and scientific standards.
Semi-automatic prefilled fields based on
context, the specific project, data type, in-
volved equipment, etc.
Time time-consuming manual labour, no pre-
filled fields
time-efficient automatisation, only de-
mands review (validation and refinement)
of the prefilled fields
Interoperability Low, alone-standing, often platform-
specific or unique formats
Supports API, RO-Crate, JSON-LD
Integration Low to none, often not able to read JSON-
LD, no contextual awareness
High, access to many different sources,
creates machine-readable output, processes
JSON-LD
Standards Com-
pliance
Differs FAIR, JSON-LD
with contextually relevant and accurate metadata rec-
ommendations from the outset.
3.1 Core Functionalities
At the heart of this system lie several core functional-
ities designed to ensure its effectiveness and seamless
operation:
Access Available Sources of Information (CF1)
The system’s foundational capability is its ability to
access and retrieve data from all relevant information
sources. This includes structured data from RDMO,
as well as potentially other institutional databases, ex-
ternal registries, and semantic resources.
Present Information in Suitable Form to
System-Subcomponents (CF2)
Once accessed, information is processed and trans-
formed. This core function ensures that the retrieved
data is presented in a standardised and suitable for-
mat, enabling efficient consumption and utilisation by
all other internal system sub-components, such as the
Knowledge Base and the Suggestion Engine.
Present an Easy Way to Edit Metadata for the
Editor, Publisher and Curator (CF3)
Recognising that automated suggestions are a pow-
erful starting point but not without their risks for er-
rors or misinterpretation, a fundamental functional-
ity is providing a user-friendly interface for curators.
This ensures an easy and intuitive way for humans
to review, modify, and refine the suggested metadata,
maintaining oversight and guaranteeing accuracy.
Use Programming Interfaces of Target Platforms
to Publish and Search Metadata (CF4)
For the generated and curated metadata to be truly
impactful, the system must actively interact with the
broader research data ecosystem. This functionality
uses programming interfaces (APIs) of target plat-
forms, such as institutional repositories or data por-
tals, to seamlessly publish the rich metadata and en-
able efficient searching, thereby maximising the find-
ability and reusability of the research data.
3.2 Key Components and Core
Functions Coverage
This system can be broken down into several inter-
connected components:
User Interface (UI) for Data Description is the
primary interface where researchers can input and
review metadata. It has to be intuitive, guided,
and interactive. The core function CF3 requires
that the suggestions are made available in the UI,
to guide the user in selecting a meaningful value
for the attribute or property being edited.
RDMO Integration Module connects to the
RDMO instance to retrieve project information
(e.g. project title, abstract, principal investigator,
funding, associated DMPs), and details about
Toolchain for Dataset Description with Contextual Recommendation from Machine-Actionable Data Management Plans
509

measurement equipment, sensors, or simulations
that are already documented in RDMO. More
generally, modules are mainly integrated via
APIs-based connections. Data transferred via
API receives further semantic transformation
when the source and sink schemas are known and
independent yet interoperable via mapping.
Knowledge Base with Semantic Layer is the brain
of the suggestion system. It contains the rules,
relationships, and semantic understanding neces-
sary to generate intelligent suggestions.
Suggestion Engine (SE) takes input from the user
(partially filled metadata and context from
RDMO) and queries the Knowledge Base to gen-
erate suggestions.
External Data Source Integrator retrieves infor-
mation from other relevant systems beyond
RDMO that might hold valuable metadata (e.g.
lab inventory systems, institutional repositories,
external registries of scientific instruments, etc.).
Metadata Repository is used to store the fully en-
riched metadata (after the user input and sugges-
tions are finalised).
3.3 Workflow
The user’s journey begins within the RDMO’s intu-
itive and highly flexible user interface, designed to
allow for extensive customisation through Question-
naire Definitions. These definitions are managed by a
superuser (see 1 in Figure 1) and are crafted to tailor
the questions presented to researchers (see 2 ). Cru-
cially, these questionnaires have a defined data model
that can be directly mapped and utilised in subsequent
stages of the research data management workflow, en-
suring seamless data flow and consistency.
3.3.1 Initiating Data Description
A researcher, having completed their data collection
or simulation, navigates to the system to begin de-
scribing their new dataset. They select the relevant
RDMO project from a pre-populated list (populated
by the RDMO Integration Module). This initial se-
lection immediately provides the system with crucial
context.
3.3.2 Initial Contextual Pre-Population
(RDMO-driven)
Upon selecting the project, the system instantly pre-
populates (in 3 ) several core metadata fields based
on the information already available in the associated
RDMO DMP. This includes:
1. Project Title, Abstract, and Principal Investigator,
2. Funding information (grant numbers, funding
agencies) and
3. High-level data types (e.g. ”experimental data” or
”simulation output”).
Furthermore, the system broadcasts important in-
formation (in 4 ) to further software components
(e.g. Electronic Lab Notebookss (ELNs)) and facil-
itates, thereby, a potentially data description step (in
5 ). The concrete research operation produces the re-
sulting dataset ( 6 ) and makes it available for further
processing by the toolchain.
3.3.3 Receiving Contextual Suggestions (RDMO
and Semantic Knowledge)
During the process, the Suggestion Engine springs
into action whenever fields are not directly pre-
populated and infers both the RDMO data and its own
integrated Knowledge Base:
• If the RDMO project details indicate the use of
a specific measurement equipment, the system
proactively suggests relevant instrument types,
manufacturer details, and common measurement
units or parameters associated with that equip-
ment.
• Similarly, if RDMO outlines the use of particu-
lar sensors, the system suggests appropriate units
(Celsius, Kelvin, etc.), temporal resolution, or rel-
evant calibration procedures.
• For simulation data, suggestions are based on the
software documented in RDMO and include soft-
ware names, versions, relevant physical constants
or models used in the simulation.
• For fields like ”Keywords” or ”Scientific Disci-
pline,” the system suggests terms extracted from
the project abstract in RDMO or broader ontolog-
ical terms related to the project’s primary domain.
3.3.4 Interacting with Suggestions
Suggestions are presented in a clear, non-intrusive
manner as highlighted text, auto-complete drop-
downs, or clickable buttons next to the relevant field.
The researcher can then:
1. Accept a suggestion with a single click, instantly
populating the field.
2. Modify a suggestion if it is close but not perfectly
accurate.
3. Ignore/Reject a suggestion and, if preferred, man-
ually enter their own value.
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
510

3.3.5 Refinement and Validation
As the researcher (in 7 ) fills in more fields, the sys-
tem can dynamically refine its suggestions, leveraging
the newly entered information for even greater accu-
racy.
Before the final submission (
8 and 9 ), the sys-
tem performs validation checks, ensuring all manda-
tory fields are complete and values adhere to estab-
lished standards (e.g. valid date formats, correct unit
types).
The workflow seamlessly integrates planning in-
formation with intelligent, context-aware suggestions.
Several semantic transformations are inherently part
of the different system interfaces and are a core func-
tion of the proposed system.
4 ADVANTAGES AND IMPACT
The adoption of the proposed system yields a mul-
titude of significant advantages, primarily aimed at
reforming research data management practices. The
foremost among these are substantial efficiency gains,
which directly translate into a marked reduction in the
time researchers must dedicate to manual metadata
entry. By automating large portions of this process,
the system effectively frees valuable researcher time,
allowing them to redirect their focus back to core sci-
entific inquiry and innovation.
Beyond mere efficiency, the system enables a dra-
matic improvement in metadata quality and consis-
tency. The intelligent suggestion mechanism, draw-
ing from structured RDMO data and semantic knowl-
edge, inherently leads to the minimisation of errors
and omissions that frequently plague manual input.
Moreover, it actively promotes adherence to estab-
lished standards and controlled vocabularies, moving
away from free-text ambiguity towards standardised,
machine-readable descriptions. This, in turn, funda-
mentally enhances semantic interoperability, ensuring
that data from different sources can be seamlessly in-
tegrated and understood across various platforms and
disciplines.
The proposed system directly contributes to the
promotion of the FAIR Principles for research data.
Its automated (like encouraged in Rec. 8 from (Eu-
ropean Commission. Directorate General for Re-
search and Innovation., 2018), p. 45) and standard-
ised metadata generation capabilities make data inher-
ently more Findable by search engines and data cat-
alogues, more Accessible through consistent descrip-
tions, more Interoperable due to semantic alignment,
and ultimately more Reusable by a broader scientific
community.
Furthermore, a key strength of this approach lies
in its ability to leverage existing infrastructure. In-
stead of requiring a complete overhaul of institutional
data management strategies, the system intelligently
builds upon and extends existing investments in tools
like RDMO. This not only optimises resource utilisa-
tion but also significantly increases the overall value
proposition of these pre-existing data management
planning efforts.
Finally, the system is designed with scalability
and adaptability in mind. Its modular architecture
and reliance on configurable semantic rules mean it
possesses considerable potential for straightforward
adaptation to the unique metadata requirements of
various scientific disciplines, as well as for accommo-
dating evolving metadata standards and best practices
over time. This ensures its long-term relevance and
utility in a rapidly changing data landscape.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
OUTLOOK
At its core, the proposed system represents a crucial
step forward in research data management. By intel-
ligently leveraging existing information from RDMO
and integrating it with robust semantic knowledge,
it directly reduces the inefficiencies, inconsistencies,
and manual burdens widespread in current metadata
creation. This system not only streamlines the pro-
cess but also elevates the quality and interoperability
of research data, ultimately fostering a more efficient
and effective environment for scientific discovery and
data reusability.
Building on the robust foundation of the proposed
system, several exciting paths for future research and
development open, promising to further enhance its
intelligence, reach, and utility in research data man-
agement. The following sections present an overview.
Incorporating ML for More Advanced
Suggestions
While the initial system relies on rule-based semantic
reasoning, integrating machine learning (ML) models
can unlock a new level of intelligence. This includes:
Natural Language Processing (NLP). Analysing
free-text descriptions within RDMO (e.g. project
abstracts, methodology sections) or existing meta-
data to extract entities, topics, and relationships
that can improve suggestions.
Recommendation Profiles. Learning from patterns
in previously described datasets and user interac-
Toolchain for Dataset Description with Contextual Recommendation from Machine-Actionable Data Management Plans
511
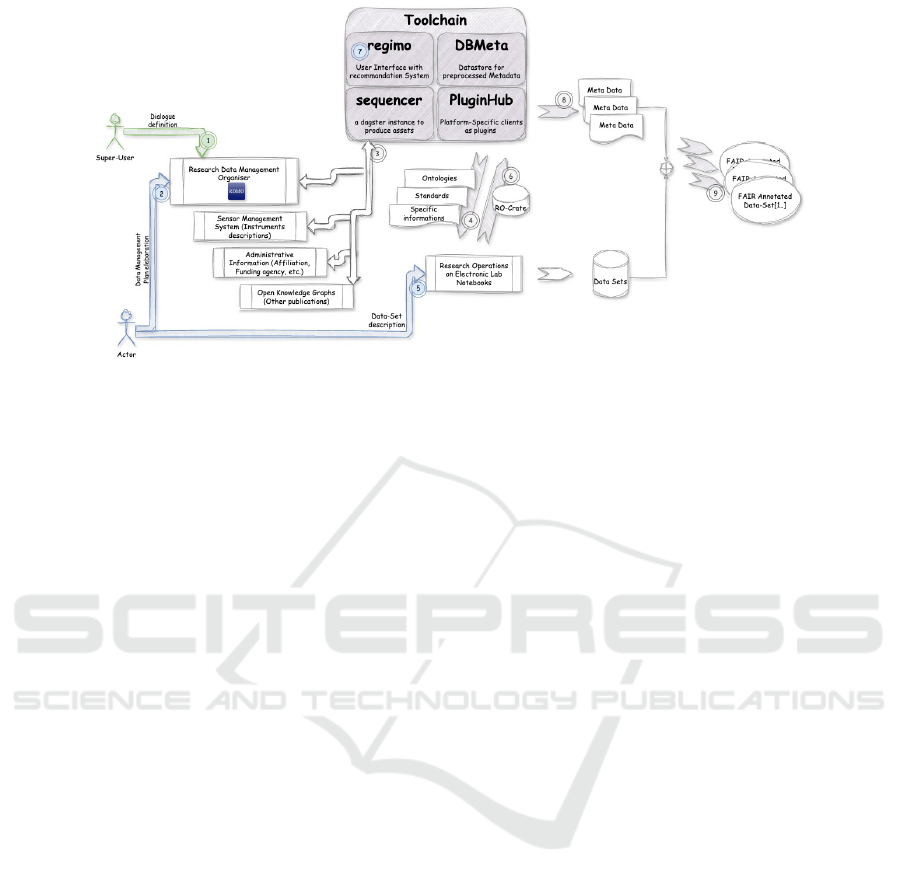
Figure 1: System Key Components with References to Workflow-Steps.
tions (e.g. accepted/rejected suggestions) to pro-
vide highly personalised and accurate recommen-
dations for metadata values. This can address
the ”cold start” problem for new types of data or
equipment.
Anomaly Detection. Using Machine Learning (ML)
to identify potential inconsistencies, gaps, or un-
usual values in metadata, prompting users to re-
view and correct. First approaches are shown in:
(Wu et al., 2023).
Active Learning. Implementing active learning
strategies where the system intelligently queries
the user for input on uncertain suggestions,
for continuously refining and improving its
underlying models. This creates a powerful
human-in-the-loop learning mechanism.
Deeper Integration with ELNs and Laboratory
Information Management Systems (LIMS)
ELNs and LIMS are where much of the raw exper-
imental and observational data, along with detailed
methodologies, are first recorded. Future work could
focus on:
Automated Metadata Extraction from ELN
Entries. Developing parsers and NLP models
to automatically extract relevant metadata (e.g.
instrument settings, reagent batch numbers, en-
vironmental conditions, experimental protocols,
etc.) from structured and unstructured ELN
entries.
Real-Time Metadata Flow. Establishing seamless,
automated pipelines for metadata to flow directly
from ELNs and LIMS into the metadata sugges-
tion system, drastically reducing manual entry
post-experiment.
Linking Data Provenance. Enriching metadata
with a detailed provenance trail directly from
ELNs or data orchestrators, linking specific data
points back to the exact experimental steps and
equipment used.
Integration with Other Research Information
Systems
Integrating with other existing research information
systems offers significant opportunities to automat-
ically enrich metadata with contextual details that
are often difficult to track manually. This includes
leveraging information from Current Research Infor-
mation Systems (CRIS) or ORCID profiles to au-
tomatically suggest accurate author details, affilia-
tions, and persistent researcher IDs, ensuring proper
attribution and discoverability. The system could
also connect to external or institutional instrument
registries, pulling detailed specifications, calibration
data, and even maintenance logs for specific equip-
ment or sensors, thereby greatly enriching the meta-
data associated with experimental data. Furthermore,
for data derived from simulations or analyses, inte-
grating with software repositories like GitHub or in-
stitutional code archives allows the system to auto-
matically suggest crucial details such as software ver-
sions, dependencies, and licensing information, en-
suring transparency and reproducibility.
Advanced Semantic Reasoning and Knowledge
Graph Expansion
Future developments aim to extend beyond basic data
mappings by integrating more advanced inferencing
and enrichment mechanisms. An example would be a
system that is able to recognise particular sensor types
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
512

and then automatically infers the common measure-
ments or the associated physical quantities. Even if
not explicitly stated, the system can capture the infor-
mation and reduce manual labour.
User Experience (UX) and Interactive Feedback
Mechanisms
Beyond core functionality, refining the user experi-
ence is paramount for adoption and continuous im-
provement. A key area is Explainable AI for Sugges-
tions, where the system provides clear, concise ex-
planations for its recommendations. Transparent ex-
planations like ”This unit was suggested because it
is commonly associated with this sensor type, which
is listed in your RDMO DMP for this project.” are
important to build user trust and aid understanding.
Furthermore, exploring gamification and incentives
could encourage researchers to adhere to metadata
best practices and provide valuable feedback, trans-
forming a potentially tedious task into an engag-
ing one. Finally, developing features for collabora-
tive metadata curation would empower multiple re-
searchers or data stewards to jointly review and refine
suggested metadata, especially for complex or inter-
disciplinary datasets, fostering a shared sense of own-
ership and accuracy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This publication was supported by the Helmholtz
Metadata Collaboration (HMC), an incubator plat-
form of the Helmholtz Association within the frame-
work of the Information and Data Science strategic
initiative.
The authors would like to thank the German Fed-
eral Government, the German State Governments,
and the Joint Science Conference (GWK) for their
funding and support as part of the NFDI4Energy
consortium. The work was funded by the Ger-
man Research Foundation (DFG) – 501865131 within
the German National Research Data Infrastructure
(NFDI, www.nfdi.de).
REFERENCES
Alper, P., Belhajjame, K., Goble, C. A., and Karagoz, P.
(2013). Enhancing and abstracting scientific workflow
provenance for data publishing. In Proceedings of the
Joint EDBT/ICDT 2013 Workshops, pages 313–318,
Genoa Italy. ACM.
Anders, I., Enke, H., Hausen, D. A., Henzen, C., Jagusch,
G., Lanza, G., Michaelis, O., Peters-von Gehlen, K.,
Rathmann, T., Rohrwild, J., Sch
¨
onau, S., Wedlich-
Zachodin, K. V., and Windeck, J. (2024). The Re-
search Data Management Organiser (RDMO) – a
Strong Community Behind an Established Software
for DMPs and Much More. Data Science Journal,
23:28.
Booshehri, M., Emele, L., Fl
¨
ugel, S., F
¨
orster, H., Frey,
J., Frey, U., Glauer, M., Hastings, J., Hofmann, C.,
Hoyer-Klick, C., H
¨
ulk, L., Kleinau, A., Knosala, K.,
Kotzur, L., Kuckertz, P., Mossakowski, T., Muschner,
C., Neuhaus, F., Pehl, M., Robinius, M., Sehn, V., and
Stappel, M. (2021). Introducing the Open Energy On-
tology: Enhancing data interpretation and interfacing
in energy systems analysis. Energy and AI, 5:100074.
Borgman, C. L. (2016). Big data, little data, no data:
scholarship in the networked world. The MIT Press,
Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England, first mit
press paperback edition edition.
European Commission. Directorate General for Research
and Innovation. (2018). Turning FAIR into reality: fi-
nal report and action plan from the European Com-
mission expert group on FAIR data. Publications Of-
fice, LU.
Miksa, T., Simms, S., Mietchen, D., and Jones, S.
(2019). Ten principles for machine-actionable data
management plans. PLOS Computational Biology,
15(3):e1006750.
Mozgova, I., Jagusch, G., Freund, J., Kraft, A., Gl
¨
uck,
T., Herrmann, K., Kn
¨
ochelmann, M., and Lachmayer,
R. (2022). Product Life Cycle Oriented Data Man-
agement Planning with RDMO at the Example of
Research Field Data. In E-Science-Tage 2021. hei-
BOOKS.
Sasse, J., Darms, J., and Fluck, J. (2022). Seman-
tic Metadata Annotation Services in the Biomedical
Domain—A Literature Review. Applied Sciences,
12(2):796.
Windeck, J., Schr
¨
oder, M., Frenzel, J., Kusmierz,
S., Fuchs, H., and Klar, J. (2024). Bausteine
Forschungsdatenmanagement : 2024, 2Connecting
RDM Services. Bausteine Forschungsdatenman-
agement, (2). Medium: application/pdf Publisher:
Philipps-Universit
¨
at Marburg.
Wu, M., Brandhorst, H., Marinescu, M.-C., Lopez, J. M.,
Hlava, M., and Busch, J. (2023). Automated metadata
annotation: What is and is not possible with machine
learning. Data Intelligence, 5(1):122–138.
Toolchain for Dataset Description with Contextual Recommendation from Machine-Actionable Data Management Plans
513
