
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity
Assumptions for Control Applications
Ricus Husmann
a
, Sven Weishaupt
b
and Harald Aschemann
c
Chair of Mechatronics, University of Rostock, Rostock, Germany
Keywords:
Machine Learning in Control Applications.
Abstract:
In this paper, we present an extension to the recursive Gaussian Process (RGP) regression that enables the
satisfaction of inequality constraints and is well suited for a real-time execution in control applications. The
soft inequality constraints are integrated by introducing an additional extended Kalman Filter (EKF) update
step using pseudo-measurements. The sequential formulation of the algorithm and several developed heuris-
tics ensure both the performance and a low computational effort of the algorithm. A special focus lies on an
efficient consideration of monotonicity assumptions for GPs in the form of inequality constraints. The algo-
rithm is statistically validated in simulations, where the possible advantages in comparison with the standard
RGP algorithm become obvious. The paper is concluded with a successful experimental validation of the
developed algorithm for the monotonicity-preserving learning of heat transfer values for the control of a vapor
compression cycle evaporator, leveraging a previously published partial input output linearization (IOL).
1 INTRODUCTION
A lot of progress can be noticed regarding the online
identification of system models. An example for a
basic method is given by the definition of paramet-
ric functions like polynomial ansatz functions and the
subsequent use of a recursive least-squares regres-
sion as described in (Blum, 1957). If models with
non-measurable states or parameters are to be identi-
fied, this method can be extended to linear Kalman
Filters (KF) or Unscented/Extended Kalman Filters
(UKF/EKF) as proposed in (Kalman, 1960), (Julier
and Uhlmann, 1997). In the presence of additional in-
equality constraints, especially Moving Horizon Esti-
mation (MHE) techniques are suitable (Haseltine and
Rawlings, 2005). If a more general approach is envis-
aged, there exist online-capable training methods of
neural networks as discussed in (Jain et al., 2014).
Gaussian Processes (GP) have been established
as a popular non-parametric alternative to neural net-
works (NNs). They are usually more data-efficient
than neural networks, robust to overfitting and – as
main advantage in comparison to NNs – provide an
uncertainty quantification for the predicted value, see
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-0480-8877
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-0601-4605
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7789-5699
(Sch
¨
urch et al., 2020). The non-parametric character
and the O(n
3
) rise of computational load in depen-
dency of the utilized data points, however, poses a big
challenge for their online implementation. Neverthe-
less, the literature offers suitable methods to address
this problem, like active-set methods as described in
(Qui
˜
nonero-Candela and Rasmussen, 2005), which
limit the number of utilized measurement points. Fur-
thermore, a promising algorithm was presented by
(Huber, 2013) with the recursive Gaussian Process re-
gression (RGP). The idea here is to define the GPs as
parametric functions based on user-defined basis vec-
tors. This preserves many benefits of the GP regres-
sion while maintaining a small computational load.
For many modeling tasks, a certain previous
knowledge is available. This may include bounds
on model outputs or monotonicity assumptions. This
knowledge might come from physical properties or
in the form of stability-conserving constraints in a
control setting. Nevertheless, the application of this
knowledge during learning has the potential to pro-
vide superior models with far less data. In neural
networks, such assumptions might be considered by
an altering of the reward function as in (Desai et al.,
2021). For standard GPs, a number of methods are
available for considering assumptions, e.g. regarding
the system structure as presented in (Beckers et al.,
2022) or for inequality constraints as shown in (Veiga
340
Husmann, R., Weishaupt, S. and Aschemann, H.
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity Assumptions for Control Applications.
DOI: 10.5220/0013783100003982
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2025) - Volume 1, pages 340-349
ISBN: 978-989-758-770-2; ISSN: 2184-2809
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

and Marrel, 2020). To the best of our knowledge,
however, the integration of inequality constraints for
recursive GPs represents a new development.
In (Husmann et al., 2024b), a partial IOL for Va-
por Compression Cycle (VCC) Control including an
integral feedback regarding the heat transfer value
was presented. As mentioned in that paper, the usage
of the steady state of the integrator to derive a data-
based model seems a promising idea. Since mono-
tonicity assumptions hold for the input dependencies
of such a heat transfer value model, this application
represents an interesting candidate for the validation
of the RGP algorithm with the inclusion of mono-
tonicity assumptions.
The main contributions of the paper are:
• Computationally efficient consideration of in-
equality constraints w.r.t. Gaussian variables in
a sequential EKF update
• Integrating monotonicity assumptions into RGP
regression by means of inequality constraints
• Real-time implementation of the presented
online-learning algorithm regarding a data driven
RGP model for the heat-transfer value of a VCC
The paper is structured as follows: First, we re-
capitulate the RGP in Sec. 2. Then, the generalized
approach for considering inequality constraints is pre-
sented in Subsec. 3.1. Afterwards, we introduce the
special case of formulating GP monotonicity as such
a constraint in Subsec. 3.4, summarize and discuss the
complete algorithm. As a first validation in Sec. 4, we
statistically analyze the validity of the algorithm for a
simulation example. Finally, an experimental valida-
tion is provided in Sec. 5 with an implementation of
the real-time algorithm on a VCC test rig. The paper
finishes with a conclusion and an outlook.
2 RECURSIVE GAUSSIAN
PROCESS REGRESSION
In this chapter, we briefly describe recursive Gaus-
sian Process regression (RGP) as presented in (Hu-
ber, 2013) and extended in (Huber, 2014). As usual,
we utilize a Squared Exponential (SE) kernel
k(x
x
x, x
x
x
′
) = σ
2
K
· exp(−(x
x
x − x
x
x
′
)
T
(x
x
x − x
x
x
′
)(2L)
−1
) (1)
with a zero mean function m(X
X
X) = 0. In our applica-
tion, the hyperparameters L and σ
K
are user-defined.
As elaborated in Subsec. 2.1, a joint length scale L
is defined for all input dimensions, and the possibly
different input ranges are addressed by an extra nor-
malization step. For each GP, we consider only one
measurement y
k
per time step k, with a corresponding
measurement variance σ
2
y
. As detailed in Subsec. 2.1,
X
X
X refers to the constant basis vectors, which are de-
fined during initialization, and X
X
X
k
denotes the current
test input. The mean values µ
µ
µ
g
k
and the covariance ma-
trix C
C
C
g
k
of the kernels, which are updated recursively,
give the RGP algorithm a KF-like structure.
The following variables can be precalculated of-
fline:
Offline
K
K
K = k(X
X
X,X
X
X), (2)
K
K
K
I
= K
K
K
−1
,
µ
µ
µ
g
0
= 0
0
0 ,
C
C
C
g
0
= K
K
K .
Given a zero mean function and a single measurement
per time step, the inference step simplifies to:
Inference
J
J
J
k
= k(X
X
X
k
, X
X
X)· K
K
K
I
, (3)
µ
p
k
= J
J
J
k
· µ
µ
µ
g
k
,
C
p
k
=
:
σ
2
K
k(X
X
X
k
, X
X
X
k
) + J
J
J
k
(C
C
C
g
k
− K
K
K)J
J
J
T
k
,
where the superscript p indicates the GP prediction
for the test inputs X
X
X
k
. This prediction is used in the
following update step:
Update
G
G
G
k
= C
C
C
g
k
J
J
J
T
k
· (C
p
k
+ σ
2
y
)
−1
, (4)
µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
= µ
µ
µ
g
k
+ G
G
G
k
· (y
k
− µ
p
k
),
C
C
C
g
k+1
= C
C
C
g
k
− G
G
G
k
J
J
J
k
C
C
C
g
k
.
2.1 Input Normalization
We define the basis vectors for all input axes as an
equidistant grid with step size 1. This leads to a
∏
n
X
i=1
N
i
× n
X
-dimensional matrix which contains
all vertices of the grid, where n
X
denotes the input
dimension of the GP, and N
i
the number of points in
the respective dimension. An example for the basis
vectors for n
X
= 2 , N
1
= 2 and N
2
= 3 is
X
X
X =
X
X
X
T
1
X
X
X
T
2
T
=
0 1 0 1 0 1
0 0 1 1 2 2
T
. (5)
To consider the ranges of the actual inputs ζ
i
in each
dimension, we introduce the normalization step
X
i,k
= f
norm
(ζ
k,i
) = (ζ
i,k
− ζ
i
) ·
N
i
− 1
ζ
i
− ζ
i
| {z }
β
i
, (6)
which is applied before each GP evaluation. Here
ζ
i
and ζ
i
denote the corresponding lower and upper
bounds of the input, and β
i
is a constant factor, which
is used in Subsec. 3.4.
The normalization and the use of a joint length L
was originally introduced to handle numerical issues
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity Assumptions for Control Applications
341

that may occur for large L in the standard inversion-
based RGP formulation applied in this paper. With the
normalization step, a universal maximum L
max
– inde-
pendent of the system – can be determined to main-
tain numerical stability. Please note that an alterna-
tive decomposition-based online solution is available,
which is described in (Husmann et al., 2025). An ad-
ditional benefit, independent of the RGP formulation
is given, however, by the reduction of free hyperpa-
rameters. Consequently, it has also been used in (Hus-
mann et al., 2025).
3 MONOTONICITY
CONSTRAINT INTEGRATION
In this chapter, we present our implementation to en-
force (soft) monotonicity constraints for RGPs. The
proposed method is based upon an EKF update for
inequality constraints, which is described in the se-
quel after the precise problem formulation. Since the
real-time capability is required, we put emphasis on
a computational speedup of the algorithm by usage
of reformulations and heuristics in the next subsec-
tions. Afterwards, we present the formulation of GP
monotonicity as a constraint, summarize and discuss
the complete algorithm.
We consider a hidden function y
k
= z
k
(ζ
ζ
ζ
k
) that is
dependent on deterministic inputs ζ
ζ
ζ
k
. The output y
k
of the hidden function z
k
is measurable, with zero-
mean Gaussian measurement noise with a variance
of σ
2
y
. We assume previous knowledge of the mono-
tonicity of z
k
w.r.t. its inputs, which can be stated in an
inequality constraint regarding the partial derivatives
∂z
k
∂ζ
i
≷ 0. To enable safety margins, this is generalized
to
∂z
k
∂ζ
i
≷ B
i
, where B
i
is a constant characterizing the
boundary of the constraint.
3.1 EKF Update for Inequality
Constraints
The direct consideration of hard inequality constraints
on Gaussian variables leads to truncated Gaussians,
see (Tully et al., 2011). For univariate Gaussians, the
resulting mean and covariance can be calculated ef-
ficiently. For multivariate Gaussians and inequality
constraints that dependent on several Gaussian input
variables, however, exact solutions usually necessitate
numerical methods. Here, (Simon, 2006a) provides
an overview. (Simon, 2006a) also discusses the use
of equality constraints as exact pseudo-measurements
within a KF update. This is related, however, to some
numerical issues since exact measurements lead to
rank-deficient updates in a KF. The alternative soft
constraints, where the pseudo-measurement is consid-
ered with a small uncertainty, are not subject to this
problem. In this paper, hence, we build upon this ap-
proach and extend it towards inequality constraints.
The basic idea is to implement inequality con-
straints as pseudo-measurements using a ReLU mea-
surement function as well as an EKF-update. In the
case of an inactive inequality constraint in the cur-
rent step, the ReLU function in combination with the
EKF ”hides” the inequality constraint in the update,
otherwise it is considered as an equality constraint.
Here, some parallels to the active-set method for con-
strained optimization become obvious, see (Nocedal
and Wright, 2006). These parallels are for exam-
ple also drawn in (Gupta and Hauser, 2007). There
however in combination with, projection and gain-
limiting methods instead of pseudo-measurements.
Of course, a truncated Gaussian may differ quite dra-
matically in shape from a Gaussian distribution. As a
results, this linearization-based approach may cause
large errors in the covariance. To rule out over-
approximation errors by this effect, the overall co-
variance update by the EKF inequality constraint is
discarded at the end, as described later. This measure
contributes to the ”softness” of the constraints.
To simplify the implementation, we standardize
all inequalities j by means of the sign indicator vari-
able s
j
: ˆy
IC,1
< B
1
≡ s
1
· ( ˆy
IC,1
− B
1
) < 0 with s
1
=
1, ˆy
IC,2
> B
2
≡ s
2
· ( ˆy
IC,2
− B
2
) < 0 with s
2
= −1.
This corresponds to linear inequalities of the type
s
j
(h
T
IC, j
x
x
x
k
− B
j
) < 0, where x
x
x
k
denotes the state vec-
tor. Now, we introduce the nonlinear measurement
function, which is evaluated with the mean values
ˆy
IC, j
=
˜
h
IC, j
(x
x
x
k
= µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
) = ReLU(s
j
(h
T
IC, j
µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
−B
j
)).
(7)
Due to the standardization of the inequalities, all
the pseudo-measurements become y
IC, j
= 0. The
measurement functions
˜
h
h
h
IC
=
˜
h
IC,1
,
˜
h
IC,2
, ..
T
can be
concatenated in a vector.
The partial derivative of the measurement, neces-
sary for the EKF update, is given by
ˆ
h
h
h
T
IC, j,k
=
∂
˜
h
IC, j
(x
x
x
k
)
∂x
x
x
k
x
x
x
k
=µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
!
T
=
s
j
h
T
IC, j
if s
j
(h
T
IC, j
µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
− B
j
) > 0
[0, 0, ..] else,
(8)
which can be concatenated as well to the linearized
measurement matrix
ˆ
H
H
H
IC,k
=
h
ˆ
h
h
h
IC,1,k
,
ˆ
h
h
h
IC,2,k
, ..
i
T
.
The update can then be computed according to a stan-
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
342
dard EKF, with the pseudo-measurements y
IC, j
= 0
˜
G
G
G
k
= C
C
C
g
k+1
ˆ
H
H
H
T
IC,k
(
ˆ
H
H
H
IC,k
C
C
C
g
k+1
ˆ
H
H
H
T
IC,k
+ R
R
R
IC
)
−1
, (9)
µ
µ
µ
c
k+1
= µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
−
˜
G
G
G
k
·
˜
h
h
h
IC
(µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
) ,
C
C
C
c
k+1
= C
C
C
g
k+1
−
˜
G
G
G
k
ˆ
H
H
H
IC,k
C
C
C
g
k+1
,
where R
R
R
IC
is the small diagonal pseudo-measurement
noise matrix, with all R
R
R
IC
( j, j) = r
IC
. The superscript
c denotes the constrained mean values and covari-
ance.
3.2 Reduction of the Computational
Load
Since we strive for real-time applicability of the
algorithm, computational efficiency is crucial.
Thus, instead of one batchwise EKF update, we
perform n
IC
sequential EKF updates for each pseudo-
measurement. The sequential KF is theoretically
identical to the batchwise one – as long as the
(pseudo-)measurements are uncorrelated, see (Si-
mon, 2006b). This assumption is met in our case
because R
R
R
IC
is diagonal. For the EKF, additional
conditions have to be taken into account as discussed
in Subsec. 3.7. Please note that numerical differences
between the batchwise and sequential KF update may
occur for large dimensions n
IC
. Consequently, the
exact reformulation of the batchwise EKF update to
a sequential EKF update can be stated as follows:
Set C
C
C
c
k+1,1
= C
C
C
p
k+1
and µ
µ
µ
c
k+1,1
= µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
.
For j = 1, . . . , n
IC
:
˜
G
G
G
k, j
= C
C
C
c
k+1, j
ˆ
h
h
h
T
IC,k, j
(
ˆ
h
h
h
IC,k, j
C
C
C
c
k+1, j
ˆ
h
h
h
T
IC,k, j
+ r
IC
)
−1
,
µ
µ
µ
c
k+1, j+1
= µ
µ
µ
c
k+1, j
−
˜
G
G
G
k, j
˜
h
IC, j
(µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
) , (10)
C
C
C
c
k+1, j+1
= C
C
C
c
k+1, j
−
˜
G
G
G
k, j
ˆ
h
h
h
IC,k, j
C
C
C
c
k+1, j
.
As discussed in the previous subsection, the
rows
ˆ
h
h
h
IC,k, j
of
ˆ
H
H
H
IC,k
are zero if the respective
constraint j is not active. Since an EKF update with
a zero measurement vector has no effect, another
exact reformulation can be applied, which leads to a
dramatic speedup.
Set C
C
C
c
k+1,1
= C
C
C
p
k+1
and µ
µ
µ
c
k+1,1
= µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
.
Evaluate t
t
t
k
= H
H
H
IC
µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
with H
H
H
IC
= [h
h
h
IC,1
, h
h
h
IC,2
, ..]
T
.
For j = 1, . . . , n
IC
:
If s
j
(t
t
t
k
( j) − B
j
) > 0:
˜
G
G
G
k, j
= C
C
C
c
k+1, j
h
h
h
IC, j
(h
h
h
T
IC, j
C
C
C
c
k+1, j
h
h
h
IC, j
+ r
IC
)
−1
,
µ
µ
µ
c
k+1, j+1
= µ
µ
µ
c
k+1, j
−
˜
G
G
G
k, j
s
j
(t
t
t
k
( j) − B
j
) , (11)
C
C
C
c
k+1, j+1
= C
C
C
c
k+1, j
−
˜
G
G
G
k, j
h
h
h
T
IC, j
C
C
C
c
k+1, j
.
Here, we also used the property s
2
j
= 1.
Update if
Update to
Update if
Update to
˜
B
j
δ
u,j
δ
b,j
s
j
h
T
IC,j
x
k
− B
j
> 0
h
T
IC,j
x
k
B
j
s
j
h
T
IC,j
x
k
− B
j
> 0
h
T
IC,j
x
k
Without Update Heuristic
With Update Heuristic
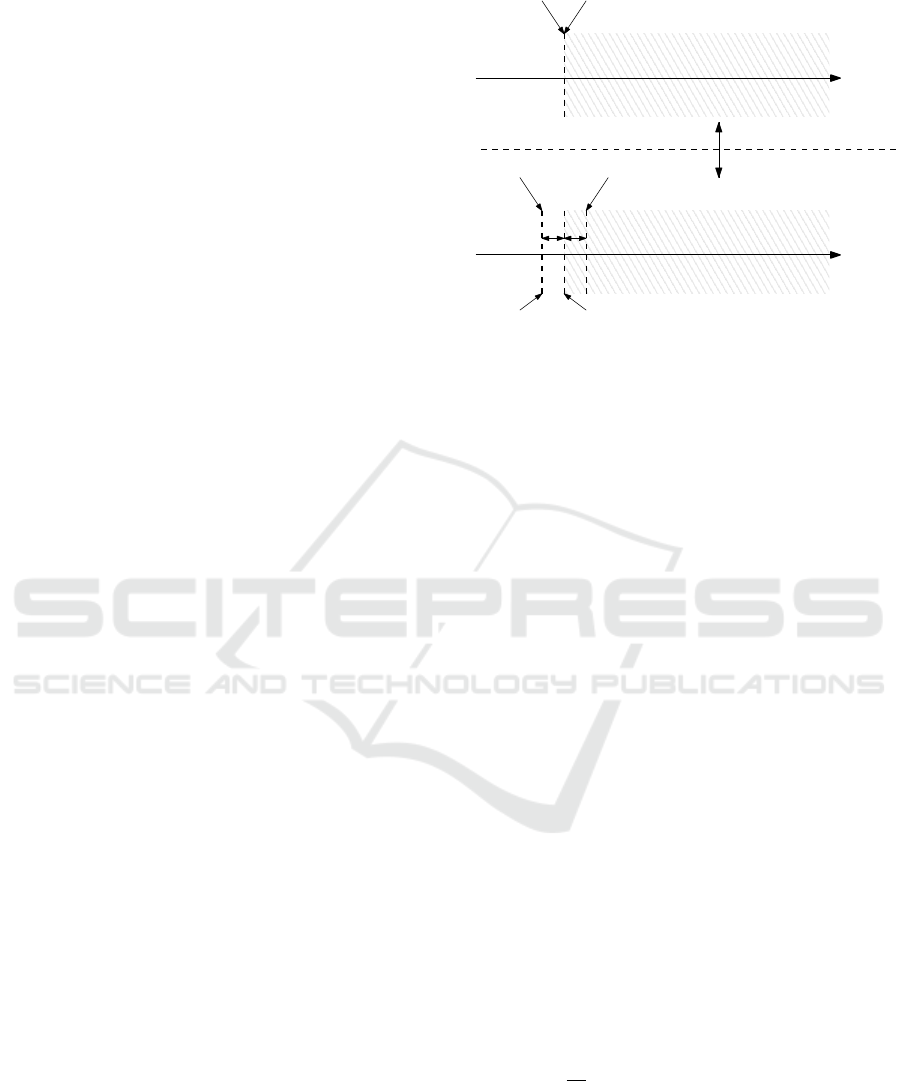
Figure 1: Schematic illustration of the update heuristic.
3.3 Upper-Bounding the Computational
Load
Since the algorithm is utilized for model learning,
we can expect that our measurements, in majority,
do not violate our constraints, but the constraint in-
tegration rather improves the speed at which learning
takes place. To further reduce the maximum computa-
tional load per time step, we upper-bound the sequen-
tial pseudo-measurement updates per time step to
˜n
IC
≤ n
IC
. Practice has shown that in cases where the
actual hidden function is close to the bounds, noise
and numerical errors may lead to repetitive updates
w.r.t. certain constraints. In combination with the
upper-bounding of the pseudo-measurement updates
per time step, this may lead to cases where certain
constraints are not considered altogether. Thus, we in-
troduce an additional heuristic to enable a hysteresis-
like behavior: As illustrated in Fig. 1, we only update
if s
j
(t
t
t
k
( j) − B
j
) > δ
b, j
. Moreover, we update to the
value
˜
B
j
= B
j
−δ
u, j
s
j
, where δ
b, j
≥ 0 and δ
u, j
≥ 0 are
both small non-negative constants.
3.4 GP Monotonicity Assumptions as
Constraints
Monotonicity assumptions on a real, continuously
differentiable function z
k
(ζ
ζ
ζ) can be stated as inequal-
ity constraints of its partial derivatives w.r.t. its in-
puts, e.g.
∂z
k
∂ζ
i
≷ 0. According to the derivation in
(McHutchon, 2015), the mean values of the partial
derivative of a GP with SE kernels in the test grid X
X
X
k
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity Assumptions for Control Applications
343

w.r.t. the input ζ
i,k
is given by
∂µ
µ
µ
p
k
∂ζ
i,k
=
−
β
i
L
X
X
X
i,k
− X
X
X
T
i
⊙ k(X
X
X
k
, X
X
X)
· K
K
K
I
|
{z }
H
H
H
IC,l,k
·µ
µ
µ
g
k
,
(12)
where ⊙ denotes the Schur- or Hadamard product.
This function is linear in the mean values of the
RGP. For a constant test grid
˜
X
X
X, the linear gain ma-
trix H
H
H
IC,l,k
is also time-invariant. For simplicity, we
only consider one monotonicity assumption per di-
mension, where l = 1, . . . , n
l
with n
l
≤ n
ζ
indicate
the input dimensions for which monotonicity assump-
tions exist. Consequently, each dimension is charac-
terized by only one set of values s
l
, B
l
, δ
B,l
and δ
U,l
.
As a constant test grid is considered for the mono-
tonicity, we can state the mean values of the partial
derivatives at the test vector grid using linear pseudo-
measurement matrices. They can be calculated by
means of
∂µ
µ
µ
p
k
∂ζ
l
=
−
β
l
L
˜
X
X
X
l
− X
X
X
T
l
⊙ k(
˜
X
X
X, X
X
X)
· K
K
K
I
| {z }
H
H
H
IC,l
·µ
µ
µ
g
k
(13)
for all dimensions l that comply with monotonicity
assumptions. Here, the matrices H
H
H
IC,l
can be calcu-
lated offline.
As confirmed in a comparison with the exact co-
variance of the partial derivative, see (McHutchon,
2015), the usage of these measurement functions
for the covariance prediction of the partial derivative
leads to further linearization errors. This error van-
ishes if
˜
X
X
X = X
X
X holds. In the following, we therefore
choose the monotonicity test vector grid equal to the
basis vector grid – which is reasonable for most ap-
plications anyway.
3.5 Inequality Constraints on the GP
Output
Even though it is not employed in this paper, the
consideration of inequality constraints on GP out-
puts is included here for completeness. Like the
monotonicity constraints, output constraints are eval-
uated on a grid. If the chosen test grid is also
identical to the basis vector grid, the corresponding
output equation becomes µ
µ
µ
p
k+1
= J
J
J
k
(X
X
X)µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
. Since
J
J
J
k
(X
X
X) = k(X
X
X, X
X
X)K
K
K
I
= I
I
I holds, the respective pseudo-
measurement matrix becomes the identity matrix
H
H
H
IC
= I
I
I and leads to the simplification t
t
t
k
= µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
.
Please note that for soft GP output constraints, other
measures, like a bounding of the measurements y
k
or
the RGP mean values µ
µ
µ
g
k
, might be more efficient and
effective.
3.6 Summary of GP Monotonicity
Constraints
This section summarizes the pseudo-measurement
updates for constraints related to monotonicity as-
sumptions in the RGP. The extended RGP algorithm
will in the following referred to as RGPm. Please
note that the index k denoting the time step is omitted
for simplicity. In addition to the offline precomputa-
tions (2) for the standard RGP in Sec. 2, the following
measurement matrices need to be calculated for each
input dimension with a monotonicity assumption:
For l = 1, . . . , n
l
:
H
H
H
IC,l
=
−
β
l
L
X
X
X
l
− X
X
X
T
l
⊙ K
K
K
· K
K
K
I
. (14)
Also the boundaries
˜
B
l
= B
l
− δ
u,l
s
l
and δ
b,l
for
the update heuristic as well as the upper limits per
dimension ˜n
IC,l
have to be defined.
For each time step k, after the evaluation of the
RGP inference (3) and update steps (4) from Sec. 2,
the pseudo-measurement update is computed as
follows:
Set C
C
C
c
1,1
= C
C
C
g
k+1
and µ
µ
µ
c
1,1
= µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
.
For l = 1, . . . , n
l
:
Evaluate t
t
t
l
= H
H
H
IC,l
C
C
C
c
l,1
, with H
H
H
IC,l
=
[h
h
h
IC,l,1
, h
h
h
IC,l,2
, ..]
T
and set counter m = 1.
For j = 1, . . . , n
IC,l
:
If s
l
(t
t
t
l
( j) −
˜
B
l
) > δ
b,l
and m ≤ ˜n
IC,l
: , (15)
˜
G
G
G
l, j
= C
C
C
c
l, j
h
h
h
IC,l, j
(h
h
h
T
IC,l, j
C
C
C
c
l, j
h
h
h
IC,l, j
+ r
IC
)
−1
µ
µ
µ
c
l, j+1
= µ
µ
µ
c
l, j
−
˜
G
G
G
l, j
s
l
(h
h
h
IC,l, j
µ
µ
µ
c
l,1
−
˜
B
l
)
C
C
C
c
l, j+1
= C
C
C
c
l, j
−
˜
G
G
G
l, j
h
h
h
IC,l, j
C
C
C
c
l, j
m = m + 1
µ
µ
µ
g
l+1,1
= µ
µ
µ
c
l, ˜n
IC,l
and C
C
C
c
l+1,1
= C
C
C
c
l, ˜n
IC,l
Set µ
µ
µ
g
k+1
= µ
µ
µ
c
n
l
, ˜n
IC,l
, but reset C
C
C
g
k+1
= C
C
C
c
1,1
.
3.7 Discussion
In general, a consideration of monotonicity con-
straints with a test vector grid unequal to the basis
vector grid is possible and was successfully imple-
mented. It tends to be, however, numerically unsta-
ble, most likely due to linearization errors w.r.t. the
covariance prediction.
As pointed out, the implemented monotonicity
constraints are only soft constraints. This means in
practice that the GP will adhere to the measurements
if these consistently contradict the monotonicity as-
sumptions. This scenario would be caused by wrong
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
344
assumptions regarding either the monotonicity itself
or the measurement quality. Although still not guar-
anteeing constraint satisfaction, a safety margin can
be added by changing B
l
accordingly. For safety-
critical constraints, an additional evaluation on a finer
grid as well as a subsequent output correction may be
useful.
A UKF may be more suited for handling the non-
linearities in the presented pseudo-measurement up-
date. Nevertheless, it would prevent most of the re-
formulations which facilitate the envisaged real-time
implementation. Consequently, it was not considered
further.
Please note that piece-wise monotonicity can also
be addressed as long as the regions are definable
through sets of basis vector points. This variation
and the direct output constraints in Subsec. 3.5 have
already been successfully validated but are not de-
scribed for the sake of brevity.
Please note that the sequential update of the EKF
involves an additional condition for the equivalence to
a batchwise update. Here, the linearization point has
to be identical. This condition is fulfilled within each
input dimension by introducing the intermediary vari-
ables t
t
t
k
and t
t
t
l
in Subsecs. 3.2 and 3.4, respectively. It
is, however, not fulfilled over all input dimensions l in
Subsec. 3.4. Thus, even without the bounded number
of updates and the update heuristic, a slight deviation
is present between the sequential EKF and the batch-
wise EKF if several monotonicity assumptions apply.
4 VALIDATION BASED ON
SIMULATIONS
As a first validation example, the hidden static func-
tion z
k
= 2(1 + 0.1ζ
k
+ ζ
3
k
) is learned. The input ζ
k
is picked from a random uniform distribution over the
complete input range ζ
k
∈ [−1, 1]. Zero-mean Gaus-
sian white noise with a variance of σ
2
y
= 1e − 2 is
added to the measured output y
k
.
The RGP hyperparameters remain constant and
are chosen as follows: L = 3, σ
K
= 1e1, and N = 21.
Obviously, the hidden function is strictly monoton-
ically increasing, so
∂z
∂ζ
> 0, B
1
= 0, and s
1
= −1
hold. The pseudo-measurement noise is chosen as
r
IC
= 1e − 8.
4.1 Simulation Results
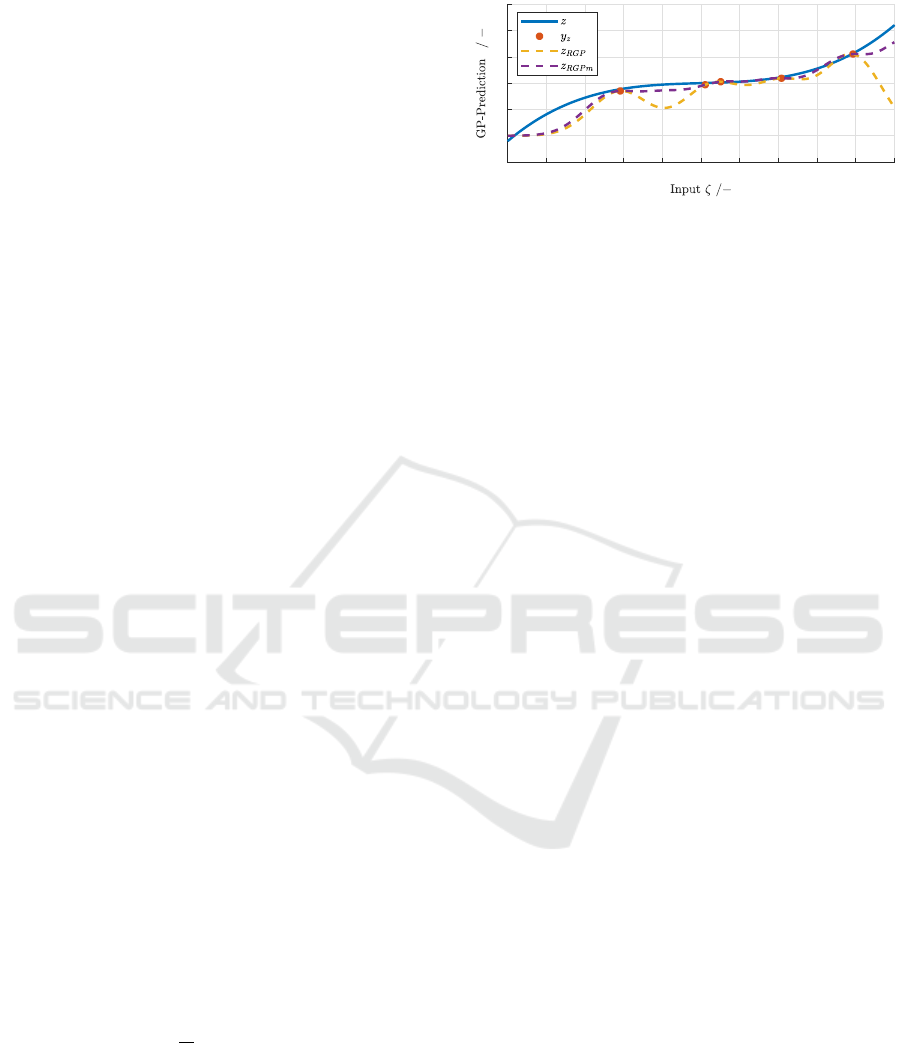
In Fig. 2, the hidden function z and its learned recon-
structions z
RGPm
and z
RGP
– with and without mono-
tonicity assumptions – are depicted after five noisy
-1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
Figure 2: RGP and RGPm outputs in comparison with the
hidden function z after 5 time steps.
measurements y
k
. It becomes obvious that the RGPm
algorithm works properly. In this example, it is ca-
pable of enforcing strict monotonicity over the whole
input range, while the curve is not significantly al-
tered in the vicinity of the actual measurement points.
The result represents a clearly better fit in comparison
with the classical RGP – especially in regions where
still no measurements are available.
For a statistical validation of the algorithm and an
assessment of the impact of the adaptations, we inves-
tigate six different variants of the algorithm:
S0 Pure RGP
S1 unlimited ˜n
IC
= n
IC
RGPm with δ
b
= 0 and δ
u
= 0
S2 ˜n
IC
= 2 limited RGPm with δ
b
= 0 and δ
u
= 0
S3 ˜n
IC
= 2 limited RGPm with boundary heuristic
δ
b
= 1e − 1 and δ
u
= 1e − 1
S4 ˜n
IC
= 5 limited RGPm with δ
b
= 0 and δ
u
= 0
S5 ˜n
IC
= 5 limited RGPm with boundary heuristic
δ
b
= 1e − 1 and δ
u
= 1e − 1
For each scenario, 500 simulation runs are con-
ducted with the described uniform random input and
the noisy output. After k = 1, 2, 5, . . . , 1000 steps, the
root mean-squares error (RMSE) between the learned
function of each variation, compared to the hidden
function over the complete input range, is calculated.
This RMSE is again averaged over all 500 simula-
tions and depicted in Fig. 3. Fig. 4 shows the aver-
age cumulative number of pseudo-measurement up-
dates (CPMU) that were conducted for the alterna-
tives S1,...,S5.
All RGPm variants perform better than the classi-
cal RGP. This advantage vanishes after a certain num-
ber of steps, and all the RMSE converge to the same
value. This could be expected because the monotonic-
ity assumptions are valid and should be represented
on average in the measurements.
It can be seen that a tighter limit on the number of
pseudo-measurement updates per time step is gener-
ally a trade-off w.r.t. the performance. Accordingly,
S1 is better than S4 and S2. In the current applica-
tion, the improvement from S4 to S1 is however quite
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity Assumptions for Control Applications
345
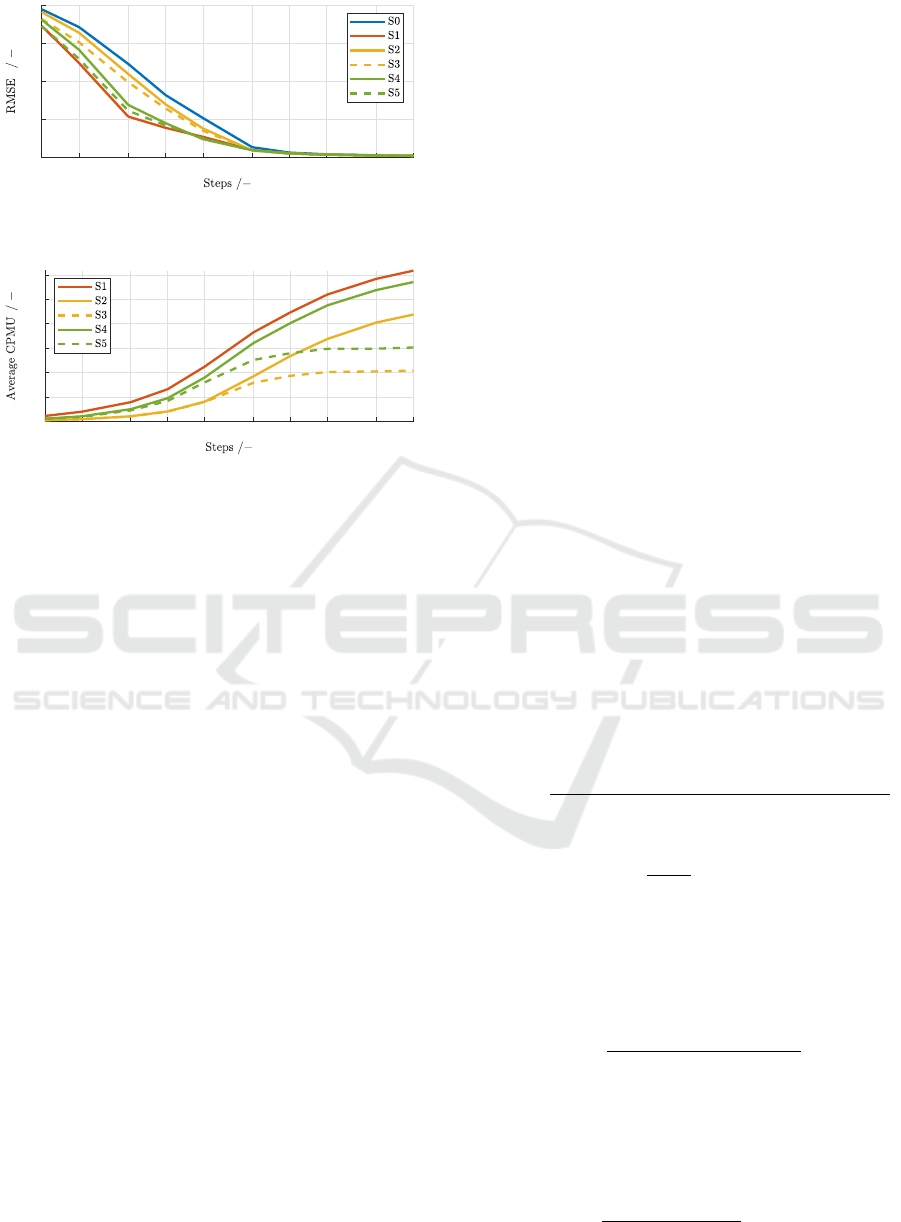
1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200 500 1000
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Figure 3: Average RMSE for 500 simulation runs of the
different RGP and RGPm variants.
1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200 500 1000
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
Figure 4: Average cumulative pseudo-measurement updates
(CPMU) for 500 simulation runs of the different RGPm
variants.
small, and reverses slightly around 20 steps. This last
effect may stem from numerical errors that could be
related to the higher number of pseudo-measurement
updates.
The heuristic approach of including outer/inner
boundaries resulted in significant improvements in the
RMSE. The reduced repeated pseudo-measurement
updates w.r.t. certain constraints are clearly visible in
Fig. 4. While S1, S2 and S4 still perform pseudo-
measurement updates after 1000 steps, the update
heuristic leads to a converging CPMU for S3 and S5,
which means that no more pseudo-measurement up-
dates are performed after a certain point. Whereas the
real-time capability is only influenced by the maxi-
mum number of updates per time step, the reduced
computational load can be seen as an additional ben-
efit.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
FOR A VAPOR COMPRESSION
CYCLE
In this chapter, the functionality of the proposed
method is investigated in a real-time application – a
counterflow evaporator as a subsystem of a VCC. As
discussed in detail in (Husmann et al., 2024a) and
(Husmann et al., 2024b), heat transfer values, espe-
cially in the presence of phase changes, depend on
process parameters and are hard to determine. In
(Husmann et al., 2024b), integral feedback was ap-
plied directly affecting the heat transfer value and
combined with a partial IOL. In addition to a stability
proof also the convergence of integrator state towards
the actual heat transfer value was proven. In this paper
we want to leverage the integrator steady state to learn
a RGP model for the heat transfer value that depends
on several process parameters. The aim is to use the
RGP model in parallel to the integrator feedback to
further improve the transient control behavior.
The algorithm was implemented on a test rig at
the Chair of Mechatronics at the University of Ro-
stock. The utilized hardware, a Bachmann PLC
(CPU:MH230), runs at a sampling time of 10ms. The
test rig is fully equipped with sensors, an electronic
expansion valve as well as a compressor with a vari-
able frequency drive. Please refer to (Husmann et al.,
2024a) and (Husmann et al., 2024b) for further details
about the test rig.
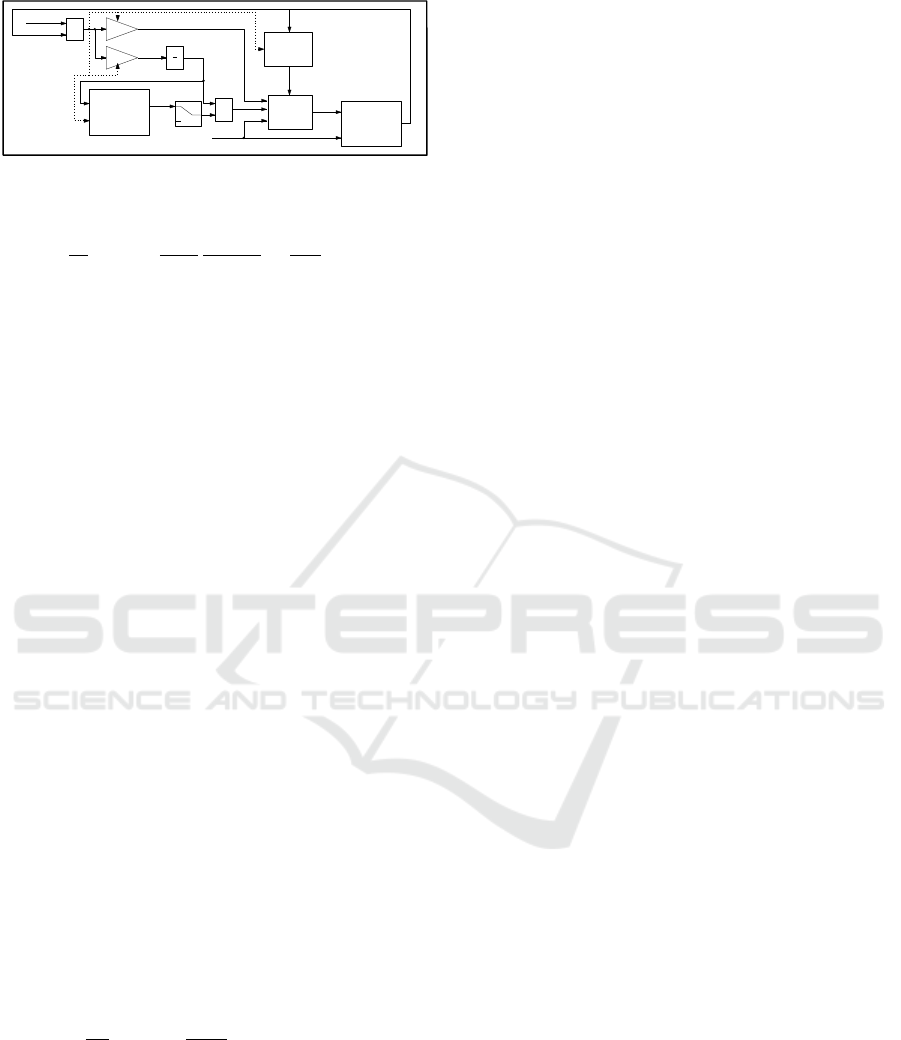
5.1 Partial IOL Control
As the partial IOL is described in detail in (Husmann
et al., 2024b), we only want to give a brief overview
in this paper. The envisioned control structure is de-
picted in Fig. 5. As shown, the control inputs are
given by the expansion valve opening u
E
and the com-
pressor speed u
C
. The control outputs are chosen as
the evaporator mean temperature y
1
= T
Evap
and the
superheating enthalpy y
2
= ∆h
SH
after the evaporator.
The control-oriented evaporator model, first derived
in (Husmann et al., 2023), is governed by the follow-
ing two ODEs
˙
h
Evap
=
˙m
E
h
Evap,in
− ˙m
C
h
Evap,out
+
˙
Q
Evap
−( ˙m
E
− ˙m
C
)h
Evap
V
Evap
ρ
Evap
(16)
and
˙
ρ
Evap
=
1
V
Evap
( ˙m
E
− ˙m
C
) . (17)
Here, the first state equation is affected by an uncer-
tain convective heat flow
˙
Q
Evap
= α · α
norm
· A
Evap
· (T
U
− T
Evap
) (18)
with α
norm
as a normalization factor. The input-
dependent mass flows are given by
˙m
E
= ζ
E
·
q
ρ
Cond,out
(p
Cond
− p
Evap
) · u
E
(19)
and
˙m
C
= ˆm
Rev
u
C
η
V
. (20)
Both outputs can be expressed in terms of the state
variables. The second output is given by
y
lin,2
= ∆h
SH
=
h
Evap
−(1−w
ρ
)h
Evap,in
w
ρ
− h
Evap,sat
(T
Evap
),
(21)
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
346
y
m
υ
IOL
u
E
Physical
System
u
C
∆h
sh
+
−
∆h
sh,d
Filter
k
R
k
I
y
m,f
e
y
1
s
ˆα
+
+
RGPm
ˆα
GP
RGP/
RGPm
Figure 5: Nonlinear tracking control structure.
and its first time derivative becomes
˙y
lin,2
=
1
w
ρ
˙
h
Evap
−
1−w
ρ
w
ρ
dh
Evap,in
dt
−
∂h
sat
∂T
T
Evap
˙
T
Evap
,
(22)
which lead to a relative degree of one. Whereas the
inverse dynamics is determined for both control in-
puts in the standard IOL proposed in (Husmann et al.,
2023), the partial IOL used here leverages the inverse
dynamics of the control input u
E
u
E
= b
3
(.)
−1
[υ
2
− a
2
(.) − b
4
(.)u
C
] , (23)
and considers the second input u
C
as a measurable
disturbance. Please note that a secondary controller
needs to be implemented for the first control output
y
1
= T
Evap
, see (Husmann et al., 2024b). In this pa-
per, however, the control input u
C
is assumed as given
because it has no relevance for the presented algo-
rithm. The partial IOL is completed with a stabilizing
feedback υ
2
= k
R
(e
y
)e
y
, with e
y
= y
2,d
− y
2
. Here the
nonlinear feedback from (Husmann et al., 2024b) is
utilized. The introduction of a parameter update law
for the heat transfer value
˙
ˆ
α = −k
I
(y
2,d
− y
2
), which
corresponds to integral control action w.r.t.
ˆ
α, dra-
matically increases the performance and guarantees
steady-state accuracy as shown in (Husmann et al.,
2024b). Since the integrator state
ˆ
α was proven to
converge to an exact representation of the lumped heat
transfer value in the control-oriented model, it is suit-
able for the training of a model.
5.2 RGPm Implementation
As input variables for the GP model, the compres-
sor speed u
C
and the superheating enthalpy y
2
= ∆h
SH
are chosen, i.e.,
ˆ
α
GP
= z(u
C
, ∆h
SH
). As known from
our own experiments and from the literature, the in-
equalities
∂α
∂u
C
> 0 and
∂α
∂∆h
SH
< 0 hold. Consequently,
they are included as monotonicity assumptions in the
RGPm algorithm. The evaluation of the GP model is
conducted with the reference value y
d,2
instead of the
current one, i.e.,
ˆ
α
GP
= z(u
C
, ∆h
SH,d
). Thereby, any
additional feedback is avoided, and the GP model ob-
tains a pure feedforward structure w.r.t. its evaluation.
This prevents stability issues.
The RGP and RGPm algorithms are implemented
with basis vector dimensions of N
1
= 5 and N
2
= 5
for the respective GP inputs, which results in N
1
N
2
=
25 basis vector points. The monotonicity update is
bounded to n
1
= n
2
= 5 steps per dimension and per
time step. The parameters for the update heuristics are
defined as follows: δ
u,1
= δ
u,2
= 0 and δ
b,1
= δ
b,2
=
2e − 6. The pseudo-measurement noise is chosen as
r
1
= r
2
= 1e −8, and the length scale is set to L = 1.5.
The signing variables for the respective monotonicity
assumptions are given by s
1
= −1 and s
2
= 1 and the
safety margins are disabled, so B
1
= B
2
= 0.
To ensure that the integrator state is only utilized
in the vicinity of it’s equilibrium state, we employ
a heuristic which only enables the RGP update if
|e
y
| < 1 holds for 10 consecutive seconds. The numer-
ical values in this heuristic mark a trade-off between
learning speed and accuracy. With a larger error mar-
gin or a shorter time horizon, more data qualifies for
training. However, the considered data might also re-
late to system states further away from the equilib-
rium.
5.3 Results
To illustrate the functionality and advantages of the
RGPm algorithm, two consecutive experiments with
the same step-wise u
C
-trajectory are performed: the
first one for y
2,d
= 14, the other one for y
2,d
= 7. The
RGPm algorithm is trained online during both exper-
iments – without applying its output value to the con-
troller. For a comparison, the RGP algorithm is later
trained offline on the same data. The results after the
first and second experiment are depicted for both al-
gorithms in Fig. 6. Since the monotonicity updates
for the covariance matrix are discarded at the end
of each time step, both algorithms lead to the same
covariance, so that only one is depicted per experi-
ment. In the upper right picture of Fig. 6, the training
region during the experiment becomes obvious, be-
cause the covariance is small there. When comparing
the mean values for the RGPm (upper left) and RGP
(upper middle), it becomes evident that the learned
model within the input region used for the training is
nearly identical. Outside of this region, however, the
shapes vary drastically. While the monotonicity as-
sumptions in the RGPm model lead to a physically
viable model shape, this cannot be stated for the stan-
dard RGP model. Here, the overall shape is only de-
fined by the limited amount of data available in the
non-trained region. As shown in the comparison of
the trained models after the second experiment for
both RGPm (lower left) and RGP (lower middle), the
differences between the models decline with the avail-
ability of data. This reinforces the findings from the
simulation study.
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity Assumptions for Control Applications
347
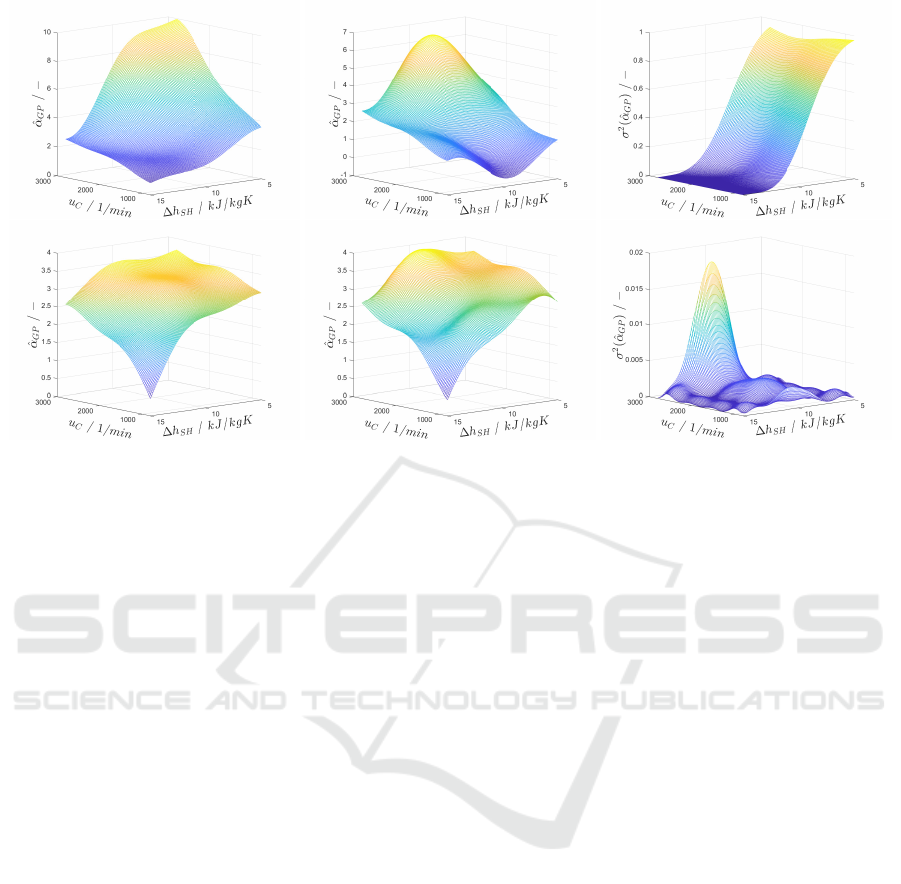
Figure 6: GP model predictions from left to right: RGPm (online), RGP (offline comparison for same data) and covariances
of both variants. From top to bottom: after the first u
C
-trajectory for y
2,d
= 14, and after the second u
C
-trajectory for y
2,d
= 7.
The softness of the constraints in the RGPm algo-
rithm becomes clear for low superheating and large
compressor speeds. Here, the monotonicity con-
straints are slightly violated, however much less than
in the standard RGP algorithm. The violation may be
fixed by safety margins and a more involved heuristic
for the RGP update.
The evaluation of the overall control performance
with the trained model is outside of the scope of
this paper, since a more detailed comparison would
need additional concepts and algorithms, e.g. suitable
training strategies. A quick validation of the RGPm
model after the second experiment, depicted in Fig.
6 (lower left corner), can be performed by deactivat-
ing the integrator feedback control and running a u
C
test trajectory together with a learned
ˆ
α
GP
and with a
constant α. Here, for a reference value of y
d
= 13,
which wasn’t used for the training, a 28 % reduc-
tion in RMSE could be achieved, which represents a
promising first result for the application of the trained
RGPm model.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND
OUTLOOK
This paper presents an extension of the recursive
Gaussian Process regression (RGP) algorithm to en-
force (soft) constraints during an online training.
Here, the consideration of monotonicity assumptions
in the GP model is emphasized as well as their imple-
mentation as constraints. The algorithm is statistically
validated in simulations. Moreover, different sim-
plifications are introduced to enable a real-time use,
and their effect on the performance is investigated.
A real-time implementation on a test rig is presented
afterwards, where the learning of heat transfer value
models for an evaporator is considered. The evap-
orator is a main component of a vapor compression
cycle operated by a previously published partial IOL.
Here, the extension of a standard RGP regression by
monotonicity constraints results in a significantly bet-
ter modeling – especially if few data is available.
A combination of the extension presented in this
paper with the Kalman Filter integration of the RGP
(KF-dRGP), is straightforward and allows for an RGP
training with constraints if the output of the hid-
den function is not directly measurable. For systems
where a hard constraint satisfaction is crucial, further
investigations are still necessary. As discussed ear-
lier, an additional safety step with a calculation of the
constraint satisfaction on a finer grid could be suit-
able. As mentioned in Sec. 5, the full integration of
the GP model within the partial IOL for the VCC con-
trol necessitates further work. It is obviously desir-
able, for example, to simultaneously learn and apply
the learned model. This does, however, introduce an
additional feedback loop into the system, which may
affect the stability. Here, the presented output and
monotonicity bounds mark important tools. Given
promising first results, steps in this direction will be
topics of future work.
ICINCO 2025 - 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
348

REFERENCES
Beckers, T., Seidman, J., Perdikaris, P., and Pappas, G. J.
(2022). Gaussian process port-hamiltonian systems:
Bayesian learning with physics prior. In 2022 IEEE
61st Conference on Decision and Control (CDC),
pages 1447–1453.
Blum, M. (1957). Fixed memory least squares filters using
recursion methods. IRE Transactions on Information
Theory, 3(3):178–182.
Desai, S. A., Mattheakis, M., Sondak, D., Protopapas, P.,
and Roberts, S. J. (2021). Port-hamiltonian neural net-
works for learning explicit time-dependent dynamical
systems. Physics Review E, 104:034312.
Gupta, N. and Hauser, R. (2007). Kalman filtering with
equality and inequality state constraints.
Haseltine, E. L. and Rawlings, J. B. (2005). Critical evalua-
tion of extended Kalman filtering and moving-horizon
estimation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Re-
search, 44(8):2451–2460.
Huber, M. F. (2013). Recursive Gaussian process re-
gression. In 2013 IEEE International Conference
on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pages
3362–3366.
Huber, M. F. (2014). Recursive Gaussian process: On-line
regression and learning. Pattern Recognition Letters,
45:85–91.
Husmann, R., Weishaupt, S., and Aschemann, H. (2023).
Nonlinear control of a vapor compression cycle by
input-output linearisation. In 27th International Con-
ference on Methods and Models in Automation and
Robotics (MMAR), pages 193–198.
Husmann, R., Weishaupt, S., and Aschemann, H. (2024a).
Control of a vapor compression cycle based on a
moving-boundary model. In 2024 28th International
Conference on System Theory, Control and Comput-
ing (ICSTCC), pages 438–444.
Husmann, R., Weishaupt, S., and Aschemann, H. (2024b).
Nonlinear control of a vapor compression cycle based
on a partial IOL. In IECON 2024 - 50th Annual
Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Soci-
ety, pages 1–6.
Husmann, R., Weishaupt, S., and Aschemann, H. (2025).
Direct integration of recursive Gaussian process re-
gression into extended Kalman filters with applica-
tion to vapor compression cycle control. In 13th IFAC
Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systems NOLCOS
2025.
Jain, L. C., Seera, M., Lim, C. P., and Balasubramaniam,
P. (2014). A review of online learning in supervised
neural networks. Neural computing and applications,
25:491–509.
Julier, S. J. and Uhlmann, J. K. (1997). A new ex-
tension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems.
In Proc. of AeroSense: The 11th Int. Symp. on
Aerospace/Defence Sensing Simulation and Controls.
Kalman, R. E. (1960). A new approach to linear filtering
and prediction problems. Transactions of the ASME–
Journal of Basic Engineering, 82(Series D):35–45.
McHutchon, A. J. (2015). Nonlinear modelling and con-
trol using Gaussian processes, chapter A2, pages 185–
192.
Nocedal, J. and Wright, S. J. (2006). Numerical Opti-
mization, chapter 16.5, pages 467–480. Springer New
York, NY.
Qui
˜
nonero-Candela, J. and Rasmussen, C. E. (2005). A uni-
fying view of sparse approximate Gaussian process
regression. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
6:1939–1959.
Sch
¨
urch, M., Azzimonti, D., Benavoli, A., and Zaffalon,
M. (2020). Recursive estimation for sparse Gaussian
process regression. Automatica, 120.
Simon, D. (2006a). Optimal State Estimation, chapter 7.5,
pages 212–222. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Simon, D. (2006b). Optimal State Estimation, chapter 6.1,
pages 150–155. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Tully, S., Kantor, G., and Choset, H. (2011). Inequality
constrained Kalman filtering for the localization and
registration of a surgical robot. In 2011 IEEE/RSJ In-
ternational Conference on Intelligent Robots and Sys-
tems, pages 5147–5152.
Veiga, S. D. and Marrel, A. (2020). Gaussian process re-
gression with linear inequality constraints. Reliability
Engineering & System Safety, 195:106732.
Recursive Gaussian Process Regression with Integrated Monotonicity Assumptions for Control Applications
349
