
Software Testing Evidence: Results from a Systematic Mapping
Artur S. Farias
1 a
, Rodrigo Rocha
1,2 b
, Igor Vanderlei
2 c
, Jean Araujo
2 d
, Andr
´
e Ara
´
ujo
1 e
and
Jamilson Dantas
3 f
1
Computing Institute Federal University of Alagoas, Maceio, Brazil
2
Federal University of Agreste of Pernambuco, Garanhuns, Brazil
3
Federal University of Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil
Keywords:
Software Testing, Systematic Mapping, Software Testing Evidence.
Abstract:
Software testing is a fundamental aspect of software development, essential for ensuring product quality and
reliability. This paper presents the findings of a systematic mapping of the literature, aimed at addressing
key research questions related to software testing practices. The study investigates the types of software
testing that are most commonly utilized, the predominant approaches employed, the challenges encountered
during testing execution, the reported benefits of implementing software testing, the best practices acknowl-
edged by the industry for efficient testing, and the tools and technologies frequently applied in the field. The
research methodology followed a structured protocol that guided the systematic mapping across five scien-
tific databases: IEEEXplore, ACM, Science Direct, Springer Link, and Scopus. Following a comprehensive
screening process, a total of 341 primary studies were systematically reviewed. The results provide valuable
insights into current software testing practices and highlight the challenges faced in this area. Additionally,
this study identifies effective solutions and best practices, assisting researchers and industry professionals in
improving their software testing processes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Software has become an essential component of most
systems and is deeply embedded in modern society’s
daily life. Technological advancements, including
open systems and highly automated or networked de-
vices, have significantly increased the complexity of
software systems (Pudlitz et al., 2020). Addressing
quality assurance, the field of software testing is in-
creasingly gaining significance in the technology in-
dustry due to various factors, including the demand
for complex and high-quality computing systems, a
wide diversity of testing tools, and the automation of
testing processes. The ISO IEC IEEE 2022 (N. A.,
2022) defines software testing as a systematic activ-
ity in which a system or component is executed un-
der defined conditions. During this process, results
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-5576-124X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1993-5044
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1939-6979
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-8842-2536
e
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-3661-3618
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9009-7659
are observed or recorded, allowing for an evaluation
of specific characteristics or aspects of the system or
component.
Software testing is an integral part of modern soft-
ware engineering. Its adoption is influenced by many
factors beyond tools or technology (Swillus and Zaid-
man, 2023). Kassab et al. (Kassab et al., 2017) em-
phasize that as software quality becomes increasingly
important, the significance of testing strategies also
progressively rises. Swillus and Zaidman (Swillus
and Zaidman, 2023) emphasize the significance of
employing software testing to ensure higher quality in
the delivery of software products and services, while
also identifying various challenges and limitations in
the application of such testing. Additionally, the lit-
erature presents several experimental studies (Moussa
et al., 2022; Barbosa et al., 2023; Paiva et al., 2023)
that seek to propose solutions aimed at mitigating
these challenges and limitations in the use of software
testing.
This paper investigates the context of software
testing, searching a evidence set about the types of
software testing, the predominant approaches em-
ployed, the challenges generally seen during test-
386
Farias, A. S., Rocha, R., Vanderlei, I., Araujo, J., Araújo, A. and Dantas, J.
Software Testing Evidence: Results from a Systematic Mapping.
DOI: 10.5220/0013739100003985
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2025), pages 386-393
ISBN: 978-989-758-772-6; ISSN: 2184-3252
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

ing process, the reported benefits/advantages result-
ing from the adoption of software testing, the best
practices recognized by the software industry for ef-
ficient testing and the tools and technologies often
applied in the field. To address six research ques-
tions and investigate effective software test planning
and execution, this research methodology adhered to
Kitchenham’s guidelines (Kitchenham and Charters,
2007). This study covers the period from 2014 to
2024 and conducted a thorough search across five sci-
entific databases: IEEEXplore, ACM, Science Direct,
Springer Link, and Scopus. Following a widespread
screening process, a total of 341 primary studies were
systematically reviewed.
This research provides a systematic mapping of
software testing practices, revealing previously under-
researched correlations between testing methodolo-
gies, tools, resource constraints, and project out-
comes. Results highlight the prevalence of specific
testing types, along with obstacles such as resource
limitations and inconsistent processes. Conversely,
the substantial benefits of effective testing—improved
quality, reduced costs, and increased user satisfac-
tion—are also identified. The findings uncover valu-
able guidance and practical recommendations for op-
timizing testing processes and tool selection, ulti-
mately enhancing efficiency and effectiveness.
The remainder of the work is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents the necessary context to understand
the study. Section 3 presents information on how
the systematic mapping of the literature was carried
out, containing the research questions, search strat-
egy, quality assessment and Selection and Extraction
Process. Section 4 discusses the results separated by
research questions. In Section 5 there is a discussion
about threats to the validity of the work presented and
finally the section 6 presenting the conclusion and fu-
ture works.
2 RELATED WORK
Santos et al.(Santos et al., 2022) investigated software
testing practices within Brazilian companies, aiming
to identify prevalent testing techniques, selection pro-
cesses, challenges faced, and tools employed. The re-
sults indicated that system-level testing was the most
common, with functional and structural testing tech-
niques being predominantly used. Major challenges
included insufficient prioritization of testing, inade-
quate training, and resource constraints.
Kiran et al.(Kiran et al., 2019) present a system-
atic literature review (SLR) comprising 58 studies,
categorizing them into five groups. The review high-
lights the prevalence of meta-heuristic algorithms and
the lack of attention to clustering-based methods. The
findings suggest a lack of standardization across dif-
ferent approaches and tools, which hinders compar-
isons between studies and the identification of best
practices.
Fulcini et al.(Fulcini et al., 2023) provide a multi-
vocal literature review (MLR) examining the applica-
tion of gamification in software testing. They con-
ducted a thorough search encompassing both white
and grey literature, identifying 73 relevant contribu-
tions, and analyzed common gamification mechanics
along with their associated benefits and drawbacks.
The review highlights a significant gap in empirical
evidence supporting the claimed benefits, particularly
in industrial settings, and advocates for a more stan-
dardized methodology for evaluating the effectiveness
of gamified testing practices.
Raulamo et al.(Raulamo-Jurvanen et al., 2017) in-
vestigated how software professionals select test au-
tomation tools by employing a systematic mapping
process and conducting a grey literature review of
60 sources. The results highlighted the absence of
a systematic approach to tool selection, with deci-
sions based on technical aspects, cost, vendor support,
and team considerations. The main findings identified
twelve criteria, with an emphasis on usability, cost,
and alignment with project requirements.
These related works are robust in their methodolo-
gies, present diverse results and have different char-
acteristics, thereby contributing significantly to the
field. The Table 1 presents the finding evidence as
answers and results from each study. Only one work
considered the phases of software testing, in the same
way that only this research considered the best prac-
tices exercised in software projects, which indirectly
includes data for Selection criteria. The types of stud-
ies range from surveys, systematic mapping, to sys-
tematic literature reviews. In general, a common lim-
itation observed in Related works is the scopes in
terms of period, focus, or location. In contrast, this
study adopts a broader view, covering different con-
texts and tools.
Table 1: Finding Evidence in Related Works.
Approaches
Benefits
Best practices
Challenges
Phases
Selection criteria
Tools
Types
This Research
(Santos et al., 2022)
(Kiran et al., 2019)
(Fulcini et al., 2023)
(R-Jurvanen et al, 2017)
Software Testing Evidence: Results from a Systematic Mapping
387

3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:
MAPPING STUDY
A systematic literature mapping consolidates evi-
dence from existing primary studies, with the specifi-
cation of research questions being a key component of
the process. This research was structured into several
macro phases, beginning with the initial step of defin-
ing the research questions within the proposed theme,
followed by the development of the research proto-
col. The next phase involved the essential Data Col-
lection Process, which included defining key search
terms, establishing the search string, and identifying
the search databases. The subsequent step was Search
String Calibration and Testing in Search Databases,
aimed at enhancing the process of identifying and se-
lecting relevant papers. The penultimate phase com-
prised establishing inclusion and exclusion criteria for
articles, culminating in the execution of the selection
of primary studies. The Information Extraction Pro-
cess was primarily divided into three parts: the first,
Dataset Configuration, pertains to the setup and or-
ganization of how the data would be structured and
stored; the second involved the actual execution of the
information extraction; and the final phase, resulting
from the first two, was Dataset Construction.
The pre-analysis phase allows for a moderate ex-
amination of the information and aids in forming ini-
tial insights regarding the results. This phase includes
the activities of General Study and Discussion on the
Dataset, along with the preliminary preparation of
Graphs and Tables for Indicators. Next, in the Quality
Assessment phase, the articles are evaluated for their
relevance and alignment with the research questions,
resulting in a classification of the primary studies. Fi-
nally, two major analysis phases are conducted: the
first concerns a more in-depth general analysis of the
data, examining the primary studies and their results,
while generating overall result graphs.
3.1 Research Questions and Protocol
Definition
The primary goal of this study is to synthesize and
investigate the state of the art in software testing,
with the intention of addressing the central research
question (RQ): How can software tests be planned
and executed more efficiently? Thus, six research
questions have been formulated. The research ques-
tions: ”RQ1 What types of software testing are most
used?”, ”RQ2 What are the main software testing ap-
proaches?”, ”RQ3 What are the challenges reported
while performing software testing?”, ”RQ4 What
benefits/advantages are reported from applying soft-
ware testing?”, ”RQ5 What does the software indus-
try consider to be best practices for efficiently apply-
ing software testing?”, ”RQ6 What are the most used
tools or technologies in the context of software test-
ing?”. The developed research protocol is available at
https://l1nk.dev/9WIsH.
3.2 Data Collection Process
The search strategy was defined based on nine key
terms: Software, Testing, Methodology, technique,
practice, Challenges, Problems, Benefits, Advan-
tages, and Tools. These terms were combined
to form the final search string: ((”Software Test-
ing”) AND (Methodology OR technique OR practice)
AND (Challenges OR Problems) AND (Benefits OR
Advantages) AND (Tools)). Searches were conducted
across five databases: IEEE Xplore Digital Library,
ACM Digital Library, ScienceDirect, Springer Link,
and Scopus. The inclusion criteria specified articles
published between 2014 and 2024 and related to soft-
ware testing. Exclusion criteria were applied to re-
move articles with less than five pages, those not in
English, works not available for download, and book
chapters.
The selection process began with 1,941 results. A
multi-stage screening process, involving three collab-
orators and a tie-breaker, was used to filter the articles.
The initial selection removed duplicates and articles
outside the specified publication dates. A second se-
lection phase further filtered the results based on rel-
evance to the research questions and accessibility of
the full text. This rigorous process resulted in a final
set of 341 primary studies for analysis.
3.3 Information Extraction Process
The Information Extraction Process began with the
Dataset Configuration, which involved setting up and
organizing how the data would be structured and
stored. This process was carried out in several stages,
using forms and spreadsheets. In the first stage, bib-
liographic data from all the papers were collected.
Once this was completed, the second stage focused
on gathering responses to the research questions.
The third stage involved the use of the AI tool
GPT-4 Turbo, querying each primary article for an-
swers to the research questions. The query text was
specific to each research question and indicated where
the information was located in the article, aiming to
confirm or supplement the information already iden-
tified in the manual extraction. The responses gener-
ated by the AI tool were separately analyzed through
a second reading of the paper to evaluate whether the
indicated answers were consistent.
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
388

3.4 Compliance Assessment and Data
Analysis Steps
At the end of the entire selection and data extrac-
tion process, a list of questions was also established
to conduct a compliance assessment of the studies,
serving as criteria to evaluate each work individually.
There are ten criteria, each of which receives a score
represented by a few possible values. There are only
three distinct possible scores. 1.0, indicates that the
study fully met the criterion in question. 0.5, indicates
that the study partially met the criterion. Finally 0.0
indicates that the study did not meet the criterion. The
defined values are applied to each of the ten quality
criteria, and by summing up all ten individual scores,
the final score of the study is obtained, ranging from
0.0 to 10.0. This forms the overall quality score of the
study. The ten quality and compliance criteria can be
seen in Table 2:
Table 2: Criteria for evaluating the compliance assessment
of studies.
Does the study clearly define its objectives or research questions?
Does the study provide a clear description of the context in which the research was
conducted?
Is the study coherent and well-structured, allowing for evaluation?
Are the findings presented clearly?
Does the study address which types of software testing are most commonly used?
Does the study address the main software testing approaches?
Does the study address the challenges encountered during software testing?
Does the study address the benefits or advantages of applying software testing?
Does the study address what the software industry considers to be best practices for
efficient software testing?
Does the study address the most commonly used tools or technologies in the context of
software testing?
The data analysis involved a multi-phase process.
It began with a preliminary examination of the dataset
and the construction of initial graphs and tables. This
was followed by a more in-depth general analysis to
prepare broader results. The final and most crucial
phase involved a detailed discussion of how each pri-
mary study addressed the research questions, with the
data organized into tables and graphs for presentation.
Finally, an analysis of the threats to the validity of
both the work and the primary studies was conducted.
4 SOFTWARE TESTING
EVIDENCE
From the 341 approved primary studies, various cat-
aloging data (such as year, country, database, confer-
ence or journal, and authors) were collected to pro-
vide a comprehensive overview of the research land-
scape. All 341 studies were published between 2014
and 2024. While the distribution of studies was gener-
ally consistent over the years, there were fluctuations,
with the highest number of selected studies in 2024
(16.11% of the total) and the lowest in 2022 (4.90%).
This distribution highlights a consistent spread over
the years, despite fluctuations in specific periods.
Table 3: Main authors among the selected primary studies.
Author N % Author N %
Vahid Garousi 11 0.89 Andrea Arcuri 8 0.64
Michael Felderer 6 0.48 Zhenyu Chen 6 0.48
Chunrong Fang 5 0.40 Gordon Fraser 5 0.40
Rudolf Ramler 5 0.40 Wasif Afzal 5 0.40
Andy Zaidman 4 0.32 Emil Al
´
egroth 4 0.32
Mike Papadakis 4 0.32 Robert Feldt 4 0.32
Santiago Matalonga 4 0.32 Stephen H. Edwards 4 0.32
The data shown in Table 3 presents the main au-
thors responsible for the selected studies. A total of
1,242 authors were identified, categorized as primary
authors or co-authors. Among them, 14 authors with
the highest participation rates were selected, while
the remaining 1167 authors, account for 93.99% of
the participants. Among these authors, Vahid Garousi
stands out with the highest representation, contribut-
ing to 11 selected studies, representing 0.89%. The
diversity of authors, comprising 93.99% of the se-
lected studies, alongside the top contributors, demon-
strates that the field is highly collaborative, with var-
ious researchers providing significant insights from
different perspectives on the topic.
For the ACM database, decreased from 170 to 168
after analyzing the DOI links, still representing the
database with the highest number of approved stud-
ies at 49.26% of the selected works. For IEEE, the
number of studies increased from 25 to 58, totaling
17.01%. The SpringerLink database increased from
31 to 36 studies, and ScienceDirect from 65 to 70,
representing 10.56% and 20.53%, respectively. Fi-
nally, the Scopus database dropped significantly from
50 studies to just 2, indicating that most selected stud-
ies from this database originated elsewhere. One such
source was ScitePress, which was not part of the ini-
tial search but now accounts for 0.59% of the system-
atic mapping studies.
Table 4: Journals or conferences of the selected studies.
Conference N % Conference N %
Information and Software Technol-
ogy
33 9.68 Systems and Software 33 9.68
TOSEM 20 5.87 ICSE 13 3.81
ESEM 12 3.52 Software Quality Jour-
nal
11 3.23
ISSTA 9 2.64 SAST 9 2.64
ESEC/FSE 8 2.35 ICST 8 2.35
SBES 8 2.35 ASE 7 2.05
CSUR 6 1.76 ITiCSE 6 1.76
The date shown in Table 4 presents the main
journals, conferences, and proceedings where the se-
lected studies were published. In total, the 341 se-
lected studies were published in 131 distinct events
or journals, with the 14 with the highest number of
selected works being featured in the table. The re-
maining journals and conferences account for 46.31%
of the selected works, while the top 14 account for
53.69%, representing the majority of the selected
Software Testing Evidence: Results from a Systematic Mapping
389
studies. This demonstrates that the subject matter
has significant importance to the scientific commu-
nity, being discussed in prestigious and academically
rigorous events and journals.
Finally, the locations where each selected study
was published. To obtain the places, the Scimago
Journal & Country Rank website (SCIMAGO, 2024)
was used by searching for the name of the event
or journal. The largest number of selected stud-
ies was obtained from events or journals from the
United States, with a total of 135 studies, representing
39.82% of the selected works. The Netherlands with
45 selected studies, representing 13.27%, followed by
Brazil with 21 studies, representing 6.19%.
4.1 General Data on Responses to
Research Questions
The first research question is about software testing
types. A total of 82 different software testing types
were identified, totaling 946 citations. From the com-
plete list of testing types, the study considered the
16 most cited ones, with the Unit Testing ranked
first, mentioned in 149 studies (15.75%). Regression
Testing followed with 105 mentions (11.10%) of the
data, and System Testing came next with 83 men-
tions (8.77%). Among all other testing types cited
but not included in the charts, there were 168 men-
tions (17.76%), indicating significant diversity in the
testing types addressed.
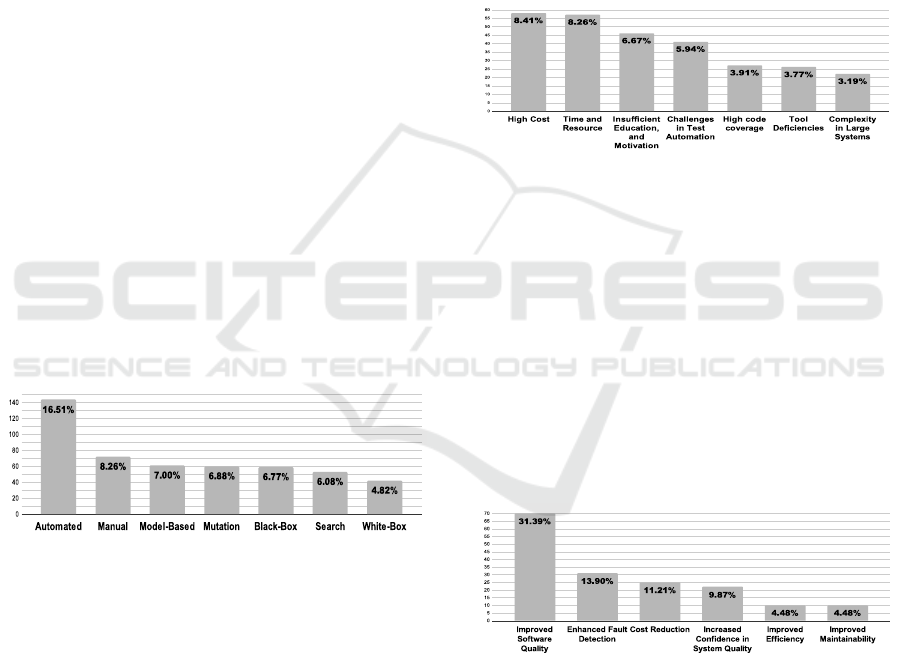
Figure 1: Most cited testing approaches.
The second research question, it is about the
Methodologies or Approaches, a total of 136 differ-
ent ones were mentioned, with a total of 872 cita-
tions. the study considered the 15 most cited ones,
the chart in Figure 1 shows the 7 most cited. Leading
the list with the highest number of citations is Auto-
mated Testing, with 144 mentions (16.51%). Manual
Testing, with 72 mentions (8.26%) of the data. It is
followed by Model-Based Testing with 61 citations
(7.00%). Among all the Methodologies cited but not
included in the chart, there are 238 citations (27.27%)
This may also indicate a significant diversity of ap-
proaches.
Aiming to answer the third research question re-
garding the challenges, a total of 112 distinct chal-
lenges were identified, with a total of 690 citations.
The graph shown in Figure 2 presents the 7 challenges
with the highest number of citations among the 13
challenges analyzed. High Cost of Testing was cited
in 58 different studies (8.41%), making it the most
cited challenge. Close behind is the challenge of Time
and Resource Constraints in Software Testing, with
57 citations (8.26%). Next is the challenge of Insuf-
ficient Education, Skills, and Motivation in Software
Testing, with 46 citations (6.67%). Other cited chal-
lenges that are not included in the graph total 99 dis-
tinct challenges (47.51%), which together account for
328 citations.
Figure 2: Most cited testing challenges.
In fourth research question, the benefits of soft-
ware testing with a total of 20 distinct advantages,
with 223 total citations. The chart shown in Figure 3
presents the 6 most citad among the 15 main benefits
of software testing. The most frequently cited advan-
tage, with 70 mentions (31.39%), is Improved Soft-
ware Quality being the only benefit with more than 50
mentions in this category. Following this, Enhanced
Fault Detection was cited 31 times (13.90%). Just be-
low, Cost Reduction received 25 citations (11.21%).
Other benefits not included in the chart totaled only 8
citations, representing 3.61% of the overall citations.
Figure 3: Main Advantages of Software Testing.
For best practices in software testing (RQ5), a to-
tal of 138 distinct practices were identified, receiv-
ing a total of 301 citations. The graph shown in Fig-
ure 4 illustrates the 5 most relevant best practices in
terms of citations among the 10 main best practices
of the studies. The practice with the highest num-
ber of citations is Test Automation, with 20 citations
(6.64%). It is followed by a tie between Compre-
hensive Skill Development and Structured Training in
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
390
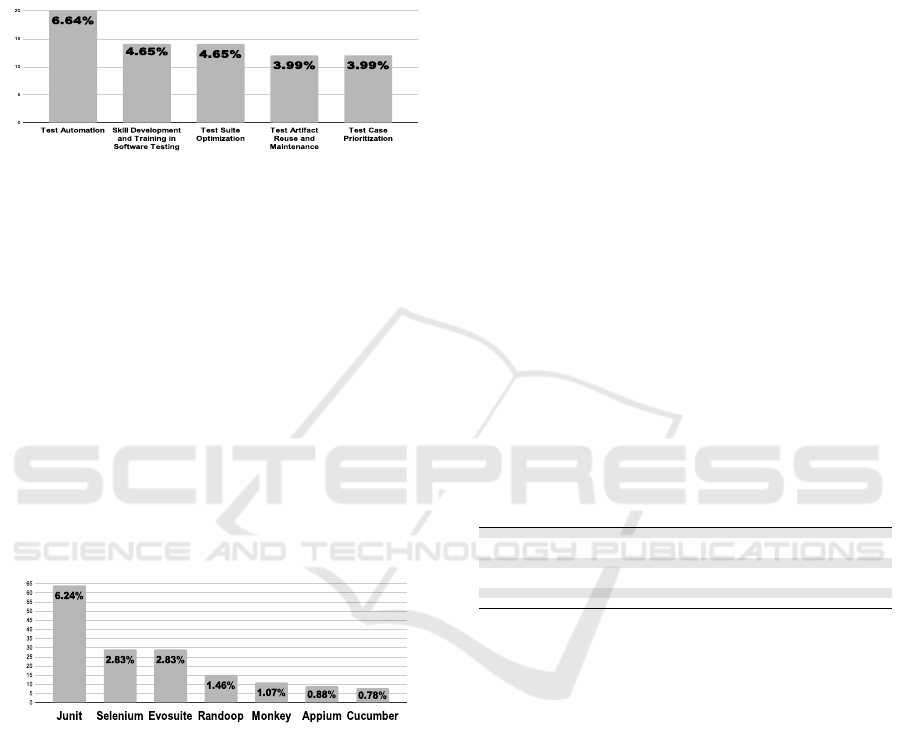
Software Testing and Test Suite Optimization, both
with 14 citations ( 4.65%) each. The best practices
not shown in the graph account for a total of 192 ci-
tations (63.80%). These values are distributed among
128 distinct best practices, each with three or fewer
citations.
Figure 4: Main best practices in testing.
Regarding the research question about tools for
software testing cited in the studies, a total of 654
different tools were mentioned across 341 works in
the systematic literature mapping. The total sum of
citations amounts to 1026. The chart in Figure 5
shows the 7 most cited tools in the 17 analyzed stud-
ies. Starting with the tool with the highest number of
citations, JUnit was mentioned in 64 studies (6.24%).
It is the only tool cited in more than 50 studies. The
next tools, Evosuite and Selenium, was cited 29 times
(2.83%) each. Among the 654 tools, 532 were cited
only once in the studies. For all the software testing
tools cited that are not included in the chart, there are
796 citations (77.61%). This is three times the num-
ber of citations for the top 17 tools.
Figure 5: Most cited software testing tools.
5 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
In addressing the first research question, the high
number of citations for Unit Testing suggests it is
the most widely used or discussed type, possibly due
to its fundamental role in ensuring code quality in
the early stages of development. The collected data
also suggest the relevance of Regression Testing and
System Testing, highlighting concerns about stability
and overall system functionality. Similarly, Mobile
Testing, even with lower frequency, may indicate the
growing impact of mobile technologies in the field.
In second research question, the continuous evo-
lution of software environments, especially with the
adoption of agile practices and microservices archi-
tectures, drives innovation in methodologies such
as cloud testing, continuous integration testing, and
service-oriented testing. From the responses to
methodologies research question, can be highlight the
high frequency of citations for Automated Testing, re-
flecting a trend toward automation in the field of soft-
ware testing. Similarly, the number of citations for
Manual Testing suggests that human approaches still
hold importance in the software testing process or that
there are still instances where automation is not fea-
sible. The citations for Mutation Testing and Model-
Based Testing may indicate concerns about the effec-
tiveness of test cases and the need for more optimized
techniques.
5.1 Answers to RQ3: Challenges
With the small group of 13 challenges concentrating
most of the citations in software testing, recurring is-
sues such as high cost and time and resource con-
straints are highlighted. At the same time, the pres-
ence of 99 additional challenges, representing nearly
half of the citations (47.51%), underscores the diver-
sity and complexity of the difficulties faced in the
field.
Table 5: Main challenges in testing.
Name N % Name N %
Test Efficiency and Effec-
tiveness
53 22.74 Test Maintenance and
Management
47 20.17
Test Automation 32 13.73 System Complexity 24 10.30
Communication and Col-
laboration
17 7.30 Test Coverage and Effec-
tiveness
17 7.30
Resources and Time 16 6.87 Knowledge and Training 15 6.44
Test Environment 10 4.29 Security in Testing 2 0.86
The Table 5 shows the distribution of the 112 soft-
ware testing challenges into 10 categories. The cate-
gory with the largest number of challenges is Test Ef-
ficiency and Effectiveness, with 53 challenges, which
may reflect the complexity and relevance of this area
in the context of software testing. Next, the analysis
has Test Maintenance and Management with 47 chal-
lenges allocated, which may demonstrate the impor-
tance of managing and maintaining tests throughout
the software lifecycle. The categories Test Automa-
tion and System Complexity also stand out, with 32
and 24 challenges allocated, respectively, indicating
the relevance of test automation, as well as the ob-
stacle of system complexity as critical factors in the
testing process.
5.2 Answers to RQ4: Benefits
Based on the data, It is considered that the most sig-
nificant perceived advantage in studies on software
testing is Improved Software Quality, as it accounts
Software Testing Evidence: Results from a Systematic Mapping
391

for more than one-third of the total citations. Other
relevant advantages include Cost Reduction and En-
hanced Fault Detection, demonstrating that the soft-
ware industry tends to focus on efficiency and relia-
bility. Additionally, the low number of distinct bene-
fits and the more uniform distribution of citations may
indicate that software testing benefits are already well
recognized, with a stronger consensus among them.
Table 6: Quantity of good practices for each benefit.
Benefit Practice %
Enhanced Fault Detection 20 14.51
Improved Efficiency 14 10.14
Improved Resource Allocation and Decision Support 13 9.42
Improved Maintainability 11 7.97
Improved Code Coverage 9 6.52
Quality Assurance and Improvement 9 6.52
Cost Reduction 8 5.8
Increased Confidence in System Quality 8 5.80
Improved Test Effectiveness and Knowledge Transfer 7 5.07
Improved Requirement Validation and Traceability 5 3.62
Enhanced Software Security 5 3.62
Process Alignment Benefit 5 3.62
Improved Software Quality 4 2.90
Improved Validation and Feedback through Crowdsourced
Testing.
4 2.90
Reliability Enhancement 4 2.90
Customer Satisfaction Assurance 4 2.90
Improved Test Suite Quality 3 2.17
Improved Reproducibility and Bug Detection 2 1.45
Real-World Testing and Platform Coverage 2 1.45
Deadlock Detection 1 0.72
Table 6 shows the results of the relationship be-
tween the 20 Benefits of using software testing found
during the mapping and the 138 Best practices. In
this way, Enhanced Fault Detection obtained 20 Best
practices associated with it, demonstrating the focus
on the method and efficiency with which faults are de-
tected. Next, Improved Efficiency with 14, Improved
Resource Allocation and Decision Support with 13,
and Improved Maintainability with 11, emphasizing
optimizing tests, allocating resources effectively, and
ensuring ease of maintenance over time.
5.3 Answers to RQ5: Best Practices
The 10 most cited practices represent a relatively
small fraction of the total 301 citations. Addition-
ally, the distribution of citations suggests that no sin-
gle practice is overwhelmingly dominant, but rather a
wide variety of approaches are recognized in the field.
Table 7: Distribution of best practices in software testing.
Name N % Name N %
Test Strategy and
Planning
62 23.48 Test Quality and Im-
provement
49 18.56
Test Automation 30 11.36 Risk and Defect Man-
agement
28 10.61
Collaboration and
Communication
23 8.71 Test Coverage and Ef-
ficiency
23 8.71
Reviews and Feed-
back
20 7.58 Test Maintenance and
Reusability
16 6.06
Security Testing 12 4.55 Manual Testing 1 0.38
The graph shown in Table 7 presents the distribu-
tion of the 138 best practices in 10 categories. The
category with the highest number of best practices is
Test Strategy and Planning, with 62 best practices, in-
dicating that the main best practices aim to improve
how tests are planned and managed. Next, it observes
Test Quality and Improvement with 49 best practices,
showing that the main intention of the best practices is
to enhance the quality of the tests performed. The cat-
egories Test Automation and Risk and Defect Man-
agement also stand out, with 30 and 28 best practices,
respectively, indicating concern about how tests are
automated, as well as concern about mitigating risks
that may arise during testing phases.
5.4 Answers to RQ6: Tools
These findings indicate a significant diversity of soft-
ware testing tools. Another point highlighted is the
fragmentation in the use of testing tools, which can
result in considerable time spent choosing which tools
to use. Among these tools, JUnit stands out as a po-
tentially widely used tool, suggesting its recognition
as a standard or broadly accepted solution for soft-
ware testing.
Table 8: Information collected from testing tools.
Tool Language Platform Testing
junit java desktop, backend/api, web, mobile unit
evosuite java desktop, backend/api, web unit
selenium all (script) web, mobile functional, interface
randoop java, .net desktop, backend/api, web unit
monkey java,
kotlin,
dart,
javascript
mobile random, unit
appium java,
kotlin,
dart,
javascript
web, mobile functional, non-
functional
cucumber ruby, java,
javascript
backend/api, web, mobile acceptance
µtest c backend/api unit
robot python,
java
desktop, backend/api, web, mobile mobile, web, inter-
face
mockito java desktop, backend/api, web, mobile unit
testng java desktop, web, mobile unit, functional, end-
to-end, integration,
etc.
sikuli java desktop, web, mobile web, interface
robotium java,
javascript
mobile functional, system,
acceptance
nunit .net, mono desktop, backend/api unit
evomaster java,
kotlin, c#,
javascript,
python
desktop, backend/api, web system, regression,
fuzzing
jacoco java desktop, backend/api, mobile coverage
dynodroid java mobile mobile
guitar java, .net descktop, web interface
bugzilla all all —
espresso kotlin, java web, mobile interface, web
Table 8 presents data regarding the 20 most cited
software testing tools. There is a wide range of tools
available for testing in Java. Among the selected
tools, 11 can be used for desktop applications, 10 for
Backend/API, 13 for web tools, and mobile. Among
the tools analyzed, unit testing is the most common (8
tools), followed by interface (5), functional (4), and
web testing (3). Finally, it is noteworthy that all 20
tools with the highest number of citations were open-
source.
6 FINAL REMARKS
The software industry continues to face growing pres-
sure to deliver high-quality, reliable, and efficient
systems that can meet evolving user demands and
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
392

technological transformations. Within this scenario,
software testing plays a fundamental role in ensur-
ing product quality, maintainability, and user satis-
faction. This research addressed six research ques-
tions and offers a comprehensive overview of current
software testing practices. The analysis covered the
most frequently adopted testing types, predominant
approaches, reported challenges and benefits, widely
recognized best practices, and the tools and technolo-
gies most commonly used in the field. This study pre-
sented a systematic mapping based on a broad set of
primary studies.
The identified best practices, combined with an
understanding of the challenges and limitations, pro-
vide valuable guidance for software development
teams and testing professionals seeking to improve
their processes. This comprehensive analysis of com-
monly used tools and technologies provides practi-
cal recommendations for selecting and implementing
tools, thereby enhancing the effectiveness and effi-
ciency of software testing efforts. Software testing
has demonstrated clear benefits, including improved
product quality, enhanced fault detection, and cost
reduction. The study highlights a diverse yet frag-
mented set of best practices and tools, with JUnit, Se-
lenium, and EvoSuite among the most prominent.
The main threats to the validity of the study stem
from two factors. First, the limited number of collab-
orators, 3 in total, faced with a large volume of arti-
cles during the initial selections and primary studies
may have introduced bias in the interpretation of re-
sults and affected the replicability of the research, de-
spite the use of rigorous strategies and computational
tools in data extraction. Second, in article selection,
65 works were excluded due to lack of access to the
full text. As future work, the development of stan-
dardized frameworks is suggested to support testing
decisions across various project environments. Ad-
ditionally, further studies are recommended to eval-
uate the effectiveness of testing techniques and tools
in real-world contexts, particularly in agile develop-
ment, DevOps pipelines, and artificial intelligence-
driven testing environments.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Financial support for this research was provided by
the CAPES Social Demand Program and the Fed-
eral University of Alagoas (UFAL). We also thank the
UFAL Institute of Computing (IC) and the DKD Lab
from the Federal University of the Agreste of Pernam-
buco (UFAPE).
REFERENCES
Barbosa, C., Uch
ˆ
oa, A., Coutinho, D., Assunc¸
˜
ao, W. K. G.,
Oliveira, A., and Garcia, A. (2023). Beyond the code:
Investigating the effects of pull request conversations
on design decay. In 2023 ACM/IEEE International
Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and
Measurement (ESEM), New Orleans, LA, USA.
Fulcini, T., Coppola, R., Ardito, L., and Torchiano, M.
(2023). A review on tools, mechanics, benefits, and
challenges of gamified software testing. ACM Com-
put. Surv., 55(14s).
Kassab, M., DeFranco, J. F., and Laplante, P. A. (2017).
Software testing: State of the practice. IEEE Software,
34:46 – 52.
Kiran, A., Butt, W. H., Anwar, M. W., Azam, F., and Maq-
bool, B. (2019). A comprehensive investigation of
modern test suite optimization trends, tools and tech-
niques. IEEE Access, 7:89093–89117.
Kitchenham, B. and Charters, S. M. (2007). Guidelines
for performing systematic literature reviews in soft-
ware engineering. Technical Report EBSE-2007-001,
Keele University and Durham University.
Moussa, R., Guizzo, G., and Sarro, F. (2022). Meg: Multi-
objective ensemble generation for software defect pre-
diction. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM / IEEE In-
ternational Symposium on Empirical Software Engi-
neering and Measurement, pages 159 – 170, Helsinki
Finland.
N. A. (2022). International Standard—Software and Sys-
tems Engineering Software Testing–Part 1: General
Concepts.
Paiva, T., Oliveira, T., Pillat, R., and Alencar, P. (2023).
Supporting the automated generation of acceptance
tests of process-aware information systems. In Pro-
ceedings of the 19th International Conference on Web
Information Systems and Technologies - WEBIST,
pages 128 – 139.
Pudlitz, F., Brokhausen, F., and Vogelsang, A. (2020). What
am i testing and where? comparing testing procedures
based on lightweight requirements annotations. Em-
pirical Software Engineering, 24(4):2809–2843.
Raulamo-Jurvanen, P., M
¨
antyl
¨
a, M., and Garousi, V. (2017).
Choosing the right test automation tool: a grey litera-
ture review of practitioner sources. In Proceedings of
the 21st International Conference on Evaluation and
Assessment in Software Engineering, EASE ’17, page
21–30, New York, NY, USA. Association for Comput-
ing Machinery.
Santos, I., M. Melo, S., S. L. Souza, P., and R. S. Souza, S.
(2022). A survey on the practices of software testing:
a look into brazilian companies. Journal of Software
Engineering Research and Development, 10:11:1 –
11:15.
SCIMAGO (2024). Scimago journal & country rank. Aces-
sado em: 16 novembro 2024.
Swillus, M. and Zaidman, A. (2023). Sentiment overflow
in the testing stack: Analyzing software testing posts
on stack overflow. Journal of Systems and Software,
205:111804.
Software Testing Evidence: Results from a Systematic Mapping
393
