
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines
Otmane Azeroual
1,2 a
1
German Centre for Higher Education Research and Science Studies (DZHW), 10117 Berlin, Germany
2
University of Hagen, 58097 Hagen, Germany
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Explainable AI (XAI), Self-Adaptive Data Pipelines, Real-Time Streaming,
Concept Drift, Trustworthy AI.
Abstract: The increasing use of real-time data streams in application areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), financial
analytics, and social media demands highly flexible and self-adaptive data pipelines. Modern AI techniques
enable the automatic adjustment of these pipelines to dynamically changing data landscapes; however, their
decision-making processes often remain opaque and difficult to interpret. This paper presents and evaluates
novel approaches for integrating Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) into self-adaptive real-time data
pipelines. The goal is to ensure transparent and interpretable data processing while meeting the requirements
of real-time capability and scalability. The proposed methods aim to strengthen trust in automated systems
and simultaneously address regulatory demands. Initial experimental results demonstrate promising
improvements in both explainability and adaptivity without significant performance degradation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid increase in data—especially in the form of
real-time data streams—is increasingly shaping a
wide range of industries and applications. With the
emergence of technologies such as the Internet of
Things (IoT), social media platforms, and high-
frequency financial trading, vast volumes of data are
being continuously and rapidly generated (Cacciarelli
& Kulahci, 2024). The analysis and processing of this
data in real time is essential for enabling swift
decision-making and automation across various
domains, from industrial manufacturing to
cybersecurity (Zaharia et al., 2016). In this context,
self-adaptive data pipelines are gaining growing
importance, as they are capable of dynamically
responding to changing conditions and adjusting the
data flow accordingly (Sresth et al., 2023).
However, while many systems are able to
autonomously adapt to changing data streams, they
often lack the ability to make these adaptations
transparent and understandable. This raises the
central research question of this work: How can
explainability be integrated into self-adaptive data
pipelines without compromising real-time
capabilities?
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5225-389X
Self-adaptive data pipelines are systems that not
only continuously ingest and process data but also
autonomously adjust their internal structure,
parameters, and algorithms in response to changing
data conditions or environmental factors (Zaharia et
al., 2016). This is particularly relevant when dealing
with so-called concept drift effects, where the
underlying data distribution changes over time (Gama
et al., 2014). Such changes can significantly impair
model performance if not detected and addressed
promptly. Traditional, static pipelines that operate
without adaptive mechanisms are at a disadvantage in
such scenarios and may quickly produce outdated or
incorrect results (Krawczyk, 2016).
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI)—
and especially machine learning methods—into these
adaptive systems makes it possible to manage the
complexity and dynamics of streaming data. AI
models can detect patterns, make predictions, and
automatically implement adjustments to optimize
data processing (Gomes et al., 2023). This automation
enhances not only the efficiency and accuracy but
also the scalability of data pipelines in real-time
environments. In addition, self-learning algorithms
allow systems to proactively respond to new data
428
Azeroual, O.
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines.
DOI: 10.5220/0013736100004000
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2025) - Volume 2: KEOD and KMIS, pages
428-437
ISBN: 978-989-758-769-6; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

characteristics without requiring human intervention
(Gama et al., 2014).
Despite the obvious advantages of AI-powered
adaptive pipelines, significant challenges remain—
particularly regarding the transparency and
interpretability of their automatic adjustments
(Azeroual, 2024). Modern AI models are often
perceived as black-box systems, with internal
decision-making processes that are difficult to
understand and explain (Adadi & Berrada, 2018).
This lack of transparency hampers error diagnosis,
debugging, and user acceptance by both end-users
and decision-makers (Doshi-Velez & Kim, 2017).
Moreover, regulatory requirements—such as those
mandated by the General Data Protection Regulation
(GDPR)—are becoming increasingly stringent,
making explainable and traceable data processing
essential (Rudin, 2019).
Against this backdrop, the research field of
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has
emerged, aiming to design models whose decisions
and adjustments are understandable and interpretable
by humans (Arrieta et al., 2020). However, many
existing XAI methods focus on static, batch-based
models and fail to consider the specific requirements
of real-time streaming and adaptive systems (Guidotti
et al., 2018). In real-time environments, explanations
must be delivered quickly, dynamically, and
contextually, supporting users in interpreting model
behavior without compromising system latency or
efficiency (Abbas & Eldred, 2025).
The integration of XAI into self-adaptive real-
time data pipelines thus represents a timely and
critical research challenge. The objective is to
develop approaches that not only maintain the
adaptability of pipelines but also provide transparent
and comprehensible explanations for their dynamic
adjustments. Key challenges include minimizing
latency, ensuring scalability, and handling
continuously changing data contexts (Ribeiro et al.,
2016). Addressing these aspects is crucial for
building user trust and enabling the deployment of
AI-based systems in safety-critical and regulated
application domains.
This paper presents a novel system architecture
that integrates XAI into self-adaptive real-time data
pipelines. The goal is to combine adaptivity and
explainability to enable transparent, interpretable,
and high-performing data processing. The modular
pipeline handles concept drift and is evaluated
through empirical experiments and user feedback,
aiming to strengthen trust in AI while meeting
practical and regulatory requirements.
2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND/
FOUNDATIONS
2.1 Data Pipelines: Structure, Function,
and Challenges in Real-Time
Streaming
Data pipelines are structured sequences of processing
steps that guide data from acquisition through
transformation to analysis (Hashem et al., 2015). In
modern applications, these pipelines often need to
handle large volumes of data streams in real time,
which imposes specific requirements on latency,
scalability, and fault tolerance (Zaharia et al., 2016).
Real-time streaming pipelines enable the continuous
processing of data in motion, for example through
frameworks such as Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, or
Apache Spark Streaming (Kreps et al., 2011; Carbone
et al., 2015). A central challenge lies in ensuring data
consistency and quality despite high data rates and
potential failures (Liu et al., 2021).
2.2 Self-Adaptivity: Concepts and
Mechanisms
Self-adaptivity refers to a system's ability to
autonomously adjust its behavior to changing
environmental conditions without human
intervention (Salehie & Tahvildari, 2009). In data-
driven pipelines, this is especially relevant when data
distributions change—a phenomenon known as
concept drift (Gama et al., 2014). Concept drift
describes the temporal shift in the underlying data
distribution, which can lead to performance
degradation of static models (Widmer & Kubat,
1996). Adaptive mechanisms such as online learning
or model retraining are used to detect and compensate
for such changes (Krawczyk, 2016). Automated
machine learning (AutoML) supports these processes
by autonomously optimizing model parameters and
generating new models (He et al., 2021).
2.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
Machine Learning (ML) in Adaptive
Systems
AI, particularly ML, enables adaptive systems to
learn from data and dynamically improve decision-
making (Russell & Norvig, 2016). In real-time
streaming scenarios, online learning methods are
frequently applied to incrementally update models
and reflect current data (Bifet et al., 2018). Concept
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines
429

drift detection techniques are essential to maintain
model accuracy over time (Lu et al., 2018).
Combinations of supervised, unsupervised, and
reinforcement learning methods are employed to
address various challenges in self-adaptive systems
(Mohammadi et al., 2018).
However, the integration of ML into adaptive
systems also increases complexity, making it harder
for users to understand why specific adaptations
occur—especially in real-time environments. This
highlights the need for mechanisms that make such
dynamic decisions transparent, which is where XAI
becomes crucial.
2.4 Explainable AI (XAI): Definitions,
Methods, Limitations
XAI refers to methods and techniques that make the
decisions of AI systems understandable and
transparent to humans (Doshi-Velez & Kim, 2017).
The goal is to enhance trust in AI, especially in safety-
critical applications (Arrieta et al., 2020). XAI
methods can be categorized into intrinsic models
(e.g., decision trees) and post-hoc explanations (e.g.,
LIME, SHAP) (Ribeiro et al., 2016; Lundberg & Lee,
2017). Despite recent advances, limitations remain
regarding scalability, interpretability, and
applicability to complex, dynamic systems (Adadi &
Berrada, 2018). Furthermore, ensuring explanation
stability over time and mitigating the risk of
misleading or inconsistent explanations in self-
adaptive models remain open research questions.
2.5 Specific Challenges of XAI in
Real-Time and Streaming Contexts
The application of XAI in real-time streaming and
self-adaptive systems imposes additional
requirements: explanations must be provided with
low latency, continuously updated, and adapted to
changing data contexts (Abbas & Eldred, 2025). This
places high demands on the efficiency of explanation
methods and their ability to interpret dynamic models
(Guidotti et al., 2018). Research shows that many
established XAI techniques cannot be directly applied
to real-time data streams, as they are often batch-
oriented and computationally intensive (Molnar,
2020). New approaches aim to develop adaptive,
lightweight, and context-sensitive explanations for
streaming data (Lundberg et al., 2020).
The need for lightweight, adaptive explanation
mechanisms in streaming contexts underscores the
research gap this work aims to address—namely, the
lack of integrated solutions that combine real-time
adaptivity with explainability in a coherent, scalable
system.
3 STATE OF RESEARCH
The rapid development of data-driven systems and
the increasing importance of real-time streaming data
have led to intensified research on adaptive data
pipelines in recent years. These pipelines are
designed to autonomously adjust to changing data
environments in order to continuously deliver
accurate and reliable results (Gama et al., 2014; Kiran
et al., 2021). In particular, the challenge of concept
drift—i.e., the temporal change in the underlying data
distribution—requires flexible and adaptive
approaches capable of continuously updating models
and responding to new conditions (Widmer & Kubat,
1996; Krawczyk, 2017). The integration of AI and
ML plays a central role in enabling automated
decision-making within the pipeline and ensuring
autonomous adaptation to shifting data streams (He et
al., 2021; Bifet et al., 2018).
Many existing adaptive systems rely on online
learning techniques, which allow models to be
incrementally trained with new data, thereby
maintaining model performance during live operation
(Lu et al., 2018). Additionally, AutoML techniques
are integrated to automate the processes of model
selection and optimization, reducing the need for
human intervention (He et al., 2021). Despite these
advances, most studies focus on individual aspects of
the pipeline—such as model updating or data
preprocessing—and tend to neglect a holistic
perspective that includes the explainability and
transparency of automatic decisions (Kiran et al.,
2021).
XAI is a growing research field aimed at
increasing trust in AI systems, particularly in safety-
critical and regulated application areas (Doshi-Velez
& Kim, 2017; Arrieta et al., 2020). XAI encompasses
methods that make the internal decision processes of
often complex black-box models comprehensible
(Molnar, 2020). Broadly speaking, XAI methods can
be divided into intrinsically interpretable models and
post-hoc explanation techniques (Ribeiro et al., 2016;
Lundberg & Lee, 2017). While intrinsic models such
as decision trees or linear regression are transparent
by design, post-hoc approaches like LIME or SHAP
provide explanations for arbitrary models without
modifying the underlying architecture (Ribeiro et al.,
2016; Lundberg & Lee, 2017).
However, most established XAI methods have
been developed for static, batch-oriented data
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
430
environments. Real-time streaming contexts pose
new challenges: data distributions may change
dynamically, models need to be continuously
adapted, and explanations must also be delivered
rapidly and adaptively to ensure transparency in
decision-making at all times. Providing explanations
in real time further requires resource-efficient
algorithms that are compatible with high data
throughput and low-latency requirements (Guidotti et
al., 2018). Current research efforts therefore focus on
developing incremental and lightweight XAI
methods specifically tailored for streaming data
(Lundberg & Lee, 2017). However, these approaches
are still in an early stage and often address only partial
aspects—such as the explanation of individual
predictions—without fully covering the complex
adaptation mechanisms of entire pipelines.
An analysis of current research clearly reveals a
significant gap: there are very few integrated
approaches that combine self-adaptive data pipelines
with XAI methods to ensure continuous transparency
and traceability in real-time streaming environments
(Arrieta et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2022). Most studies
focus either on the adaptivity of the pipeline or the
explainability of individual models, but not on the
combination of both aspects in a dynamic, stream-
based context. What is missing is an end-to-end
approach that simultaneously ensures (1) continuous
model adaptation, (2) timely and relevant
explanations, and (3) seamless integration into real-
time data pipelines.
Table 1: Classification of Existing Approach.
Table 1 provides an overview of selected relevant
research works, classifying them according to their
approaches to adaptive pipelines, AI integration,
application of XAI methods, and real-time
capabilities.
This overview illustrates that while substantial
work exists on adaptive pipelines and XAI models
individually, the fusion of both domains in real-time
environments remains largely unexplored. This
research gap represents a critical barrier to the
acceptance and broader deployment of automated,
self-adaptive systems, as transparency and
traceability are essential prerequisites for trust and
compliance (Arrieta et al., 2020).
The present paper addresses this intersection and
aims to develop novel approaches that seamlessly
integrate XAI methods into adaptive real-time data
pipelines to ensure both high performance and
transparency.
4 METHODOLOGY / CONCEPT
DEVELOPMENT
This paper focuses on the development of an
innovative approach for implementing explainable,
self-adaptive real-time data pipelines, aiming to close
existing research gaps at the intersection of adaptivity
and explainability. The methodology is based on the
design and implementation of a modular,
dynamically adjustable system capable of
continuously and autonomously responding to
changes in incoming data streams, while
simultaneously providing understandable
explanations for its decisions and adaptations at any
time. The concept is designed to enhance
transparency and traceability of self-adaptive
processes without compromising key real-time
requirements such as latency and performance.
The proposed approach relies on a tightly
integrated combination of advanced ML techniques
and explainable AI (XAI) technologies. At its core,
the system uses online learning algorithms that
continuously update model parameters based on new
incoming data, maintaining model accuracy even as
data distributions shift. These methods are
particularly well-suited for reacting to concept drift—
i.e., changes in the statistical structure of the data—
that would otherwise significantly degrade model
performance without automatic adaptation. In
addition, AutoML techniques are integrated to
automate the selection and optimization of model
hyperparameters, enabling the pipeline to operate
largely autonomously. This reduces the need for
human intervention and allows for flexible and
scalable model maintenance in productive real-time
environments.
LIME and SHAP were selected due to their wide
acceptance, ability to generate local feature
attributions, and extensibility. Despite their original
design for batch scenarios, we extend them to operate
in a streaming context by implementing window-
based updates and approximation strategies.
Parallel to adaptive modeling, the integration of
XAI methods is a central element of the design.
Resource-efficient, incremental explanation
approaches are developed, tailored to continuous data
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines
431
streams, enabling timely generation of explanations.
In contrast to traditional post-hoc explanation
methods, which are often computationally intensive
and designed for static datasets, this methodology
supports ongoing explanation generation that reflects
the dynamics of the data stream and transparently
illustrates changes in decision-making logic. For
instance, feature importance scores and local
surrogate models are incrementally updated to
provide fast yet precise and context-sensitive insights
into the behavior of adaptive models. Explanations
are hierarchically structured to offer different levels
of detail suited to various stakeholders—from
technical experts to domain users—thereby
enhancing both comprehensibility and relevance.
The technical realization of the approach is based
on a modular system architecture that integrates
components for data ingestion, preprocessing, model
training and updating, explanation generation, and
monitoring/control. For data ingestion and
processing, established streaming frameworks such
as Apache Kafka or Apache Flink are employed,
ensuring high throughput and low latency as a robust
foundation for real-time operations. The adaptive
modeling module implements both online learning
algorithms and AutoML components, which
automatically determine suitable model
configurations and seamlessly integrate them into
operation. In parallel, a dedicated explanation module
operates as a lightweight microservice, tightly
coupled with the adaptive models to access relevant
contextual information required for explanation
generation. The monitoring component continuously
evaluates data distribution, model quality, and
explanation performance, controlling the adaptive
pipeline by triggering model updates or issuing alerts
in case of potential misadaptations. This establishes a
closed feedback loop that ensures both the automation
and transparency of data processing.
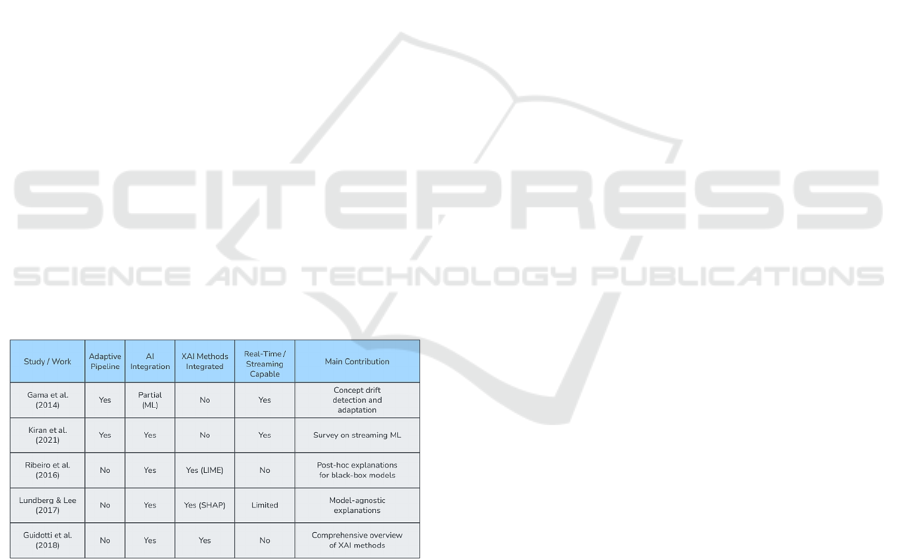
The modular architecture of this system is
illustrated in Figure 1. It highlights the close
integration of individual components—from data
ingestion and adaptive modeling to explanation
generation and pipeline monitoring/control. The
diagram particularly emphasizes the closed control
loop that enables continuous self-adjustment of the
models and the ongoing generation and provision of
explanations in real time. This forms a critical
foundation for ensuring high adaptability and
comprehensive transparency in dynamic, data-
intensive environments, while also facilitating
scalability, fault tolerance, and ease of
maintenance—key requirements for deploying
robust, trustworthy AI solutions in real-world
streaming applications.
Figure 1: Modular architecture of the proposed explainable,
self-adaptive real-time data pipeline.
As part of the development, specific criteria for
explainability and real-time capability are also
defined and systematically evaluated. The generated
explanations must be comprehensible and traceable
for various user groups and provide both local and
global insights into model decisions and adaptations.
At the same time, the pipeline must not delay data
stream processing, requiring all components to be
optimized for efficiency and resource usage. Through
this integrative and iterative approach, a robust,
scalable, and trustworthy real-time data processing
system is created that addresses the demands of
modern data-driven systems.
Success of the system is defined along three core
criteria: (1) accuracy and adaptability of the model
under concept drift, (2) latency of both predictions
and explanations, and (3) user-perceived clarity and
usefulness of the explanations across different
stakeholder groups.
5 IMPLEMENTATION AND
EXPERIMENTAL
EVALUATION
To validate the proposed concept of an explainable,
self-adaptive real-time data pipeline, a prototype
system was designed, implemented, and rigorously
evaluated using realistic application scenarios that
reflect practical challenges in dynamic environments.
The implementation emphasized a modular and
extensible architecture that incorporates dedicated
components for data ingestion, real-time processing,
adaptive modeling, explainability, as well as
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
432
continuous monitoring and control. This modular
design allows for flexible integration and dynamic
combination of various state-of-the-art AI and XAI
methods, enabling comprehensive testing and
optimization under stringent real-time conditions.
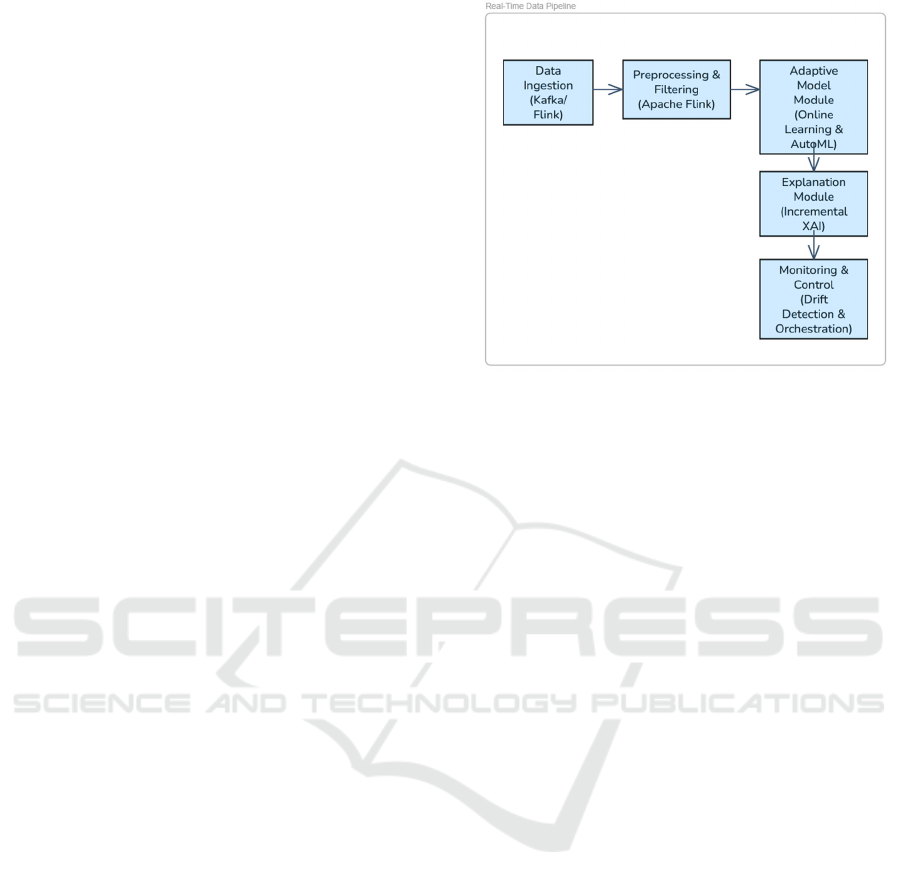
The overall system architecture is depicted in
Figure 2. Data ingestion is managed through an
Apache Kafka cluster, which ensures reliable,
scalable, and fault-tolerant distribution of incoming
high-velocity data streams. For preprocessing,
Apache Flink is employed to perform essential real-
time operations such as data cleansing, feature
extraction, and feature scaling, thereby preparing the
raw data for downstream modeling tasks without
introducing significant latency. The adaptive
modeling module incorporates incrementally learning
algorithms—primarily Online Random Forests and
Hoeffding Trees—combined with a lightweight
AutoML mechanism that continuously optimizes
hyperparameters to maintain model performance.
This setup enables the system to dynamically adapt to
evolving data distributions, with a particular focus on
effectively detecting and reacting to concept drift.
To address the critical aspect of explainability, a
dedicated module was integrated that leverages
streaming-capable variants of popular explanation
methods like SHAP and LIME. Explanations are
generated for every individual prediction in real-time
and presented through an interactive web interface,
offering users transparent insights into the model’s
decision-making process. Complementing these
components, the "Monitoring & Control" subsystem,
built on Prometheus and a rule-based engine,
continuously supervises system health, evaluates
model quality, and triggers adaptive adjustments to
modeling parameters as necessary to maintain
optimal performance.
Figure 2: System Overview with Data Flow.
Figure 2 illustrates the data and control flow between
system components: solid lines represent the
continuous data flow (e.g., from Kafka → Flink →
Modeling → Explanation), while dashed arrows
depict feedback and control relationships—especially
from the monitoring unit back to the modeling and
explanation modules. This feedback enables demand-
driven adjustments without restarting the system,
which is crucial for meeting real-time requirements.
Two application scenarios were chosen for
evaluation: an industrial IoT scenario with simulated
machine data, and a financial scenario using modified
real-time credit card transaction data. The industrial
IoT case simulates predictive maintenance on
streaming sensor data from manufacturing machines.
This scenario reflects a typical real-time environment
where early detection of equipment faults can prevent
costly downtimes. The financial scenario uses
anonymized credit card transaction streams to detect
anomalies indicative of fraudulent activities. Both
scenarios are characterized by stringent latency
requirements and dynamic data distributions, making
them ideal testbeds for evaluating adaptive modeling
and explainability under realistic operational
conditions.
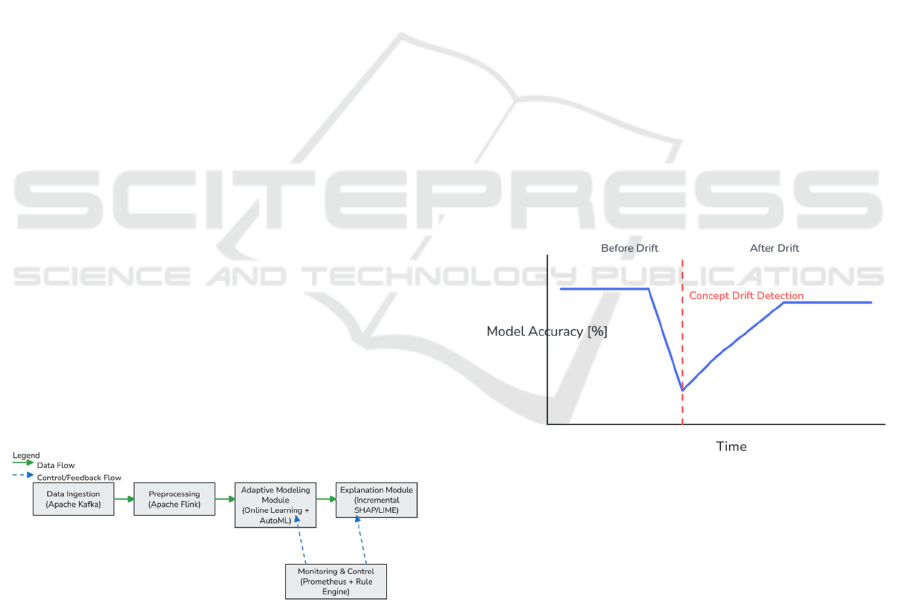
The impact of concept drift on model
performance is illustrated in Figure 3. The figure
shows the model’s accuracy over time. A significant
drop in performance is observed immediately after
the simulated drift point (marked by a red vertical
line). However, due to the system’s automatic
adaptability, accuracy quickly recovers. This pattern
demonstrates that the system not only responds to
drift events but is also capable of restoring model
quality within short timeframes.
Figure 3: Model Performance Before and After Concept
Drift.
Another focus was the evaluation of the model
decision explainability. To this end, a real-time
dashboard was developed that displays the top
contributing features for each prediction as well as a
locally approximated decision structure. Figure 4
illustrates a typical output from this dashboard: on the
left, feature importances are shown in a bar chart; on
the right, a simple decision logic is visualized using a
surrogate model to explain the specific model
decision. These explanations were continuously
generated and updated for each data point.
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines
433

Figure 4: Example Real-Time Explanation Output.
To qualitatively assess the explanations, a user study
was conducted with twelve participants from data
science and domain expert backgrounds. Participants
rated the explanations on a five-point Likert scale in
terms of clarity, usefulness, and trust.
On average, the explanations were perceived as
helpful (M = 4.3) and understandable (M = 4.5).
Participants particularly appreciated the visual
representation of feature importances and the ability
to trace model behavior changes caused by concept
drift.
Overall, the study suggests that even lightweight,
incremental explanation mechanisms can
meaningfully support user understanding and trust in
adaptive AI systems. Several participants expressed
interest in being able to adjust the depth and detail of
explanations to match their level of expertise. This
indicates that configurable explanation interfaces
could improve usability and acceptance across
diverse user groups.
In summary, the developed system is capable of
adaptively responding to data changes while
providing explainable decisions—without significant
performance losses in terms of response time or
model quality. Thus, the proposed pipeline
contributes to trustworthy AI in the context of
dynamic, high-frequency data streams.
6 DISCUSSION
The results presented in the previous section (Section
5) offer well-founded insights into the behavior of
explainable, self-adaptive real-time data pipelines
under realistic conditions. The core objective of the
evaluation was to assess the extent to which XAI
methods can be meaningfully integrated into adaptive
streaming systems without significantly
compromising real-time capability or model
performance. The findings suggest that such
integration is not only technically feasible but also
functionally beneficial. Notably, combining adaptive
learning with dynamic explainability yields
substantial improvements in trust, transparency, and
system control.
Performance analysis (cf. Figure 3) shows that
the system was able to quickly stabilize its predictive
performance following a detected concept drift. On
average, the model regained acceptable accuracy
within fewer than ten data windows—an efficiency
considered suitable for real-time systems. These
results support the assumption that AutoML-
supported online models are a powerful foundation
for self-adaptive architectures in streaming
environments. Moreover, the concurrent integration
of explainability modules did not lead to a significant
increase in inference latency (≤ 60 ms),
demonstrating that real-time capability can be
preserved despite the added interpretability.
A particularly noteworthy aspect is the system’s
ability to adapt not only its models but also the
associated explanations continuously in response to
changing data distributions. This capability
represents a clear advantage over traditional XAI
approaches, which are typically designed for static or
batch-oriented settings. The user study confirmed that
the real-time visualization of feature importances and
local decision structures (cf. Figure 4) significantly
enhanced model interpretability—for both technical
and non-technical users.
Despite these positive outcomes, the proposed
approach also presents certain limitations. A key
challenge lies in the temporal stability of
explanations: since the models are constantly
updated, the generated explanations may vary even
for similar input data. This temporal inconsistency
can lead to user uncertainty and highlights the need
for further research in explanation-stable model
adaptation. Another concern is the scalability of
explainability in ultra-high-frequency data streams: at
inference rates exceeding 10,000 events per second,
even incremental XAI methods require substantial
computational resources. Innovative strategies are
needed here—such as selective or approximate
explanation techniques that maintain interpretability
without overwhelming system performance.
In addition, the current evaluation does not yet
cover all relevant dimensions of system robustness
and generalizability. Specifically, the adversarial
sensitivity of on-the-fly explanations remains
unexplored: since local explanation methods like
SHAP and LIME are known to be vulnerable to input
perturbations, their reliability under adversarial
conditions should be further investigated. Moreover,
the impact of high-dimensional input data and
complex model architectures on the fidelity and
stability of explanations was not explicitly
benchmarked. Addressing these open issues requires
more comprehensive evaluations using standardized
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
434

datasets, adversarial scenarios, and controlled
variation of model and data complexity.
Furthermore, the absence of standardized
evaluation metrics and publicly available benchmarks
for explainability in streaming settings presents a
methodological gap. Community-driven efforts
toward shared testbeds and multidimensional
performance indicators—including latency, stability,
interpretability, and adversarial robustness—would
significantly enhance comparability and
reproducibility in this emerging field.
In practical applications, the proposed approach
opens up a range of possibilities, particularly in
mission-critical domains such as predictive
maintenance, real-time financial analytics, or medical
telemetry. The ability to make adaptive decisions
transparent not only supports regulatory compliance
(e.g., in line with the EU AI Act) but also strengthens
end-user trust in AI-driven systems. At the same time,
the modular architecture allows for flexible
adaptation to various data sources, model types, and
deployment environments.
This work also raises several important questions
for future research. First, there is the question of how
generalizable the approach is to more complex model
architectures, such as deep learning in streaming
contexts. Furthermore, combining the system with
reinforcement learning strategies for policy
adaptation presents a promising extension. Lastly,
there is a clear need for standardized metrics to
evaluate explainability in dynamic, non-deterministic
settings—an open challenge that has yet to be fully
addressed by either the XAI or the stream processing
research communities.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that
combining self-adaptivity with explainability in
streaming environments is far more than a technical
exercise. It represents a strategically significant step
toward responsible, trustworthy AI systems for real-
time applications.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper addresses the design, implementation, and
evaluation of an explainable, self-adaptive real-time
data pipeline based on modern AI and XAI methods.
The starting point was the observation that existing
data processing systems in streaming contexts
increasingly rely on ML for autonomous model
adaptation, but often without adequate consideration
of explainability and transparency of the decisions
made. This represents a significant limitation,
especially in sensitive application domains where
both regulatory requirements and end-user trust play
a central role.
By integrating incrementally learning models
with automated model selection (AutoML) and
dynamically adaptable XAI techniques, an
architectural approach was developed that operates
both adaptively and interpretable—while
simultaneously meeting real-time requirements.
Experimental evaluation using realistic scenarios
(IoT and financial data) demonstrated that the
proposed pipeline can efficiently detect concept drift
and adapt accordingly. At the same time, the system
provided understandable and visually prepared
explanations of model decisions without significantly
impacting system latency or predictive quality.
The contribution of this paper lies both
conceptually and methodologically. On the one hand,
an architectural framework was created that explicitly
enables the coupling of self-adaptivity and
explainability in streaming contexts. On the other
hand, existing XAI methods were examined and
adapted for their suitability in streaming
environments. Moreover, the developed system
offers a practical reference implementation realized
with common open-source technologies such as
Apache Kafka, Flink, Prometheus, and SHAP/LIME,
making it applicable for industrial use as well.
Nonetheless, essential challenges remain that
should be addressed in future research. In particular,
stable interpretability over time—i.e., consistency of
explanations amid evolving models—remains an
unresolved issue. There is also a need for
standardizing metrics to systematically evaluate
explainability in dynamic contexts. The use of deeper
neural networks combined with XAI for real-time
systems—for example, via distilled surrogate
models—represents another promising direction for
further investigation.
To build on these findings, future research must
also include comprehensive, multi-dimensional
evaluations—covering adversarial robustness,
explanation consistency, and scalability across
different data rates and dimensionalities.
Comparative studies with related architectural
approaches are necessary to further validate
effectiveness and identify best practices.
Furthermore, future work could extend the system
architecture with active learning mechanisms, self-
explaining user interfaces, or semantically grounded
model feedback systems to enable even closer
integration between users, the system, and
explanations. Finally, a long-term user acceptance
study under real-world conditions (e.g., in Industry
4.0 environments) would be highly valuable to
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines
435

capture the actual impact of dynamic explainability
on trust and system control.
The results presented here illustrate that
explainable, self-adaptive AI systems in real-time
data contexts are not just a theoretical vision but a
practically implementable reality—provided that
methodological robustness, system scalability, and
human-centered perspectives are given equal
consideration.
REFERENCES
Abbas, T., & Eldred, A. (2025). AI-Powered Stream
Processing: Bridging Real-Time Data Pipelines with
Advanced Machine Learning Techniques.
ResearchGate Journal of AI & Cloud Analytics.
https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26674.52167
Adadi, A., & Berrada, M. (2018). Peeking inside the black-
box: a survey on explainable artificial intelligence
(XAI). IEEE access, 6, 52138-52160. https://doi.org/
10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870052
Arrieta, A. B., Díaz-Rodríguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot,
A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., ... & Herrera, F. (2020).
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts,
taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward
responsible AI. Information fusion, 58, 82-115.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.012
Azeroual, O. (2024). Can generative AI transform data
quality? a critical discussion of ChatGPT’s capabilities.
Academia Engineering, 1(4). https://doi.org/10.20
935/AcadEng7407
Bifet, A., Gavalda, R., Holmes, G., & Pfahringer, B. (2023).
Machine learning for data streams: with practical
examples in MOA. MIT press. https://doi.org/10.75
51/mitpress/10654.001.0001
Cacciarelli, D., & Kulahci, M. (2024). Active learning for
data streams: a survey. Machine Learning, 113(1), 185-
239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-023-06454-2
Carbone, P., Katsifodimos, A., Ewen, S., Markl, V., Haridi,
S., & Tzoumas, K. (2015). Apache flink: Stream and
batch Processing in a single engine. The Bulletin of the
Technical Committee on Data Engineering, 38(4).
http://sites. computer.org/debull/A15dec/p28.pdf
Doshi-Velez, F., & Kim, B. (2017). Towards a rigorous
science of interpretable machine learning. arXiv
preprint. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1702.08608
Gama, J., Žliobaitė, I., Bifet, A., Pechenizkiy, M., &
Bouchachia, A. (2014). A survey on concept drift
adaptation. ACM computing surveys (CSUR), 46(4), 1-
37. https://doi.org/10.1145/2523813
Gomes, H. M., Read, J., Bifet, A., Barddal, J. P., & Gama,
J. (2019). Machine learning for streaming data: state of
the art, challenges, and opportunities. ACM SIGKDD
Explorations Newsletter, 21(2), 6-22. https://doi.org/1
0.1145/3373464.3373470
Guidotti, R., Monreale, A., Ruggieri, S., Turini, F.,
Giannotti, F., & Pedreschi, D. (2018). A survey of
methods for explaining black box models. ACM
computing surveys (CSUR), 51(5), 1-42. https://doi.
org/10.1145/3236009
Hashem, I. A. T., Yaqoob, I., Anuar, N. B., Mokhtar, S.,
Gani, A., & Khan, S. U. (2015). The rise of “big data”
on cloud computing: Review and open research issues.
Information systems, 47, 98-115. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.is.2014.07.006
He, X., Zhao, K., & Chu, X. (2021). AutoML: A survey of
the state-of-the-art. Knowledge-based systems, 212,
106622. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.00709
Kiran, B. R., Sobh, I., Talpaert, V., Mannion, P., Al Sallab,
A. A., Yogamani, S., & Pérez, P. (2021). Deep
reinforcement learning for autonomous driving: A
survey. IEEE Transactions on intelligent
transportation systems, 23(6), 4909-4926. https://doi.
org/10.1109/TI TS.2021.3054625
Krawczyk, B. (2016). Learning from imbalanced data: open
challenges and future directions. Progress in artificial
intelligence, 5(4), 221-232. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s13748-016-0094-0
Kreps, J., Narkhede, N., & Rao, J. (2011). Kafka: A
distributed messaging system for log processing. In
Proceedings of the NetDB (Vol. 11, No. 2011, pp. 1-7).
https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:18534081
Liu, C., Peng, G., Kong, Y., Li, S., & Chen, S. (2021). Data
quality affecting Big Data analytics in smart factories:
research themes, issues and methods. Symmetry, 13(8),
1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13081440
Lu, J., Liu, A., Dong, F., Gu, F., Gama, J., & Zhang, G.
(2018). Learning under concept drift: A review. IEEE
transactions on knowledge and data engineering,
31(12), 2346-2363. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.
2004.05785
Lundberg, S. M., & Lee, S. I. (2017). A unified approach to
interpreting model predictions. Advances in neural
information processing systems, 30. https://doi.org/
10.48550/arXiv.1705.07874
Mohammadi, M., Al-Fuqaha, A., Sorour, S., & Guizani, M.
(2018). Deep learning for IoT big data and streaming
analytics: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys &
Tutorials, 20(4), 2923-2960. https://doi.org/10.1109/
COMST.2018.2844341
Molnar, C. (2020). Interpretable machine learning. Lulu.
com. https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016). " Why
should i trust you?" Explaining the predictions of any
classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD
International Conf. on Knowledge Discovery and data
Mining (pp. 1135-1144). https://doi.org/10.1145/
2939672.293977
Rudin, C. (2019). Stop explaining black box machine
learning models for high stakes decisions and use
interpretable models instead. Nature machine
intelligence, 1(5), 206-215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s4
2256-019-0048-x
Russell, S. J., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial intelligence: a
modern approach. pearson. https://elibrary.pearson.de/
book/99.150005/9781292401171
KMIS 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
436

Salehie, M., & Tahvildari, L. (2009). Self-adaptive
software: Landscape and research challenges. ACM
transactions on autonomous and adaptive systems
(TAAS), 4(2), 1-42. https://doi.org/10.1145/
1516533.1516538
Sresth, V., Nagavalli, S. P., & Tiwari, S. (2023).
Optimizing Data Pipelines in Advanced Cloud
Computing: Innovative Approaches to Large-Scale
Data Processing, Analytics, and Real-Time
Optimization. International Journal of Research and
Analytical Reviews, 10, 478-496. https://doi.org/10.
54660/.IJMRGE.2022.3.1.112-120
Widmer, G., & Kubat, M. (1996). Learning in the presence
of concept drift and hidden contexts. Machine learning,
23, 69-101. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116900
Zaharia, M., Xin, R. S., Wendell, P., Das, T., Armbrust, M.,
Dave, A., ... & Stoica, I. (2016). Apache spark: a unified
engine for big data processing. Communications of the
ACM, 59(11), 56-65. https://doi.org/10.1145/2934664
Beyond Black Boxes: Adaptive XAI for Dynamic Data Pipelines
437
