
Optimization Method for Inverse Kinematics of Quadruped Robot
Based on Improved Longicorn Whisker Algorithm
Qi
Tang, Shaohui Liu, Zhuojun Wu, Hao Liu and Peidong Jiang
Foshan Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Power Grid Co., Ltd, Foshan, 528000, Guangdong, China
Keyword: Quadruped Robot; Longhorn Whisker Algorithm; Kinematics; Inverse Solution Optimization
Abstract: With the deepening of the enabling development role of robotics related industries, new types of robots have
gradually been integrated into many fields of production and life. Due to the advantages of quadruped robots
such as strong stability during movement, fast movement speed, high controllability, and strong adaptability
to the ground, it has become a research focus in the field of intelligent manufacturing related to robots and
humans. The inverse kinematics optimization method for quadruped robots based on the improved Longicorn
whisker algorithm is a major breakthrough in the field of robotics. This method utilizes an improved
Longicorn beard algorithm to solve complex inverse kinematics problems for quadruped robots. The
Longicorn beard algorithm is inspired by the sensory system of insects, which uses their antennae to detect
and respond to changes in the environment. An improved version of the algorithm combines a more accurate
and effective method to solve inverse kinematics problems. The inverse kinematics optimization method for
quadruped robots based on the improved Longicorn whisker algorithm has many advantages over traditional
methods. It can quickly and accurately solve complex problems, and is very suitable for use in real-time
applications. In addition, this method has strong adaptability and can be used for different types of robots.
Overall, the inverse kinematics optimization method for quadruped robots based on the improved Longicorn
beard algorithm represents a significant advance in robotics technology. Its potential applications range from
industrial automation to medical robotics.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, with the rapid development of high-
tech industries such as artificial intelligence, and the
continuous exploration and deepening of the role of
robotics in the empowerment and development of
related industries, new types of robots have gradually
been integrated into many fields of national
production and life. Emerging disciplines such as
robotics have become the main driving force for
national development, and more and more countries
have started exploring and researching artificial
intelligence fields such as robotics, China has also
proposed the "Made in China 2025" intelligent
manufacturing development strategy, and the
transition from traditional technology industries to
advanced intelligent manufacturing has become a hot
spot and development trend in scientific and
technological research (Huang, Wu, et al. 2021).
In the process of research in the field of robotics,
the application of mobile robots to various fields of
national production and life, such as the service
industry and manufacturing industry, not only
liberates human resources and improves people's
quality of life, but also represents a revolution in
production technology. Therefore, research in the
field of mobile robots has always been in an important
position.
For unstructured terrain, quadruped robots have
stronger adaptability than traditional wheeled or
tracked vehicles. Therefore, quadruped robots have
become a research hotspot in the field of mobile
robots. Inverse kinematics solution (IK problem) is
one of the key research issues in the kinematics of 12
degree of freedom quadruped robots (Qin, Dong et al.
2021). It is of great significance for the research of
trajectory planning, dynamic characteristics analysis,
and motion control of mobile robots. Currently, there
are algebraic methods, numerical methods, and
intelligent optimization algorithms for solving IK
problems. Algebraic method has a fast solution speed,
but it has strict requirements for robot configuration
and is not universal. The numerical solution has
strong versatility, but the setting of initial values has
934
Tang, Q., Liu, S., Wu, Z., Liu, H. and Jiang, P.
Optimization Method for Inverse Kinematics of Quadruped Robot Based on Improved Longicorn Whisker Algorithm.
DOI: 10.5220/0013735200004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 3, pages 934-942
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

a significant impact on the convergence effect. In
intelligent optimization algorithms, the parallel
general network based on RBF neural network and
BP neural network solves IK problems faster than
algebraic methods, and has strong real-time
performance (Biswal, and Mohanty 2021). However,
when neural networks are applied to robots with
different configurations, it is necessary to retrain the
network, resulting in a weak generalization ability.
The hybrid genetic algorithm introduces the concepts
of exploration and development, using real-coded
HGA and binary competition selection operators to
evaluate multiple inverse kinematics solutions of
articulated and Puma manipulators (Schreiber, and
Gosselin 2022). However, genetic algorithms have a
complex structure and a large amount of computation,
which weakens the real-time performance of IK
problem solving. The hybrid algorithm of the multi-
directional exploration feedback strategy, Tianniuxu
and genetic algorithm, increases the search ability of
the algorithm, but also increases the computational
complexity of the algorithm when exploring different
directions. Artificial bee colony algorithm for solving
inverse kinematics problems of redundant robot arms
has the characteristics of good robustness and strong
global optimization ability (Zhou, Yu et al. 2021).
However, this method has a complex structure and
weak local optimization ability.
In fact, the Tianniu whisker algorithm (BAS) is an
intelligent optimization algorithm based on
individuals. Since there is only a single Tianniu
during the iteration, it is lower in time and space
complexity than the swarm intelligence algorithm,
and its efficiency is also higher.
However, traditional BAS has the characteristics
of low convergence speed and strong oscillation
during the convergence process, which reduces the
accuracy of the results and is difficult to meet the real-
time and accuracy requirements of the inverse
kinematics solution process for a 12 degree of
freedom quadruped robot (Zhang, Zhu, et al. 2021).
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Current Research Status of
Longicorn Whisker Search
Algorithm in China
Based on imitating the predatory behavior of
longicorn beetles in nature, Jiang Xiangyuan
proposed a bionic intelligent optimization algorithm
with meta heuristics, high randomness, and fast
convergence in 2017, called the Beetle Antennae
Search Algorithm (BAS). In nature, the predation of
longicorn beetles mainly relies on the antennae
distributed on both sides of the head. The odor
receptors in the antennae sense the concentration of
pheromones emitted by prey in the air (Chandan,
Shah, et al. 2021). When the odor receptors sense
both sides! When there is a difference in the
pheromone concentration of the antennae, the
longicorn beetle will move a certain distance towards
the side with the higher pheromone concentration,
thereby repeatedly approaching the target and finally
finding food.
Over time, many researchers have conducted in-
depth research on longicorn whisker search
algorithms and applied them to multiple research
fields such as parameter tuning, power scheduling,
neural network pre training, and path planning. In his
paper, Associate Professor Jiang Xiangyuan used the
proposed longicorn whisker search algorithm to
conduct simulation tests on the Michalewicz test
function and the Goldstein Price test function from
the perspective of convergence and local minimum
avoidance (Zohour, Belzile, et al. 2021). The test
results show that the longicorn whisker search
algorithm can complete accurate numerical
optimization after fewer search iterations.
Subsequently, Jiang Xiangyuan et al. proposed a
BAS-WPT (BAS-Without Parameter Tuning)
algorithm that does not require parameter adjustment
for the optimized object, and further expanded the
Tianniu whisker search algorithm to the field of
multi-objective optimization. BAS-WPT algorithm
uniformly maps the optimized parameters of different
orders of magnitude and different value ranges to the
same constraint range by normalizing the optimized
parameters, simplifying the time and computational
complexity of parameter tuning to a certain extent,
and using the penalty function to deal with inequality
constraint problems, also improving the optimization
ability of the Taurus whisker search algorithm in
multi-objective optimization problems (He, Shao, et
al. 2021). Dangke et al. 185 further improved the step
attenuation strategy in the original longicorn whisker
search algorithm and proposed a variable step
longicorn whisker search strategy, taking into account
the convergence speed and accuracy of the algorithm.
Since its introduction, the Tianniu whisker search
algorithm has attracted the attention of many
researchers. Due to its advantages such as small
computational complexity, strong randomness, rapid
convergence, and simple optimization strategies, the
Tianniu whisker search algorithm has been applied
and recognized in many aspects of the optimization
Optimization Method for Inverse Kinematics of Quadruped Robot Based on Improved Longicorn Whisker Algorithm
935
field. Currently, the application of the Tenebrio
Tenebrio search algorithm is mostly concentrated in
the combination with other algorithms, and few
studies have made further improvements on the
Tenebrio Tenebrio search algorithm (Ju, 2021. On the
basis of detailed and in-depth research, this paper
improves the search strategy of the longicorn's
whisker search algorithm, and applies it to the
obstacle avoidance path planning problem of
quadruped robots based on its fast computing
characteristics, achieving rapid planning of the
running path of quadruped robots in the working
environment with obstacles.
2.2 Longhorn Whisker Search
Algorithm
As a kind of meta heuristic optimization algorithm,
the longicorn whisker search algorithm mainly
derives its search strategy from imitating the
predatory behavior of longicorn. In nature, longicorn
beetles mainly rely on the antennae distributed on
both sides of their heads (Biswal, and Mohanty 2021).
The odor receptors in the antennae can obtain
pheromones scattered in the air. Due to the different
distances between the two antennae from food, the
odor concentration obtained also varies. When a high
odor concentration is detected on one side, the
longicorn moves in the direction indicated by that
side, thereby continuously updating its position and
finally obtaining food (Tholapu, Sudheer et al. 2021).
The search behavior of the longicorn whisker search
algorithm can be simplified to the geometric model
shown in Figure 1. The blue triangle in the figure
represents a longicorn, and the two corners on the
long side of the triangle represent two longicorn
antennae, which are equally spaced on both sides of
the longicorn's head (Devi, Jadhav, et al. 2021). The
length of the connecting line between the midpoints
of the long sides of the front and rear triangles is used
as the search step for longicorn movement (Wang
2021). The color depth of the light blue area indicates
the strength of the fitness function value, This can
graphically represent a conceptual diagram of the
search behavior of the longicorn whisker search
algorithm.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of optimization of longicorn
whisker search algorithm
The search behavior in Figure 1 can be described
as follows: At the beginning of the search, the
longicorn generates a random head orientation at the
current position, and the antennae distributed on both
sides of the head perceive the fitness value of their
respective positions; When there is a difference in the
fitness value between the two sides, the longicorn
moves a certain search step towards the side with the
high fitness value; When the longicorn moves to the
searched position, the single search process ends, and
the search step length should be shortened based on
the last moving distance. In this way, Taurus
continues to advance and eventually converges to a
certain value in a certain region (Megalingam,
Tantravahi, et al. 2021).
The mathematical model of the longicorn whisker
search algorithm is as follows:
2.2.1 Establish a Fitness Evaluation Function
First of all, it is necessary to establish a fitness
evaluation function f (x) for the optimization
objective, and use the coordinates of the centroid of
the head of Tianniu as the independent variable x. The
value of the fitness evaluation function varies with the
change in the centroid coordinates of the taurus head,
and its value should directly reflect the merits of the
optimization problem. The function is represented as
follows:
min
𝑓
(𝑥),𝑥∈𝑅
(1
)
In the formula, k represents the dimension of the
independent variable x, and the optimization goal of
the fitness evaluation function is the minimum value
of the function.
2.2.2 Generate Random Orientation
Then, a random search direction b needs to be
generated, and the normal direction of the random
search direction represents the direction of the
longicorn.
𝑏
⃗
=
𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑑(𝑘,1)
∥𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑑(𝑘,1)∥
(2
)
Where rand (k, 1) represents a randomly
generated k within the range of [- 1,1] × A one-
dimensional vector, where the random search
direction b is consistent with the dimension of the
independent variable x. The purpose of dividing rand
(k,1) by its own modulus is to unit the random search
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
936

direction b, thereby reducing the numerical
differences brought about by the search direction.
2.2.3 Generation of left and right fitness
values
Subsequently, based on the generated random
search direction, the right side of the longicorn is
marked as positive in the search direction, and the left
side of the longicorn is marked as negative. Then, the
fitness values of their respective positions are
obtained based on the distance between the left and
right tentacles of the longicorn. The coordinates of the
tentacles on the left and right sides of the longicorn
are shown as follows:
𝑥
=𝑥
+𝑑
𝑏
⃗
/2,
(3)
𝑥
=𝑥
−𝑑
𝑏
⃗
/2
(4)
Where, xr and xl represent the coordinates of the
right and left tentacles of the centroid of the head of
the longicorn bull, respectively, and d 'represents the
distance between the left and right tentacles, which is
affected by the search step size δ And the size of the
search step decreases as the number of iterations
increases. The iterative representation of search step
length and whisker spacing is as follows:
𝛿
=𝜆𝛿
,
(5)
𝑑
=𝜕
/𝑐
(6)
Where, λ Represents a constant with a value
between [0,1], which represents the search step size δ
Attenuation rate of; C is a constant that represents the
distance d between the left and right tentacles and the
search step length δ The correlation coefficient of.
After obtaining the coordinates of the left and right
tentacles, it is also necessary to bring xr and xl into
the fitness evaluation function to obtain the fitness
values f (xr) and f (xl) for their respective positions.
The centroid iteration of Taurus is determined by
the search direction b and the search step length 8.
These two variable parameters also constitute the core
search strategy of the Taurus whisker search
algorithm. In the early stage of search, a sufficiently
large search step can effectively explore the value
range of independent variables, ensuring efficient
global search capabilities; When encountering local
extremum, it is possible to deviate from the local
extremum by virtue of a large search step size and a
completely random search direction; In the later stage
of the search, due to the continuous attenuation of the
step length, the longicorn beetle converges in a
certain search area and eventually converges to a
certain value.
3 OPTIMIZATION OF INVERSE
KINEMATICS OF QUADRUPED
ROBOT BASED ON IMPROVED
LONGICORN WHISKER
ALGORITHM
3.1 Improved Design of Longicorn
Whisker Search Algorithm
The Tianniu whisker search algorithm has many
advantages such as simple structure, strong
randomness, and rapid convergence, but its
disadvantages are also relatively obvious. For
example, when dealing with large-scale
combinatorial optimization and multi-extremum
optimization problems, due to the attenuation rate of
the search step size and the completely random search
direction, there will be problems such as poor search
efficiency, non optimal results, and blind search
wasting computational resources; At the same time,
when dealing with complex nonlinear strongly
coupled optimization problems such as obstacle
avoidance path planning for robotic arms, it is
necessary to comprehensively consider various
performance requirements, improve search
efficiency, and satisfy the optimality of the solution
as much as possible, avoiding the waste of computing
resources. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the
original Tianniu whisker search algorithm to improve
its efficiency in complex optimization problems
while retaining its efficient global search and
convergence characteristics.
The core strategy of the locally variable step size
search mechanism is: during the current iteration
process, if the optimal solution of the algorithm is
updated, the global search step size will be locked and
assigned to the locally variable step size. Relying on
the self attenuation of the locally variable step size,
the convergence and local optimization of the current
iteration will be completed, achieving rapid
exploration of the optimal value of the potential
optimal region.
This locally variable step size only exists in the
locally variable step size search mechanism. This
Optimization Method for Inverse Kinematics of Quadruped Robot Based on Improved Longicorn Whisker Algorithm
937

article redesigns the self attenuation of this locally
variable step size as follows:
𝛿
=𝛿
(7)
𝛿
=𝛿
+𝛿
cos
⋅
,𝑖∈
[
0,𝑚
]
(8)
Where, δ Is an independent variable composed
of δ' Initialize and then attenuate independently. T
represents the number of iterations in the search
process of the main program of the Taurus whisker
search algorithm, and i represents the number of
iterations in the search process of the local variable
step size search mechanism, δ "Min is a constant
that represents the minimum value of the locally
variable step size search mecha
nism, and m
represents the maximum number of iterations of the
locally variable step size search mechanism. The
selection of its size requires comprehensive
consideration of search accuracy and search speed.".
𝑥
=𝑥
+𝛿
𝑏
⃗
/𝑐
(9)
𝑥
=𝑥
−𝛿
𝑏
⃗
/𝑐
(10)
Where, x_ Bst ^ i is an iterative model of a locally
variable step size search mechanism, which performs
iterative updates of data in the local mechanism.
When the mechanism exits the iteration and returns to
the main program of the Tianniuxu search algorithm,
it is necessary to return the optimal solution of the
local search results to the main program for storage,
so that the algorithm can compare with other local
optimal values obtained after the main program
search.
The process of an improved longicorn whisker
search algorithm with a locally variable step size
search mechanism is as follows:
1) The starting condition of the local variable step
size search mechanism.
The main program of the algorithm starts,
initializes parameters such as search step size and
attenuation coefficient, and updates the optimal
solution using the optimization strategy of the
Tenebrio search algorithm. When the global optimal
solution of the algorithm is updated, the program
switches to a local variable step size search
mechanism.
2) Parameter initialization of local variable step
size search mechanism and single search iteration
strategy.
Lock the global search step size and assign a value
to the local variable step size, and assign the current
global optimal solution and its fitness value to the
local optimal solution and its fitness value. The single
iteration process of local variable step size is as
follows: First, generate a new local search direction
to guide the local variable step size search; Then,
complete a single search iteration with locally
variable step size according to Equations (8), (9), and
(10), and compare the search results with the local
optimal solution; Finally, update the local optimal
solution based on the comparison between the search
results and the local optimal solution, complete the
local variable step size attenuation according to
Formula (9), and end the single iteration.
3) After exiting the local variable step size search
mechanism, the local optimal solution is stored and
returned to the main algorithm program.
The local variable step size search mechanism
ends the iteration after m searches, saves the local
optimal solution and its fitness value, and returns
them to the local optimal solution set in the main
program of the algorithm. It serves as a parallel
solution set for the optimal solution in the main
program of the algorithm, and is used to compare and
obtain the global optimal solution after the algorithm
finishes searching.
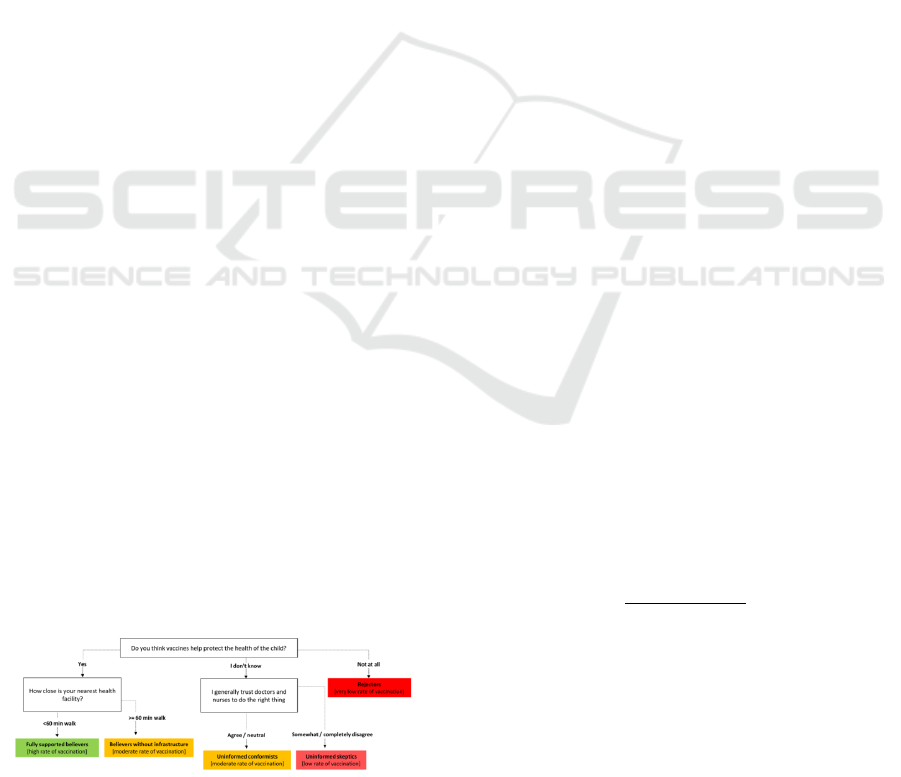
3.2 Kinematic Analysis of Quadruped
Robot
Kinematics analysis is the basis for subsequent
mechanism dynamics analysis, foot workspace
solution, and foot motion trajectory planning.
According to motion control requirements,
kinematics is decomposed into forward and inverse
kinematics analysis. Positive kinematics refers to
deriving the posture and position of the foot end
position coordinates in the torso coordinate system
based on the changes in the rotation angle of each link
joint under the condition that the structural dimension
parameters of each leg link are known. Inverse
kinematics refers to the inverse calculation of the
angle of each joint based on the known position
coordinates of the foot end relative to the fuselage
coordinate system and the position relationship and
size of the connecting rod. The specific analysis
process is shown in Figure 2. In this process, the force
problem during the motion of a quadruped robot can
be temporarily ignored, and the research is aimed at
the coordinate system relationship between the
various links of the legs of the quadruped robot. The
analysis of the joint space and foot end motion
position of the robot leg structure lays a theoretical
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
938
foundation for subsequent motion gait planning and
motion control, and is of great significance for the
research and development of quadruped robots.
Figure 2: Kinematic Analysis Flow Chart
The four legs adopt the same structural design, so
it is possible to configure the joints of the legs
according to specified motion requirements.
Currently, research on the joint configuration of
quadruped robots includes: full knee, front knee back
elbow, front elbow back knee, and full elbow. Due to
the respective advantages and disadvantages of
various joint configurations, their applicable
environments vary. The joint configurations of the
full knee and full elbow legs have the characteristics
of uniform structure, facilitating joint control, Among
them, the full knee pose has a wider range of motion
space and can achieve strong dynamic stability during
movement, so its application is more extensive; The
front knee, back elbow, and front elbow, back knee
leg joint configurations have a relatively large support
area due to the large distance between the front and
rear foot ends and the ground, so they have strong
static stability. Based on the principles of bionics,
most mammals use a full elbow joint configuration.
Although its motion stability is still somewhat
different from that of the front elbow back knee joint,
it has strong controllability and environmental
adaptability due to comprehensive consideration of
motion stability and speed requirements.
Considering the simplicity and modifiability of
structural modeling, this article uses SolidWorks
software to design the structure of various parts of the
body and legs of a bionic quadruped robot. Models
are drawn in three-dimensional drawing software
based on the actual dimensions of various
accessories, and a virtual prototype of the designed
bionic quadruped robot is simulated based on
functional module planning and overall design
requirements. The assembled three-dimensional
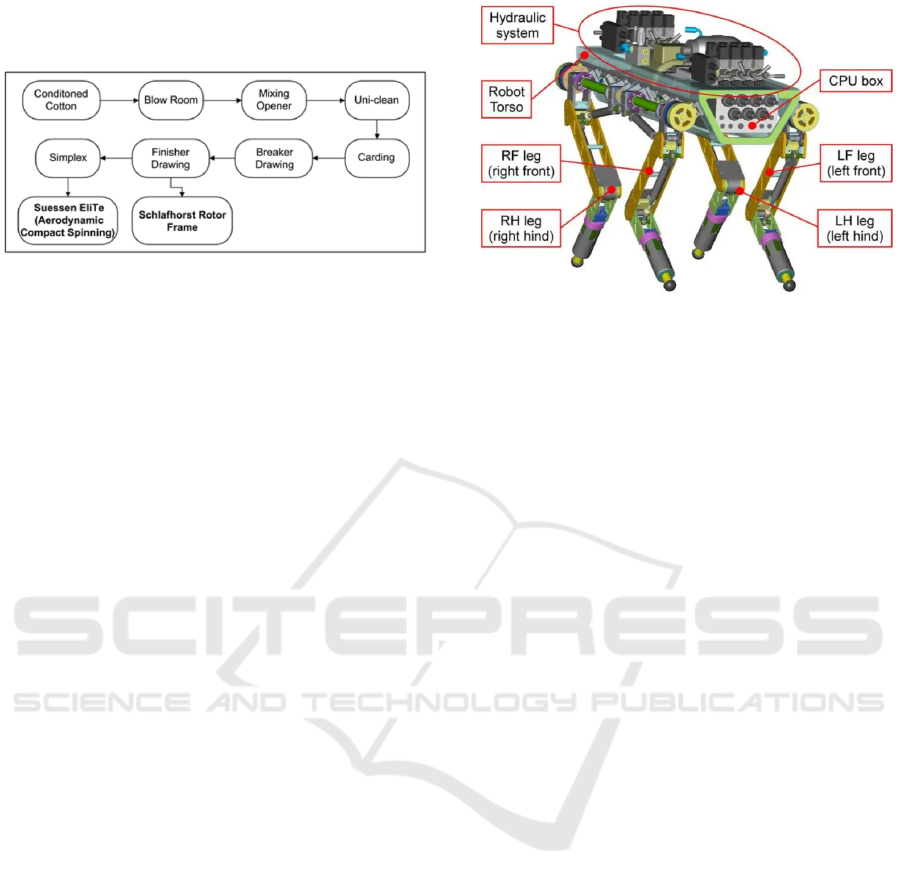
model structure is shown in Figure 3 below:
Figure 3: Three-dimensional model diagram of quadruped
robot
The forward kinematics of the robot described
above can calculate the foot end coordinate position
based on the joint rotation angle. However, the actual
robot motion control process is to calculate the joint
angle control amount based on the planned foot end
position coordinates, and set the joint drive according
to the control method, thereby achieving the motion
control effect for the robot and human. Therefore, in
the process of motion control for quadruped robots, it
is also necessary to solve the inverse kinematics of
the foot ends. According to the definition, inverse
kinematics is based on the trajectory equation of the
foot end that has been planned, and information such
as the posture of the foot end, the position coordinates
relative to the fuselage, and the length of each link is
known, and then the obtained posture positions are
used to inverse deduce the variable values at each
joint.
This article takes the left front leg as an example
to solve the inverse kinematics of the foot end. The
position coordinates of the foot end position
coordinate system {4} in the fuselage coordinate
system and the designed mechanical structure
dimensions are known, and the joint rotation angles
at the hip joint, shoulder joint, and knee joint are
calculated. Taking a single leg as an example, in order
to facilitate joint angle calculation, the base
coordinate system to be solved is set as the temporary
coordinate system {0} on the shoulder joint
coordinate. The motion control of the quadruped
robot leg is achieved based on joint angle control. The
foot position coordinate system is solved based on the
above positive motion:
𝑃=[
𝑃
𝑃
𝑃
]
(1
)
Optimization Method for Inverse Kinematics of Quadruped Robot Based on Improved Longicorn Whisker Algorithm
939
To solve inverse kinematics, the rotation angle
function of each joint can be obtained from the above
formula, as shown below:
⎩
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎪
⎪
⎧
𝜃
=−arctan (
𝑃
𝑃
) − arctan (
𝐿
𝑃
+𝑃
−𝐿
)
𝜃
=arccos [
𝐿
+(𝑃
+𝑃
+𝑃
−𝐿
−𝐿
−𝐿
)/2𝐿
𝑃
+𝑃
+𝑃
−𝐿
] − arctan (
𝑃
+
𝜃
=−arccos (
𝑃
+𝑃
+𝑃
−𝐿
−𝐿
−𝐿
2𝐿
𝐿
)
(1
)
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Conduct joint control simulation through Solidworks
and Matlab/Simulink, associate the modeling system
with the control system, simplify the calculation
process of model building in the control system, and
make the results of the simulation run directly
observable. In the imported single leg model,
parameter values such as coordinate system
conversion calibration, gravity, fixed relationship,
linkage, and joint rotation have been given in the
system, so additional settings are not allowed. Based
on this virtual prototype, a control module is built
according to the above planning, and trajectory
control and detection of parameters such as the angle
and angular velocity of the moving joint are
performed through the control, sensor, and detection
modules in the Simulink toolbox, The control system
shown in Figure 4 is mainly composed of a virtual
prototype module, a control module, and a detection
module.
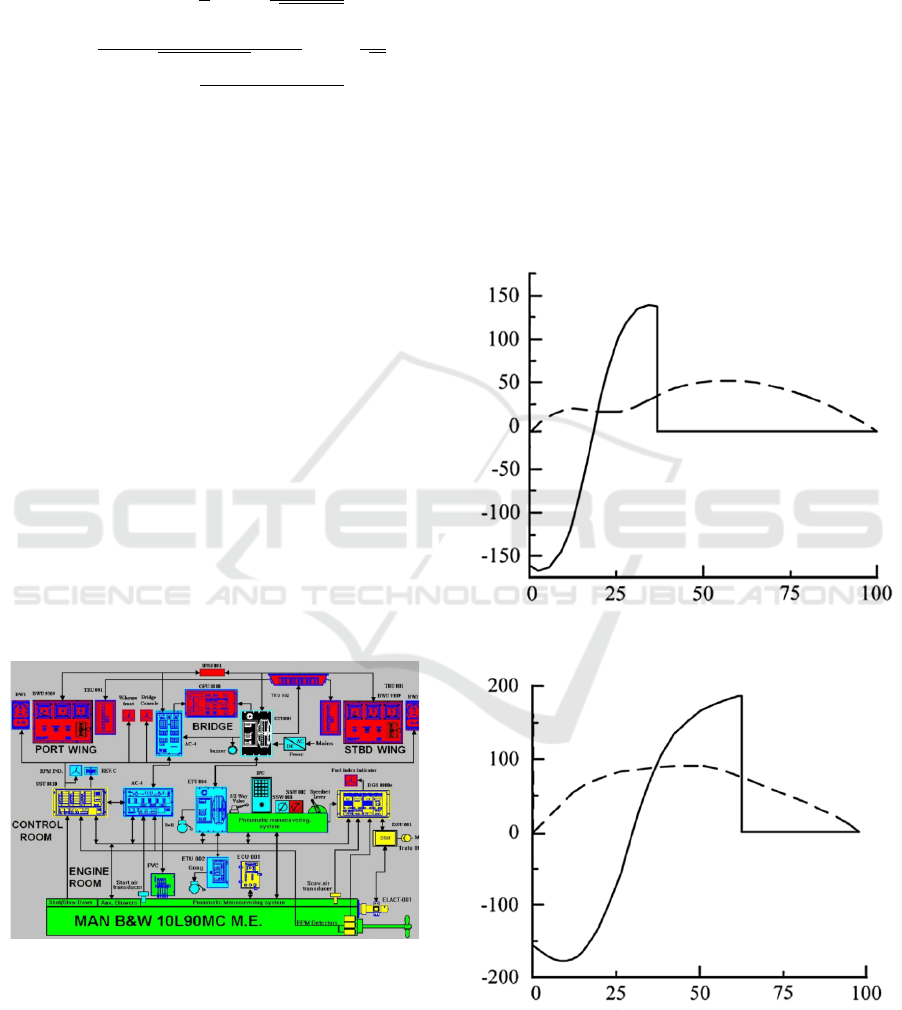
Figure 4: Single Leg Control System Diagram
From the above figure, it can be seen that the foot
trajectory planning control is performed on the built
single leg control model, and the model is built based
on the improved trajectory described above. Inverse
kinematics is used to solve the planned trajectory,
calculate the joint rotation angle as the input variable
of the virtual prototype rotational joint, drive the
joint, set the sensor module to collect the angle and
angular velocity changes of the rotational joint, and
store the data, The feasibility of trajectory planning
and motion control is demonstrated by analyzing the
change curve.
The sensor detection device is set for the angle
and angular velocity of the rotational joint. The
change diagram of the rotation angle of the hip and
knee joints under the foot end trajectory planning
based on the improved trajectory is shown below.
Figures 5 and 6 show the driving angle change
diagram of the hip and knee joints. Within a motion
cycle, the driving angle changes smoothly and does
not produce angle mutations, verifying the rationality
of trajectory planning.
Figure 5: Hip joint drive angle
Figure 6: Knee drive angle
For comparison, the two motion modes use the
same physical dimensions (see Table 1). The
researchers considered the physical properties of the
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
940

hind legs of 42 cheetahs, Acinonyx Jubatus. In order
to evaluate the effectiveness of these two models, we
used the kinematics and dynamics equations of the
model to simulate running cheetahs, greyhounds, and
bobcats (rotary galloping), as well as horses,
antelopes, and alpacas (lateral galloping).
Table 1: Physical parameters of the model used
Paramete
r
MMS SLIP
Stride len
g
th 2.152
m
1, .4834
m
Ho
pp
in
g
hei
g
ht 0.31969
m
0.35304
m
Normal effort 16.1752 N . 0N
Tangential stress - 76.0275 N - 76.0275 N
According to the analysis of the two control
experiments conducted on the physical prototype, it
can be seen that the control strategy for the developed
quadruped robot is feasible, and the prototype
production has certain rationality. In Experiment 1,
the quadruped robot has completed the in situ gait
movement according to the diagonal gait law, and in
Experiment 2, the walking gait experiment has been
completed in a laboratory environment without
external power supply, The experimental results show
that the quadruped robot designed in this paper has a
reasonable structure, and the drive and control
modules are feasible. Based on the joint simulation
theory of the entire machine, a motion control system
is built, and the planned foot trajectory is verified
using external power supplies and controllers. The
experimental results show that the quadruped robot
can basically complete the control movement of the
planned gait according to design expectations.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the work requirements of quadruped robots
and the design concept of functional modular
division, this paper completes the design of the
overall mechanical system of quadruped robots, and
uses Solidworks 3D software to establish a virtual
prototype of quadruped robots. Improving the
traditional compound cycloid and polynomial
trajectory to complete foot end gait and trajectory
planning. Simplify the control process, temporarily
ignoring the lateral motion of the joint, and only
analyzing the rotation of the hip and knee joints.
Based on this, a single leg simulation model is
established. Based on the principle of zero impact
force, the composite cycloid and polynomial
trajectory are optimized and analyzed. The composite
cycloid is proposed as a fusion trajectory of the lateral
trajectory and the octagonal polynomial as a vertical
trajectory. This trajectory has transition segments to
achieve smooth control of the joint drive function,
and has good obstacle surmounting function. Build a
control module to simulate the planned foot
trajectory, and verify the rationality of gait planning
using Simulink.
REFERENCES
Huang L , Wu X , Wang X . Gait planning of a quadruped
robot integrating inverse kinematics and CPG[C]//
Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication XI.
2021.
Qin Y , Dong S , Pang R , et al. Design and Kinematic
Analysis of a Wall-climbing Robot for Bridge
appearance Inspection[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth
and Environmental Science, 2021, 638(1):012062.
Biswal P , Mohanty P K . Modeling and Effective Foot
Force Distribution for the Legs of a Quadruped
Robot[J]. Robotica, 2021:1-14.
Schreiber L T , Gosselin C . Determination of the Inverse
Kinematics Branches of Solution Based on Joint
Coordinates for Universal Robots-Like Serial Robot
Architecture[J]. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics:
Transactions of the ASME, 2022(3):14.
Zhou R , Yu H , Yun S N , et al. INVERSE KINEMATICS
OF A SURGICAL ROBOT FOR TELEOPERATION
WITH HARDWARE CONSTRAINTS:,
WO2021251989A1[P]. 2021.
Zhang H , Zhu Z , Yuan J . Non-inverse kinematics of
free-floating space robot based on motion planning of
sampling[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical
University, 2021, 39(5):1005-1011.
Chandan S , Shah J , Singh T P , et al. Inverse kinematics
analysis of 7-degree of freedom welding and drilling
robot using artificial intelligence techniques -
ScienceDirect[J]. 2021.
Zohour H M , Belzile B , St-Onge D . Kinova Gen3-Lite
manipulator inverse kinematics: optimal polynomial
solution[J]. 2021.
He J Y , Shao J P , Gao B W , et al. Suppression of
Quadruped Robot Body Disturbance by Virtual Spring-
Damping Model[J]. Complexity, 2022, 2022.
Ju H . AXIS-INVARIANT-BASED INVERSE
KINEMATICS MODELING AND SOLVING
METHOD FOR MULTI-AXIS ROBOT:,
EP3838501A1[P]. 2021.
Biswal P , Mohanty P K . Kinematic and Dynamic
Modeling of a Quadruped Robot[M]. 2021.
Tholapu S , Sudheer A P , Joy M L . Kinematic Modelling
and Structural Analysis of a Spherical Robot: BALL-
E[J]. IOP Conference Series Materials Science and
Engineering, 2021, 1132(1):012034.
Devi M A , Jadhav P D , Adhikary N , et al. Trajectory
Planning & Computation of Inverse Kinematics of
SCARA using Machine Learning[C]// 2021
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Smart Systems (ICAIS). 2021.
Optimization Method for Inverse Kinematics of Quadruped Robot Based on Improved Longicorn Whisker Algorithm
941

Wang L . Deep-learning damped least squares method for
inverse kinematics of redundant robots[J].
Measurement, 2021, 171(1).
Megalingam R K , Tantravahi S , Tammana H , et al.
Inverse Kinematics of Robot Manipulator Integrated
with Image Processing Algorithms[M]. 2021.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
942
