
The Data Driven Recruitment: Revolutionizing Talent Acquisition
Yeresime Suresh
1 a
, Channabasamma A
2 b
and Srinivasulu M
3
1
Dept. of CSE - Artificial Intelligence, Ballari Institute of Technology and Management, Ballari, India
2
Dept. of Computer Science & Engg., Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Bowrampet, Hyderabad-500043, India
3
Dept. of MCA, UBDTCE, Davangere, India
Keywords:
Analytics, Candidate, Data Driven, Diagnostic, Predictive, Prescriptive.
Abstract:
The integration of data analytics has driven a new wave of transformation in the traditional recruitment process,
revolutionizing talent acquisition today. This study analyzes the significant impact of data-driven strategies
on recruitment and highlights the key elements that drive this paradigm shift. The article introduces the
function of big data as well as strong analytics since it enables individuals to find or access internal or external
candidates who meet their needs or who best fit their organization among many other operations. Advanced
algorithms and machine learning models can help recruiters to make more informed predictions now, therefore
increasing hiring process efficiency. In continuance of the discussion is the issue of how analytics can be
used by managers seeking to improve diversity and inclusion in their organization. Through studying past
recruitment records, biases can be clearly spotted and checked for fostering a more equitable and diverse labor
force. The article also examines likely difficulties and ethical concerns existing in data-based recruitment
highlighting responsible and open practices.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is now common for organizations to use data-
focused methods in this changing landscape of talent
acquisition. Technology has emerged and different
business dimensions have become digitalized leading
to a new way of attracting, evaluating and selecting
candidates (Sharma and Khan, 2022). This transition
is about analytics going into recruitment processes as-
sisting companies with informed choice-making, effi-
ciency improvement, and proper staffing.
Classic methods of recruitment were based on in-
tuition, experience, making the process subjective and
prone to biases; however, analytics came with it a
particular era where decisions are made upon solid
facts analyzed from vast resources. The data-driven
recruiting revolution is not just another fashion; it’s
also an essential strategic necessity for firms compet-
ing in rapid transformational work environment.
The shift towards data-driven recruitment is driven
by the recognition that talent is crucial for any or-
ganization, and inadequacies in selection can greatly
impact its outcomes (Sharma and Khan, 2022). By
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8372-3612
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4689-0638
leveraging analytics, recruiters and HR team can
make use of giant heaps of data to identify trends,
forecast the success of candidates and also stream-
line the process of recruitment. This is not only time-
saving but also results in more accurate and efficient
recruitment outcomes.
This research seeks to investigate how data-driven
recruitment revolution has impacted on hiring pro-
cesses through exploring key ways analytics have
transformed hiring landscapes. Amongst them are the
use of prescriptive analytics in talent sourcing as well
as descriptive, diagnostic and predictive analytics. As
organizations strive to build agile, diverse, and high-
performing teams, the integration of analytics into re-
cruitment practices emerges as a powerful, fostering a
more strategic and objective approach to talent acqui-
sition.
The arrangement for rest of the paper is as fol-
lows: Section 2 examines the investigations that have
been performed in connection with the intended task.
Section 3 offers a concise an overview of the planned
approach work. Section 4 presents the applicability of
analytics in HR, and Section 5 serves as the conclu-
sion of the study.
Suresh, Y., A, C. and M, S.
The Data Driven Recruitment: Revolutionizing Talent Acquisition.
DOI: 10.5220/0013734600004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 3, pages 901-907
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
901

2 BACKGROUND OF HR
ANALYTICS AND ITS TYPES
Talent acquisition is a process that, unlike the nor-
mal recruitment process, occurs when companies try
to fill the talent pool in their organizations. Recruit-
ment will not only focus on open positions but will
also take into account the company’s goals. Because
the stakes are higher, it’s more important to develop
tactical HR analytics and data from recruiting to cap-
ture the right talent.
Recruiting, identifying, and motivating the right
employees is equally important in workforce man-
agement (Sinha, Khusru et al. 2021). HR analyt-
ics eliminates the trial-and-error method and helps
to reduce the skill gap by refining the process. A
blend of the man-power and right skill sets can lead
to successful business results. HR analytics can sig-
nificantly enhance organizational efficiency by opti-
mizing workforce planning, thereby reducing costs.
Inaccurate staffing—whether it’s overstaffing, under-
staffing, or hiring the wrong talent—can adversely af-
fect the bottom line. Implementing effective analytics
helps ensure the right talent is in place, fostering a
high-performing organization.
The four types of HR analytics—descriptive, diag-
nostic, predictive, and prescriptive (Figure 1)—each
offer a unique perspective on a company’s data. While
each type has its own advantages and disadvantages,
they are interrelated and build upon one another.
2.1 Descriptive Analytics
Raw data, on its own, lacks utility and fails to provide
insights into causality. However, once combined, it
becomes invaluable. Descriptive analytics is the sim-
ple type of analytics that is commonly utilized for
generating reports, KPIs (Key Performance Indica-
tors) and business metrics that enable companies to
track performance and other trends. It transforms his-
torical data into comprehensible summaries, facilitat-
ing performance tracking and trend analysis. For in-
stance, an organizational report detailing every em-
ployee fall under descriptive analysis. Even further
breakdowns by demographics fall within this cate-
gory. More complex metrics such as turnover rates or
time-to-fill positions also exemplify descriptive ana-
lytics, as they are based on historical data to elucidate
past occurrences (Sarah, et al. 2018). However, a sole
focus on descriptive analytics can lead to a reactive
approach. As HR evolves to meet dynamic business
needs, a shift towards proactive strategies becomes
imperative.
2.2 Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics transforms data into meaningful
insights by identifying patterns, variances, and causal
relationships, while also taking into account internal
and external factors. It explains the reasons behind
the events highlighted by descriptive analytics (Kaur
and Phutela, 2018). For example, a diagnostic report
might rank the reasons why salespeople have left an
organization, such as low quota attainment or higher
base salaries offered by competitors. By revealing the
underlying causes of the events shown by descriptive
data, diagnostic analytics makes it easier to determine
where to focus efforts to address and mitigate prob-
lems.
2.3 Predictive Analytics
While descriptive analytics looks backward, predic-
tive analytics focuses on the future. Statistical mod-
els and forecasts aim to predict what might occur in
the future based on patterns in data. These models
are built on patterns identified through descriptive an-
alytics, with the goal of proactively meeting the or-
ganization’s needs. For instance, predictive analytics
can assist the talent acquisition team in determining
if a candidate is compatible with the organization’s
culture before making a hiring decision (Sarah, et al.
2018). It can also estimate how long a person is likely
to continue in the company.
2.4 Prescriptive Analytics
Once the future is predicted, the next step is determin-
ing what actions to take. Prescriptive analytics offers
recommendations on how to act on forecasts and past
results.
This analysis method is particularly valuable for
organizations during peak or busy time. For exam-
ple, a retailer might use prescriptive analytics to de-
cide how many employees to schedule during the hol-
idays, or a park might determine staffing needs for the
summer months. Additionally, prescriptive analytics
can help tailor the onboarding process for new hires
based on their specific skills and strengths (Bertsimas
and Kallus, 2020)
2.4.1 Benefits of Prescriptive Analytics over
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics forecasts the most likely outcome
of an action, while prescriptive analytics takes a most
preemptive approach by recommending which ac-
tions or decisions are most likely to result in the de-
sired outcome. In the realm of HR challenges, like
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
902
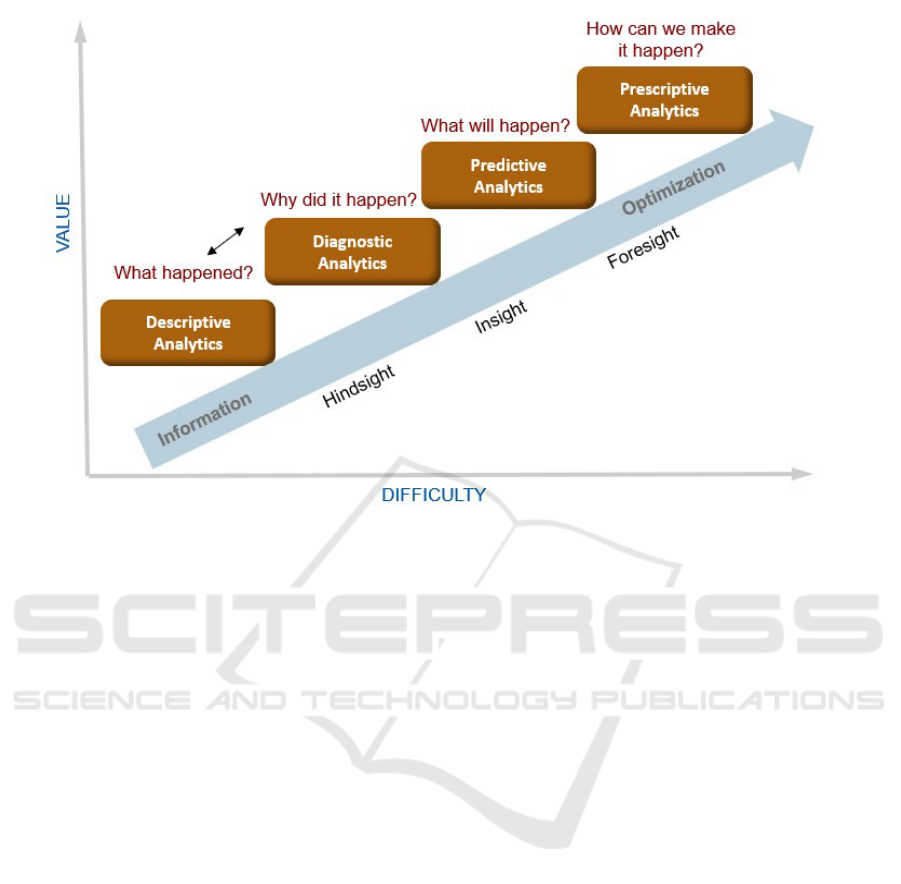
Figure 1: Types of HR Analytics
employee retention, predictive analytics can pinpoint
which employees are at highest risk of leaving. In
contrast, prescriptive analytics would suggest the best
course of action to retain those employees. Besides
employee retention, prescriptive analytics can also
be utilized in various tasks that drive organizational
growth (Paauwe, Boon, et al. 2018). When leverag-
ing prescriptive analytics over predictive analytics in
resume analytics, organizations can achieve more tar-
geted and actionable outcomes.
Here are the key benefits, supported by key find-
ings that highlight the improvements and efficiencies
gained:
• Enhanced Quality of Hire:
Predictive Analytics: Identifies candidates who
are likely to perform well based on historical
data. Prescriptive Analytics: Recommends the
best candidates to hire and suggests specific ac-
tions to optimize the hiring process (Artar, Bal-
cioglu, et al. 2024).
Findings:
– Quality of Hire Improvement: Organizations
using prescriptive analytics report a 25
– Success Rate of Recommendations: 80% of
candidates recommended by prescriptive ana-
lytics meet or exceed performance expectations
within their first year.
• Increased Efficiency in Hiring:
Predictive Analytics: Estimates the time it will
take to fill a position based on past data. Pre-
scriptive Analytics: Suggests strategies to stream-
line the recruitment process, reducing time-to-fill
(Pessach, Singer, et al. 2020).
Findings:
– Reduction in Time-to-Fill: Companies using
prescriptive analytics experience a 30% reduc-
tion in time-to-fill, from an average of 45 days
to 31.5 days.
– Interview-to-Offer Ratio Improvement: The
interview-to-offer ratio improves by 20%, in-
dicating a more efficient selection process.
• Improved Diversity and Inclusion:
Predictive Analytics: Identifies trends in diversity
hiring.
Prescriptive Analytics: Recommends specific ac-
tions to enhance diversity by removing biases in
the hiring process.
Findings:
– Increase in Diversity Hiring Rate: Organiza-
tions see a 35% increase in diversity hiring rates
when using prescriptive analytics.
– Bias Reduction: Language bias in job descrip-
tions is reduced by 40%, leading to a more di-
verse candidate pool.
• Optimization of Recruitment Costs:
The Data Driven Recruitment: Revolutionizing Talent Acquisition
903

Predictive Analytics: Estimates recruitment costs
based on historical data. Prescriptive Analytics:
Recommends cost-effective strategies for recruit-
ment (Ehrlich and Montes, 2024).
Findings:
– Reduction in Cost-per-Hire: Companies using
prescriptive analytics see a 25% decrease in
cost-per-hire, from 4, 000 to 3, 000 on an av-
erage.
– Return on Recruitment Investment (RoRI): Im-
proved by 20%, reflecting better financial re-
turns on recruitment spending.
• Better Strategic Workforce Planning:
Predictive Analytics: Forecasts future hiring
needs based on trends. Prescriptive Analytics:
Provides specific hiring plans and strategies to
meet future demands (Bandari, 2019).
Findings:
– Workforce Planning Accuracy: Accuracy im-
proved by 20%, leading to more precise align-
ment of workforce supply with demand.
– Skill Gap Closure Rate: Organizations experi-
ence a 15% faster closure rate of identified skill
gaps.
• Reduced Employee Turnover:
Predictive Analytics: Identifies employees at
risk of leaving. Prescriptive Analytics: Rec-
ommends interventions to retain key employees
(Margherita, 2022).
Findings:
– Reduction in Employee Turnover Rate: Em-
ployee turnover decreases by 20%, from 15%
to 12
– Retention Rate of Prescribed Actions: 85%
of employees targeted by prescriptive interven-
tions remain with the company, compared to
70% using only predictive analytics.
These statistical results demonstrate the tangible ben-
efits of prescriptive analytics, leading to better quality
hires, increased efficiency, improved diversity, opti-
mized costs, enhanced candidate experience, more ac-
curate workforce planning, and reduced turnover. In
summary, with reliable and robust data, prescriptive
analytics is the most effective tool to empower HR
managers in their daily tasks across various areas.
3 HOW ANALYTICS IS
TRANSFORMING THE
RECRUITING INDUSTRY?
All innovation begins with knowledge, and data is
the holy grail for an analyst, who may use the data
to either represent the past - Descriptive Analytics,
predict the future - Predictive Analytics, or prescribe
a mode of action to acquire the desired result in the
future - Prescriptive Analytics.
Advantages of analytics in recruiting over tradi-
tional recruiting are as follows:
• It offers objective insights into the effectiveness
and cost of recruiting.
• It helps in tracking potential candidates to create
future employees.
• It creates a strong talent pool and maintains a solid
record of each candidate.
• It unlocks opportunities to learn and enhance the
recruitment process.
• It facilitates the recruitment process, enabling bet-
ter and more timely hiring decisions.
• It allows for the prediction of high-performing
candidates and poor performers.
Predictive analytics can provide insights into var-
ious categories and answer key questions, including:
• Candidate sources: Which sourcing platforms
(job boards, social media, referrals, etc.) are most
effective?
• Candidate screening: What is the typical time
frame for the candidate screening process? Which
screening methods yield the best results, and
which are ineffective?
• Lead times: How long is the duration from appli-
cation submission to extending a job offer? How
does this influence the drop-off rates?
• Future employment needs: Which job positions
are expected to be vacant in the near future? and
what will the specific requirements of hiring man-
agers?
• Future employee performance: What is the like-
lihood that a new hire will perform well in their
position?
• Retention rates: How long do new hires typically
remain with the company? What factors affect the
probability of other candidates leaving the com-
pany?
• Hiring bottlenecks: Where are the common bot-
tlenecks in the hiring process? What impact do
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
904

these bottlenecks have, and how can they be ef-
fectively resolved?
• Urgency of hiring: Which roles and skills are ur-
gently needed to fulfill the company’s immediate
requirements?
Predictive analytics can assist recruiting and hir-
ing professionals in:
• Identifying strong candidates for open positions
• Making quicker and more informed offers to can-
didates
• Enhancing the overall candidate experience
4 APPLICATIONS OF ADVANCED
ANALYTICS IN HR
4.1 Acquiring the Ideal Talent through
Competency Acquisition Analytics
Finding the right talent is vital for a company’s suc-
cess, as employees are one of the largest investments
and key assets for most businesses. Competency ac-
quisition analytics can be utilized to determine if the
right talent is being acquired. The first step is to iden-
tify the core competencies essential for business suc-
cess. These competencies are then compared with the
existing workforce, current skill sets, and potential for
development. This process helps identify any talent
gaps. The HR team can then assess whether to train
existing employees to fill these gaps or hire new talent
with the necessary competencies (Elarabi and Johari,
2014).
4.2 Assess Recruitment Channel
Just as significant is understanding where to find the
finest talents, this is just important as hiring them.
Recruitment channel analytics is a process that deter-
mines which are the most effective recruitment chan-
nels used to attract top-tier employees. This entails
studying historical employee data, conducting sur-
veys and feedbacks while at the same time assessing
such key performance indicators like the return per
employee and human capital value added. Organiza-
tions can gain valuable insight into the efficiency of
different channels by drilling down into this informa-
tion.
4.3 Classification Analysis to Assess
Team Success Rates
By examining previous data, classification analysis
identifies trends that aid in determining which cate-
gory a specific observation or data entity falls under.
For example, this approach may be useful in HR de-
termining team composition and other contextual fac-
tors that lead to team success (Ribeiro and Gomes,
2022). Rather than forming teams only considering
metrics like work experience and resource availabil-
ity, organizations may utilize insights from classifi-
cation analytics that help comprehend issues such as
leadership style, team dynamics, project duration, and
team size among others to enhance team’s success
rate. By forecasting a team’s success rate ahead, or-
ganizations can form effective teams for each project.
4.4 Attrition Analysis
High attrition is a big challenge for HR teams and can
be expensive to companies because of costs for job
advertisements, recruitment, orientation and training
of new staff to fill the gaps. One of the effective strate-
gies to reduce attrition is when the company leverages
advanced analytics and natural language processing
(NLP) tools to analyze employee reviews from em-
ployment sites such as Glassdoor, Indeed and Compa-
rably. With this analysis in place, companies may de-
termine how well the employees are satisfied by their
brand hence revealing common factors attributing to
high labor turnover.
4.5 Customizing Training Programs
Rather than applying standard programs and generic
training methods across all workers, learning out-
comes can be enhanced by designing around personal
preferences of courses. This involves utilizing ’adap-
tive’ learning technology, where data analytics deter-
mines the optimal learning pace, mode of training,
and suitable content for each employee. By moni-
toring corporate training programs and collecting em-
ployee feedback, valuable data can be gathered to cre-
ate more effective and efficient professional develop-
ment initiatives.
4.6 Capacity Analytics and Utilization
Advanced analytics in HR offers significant business
advantages, notably in cost reduction. Capacity Ana-
lytics enables HR teams to:
• Assess team capacity and utilization levels effec-
tively.
The Data Driven Recruitment: Revolutionizing Talent Acquisition
905

• Identify the activities team members are engaged
in, and their work schedules.
• Analyze the processes, tools, and applications uti-
lized for work and their associated costs.
• Evaluate operational efficiency to determine if
teams are overworked or underutilized.
4.7 Improving Employee Performance
While traditional methods like peer and manager re-
views and monitoring KPIs are widely employed to
gauge and manage employee performance, their ef-
fectiveness in driving improvement is limited. In fact,
a PwC (Price Waterhouse Coopers, the second-largest
professional services network in the world) report on
Performance Management highlights that 52% of or-
ganizations have either implemented or are contem-
plating changes to employee performance manage-
ment in the near future(Samtani, 2022), (Nahar, Is-
lam, et al. 2017).
Employee performance analytics enables more ef-
ficient measurement of individual employee perfor-
mance by leveraging both historical and real-time
data. It offers both retrospective and forward-looking
analyses, providing insights into past performance
and strategies for improvement. Through the result-
ing insights, high performing employees can be iden-
tified, and employees who require additional training
and motivation to enhance their performance can be
understood.
4.8 Boost Recruitment
Utilizing data gathering and employing data mining
techniques alongside artificial intelligence (AI) can
aid in identifying the most suitable candidates while
mitigating human biases.
4.9 Analysis for detecting anomalies
The analysis of detecting anomalies serves to identify
unexpected or aberrant patterns. In HR management,
this evaluation can play a vital role in uncovering re-
lationships between workplace accidents and employ-
ees who may be fatigued due to extended work dura-
tion(s). HR teams can prevent workplace accidents
and injuries by taking precautionary measures when
resources that exceed predefined thresholds for work
duration are identified.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The data-driven revolution in recruitment is charac-
terized by its ability to optimize processes, improve
decision-making, enhance diversity. In the face of an
expanding adoption of analytics by firms, recruitment
landscape keeps changing with promises of efficiency,
fairness and a more meaningful approach towards ac-
quiring talent. The use of data analytics in recruit-
ment has not only accelerated the hiring process but
also made it more impartial reducing the impact of hu-
man biases. By leveraging prescriptive analytics, or-
ganizations can proactively find potential candidates,
align them with appropriate roles, and streamline their
recruitment process for greater efficiency and effec-
tiveness.
REFERENCES
Sharma, P. and Khan, W.A., 2022. Revolutioniz-
ing Human Resources Management with Big
Data: From Talent Acquisition to Workforce Op-
timization. International Journal of Business In-
telligence and Big Data Analytics, 5(1), pp.35-
45.
Sinha, Arvind Kumar, Md Amir Khusru Akhtar, and
Ashwani Kumar. ”Resume screening using nat-
ural language processing and machine learning:
A systematic review.” Machine Learning and In-
formation Processing: Proceedings of ICMLIP
2020 (2021): pp. 207-214.
Kemp, Sarah E., et al. ”Introduction to descriptive
analysis.” Descriptive analysis in sensory eval-
uation (2018): 1-39.
Kaur, Harkiran, and Aanchal Phutela. ”Commentary
upon descriptive data analytics.” In 2018 2nd In-
ternational Conference on Inventive Systems and
Control (ICISC), pp. 678-683. IEEE, 2018..
Kakulapati, V., Chaitanya, K.K., Chaitanya, K.V.G.
and Akshay, P., 2020. “Predictive analytics
of HR-A machine learning approach”, Journal
of Statistics and Management Systems, 23(6),
pp.959-969.
Bertsimas, D. and Kallus, N., 2020. From predictive
to prescriptive analytics. Management Science,
66(3), pp.1025-1044.
Paauwe, J. and Boon, C., 2018. Strategic HRM: A
critical review. Human resource management,
pp.49-73.
Artar, M., Balcioglu, Y.S. and Erdil, O., 2024. Im-
proving the quality of hires via the use of ma-
chine learning and an expansion of the per-
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
906

son–environment fit theory. Management Deci-
sion.
Pessach, D., Singer, G., Avrahami, D., Ben-Gal,
H.C., Shmueli, E. and Ben-Gal, I., 2020. Em-
ployees recruitment: A prescriptive analytics ap-
proach via machine learning and mathematical
programming. Decision Support Systems, 134,
p.113290.
Ehrlich, G. and Montes, J., 2024. Wage rigidity
and employment outcomes: Evidence from ad-
ministrative data. American Economic Journal:
Macroeconomics, 16(1), pp.147-206.
Bandari, V., 2019. Exploring the transformational po-
tential of emerging technologies in human re-
source analytics: a comparative study of the
applications of IoT, AI, and cloud computing.
Journal of Humanities and Applied Science Re-
search, 2(1), pp.15-27. Grossman, K.W. and
Schoolderman, A., 2022. Candidate Experience:
How to Improve Talent Acquisition to Drive
Business Performance. Kogan Page Publishers.
Margherita, A., 2022. Human resources analytics: A
systematization of research topics and directions
for future research. Human Resource Manage-
ment Review, 32(2), p.100795.
Elarabi, H.M. and Johari, F., 2014. The impact of hu-
man resources management on healthcare qual-
ity. Asian journal of management sciences & ed-
ucation, 3(1), pp.13-22.
Ribeiro, J.L. and Gomes, D., 2022. The (Un) sus-
tainable Process of Devolution of HRM Respon-
sibilities to Line Managers. In Sustainable Hu-
man Resource Management (pp. 103-144). River
Publishers.
Samtani, D.D., 2022. The advantages of using pre-
scriptive analytics in recruitment and perfor-
mance management processes by HR profes-
sionals based in Ireland (Doctoral dissertation,
Dublin, National College of Ireland).
Nahar, R., Islam, R. and Ullah, K.T., 2017. Identify-
ing the factors for reducing employee turnover
rate in aviation business: Bangladesh context.
Australian Academy of Business and Economics
Review, 3(1), pp.39-46.
The Data Driven Recruitment: Revolutionizing Talent Acquisition
907
