
Diverse Methodologies & Tools Used in Plagiarism Detection
Anchal Pokharana
a
and Urvashi Garg
b
Department of Computing Science,
Chandigarh University, Mohali, India
Keywords: Plagiarism Checking Methods, Plagiarism Detection Techniques, Tools for Plagiarism Checking.
Abstract: Plagiarism detection is now a days a challenging issue in various languages, everyone is dealing with lots and
lots of online data and documents, all are sharing files, documents, and presentations for work as well as
education purpose. After covid this thing became very normal for all students and employees. Online data
sharing and document sharing has become part of everyone’s daily routine, but everyone should know the
shared data has not been plagiarized in any manner, plagiarism has become a big challenge now a days,
plagiarism is basically copying the content from some other source without giving credit. In this paper diverse
plagiarism checking software’s, tools and methodologies have been discussed and comparison have been
made based on accuracy, time complexity, limitations, and many other parameters. so, this paper has been
designed in such a way that paper is divided in some sections, the very first section is all about plagiarism,
types of plagiarism, the second section is all about the existing software’s, tools, and their issues while
plagiarism checking. last section included the comparison of the work done by various authors and common
findings has been shared. For the whole work a detailed review procedure has been utilized for reviewing the
papers in depth. The major issue found in this paper is that, not even a single dedicated software is available
for plagiarism detection specifically in Hindi language content.
1 INTRODUCTION
In research, plagiarism refers to the act of presenting
someone else's ideas, work, or words as your own
without giving credit to the original source. This
includes using someone else's written or spoken
words, ideas, data, images, or other materials without
proper citation, and it is considered unethical and
unacceptable in academic and scientific communities.
Plagiarism undermines the integrity of the research
process by misrepresenting the author's contributions,
and it can have serious consequences, such as damage
to one's reputation, loss of credibility, and potential
legal consequences. To avoid this situation of
plagiarized content, it is necessary to genuinely cite
all the sources of the work and give proper and
sincere credit to the original authorsss, who worked
hard. It is important to understand the principles of
academic integrity and to properly cite all the sources
used in work to avoid plagiarism.
Plagiarism can be of many types each with its own
features parameters and implications. Some of the
basic types of plagiarism are:
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3177-1492
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3395-9942
• Copy and paste plagiarism: This occurs when
a person copies and pastes a piece of text
from a source without attribution, giving the
impression that the words are their own.
• Paraphrasing plagiarism: This involves
rewriting someone else's words or ideas
without proper citation. • Self-plagiarism:
This is the act of submitting one's own
previously published work as new, without
acknowledging that it has been published
before.
• Patchwork plagiarism: This happens when a
person combines several sources without
proper attribution, creating a new work that is
largely made up of someone else's ideas and
words.
• Mosaic plagiarism: This type of plagiarism
involves using different phrases or sentences
from several sources without proper
attribution, creating a patchwork of borrowed
material.
• Accidental plagiarism: This is plagiarism that
occurs unintentionally, often due to a lack of
knowledge or understanding of citation rules.
Pokharana, A. and Garg, U.
Diverse Methodologies & Tools Used in Plagiarism Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013733300004664
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Futuristic Technology (INCOFT 2025) - Volume 3, pages 811-820
ISBN: 978-989-758-763-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
811
Regardless of the type, all forms of
plagiarism are considered a violation of
academic and professional integrity and can
have serious consequences. (Garg and Goyal,
2016)
2 PLAGIARISM DETECTION
PROCESS
The plagiarism detection process typically involves
using specialized software or tools to compare a
submitted document against a database of existing
texts and identifying any matches or similarities.
These tools may use algorithms that analyze word
choice, sentence structure, and other factors to detect
potential plagiarism. In addition, some plagiarism
detection tools may use machine learning or artificial
intelligence techniques to improve the accuracy of
their analysis. Once potential instances of plagiarism
are identified, it is up to the human evaluator to
review the results and determine whether any action
needs to be taken.
Plagiarism detection is the process of identifying
instances of plagiarism in a document or work. Here
are the common steps involved in plagiarism
detection:
1. Upload the document: The document in
question is uploaded to a plagiarism
detection tool or software.
2. Scanning: The tool scans the document
and compares it with a database of
existing texts, including online and
offline sources, academic papers, and
other documents.
3. Report generation: The plagiarism
detection tool generates a report that
highlights any similarities between the
uploaded document and the sources in
the database.
4. Analysis: The report is then analyzed to
determine the extent of plagiarism,
whether it is accidental or deliberate, and
what actions need to be taken.
5. Correction and citation: If plagiarism is
detected, the writer is typically required
to make corrections to the document and
properly cite all sources. In some cases,
further actions may be taken, such as
disciplinary measures or legal action.
It's important to note that plagiarism detection
tools are not foolproof and should be used as a tool to
assist in the detection of plagiarism, not as a substitute
for critical thinking and careful citation
3 SOLUTIONS APPROACHES &
RESULTS IN PLAGIARISM
Numerous internal fields, methodologies, tools,
solution approaches and issues have been found,
while reviewing the research papers between the year
2016 to 2023. Following table showcasing the
detailed methods and results in these year’s work.
Table 1: Solution Approaches & Results
Year Solution Approach
use
d
Obtained Result
2016 An approach was
suggested in which
two stages included
such as to retrieve the
candidate and assess
the pairwise
document similarity.
This approach was
planned based on a
keyword- focused
technique. Due to
the occurrence of
plagiarism in portions
of the text, the
major focus was
on segmenting
statements into
fragments or
chunks
for
detecting
the
base similarity. A
topic- based
segmentation
algorithm was
put forward for
converting the
suspected document
file into multiple
set of passages.
Moreover, the
documents containing
fine
matching
passages were
retrieved using a
proximity-based
framework.
The experimental
outcomes indicated
that the suggested
approach had
generated effective
outcomes for
detectingthe
plagiarism. (Ehsan
and Shakery, 2016)
2017 Developed a system
known as Decode 5
to detect the
plagiarism for
analyzing data on
WWW and on use
r
-
Presented work
conducted load
testing on the
deployed system,
demonstrating the
b
enefits of a
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
812
defined collections,
moreover its
implementation was
done as a DSS.
distributed
deployment, and
demonstrating
adequate results from
a scientific and
business perspective.
This led to the
conclusion that
algorithms designed
for small-scale
plagiarism detection
could be modified for
use in a platform at a
commercial level (V.
and Velásquez,, 2017)
2017 An approach for
detecting plagiarism
using the weighted
local maximum value
of LCS with a
distributed format.
The dataset of a
plagiarism finding
contest was used to
test the suggested
approach as well as
two additional basic
methods based on
LCS.
The extensive
experiments
demonstrate the utility
of the suggested
approach in
applications requiring
stringent plagiarism
identification. (Baba,
Nakatoh, et al. , 2017)
2017 An External
Plagiarism Detection
System (EPDS),
which combined the
semantic data as well
as syntactic data with
SRL methodology.
The suggested strategy
proved effective at
identifying various
forms of plagiarism.
The experiment's
findings so showed
that the suggested
approach could boost
performance. (Abdi,
Shamsuddin, et al. ,
2017)
2017 SCAM (Standard
Copy Analysis
Mechanism)
plagiarism detection
method has been used
, which developed a
relative scale to
identify overlap by
comparing the
number of words that
were shared between
the test document
and the registered
document.
The suggested
detection method
compared documents
using natural
language. To manage
data with large
amounts with Hadoop
and for identify
plagiarism, this
work-built Map-
Reduce based SCAM
method. The typical
Scam algorithm was
intended for
processing small
amounts of data, not
large amounts.
(Dwivedi and Tiwary,
2017
)
2017 Offered a
performance increase
to the method's
implementation as
well as a plagiarism
detection technique
conditioned on
approximate string
matching to be used
in "copy and paste"
plagiarism types
.Two different types
of estimates of the
output utilised for
plagiarism finding
allowed for the
majority of
calculations to be
skipped, though the
accuracy loss was
tolerable.
According
to
the
research
observations, the
enhancement might
cut the processing
time in half for an
accuracy reduction of
6.4% compared to the
algorithm's standard
deployment. (Baba,
2017)
2017 Presented and
assessed an app to
validate resemblances
of documents. Those
texts' word similarity
percentages were
used to compare the
degree of similarity
between them. The
similarity value could
be used to identify
plagiarism in written
work. This program
made use of a web-
based k-gram and a
winnowing method.
By contrasting the
system's output with
the output produced
by a human, this
effort assessed the
accuracy of the
system. The
disparities in between
the systems as well as
respondents were 7%
for k-gram 25 & 4%
for k-gram 20. Also
mentioned was how
long the application
would take to
process. (Sutoyo, et al.
, 2017
)
2018 Developed a PD
solution for Urdu text
documents that could
identify many types
of plagiarism. This
paper employed the
cosine, Generalized
Jaccard, Damerau
Levenshtein
Distance technique,
and Waterman
algorithm approaches
to achieve its goals.
With two ML
classifiers— Naive
Bayes and SVM. This
work defined two
types of
classification: binary
and multi-
classification.
According on the
research
observations, the
suggested DLDM
approach
outperformed existing
methods for both
binary and multiclass
classification.
Additionally, the
cosine and waterman
algorithms
outperformed the G-
jaccard algorithm.
For better outcomes,
researchers intend to
incorporate
information on
Syntactic and
semantic similarities
in the future. (Ali,
Ahmed, et al. , 2018
)
Diverse Methodologies & Tools Used in Plagiarism Detection
813
2018 MCANN and BP
neural networks to
construct two systems
for identifying
plagiarism in Nepali
language existing
literature. On two
separate datasets,
both frameworks
were put to the test,
and the findings were
examined and
critiqued. MCANN
converged more
quickly than the
conventional BP
algorithm.
After comparing the
papers line-by-line
and paragraph-by-
paragraph, it was
discovered that the
mean accuracy of BP
and MCANN was in
the range of 98.657
and 99.864,
respectively. In
contrast to BP,
MCANN proved
effective in detecting
plagiarism in
documents written in
Nepali. (Bachchan
and Timalsina, 2018)
2018 Presented a two-step
method for detecting
plagiarism: text
alignment and
candidate retrieval.
The candidate
documents were
extracted using the k-
means clustering
approach after
creating a vector
representation at the
document level using
a Convolutional
Neural Network
(CNN) in the initial
stage . The features
were retrieved at the
sentence-level using a
CNN in order to
align the text. The
copied sentences
were eventually
found by applying
the classification
methods.
Both the generated
corpus used in the
AAI competition and
the generated corpus
used in the PAN2015
competition were
subjected to trials.
The first corpus's
precision and recall
were reached at 0.843
and 0.806,
respectively, whereas
the second corpus's
were at 0.833 and
0.826. (Lazemi,
Ebrahimpour-Komleh,
et al. , 2018)
2018 A task similarity
detection tool to help
instructors in
identifying the
similarity of student
assignments. The
Rocchio approach
was employed in this
study to identify
word similarity.
The accuracy was
74.6%, The Rocchio
approach was capable
of classifying
documents that were
comparable.
(Soyusiawaty, Jones,
et al. , 2018)
2019 Suggested a fusion of
CKR method in
order to plagiarism
detection. Outcomes
of conceptual were
integrated with BoW
(bag-of-words)
The outcomes
depicted that the
suggested method
was more accurate in
comparison with the
existing techniques
an
d
p
rove
d
as a toll
systems through a
dynamic
interpolation factor.
for embedding in
cross-language
systems of detecting
plagiarism.
(Meuschke, Stange, et
al. , 2019
)
2019 Constructed a DNN
& Sinhala text
corpus-based word
embedding
framework . This was
accomplished with
the help of UCSC
Sinhala News corpus
and the word2vec
technique.
The developed
framework was put
into practice and
examined using a
brand-new data set,
and it was discovered
to be 97% accurate at
identifying
plagiarism. (Roostaee,
Sadreddini, et al. ,
2019
)
2019 This work
incorporated a
few heuristics, such
as string compression
and assessment of
detection probability,
with the basic
detection approach to
enhance accuracy of
the detection of the
copied sections and
shorten computation
times.
This
approach
was
simple to use and set
up, and it only
required one parameter
to determine whether
Something was
plagiarized. The
work's final
contribution
demonstrated,
using
actual data, the
effectiveness of the
suggested strategy,
particularly the added
heuristics. (Arachchi
and Charles, 2019
)
]
2019 Discovered
that
the
computational
efficiency of a
winnowing method
used in a cross-
language plagiarism
detection system
developed one of the
universities in
Indonesia, was a
problem for practical
im
p
lementation.
The execution time
was compared, the
outcome of the
overall parallelized
computation was able
to accelerate by 1.07
to 3.52 times.
(Sakamoto and Tsuda,
2019)
2019 Presented a plagiarism
corpus for Thai, to
evaluate
and
compare
all
the
algorithms for
plagiarism detection.
They have shown that
the suspicious
documents in the
corpus is manually
designed by utilizing
different techniques.
Which make the
suspicious records
more sensible as well
as challenging
(Thaiprayoon,
Palingoon, et al. ,
2019)
2019 String matching
a
pp
roach is a
The system for
p
la
g
iarism detection
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
814
“character
by
character”
matching
method. This
approach could also
use hashing block of
the character and then
use n-Gram to
match the hashing
block. But before
n-Gram, file or
document need all
pre-processing
steps.
with a string matching
methodology creates
a level of the closeness
of the record
by
working
out the N-Gram result
with Dice's Likeness
Coefficient. For text
Extraction on a
framework worked
With tokenization,
stop word expulsion,
and stemming. The
text then, at that
point, randomized
utilizing the Rabin-
Karp technique.
(Parwita, Indradewi, et
al. , 2019)
2021 Method for detecting
text and cross-
language plagiarism
in both English and
Albanian. By
keeping track of
student work using
this approach, it was
hoped that this paper
improved the standard
and
accountability in
educational settings
and universities.
Python and PHP were
used to construct the
system, which was
web-
b
ased.
Multiprocessing was
used in this work to
speed up the system's
performance. The
outcomes of the trials
demonstrate that this
approach was
applied to the
detection of text and
cross-languag
plagiarism. (Shkurti,
Ajdari, et al. , 2021)
2021 A
computerized
method
that was
capable of
quickly
identifying
plagiarism-causing
similarities in
scientific or writing
articles. VSM
method with TF and
IDF method have
b
een used.
The findings showed
that using these
method together
shows that the
similarity value of 1
(100%). (Wahyudi,
Zarlis, et al. , 2021)
2021 Attempted
to
create
a
system
or
application in
order to identify
similarities
between
Indonesian
documents utilizing
the Rabin-Karp
algorithm, the
Stemming
This algorithm
swiftly identified
document similarities,
particularly in
documents, with least
time. (Hartanto,
Pristyanto, et al. ,
2021)
methodology, and
the Cosine
Similarity approach
as a Distance-
Based Similarity
Measure.
2022 The approach to
automatically identify
various forms of
plagiarism from two
languages was
proposed in this
paper. With the use
of the Doc2Vec
model, which
forecasted semantic
similarity between
documents and
phrases, this strategy
was built on
sentence modelling
in an effort to
recover copied
passages from
documents. For
Arabic and English,
respectively, this
work used
AraPlagDet and the
PAN corpus just
detecting
p
lagiarism.
A record of
questionable
documents that were
manually and
intentionally
plagiarised along with
their origins were
made available by
t h e PAN and
AraPlagDet corporas.
(Setha and Aliane,
2022)
2022
Deep learning system
for the statement text
plagiarism detection
which utilized a
network of Siamese
LSTM and word-
based embeddings.
Suggested approach
used Word2Vec and
Glove approaches to
create the network’s
input Then, a mix of
Manhattandistance
and cosine
similarity metrics
were used to
calculate the
percentage of
plagiarism in the
network's two
outputs.
Extensive
experiments on the
PAN-PC-11 and
Webis-CPC datasets
showed that the
embeddings
from the Word2Vec
architecture gave the
most accurate
detection scores. By
employing word2vec
embeddings. the
approach
achieved
F1-measure of 0.816,
0.91 recall, and 0.924
accuracy for the
PAN-PC-11 corpus
and F1-
measures of 0.793,
0.852 recall, and
0.902 precision for
the Webis-CPC-11
corpora. (Saeed and
Ta
q
a, 2022
)
2023
N-gram Overlap and
Word Embedding-
based approaches
achieving an F1 score
This model was
ineffective to detect
plagiarism from all
kinds of documents.
Diverse Methodologies & Tools Used in Plagiarism Detection
815
of 0.63, surpassing
the highest results
attained by the N-
gram Overlap
(baseline) approach
with an F1 score of
0.53.
(Mehal, Muneer, et al.
2023)
4 PLAGIARISM DETECTION
TOOLS
This is a digital world, in this day-by-day plagiarism
is becoming a big issue in the field of research and
education so detecting plagiarism is now a big
challenge for all of us., There are numerous
plagiarism detection tools available online, both free
and paid, that can help detect instances of plagiarism
in a document or work, In which some popular
plagiarism detection plagscan, plagiarism checker,
Turnitin and Grammarly are there, here I have
compared all of the available tools by taking two
different samples, one in English language and
another one is in Hindi language, along with that the
results provided by these tools have been discussed.
Figure 1: Grammarly plagiarism result for English content
Fig 1 showcasing the plagiarism result on a
sample with English content, although the content is
copied from the web but its showing that the content
is plagiarism free, some grammatical and other
different issues are depicted. Basically, Grammarly is
an online grammar checker that also includes a
plagiarism detection feature. It checks for similarities
in a document against a database of online sources.
Figure 2: Grammarly plagiarism result for Hindi content
Fig 2 showcasing the plagiarism result on a
sample with Hindi content, although the content is
copied from the web, but its showing that the content
is plagiarism free. this tool is not for Hindi language,
cannot read and understand the Hindi worlds as per
its detailed report
Figure 3: Check Plagiarism result for English content
Fig 3 showcasing the plagiarism result of check
plagiarism tool on a sample with English content,
although the content is fully copied from the web but
its showing that the content is having only 20%
plagiarism.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
816

Figure 4: Check Plagiarism result for Hindi content
Fig 4 showcasing the plagiarism result of check
plagiarism tool on a sample with Hindi content,
although the content is copied directly from the web,
but its showing that the content is 100% unique
basically this tool is not for Hindi language, cannot
read and understand the Hindi worlds as seen in the
image.
Figure 5: PlagScan result for English content in first attempt
Fig 5 showcasing the plagiarism result of plagscan
tool on a sample with English content, this is a
plagiarism detection tool that checks documents
against a database of sources, including academic
journals, websites, and other online sources. Here the
sample content is directly taken from the web but its
showing that the content is having 71.6% plagiarism.
Figure 6: PlagScan result for English content in second
attempt
Fig 6 depicts the plagiarism results on the second
attempt of the same sample content, it is showing that
content is 99.2% plagiarized.
Figure 7: Plag Scan result for Hindi content in first
attempt
Fig 7 showcasing the plagiarism result of plagscan
tool on a sample with Hindi content, according to the
report this content is completely plagiarism free. This
tool is also not working for Hindi documents.
Figure 8: Turnitin result for English content
Fig 8 showcasing the plagiarism result of Turnitin
tool on English document. Turnitin is one of the most
widely used plagiarism detection tools, primarily
used in educational institutions. It compares a
document against a vast database of sources,
including academic journals, books, and websites.
here the sample document is taken from the internet
and its showing that the content is 100% plagiarized,
with proper recourse.
Figure 9: Turnitin result for Hindi content
Fig 9 showcasing the plagiarism result of Turnitin
tool on a sample with Hindi content, although the
content is copied directly from the web, but its
showing that the content is 100% unique basically
this tool is not for Hindi language, cannot read and
understand the Hindi words as seen in the image.
Diverse Methodologies & Tools Used in Plagiarism Detection
817
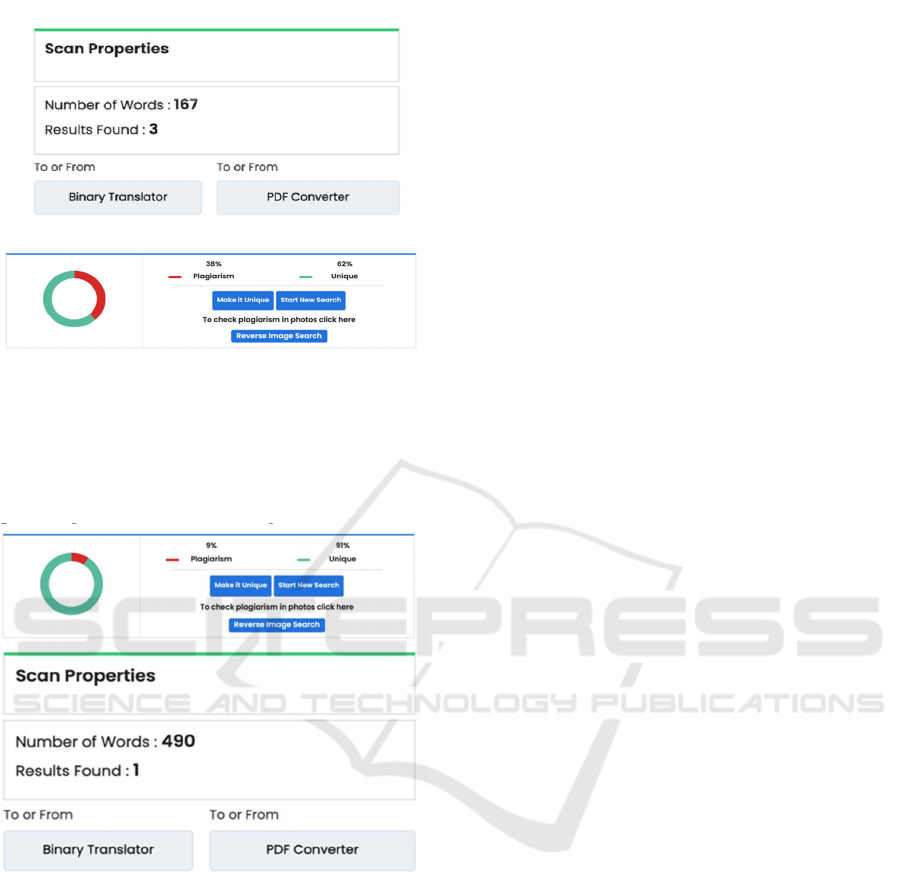
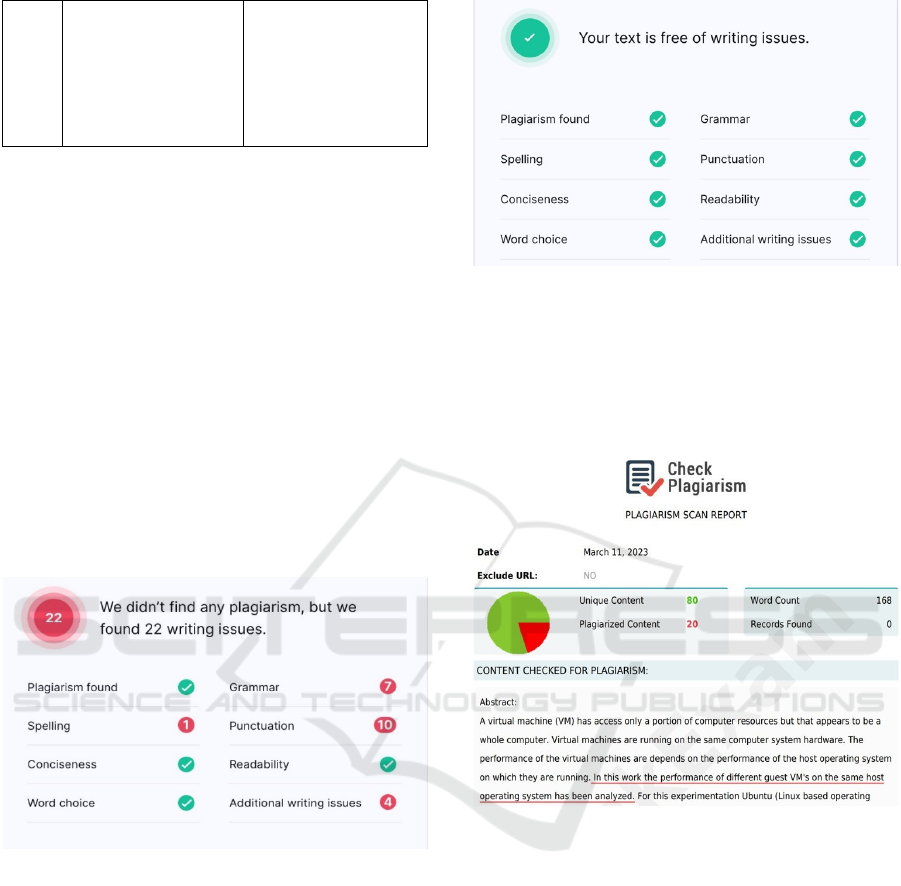
Figure 10: Dupli checker result for English content
Fig 10 showcasing the plagiarism result on a
sample with English content, although the content is
copied from the web but its showing that the content
is having only 38% plagiarism. This tool is not
providing the exact results on English content.
Figure 11: Dupli checker result for Hindi content
Fig 11 showcasing the plagiarism result on a
sample with Hindi content, although the content is
copied from the web, but its showing that the content
is having only 9% plagiarism. this tool is not for Hindi
language, cannot read and understand the Hindi
worlds as per its detailed report. After checking with
these tools, it has been noticed that no plagiarism
detection tool is 100% accurate, and it's always best
to use multiple tools and your own critical thinking to
detect plagiarism in a document or work.
5 COMMON FINDINGS & GAPS
IN THE RESEARCH
Some research gaps have been concluded after going
through various algorithms in the field of plagiarism
detection. Different research gaps are defined as: -
• The method suggested earlier to check the
plagiarism avoid the references. It is essential
to consider the referred content as the
plagiarized due to its impact on the model.
• Machine Learning (ML) model can be
implemented for enhancing the accuracy to
check the plagiarism.
• A proper algorithm for retrieval of the
document from the internet can be
formulated. Normally the title of the paper
has been used as a query to retrieve the
documents from the internet. But sometimes,
the system fails to retrieve the proper
document if the title of the paper is not
properly given and hence it gives a similarity
score of 0%. This leads to incorrect results.
• There is the need to develop improved
methods and algorithms that can effectively
detect plagiarism in various languages,
including Hindi, Urdu, and Nepali. These
methods should consider the specific
linguistic characteristics and complexities of
each language to enhance accuracy and
address challenging cases of plagiarism
detection.
• The literature reviews highlight the
requirement for improved methods in
plagiarism detection, considering factors
such as word similarity percentages, text
alignment, and fusion of concept based and
keyword-based retrieval. Additionally,
comparative studies are needed to assess the
accuracy and efficiency of these methods in
plagiarism detection systems.
• PDF or HTML reports need to be generated
after plagiarism checking. Also, the text
highlighting method needs to be
implemented effectively for better result.
• Research gap highlights that there is no single
dominant or widely recognized plagiarism
detection tool exclusively for the Hindi
language. However, some general-purpose
plagiarism detection tools, such as
Grammarly, plagscan, Copyscape and urkund
offer support for multiple languages,
including Hindi. These tools utilize
algorithms and databases to identify potential
instances of plagiarism in Hindi content.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
818

Many people relying on urkund for
plagiarism detection in Hindi content but
urkund has limited coverage and accuracy in
detecting instances of plagiarism. While
Urkund supports multiple languages,
including Hindi, its database for Hindi
sources may be relatively smaller and less
comprehensive compared to its English
database. This limitation can result in missed
matches or reduced accuracy in identifying
plagiarism in Hindi content. Additionally, the
nuances of the Hindi language, including
cultural and contextual references, may pose
challenges for Urkund's algorithms,
potentially leading to false positives or
missed instances of plagiarism.
6 CONCLUSION AND SCOPE OF
WORK
This work proceeded with various algorithms,
procedures and methodologies handled by different
researchers, and discussed these approaches on
various parameters. Despite of wide variety of
techniques available for plagiarism detection, there
are still some research gaps and challenges that need
to be addressed. For example, some methods may
struggle to detect plagiarism when the plagiarized
text has been paraphrased or reworded, while others
may struggle to handle certain types of document
formats or languages. Additionally, there are ethical
and legal issues to consider when implementing
plagiarism detection, such as ensuring that the
privacy of students or other users is respected.
After reviewing all the papers from 2016 to 2023,
it has been found to construct intra-corpus a
productive system can be planned alongside that a
viable AI model can be proposed for the
counterfeiting recognition, A huge local database can
be created in the system. Most of the commercial
software’s uses the local corpus for speedup the
search and reduces the processing of the system.
Plagiarism checking in Hindi documents has not been
working properly, so ML technique can be deployed
to design a tool specifically for Hindi content along
with that most of the work suggested earlier are not
deployed on web, it is required to build a web
interface for better experience.
REFERENCES
U. Garg and V. Goyal, “Maulik: A Plagiarism Detection
Tool for Hindi Documents”, Indian Journal of Science
and Technology, vo. 9, no. 12, pp. 1- 11, 2016
N. Ehsan and A. Shakery, “Candidate document retrieval
for cross- lingual plagiarism detection using two-level
proximity information”, Information Processing &
Management, November 2016
G. P. V. and J. D. Velásquez, “Docode 5: Building a real-
world plagiarism detection system”, Engineering
Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32, no. 4,
pp. 1703-1712, September 2017
K. Baba, T. Nakatoh and T. Minami, “Plagiarism detection
using document similarity based on distributed
representation”, Procedia Computer Science, vol. 10,
pp. 89798-89822, 2017
A. Abdi, S. M. Shamsuddin and R. M. Aliguliyev, “A
linguistic treatment for automatic external plagiarism
detection”, Knowledge-Based Systems, vol. 19, no. 3,
pp. 1817-1826, 1 November 2017
J. Dwivedi and A. Tiwary, "Plagiarism detection on bigdata
using modified map-reduced based SCAM algorithm,"
2017 International Conference on Innovative
Mechanisms for Industry Applications (ICIMIA),
2017, pp. 608-610
K. Baba, "Fast plagiarism detection based on simple
document similarity," 2017 Twelfth International
Conference on Digital Information Management
(ICDIM), 2017, pp. 54-58
R. Sutoyo et al., "Detecting documents plagiarism using
winnowing algorithm and k-gram method," 2017 IEEE
International Conference on Cybernetics and
Computational Intelligence (CyberneticsCom), 2017,
pp. 67-72
W. Ali, T. ahmed, Z. Rehman, A. U. Rehman and M.
Slaman, "Detection of Plagiarism in Urdu Text
Documents," 2018 14th International Conference on
Emerging Technologies (ICET), 2018, pp. 1-6
R. K. Bachchan and A. K. Timalsina, "Plagiarism Detection
Framework Using Monte Carlo Based Artificial Neural
Network for Nepali Language," 2018 IEEE 3rd
International Conference on Computing,
Communication and Security (ICCCS), 2018, pp. 122-
127
S. Lazemi, H. Ebrahimpour-Komleh and N. Noroozi,
"Persian Plagirisim Detection Using CNN s," 2018 8th
International Conference on Computer and Knowledge
Engineering (ICCKE), 2018, pp. 171-175
D. Soyusiawaty, A. H. S. Jones and P. Widiandana,
"Similarity Detection of Student Assignments Using
Rocchio Method," 2018 12th International Conference
on Telecommunication Systems, Services, and
Applications (TSSA), 2018, pp. 1-4
N. Meuschke, V. Stange, M. Schubotz, M. Kramer and B.
Gipp, "Improving Academic Plagiarism Detection for
STEM Documents by Analyzing Mathematical Content
and Citations," 2019 ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on
Digital Libraries (JCDL), 2019, pp. 120-129
Diverse Methodologies & Tools Used in Plagiarism Detection
819

M. Roostaee, M. H. Sadreddini and S. M. Fakhrahmad, “An
effective approach to candidate retrieval for cross-
language plagiarism detection: A fusion of conceptual
and keyword-based schemes”, Information Processing
& Management, vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 248-260, 1
November 2019
T. KasthuriArachchi and E. Y. A. Charles, "Deep Learning
Approach to Detect Plagiarism in Sinhala Text," 2019
14th Conference on Industrial and Information Systems
(ICIIS), 2019, pp. 314-319
D. Sakamoto and K. Tsuda, “A Detection Method for
Plagiarism Reports of Students”, Procedia Computer
Science, 14 October 2019
S. Thaiprayoon, P. Palingoon and K. Trakultaweekoon,
"Design and Development of a Plagiarism Corpus in
Thai for Plagiarism Detection," 2019 11th International
Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering
(KSE), 2019, pp. 1-5
W. G. S. Parwita, I. G. A. A. D. Indradewi and I. N. S. W.
Wijaya, "String Matching based Plagiarism Detection
for Document in Bahasa Indonesia," 2019 5th
International Conference on New Media Studies
(CONMEDIA), 2019, pp. 54-58
L. Shkurti, J. Ajdari, F. Kabashi and V. Fusa, "PlagAL:
Plagiarism detection system for Albanian texts," 2021
10th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded
Computing (MECO), 2021, pp. 1-5.
R. Wahyudi, M. Zarlis, S. Efendi and T. F. Abidin,
"Determination of Sentence Similarity Level Using
Vector Space Model (VSM) and Word Relationship
Weighting for Plagiarism Detection for Indonesian
Documents," 2021 International Conference on Data
Science, Artificial Intelligence, and Business Analytics
(DATABIA), 2021, pp. 142-153
A. D. Hartanto, Y. Pristyanto and A. Saputra, "Document
Similarity Detection using Rabin-Karp and Cosine
Similarity Algorithms," 2021 International Conference
on Computer Science and Engineering (IC2SE), 2021,
pp. 1-6
I. Setha and H. Aliane, "Enhancing automatic plagiarism
detection: Using Doc2vec model," 2022 International
Conference on Advanced Aspects of Software
Engineering (ICAASE), 2023, pp. 1-5
A. A. M. Saeed and A. Y. Taqa, "Textual Plagiarism
Detection Using Embedding Models and Siamese
LSTM," 2022 International Conference for Natural and
Applied Sciences (ICNAS), 2022, pp. 95-100
G. Mehal, I. Muneer, R.M.A. Nawab, " Urdu Text Reuse
Detection at Phrasal level using Sentence Transformer-
based approach," 2023 Expert Systems with
Applications, Volume 234.
Grammarly: Retrieved from
https://www.grammarly.com/plagiarism- checker, Date
Accessed 27th June,2023
Plagscan: www.plagscan.com/en/ Date Accessed 24th
June,2023
Turnitin: Leading Plagiarism Detection Tool. Retrieved
from http://www.turnitin.com. Date Accessed: 20th
June, 2023.
Duplichecker: Retrieved from
https://www.duplichecker.com/ Date Accessed 28th
June,2023
Copyscape: Retrieved from
http://www.copyscape.com/plagiarism.php Date
Accessed: 20th June, 2023.
INCOFT 2025 - International Conference on Futuristic Technology
820
