
JARGES: Detecting and Decoding Jargon for Enterprise Search
Colin Daly
1,2 a
and Lucy Hederman
1,2 b
1
The ADAPT SFI Research Centre, Ireland
2
School of Computer Science and Statistics, Ireland
Keywords:
Enterprise Search, Learning to Rank, Jargon, Language Modelling.
Abstract:
Newcomers to an organisation often struggle with unfamiliar internal vocabulary, which can affect their ability
to retrieve relevant information. Enterprise Search (ES) systems frequently underperform when queries contain
jargon or terminology that is specific to the organisation. This paper introduces ‘JARGES’, a novel feature for
detecting and decoding jargon for ES. It is designed to enhance a ranking model combining Learning to Rank
(LTR) and transformer-based synonym expansion. The ranking model is evaluated using the ENTRP-SRCH
dataset. Our experiments showed, however, that the JARGES feature yielded no significant improvement over
the baseline (nDCG@10 = 0.964, ∆ = 0.001, p> 0.05). These failures are likely due to the dataset’s lack
of jargon-rich pairs. This highlights the need for larger ES datasets derived from click-through data or other
implicit feedback to detect subtle ranking signals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprise Search (ES) plays a key role in enabling
organisations to efficiently access internal knowledge.
But ES systems are often perceived to be ‘relevance-
blind’ (Turnbull and Berryman, 2016) as users “can-
not find the information they seek within an accept-
able amount of time, using their own enterprise search
applications” (Bentley, 2011). For newcomers, this
challenge is compounded by the prevalence of spe-
cialised jargon and terminology unique to an organi-
sation.
Such jargon, while familiar to long-term employ-
ees, can impede effective searches by new staff or ex-
ternal stakeholders. This is sometimes referred to as
‘vocabulary mismatch’ (Ganguly et al., 2015). Query
formulation using incorrect terms or phraseology can
lead to poor ranking and recall of query results, with
a potential reduction in staff productivity.
To address this problem, we propose a ranking
model that integrates Learning to Rank (LTR) and
Language Modelling (LM). The LM component is
called ‘JARGES’ (JARGon for Enterprise Search),
and is designed to detect and decode jargon in ES
queries and corpora. The detection and decoding
stages of JARGES are demonstrated in Figure 1.
This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of this
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7218-7765
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6073-4063
approach in improving search result rankings, par-
ticularly for content rich in organisational terminol-
ogy. To test this hypothesis, we perform a quan-
titative evaluation of the performance of an LTR
ranking model with and without JARGES using the
LTR-formatted ENTRP-SRCH dataset (2,544 human-
annotated Q-D pairs) (Daly, 2023). We subsequently
perform a qualitative analysis of the decoded jargon
terms via their contextual synonyms.
While the quantitative experiments did not result
in an improved ranking performance, the nuances of
enterprise specific terminology may have been bet-
ter captured had a larger and more diverse ES dataset
been available. Moreover, JARGES offers a promis-
ing direction for decoding organisational language
and semantic search.
2 RELATED WORK
Enterprise Search (ES) can be simply defined as find-
ing the information needed from within an organi-
sation (Bentley, 2011) or as a service that “enables
employees to find all the information the company
possesses without knowing where the information is
stored” (White, 2015).
Jargon is enterprise specific vocabulary that em-
ployees/members can understand. It encompasses
words, phrases, expressions, and idioms that are not
Daly, C. and Hederman, L.
JARGES: Detecting and Decoding Jargon for Enterprise Search.
DOI: 10.5220/0013729500004000
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2025) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 357-363
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
357
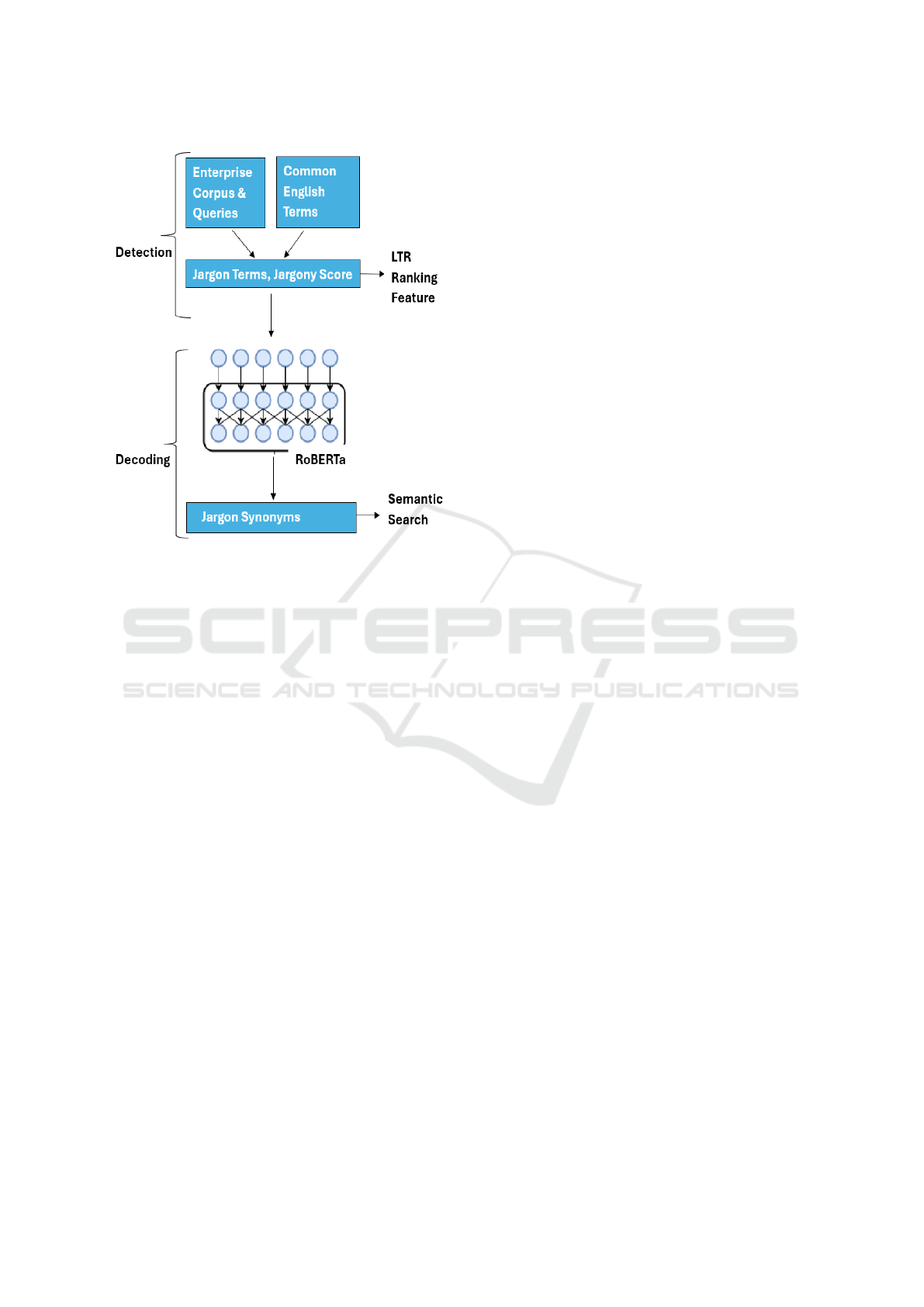
Figure 1: Architecture of the JARGES algorithm, including
the detection (classification) and decoding (synonym gener-
ation) stages.
universally familiar or properly understood.
Although excessive use of jargon and terminology
in organisations is often perceived as exclusionary, we
use the terms here in a positive context for conveying
complex ideas, processes, or services among employ-
ees/members who share common knowledge of the
enterprise. In this context, jargon and terminology fa-
cilitate efficient communication.
The challenge of detecting and decoding enter-
prise jargon/terminology within a corpus lends itself
to the fields of natural language processing (NLP)
and LM. Comparative TF-IDF scoring and sparse ma-
trix vectorisation can be used for tasks like plagia-
rism classification (Pudasaini et al., 2024) and also
to distinguish word or phrase salience patterns be-
tween corpora (Belfathi et al., 2024). The TF-IDF
divergence calculation is computationally lightweight
and can be executed using the standard IT hardware
commonly available in most organisations. Word em-
beddings are another NLP tool that can capture se-
mantic relationships between words in text data via
dense vector matrices. LMs, such as Google’s Bidi-
rectional Encoder Representations from Transform-
ers (BERT) (Devlin et al., 2019), are trained on large
datasets containing vast amounts of text from diverse
sources. While embeddings and transformers are
regularly used in e-commerce (Singh et al., 2023)
and commercial search engines (Li et al., 2017),
their application for ES has not been sufficiently ex-
plored. A 2024 study by Belfathi to classify docu-
ment genres used BERT to distil ‘linguistic attributes’
for legal terms and demonstrated elevated ranking
performance for specific tasks in the LegalGLUE
dataset (Belfathi et al., 2024).
In 2019, Facebook developed an improved ver-
sion of BERT called RoBERTa (Robustly Optimised
BERT Approach) (Liu et al., 2019). Studies have
shown that RoBERTa’s larger training data leads to
superior generation of synonyms. RoBERTa is espe-
cially effective for jargon by leveraging its ability to
discern subtle contextual nuances that smaller models
like BERT might miss.
Learning to Rank (LTR) is the application of su-
pervised machine learning techniques to train a model
to list the best ranking order (Li, 2011; Xu et al.,
2020). In the context of search results, LTR involves
combining ranking signals to present the best order
of documents for a given query. LTR computes the
optimum ‘weight’ (importance) of signals, which can
be extracted from an ES corpus and associated query
log data. While LTR has been in use since 2004,
major commercial Web Search (WS) providers like
Baidu and Google still use LTR in 2024 (Wang et al.,
2024; Google, 2025), with Baidu referring to it as the
“standard workhorse” (Wang et al., 2024) for rank-
ing search results. LTR methods, such as Lamb-
daMART (Burges et al., 2005), optimise ranking by
learning from relevance-labelled data, often evaluated
using metrics like normalised discounted cumulative
gain (nDCG), as seen in (Liu, 2010). For ES, LTR has
been adapted to handle domain specific challenges,
including the presence of jargon, though with mixed
success due to dataset limitations (Hawking, 2004). A
test collection or dataset based on Enterprise Search is
hard to come by, as organisations are not inclined to
open their intranet to public distribution, even for re-
search purposes (Craswell et al., 2005; Cleverley and
Burnett, 2019).
3 METHODS
This section outlines the methodology employed
to create the JARGES feature, integration with an
Apache Solr ES service, and the subsequent evalua-
tion of the LTR ranking model. The ranking model is
trained and evaluated using the ENTRP-SRCH dataset,
and incorporates offline A/B testing to assess ranking
performance.
KDIR 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
358

3.1 JARGES
The JARGES algorithm is designed to detect and de-
code jargon. It processes three input files and gener-
ates two output lists, as depicted in Figure 2. These
outputs are tailored to enhance distinct components of
Enterprise Search (ES):
• A ranked list of the organisation’s detected jargon
terms, ordered by their ‘jargony’ score. This list
serves as a ranking function for integration into an
LTR model.
• A list of synonyms for each decoded jargon term
from within the organisation. This output enables
query expansion in the search engine, thereby im-
proving recall.
Figure 2: The three inputs for the JARGES algorithm,
which outputs two lists (for ranking and recall respectively).
In this study, we use the ENTRP-SRCH LTR dataset,
which includes 2544 human-annotated Q-D pairs of
twenty most frequent queries of a large third-level ed-
ucation institution. One popular PDF document in the
corpus is entitled ‘jargon buster’ and describes 126
commonly used jargon terms within the institution.
The full code for the JARGES ranking and recall fea-
ture has been published to GitHub
1
.
3.1.1 Detection
The JARGES feature is centred on the relative unusu-
alness of words, such as those used in organisational
jargon/terminology. Figure 3 is a demonstration of
how JARGES works when applied to a real sentence
in the organisation’s corpus. Detection works by
harnessing TF-IDF (Term Frequency, Inverse Docu-
ment Frequency). TF-IDF is a core NLP statistical
technique and was chosen as it is better at detecting
semantic importance than raw word counts (Jones,
1972). TF-IDF is used identify important (single and
multi-word) terms in an enterprise corpus and com-
pare their scores against general English frequencies.
A substantial difference between the two scores indi-
cates that the term may have a degree of jargon. While
1
https://github.com/colindaly75/JARGES
using TF-IDF to compare term salience across cor-
pora is not new, its application to Enterprise Search
for ranking jargon terms is novel.
Figure 3: An example of jargon / non-jargon classification
by JARGES when applied to a sentence in the corpus.
ES Corpus Vectorisation. The TfidfVectorizer
python library (Pedregosa et al., 2011) is used to con-
vert a collection of raw text document into a matrix
of TF-IDF features. It splits and tokenises the docu-
ment’s words into n-grams and then computes the TF-
IDF score for each n-gram in a document. The text
is vectorised into a numerical matrix where each row
represents a document and each column represents a
word’s TF-IDF score.
Detecting Divergence. The challenge is to detect en-
terprise specific words, phrases, expressions, and id-
ioms that diverge from those universally familiar or
understood outside of the organisation. This diver-
gence is measured by computing the absolute differ-
ence in TF-IDF scores for the terms.
SpaCy is an open source Python NLP library for
fast text processing that includes a small, pre-trained
statistical model for English called ‘en core web sm’.
The model is trained on web and news text data.
SpaCy has been shown to work well for standardised
English (e.g., formal writing, news, technical docu-
ments). For this reason, we use it as our reference
source of TF-IDF for common English.
Jargony. Moreover, the magnitude of the divergence
between the common score and the corpus score rep-
resents a measure of ‘jargony’ (i.e. how much jargon
is likely imbued in the term). For example, TfidfVec-
torizer computes the TF-IDF score of the word ‘black-
board’ in common English (i.e. en core web sm) is
X, whereas the score recorded from the organisation
corpus is Y. In the event where a term does not occur
in common English, but occurs frequently in the or-
ganisation’s corpus, this too is treated as jargon (e.g.
the ‘SCSS’ term shown in Table 1).
Refining the List. The size of the sorted list, which
includes both the jargon term and its corresponding
jargony score, is determined by the min divergence
parameter. In the case of our corpus, this was set
to be 15%, meaning that any jargon term with a TF-
JARGES: Detecting and Decoding Jargon for Enterprise Search
359
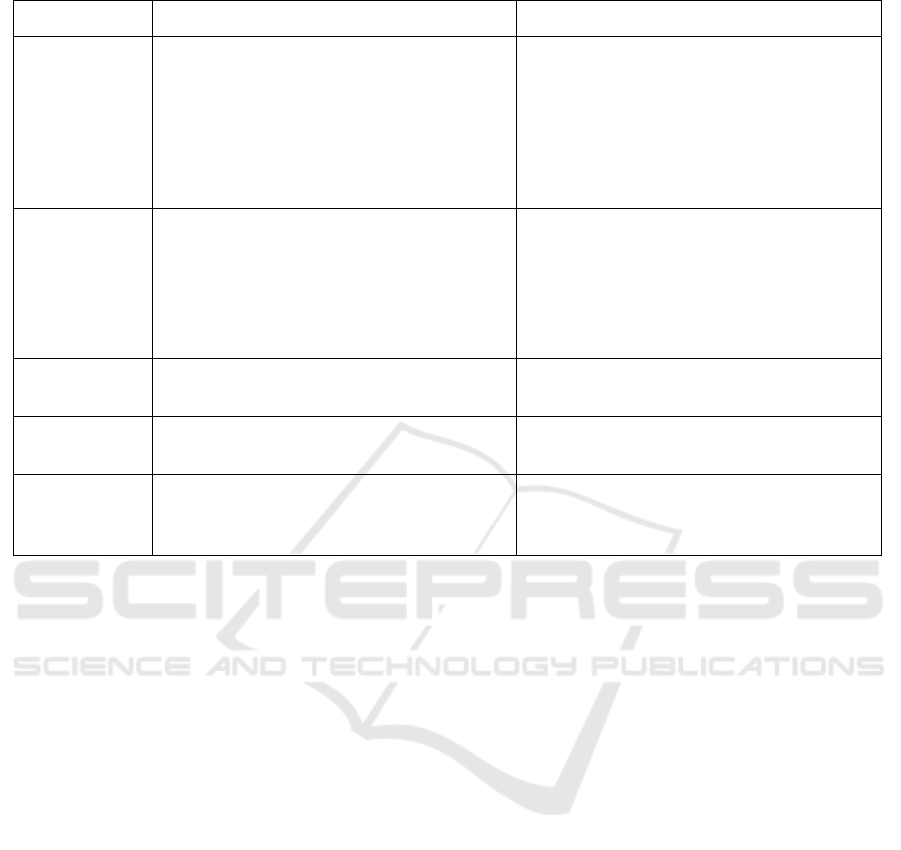
Table 1: JARGES classification. The terms in red font were successfully classified as jargon.
Jargon Term Wikipedia-api Definition Meaning within Organisation
Blackboard A reusable writing surface on which text
or drawings are made with sticks of
calcium sulphate or calcium carbonate,
known, when used for this purpose, as
chalk. Blackboards were originally made
of smooth, thin sheets of black or dark grey
slate stone.
Blackboard is an abbreviation of ‘Black-
board Learn’, which is the organisation’s
Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). Stu-
dents can use Blackboard to access lecture
notes, online assignments and other activi-
ties.
Atrium One of the two upper chambers in the
heart that receives blood from the circu-
latory system. The blood in the atria is
pumped into the heart ventricles through
the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid
heart valves.
Event space and meeting place in the Din-
ing Hall building which is often used by
student societies.
SCSS No definition. Initialism for ‘School of Computer Science
and Statiscics’.
Botany Bay An open oceanic embayment, located in
Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
A residential square located behind the
Graduates’ Memorial Building.
Hilary Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton (n
´
ee Rod-
ham;[a] born October 26, 1947) is an
American politician, lawyer and diplomat.
Hilary is the second of The University’s
three annual semesters, running from Jan-
uary to April.
IDF divergence smaller that this is discarded. This
is the same as the threshold adopted in Belfathi’s
study (Belfathi et al., 2024). Moreover, on visual in-
spection, the terms below this threshold did not intu-
itively appear jargon-like. This list is further refined
by filtering the jargon terms with those query terms
previously submitted to the search engine (this is the
ES query history input shown in Figure 2). Two years
of ES log data included 62,044 unique query terms.
The resultant list (named refined-jargon-list.txt) con-
sists of overlapping terms that are a) likely to be jar-
gon and b) have a history of being queried. For our
corpus, the refined list consisted of 547 records.
Blind Spot. A key limitation of the JARGES algo-
rithm is its reliance on TF-IDF score divergence be-
tween common terms and corpus specific terms. A
situation can occur when the divergence is too small
for detection, even where a term is clearly jargon. For
instance, as illustrated in the last row of Table 1, the
jargon term ‘Hilary’. The top Wikipedia-api defini-
tion presented changes the spelling from Hilary to
Hiliary (i.e. Clinton). The term Hilary exhibits com-
parable prominence in both sources, thereby prevent-
ing its identification as jargon. Resolving this issue
would require an alternative algorithm that differenti-
ates terms based on semantic meaning instead of TF-
IDF scoring.
3.1.2 Decoding
In the decoding stage, the RoBERTa language model
is adapted for synonym generation by fine tuning it
on the organisation’s corpus. RoBERTa is used to
predict plausible alternatives for the previously de-
tected jargon terms. Synonyms can enhance semantic
search by enabling the system to recognise and re-
trieve conceptually related terms beyond exact key-
word matches.
The synonyms are output to a text file in a format
that can be understood by the search engine. A practi-
cal consideration for Apache Solr is that the more spe-
cific terms should be listed in the file before general
ones (The Apache Software Foundation., 2004). The
synonyms are therefore ordered by their jargony score
(computed in the detection phase). To further priori-
tise specific over more general synonyms, the Solr
SynonymGraphFilterFactory is used as it has better
handling of multi-term and large synonym sets than
the default SynonymFilterFactory . This allows for
query-time synonym expansion, where unprioritised
synonyms are added to the query, while the original
query term is still gets top billing. The synonyms of
the jargon query terms should align with the descrip-
tion in the organisation’s ‘jargon buster’ PDF docu-
ment.
KDIR 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
360
3.2 LTR Ranking Model
Our ES LTR ranking model is generated using eight
features as part of the ENTRP-SRCH dataset. These fea-
tures include BM25, recency, document hits, linkrank
and click-though rate and are described fully in (Daly
and Hederman, 2023). A ninth feature, representing
JARGES is then added to the dataset to test its im-
pact. Table 2 describes the hyper-parameters used for
the LTR calculation.
Table 2: Hyperparameters used in the Learning to Rank ex-
periment.
Parameter Value
Dataset ENTRP-SRCH
Algorithm GradientBoosting
n estimators 100
max depth 3
learning rate 0.1
rank nDCG
random state 42
n splits 5
num features 8 (9 incl. JARGES)
4 EVALUATION
We conducted an A/B test comparing the ranking per-
formance for two models generated and evaluated us-
ing the ENTRP-SRCH dataset. The first model incor-
porated eight features from our base model, while
the second additionally included the JARGES feature.
By convention, we use the nDCG@10 metric, which
evaluates nDCG using the top 10 ranked results for
each query. The ranking scores for both models are
displayed in Table 3. The results indicate no signifi-
cant percentage change between the two.
Table 3: A/B test results for ranking models with the per-
centage change in nDCG score after implementation of the
JARGES feature.
Feature nDCG@10
Base LTR model 0.9646 ± 0.001
With JARGES 0.9639 ± 0.001
Percentage change 0.0007%
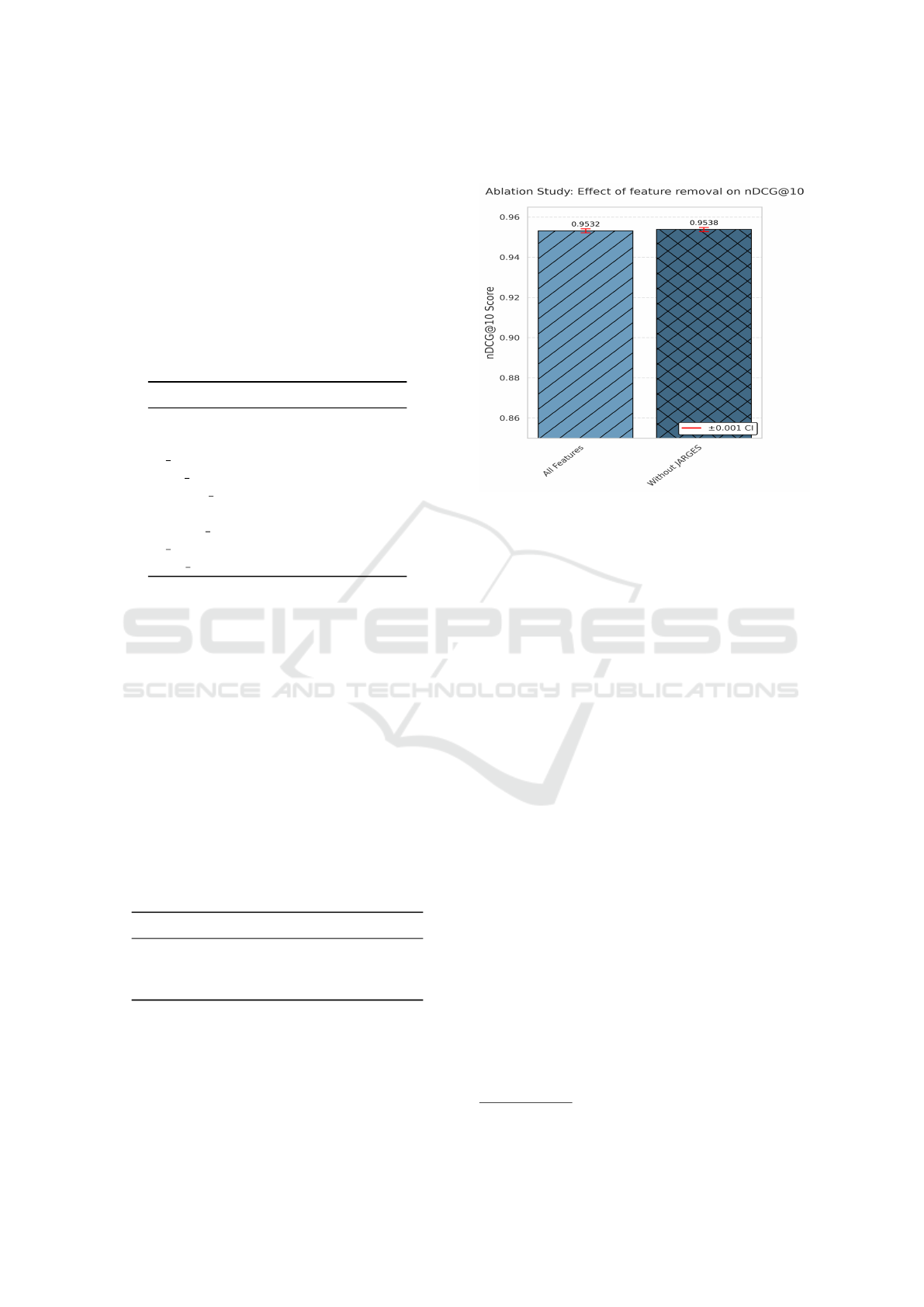
We also conducted a ‘leave-one-out’ ablation
study to evaluate the contribution of individual fea-
tures. This method systematically removes one fea-
ture at a time to measure its impact on the overall
model performance. As shown in Figure 4, remov-
ing the JARGES feature from the baseline model has
a negligible effect on ranking performance.
Figure 4: LTR ranking model performance (as measured by
nDCG@10) with and without JARGES.
Both experiments showed that there is no statisti-
cally significant improvement for nDCG@10 at the
5% level (with n=20, σ ≈ 0.01, the p value is >
0.05)
2
. This is attributed to the ENTRP-SRCH dataset’s
limited query diversity and scarcity of jargon rich
Query-Document pairs, which deflated the perfor-
mance score of the JARGES feature.
The ‘Jargon Buster’ PDF file acts as a indepen-
dent reference for assessing both the precision and
the comprehensiveness of the decoded jargon terms
(i.e. synonyms). Of the 126 jargon terms defined in
the PDF, 53 also appear in our generated list. Further-
more, a cursory inspection of the synonyms generated
for these terms appears to reflect the correct semantic
context. Some examples are shown in Table 4. In the
case of the polysemous ‘forum’ term, JARGES de-
tects the correct organisational meaning.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This study proposed the innovative ‘JARGES’ LM
based feature for detecting and decoding jargon, and
investigated the subsequent performance of ES rank-
ing models calibrated with LTR weightings. Quan-
titative testing using the ENTRP-SRCH dataset failed
to demonstrate a statistically significant increase in
ranking performance, as evidenced by an nDCG@10
2
https://github.com/colindaly75/JARGES
JARGES: Detecting and Decoding Jargon for Enterprise Search
361
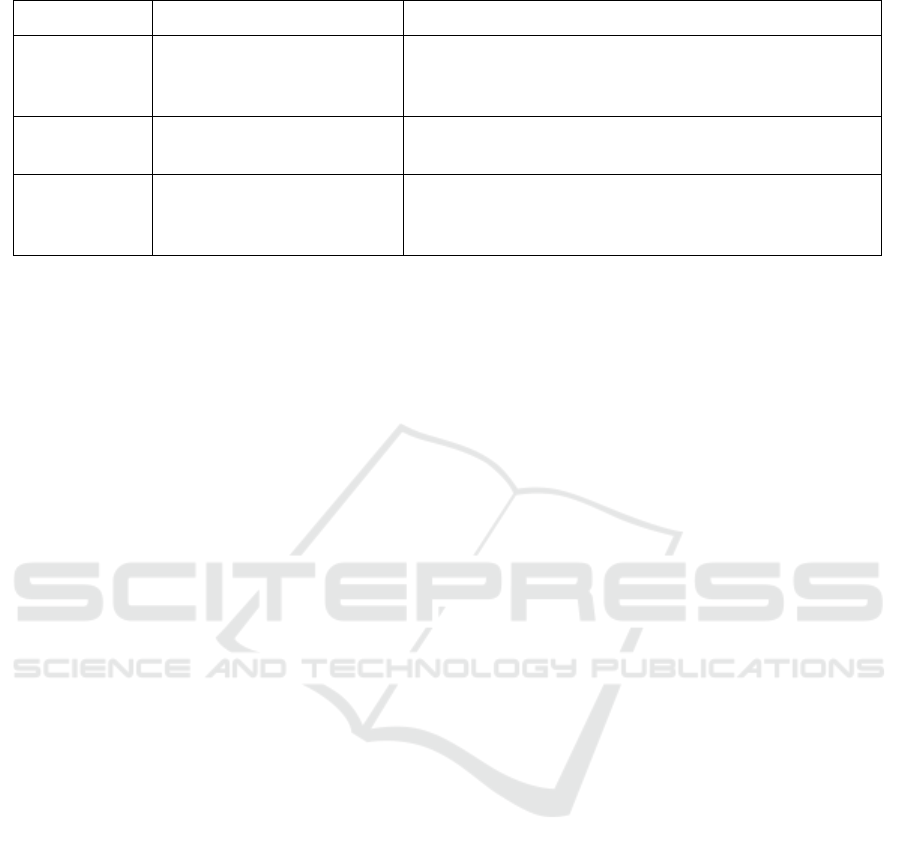
Table 4: Some examples of correctly decoded jargon terms via their contextual synonyms generated by RoBERTa.
Jargon Term Synonyms Meaning per ‘Jargon Buster’ document
pav pavilion, pavilion bar Formally, the Pavilion Bar. The University’s student bar,
managed by the Sport Union, located at the eastern end
of College Park.
tangent climate entrepreneurship,
social data science
The ideas workspace, providing courses and events cen-
tred on business and innovation.
forum cafe, restaurant College-operated eatery located in the Business School.
Here you’ll find hot and cold lunch offerings, barista cof-
fee, and - often - pop-ups run by local businesses.
change of less than 0.001 (where p > 0.05). This re-
sult is disappointing, but not entirely unexpected, as
the ENTRP-SRCH is small, with limited query diversity
and a scarcity of jargon rich Q-D pairs. In spite of this,
the qualitative analysis of the generated synonyms re-
vealed promising results for recall as a foundation for
semantic search.
Future work plans will employ additional inde-
pendent datasets to address the limitations of our
ENTRP-SRCH dataset, which centres on just twenty of
the most frequently submitted queries. The use of
click-through data in place of human judgements for
Q-D pair annotation would facilitate larger and more
diverse ES datasets that are better able to capture the
nuances of enterprise specific terminology. Finally, it
would be interesting to perform a longitudinal study
to gauge the JARGES impact on semantic and ex-
ploratory search, based on query expansion and recall
on a real-world ES system.
REFERENCES
Belfathi, A., Gallina, Y., Hernandez, N., Dufour, R., and
Monceaux, L. (2024). Language Model Adaptation
to Specialized Domains through Selective Masking
based on Genre and Topical Characteristics. arXiv,
2402.12036.
Bentley, J. (2011). Mind the Enterprise Search Gap: Smart-
logic Sponsor MindMetre Research Report.
Burges, C., Shaked, T., Renshaw, E., Lazier, A., Deeds, M.,
Hamilton, N., and Hullender, G. (2005). Learning to
rank using gradient descent. In ICML 2005 - Proceed-
ings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine
Learning, pages 89–96.
Cleverley, P. H. and Burnett, S. (2019). Enterprise search
and discovery capability: The factors and generative
mechanisms for user satisfaction:. Journal of Infor-
mation Science, 45(1):29–52.
Craswell, N., Cambridge, M., and Soboroff, I. (2005).
Overview of the TREC-2005 Enterprise Track. In
TREC 2005 conference notebook, pages 199–205.
Daly, C. (2023). Learning to Rank: Performance and
Practical Barriers to Deployment in Enterprise Search.
In 3rd Asia Conference on Information Engineering
(ACIE), pages 21–26. IEEE.
Daly, C. and Hederman, L. (2023). Enterprise Search:
Learning to Rank with Click-Through Data as a Sur-
rogate for Human Relevance Judgements. In 15th In-
ternational Conference on Knowledge Discovery and
Information Retrieval (KDIR), pages 240–247.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Google, K. T., and
Language, A. I. (2019). BERT: Pre-training of Deep
Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understand-
ing. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North,
pages 4171–4186.
Ganguly, D., Roy, D., Mitra, M., and Jones, G. J. (2015).
A word embedding based generalized language model
for information retrieval. SIGIR 2015 - Proceedings
of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on
Research and Development in Information Retrieval,
pages 795–798.
Google (2025). Search and SEO Blog — Google Search
Central — Google Search Central Blog — Google for
Developers.
Hawking, D. (2004). Challenges in Enterprise Search. In
Proceedings of the 15th Australasian Database Con-
ference - Volume 27, ADC ’04, page 15–24, AUS.
Australian Computer Society, Inc.
Jones, K. S. (1972). A statistical interpretation of term
specificity and its application in retrieval. Journal of
Documentation, 28(1):11–21.
Li, H. (2011). A Short Introduction to Learning to Rank.
IEICE Transactions, 94-D:1854–1862.
Li, L., Deng, H., Dong, A., Chang, Y., Baeza-Yates, R.,
and Zha, H. (2017). Exploring query auto-completion
and click logs for contextual-aware web search and
query suggestion. 26th International World Wide Web
Conference, WWW 2017, pages 539–548.
Liu, T.-Y. (2010). Learning to Rank for Information Re-
trieval, volume 3. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2nd
edition.
Liu, Y., Ott, M., Goyal, N., Du, J., Joshi, M., Chen, D.,
Levy, O., Lewis, M., Zettlemoyer, L., and Stoyanov,
V. (2019). RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT
Pretraining Approach. arXiv, 1(abs/1907.11692).
Pedregosa, F., Michel, V., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Pretten-
hofer, P., Weiss, R., Vanderplas, J., Cournapeau, D.,
KDIR 2025 - 17th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
362

Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Thirion,
B., Grisel, O., Dubourg, V., Passos, A., Brucher, M.,
Perrot and
´
Edouardand, M., Duchesnay, A., and Duch-
esnay EDOUARDDUCHESNAY, F. (2011). Scikit-
learn: Machine Learning in Python. The Journal of
Machine Learning Research, 12:2825–2830.
Pudasaini, S., Miralles-Pechu
´
an, L., Lillis, D., and Sal-
vador, M. L. (2024). Survey on Plagiarism Detection
in Large Language Models: The Impact of ChatGPT
and Gemini on Academic Integrity. Journal of Aca-
demic Ethics, 11(04).
Singh, S., Farfade, S., and Comar, P. M. (2023). Multi-
Objective Ranking to Boost Navigational Suggestions
in eCommerce AutoComplete. ACM Web Conference
2023 - Companion of the World Wide Web Conference,
WWW 2023, pages 469–474.
The Apache Software Foundation. (2004). Apache Solr.
Turnbull, D. and Berryman, J. (2016). Relevant Search.
Manning Publications Co., New York.
Wang, Q., Li, H., Xiong, H., Wang, W., Bian, J., Lu, Y.,
Wang, S., Cheng, Z., Dou, D., and Yin, D. (2024). A
Simple yet Effective Framework for Active Learning
to Rank. Machine Intelligence Research, 21(1):169–
183.
White, M. (2015). Critical success factors for enterprise
search.
Xu, J., Wei, Z., Xia, L., Lan, Y., Yin, D., Cheng, X.,
and Wen, J.-R. (2020). Reinforcement Learning to
Rank with Pairwise Policy Gradient. In Proceedings
of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on
Research and Development in Information Retrieval,
volume 10, page 10, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
JARGES: Detecting and Decoding Jargon for Enterprise Search
363
