
Toward Decentralized Digital Asset Management on the Blockchain
Luiz Vasconcelos J
´
unior, Bryan Diniz Borck, Celso Massaki Hirata
a
and Juliana de Melo Bezerra
b
Department of Computing Science, Instituto Tecnol
´
ogico de Aeron
´
autica (ITA), S
˜
ao Jos
´
e dos Campos, Brazil
Keywords:
Blockchain, Smart Contract, Asset Management, Decentralization, Cryptocurrency, Fund, Investment.
Abstract:
The emergence of cryptocurrencies has significantly altered the financial landscape, introducing both opportu-
nities and challenges, particularly within asset management. By harnessing the immutability and transparency
of blockchain technology, our goal is to present a model that enables the decentralization of the traditional
hedge fund industry by removing intermediaries. Our approach integrates smart contracts and pioneering
standards like ERC-6551, offering a way for managers to hold and operate investors’ assets securely. Further-
more, the model facilitates decentralized decision-making, enabling investors to participate in fund governance
using voting mechanisms. This work outlines a concrete path toward decentralizing asset management, mark-
ing a significant step in reshaping traditional practices and fostering innovation in the financial sector.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the evolving landscape of finance, asset manage-
ment has been a cornerstone, traditionally involving
the stewardship of investments like stocks, bonds, and
real estate. This field has seen considerable evolution
with the advent of sophisticated instruments, diverse
portfolios, and global investment opportunities. How-
ever, the most transformative change in recent years
has come with the emergence of cryptocurrencies.
The birth of cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin at the
helm, has revolutionized the concept of value transfer,
presenting a novel asset class that is not bound by tra-
ditional financial systems or geopolitical borders. The
growth of this market has been exponential, reflecting
a broader shift towards digital assets and compelling
the development of a crypto asset management mar-
ket. This burgeoning sector is swiftly expanding as
investors seek to capitalize on the volatility and po-
tential high returns of crypto assets.
The backbone of this transformation is blockchain
technology, a decentralized ledger that meticulously
records transactions across a network of computers
(Yaga et al., 2018). Blockchain’s inherent proper-
ties such as immutability, transparency, and security
have positioned it as the fundamental infrastructure
for cryptocurrencies (Ma and Huang, 2023) and for
many other applications in the real world (Vyas et al.,
2023b). The decentralization of blockchain technol-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9746-7605
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4456-8565
ogy not only enhances security but also democratizes
financial transactions by removing the need for cen-
tral intermediaries.
In traditional finance, intermediaries such as
banks and custodians are essential for trust and the ex-
ecution of transactions. Blockchain, however, ensures
trust through its consensus mechanisms and crypto-
graphic proofs, paving the way for secure peer-to-peer
transactions without centralized control. The secu-
rity in transactions, particularly in the realm of as-
set management, is paramount. Blockchain’s archi-
tecture provides a level of security that is critically
important for investors and asset managers alike, safe-
guarding against fraud and unauthorized access.
Despite these advancements, the majority of
crypto transactions today occur on centralized ex-
changes. These platforms, while user-friendly, hold
the same structural vulnerabilities as traditional finan-
cial systems, including the risk of hacks, fraud, and
mismanagement. They operate as de facto custodians
of assets, which contradicts the decentralized ethos
of blockchain. The aspiration to decentralize this as-
pect of the cryptocurrency market has been gaining
momentum. We intend to investigate this significant
gap by proposing a blockchain-based approach that
removes the custodian.
The blockchain technology can streamline many
complex and labor-intensive processes in hedge fund
operations, such as compliance checks and perfor-
mance fee calculations, through smart contracts. Ad-
ditionally, the immutability and transparency inher-
Vasconcelos Júnior, L., Borck, B. D., Hirata, C. M. and Bezerra, J. M.
Toward Decentralized Digital Asset Management on the Blockchain.
DOI: 10.5220/0013726900003985
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2025), pages 189-196
ISBN: 978-989-758-772-6; ISSN: 2184-3252
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
189

ent in blockchain foster greater investor trust. It is
estimated that blockchain could reduce financial ser-
vices infrastructure costs up to $20 billion annually
(Wyman et al., 2015).
The launch of the ERC-6551 standard marked
a critical advancement in blockchain security and
functionality, and was considered one of the most
significant improvements in the tokenization ecosys-
tem (Thornton, 2022). ERC-6551 introduces Token
Bound Accounts (TBAs), creating a smart contract
wallet for every NFT (Non-Fungible Token), mak-
ing them more composable, dynamic, and interac-
tive. These accounts provide an immutable record
of all on-chain activities, thereby enhancing the re-
liability and utility of digital assets. This innovative
standard opens new possibilities in blockchain appli-
cations, presenting an opportunity for the hedge fund
industry to integrate advancements while adhering to
strict security and compliance standards.
Our proposal leverages the ERC-6551 protocol,
providing a decentralized model that empowers as-
set managers to securely hold and manage investors’
assets on chains based on the Ethereum Virtual Ma-
chine (EVM). This innovation is poised to disrupt
the current asset management paradigm, offering a
decentralized alternative that ensures security, trans-
parency, and control for both investors and managers,
without the need for intermediaries. We also explore
the opportunity of establishing a Decentralized Au-
tonomous Organization (DAO), to facilitate decen-
tralized decision-making by investors and promote
broader community governance.
The paper is structured as follows. In the next sec-
tion, we provide the background of our work. Section
3 presents our model for decentralizing asset manage-
ment using blockchain. Section 4 delves into the ini-
tial results, elucidating the proof-of-concept that was
developed. The final section concludes the paper, ad-
dressing broader implications and outlining the sub-
sequent steps.
2 BACKGROUND
There is a substantial body of work related to utiliz-
ing blockchain to decentralize financial systems and
industries. The whitepaper presented in (Madeira
et al., 2023) discusses a blockchain-based platform,
named DeLend, for managing real-world assets in
credit, particularly for small and medium-sized en-
terprises (SMEs) in Brazil. This work employs Non-
Fungible Tokens (NFTs) to represent funds and liq-
uidity pools, creating opportunities for executing real
operations with investors and borrowers. It is similar
to our approach; however, our perspective differs as
we focus on the decentralized management of digital
assets rather than credit-related aspects.
Pablo et al. address the limitations of current Non-
Fungible Token (NFT) platforms and introduce Uni-
Con, a novel infrastructure for digital asset manage-
ment (Pablo et al., 2021). UniCon aims to overcome
shortcomings of NFT platforms by implementing a
scalable infrastructure that is not tied to any specific
blockchain, supports transactions in any digital cur-
rency, and incorporates verified digital identities to
reduce fraud. The system is designed to be univer-
sal and scalable, enabling efficient management and
transfer of digital assets. Using an EVM-compatible
blockchain, our proposal integrates the ERC-6551
standard to allow asset managers to hold multiple to-
kens from investors.
ERCs stands for “Ethereum Request for Com-
ments”. ERCs are a set of technical standards
used to create and manage tokens on the Ethereum
blockchain. These standards provide guidelines for
the development of smart contracts and dApps (de-
centralized applications) that can be applied to create,
manage, and exchange tokens on the Ethereum net-
work. ERCs define a set of rules that all Ethereum-
based tokens must follow, ensuring consistency and
interoperability within the ecosystem. In a way to
provide a foundation for our proposal, we describe the
main types of ERCs, including ERC-20, ERC-721,
and ERC-6551.
ERC-20 is the most widely known and used ERC
standard that defines a common interface for creating
fungible tokens, allowing them to be seamlessly in-
tegrated with wallets, exchanges, and smart contracts
by standardizing key functions such as transfers, ap-
provals, and balance tracking. ERC-721 introduces
the concept of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), which
are unique and cannot be interchanged on a one-for-
one basis. Each ERC-721 token is distinct and can
represent ownership of specific assets. ERC-721 laid
the foundation for the NFT market, revolutionizing
the way we think about digital ownership and spawn-
ing new forms of digital collectibles and art. ERC-
6551 is a new standard for NFTs introducing Token
Bound Accounts (TBAs), which relate a smart con-
tract account for a given ERC-721 token, enhancing
security and control. ERC-6551 offers dynamic and
interactive experiences for NFT collectors and cre-
ators, improving fraud prevention, ownership control,
and interoperability. Its applications extend to self-
governing entities like DAOs, token distribution and
secure supply chain solutions (Vyas et al., 2023a).
In the asset management industry, the application
of ERC protocols brings three main benefits. The first
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
190

gain is the tokenization of assets, since NFTs enable
the tokenization of real-world assets, simplifying the
digital buying, selling, and trading of assets. This
tokenization extends to a diverse range of assets, in-
cluding real estate, art, and intangible assets like in-
tellectual property. The second benefit is related to
improved transparency and security, as the utilization
of blockchain ensures that all transactions are trans-
parent and immutable. It minimizes the risk of fraud,
fostering increased trust among the parties involved in
transactions. The third advantage is automated com-
pliance and governance, since smart contracts, inte-
gral to ERC protocols, enable the automation of var-
ious compliance and governance tasks. This automa-
tion reduces reliance on intermediaries, streamlining
processes and enhancing overall efficiency.
3 A BLOCKCHAIN-BASED
MODEL FOR
DECENTRALIZING ASSET
MANAGEMENT
In this section, we outline our proposal, beginning
with a review of the actors within a conventional mar-
ket structure governed by centralized management.
Subsequently, we elucidate the transition towards de-
centralization, highlighting independence from custo-
dial entities and the consolidation of investor partici-
pation in decision-making processes.
3.1 Traditional Market
Asset management today involves a complex web
of interactions between investment funds, custodi-
ans, and exchanges. Investment funds, often com-
prising diverse portfolios of digital assets, operate
within a centralized structure, where fund managers
wield significant control over decision-making pro-
cesses. These managers devise strategies, allocate
assets, and rebalance assets based on market condi-
tions, investors’ preferences, and the fund’s overar-
ching goals. However, the centralized nature of these
operations introduces inherent vulnerabilities, such as
single points of failure, compromised trust, and sus-
ceptibility to regulatory changes.
In the current landscape, custodians play a piv-
otal role by safeguarding the digital assets held by
funds. These custodial entities serve as trusted in-
termediaries, responsible for secure storage, mainte-
nance, and, at times, even execution of transactions
on behalf of the funds (Davies, 2023). Addition-
ally, exchanges act as the marketplace where assets
are bought, sold, and traded. The interplay between
funds, custodians, and exchanges lays the foundation
for the asset management landscape, influencing the
efficiency, security, and overall success of digital as-
set portfolios.
To provide context, the traditional market cur-
rently involves the following stakeholders: Investor,
Distributor, Exchange, Custodian and Fund. The In-
vestor, whether an individual or organization, allo-
cates capital with the expectation of generating profit
over time. On the other hand, the Distributor acts
as an intermediary, marketing and selling financial
products to investors. The Exchange serves as a cru-
cial platform for buying and selling financial assets.
Simultaneously, the Custodian is an entity that safe-
guards and manages financial assets. Ultimately, the
Fund refers to a pooled investment vehicle managed
professionally.
The flow of a traditional fund investment can be
explained through the relations among the stakehold-
ers as outlined below.
• Investor & Fund: Investors obtain a share in the
fund by paying a management fee to the man-
ager and a performance fee based on a percent-
age above the market benchmark. The fee struc-
ture aligns the managers’ interests with the invest-
ment, as they earn fees for effectively operating
the fund.
• Distributor & Fund: Acting as a crucial inter-
mediary, the distributor bridges the gap between
the fund and potential investors. Responsibili-
ties involve the promotion and sale of the fund’s
financial products. Through collaborations and
agreements, distributors contribute to expanding
the fund’s reach, increasing assets under manage-
ment, and enhancing overall visibility and acces-
sibility.
• Exchange & Fund: Exchanges serve as essential
platforms where funds actively engage in trading
activities. Here, funds can acquire or dispose of
assets in line with their investment strategies. By
providing a transparent environment, exchanges
enable funds to execute trades based on real-time
market conditions, contributing to the price dis-
covery process and helping achieve investment
objectives.
• Custodian & Fund: Custodians play a pivotal role
in safeguarding the fund’s assets, ensuring secure
holdings resistant to theft or loss. Beyond asset
safekeeping, custodians assist in transaction set-
tlements and provide administrative services, en-
suring a smooth operational flow and compliance
with regulatory requirements.
Toward Decentralized Digital Asset Management on the Blockchain
191

The core idea of decentralized asset management
is to eliminate reliance on custodial entities, as we ex-
plain as follow.
3.2 Towards Decentralization
The centralized control exerted by fund managers
and the reliance on custodians introduce counter-party
risks and potential conflicts of interest. Furthermore,
the interaction between funds and exchanges can be
hindered by inefficiencies, delays, and sometimes ex-
orbitant transaction costs. Regulatory compliance, a
critical aspect of the financial industry, adds an addi-
tional layer of complexity, with funds and custodians
navigating through a maze of evolving guidelines.
In the context of the decentralized future, how-
ever, there lies a promising prospect for mitigating
these challenges. Blockchain technology and decen-
tralized finance (DeFi) protocols offer the potential
to revolutionize the asset management industry by re-
moving traditional players, causing a good disruption
in the financial enviroment (Sarathy, 2023). By lever-
aging the power of smart contracts and blockchain,
asset management can become more secure, efficient,
and resistant to centralized risks. This shift towards
decentralization not only addresses current challenges
but also opens doors to new possibilities, fostering a
more inclusive and resilient digital asset management.
Our proposed model can be seen in Figure 1. Here
all stakeholders (presented in the traditional market)
are kept, except the Custodian. The traditional Dis-
tributor is replaced by a component called Whale Fi-
nance, which is a system supported by blockchain
to allow secure transactions. The Exchange is repre-
sented by an online platform focused on swap trading,
for instance, Uniswap (Uniswap, 2023). Uniswap is a
decentralized cryptocurrency exchange protocol that
operates on the Ethereum blockchain. It enables users
to swap various Ethereum-based tokens directly from
their wallets without the need for a traditional order
book or centralized intermediary (Sadykhov et al.,
2023).
The relations shown in Figure 1 are detailed here.
Investor pays performance and administration fees to
Distributor, whereas he keeps earning profit of his in-
vestments. Manager receives fees due to the manage-
ment of the fund. Manager in fact works through the
Whale Finance to create the fund and operate it using
swaps (i.e., the exchange of tokens). Swaps are now
on-chain transactions using the available Exchange.
As we can note, the Custodian is removed. Below,
we detail how the incorporation of ERC-6551 allows
it. We explain the fund creation, the investment flow,
and the swap flow, which are implemented through
three main Solidity smart contracts, namely: Whale-
Finance.sol, SafeAccount.sol, and QuotaToken.sol.
3.3 Removing the Custodian
The WhaleFinance.sol contract is the core contract
that allows the operationalization of decentralized as-
set management. This contract inherits from the
ERC721 standard (the implementation of an NFT col-
lection) implemented by Open Zeppelin (OpenZep-
pelin, 2023). So, the fund is represented by an NFT.
Figure 2 shows the flow of fund creation. The Whale-
Finance.sol creates (or mints) a fund with the follow-
ing parameters:
• Name: The official title of the fund, used for
recognition and branding.
• Symbol: A unique series of letters representing
the fund in the stock market, used for quick iden-
tification.
• Manager Address: The designated account for
managing the fund’s financial transactions and
maintaining records. It is indeed the manager’s
account, being represented in Figure 2 by the re-
lation between NFT and Manager.
• Tokens: Digital assets within the fund that can
represent shares or other assets, facilitating flexi-
ble transactions. One example is the token zUSD,
a stablecoin of USD coin.
• Administration Fee: A charge levied to cover the
fund’s operational costs, maintaining its viability.
• Performance Fee: A fee charged based on the
fund’s performance, serving as an incentive to
managers.
• Open Investment Date: The earliest time at which
investments can be made into the fund, helping to
manage the inflow of capital.
• Close Investment Date: The latest time at which
the fund stops accepting new investments, assist-
ing in portfolio stability.
• Maturation Date: The projected time for the fund
to reach its investment goals, guiding investors on
expected returns.
Our solution makes use of ERC-6551 (the stan-
dard for Token Bound Accounts, TBAs) to avoid
dependence on a Custodian by establishing the
logic that allows an NFT to own a smart con-
tract account (known as TBA). Through this strat-
egy, the fund can validate ownership by a desig-
nated manager (given an NFT) and execute trans-
actions involving its assets registered in an ac-
count (given a TBA). The ERC-6551 standard de-
fines two interfaces: IERC6551Registry.sol and
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
192
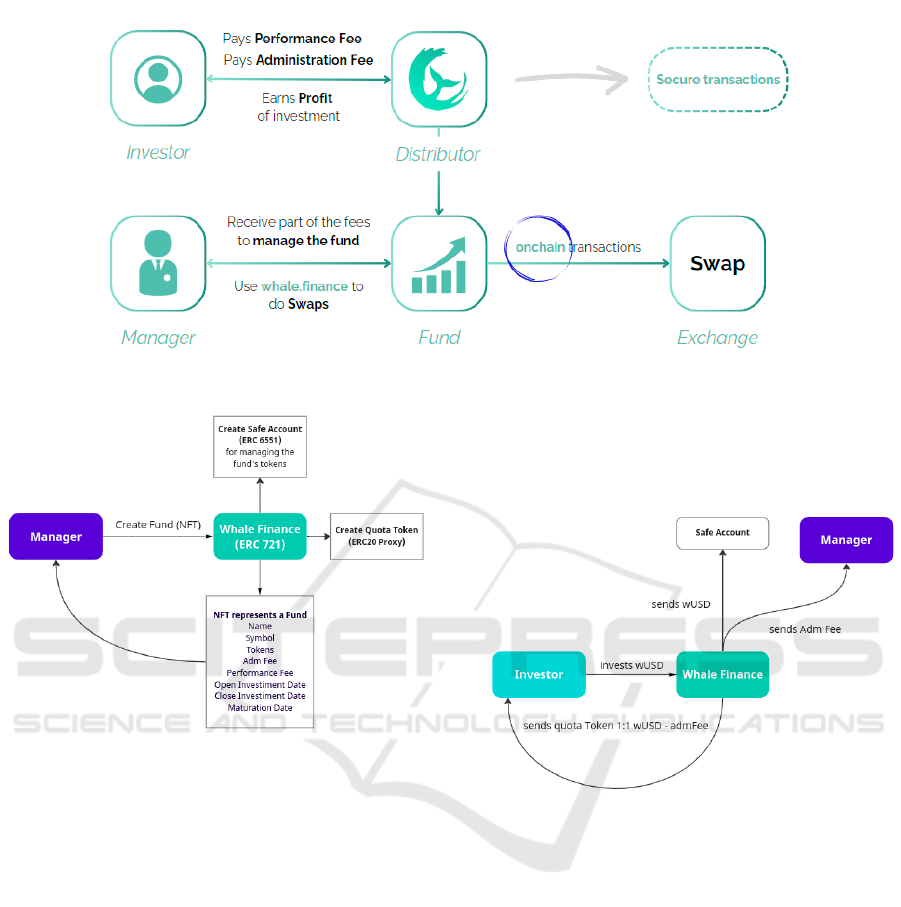
Figure 1: A Decentralized Asset Management Model supported by Blockchain.
Figure 2: Fund creation flow.
IERC6551Account.sol. The registry is the contract
used to create accounts. According to Figure 2, an ac-
count is linked to the fund address (here represented
by the NFT created through WhaleFinance.sol) and
to the account implementation (here represented by
SafeAccount.sol). The SafeAccount.sol contract, in
fact, inherits from the IERC6551Account.sol and im-
plements additional features related to swap. The
fund creation flow, in Figure 2, is also responsible for
defining a token (using the standard ERC-20) used to
create fund quotas, allowing later investors to acquire,
hold, and trade fund quotas in a standardized and in-
teroperable format.
The investment flow is represented in Figure 3.
For the purpose of standardization, a trusted stable-
coin can be chosen for investments. Here, wUSD is
used to illustrate the scenario. The investor sends the
assets to the fund through the Whale Finance. The
assets that the fund owns are then deposited in the re-
lated Safe Account, and the manager is able to control
them in a safe and limited way. After investing, the
Investor receives tokens (known as Quota Token) of
the fund. Here, for example, we define the quantity of
Quota Tokens as the total invested minus the adminis-
tration fee.
Figure 3: Investment flow.
Sending the assets to the Safe Account, the man-
ager (who holds the fund) is able to make invest-
ments, in particular through a decentralized exchange.
This investment is performed using a swap, where the
manager swaps the stablecoin sent by the investor for
other assets, such as WETH, WBTC, LINK or any fun-
gible asset with a liquidity pool. In our proposal,
the SafeAccount.sol implements the logic of swap-
ping using the interface IV2SwapRouter.sol to inter-
act with the decentralized exchange (DEX) Uniswap.
The flow is shown in Figure 4. To implement that, we
have forked Uniswap and deployed our version in an
Ethereum testnet so that we can use it for testing.
3.4 Empowering Investors
When minting a fund, as indicated in Figure 2, an-
other contract is created: the QuotaToken.sol. This
Toward Decentralized Digital Asset Management on the Blockchain
193
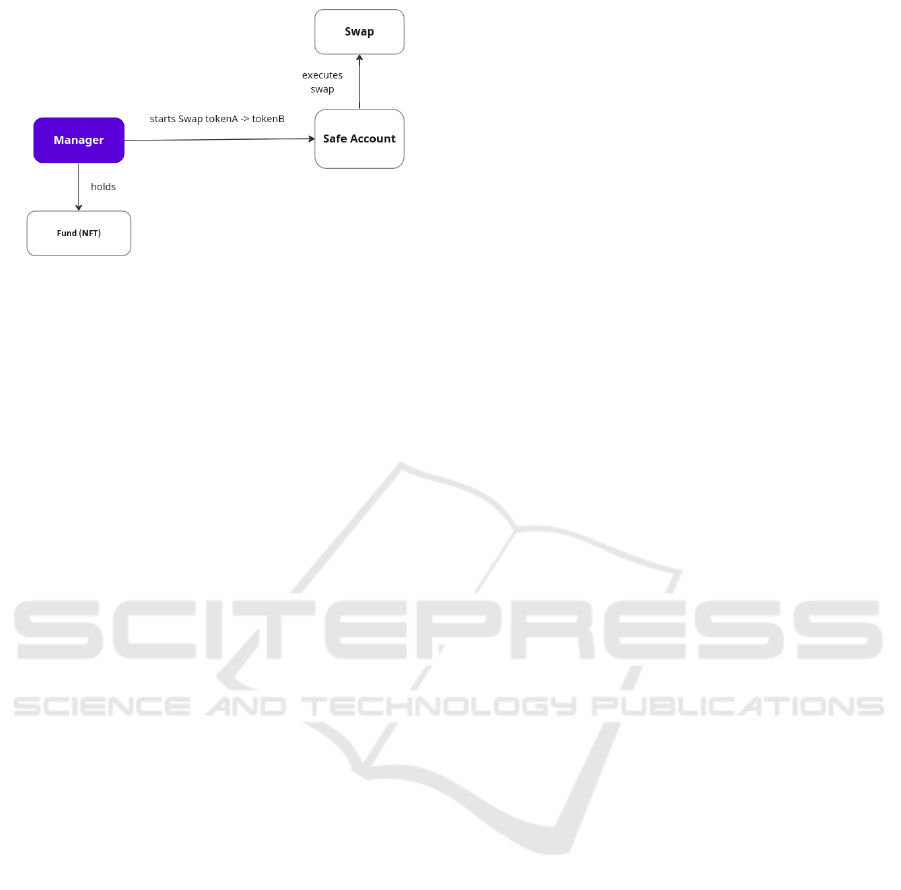
Figure 4: Indirect swap flow.
contract inherits from the ERC-20, the standard for
fungible tokens deployment. The idea is that the in-
vestors will own these tokens both for redeeming pos-
sible yields after the fund is mature and voting on pos-
sible proposals for changes in the fund. The opportu-
nity of voting is the foundation to implement a DAO
(Decentralized Autonomous Organization), where de-
cisions are made collectively by members based on
the voting mechanisms without the interference of the
central authority (in this case, the fund manager).
According to Figure 3, investors receive Quota To-
kens upon making an investment. Consequently, in-
dividuals with higher investment amounts will pos-
sess more tokens, granting them increased influence
in making future decisions related to the fund. This
approach empowers investors by transforming them
from passive observers of the manager’s decisions to
active contributors, enabling them to play a role in en-
hancing the overall fund performance.
Specifically regarding the contract development,
QuotaToken.sol is implemented as ERC-20 token and
BeaconProxy, following Open Zeppelin standards.
Each fund has its own Quota Token that is initial-
ized when the fund is created. The QuotaToken.sol is
deployed to an address and each new quota uses this
implementation to be created. The Beacon delegates
the calls to the unique QuotaToken.sol implementa-
tion, so we can upgrade the implementation without
the need to update every fund contract.
Voting is particularly important in case of in-
vestors desires to change the moment of closing in-
vestments (parameter Close Investment Date of the
fund) to allow or prevent new contributions. Besides,
investors may want to change the moment of invest-
ment redemption (parameter Open Reedem Date of
the fund), for instance, if a manager is performing
poorly in the fund, and investors want to redeem their
investments earlier to avoid further losses, prompting
the need to initiate a vote. Moreover, investors can
vote to propose specific investment transactions (the
swaps).
Given the voting about Open Reedem Date in
WhaleFinance.sol, there are functions to consider as-
pects as the creation of the change proposal, the vot-
ing process, the change implementation, and the us-
age of Quota Tokens in voting. In the beginning, an
investor creates a new proposal to change the redemp-
tion timestamp of a specific fund. The proposal be-
comes open to voting during a specified voting pe-
riod. Investors can vote on the proposal considering
their Quota Tokens. It is possible to check the quantity
of votes received by a specific proposal, offering an
overview of the total accumulated support for chang-
ing the fund’s redemption timestamp. If the proposal
is approved with a sufficient percentage of votes, the
fund’s redemption timestamp is updated. After the
proposal is approved or after the voting deadline ex-
pires, investors can withdraw their Quota Tokens that
were linked to that proposal.
4 A PROOF OF CONCEPT
A proof of concept was developed to validate our pro-
posal, focused on following the best practices for the
smart contracts application, according to the direc-
tives found in (Mustafa et al., 2023). To integrate
smart contracts, an app was developed using Type-
script.js (a language focused on project scalability),
Tailwind.CSS (a framework to facilitate page design),
and Vite.js (a build tool to better initialize the project
on the web). From this stack, a way was conceived
for users (including investors and managers) to have
a good user experience.
A manager has the ability to create a fund, moni-
tor its performance, and execute token swaps to man-
age the fund (as illustrated in Figure 5). Investors can
access statistics (such as performance charts) of the
available funds (refer to Figure 6), enabling them to
choose funds to invest. In terms of the voting pro-
cess, investors can initiate new proposals to modify
the open redemption date and participate in voting for
existing proposals.
Aiming to test the smart contract transactions, the
creation of our proof of concept with Forge (ForgeS-
tandardLibrary, 2023) allows the use of native solid-
ity tests. The tests cover different functionalities of
the WhaleFinance.sol smart contract, including fund
creation, investment, proposal rejection, and proposal
acceptance, as follows:
• testCreateFund(): It tests the creation of a new
fund, checking if the returned values are correct
and if the fund owner matches the expected ad-
dress.
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
194
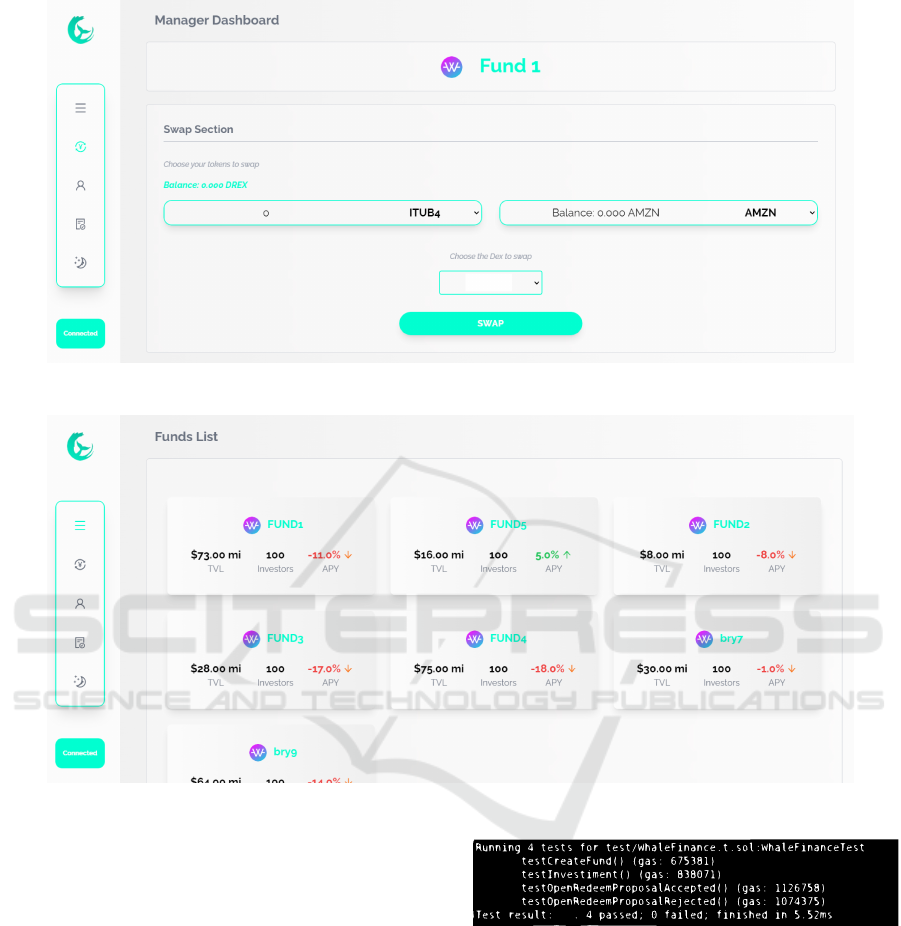
Figure 5: Manager dashboard.
Figure 6: List of funds to invest.
• testInvestiment(): It tests the investment process
in a fund. It verifies whether an investor can invest
a specific amount in a newly created fund. After
the investment, it checks if the investor’s quota to-
ken balance has been updated correctly.
• testOpenRedeemProposalRejected(): It simulates
a proposal for changing the open redeem times-
tamp being rejected. It tests whether the func-
tionality of voting and rejecting a proposal for a
timestamp change works properly.
• testOpenRedeemProposalAccepted(): It simu-
lates a proposal for changing the open redeem
timestamp being accepted. It tests whether the
functionality of voting and accepting a proposal
for a timestamp change works properly.
All tests passed, as shown in Figure 7, confirm-
ing that the features behave as intended. These are
Figure 7: Test results using Forge.
initial unit tests focused on validating isolated func-
tionalities. However, more test scenarios must be de-
fined and executed, including clear specifications of
expected inputs and outputs. In addition, larger-scale
evaluations that involve multiple users are necessary
to assess the system’s feasibility and performance.
Our proposal, named Whale Finance, has im-
mense potential for expansion and integration. By
incorporating advanced features, comprehensive an-
alytics, and robust security protocols, the platform’s
capabilities can be significantly extended, enhancing
both its functionality and overall appeal. The inte-
Toward Decentralized Digital Asset Management on the Blockchain
195

gration with well-established financial applications,
cryptocurrency exchanges, and wallet services would
not only extend the model’s reach but also promote
a more seamless and user-friendly experience. Fur-
thermore, forming strategic partnerships with lead-
ing financial institutions and fintech firms can provide
Whale Finance with broader market access, invalu-
able expertise, and enhanced credibility.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Our proposed blockchain-based model, the Whale Fi-
nance, aims to advance the asset management in-
dustry through the implementation of a decentralized
paradigm using the ERC-6551 protocol. The main
advantage is the ability to offer a more autonomous
and cost-effective solution for asset management. By
not relying on intermediaries, Whale Finance reduces
operational costs and offers greater control to both in-
vestors and managers.
This approach stands out for its innovative use of
blockchain technology, particularly in hedge funds,
ensuring the efficiency, transparency, and security of
financial transactions. The incorporation of smart
contracts and the utilization of the Ethereum Virtual
Machine (EVM) further streamline processes, ensur-
ing compliance with regulatory standards while main-
taining flexibility and ease of transactions.
By developing a proof of concept, we overcame
numerous challenges, including technical complexi-
ties associated with blockchain implementation and
integration with existing financial systems. However,
we recognize that the real-world adoption of the pro-
posed model may also face significant challenges,
particularly regarding the widespread understanding
and acceptance of blockchain technology within the
traditional finance sector.
To demonstrate the proposal’s efficacy in real-
world scenarios, a thorough and systematic validation
process is paramount. This process begins with rig-
orous market testing, accompanied by the collection
of user feedback. The analysis of performance met-
rics, including user engagement, transaction volume,
and security effectiveness, is essential over the testing
period. These indicators will shed light on how well
our proposal resonates with the market and its opera-
tional efficiency. Additionally, a comparative analysis
with existing asset management solutions can illumi-
nate our competitive edges.
For future work, the focus will be on enhancing
the scalability of the system, increasing user adop-
tion by simplifying the interface and user experience,
and continuously updating the proposal to align with
evolving blockchain technologies and financial regu-
lations. Additionally, further research and develop-
ment will be geared towards expanding the platform’s
capabilities to encompass a broader range of assets
and services, thus broadening its applicability and im-
pact in the global financial landscape.
REFERENCES
Davies, J. (2023). Enhanced scalability and privacy
for blockchain data using merklized transactions in
blockchain technologies. Frontiers in Blockchain.
ForgeStandardLibrary (2023). https://book.getfoundry.sh/
reference/forge-std/.
Ma, W. and Huang, K. (2023). Blockchain and Web3:
Building the Cryptocurrency, Privacy, and Security
Foundations of the Metaverse. Wiley.
Madeira, G., Novaes, F., Cerqueira, A., Steler, F., and Car-
valho, L. (2023). Cbdcs, open finance, and tokeniza-
tion as tools to improve financial intermediation: Ap-
plication to a smes’ credit platform.
Mustafa, I., McGibney, A., and Rea, S. (2023). Smart con-
tract life-cycle management: An engineering frame-
work for the generation of robust & verifiable smart
contracts (grv-sc) in financial blockchain. Frontiers in
Blockchain.
OpenZeppelin (2023). https://github.com/OpenZeppelin.
Pablo, R., Pouwelse, J., and Vos, M. D. (2021). Unicon:
Universal and scalable infrastructure for digital asset
management.
Sadykhov, R., Goodell, G., Montigny, D. D., Schoernig, M.,
and Treleaven, P. (2023). Decentralized token econ-
omy theory (detect): Token pricing, stability and gov-
ernance for token economies. Frontiers in Blockchain.
Sarathy, R. (2023). Enterprise Strategy for Blockchain:
Lessons in Disruption from Fintech, Supply Chains,
and Consumer Industries. The MIT Press.
Thornton, G. (2022). 2023 outlook for blockchain and dig-
ital assets in business. Grant Thornton.
Uniswap (2023). https://uniswap.org/.
Vyas, N., Beije, A., and Krishnamachari, B. (2023a).
Blockchain and the Supply Chain: Concepts, Strate-
gies and Practical Applications. Kogan Page.
Vyas, S., Shukla, V. K., Gupta, S., and Prasad, A.
(2023b). Blockchain Technology: Exploring Oppor-
tunities, Challenges, and Applications. CRC Press.
Wyman, O., Group, A., and Innoventures, S. (2015). The
fintech 2.0 paper: rebooting financial services.
Yaga, D., Mell, P., Roby, N., and Scarfone, K.
(2018). Blockchain technology overview NIS-
TIR 8202. https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/ir/2018/
NIST.IR.8202.pdf Accessed on 2024-01-02.
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
196
