
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious
Penetration Testing
Xiaojuan Cai
1 a
, Lulu Zhu
1 b
, Zhuo Li
1 c
and Hiroshi Koide
2 d
1
Department of Information Science and Technology, Information Science and Electrical Engineering, Kyushu University,
Fukuoka, Fukuoka, Japan
2
Section of Cyber Security for Information Systems, Research Institute for Information Technology, Kyushu University,
Fukuoka, Fukuoka, Japan
Keywords:
Internet Security, Penetration Testing, Reinforcement Learning, Constrained Optimization.
Abstract:
Penetration testing, which identifies security vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them, is essen-
tial for strengthening cybersecurity defenses. Effective testing helps discover deep, high-impact vulnerabilities
across complex networks, while efficient testing ensures fast execution, low resource utilization, and reduced
risk of detection in constrained or sensitive environments. However, achieving both effectiveness and effi-
ciency in real-world network environments presents a core challenge: deeper compromises often require more
actions and time. At the same time, excessively conservative strategies may miss critical vulnerabilities. This
work addresses the trade-off between maximizing attack performance and minimizing operational costs. We
propose a multi-objective reinforcement learning framework that minimizes costs while maximizing rewards.
Our approach introduces a Lagrangian-based policy optimization scheme in which a dynamically adjusted
multiplier balances the relative importance of rewards and costs during learning. We evaluate our method
on benchmark environments with varied network topologies and service configurations. Experimental results
demonstrate that our method achieves successful penetration performance and significantly reduces time costs
compared to the baselines, thereby improving the adaptability and practicality of automated penetration testing
in real-world scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
Penetration testing is an essential defense strategy in
cybersecurity, which identifies network vulnerabili-
ties before malicious actors exploit them. Penetra-
tion testing involves simulating realistic attack scenar-
ios, such as unauthorized access, lateral movement,
or privilege escalation, to assess the security posture
of systems, networks, or applications (Teichmann and
Boticiu, 2023; Jeff and Kala, 2024; Hayat and Gatlin,
2025).
As the complexity of network systems grows, the
increasing cybersecurity challenges make penetration
testing play a more critical role, especially in cloud in-
frastructures, IoT deployments, and software-defined
environments (Skandylas and Asplund, 2025; Ankele
et al., 2019). In these dynamic and complex network
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-4242-8420
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-5889-1374
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0602-7664
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-7111-8053
environments, the effectiveness of penetration testing
refers to discovering high-impact vulnerabilities and
reaching sensitive targets. Effective penetration test-
ing policies help identify vulnerabilities before the
deployment of network systems and avoid severe fi-
nancial loss (Bandar Abdulrhman Bin Arfaj, 2022;
Fadhli, 2024; Caddy, 2025). On the other hand, pen-
etration testing must be efficient. The reason is that
penetration testing policies have to identify vulnera-
bilities in sensitive, dynamic, or large-scale systems,
while time, bandwidth, stealth, and resource usage are
all constrained (Li et al., 2025b; Kong et al., 2025;
Li et al., 2025a). Efficient testing minimizes risks,
avoids unnecessary exposure, and ensures real-world
practicality (Zennaro and Erd
˝
odi, 2023).
However, effectiveness and efficiency are often
in conflict for penetration testing policies. Achiev-
ing deeper compromises typically demands more time
and incurs higher risk, while overly conservative
strategies may terminate early or fail to identify seri-
ous vulnerabilities (Erd
˝
odi and Zennaro, 2022; Pham
et al., 2024; Luo et al., 2024). Balancing this trade-off
374
Cai, X., Zhu, L., Li, Z. and Koide, H.
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013713400003985
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2025), pages 374-385
ISBN: 978-989-758-772-6; ISSN: 2184-3252
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

remains a central challenge in the design of automated
penetration testing systems.
To enhance the effectiveness, various automated
penetration testing techniques have been proposed.
Traditional rule-based penetration testing methods of-
ten rely on developers’ background knowledge and
conventional rule-based testing techniques (Ankele
et al., 2019; Raj and Walia, 2020; Malkapurapu
et al., 2023; Jeff and Kala, 2024; Skandylas and As-
plund, 2025; Wieser et al., 2024). However, design-
ing scalable and adaptive testing methods for com-
plex systems remains an open and pressing research
challenge. DL-based approaches have been applied
to penetration testing, particularly in IoT environ-
ments, to improve automation and accuracy (Koroni-
otis et al., 2021). Recent advances in deep learning
(DL) have shown promise in simulating complex at-
tack behaviors and automatically assessing system se-
curity (Koroniotis et al., 2021; Alaryani et al., 2024;
Deng et al., 2024; Antonelli et al., 2024; Kong et al.,
2025; Nakatani, 2025). Nevertheless, adopting DL
in real-world penetration testing still faces challenges
such as limited generalization and training data de-
pendency.
To further improve effectiveness while increasing
efficiency, reinforcement learning (RL) has been in-
creasingly used for penetration testing. RL models
penetration testing as a sequential decision-making
process, where an agent learns to exploit vulnerabil-
ities through trial-and-error interactions with a simu-
lated environment (Hoang et al., 2022; Bianou and
Batogna, 2024; Ahmad et al., 2025). Many prior
works have shown strong results (Cody et al., 2022;
Li et al., 2025a; Yao et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024a;
Zhou et al., 2025; Pham et al., 2024; Li et al., 2025b;
Yang et al., 2024; Zennaro and Erd
˝
odi, 2023; Li et al.,
2024b), mainly because once state and action spaces
are well-defined, the learned testing policy can scale
across scenarios with limited manual effort, as suc-
cessful exploit outcomes drive reward signals. How-
ever, most RL-based methods optimize a single ob-
jective, typically about task success, which makes it
challenging to balance effectiveness and efficiency.
As a result, jointly optimizing for both penetration
success and operational cost remains a critical yet un-
derexplored direction.
To address the conflict and explicitly balance the
trade-off between effectiveness and efficiency in pen-
etration testing, this paper proposes a multi-objective
RL-based framework for optimizing penetration test-
ing policies that aims to improve testing effectiveness
while minimizing operational costs. Unlike classical
RL approaches that focus exclusively on reward max-
imization, our method jointly optimizes two objec-
tives: attack-specific rewards and time-sensitive costs.
To balance these competing objectives, we incorpo-
rate a Lagrangian multiplier, which is dynamically ad-
justed during policy training. When the accumulated
cost exceeds a high level, the agent shifts its behav-
ior to prioritize cost reduction; conversely, when costs
remain low, the agent emphasizes reward maximiza-
tion. This adaptive mechanism enables efficient and
cost-aware penetration strategies in complex network
environments.
We validate our method through comprehensive
experiments on the Network-Attack-Simulator bench-
mark. To evaluate performance across varying lev-
els of complexity, we select three tasks that differ in
the number of hosts, service configurations, sensitiv-
ity levels, and network topologies. The experimental
results show that our method significantly improves
penetration testing effectiveness and efficiency by ex-
ploring 3,475 more unique penetration paths, while
reducing the operational time cost by 88.27% over
the best-performing baseline method in an advanced
complex network environment. For more implemen-
tation details and experimental results, please refer to
our public repository in https://github.com/cxjuan/pe
netration test.
2 BACKGROUND
We learn a Lagrangian-based and multi-objective RL
policy to maximize rewards, minimize costs, and
adaptively balance the trade-off between them during
penetration testing. This section outlines the model-
ing and algorithmic background.
2.1 Markov Decision Process
An Markov Decision Process (MDP) is formally de-
fined by a tuple (S, A, P, R, γ), where, S is the set
of possible states, A is the set of available actions,
P(s
′
|s, a) is the transition probability function repre-
senting the probability of transitioning to state s
′
from
state s after taking action a, R(s, a) is the reward func-
tion, indicating the immediate reward received after
taking action a in state s, γ ∈ [0, 1) is the discount fac-
tor, which balances the importance of immediate and
future rewards.
2.2 Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a learning paradigm
where an agent interacts with an environment to
learn a policy that maximizes cumulative rewards
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing
375

over time (Chadi and Mousannif, 2023). The en-
vironment is typically modeled as a Markov Deci-
sion Process (MDP), which provides a mathematical
framework for sequential decision-making under un-
certainty (Sutton and Barto, 2018; Chadi and Mou-
sannif, 2023).
At each time step t, the agent observes the cur-
rent state s
t
∈ S , selects an action a
t
∈ A based on
its policy π(a|s), receives a reward r
t
= R(s
t
, a
t
), and
transitions to a new state s
t+1
∼ P(·|s
t
, a
t
). The goal
of the agent is to learn a policy π that maximizes the
expected return:
E
π
"
∞
∑
t=0
γ
t
R(s
t
, a
t
)
#
.
To evaluate policies, the action value functions is
commonly used by following demonstrations:
Q
π
(s, a) = E
π
"
∞
∑
t=0
γ
t
R(s
t
, a
t
) | s
0
= s, a
0
= a
#
.
A policy is considered optimal if it achieves the
highest possible expected return from any initial state.
The corresponding optimal value functions, V
∗
(s) and
Q
∗
(s, a), satisfy the Bellman optimality equations.
Various RL algorithms, such as Q-learning, policy
gradients, and actor-critic methods, aim to approxi-
mate these optimal value functions or policies through
interaction with the environment (Wang et al., 2022).
2.3 Constrained Markov Decision
Process (CMDP)
While standard MDPs aim solely to maximize re-
wards, many real-world applications, such as penetra-
tion testing and robotics, require satisfying additional
constraints, such as limited time, energy, or risk ex-
posure (Li, 2023). The Constrained Markov Decision
Process (CMDP) (Altman, 1999) extends the MDP
framework by introducing one or more cost functions.
A CMDP is defined as (S , A, P, R, C, γ, d), where
C(s, a) is a cost function and d is a cost threshold.
The objective is to find a policy π that maximizes the
expected cumulative reward while satisfying the con-
straint on cumulative cost:
max
π
E
π
"
∞
∑
t=0
γ
t
R(s
t
, a
t
)
#
,
subject to E
π
"
∞
∑
t=0
γ
t
C(s
t
, a
t
)
#
≤ d.
2.4 Deep Q-Networks (DQN)
DQN is constructed on the concept of Q-learning.
The Q-learning algorithm seeks to learn the opti-
mal action-value function Q
∗
(s, a), which satisfies the
Bellman optimality equation:
Q
∗
(s, a) = E
s
′
R(s, a) +γ max
a
′
Q
∗
(s
′
, a
′
)
.
Deep Q-Networks (DQN) (Mnih et al., 2013) ap-
proximate Q
∗
(s, a) using a neural network parameter-
ized by θ, denoted as Q
θ
(s, a). The network is trained
to minimize the temporal difference (TD) loss:
L(θ) = E
(s,a,r,s
′
)∼D
h
(Q
∗
θ
′
(s, a) −Q
θ
(s, a))
2
i
,
where θ
′
denotes the parameters of a target network
that is periodically updated from θ, s
′
is the next state
of s by executing action a, a
′
is the action with the
highest predicted return and is selected by the policy
in state s
′
, and D is a replay buffer storing past transi-
tions to improve sample efficiency and stability.
DQN has achieved notable success in various do-
mains such as Atari games and network intrusion de-
tection, but it is inherently designed for reward maxi-
mization without considering cost or constraints (Guo
et al., 2025; Dana Mazraeh and Parand, 2025; Xu
et al., 2025).
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Policy Optimization Objectives
Each episode yields a sparse reward and one or more
cost signals for constraint violations. At each step, the
policy receives a state vector that summarizes the net-
work’s status, including connectivity, services, privi-
leges, and alerts. Based on this input, action values for
expected returns are estimated. The highest-valued
action is selected and executed.
Actions include scanning, exploiting, privilege es-
calation, and lateral movement. These actions are dis-
crete and tailored to penetration testing. Each action
incurs a fixed cost of 1, while a reward of 100 is only
given upon successful penetration, with no intermedi-
ate rewards during the testing phase.
Our approach aims to learn a policy that consis-
tently selects actions that maximize cumulative re-
wards while minimizing cumulative costs per episode,
leading to efficient and constraint-aware penetration
strategies.
To estimate the long-term value and cost associ-
ated with each state-action pair (s
t
, a
t
), we compute
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
376

Algorithm 1: Optimizing Penetration Testing Policy with Lagrangian Multiplier.
Input : Environment E, replay buffer B, episodes N, discount factor γ, learning rate η
Output: Optimized policy π
Initialize Q-networks Q
R
, Q
C
, and Lagrange multiplier λ ← 1;
Initialize cost history buffer H ←
/
0 ; // Track episodic costs for averaging
for k ← 1 to N do
Reset environment, get initial state s
0
;
C
k
← 0 ; // Initialize discounted cumulative cost for episode
while episode not terminated do
Select action a
t
= argmax
a
Q
R
(s
t
, a) − λQ
C
(s
t
, a)
; // Trade off reward and penalized cost
Execute a
t
, observe next state s
t+1
, reward r
t
, cost c
t
= 1;
C
k
← C
k
+ γ
t
c
t
; // Update discounted cost
Store transition (s
t
, a
t
, r
t
, c
t
, s
t+1
) in replay buffer B;
s
t
← s
t+1
;
Sample mini-batch from B and update Q
R
, Q
C
via Bellman targets ; // Train Q-networks
Append C
k
to H ;
Compute average cost
¯
C =
1
|H |
∑
C
i
; // Mean episodic cost over history
Update λ ← max
0, λ + η(C
k
−
¯
C)
; // Projected gradient ascent update
the discounted episodic return and cost as follows:
R(s
t
, a
t
) =
N−1
∑
i=0
γ
i
r
t+i
,
C(s
t
, a
t
) =
N−1
∑
i=0
γ
i
c
t+i
,
Where r
t
∈ {0, 200} is the reward at timestep t, c
t
= 1
is the fixed cost per action, γ ∈ [0, 1) is the discount
factor, T is the length of the episode, N is the number
of time steps from t to end of the episode.
This formulation reflects the sparsity of the reward
signal and encourages the agent to reach the pene-
tration goal in as few steps as possible, to minimize
the accumulated operational cost. By jointly learning
from reward and cost signals, our framework guides
the policy toward efficient and stealthy penetration
strategies under predefined operational constraints.
3.2 Optimization of Value and Cost
Functions
Two separate neural networks are used to approximate
the action-value and cost-value functions. Each net-
work takes the current state as input and outputs a vec-
tor representing the estimated value or cost for every
possible action.
Formally, we employ two separate Q-functions:
• Q
R
(s, a) estimates the expected return (cumulative
reward).
• Q
C
(s, a) estimates the expected cumulative cost.
These functions are learned using separate Bell-
man equations:
Reward Bellman target:
y
R
= R(s, a) + γmax
a
′
Q
R
(s
′
, a
′
),
Cost Bellman target:
y
C
= C(s, a) + γmax
a
′
Q
C
(s
′
, a
′
).
a
′
is the action with the highest action value and cost
in the respective Bellman functions. The above Bell-
man function indicates that, for example, the target
of the value function is computed by the sum of the
current reward and future action returns. Each Q-
function is trained by minimizing the mean squared
temporal difference (TD) error over a batch of transi-
tions:
L
R
= E
(s,a,r,s
′
)
(Q
R
(s, a) −y
R
)
2
,
L
C
= E
(s,a,c,s
′
)
(Q
C
(s, a) −y
C
)
2
.
This dual-Q learning structure allows us to eval-
uate actions by their expected rewards and the risks
or costs they incur, forming the foundation for
constraint-aware decision-making.
3.3 Lagrangian-Based Multi-Objective
Optimization
Our method adopts a Lagrangian-based primal-dual
optimization framework to enforce cost constraints
during learning. A key distinction of our approach
is that the Lagrange multipliers λ are not only used
during policy optimization but are also directly incor-
porated into the action selection process. That is, the
policy selects actions by maximizing a reward sig-
nal adjusted by the current penalty weights, which
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing
377

ensures that the agent explicitly considers constraint
penalties when choosing actions, even during evalua-
tion:
a
t
∼ π(a | s
t
;λ) = argmax
a
[R(s
t
, a) −λC(s
t
, a)].
To enforce long-term constraint satisfaction, the
Lagrange multiplier λ
i
is modeled as a learnable
scalar and updated using projected gradient ascent
based on the gap between the current episodic cost
and the historical average cost. Specifically, let i de-
note episode numbers during training, and let k denote
the current episode number. The update rule is:
λ ←
λ + η
C
n
−
∑
N
i=0
C
i
N
+
, ∀i,
where η is the dual learning rate and [·]
+
projects onto
the non-negative reals. C
n
is the episodic cost of the
current episode, compared with the average of history
episodes. If C
n
is greater than the historical average,
then the λ will increase, strengthening the impact of
costs in action selection. It decreases λ when the cur-
rent episodic cost is lower than its historical average,
allowing the agent to adaptively balance task perfor-
mance and constraint satisfaction over time. Note that
λ is set to 1 when the training starts.
3.4 Multi-Objective Policy Optimization
We frame penetration testing as a constrained
decision-making problem, where the agent aims to
maximize success while minimizing cost. At each
step, it selects actions by maximizing the expected re-
ward minus a cost penalty scaled by a learnable La-
grange multiplier.
Rewards are sparse and only given upon success-
ful exploits, escalations, or goal completion, while
each action incurs a unit cost. Transitions are stored
in a replay buffer to train separate Q-networks for re-
wards and costs. After each episode, the Lagrange
multiplier is updated via projected gradient ascent to
balance performance and constraint adherence.
Through repeated learning, the agent converges to
a cost-aware strategy that optimizes both effective-
ness and efficiency. The full procedure is in Algo-
rithm 1.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Experiment Setup
We build our method on the Network-Attack-
Simulator benchmark
1
, and evaluate it against six
1
https://networkattacksimulator.readthedocs.io
state-of-the-art Safe RL baselines across three repre-
sentative environments: gen, small, and hard. gen re-
tains the tiny benchmark’s minimal topology but adds
stochasticity to test generalization. small introduces
more lateral movement paths for moderate complex-
ity. hard features complex zone structures and multi-
ple privilege escalation goals, requiring deeper plan-
ning and cost-sensitive behavior. These tasks as-
sess scalability and constraint-awareness in increas-
ing complexity.
Moreover, we compare with DQN (Mnih et al.,
2013) and set the Lagrange multiplier learning rate
to 1e-3 as well, using the same architecture for both
cost and policy networks. Our RL training process
doubles as penetration testing, with interactions serv-
ing as both learning and evaluation data.
Additionally, we implement two heuristic base-
lines: (i) a random agent selecting uniformly from
the action space, and (ii) a rule-based agent guided by
the logic of Metasploit and tools like Nmap, Nessus,
OpenVAS, Armitage, Wireshark, and Netcat (Ankele
et al., 2019; Raj and Walia, 2020; Malkapurapu et al.,
2023; Jeff and Kala, 2024; Skandylas and Asplund,
2025). Details of these baselines are in the implemen-
tation resources.
4.2 Evaluation of Training Performance
In our experiments, following the strategy of “test-
ing while training”, evaluation is conducted periodi-
cally during the training process. During the experi-
ment, we executed three rounds of penetration testing
in each environment. In each round of testing, we set
the total training budgets to 50,000 and 100,000 steps
for gen, small, and hard, respectively.
In Figure 1, we present the average trends of
episodic returns and costs during the training of base-
lines (e.g., standard DQN, random- and rule-based
method) and the Constrained-DQN penetration test-
ing policies. Each point on the curves represents the
evaluated episodic returns and costs of the policies at
the corresponding time steps. A higher return indi-
cates a greater likelihood of successfully compromis-
ing the network system, while a higher cost reflects a
longer task completion time.
Our method, the Constrained-DQN, consistently
outperforms baseline agents by achieving higher cu-
mulative returns and lower episodic costs. In par-
ticular, on the gen, the Constrained-DQN achieves
substantial improvements in both return and cost
throughout the training process. In the more challeng-
ing small and hard tasks, it demonstrates even greater
efficiency in earning reward and cost reduction. No-
tably, in hard, compared to DQN and two other base-
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
378
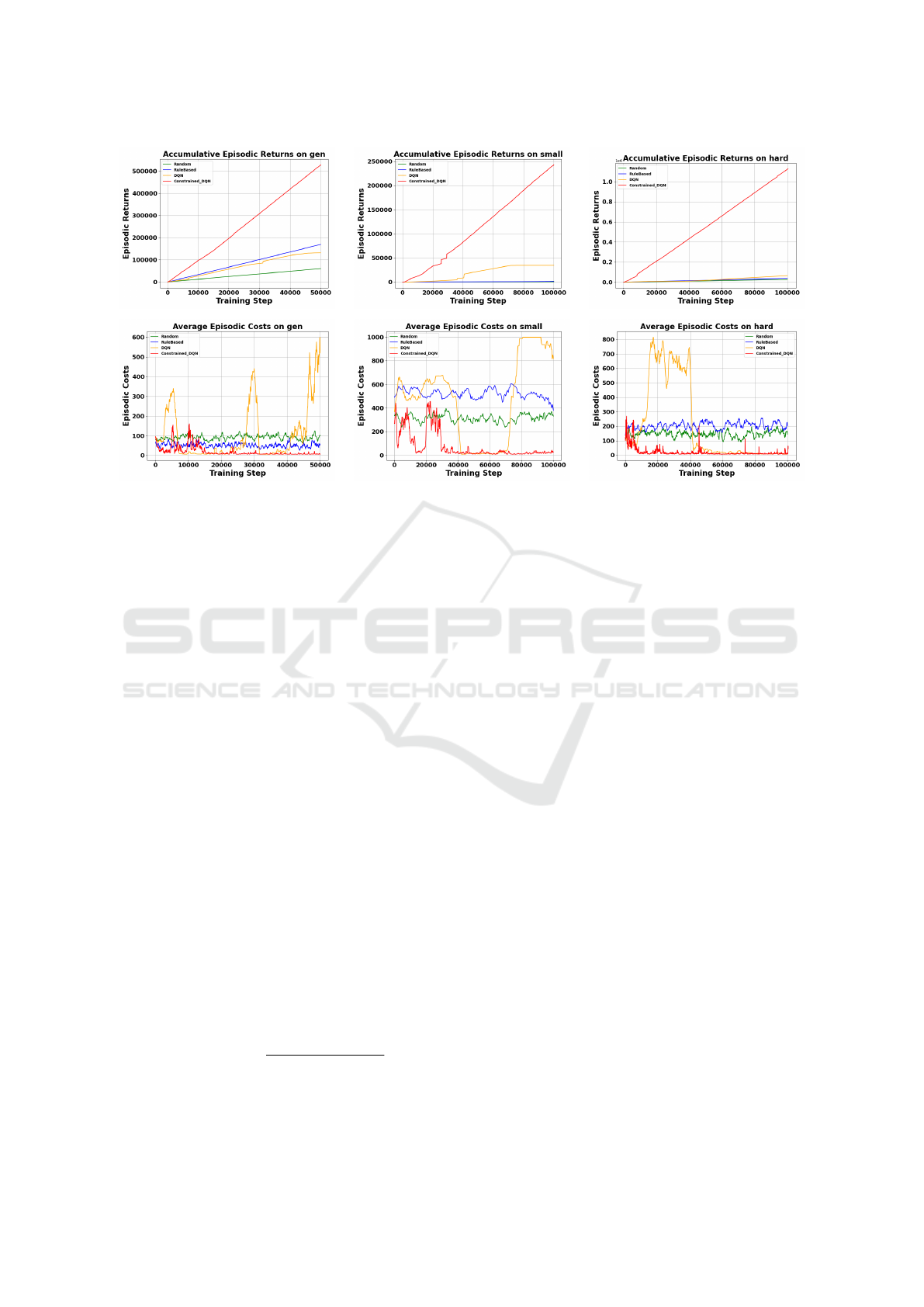
Figure 1: Average trends of episodic returns and costs achieved by random- and rule-based penetration testing method, DQN,
and Constrained-DQN penetration testing policies.
lines, our method shows significant capabilities of re-
ducing costs from the early training phases, and out-
performs all baselines in cumulative rewards.
These results indicate that our approach improves
penetration testing effectiveness and efficiency by in-
creasing the success rate and reducing the time re-
quired to complete the task.
4.3 Evaluation of Penetration Testing
Performance
We evaluated our proposed method against three
baselines (e.g., standard DQN, random- and rule-
based methods) across three representative penetra-
tion testing tasks with varying difficulty levels: gen-
eral (gen), small-scale (small), and complex scenar-
ios (hard). We trained all the methods under identical
conditions with fixed training steps for each task.
To comprehensively evaluate our penetration test-
ing policies, we measure the average number of test-
ing episodes, the number of discovered penetration
paths, path uniqueness and exclusivity, average path
length and cost, and the overall success rate. Unique
paths refer to those that were identified by our policies
but were absent in the baseline evaluation. The com-
putation of the overall success rate is in the following
equation:
SuccessRate =
|Unique Paths|
|Testing E pisodes|
,
|Unique Paths| refers to the number of distinct
penetration paths discovered by a method, counted by
eliminating repeated paths within the same method,
and |TestingE pisodes| is the total number of testing
episodes conducted within the same training budget
(i.e., number of steps).
Table 1 summarizes the results, demonstrating
that our method consistently outperforms all baseline
methods across metrics and tasks. In the gen task with
50,000 training steps, our approach achieves an aver-
age of 4,697.0 testing episodes, discovering 4,692.33
penetration paths, 2,258.67 unique paths, and 1,025.0
exclusive paths. It improves the success rate by ap-
proximately 23.72% over the best-performing base-
line (RuleBased), increasing from 3.651% to 4.517%,
while reducing the average cost by 55.57%.
More notably, in the more complex small and hard
tasks, our method shows significantly stronger explo-
ration and exploitation capabilities. For instance, in
the hard scenario, it discovers over five times (com-
pared to Random), seven times (compared to Rule-
Based), and fourteen times (compared to DQN) more
total penetration paths, and six times, four times,
and nine times more unique paths, respectively. It
also achieves nearly a fivefold increase in success
rate compared to the random-based method (4.462%
vs. 0.685%), a threefold increase over the rule-based
method (4.462% vs. 0.987%), and an eightfold in-
crease over DQN (4.462% vs. 0.465%), all while
maintaining the lowest average costs (23.875).
Our method’s effectiveness relies on reducing
penetration testing costs. Specifically, with the same
training time steps, our method can always finish the
penetration testing with fewer time steps than the
baselines. This advantage enables our method to test
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing
379

Table 1: Averaged penetration testing results of baselines and our method on selected tasks. We consider the random-based
penetration testing method, the rule-based penetration testing method, and DQN as baselines against our Constrained-DQN.
Better results are highlighted in blue.
Tasks
Methods
Training
Steps
Experienced
Episodes
Penetration
Paths
Unique
Paths
Exclusive
Paths
Ave. Path
Lengths
Avg.
Costs
Avg. Success
Rates (%)
gen
Random 50,000 1,090.0 1,088.0 544.0 181.333 91.901 91.743 1.088
RuleBased 50,000 1,894.0 1,892.0 1,825.667 914.333 52.550 52.539 3.651
DQN 50,000 717.667 682.333 456.333 254.333 78.187 105.263 0.913
Ours 50,000 4,697.0 4,692.333 2,258.667 1,025.0 22.592 23.188 4.517
small
Random 100,000 636.0 634.0 317.0 105.66 314.495 314.465 0.317
RuleBased 100,000 381.667 359.667 359.667 182.0 500.421 521.739 0.360
DQN 100,000 318.0 161.333 144.333 96.0 203.193 515.464 0.144
Ours 100,000 1,213.0 1,160.667 1,009.667 625.333 92.916 125.366 1.010
hard
Random 100,000 1,372.0 1,370.0 685.0 228.333 145.943 145.773 0.685
RuleBased 100,000 988.667 986.667 986.66 490.333 203.583 203.528 0.987
DQN 100,000 616.0 513.0 465.333 216.0 184.983 321.888 0.465
Ours 100,000 7,535.0 7,515.333 4,461.667 2,587.0 20.833 23.875 4.462
more episodes within a fixed testing budget. Con-
sequently, our method can detect more penetration
paths. Moreover, we infer that our method tends
to avoid repeatedly exercising the same penetration
paths since we continuously reduce the time costs
during training. Such a mechanism might help dis-
cover more unique penetration paths with short path
lengths.
Overall, the results show that our method effec-
tively discovers penetration paths and generalizes bet-
ter across different task complexities. The high num-
ber of unique and exclusive paths indicates broader
search space coverage, while shorter average path
lengths and lower costs suggest more efficient and
optimal solutions. This strong performance validates
the strength of our approach in automated penetration
testing, highlighting its potential for practical deploy-
ment.
4.4 Hyperparameter Tuning
The learning rate for the Lagrangian multiplier λ is
a critical hyperparameter. It directly influences how
quickly the agent adjusts its penalty signal in response
to constraint violations. A learning rate that is too
low may result in slow or insufficient updates to λ,
failing to enforce constraints effectively. Conversely,
an overly high learning rate can lead to unstable up-
dates, causing oscillations or divergence in cost man-
agement and policy learning. Thus, tuning this hy-
perparameter is essential to ensure stable convergence
and reliable satisfaction of constraints over training.
Experimental results on the small environment in
Figure 2 show that 1 × 10
−3
achieves the best over-
all performance on episodic returns and relatively
Figure 2: The trends of episodic returns and costs achieved
by our method with different λ learning rates on small.
lower costs than other settings. Based on our statis-
tics, 1 × 10
−3
achieves a high penetration testing suc-
cess rate and the greatest episodic return (7,489.8),
while maintaining the lowest average cost (708.87)
among all tested configurations. In contrast, the lower
rate 1 × 10
−4
shows slightly reduced task perfor-
mance, with lower returns (2,490.67) and higher costs
(786.62). The highest rate 1 × 10
−2
leads to degraded
performance across the board, including lower return
(2,618.05), and increased cost (871.47), likely due to
unstable λ updates.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Analysis of Penetration Strategy
Distribution
We analyze penetration path distributions across tasks
(gen, small, hard) using DBSCAN clustering in Jac-
card similarity space, visualized with Isomap (Sun-
dararajan, 2025; Cheng et al., 2025). Cluster struc-
tures reflect strategy similarity, while dispersion indi-
cates behavioral diversity (Sundararajan, 2025).
As shown in Figure 3, each point represents a pen-
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
380
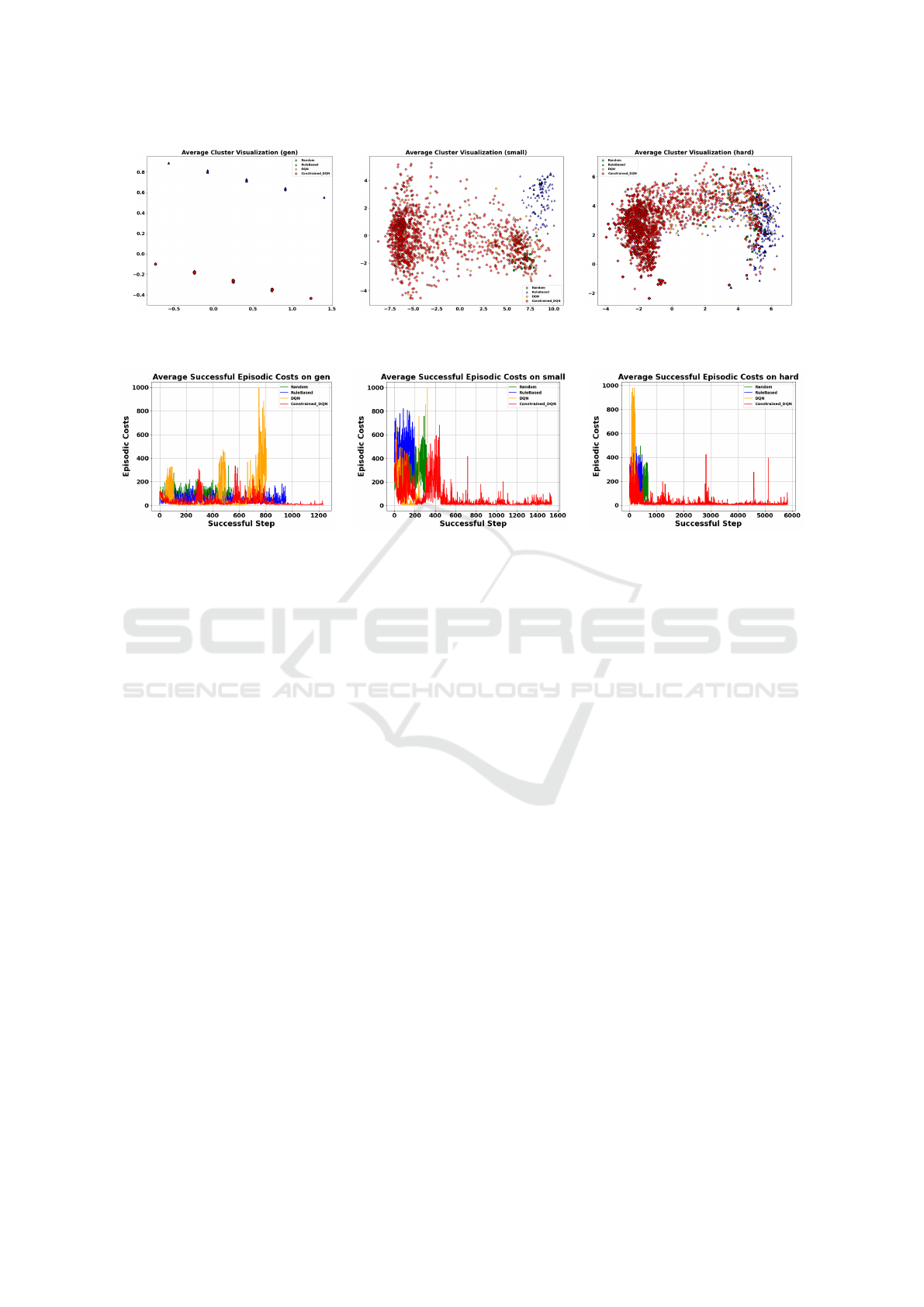
Figure 3: Average trends in the distribution of clusters of penetration test paths using Isomap. Paths are achieved by random-
and rule-based penetration testing method, DQN, and Constrained-DQN penetration testing policies.
Figure 4: Average trends of successful penetration testing episodic costs achieved by random- and rule-based penetration
testing method, DQN, and Constrained-DQN penetration testing policies.
etration path and is embedded according to its Jaccard
similarity to other paths. Tightly grouped points sug-
gest consistent and repeatable strategies, as proximity
indicates high similarity between penetration paths.
In the task of gen, our method induces only 16 clus-
ters, whereas in the more complex small and hard
tasks, it obtains 78 and 478 clusters, respectively. In
contrast, the baseline methods show fewer and less
stable clusters across scenarios. Specifically, in gen,
random-based method, rule-based method, and DQN
provide 12, 22, and 16 clusters, respectively. Mean-
while, in small, only 2 (Random), 2 (RuleBased), and
15 (DQN) clusters are observed. Meanwhile, in hard,
17 (Random), 8 (RuleBased), and 40 (DQN) clusters
are identified, respectively.
Notably, the diversity of isolated points in small
and hard shows that our policies are exploratory. It
also indicates that the Constrained-DQN generates a
significantly broader and more dispersed distribution
of penetration paths than the baselines.
5.2 Analysis of Lagrangian Multiplier λ
and Costs
As shown in Figure 4, we compare the average
episodic costs of successful penetration testing steps
achieved by the Constrained-DQN and baseline meth-
ods. The results show that our method incurs the low-
est average cost while achieving the highest number
of successful penetration steps. Meanwhile, it consis-
tently achieves a low cost per successful step, indicat-
ing higher efficiency compared to the baselines.
We analyze the relationship between the La-
grangian multiplier λ and the average cost per episode
in the gen, small, and hard environments using
the Pearson correlation coefficient (Sedgwick, 2012),
which measures the linear relationship between two
variables. In our context, it reflects how the adaptive
λ responds to the cost incurred by the policy during
training.
Across all tasks, we observed positive correlations
between λ and the average cost per episode: in gen,
the correlation is +0.297; in small, it is +0.605; and
in hard, it is +0.236. These results suggest that as the
agent encounters higher costs, the value of λ tends
to increase. This behavior reflects the design of our
method: the adaptive adjustment of λ penalizes costly
actions and reduces their selection probability, en-
couraging the agent to avoid inefficient decisions.
The agent learns to prioritize task completion
and cost efficiency through this mechanism. Unlike
standard DQN, the random- and rule-based method,
which focuses solely on maximizing returns, our con-
strained formulation incorporates cost-awareness di-
rectly into the policy learning process. This is espe-
cially critical in penetration testing scenarios, where
an agent that reaches the goal without regard for effi-
ciency is of limited practical use. The observed corre-
lations demonstrate that the adaptive λ provides an ef-
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing
381

fective internal signal for guiding cost-sensitive learn-
ing.
Overall, we introduce a multi-objective policy op-
timization scheme to learn penetration testing poli-
cies. Our method outperforms baselines in terms of
success rate, cost efficiency, and strategic diversity, as
supported by experimental results. While current lim-
itations include the use of a scalar Lagrange multiplier
and reliance on simulated environments, our method
shows potential for real-world, resource-constrained
scenarios such as enterprise or IoT networks.
6 RELATED WORKS
6.1 Rule-Based Penetration Testing
Various tools are preferred among security profes-
sionals and organizations in configured testing envi-
ronments for traditional penetration testing. For in-
stance, by setting the scope of the penetration testing
to a generic In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) system, the
authors of (Wieser et al., 2024) focus on the Wi-Fi in-
terface of the IVI model to reveal vulnerabilities that
could allow attackers to crash the system, access data,
or manipulate settings. Their study demonstrates ef-
fective testing methods tailored to the automotive en-
vironment to address the unique security challenges
in vehicular networks.
Moreover, works of (Ankele et al., 2019; Raj and
Walia, 2020; Malkapurapu et al., 2023; Jeff and Kala,
2024; Skandylas and Asplund, 2025) analyze the per-
formance of the Metasploit Framework in conjunc-
tion with other popular penetration testing tools (e.g.,
Nmap, Nessus, OpenVAS, Armitage, Wireshark, and
Netcat). The results show that a flexible and modular
architecture enables a comprehensive range of test-
ing scenarios. (Ankele et al., 2019) extracts meta-
data from diagrams and models commonly used in
typical software development processes to automate
threat modeling, security analysis, and penetration
testing without prior detailed security knowledge in a
large-scale IoT/IIoT network. This approach reduces
the reliance on deep security expertise and addresses
the scalability limitations of manual approaches in
complex industrial systems. In addition, (Malkapu-
rapu et al., 2023) discussed that a large and active
community ensures that open-source Metasploit re-
ceives frequent updates and shared resources. The
authors detail Metasploit’s modular design, extensive
exploit database, and integration capabilities, demon-
strating its utility in automating and enhancing secu-
rity assessments. Furthermore, to address the grow-
ing need for scalable and expert-independent secu-
rity testing, the authors in (Skandylas and Asplund,
2025) formalize the problem of penetration testing
as an architectural-level problem and propose a self-
organizing, architecture-driven automation tool for
penetration testing (ADAPT). They successfully ap-
plied their method to real-world environments such
as Metasploitable2/3 and virtual training networks.
6.2 Deep Learning-Based Penetration
Testing
The powerful ability to process large amounts of data
and identify patterns enables DL models to efficiently
and automatically simulate complex attack scenarios
and assess security posture during penetration test-
ing. The authors of (Koroniotis et al., 2021) aim to
address the limitations of existing penetration test-
ing tools in detecting zero-day vulnerabilities in IoT
environments due to the diversity of data generated,
hardware limitations, and environmental complexity.
Hence, they provide a deep learning-based framework
(LSTM-EVI) for vulnerability identification in smart
IoT environments. Evaluated using real-time data
on a smart airport testbed, the framework achieves
outstanding accuracy in detecting scanning attacks.
Meanwhile, in the work of (Alaryani et al., 2024), an
AI-enabled penetration testing platform (PentHack)
is designed to enhance the development of cyberse-
curity knowledge. The platform integrates the Large
Language Model (LLM) with a user-friendly GUI to
automate testing procedures and enhance user learn-
ing outcomes while supporting educational and prac-
tical applications in cyberwarfare and security. More-
over, the authors of (Deng et al., 2024) propose PEN-
TESTGPT, an LLM-powered automated penetration
testing framework that leverages domain knowledge
and a modular, self-interacting architecture to address
context loss challenges. Their proposal shows strong
performance on real-world targets, which achieves a
228.6% task-completion improvement over GPT-3.5
on benchmark penetration testing tasks.
To improve the efficiency and adaptability of ex-
ploration in complex network environments, the au-
thors of (Kong et al., 2025) proposed VulnBot, an au-
tonomous penetration testing framework based on a
multi-agent collaborative architecture. The VulnBot
enables agents to share knowledge and coordinate at-
tacks to address the limitation of a lack of task co-
ordination and excessive unstructured output. Addi-
tionally, in the work of (Nakatani, 2025), a frame-
work called RapidPen utilizes LLM to discover vul-
nerabilities and exploits autonomously. In RapidPen,
the LLM helps synthesize new command inputs based
on contextual understanding of the target and its con-
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
382

figuration. As a result, a report on the progress of
the penetration test (e.g., logs, vulnerabilities found,
commands used to obtain a shell) can be obtained by
providing the target IP address and shows strong ef-
fectiveness in discovering and exploiting vulnerabili-
ties autonomously without human intervention.
Furthermore, the work of (Antonelli et al., 2024)
improves the efficiency of data mining in the pene-
tration testing of web applications through semantic
clustering techniques. The authors utilize advanced
embedding models, such as Word2Vec and Univer-
sal Sentence Encoder, to convert word list entries
into vector representations. These vectors are then
grouped using a semantic similarity-based clustering
algorithm. The resulting clusters provide the basis for
an intelligent next-word selection strategy that signif-
icantly improves the performance of traditional brute-
force cracking methods in various web applications.
6.3 Reinforcement Learning-Based
Penetration Testing
By viewing penetration testing as an ongoing
decision-making process, RL agents can learn the op-
timal attack strategies to increase the efficiency and
coverage of penetration testing. (Cody et al., 2022)
propose an RL method for discovering data exfiltra-
tion paths in enterprise networks using attack graphs.
Their penetration testing scenario assumes that the
stolen data is seeking a stealthy exfiltration. The au-
thors design the reward function of the RL agent to
favor low-detection paths, showing promising results
in large-scale environments. Moreover, the authors
of (Li et al., 2025a) introduce a novel framework for
formalizing and refining attack patterns involving dis-
junctive, conjunctive, and hybrid causal relationships
among actions (TTCRT). By modeling these dynam-
ics as Markov Decision Processes, the framework en-
ables deep RL algorithms to discover optimal attack
paths accurately.
Otherwise, since the intelligent-led penetration
testing approaches often assume static environments,
the authors of (Yao et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024a) apply
RL in a dynamic defense environment and evaluate
with the scenario of CyberBattleSim. Results show
reduced agent performance and convergence in dy-
namic scenarios, highlighting the need for a balanced
exploration-exploitation strategy. To improve conver-
gence speed and continuous adaptation in dynamic
scenarios, the authors in the work of (Li et al., 2024a)
capture observed scenario changes to help penetration
testing agents make decisions based on historical ex-
perience. Meanwhile, the work of (Zhou et al., 2025)
addressed the challenge of non-stationarity in real-
world autonomous penetration testing. The authors
propose SCRIPT, a scalable continual RL framework.
SCRIPT enables agents to learn large-scale tasks se-
quentially, leveraging prior knowledge (positive for-
ward transfer) while mitigating catastrophic forget-
ting through new task learning and knowledge con-
solidation processes.
To tackle partial observability in penetration test-
ing, EPPTA (Li et al., 2025b) introduces a state-
estimation module within an asynchronous RL frame-
work, achieving up to 20 times faster convergence
than prior methods. To overcome limited test cov-
erage and repetitive behaviors, CLAP (Yang et al.,
2024) proposes a coverage-driven RL framework with
Chebyshev-based strategy diversification, improving
efficiency and scaling to networks with up to 500
hosts. In addition, works of (Zennaro and Erd
˝
odi,
2023; Li et al., 2024b; Pham et al., 2024) provide
efforts for an efficient penetration testing. The au-
thors of (Zennaro and Erd
˝
odi, 2023) explore the ap-
plication of RL to penetration testing through model-
ing realistic, goal-driven attack processes to capture-
the-flag (CTF) scenarios, focusing on the trade-off
between model-free learning and the use of domain
knowledge. Compared to knowledge-guided agents
with predefined heuristics, the results show that in-
tegrating limited prior knowledge can reduce learn-
ing time. A knowledge-informed RL approach for
leveraging reward machines to encode domain knowl-
edge into the RL process was proposed later (Li et al.,
2024b). Their approach improves learning efficiency
and interpretability by guiding the agent with struc-
tured symbolic rewards rather than relying solely on
trial-and-error. It highlights combining human knowl-
edge with RL for more efficient, goal-directed attack
strategies. (Pham et al., 2024) automates the post-
exploitation phase in penetration testing. Unlike treat-
ing exploitation as an end goal, the authors focus on
evaluating the security level of a system by systemat-
ically exploring post-exploitation actions. The results
show high success rates with fewer attack steps in a
complex network environment.
7 CONCLUSION
This work presents a reinforcement learning pen-
etration testing framework that employs a multi-
objective policy optimization scheme based on con-
strained DQN to jointly maximize penetration test-
ing efficiency and minimize operational cost through
adaptive Lagrangian multiplier λ. Experiments
on three penetration testing environments, gen,
small, and hard in Network-Attack-Simulator bench-
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing
383

mark, showed that the proposed method consistently
achieves higher success rates, larger coverage returns,
and more reductions in episode cost compared with
standard DQN, random- and rule-based penetration
testing methods. Statistically significant positive cor-
relations between λ and incurred cost confirm that the
dual update mechanism guides the agent to perform
lower-cost actions without sacrificing exploit quality.
These results demonstrate that constrained reinforce-
ment learning is a practical avenue for scalable, effi-
cient, and effective automated penetration testing in
real-world, resource-limited environments.
Our future work focuses on a broader considera-
tion of improving penetration testing efficiency. At
first, we will upgrade the Lagrangian multiplier λ
from a learnable scalar to a neural network. A more
complex λ helps improve the granularity and accu-
rately measure the impact of costs on selecting actions
under different states. Furthermore, we will focus
on extending our method to more complex network
systems, such as cloud-based platforms or software-
defined networks, to improve its scalability and real-
world applicability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by Hitachi Systems, Ltd.
REFERENCES
Ahmad, T., Butkovic, M., and Truscan, D. (2025). Using
reinforcement learning for security testing: A system-
atic mapping study. In 2025 IEEE International Con-
ference on Software Testing, Verification and Valida-
tion Workshops (ICSTW), pages 208–216.
Alaryani, M., Alremeithi, S., Ali, F., and Ikuesan, R. (2024).
Penthack: Ai-enabled penetration testing platform for
knowledge development. European Conference on
Cyber Warfare and Security, 23:27–36.
Altman, E. (1999). Constrained Markov Decision Pro-
cesses, volume 7. CRC Press.
Ankele, R., Marksteiner, S., Nahrgang, K., and Vallant,
H. (2019). Requirements and recommendations for
iot/iiot models to automate security assurance through
threat modelling, security analysis and penetration
testing. CoRR, abs/1906.10416.
Antonelli, D., Cascella, R., Schiano, A., Perrone, G., and
Romano, S. P. (2024). “dirclustering”: a semantic
clustering approach to optimize website structure dis-
covery during penetration testing. Journal of Com-
puter Virology and Hacking Techniques, 20(4):565–
577.
Bandar Abdulrhman Bin Arfaj, Shailendra Mishra, M. A.
(2022). Efficacy of unconventional penetration testing
practices. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing,
31(1):223–239.
Bianou, S. G. and Batogna, R. G. (2024). Pentest-ai, an
llm-powered multi-agents framework for penetration
testing automation leveraging mitre attack. In 2024
IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and
Resilience (CSR), pages 763–770.
Caddy, T. (2025). Penetration testing. In Jajodia, S., Sama-
rati, P., and Yung, M., editors, Encyclopedia of Cryp-
tography, Security and Privacy, pages 1786–1787,
Cham. Springer Nature Switzerland.
Chadi, M.-A. and Mousannif, H. (2023). Understanding
reinforcement learning algorithms: The progress from
basic q-learning to proximal policy optimization.
Cheng, Y.-Y., Fang, Q., Liu, L., and Fu, X.-M. (2025).
Developable approximation via isomap on gauss im-
age. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Com-
puter Graphics, pages 1–11.
Cody, T., Rahman, A., Redino, C., Huang, L., Clark, R.,
Kakkar, A., Kushwaha, D., Park, P., Beling, P., and
Bowen, E. (2022). Discovering exfiltration paths us-
ing reinforcement learning with attack graphs. In 2022
IEEE Conference on Dependable and Secure Comput-
ing (DSC), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Dana Mazraeh, H. and Parand, K. (2025). An innova-
tive combination of deep q-networks and context-free
grammars for symbolic solutions to differential equa-
tions. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelli-
gence, 142:109733.
Deng, G., Liu, Y., Mayoral-Vilches, V., Liu, P., Li, Y.,
Xu, Y., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Pinzger, M., and Rass, S.
(2024). PentestGPT: Evaluating and harnessing large
language models for automated penetration testing. In
33rd USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security
24), pages 847–864, Philadelphia, PA. USENIX As-
sociation.
Erd
˝
odi, L. and Zennaro, F. M. (2022). Hierarchical re-
inforcement learning for efficient and effective auto-
mated penetration testing of large networks. Journal
of Intelligent Information Systems, 59(3):375–393.
Fadhli, M. (2024). Comprehensive analysis of penetration
testing frameworks and tools: Trends, challenges, and
opportunities : Analisis komprehensif terhadap frame-
work dan alat penetration testing: Tren, tantangan,
dan peluang. Indonesian Journal of Electrical En-
gineering and Renewable Energy (IJEERE), 4(1):15–
22.
Guo, C., Zhang, L., Thompson, R. G., Foliente, G., and
and, X. P. (2025). An intelligent open trading system
for on-demand delivery facilitated by deep q network
based reinforcement learning. International Journal
of Production Research, 63(3):904–926.
Hayat, T. and Gatlin, K. (2025). Ai-powered ethical hack-
ing: Rethinking cyber security penetration testing.
Preprint on ResearchGate.
Hoang, L. V., Nhu, N. X., Nghia, T. T., Quyen, N. H.,
Pham, V.-H., and Duy, P. T. (2022). Leveraging
deep reinforcement learning for automating penetra-
tion testing in reconnaissance and exploitation phase.
In 2022 RIVF International Conference on Comput-
WEBIST 2025 - 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
384

ing and Communication Technologies (RIVF), pages
41–46.
Jeff, V. and Kala, K. (2024). Penetration testing:
An overview of its tools and processes. Interna-
tional Journal of Research Publication and Reviews,
5(3):4346–4353.
Kong, H., Hu, D., Ge, J., Li, L., Li, T., and Wu, B. (2025).
Vulnbot: Autonomous penetration testing for a multi-
agent collaborative framework.
Koroniotis, N., Moustafa, N., Turnbull, B., Schiliro, F.,
Gauravaram, P., and Janicke, H. (2021). A deep
learning-based penetration testing framework for vul-
nerability identification in internet of things environ-
ments. In 2021 IEEE 20th International Conference
on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and
Communications (TrustCom), pages 887–894.
Li, Q., Wang, R., Li, D., Shi, F., Zhang, M., Chattopad-
hyay, A., Shen, Y., and Li, Y. (2024a). Dynpen: Auto-
mated penetration testing in dynamic network scenar-
ios using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transac-
tions on Information Forensics and Security, 19:8966–
8981.
Li, S., Huang, R., Han, W., Wu, X., Li, S., and Tian, Z.
(2025a). Autonomous discovery of cyber attack paths
with complex causal relationships among optional ac-
tions. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transporta-
tion Systems, pages 1–15.
Li, S. E. (2023). Reinforcement Learning for Sequential
Decision and Optimal Control. Springer Singapore.
Li, Y., Dai, H., and Yan, J. (2024b). Knowledge-informed
auto-penetration testing based on reinforcement learn-
ing with reward machine. In 2024 International Joint
Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pages 1–9.
Li, Z., Zhang, Q., and Yang, G. (2025b). Eppta: Efficient
partially observable reinforcement learning agent for
penetration testing applications. Engineering Reports,
7(1):e12818.
Luo, F.-M., Tu, Z., Huang, Z., and Yu, Y. (2024). Efficient
recurrent off-policy rl requires a context-encoder-
specific learning rate. In Globerson, A., Mackey, L.,
Belgrave, D., Fan, A., Paquet, U., Tomczak, J., and
Zhang, C., editors, Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, volume 37, pages 48484–48518.
Curran Associates, Inc.
Malkapurapu, S., Abbas, M. A. M., and Das, P. (2023). Ex-
ploring the capabilities of the metasploit framework
for effective penetration testing. In Data Science and
Network Engineering, volume 655 of Lecture Notes in
Networks and Systems, pages 457–471. Springer Na-
ture Singapore.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Graves, A.,
Antonoglou, I., Wierstra, D., and Riedmiller, M.
(2013). Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learn-
ing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5602.
Nakatani, S. (2025). Rapidpen: Fully automated ip-to-shell
penetration testing with llm-based agents.
Pham, V.-H., Hoang, H. D., Trung, P. T., Quoc, V. D., To,
T.-N., and Duy, P. T. (2024). Raiju: Reinforcement
learning-guided post-exploitation for automating se-
curity assessment of network systems. Computer Net-
works, 253:110706.
Raj, S. and Walia, N. K. (2020). A study on metasploit
framework: A pen-testing tool. In 2020 International
Conference on Computational Performance Evalua-
tion (ComPE), pages 296–302.
Sedgwick, P. (2012). Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Bmj,
345.
Skandylas, C. and Asplund, M. (2025). Automated penetra-
tion testing: Formalization and realization. Computers
& Security, 155:104454.
Sundararajan, S. (2025). Multivariate Analysis and Ma-
chine Learning Techniques: Feature Analysis in Data
Science Using Python. Transactions on Computer
Systems and Networks. Springer Singapore, 1 edition.
Sutton, R. S. and Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement Learn-
ing: An Introduction. MIT Press.
Teichmann, F. M. and Boticiu, S. R. (2023). An overview
of the benefits, challenges, and legal aspects of pene-
tration testing and red teaming. International Cyber-
security Law Review, 4(4):387–397.
Wang, P., Liu, J., Zhong, X., Yang, G., Zhou, S., and Zhang,
Y. (2022). Dusc-dqn:an improved deep q-network for
intelligent penetration testing path design. In 2022 7th
International Conference on Computer and Commu-
nication Systems (ICCCS), pages 476–480.
Wieser, H., Sch
¨
afer, T., and Krauß, C. (2024). Penetra-
tion testing of in-vehicle infotainment systems in con-
nected vehicles. In 2024 IEEE Vehicular Networking
Conference (VNC), pages 156–163.
Xu, C., Du, J., Lai, B., Wang, H., Zheng, H., Dai, T., Liang,
Z., and and, Y. Y. (2025). Design and implementation
of an intelligent penetration security assessment sys-
tem based on graph neural network (gnn) technology.
Journal of Cyber Security Technology, 0(0):1–13.
Yang, Y., Chen, L., Liu, S., Wang, L., Fu, H., Liu, X., and
Chen, Z. (2024). Behaviour-diverse automatic pene-
tration testing: a coverage-based deep reinforcement
learning approach. Frontiers of Computer Science,
19(3):193309.
Yao, Q., Wang, Y., Xiong, X., and Li, Y. (2023). Intelligent
penetration testing in dynamic defense environment.
In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference
on Cyber Security, CSW ’22, page 10–15, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Zennaro, F. M. and Erd
˝
odi, L. (2023). Modelling penetra-
tion testing with reinforcement learning using capture-
the-flag challenges: trade-offs between model-free
learning and a priori knowledge. IET Information Se-
curity, 17(3):441–457.
Zhou, S., Liu, J., Lu, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Lin, B., Zhong,
X., and Hu, S. (2025). Script: A scalable contin-
ual reinforcement learning framework for autonomous
penetration testing. Expert Systems with Applications,
285:127827.
Multi-Objective Policy Optimization for Effective and Cost-Conscious Penetration Testing
385
