
Physical and Physiological Impact of Custom-Made Virtual Reality
Exergames for Older Adults
Cíntia França
1,2
, Hildegardo Noronha
1
, Eva Freitas
1
, Pedro Campos
1,3
,
Rui T. Ornelas
2,4
and Élvio R. Gouveia
1,2,4,5
1
LARSYS, Interactive Technologies Institute, Funchal, Portugal
2
Department of Physical Education and Sport, University of Madeira, Funchal, Portugal
3
WoW!Systems Informática Lda, Funchal, Portugal
4
CIPER, Faculty of Human Kinetics, University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal
5
Center for the Interdisciplinary Study of Gerontology and Vulnerability, University of Geneva, Carouge, Switzerland
Keywords: Aging, Physical Activity, Heart Rate, User Tests.
Abstract: Aging is associated with decreased physical fitness components, such as strength, power, cardiorespiratory
fitness, and balance, resulting in physical limitations on functional activities of daily living. The increasing
population of older adults calls for innovative strategies to support functional health, particularly through
exercise. This study has two main objectives: (1) to introduce a custom-designed virtual reality (VR)
exergame prototype, FitFest, developed to deliver physical activity (PA) sessions for older adults, and (2) to
present the results of a pilot study assessing physical and physiological responses during gameplay. Seven
older adults (mean age 67.0±3.8 years) participated in 18 user testing sessions involving two VR exergames—
Wine Fest and Flower Fest. Each session was monitored for PA intensity and heart rate (HR). The participants
spent most of their time in sedentary behavior (56.5±20.4%), followed by light PA (42.1±19.3%), averaging
436.7 steps and a heart rate of 92.1 bpm per session. Although the differences were not statistically significant,
Wine Fest led to lower sedentary behavior, higher light PA levels, and more total steps than Flower Fest. The
findings suggest that the system can potentially promote light PA among older adults, emerging as a
complementary tool to traditional PA sessions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Aging is associated with decreased physical
fitness components, such as strength, power,
cardiorespiratory fitness, and balance, resulting in
physical limitations on functional activities of daily
living (Paterson et al., 2007). There is evidence that
exercise interventions among older adults can
promote gains in functional capacities, enhancing
physical health and quality of life.
According to the World Health Organization's
physical activity (PA) guidelines, older adults should
accumulate at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity
or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week,
emphasizing aerobic capacity (WHO, 2020).
Additionally, performing muscle-strengthening and
balance activities might be crucial to prevent falls,
which has been described as a common and serious
concern among this population (Nascimento et al.,
2022). Approximately one-third of individuals aged
65 years or older living in community settings
experience at least one fall yearly, and one-half fall
more than once (Inouye et al., 2009). Although falls
often occur due to multiple factors, previous research
has related falls to poor balance and strength abilities
and gait disorders (Clemson et al., 2010). For
instance, among 619 older adults aged 69.5 years, gait
speed and body balance presented an inverse
relationship with falls, and in turn, falls negatively
impact health-related quality of life (Nascimento et
al., 2022).
There is a significant body of research advocating
the benefits of PA in reducing the risk of several age-
related morbidities and all-cause mortality (Paterson
et al., 2007). PA programs were associated with
reducing the risk of fall-related injuries by 32% to
40%, delaying the loss of physical function and
mobility (Dipietro et al., 2019). Additionally,
França, C., Noronha, H., Freitas, E., Campos, P., Ornelas, R. T. and Gouveia, É. R.
Physical and Physiological Impact of Custom-Made Virtual Reality Exergames for Older Adults.
DOI: 10.5220/0013681600003988
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2025), pages 155-162
ISBN: 978-989-758-771-9; ISSN: 2184-3201
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
155

according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of
longitudinal cohort studies, higher levels of PA were
related to an increase of 39% in the odds of healthy
aging (Daskalopoulou et al., 2017).
The continuous increase of the older adult
population worldwide demands the urgency to
provide ways to maintain and improve functional
health during aging. Due to the exponential
development of technology, exergames have emerged
as exercise platforms among several populations,
including older adults (Ismail et al., 2022).
Exergames are interactive digital tools that combine
exercise and video games. Previous research on using
exergames to improve physical fitness components
among older adults reported beneficial effects on
balance, strength, and aerobic capacity (Agmon et al.,
2011). Moreover, exergames have also been
characterized by the ability to provide mental
stimulation, which is crucial to combat age-related
cognitive declines (Deary et al., 2009). In a recent
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized
control trials to assess the effects of virtual reality
(VR) exergames on older adults’ cognition and
depression, the findings suggested VR exergames
usage as beneficial for overall cognitive function and
memory (Yen & Chiu, 2021).
Although a significant body of research has
emerged on exergame usage among older adults in
recent years, most studies were conducted using
commercial games and commercial video game
consoles such as Nintendo Wii (Agmon et al., 2011;
Kirk et al., 2013) and Xbox (with Kinect) (Yang et
al., 2020). Overall, commercial game designing
might not be appropriate to all populations, the
systems lack precision in motion detection and fail to
provide a sequential and logical gameplay targeting
multicomponent physical fitness components. On the
other hand, commercial games are typically based on
repetitive movements and scenarios, leading to
boredom or reduced motivation over time.
Additionally, balance stands out among physical
fitness components when promoting exergames
interventions in older adults (Agmon et al., 2011;
Clemson et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2020), probably
because of its relationship with falls. However, it is
worth noting that strength and aerobic capacity are
also two crucial components that must be worked on
within the older adult population (WHO, 2020).
Therefore, the purpose of this study is twofold: (1) to
present a VR custom-made exergame prototype
(FitFest) designed to provide an entire PA session to
older adults, and (2) to evaluate the acute physical and
physiological responses elicited while playing
FitFest.
2 METHODS
2.1 Game Development
2.1.1 Game Concept
FitFest consists of two exergames, composed of five
mini games each, that integrate sociocultural
narratives to create an engaging and enjoyable
exercise experience for older adults. The prototype
was developed through a multidisciplinary
collaboration involving researchers in engineering,
sports science, design and storytelling. Input from the
target population was also incorporated through
qualitative analysis to ensure the games addressed
their preferences and needs (Freitas et al., 2024)
.
The custom-made exergames were designed to
simulate a complete exercise session, approximately
45 minutes, following a structured sequence of warm-
up, main exercise phase, and cool-down. Exercise
selection was guided by established
recommendations for physical fitness training in
older adults (focusing on balance, cardiorespiratory
fitness, strength, and agility training) (Bushman &
Medicine, 2017). Additionally, recognizing the
progressive cognitive decline associated with aging
(Deary et al., 2009), the game design included
cognitive challenges to stimulate memory and
problem-solving skills—such as catching specific
items and solving puzzles. The FitFest differs
significantly from existing VR games by including
cognitive stimuli, cultural narrative, and physical
movements, aiming to foster the recommended
physical fitness guidelines for the older population.
Reflecting the cultural values emphasized by the
target group (Freitas et al., 2024), each exergame is
based on a traditional festivity from Madeira Island:
(1) Wine Fest – Inspired by Portugal’s rich
winemaking tradition, this game simulates grape
harvesting, sorting, transportation, and
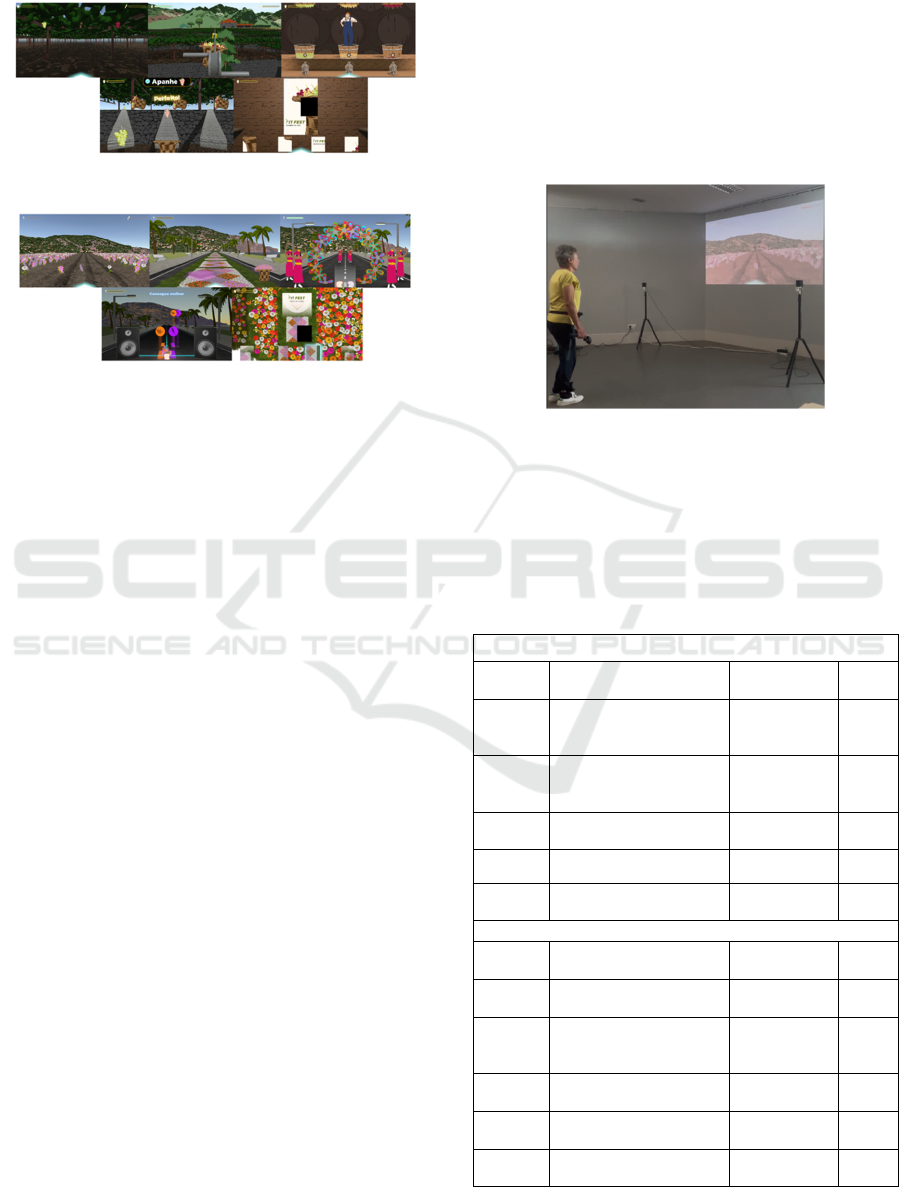
winemaking. Game illustration can be found in
Figure 1.
(2) Flower Fest – Modeled after Madeira Island’s
renowned Flower Festival, this game involves
creating floral arrangements and participating in a
traditional dance and parade celebration. Game
illustration can be found in Figure 2.
Based on the design characteristics, the Wine Fest
was expected to promote more cardiorespiratory
fitness based on the winemaking scenario, which
involved approximately 10 minutes of “stepping
grapes” movements. On the other hand, the Flower
Fest included a traditional dance scenario, with an
icSPORTS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
156
estimated duration of 10 minutes, fostering agility
and coordination alongside cardiorespiratory fitness.
Figure 1: Illustration of the Wine Fest scenarios.
Figure 2: Illustration of the Flower Fest scenarios.
To meet different individual profiles that could be
found among the target population, the exergames
include three difficulty levels: (1) elementary, (2)
standard, and (3) advanced, where the speed of the
actions, the amplitude of the movements, and the
amount of cognitive stimulus vary. The difficulty
level provides a game experience that is more
appropriate to the individuals’ capacities and needs.
To ensure that FitFest stood out from
conventional exergames, storytelling was integrated
to create a meaningful connection between the
players and the character’s journey. Players follow
the story of a 65-year-old resident seeking to
rediscover their youth and break free from
monotonous routines by exploring new experiences.
Finally, to guarantee clear instructions during the
game, a mandatory tutorial before each scenario was
included, following previous literature
recommendations in designing exergames for older
adults (Barg-Walkow et al., 2017). During the
tutorial, the players start by watching a short
gameplay video and a person doing the required
gestures. They then must replicate the movements
needed to play, in a controlled setting, ensuring the
movements were understood and the correct posture
was maintained.
2.1.2 Hardware
Based on insights from the qualitative analysis (Freitas
et al., 2024) regarding older adults’ preferences and
concerns related to technology use, a wall-projection
system was selected for the FitFest experience. This
setup helps mitigate common issues associated with
headset-based VR systems, such as safety concerns,
balance difficulties, motion sickness, and potential
anxiety. To accurately track participants' movements,
three HTC Vive trackers—positioned at the ankles and
waist—along with two handheld controllers, were
used. This configuration enabled precise tracking of
key body joints while providing a spacious 2-meter-
wide gameplay area, supporting both comfort and
freedom of movement. The gameplay setup is
presented in Figure 3.
Figure 3: FitFest gameplay set-up.
2.1.3 Software
The exergames were developed using the Unity 2022
game engine, employing a 2.5D design that combines
2D elements with 3D environments. This approach
Table 1: Summary of the characteristics of each scenario.
Wine Fest
Scenario Targeted component
Gameplay
movements
Time
(m)
1
Balance, agility,
strength, and
cardiorespiratory
Grape
harvesting
and storage
8
2 Balance and agility
Grape
storage and
selection
6
3 Strength
Grape
transportation
8
4 Cardiorespiratory Winemaking 10
5
Problem-solving and
working memory
Puzzle
solving
6
Flower Fest
Scenario Targeted component
Gameplay
movements
Time
(m)
1
Balance, agility, strength,
and cardiorespiratory
Flower picking
and storage
8
2
Balance, agility, and
strength
Creating
flower
arrangements
6
3
Balance, agility, and
cardiorespiratory
Parade 8
4
Balance, agility, and
cardiorespiratory
Traditional
dance
10
5
Problem-solving and
working memory
Puzzle solving 6
Physical and Physiological Impact of Custom-Made Virtual Reality Exergames for Older Adults
157

allowed for efficient development while preserving
visual appeal and providing depth that enhances
gameplay across various scenarios/mini games. The
design emphasizes intuitiveness and affordance to
naturally elicit the appropriate gestures from players.
Details on each scenario can be consulted in Table 1.
2.2 User Tests
A series of user tests was conducted to evaluate the
physical and physiological effects of
the FitFest exergames, focusing on PA intensity and
heart rate (HR) metrics. Additionally, participants’
ratings of perceived exertion were assessed. The
sessions took place at a local community center for
four weeks. Participants performed one exergame
session per week, using Wine Fest and Flower Fest as
alternates. The exergames sessions sequence was
equal for all participants, and the sessions were
supervised by two members of the research team to
ensure safety and protocol adherence.
Prior to testing, participants' height and body mass
were measured using a portable stadiometer (SECA
213, Hamburg, Germany; accuracy: ± 0.1 cm) and a
portable scale (SECA 760, Hamburg, Germany;
accuracy: ± 0.1 kg), respectively. During gameplay,
participants wore an accelerometer to assess PA
intensity and an HR sensor to monitor heart rate and
heart rate variability. After completing each game
scenario, participants rated their perceived exertion
using a 10-point scale using the game interface.
2.2.1 Participants
The study involved a convenience sample of seven
older adults (2 males) aged 67.0 ± 3.8 years, who
collectively completed 18 user testing sessions.
Although the experimental design considered one
session per week for each participant, compliance
was not achieved by all who participated. Two
participants completed the four sessions scheduled,
two participants completed a total of three sessions,
one participant completed two sessions, and two
participants completed only one session. Participants
were selected based on the following inclusion
criteria: (a) age 65 years or older; (b) absence of
physical or cognitive impairments; and (c) no medical
contraindications to physical exercise. All
participants were engaged in activities developed at a
local community center where the study took place.
The procedures implemented were approved by the
Ethics Committee of the University of Madeira
(Nº111/CEUMA/2024) to ensure adherence to data
protection regulations. Participation was entirely
voluntary, and informed consent was obtained from
all participants prior to the study. Data collection
adhered to the principles of the Declaration of
Helsinki and complied with all relevant ethical
guidelines and regulations.
2.2.2 Physical Activity
Physical activity (PA) intensity was measured using
the ActiGraph GT3X+ accelerometer, which
participants wore on their right hip throughout the
entire session. The device was initialized with a
sampling frequency of 30 Hz. Raw data from the
GT3X+ were converted into 10-second epochs for
analysis. Activity classification—including time
spent in sedentary behavior, light, moderate,
moderate-to-vigorous, and vigorous activity—was
determined using ActiLife software (version 6;
ActiGraph, Pensacola, FL, USA), based on validated
cutoff points established in prior research with older
adult populations (Bammann et al., 2021; Barnett et
al., 2016). The number of steps taken during the
session was also recorded. The accelerometer was
programmed individually for each participant prior to
their session, with data collection beginning at the
start of the exergame.
2.2.3 Heart Rate
During the exergame sessions, participants wore a
Polar H10 sensor to monitor heart rate (HR). The
device was secured to the chest using the
manufacturer-provided strap, ensuring optimal skin
contact. This placement allowed the sensor’s
electrodes to capture accurate, real-time HR data
throughout the session.
2.2.4 Rate of Perceived Exertion
The rate of perceived exertion (RPE) scale
(Robertson, 2004) was incorporated into the
exergame after each scenario conclusion. Using the
10-point scale (1 – extremely easy, 10 – extremely
hard), participants had to move to the right or left side
to indicate the number that would better correspond
to their effort. After selecting the number that best
represented their perceived effort, participants raised
one hand above their head to confirm their choice.
Since each exergame consists of five scenarios, this
process was repeated five times during the session.
2.3 Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics are presented as mean ±
standard deviation and were used to analyze physical
icSPORTS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
158
activity (PA) intensity and heart rate (HR) during
the FitFest exergames. To compare differences
between the Wine Fest and Flower Fest games in
terms of PA intensity, HR, and RPE, the Mann-
Whitney U test was applied. Statistical analyses and
graphical presentations were performed using IBM
SPSS Statistics 29.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)
and GraphPad Prism version 10 (GraphPad Software,
San Diego, CA, USA). The threshold for statistical
significance was set at p < 0.05.
3 RESULTS
Due to inconsistencies in the data collection process
(accelerometer malfunction), two user testing
sessions were excluded from the analysis of physical
activity (PA) intensity and heart rate (HR). As a
result, 16 sessions were included in the final
analysis—11 for Wine Fest and 5 for Flower Fest.
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics for PA
intensity and HR across all analyzed sessions.
Overall, the FitFest exergames were primarily
characterized by sedentary behavior (56.5 ± 20.4%),
followed by light-intensity activity (42.1 ± 19.3%).
On average, participants completed approximately
436.7 steps per session, with a HR of 92.1 bpm.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics for PA intensity and HR
while playing the FitFest exergames.
Variable
FitFest
Overall
Wine Fest
Flower
Fes
t
M ± SD M ± SD M ± SD
Sedentary
behavior (%)
56.5 ± 20.4 53.6 ± 22.1
62.9 ±
16.2
Light PA (%) 42.1 ± 19.3 44.7 ± 20.4 38.4 ± 17.0
Moderate PA (%) 1.4 ± 2.4 1.7 ± 2.8 0.6 ± 0.8
Moderate-to-
vigorous PA (%)
1.4 ± 2.4 1.8 ± 2.8 0.8 ± 0.9
Total steps (n) 436.7 ± 308.7 502.9 ± 345.4
291.0 ±
143.1
Steps/minute (n) 10.8 ± 7.9 12.8 ± 8.7 6.5 ± 3.4
Average HR(bpm) 92.1 ± 14.5 92.1 ± 16.6 92.2 ± 9.7
Minimum HR
(bpm)
115.0 ± 25.3 115.2 ± 29.7
114.4 ±
13.5
Maximum HR
(bpm)
71.8 ± 12.0 71.6 ± 11.7 72.0 ± 14.2
M ± SD (mean ± standard deviation) PA (physical activity), HR
(heart rate)
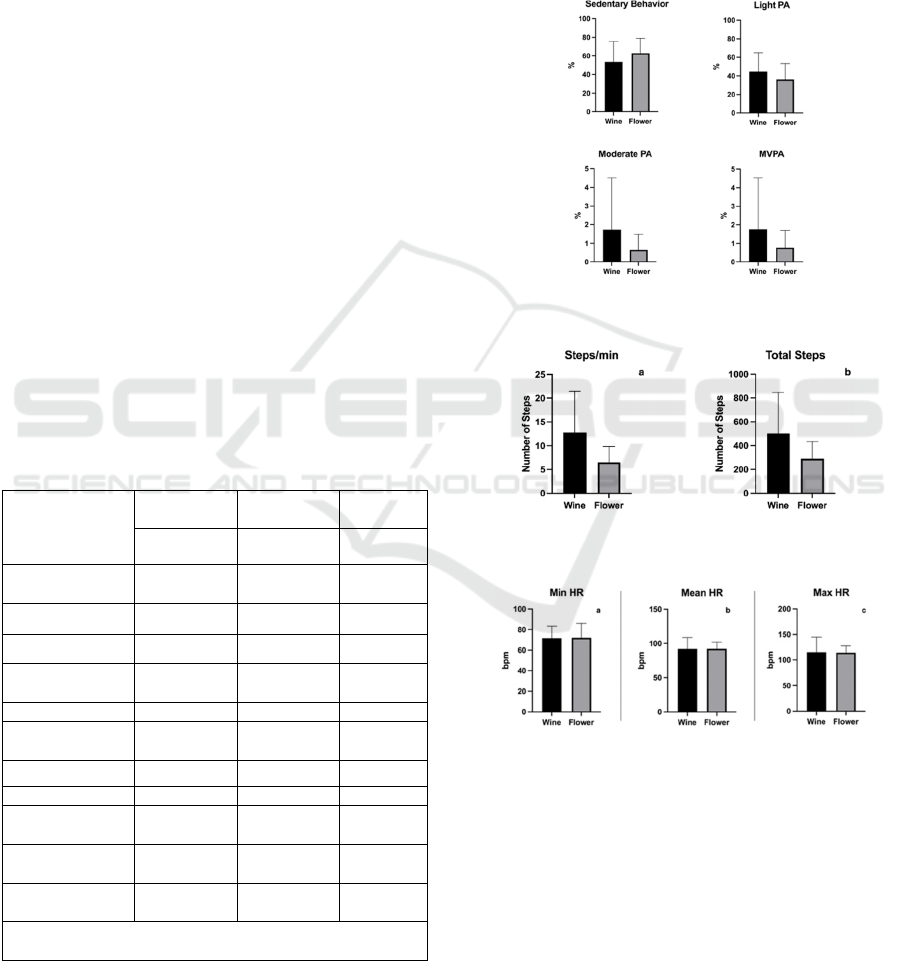
Figures 4, 5, and 6 present the comparison between
the two exergames in terms of physical activity (PA)
intensity, step count, and heart rate (HR)
measurements. Wine Fest elicited lower levels of
sedentary behavior (53.6 ± 22.1% vs. 62.8 ± 16.2%),
higher levels of light-intensity PA (44.7 ± 20.4% vs.
36.4 ± 17.0%), and a greater average number of steps
(503.0 ± 345.4 vs. 291.0 ± 143.1) compared to Flower
Fest. However, these differences did not reach
statistical significance. HR values were similar across
both exergames, with an average of 92.1 bpm.
Figure 4: Comparison between exergames regarding PA
intensity.
Figure 5: Comparison between exergames regarding the
number of steps.
Figure 6: Comparison between exergames regarding heart
rate.
The analysis of perceived exertion (RPE), as
shown in Figure 7, revealed higher exertion levels
during scenarios 3 and 4, which primarily involved
tasks targeting strength and cardiorespiratory fitness.
In contrast, scenario 2—focused on agility and
coordination—was perceived as less physically
demanding by participants.
Physical and Physiological Impact of Custom-Made Virtual Reality Exergames for Older Adults
159
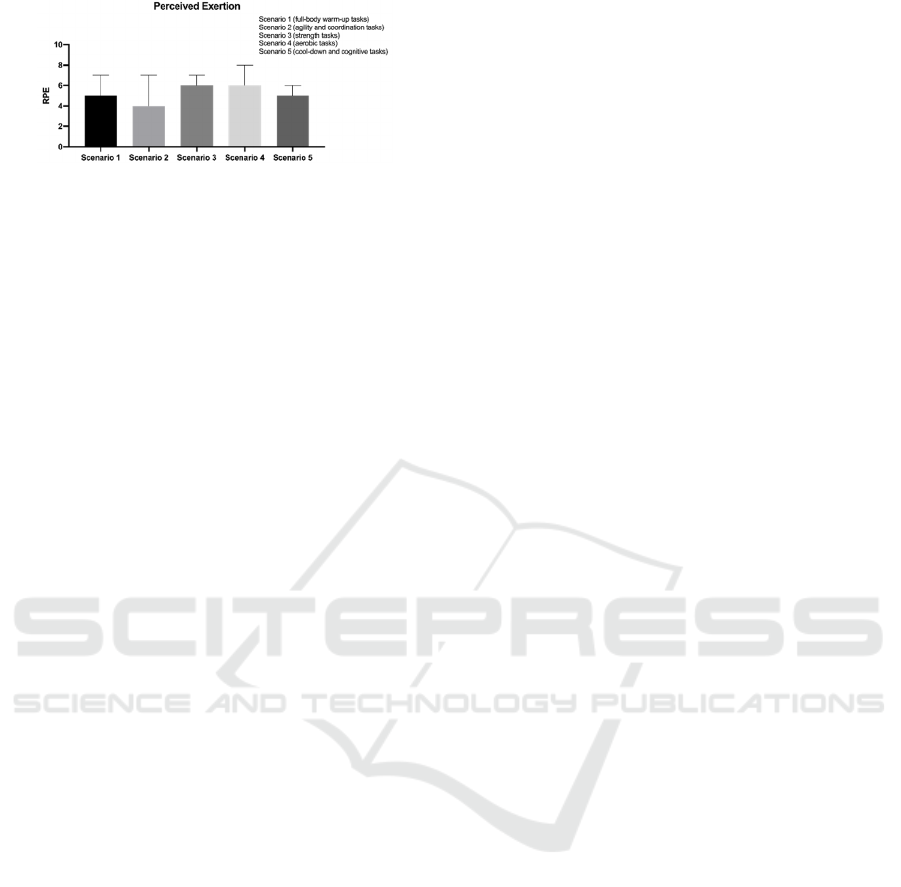
Figure 7: Rate of perceived exertion results for each
scenario.
4 DISCUSSION
This study examined the physical and physiological
responses of a custom-made VR exergame
system, FitFest, among older adults. The overall
analysis indicated that gameplay was primarily
characterized by sedentary behavior, followed by
light-intensity PA. Among the two exergames, Wine
Fest promoted slightly higher PA intensity and a
greater number of steps than Flower Fest, though
these differences were not statistically significant.
According to ACSM guidelines, moderate-
intensity PA is recommended for achieving
substantial health benefits in older adults, particularly
in cardiorespiratory fitness (Bushman & Medicine,
2017). However, FitFest did not elicit moderate-to-
vigorous PA levels. One explanation is that gameplay
included tutorial segments and interactive rating tasks
using the Borg scale between scenarios, which
contributed to reduced active time. While these
features were designed to enhance clarity and provide
recovery, they also limited continuous exertion.
Nevertheless, literature supports that even light-
intensity activities can offer health benefits
(Chodzko-Zajko et al., 2009).
The mean heart rate (HR) recorded during FitFest
gameplay aligns with light PA, corresponding to
approximately 60% of the age-predicted maximal HR
(153 bpm using 220 – age) (Fletcher et al., 2013).
Although this formula may underestimate true
maximal HR in older adults (Tanaka et al., 2001), it
remains widely accepted for clinical applications.
According to the literature, light PA is significantly
and positively related to physical health and well-
being in older populations (Buman et al., 2010).
Compared to previous studies using Kinect-based
balance-focused exergames (80–87 bpm) (Ogawa et
al., 2019) and Nintendo Wii Sports (94 ± 10 bpm)
(Kirk et al., 2013), FitFest HR values are within a
similar range, reflecting its multicomponent design
encompassing strength, balance, agility, and aerobic
tasks.
Perceived exertion ratings (RPE) revealed that
strength and aerobic scenarios were considered the
most demanding, consistent with current PA
guidelines (Chodzko-Zajko et al., 2009).
Interestingly, a cool-down scenario focused solely on
cognitive tasks was also perceived as moderately
intense. This may relate to the cognitive challenge
posed, as older adults commonly experience age-
related cognitive decline (Deary et al., 2009). Prior
research suggests that lower self-efficacy may
increase perceived exertion in older adults during
cognitively demanding tasks (Hu et al., 2007).
Therefore, cognitive components of exergames
should be tailored to avoid inducing frustration or
discouragement.
This exploratory study presents several
limitations. First, the small sample size and uneven
distribution of sessions between the participants limit
generalizability. All the participants were recruited
from a local community center, where the study took
place, and there is a need to increase the sample size
and the number of sessions for future validation of the
FitFest. Second, the short-term nature of the testing
does not allow for assessment of long-term benefits
or sustained engagement. Third, all participants
played at the same difficulty level to ensure standard
procedures during testing, which may not reflect
individual physical or cognitive capacities.
Personalized assessments and adaptive difficulty
scaling are recommended for future implementations
since they might promote gameplay scenarios more
appropriate to the individuals’ characteristics and
enhance challenge. Future research can explore users’
HR responses to adapt the difficulty level during
gameplay. Additionally, the inclusion of tutorials and
inter-scenario tasks (which corresponded to an
estimated total time of 6 minutes), while necessary for
clarity, may have affected overall activity intensity
and increased time spent in sedentary behavior.
Lastly, the lack of a control group limits the
interpretation of the FitFest effects, which should be
tackled in future longitudinal studies.
Despite these limitations, this study provides
valuable insights into the potential of FitFest, a
custom-made multicomponent VR exergame, to
promote light-intensity PA among older adults. While
it may not be a substitute for moderate-to-vigorous
PA interventions, FitFest can be a complementary
tool to traditional exercise programs implemented in
community centers to increase activity levels and
engagement. Besides, by including cognitive
stimulus, FitFest aligns physical and cognitive tasks,
which are crucial among older populations. Future
developments should focus on individualization and
icSPORTS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
160

increased intensity based on real-time adapted
difficulty. Also, reducing passive time by including
shorter tutorials and seamless scenario transitions to
maximize benefits should be considered.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all participants.
FUNDING
This research was funded by the Portuguese Recovery
and Resilience Program (PRR), IAPMEI/ANI/FCT
under the Agenda C645022399-00000057
(eGamesLab).
REFERENCES
Agmon, M., Perry, C. K., Phelan, E., Demiris, G., &
Nguyen, H. Q. (2011). A pilot study of Wii Fit
exergames to improve balance in older adults. Journal
of geriatric physical therapy, 34(4), 161-167.
Bammann, K., Thomson, N. K., Albrecht, B. M., Buchan,
D. S., & Easton, C. (2021). Generation and validation
of ActiGraph GT3X+ accelerometer cut-points for
assessing physical activity intensity in older adults. The
Outdoor Active validation study. PloS one, 16(6),
e0252615.
Barg-Walkow, L. H., Harrington, C. N., Mitzner, T. L.,
Hartley, J. Q., & Rogers, W. A. (2017). Understanding
older adults’ perceptions of and attitudes towards
exergames. Gerontechnology: international journal on
the fundamental aspects of technology to serve the
ageing society, 16(2), 81.
Barnett, A., Van Den Hoek, D., Barnett, D., & Cerin, E.
(2016). Measuring moderate-intensity walking in older
adults using the ActiGraph accelerometer. BMC
geriatrics, 16, 1-9.
Buman, M. P., Hekler, E. B., Haskell, W. L., Pruitt, L.,
Conway, T. L., Cain, K. L., Sallis, J. F., Saelens, B. E.,
Frank, L. D., & King, A. C. (2010). Objective light-
intensity physical activity associations with rated health
in older adults. American journal of epidemiology,
172(10), 1155-1165.
Bushman, B., & Medicine, A. C. o. S. (2017). ACSM's
Complete Guide to Fitness & Health, 2E. Human
Kinetics.
Chodzko-Zajko, W. J., Proctor, D. N., Singh, M. A. F.,
Minson, C. T., Nigg, C. R., Salem, G. J., & Skinner, J.
S. (2009). Exercise and physical activity for older
adults. Medicine & science in sports & exercise, 41(7),
1510-1530.
Clemson, L., Singh, M. F., Bundy, A., Cumming, R. G.,
Weissel, E., Munro, J., Manollaras, K., & Black, D.
(2010). LiFE Pilot Study: A randomised trial of balance
and strength training embedded in daily life activity to
reduce falls in older adults. Australian occupational
therapy journal, 57(1), 42-50.
Daskalopoulou, C., Stubbs, B., Kralj, C., Koukounari, A.,
Prince, M., & Prina, A. M. (2017). Physical activity and
healthy ageing: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of longitudinal cohort studies. Ageing research reviews,
38, 6-17.
Deary, I. J., Corley, J., Gow, A. J., Harris, S. E., Houlihan,
L. M., Marioni, R. E., Penke, L., Rafnsson, S. B., &
Starr, J. M. (2009). Age-associated cognitive decline.
British medical bulletin, 92(1), 135-152.
Dipietro, L., Campbell, W. W., Buchner, D. M., Erickson,
K. I., Powell, K. E., Bloodgood, B., Hughes, T., Day,
K. R., Piercy, K. L., & Vaux-Bjerke, A. (2019).
Physical activity, injurious falls, and physical function
in aging: an umbrella review. Medicine and science in
sports and exercise, 51(6), 1303.
Fletcher, G. F., Ades, P. A., Kligfield, P., Arena, R., Balady,
G. J., Bittner, V. A., Coke, L. A., Fleg, J. L., Forman,
D. E., & Gerber, T. C. (2013). Exercise standards for
testing and training: a scientific statement from the
American Heart Association. Circulation, 128(8), 873-
934.
Freitas, E., Noronha, H., França, C., Gouveia, É., Bala, P.,
Campos, P., & Dionísio, M. (2024). FitFest: Designing
a Narrative-driven Exergame to Engage Active Seniors
in Physical Activity. Proceedings of the 27th
International Academic Mindtrek Conference,
Hu, L., McAuley, E., Motl, R. W., & Konopack, J. F.
(2007). Influence of self-efficacy on the functional
relationship between ratings of perceived exertion and
exercise intensity. Journal of cardiopulmonary
rehabilitation and prevention, 27(5), 303-308.
Inouye, S. K., Brown, C. J., & Tinetti, M. E. (2009).
Medicare nonpayment, hospital falls, and unintended
consequences. New England Journal of Medicine,
360(23), 2390.
Ismail, N. A., Hashim, H. A., & Ahmad Yusof, H. (2022).
Physical activity and exergames among older adults: a
scoping review. Games for Health Journal, 11(1), 1-17.
Kirk, A., MacMillan, F., Rice, M., & Carmichael, A.
(2013). An exploratory study examining the
appropriateness and potential benefit of the Nintendo
Wii as a physical activity tool in adults aged≥ 55 years.
Interacting with Computers, 25(1), 102-114.
Nascimento, M. d. M., Gouveia, É. R., Gouveia, B. R.,
Marques, A., França, C., Freitas, D. L., Campos, P., &
Ihle, A. (2022). Exploring mediation effects of gait
speed, body balance, and falls in the relationship
between physical activity and health-related quality of
life in vulnerable older adults. International journal of
environmental research and public health, 19(21),
14135.
Ogawa, E., Huang, H., Yu, L.-F., & You, T. (2019).
Physiological responses and enjoyment of Kinect-based
exergames in older adults at risk for falls: a feasibility
study. Technology and health care, 27(4), 353-362.
Physical and Physiological Impact of Custom-Made Virtual Reality Exergames for Older Adults
161

Paterson, D. H., Jones, G. R., & Rice, C. L. (2007). Ageing
and physical activity: evidence to develop exercise
recommendations for older adults. Applied physiology,
nutrition, and metabolism, 32(S2E), S69-S108.
Robertson, R. J. (2004). Perceived exertion for
practitioners: rating effort with the OMNI picture
system. Human Kinetics.
Tanaka, H., Monahan, K. D., & Seals, D. R. (2001). Age-
predicted maximal heart rate revisited. Journal of the
american college of cardiology, 37(1), 153-156.
WHO. (2020). WHO guidelines on physical activity and
sedentary behavior: at a glance. W. H. Organization.
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/337001/97
89240014886-eng.pdf?sequence=1
Yang, C.-M., Hsieh, J. S. C., Chen, Y.-C., Yang, S.-Y., &
Lin, H.-C. K. (2020). Effects of Kinect exergames on
balance training among community older adults: A
randomized controlled trial. Medicine, 99(28), e21228.
Yen, H.-Y., & Chiu, H.-L. (2021). Virtual reality
exergames for improving older adults’ cognition and
depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized control trials. Journal of the American
Medical Directors Association, 22(5), 995-1002.
icSPORTS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
162
